Dynamic Rotational Sensor Using Polymer Optical Fiber for Robot Movement Assessment Based on Intensity Variation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
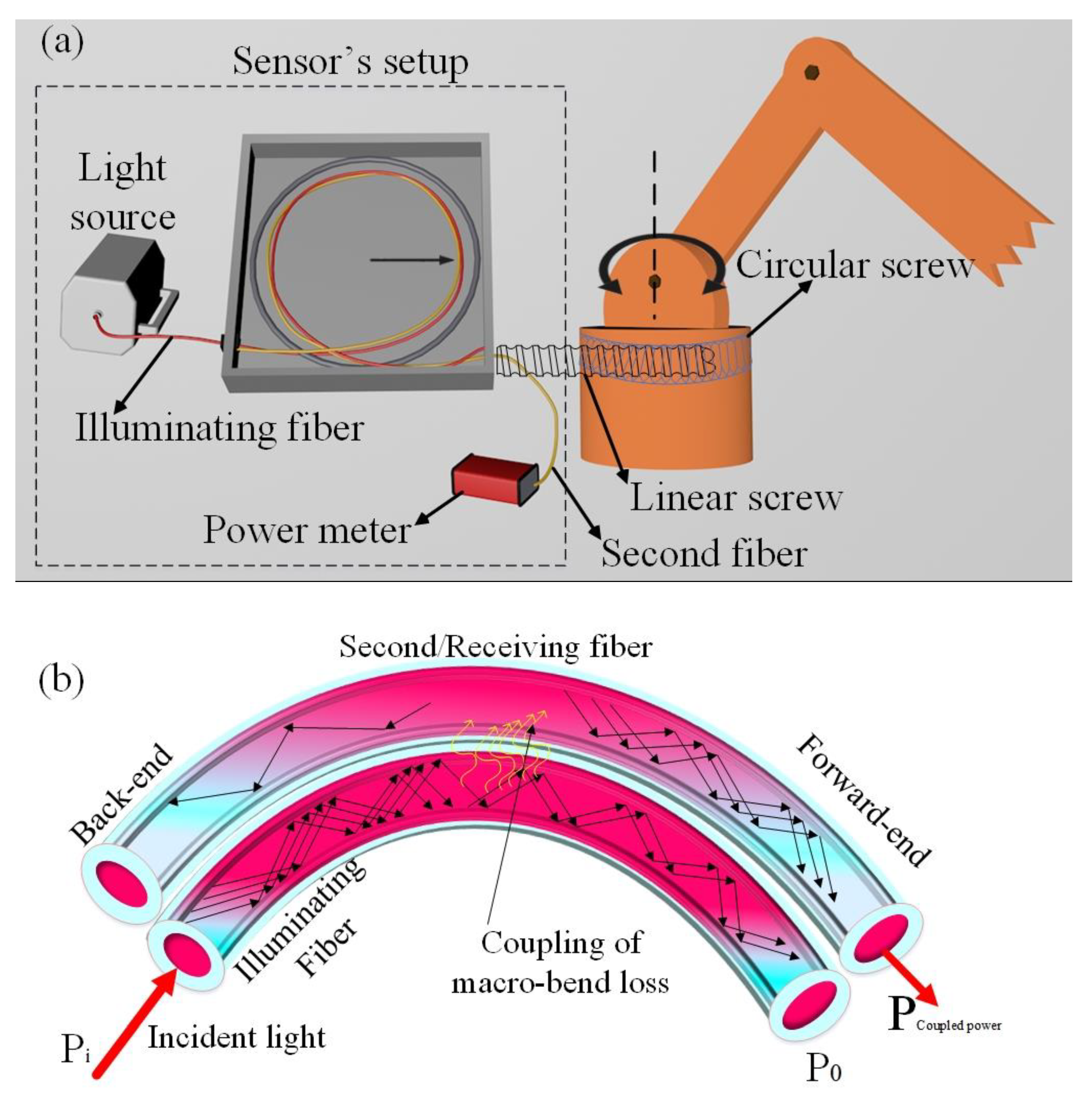
2. Materials and Methods
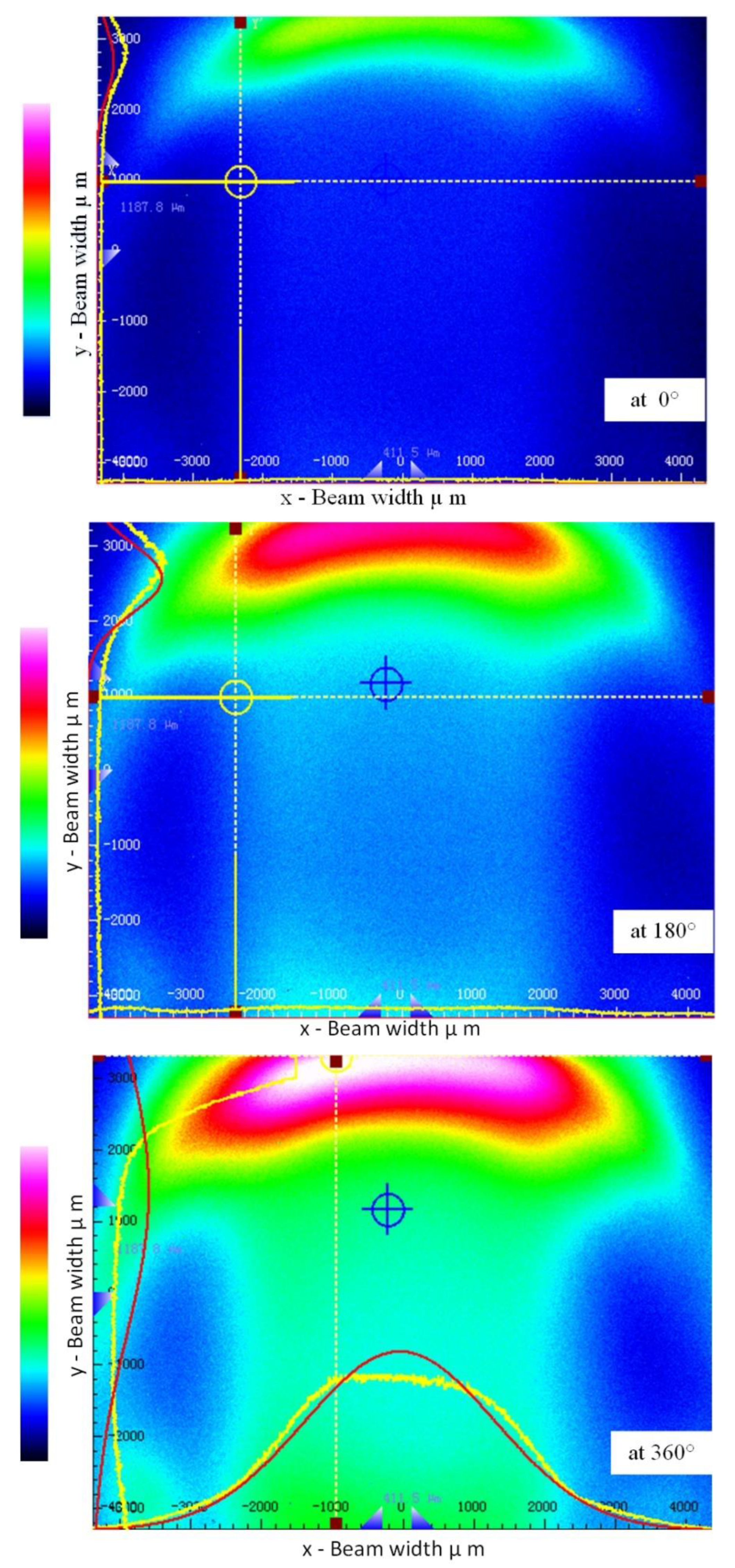
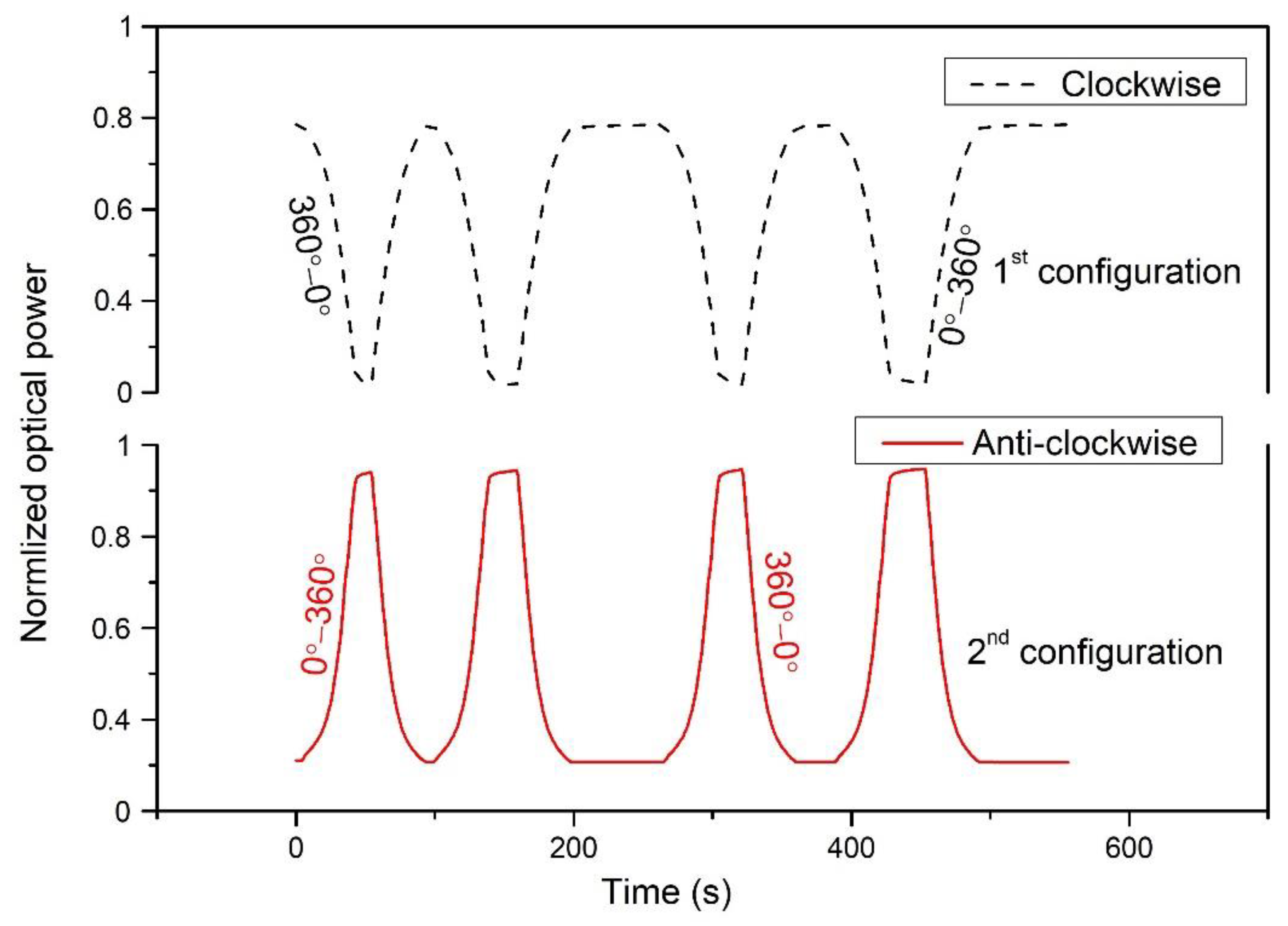
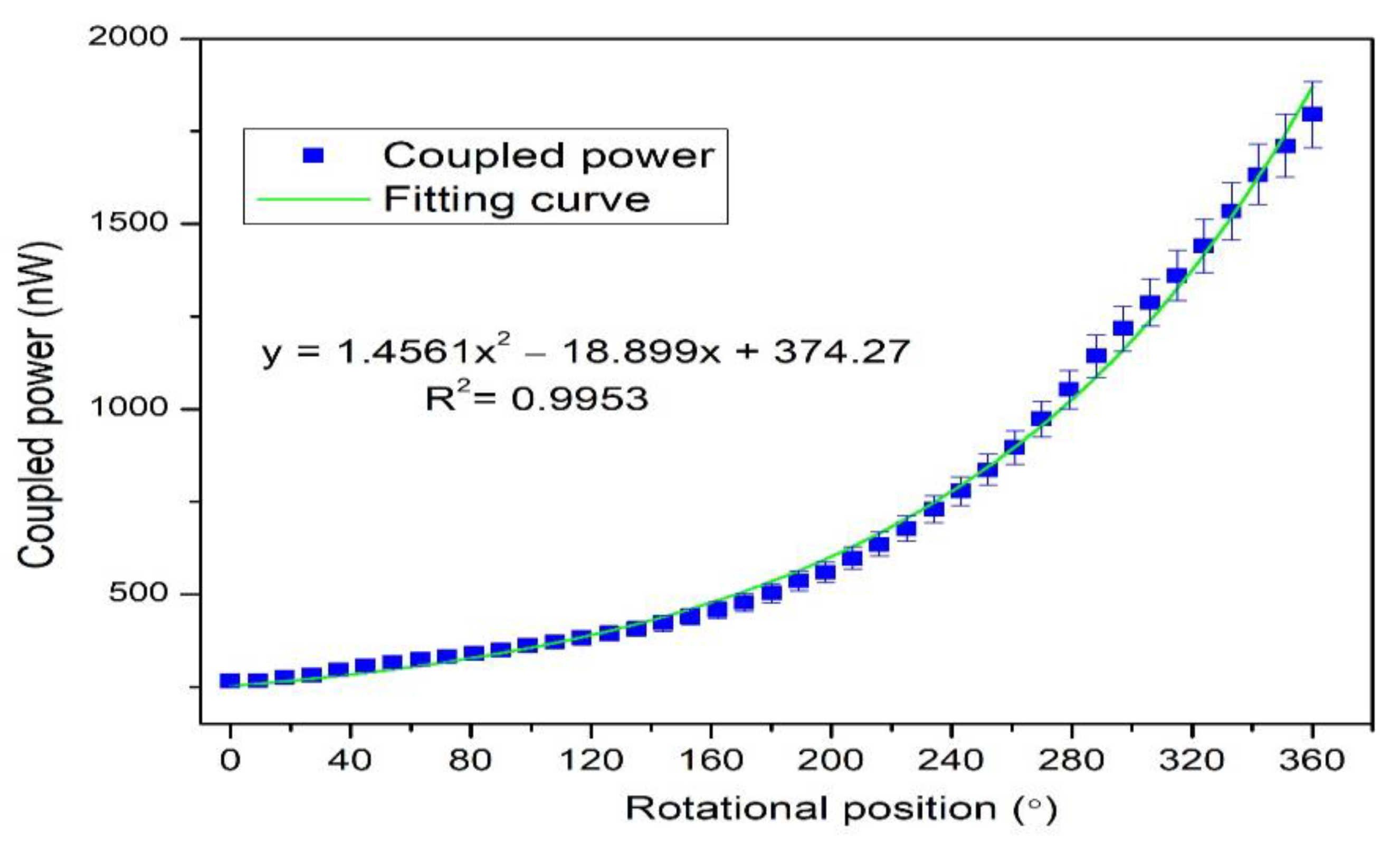
3. Experimental Work and Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, N.; Liao, Q.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, M.; Huang, Y.; Chen, R. Temperature-independent polymer optical fiber evanescent wave sensor. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghaffar, A.; Liu, W.; Yulong, H.; Zhang, H.-X.; Jia, G.; Jia, P.; Mehdi, M.; Hussain, S. Twisted macro-bend coupling based three-dimensional displacement measurement sensor using polymer fiber. OSA Contin. 2019, 2, 2773–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffar, A.; Hou, Y.-L.; Liu, W.-Y.; Dharejo, F.A.; Zhang, H.-X.; Jia, P.; Yanyun, H.; Liu, J.; Yunjun, Z.; Nasir, Z. Two-dimensional displacement optical fiber sensor based on macro-bending effect. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 120, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Ghaffar, A.; Liu, W. A Narrow Groove Structure Based Plasmonic Refractive Index Sensor. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 97289–97295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Hasnain, S.; Khan, N.A.; Bano, S.; Zuhra, F.; Ali, M.; Khan, M.; Abbas, N.; Ali, A. Design and Fabrication of a Fast Response Resistive-Type Humidity Sensor Using Polypyrrole (Ppy) Polymer Thin Film Structures. Polymers 2021, 13, 3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffar, A.; Li, Q.; Mehdi, M.; Hussain, S.; Jia, Y.-M.; Onyekwena, C.C.; Xie, Q.; Ali, N. Analysis of Force Sensor Using Polymer Optical Fiber Based on Twisting Structure. IEEE Sens. J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Chen, X. Fiber Bragg Gratings Sensors for Aircraft Wing Shape Measurement: Recent Applications and Technical Analysis. Sensors 2018, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajić, J.S.; Stupar, D.Z.; Dakić, B.M.; Živanov, M.B.; Nagy, L.F. An absolute rotary position sensor based on cylindrical coordinate color space transformation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 213, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.A.; George, B.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Technologies and Applications of Angle Sensors: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 7195–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budinski, V.; Donlagic, D. Fiber-Optic Sensors for Measurements of Torsion, Twist and Rotation: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszewicz, L.R.; Kurzych, A.; Krajewski, Z.; Dudek, M.; Kowalski, J.K.; Teisseyre, K.P. The Fiber-Optic Rotational Seismograph—Laboratory Tests and Field Application. Sensors 2019, 19, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maheshwari, M.; Yang, Y.; Upadrashta, D.; Chaturvedi, T. A Rotation Independent In-Place Inclinometer/Tilt Sensor Based on Fiber Bragg Grating. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 2943–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, A.; Kawalec, A. Some of Problems of Direction Finding of Ground-Based Radars Using Monopulse Location System Installed on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Sensors 2020, 20, 5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, V.M. Vision based landing for unmanned aerial vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2011 Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2011; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Wei, Z.; Lei, H.; Jiang, J. Four-channel synchronous dynamic measurement system for rudder angles based on line structured light. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2010, 8, 1910–1915. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, G.; Jiang, X.; Hu, Q. Research on angle dynamic measurement system for naval gun level platform. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electronics, Communications and Control (ICECC), Ningbo, China, 9–11 September 2011; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-J.; Ho, H.-N. A Vision-Based Dynamic Rotational Angle Measurement System for Large Civil Structures. Sensors 2012, 12, 7326–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellin, A.; Dolsak, G. The design and application of rotary encoders. Sens. Rev. 2008, 28, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, M.; Husain, I.; Kulkarni, A. Elimination of discrete position sensor and current sensor in switched reluctance motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1992, 28, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, M.; Husain, I.; Mahajan, S.; Ramani, K. New modulation encoding techniques for indirect rotor position sensing in switched reluctance motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1994, 30, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tameh, T.A.; Sawan, M.; Kashyap, R. Novel Analog Ratio-Metric Optical Rotary Encoder for Avionic Applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 6586–6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, S.; Umesh, S.; Asokan, S. Knee Angle Measurement Device Using Fiber Bragg Grating Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 10034–10040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimi, F. Autonomous Robots: Modeling, Path Planning and Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Koubâa, A.; Khelil, A. Cooperative Robots and Sensor Networks 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 554. [Google Scholar]
- Cherubini, A.; Navarro-Alarcon, D. Sensor-Based Control for Collaborative Robots: Fundamentals, Challenges, and Opportunities. Front. Neurorobot. 2021, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, M.; Ourselin, S.; Thompson, S.; Hawkes, D.J.; Kelly, J.; Stoyanov, D. Toward Detection and Localization of Instruments in Minimally Invasive Surgery. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 60, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gongal, A.; Amatya, S.; Karkee, M.; Zhang, Q.; Lewis, K. Sensors and systems for fruit detection and localization: A review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 116, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silwal, A.; Davidson, J.R.; Karkee, M.; Mo, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lewis, K. Design, integration, and field evaluation of a robotic apple harvester. J. Field Robot. 2017, 34, 1140–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Nouaze, J.C.; Mbouembe, P.L.T.; Kim, J.H. YOLO-Tomato: A Robust Algorithm for Tomato Detection Based on YOLOv3. Sensors 2020, 20, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, L.; Schupp, J. Sensing and Automation in Pruning of Apple Trees: A Review. Agronomy 2018, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Gohary, M.; McNames, J. Shoulder and Elbow Joint Angle Tracking with Inertial Sensors. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 2635–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gohary, M.; McNames, J. Human Joint Angle Estimation with Inertial Sensors and Validation with A Robot Arm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejnabadi, H.; Jolles, B.; Aminian, K. A New Approach to Accurate Measurement of Uniaxial Joint Angles Based on a Combination of Accelerometers and Gyroscopes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 52, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, D. A new instrumentation system for training rowers. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Granat, M.H. A practical gait analysis system using gyroscopes. Med. Eng. Phys. 1999, 21, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezekiel, S.; Arditty, H.J. Fiber-Optic Rotation Sensors and Related Technologies. In Proceedings of the First International Conference MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA, 9–11 November 1981; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Goss, W.C.; Youmans, B.R.; Nerheim, N.M.; Bartman, R.K. Closed Loop Fiber Optic Rotation Sensor. U.S. Patent 4,662,751, 5 May 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.-L.; Wang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Niu, L.; Gong, H. Angle sensor based on two cascading abrupt-tapers modal interferometer in single mode fiber. Optik 2017, 132, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, X.-G.; Cai, L. A reflective intensity modulated fiber tilt angle sensor based on an all-photonic crystal fiber interferometer. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 244, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Yang, X.; Tong, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, A. Temperature-Independent Rotational Angle Sensor Based on Fiber Bragg Grating. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 11, 1233–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, A.; Abdullah, A.; Noor, M.M.; Ibrahim, M.; Ibrahim, R.R.; Tan, T.; Zhang, J. Dynamic bending and rotation sensing based on high coherence interferometry in multicore fiber. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 135, 106716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomer, M.; Zubia, J.; Quintela, M.A.; Quintela, A.; Lopez-Higuera, J.M. Angular and displacement sensor based on POF and moire patterns. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Optical Fibre Sensors, Bruges, Belgium, 3–27 May 2005; SPIE: Prague, Czech Republic, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffar, A.; Li, Q.; Mehdi, I.; Abro, K.; Karim, N.; Onyekwena, C.C.; Mehdi, M.; Chen, B. A novel sensor design for displacement measurement using plastic optical fiber-based on face-coupling method. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2021, 67, 102684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Frizera, A.; Pontes, M.J. Sensitive zone parameters and curvature radius evaluation for polymer optical fiber curvature sensors. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 100, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartiano, D.; Geernaert, T.; Roca, E.T.; Sales, S. Bend-Direction and Rotation Plastic Optical Fiber Sensor. Sensors 2020, 20, 5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffar, A.; Li, Q.; Haider, S.A.; Sun, A.; Leal-Junior, A.G.; Xu, L.; Chhattal, M.; Mehdi, M. A simple and high-resolution POF displacement sensor based on face-coupling method. Measurement 2022, 187, 110285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, A.W. Coupled-Mode Theory for Optical Fibers. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1972, 62, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Hou, J. Taper-fused side pump combiner for all-fiber lasers and amplifiers: A review. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 130, 106353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffar, A.; Mehdi, M.; Hu, Y.; Leal-Junior, A.G.; Basit, A.; Hussain, S.; Ali, A.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Li, Q. An enlarge polymer optical fiber linear-displacement sensor based on constructive interference. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2021, 63, 102481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schermer, R.T.; Cole, J.H. Improved Bend Loss Formula Verified for Optical Fiber by Simulation and Experiment. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2007, 43, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, G.; Jia, P.; Liang, T.; Hong, Y.; Wang, H.; Ghaffar, A.; Xiong, J. Double-sided Polished Ultra-stable and Ultra-sensitive Optical Fiber Sensor. Plasmonics 2020, 15, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Sensors: An Introductory Course; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Novais, S.; Ferreira, M.S.; Pinto, J.L. Humidity sensor based on optical fiber coated with agarose gel. In Optical Sensors; SPIE: Prague, Czech Republic, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Ghaffar, A.; Hou, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, F.; Wang, J. A Micro Structure POF Relative Humidity Sensor Modified With Agarose Based on Surface Plasmon Resonance and Evanescent Wave Loss. Photon. Sens. 2020, 11, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
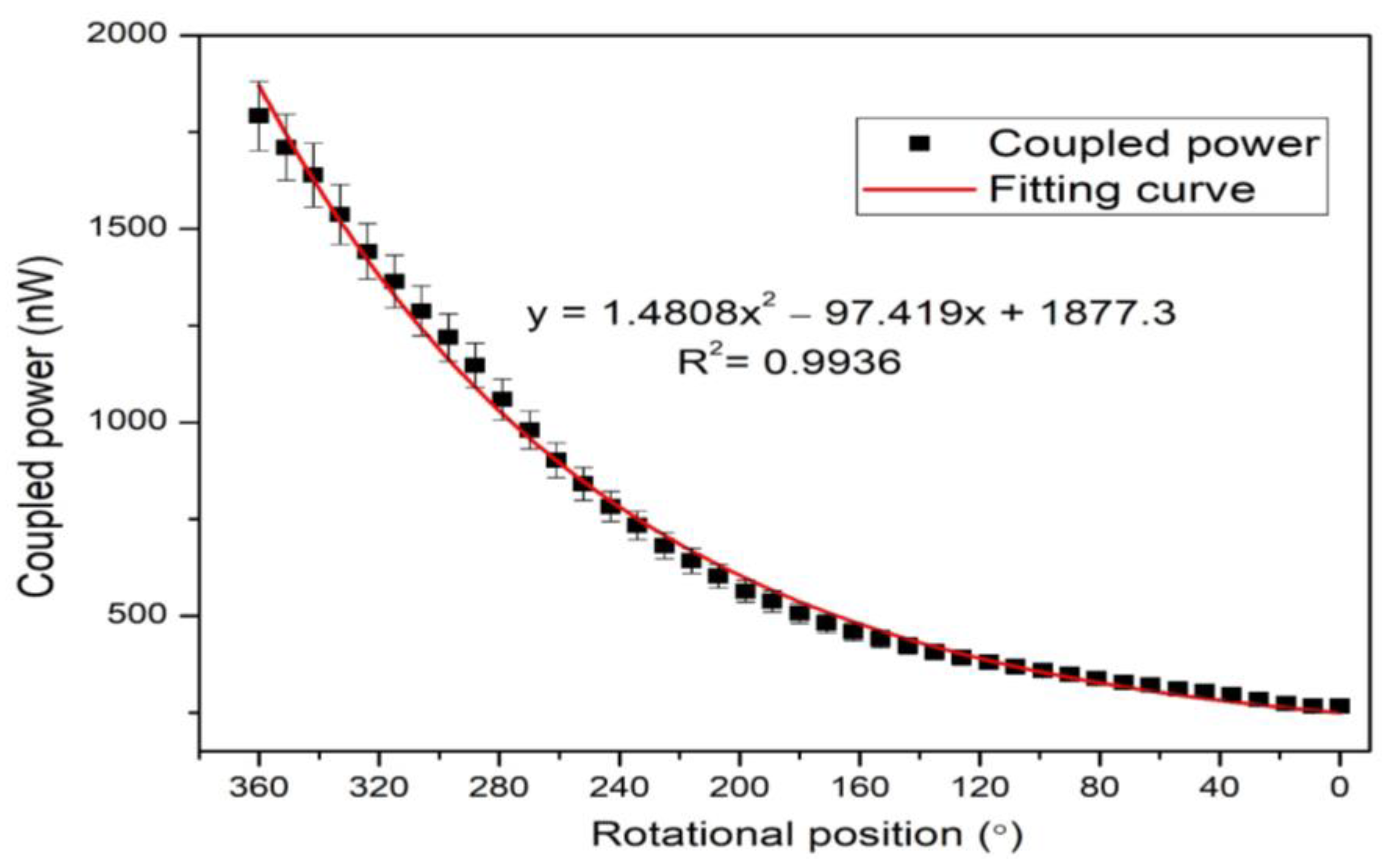
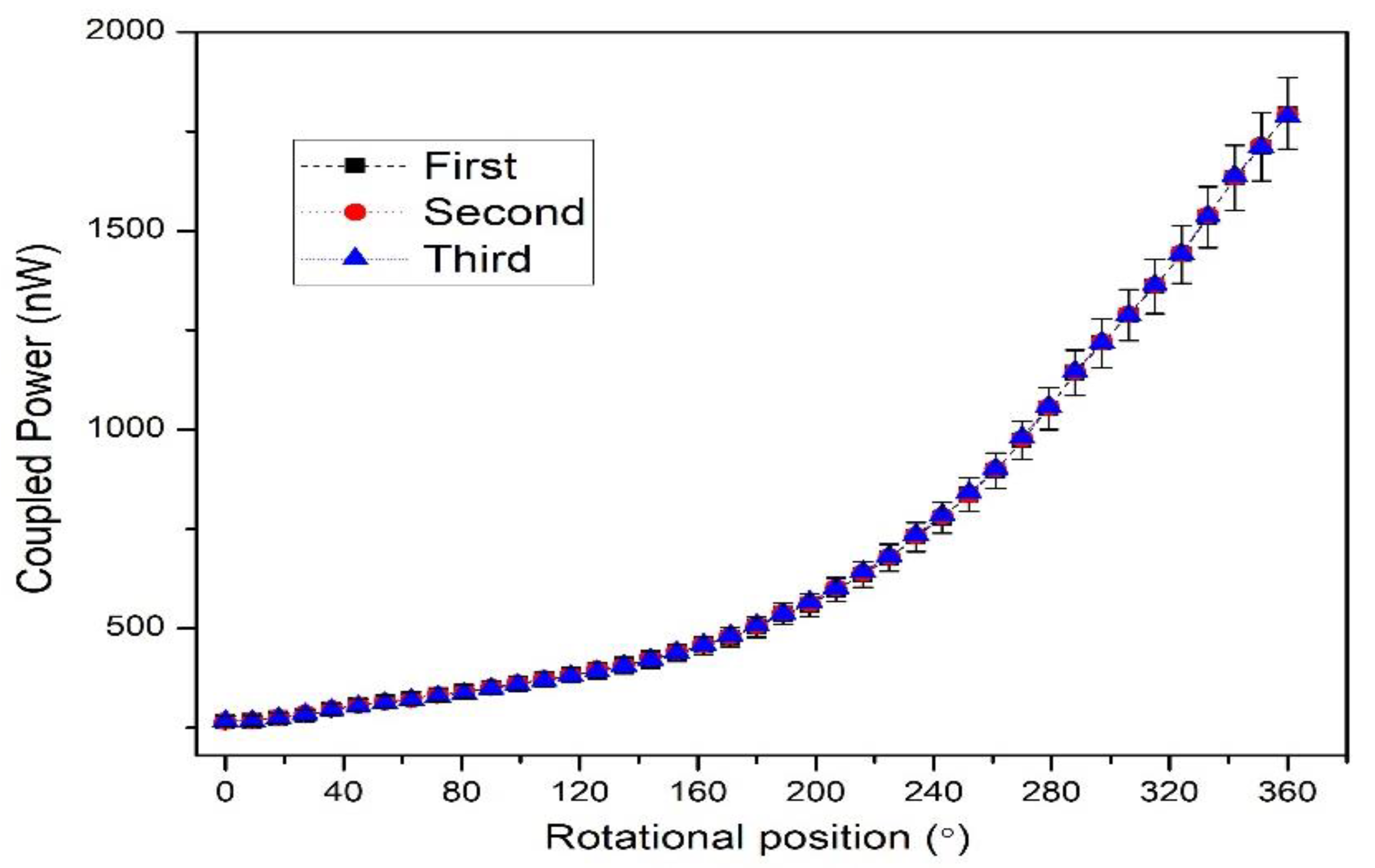
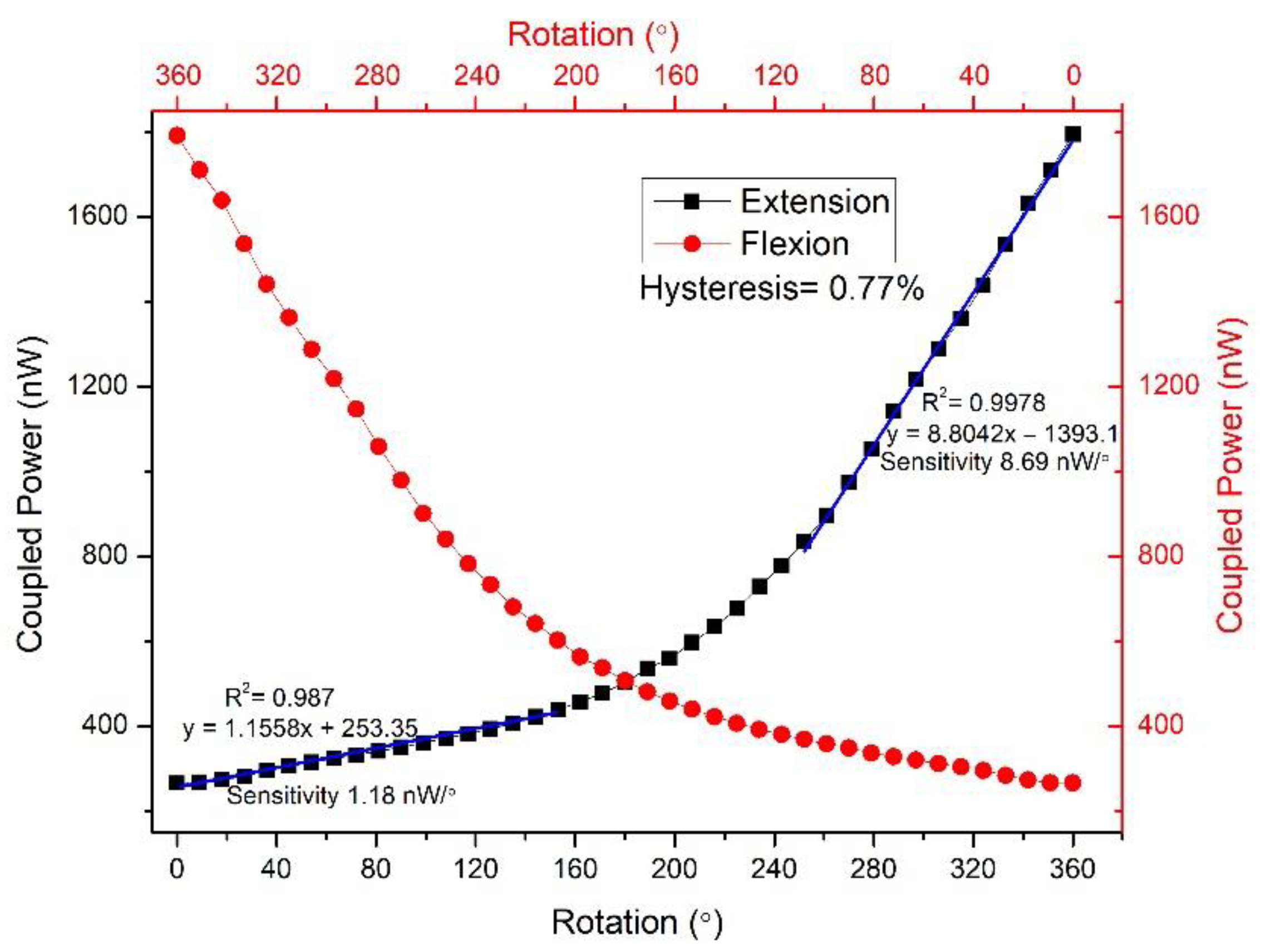
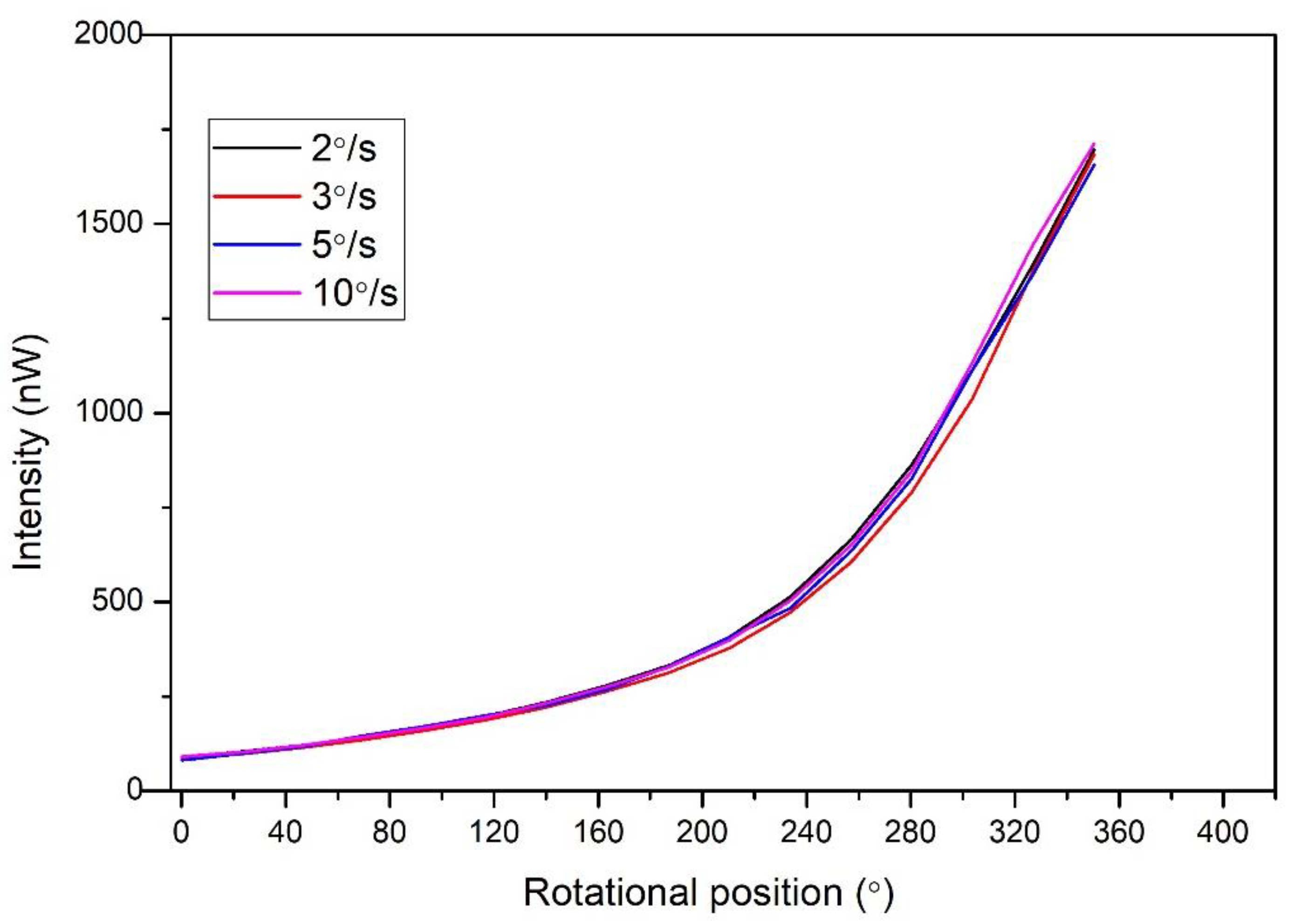
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Core material | Polymethyl methacrylate |
| Clad material | Fluoropolymer |
| Refractive Index Profile | Step refractive index |
| Numerical aperture | 0.5 |
| Transmission attenuation | 150 (dB/km) |
| Refractive Index | 1.49 |
| Core diameter | 980 µm |
| Cladding diameter | 1 mm |
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Fiber length | 1 m |
| Twisting length | 10 cm |
| Twisting region | From 40 cm to 50 cm |
| Initial bending radius | 4 cm |
| Ref. | Method | Range | Sensitivity | Fiber type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [22] | FBG sensor | 0–150° | 0.012 nm/° | FBG |
| [38] | Two abrupt-tapers modal interferometer | 0.0575° and 0.075° | 601.8 nm/° | Single-mode optical fiber |
| [39] | Interferometer | 0°–90° | 55.67 pm/◦ | PCF |
| [40] | FBG sensor | −21°–21° | 0.743 nm/° | FBG |
| [41] | Coherence interferometry | 0–360° | 6.2 fringe/° | Seven core fiber |
| [42] | Moiré pattern | 0°–30° | 2.1 µW/° | POF |
| [44] | Intensity variation | 0°–90° | 20.9 mV/◦ | POF |
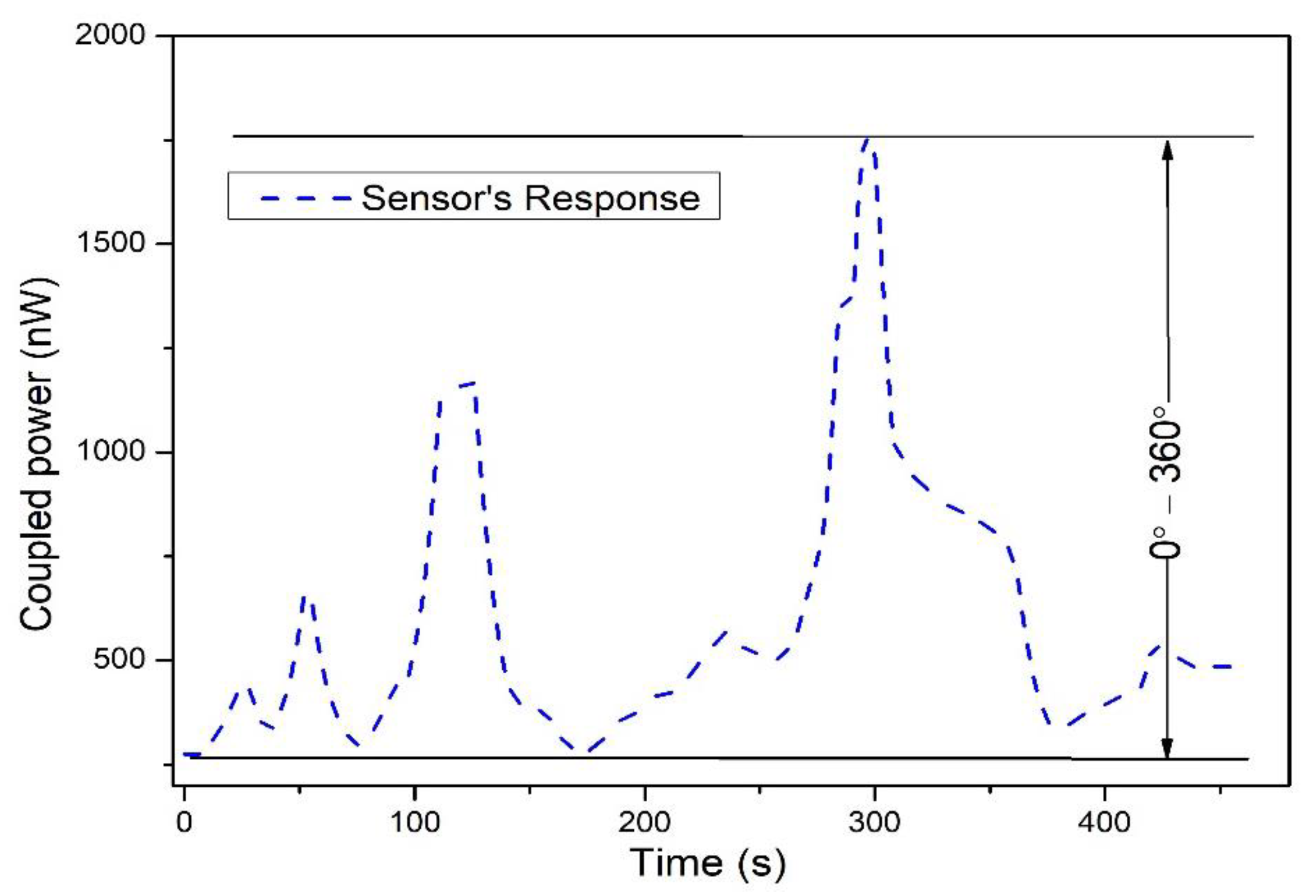
| In this work | Intensity variation | 0°–360° | 1.18 nW/° (0–163°) 8.69 nW/° (243–360°) | POF |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Ghaffar, A.; Li, Y.; Mehdi, I.; Mehdi, R.; A. Soomro, F.; Hussain, S.; Mehdi, M.; Li, Q.; Li, Z. Dynamic Rotational Sensor Using Polymer Optical Fiber for Robot Movement Assessment Based on Intensity Variation. Polymers 2022, 14, 5167. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235167
Shi J, Ghaffar A, Li Y, Mehdi I, Mehdi R, A. Soomro F, Hussain S, Mehdi M, Li Q, Li Z. Dynamic Rotational Sensor Using Polymer Optical Fiber for Robot Movement Assessment Based on Intensity Variation. Polymers. 2022; 14(23):5167. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235167
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jianwei, Abdul Ghaffar, Yongwei Li, Irfan Mehdi, Rehan Mehdi, Fayaz A. Soomro, Sadam Hussain, Mujahid Mehdi, Qiang Li, and Zhiqiang Li. 2022. "Dynamic Rotational Sensor Using Polymer Optical Fiber for Robot Movement Assessment Based on Intensity Variation" Polymers 14, no. 23: 5167. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235167
APA StyleShi, J., Ghaffar, A., Li, Y., Mehdi, I., Mehdi, R., A. Soomro, F., Hussain, S., Mehdi, M., Li, Q., & Li, Z. (2022). Dynamic Rotational Sensor Using Polymer Optical Fiber for Robot Movement Assessment Based on Intensity Variation. Polymers, 14(23), 5167. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235167







