In Situ Supramolecular Gel Formed by Cyclohexane Diamine with Aldehyde Derivative
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Preparation of Gels
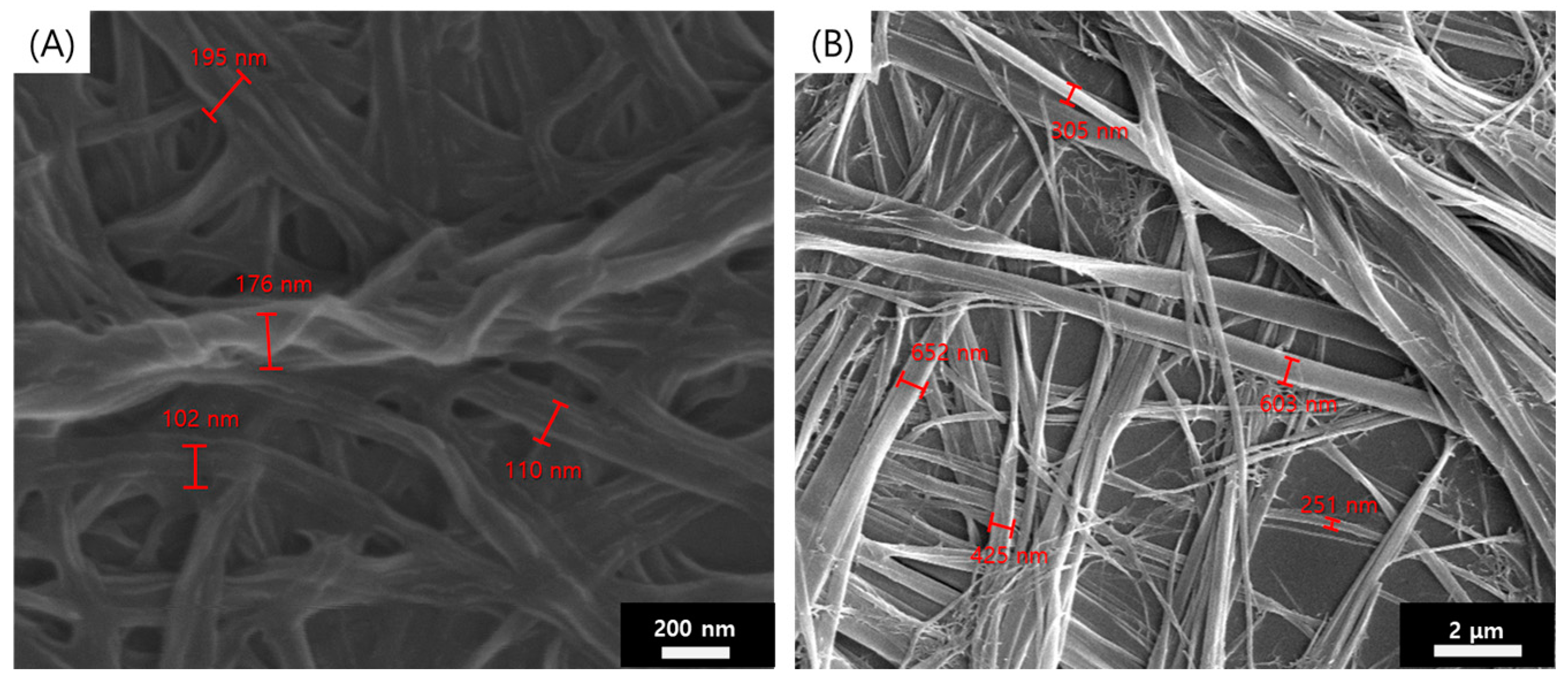
2.3. Preparation Method and Observation of SEM Samples
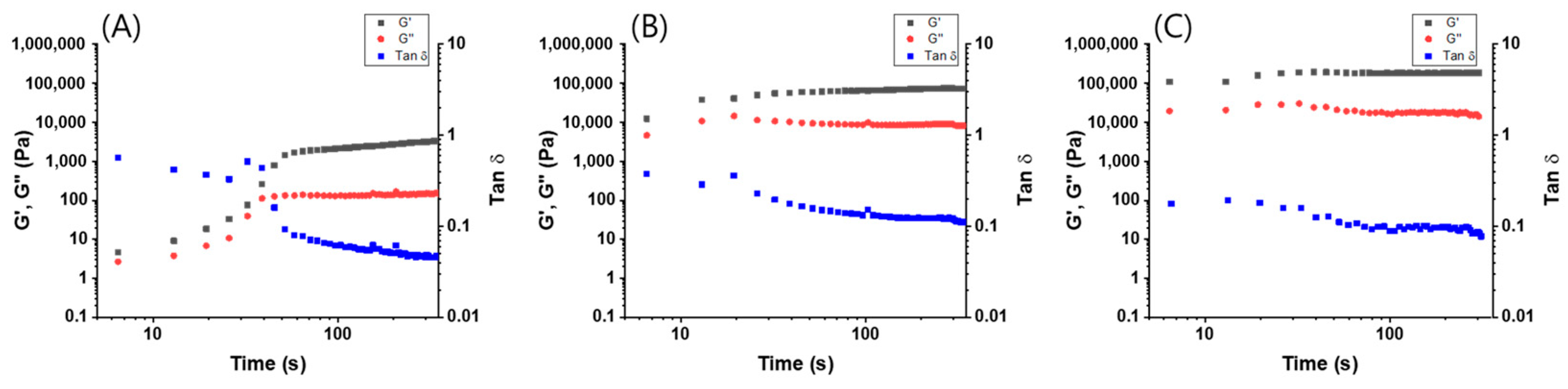
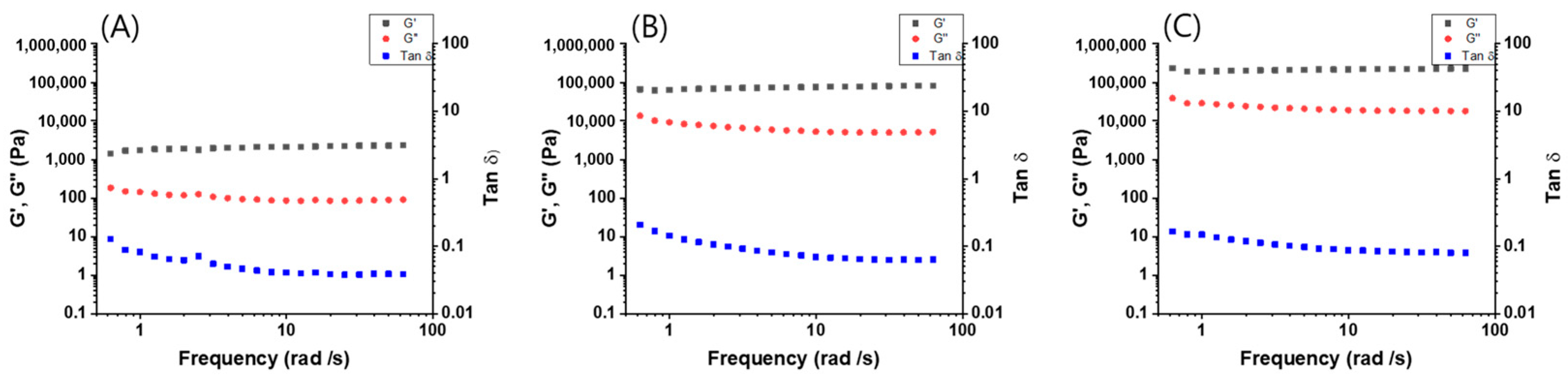
2.4. Rheological Properties
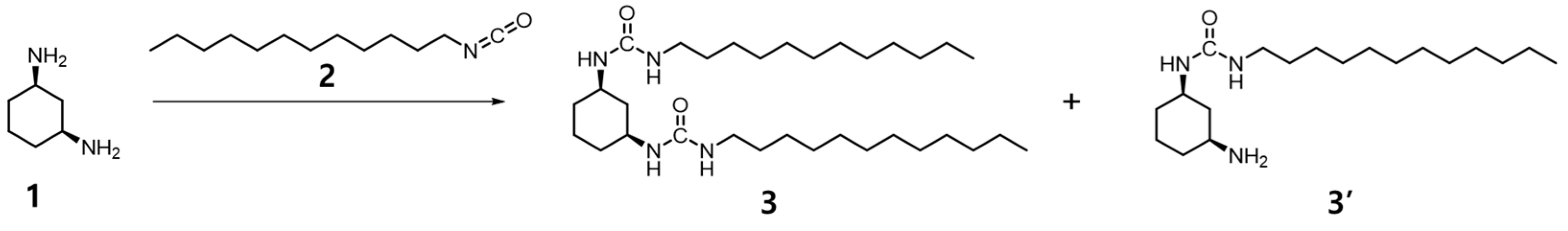
2.5. Synthesis of Compound 3
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Okesola, B.O.; Smith, D.K. Applying low-molecular weight supramolecular gelators in an environmental setting—Self-assembled gels as smart materials for pollutant removal. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 4226–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Q.; Han, W.J.; Choi, H.J. Smart and Functional Conducting Polymers: Application to Electrorheological Fluids. Molecules 2018, 23, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, M.M.; Eckes, K.M.; Suggs, L.J. Charge and sequence effects on the self-assembly and subsequent hydrogelation of Fmoc-depsipeptides. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 2693–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nonoyama, T.; Wada, S.; Kiyama, R.; Kitamura, N.; Mredha, M.T.I.; Zhang, X.; Kurokawa, T.; Nakajima, T.; Takagi, Y.; Yasuda, K.; et al. Double-Network Hydrogels Strongly Bondable to Bones by Spontaneous Osteogenesis Penetration. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6740–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, A.M.; De Laporte, L.; Tortelli, F.; Spedden, E.; Staii, C.; Atherton, T.J.; Hubbell, J.A.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk Hydrogels as Soft Substrates for Neural Tissue Engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5140–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Tarakanova, A.; Dinjaski, N.; Wang, Q.; Xia, X.; Chen, Y.; Wong, J.Y.; Buehler, M.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Design of Multistimuli Responsive Hydrogels Using Integrated Modeling and Genetically Engineered Silk–Elastin-Like Proteins. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 4113–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, S.; Dudek, D.M.; Cao, Y.; Balamurali, M.M.; Gosline, J.; Li, H. Designed biomaterials to mimic the mechanical properties of muscles. Nature 2010, 465, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, S.J.; da Silva, M.A.; Hossain, K.M.Z.; Calabrese, V.; Scott, J.L.; Edler, K.J. Non-volatile conductive gels made from deep eutectic solvents and oxidised cellulose nanofibrils. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, W.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, J.; Ameen, A.; Shi, L.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Ma, R.; Jin, S.H.; Kang, Z.; et al. Multifunctional Epidermal Electronics Printed Directly Onto the Skin. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2773–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.S.; Choi, Y.; Jung, J.H. A crown-ether-based moldable supramolecular gel with unusual mechanical properties and controllable electrical conductivity prepared by cation-mediated cross-linking. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 3900–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, N.A.; Sampath, S.; Shukla, A.K. Hydrogel-polymer electrolytes for electrochemical capacitors: An overview. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naficy, S.; Razal, J.M.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G.; Whitten, P.G. Electrically Conductive, Tough Hydrogels with pH Sensitivity. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 3425–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sangeetha, N.M.; Maitra, U. Supramolecular gels: Functions and uses. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005, 34, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Yan, X.; Han, C.; Huang, F. Characterization of supramolecular gels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6697–6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuri, D.; Zanna, N.; Tomasini, C. Low Molecular Weight Gelators Based on Functionalized l-Dopa Promote Organogels Formation. Gels 2019, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, J.; Park, J.W.; Ahn, H.J.; Jaworski, J.; Jung, J.H. Supramolecular gels with high strength by tuning of calix[4]arene-derived networks. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, J.H.; Jaworski, J.; Shinkai, S.; Jung, J.H. Luminescent calix[4]arene-based metallogel formed at different solvent composition. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 7181–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skilling, K.J.; Citossi, F.; Bradshaw, T.D.; Ashford, M.; Kellam, B.; Marlow, M. Insights into low molecular mass organic gelators: A focus on drug delivery and tissue engineering applications. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zang, S.; Xue, R.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, J.; Yan, Y. Coordination-Triggered Hierarchical Folate/Zinc Supramolecular Hydrogels Leading to Printable Biomaterials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 4530–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mredha, M.T.I.; Guo, Y.Z.; Nonoyama, T.; Nakajima, T.; Kurokawa, T.; Gong, J.P. A facile method to fabricate anisotropic hydrogels with perfectly aligned hierarchical fibrous structures. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ma, C.; Peng, L.; Yu, G. Conductive “Smart” Hybrid Hydrogels with PNIPAM and Nanostructured Conductive Polymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, P.; Yu, X.; Lan, H.; Li, Y.; Xie, D.; Li, J.; Yi, T. Sugar based nanotube assembly for the construction of sonication triggered hydrogel: An application of the entrapment of tetracycline hydrochloride. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7366–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, N.; Lv, Z.; Jiang, Z. Ultra-stretchable hydrogels with hierarchical hydrogen bonds. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.; Khabaz, F.; Godbole, R.V.; Hedden, R.C.; Khare, R. Structure and Hydrogen Bonding of Water in Polyacrylate Gels: Effects of Polymer Hydrophilicity and Water Concentration. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 15381–15393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.S.; Han, S.K.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Yuk, S.H. Hydrogen-bonded polymer gel and its application as a temperature-sensitive drug delivery system. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2393–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, B.N.; Deijs, G.S.; Manuguri, S.; Ting, M.S.H.; Williams, M.A.K.; Malmström, J. A comparative study of tough hydrogen bonding dissipating hydrogels made with different network structures. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 2934–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohna Sohna, J.-E.; Fages, F. A trisbipyridine tripodal ligand as toluene gelator. Phase transition-triggered binding of iron(ii). Chem. Commun. 1997, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terech, P.; Allegraud, J.J.; Garner, C.M. Thermoreversible Gelation of Organic Liquids by Arylcyclohexanol Derivatives: A Structural Study. Langmuir 1998, 14, 3991–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.; Weiss, R.G. Chemically Reversible Organogels: Aliphatic Amines as “Latent” Gelators with Carbon Dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 10393–10394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanabusa, K.; Suzuki, M. Physical Gelation by Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds and Development of Gelators. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 89, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Falcone, N.; Kraatz, H.-B. Supramolecular Peptide Gels: Influencing Properties by Metal Ion Coordination and Their Wide-Ranging Applications. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 1312–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Roy, S.; Ulijn, R.V. Peptide Nanofibers with Dynamic Instability through Nonequilibrium Biocatalytic Assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16789–16792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berdugo, C.; Nalluri, S.K.M.; Javid, N.; Escuder, B.; Miravet, J.F.; Ulijn, R.V. Dynamic Peptide Library for the Discovery of Charge Transfer Hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 25946–25954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Yan, Y.; Qi, J.; Deng, L.; Shao, Z.-W.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Li, B.; Sun, Z.; Li, X. Cooperative assembly of a peptide gelator and silk fibroin afford an injectable hydrogel for tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12474–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, S.R.; Vemula, P.K.; Kumar, R.; Raghavan, S.R.; John, G. Sugar-derived phase-selective molecular gelators as model solidifiers for oil spills. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidyasagar, A.; Handore, K.; Sureshan, K.M. Soft Optical Devices from Self-Healing Gels Formed by Oil and Sugar-Based Organogelators. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vibhute, A.M.; Muvvala, V.; Sureshan, K.M. A Sugar-Based Gelator for Marine Oil-Spill Recovery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7782–7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, M. Fabrication of Helical Nanoribbon Polydiacetylene via Supramolecular Gelation: Circularly Polarized Luminescence and Novel Diagnostic Chiroptical Signals for Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 30608–30615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Yajima, T.; Yamagishi, A. Helical Inversion of Gel Fibrils by Elongation of Perfluoroalkyl Chains as Studied by Vibrational Circular Dichroism. Chirality 2016, 28, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Kim, K.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Ahn, J.; Sakurai, K.; Lee, S.S.; Jung, J.H. Chiral Supramolecular Gels with Lanthanide Ions: Correlation between Luminescence and Helical Pitch. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3799–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, J.; Meng, Y.; Liu, M. Self-Assembled Polydiacetylene Vesicle and Helix with Chiral Interface for Visualized Enantioselective Recognition of Sulfinamide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 37386–37394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Kurata, H.; Prabhu, D.D.; Yamauchi, M.; Ohba, T.; Yagai, S. Water-induced helical supramolecular polymerization and gel formation of an alkylene-tethered perylene bisimide dyad. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.-M.; Yang, H.-K.; Ren, L.-J.; Zheng, P.; Wang, W. Solvent-mediated gel formation, hierarchical structures, and rheological properties of organogels. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panja, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Ghosh, K. Cholesterol-Appended Benzimidazolium Salts: Synthesis, Aggregation, Sensing, Dye Adsorption, and Semiconducting Properties. Langmuir 2017, 33, 8277–8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, S.L.M.; Korley, L.T.J. Restricting Molecular Mobility in Polymer Nanocomposites with Self-Assembling Low-Molecular-Weight Gel Additives. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 43040–43048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zweep, N.; Hopkinson, A.; Meetsma, A.; Browne, W.R.; Feringa, B.L.; van Esch, J.H. Balancing Hydrogen Bonding and van der Waals Interactions in Cyclohexane-Based Bisamide and Bisurea Organogelators. Langmuir 2009, 25, 8802–8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Loos, M.; Friggeri, A.; van Esch, J.; Kellogg, R.M.; Feringa, B.L. Cyclohexane bis-urea compounds for the gelation of water and aqueous solutions. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, T.; Kutsuna, T.; Hanabusa, K.; Ukon, M. Gelation of Room-Temperature Liquid Crystals by the Association of a trans-1,2-Bis(amino)cyclohexane Derivative. Adv. Mater. 1998, 10, 606–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanabusa, K.; Yamada, M.; Kimura, M.; Shirai, H. Prominent Gelation and Chiral Aggregation of Alkylamides Derived from trans-1,2-Diaminocyclohexane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1996, 35, 1949–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, S.; Adams, D.J. Stimuli responsive dynamic transformations in supramolecular gels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5165–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Zeng, L.-H.; Feng, J. Dynamic covalent gels assembled from small molecules: From discrete gelators to dynamic covalent polymers. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, S.J.; Parkinson, S.; Wheeldon, E.; Smith, D.K. In situ aldehyde-modification of self-assembled acyl hydrazide hydrogels and dynamic component selection from complex aldehyde mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 1947–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.; Gong, H.; Shang, J.; Jin, L.; Pan, T.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, S.; Wang, Y.; Qi, Z. Supramolecular gel based on crown-ether-appended dynamic covalent macrocycles. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, 1800731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, S.; Boháčová, K.; Dietrich, B.; Adams, D.J. Programming properties of transient hydrogels by an enzymatic reaction. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 12840–12848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panja, A.; Ghosh, K. Selective sensing of hg2+ via sol–gel transformation of a cholesterol-based compound. Supramol. Chem. 2018, 30, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Kulchat, S.; Jiang, S.; Lehn, J.-M. Gelation-driven selection in dynamic covalent C [double bond, length as m-dash] C/C [double bond, length as m-dash] N exchange. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6822–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panja, A.; Ghosh, K. Pyridyl azo-based naphthyl acetate for sensing of hydrazine and perborate in sol-gel medium. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 9448–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasachary, N.; Lehn, J.-M. Gelation-driven component selection in the generation of constitutional dynamic hydrogels based on guanine-quartet formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.-T.; Lin, J.-B.; Jiang, X.-K.; Li, Z.-T. Cholesterol-appended aromatic imine organogelators: A case study of gelation-driven component selection. Langmuir 2009, 25, 8414–8418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Visual sensing of formaldehyde via a solution-to-gel transition with cholesteryl naphthalimide-based derivatives. Dyes Pigm. 2021, 193, 109546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boekhoven, J.; Poolman, J.M.; Maity, C.; Li, F.; van der Mee, L.; Minkenberg, C.B.; Mendes, E.; van Esch, J.H.; Eelkema, R. Catalytic control over supramolecular gel formation. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, C.; Hendriksen, W.E.; van Esch, J.H.; Eelkema, R. Spatial structuring of a supramolecular hydrogel by using a visible-light triggered catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poolman, J.M.; Boekhoven, J.; Besselink, A.; Olive, A.G.L.; van Esch, J.H.; Eelkema, R. Variable gelation time and stiffness of low-molecular-weight hydrogels through catalytic control over self-assembly. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trausel, F.; Versluis, F.; Maity, C.; Poolman, J.M.; Lovrak, M.; van Esch, J.H.; Eelkema, R. Catalysis of supramolecular hydrogelation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panja, S.; Adams, D.J. Pathway dependence in redox-driven metal–organic gels. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 6130–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Esch, J.; De Feyter, S.; Kellogg, R.M.; De Schryver, F.; Feringa, B.L. Self-Assembly of Bisurea Compounds in Organic Solvents and on Solid Substrates. Chrm. Eur. J. 1997, 3, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.-H.; Kim, M.-H.; Seo, M.-L.; Lee, J.-H.; Jung, J.-H. In Situ Supramolecular Gel Formed by Cyclohexane Diamine with Aldehyde Derivative. Polymers 2022, 14, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030400
Park J-H, Kim M-H, Seo M-L, Lee J-H, Jung J-H. In Situ Supramolecular Gel Formed by Cyclohexane Diamine with Aldehyde Derivative. Polymers. 2022; 14(3):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030400
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jae-Hyeon, Min-Hye Kim, Moo-Lyong Seo, Ji-Ha Lee, and Jong-Hwa Jung. 2022. "In Situ Supramolecular Gel Formed by Cyclohexane Diamine with Aldehyde Derivative" Polymers 14, no. 3: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030400
APA StylePark, J.-H., Kim, M.-H., Seo, M.-L., Lee, J.-H., & Jung, J.-H. (2022). In Situ Supramolecular Gel Formed by Cyclohexane Diamine with Aldehyde Derivative. Polymers, 14(3), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030400






