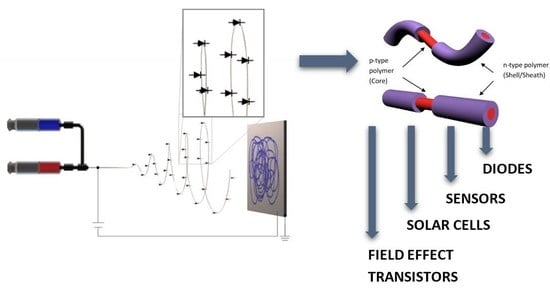
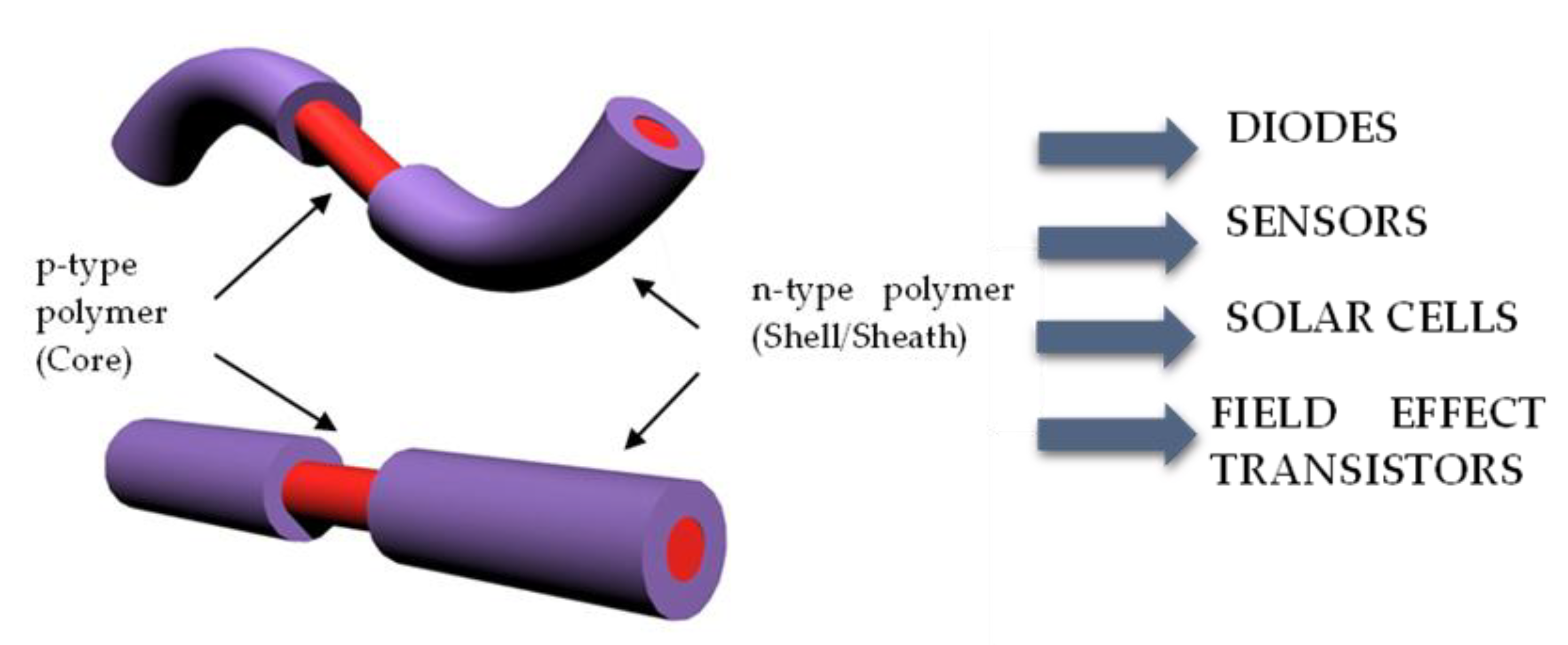
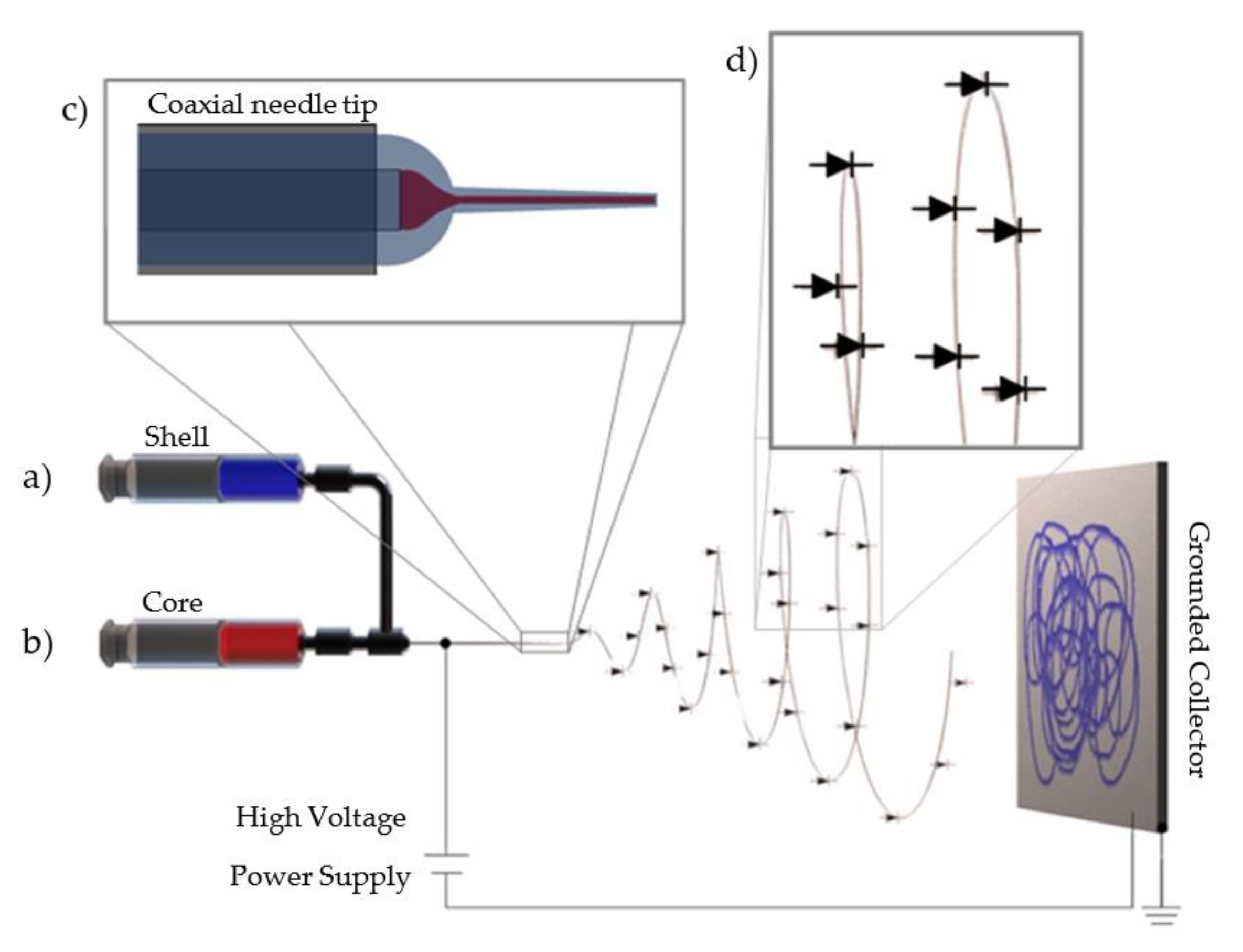
Electrospinning Technique for Fabrication of Coaxial Nanofibers of Semiconductive Polymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
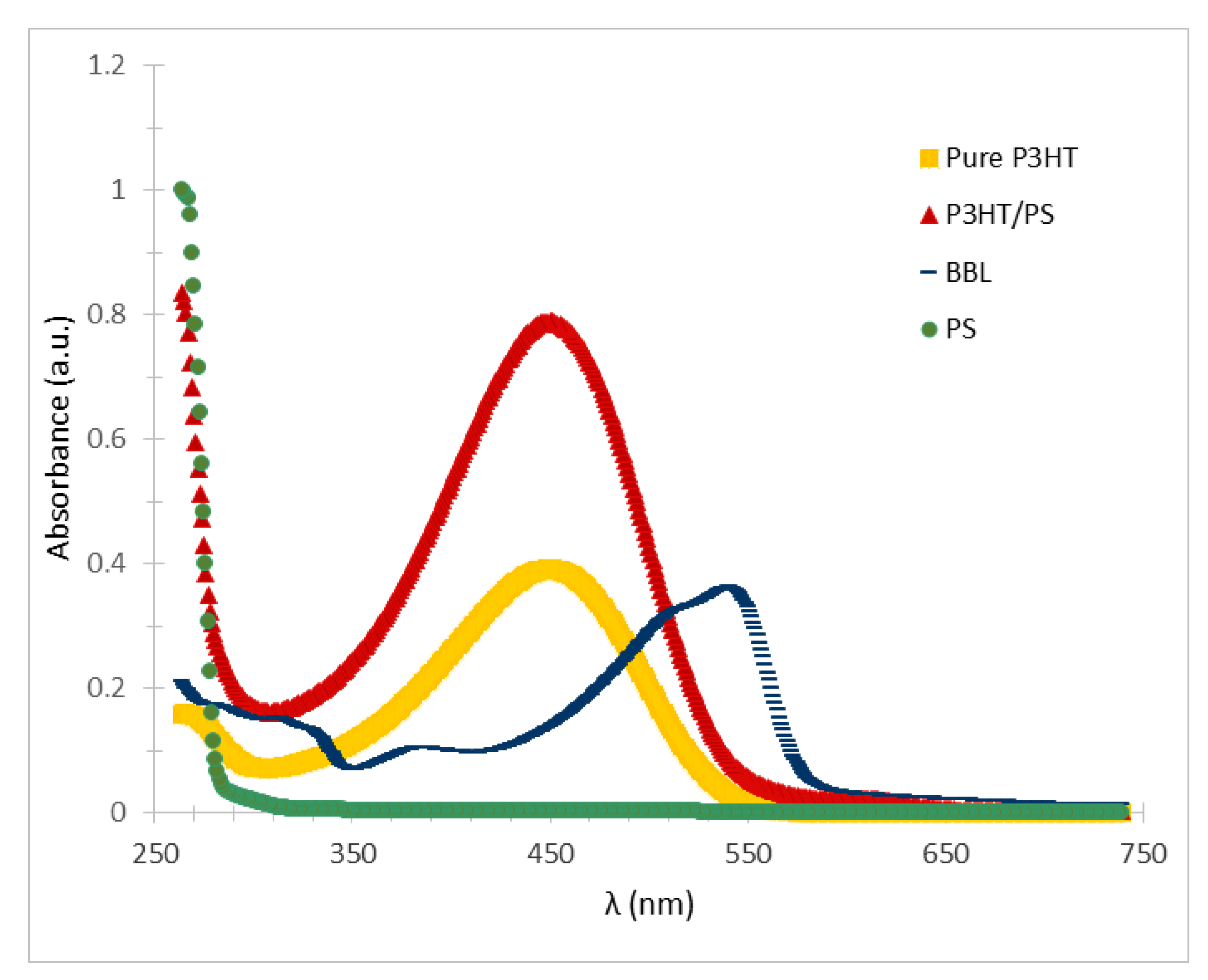
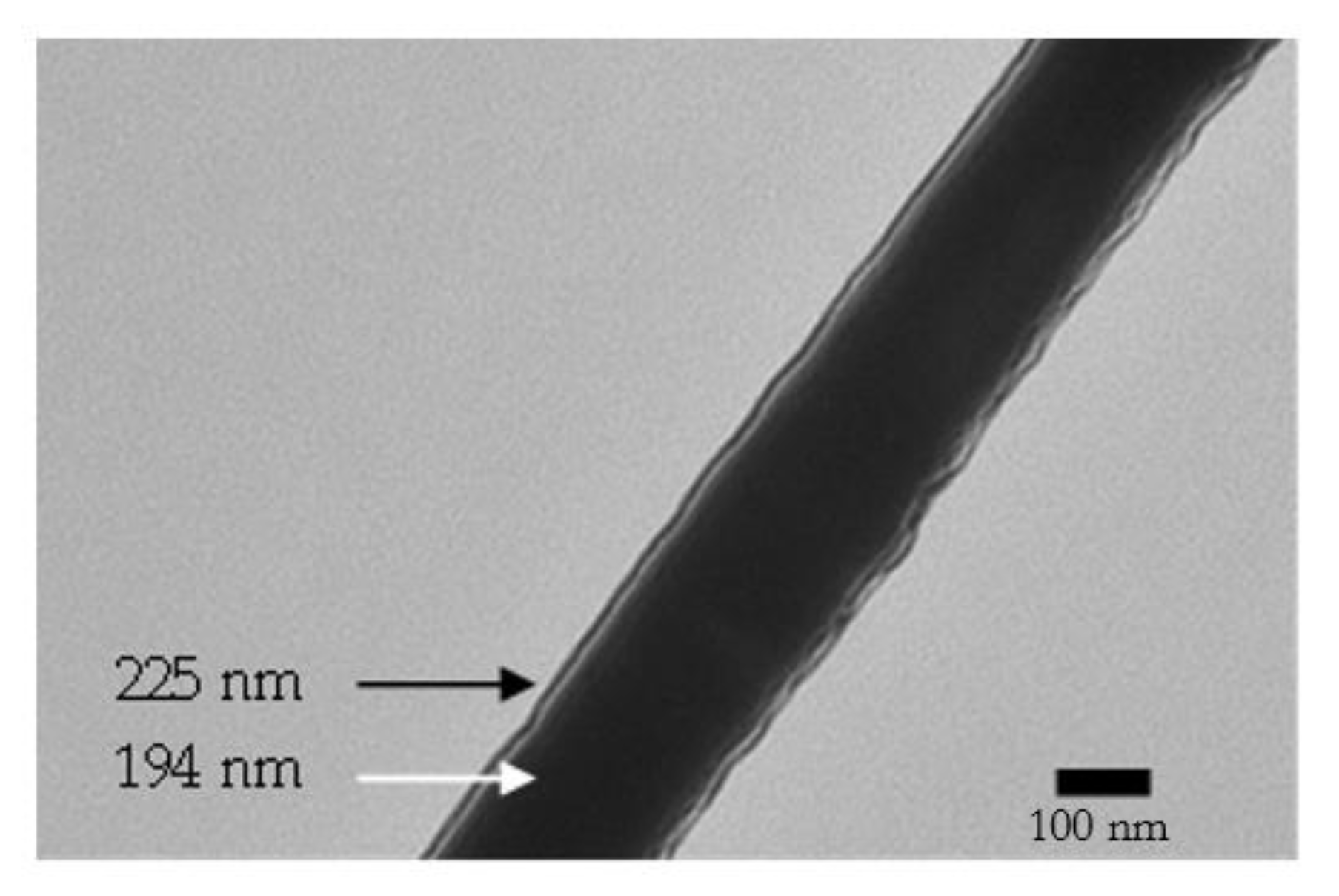
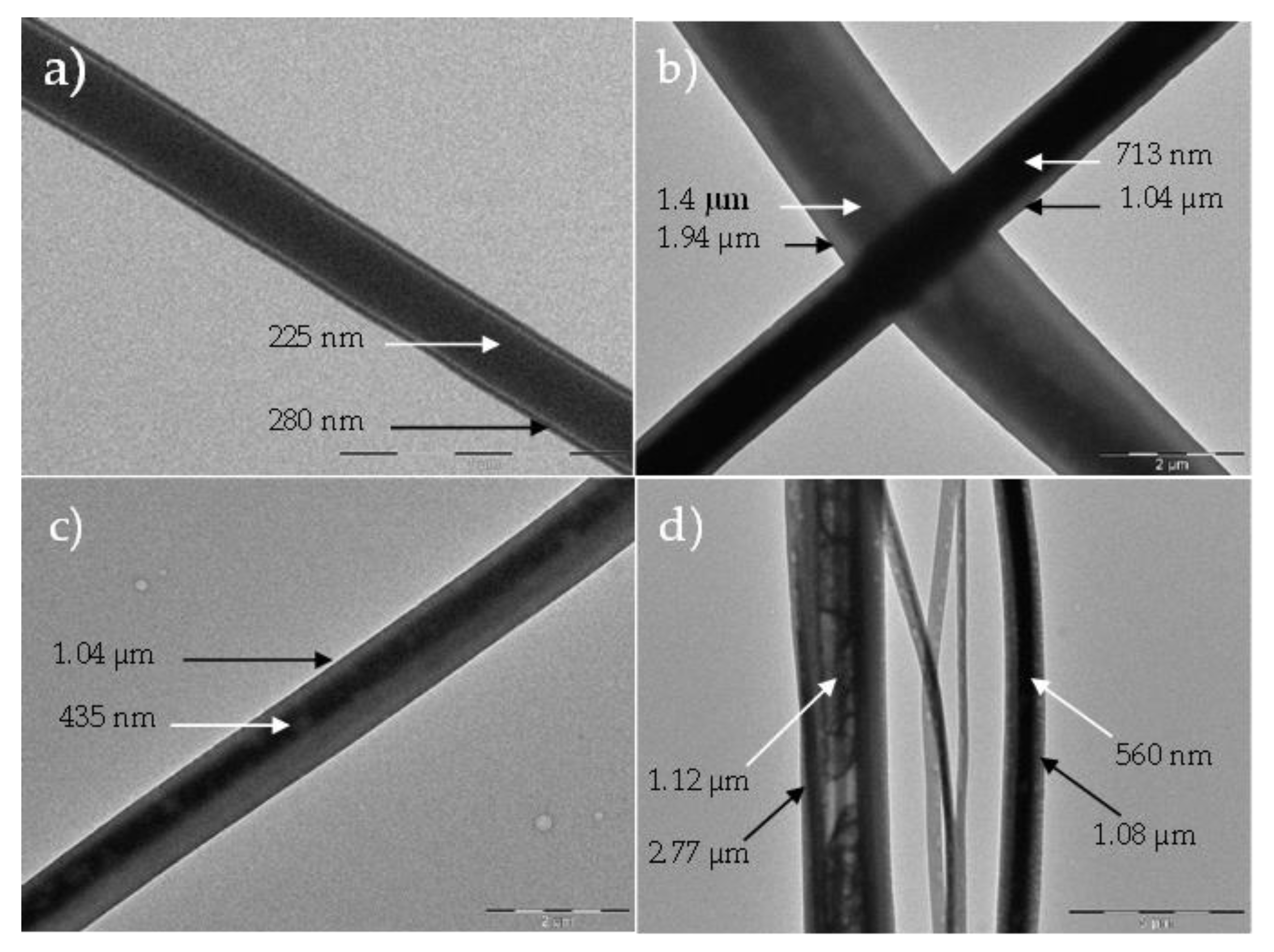
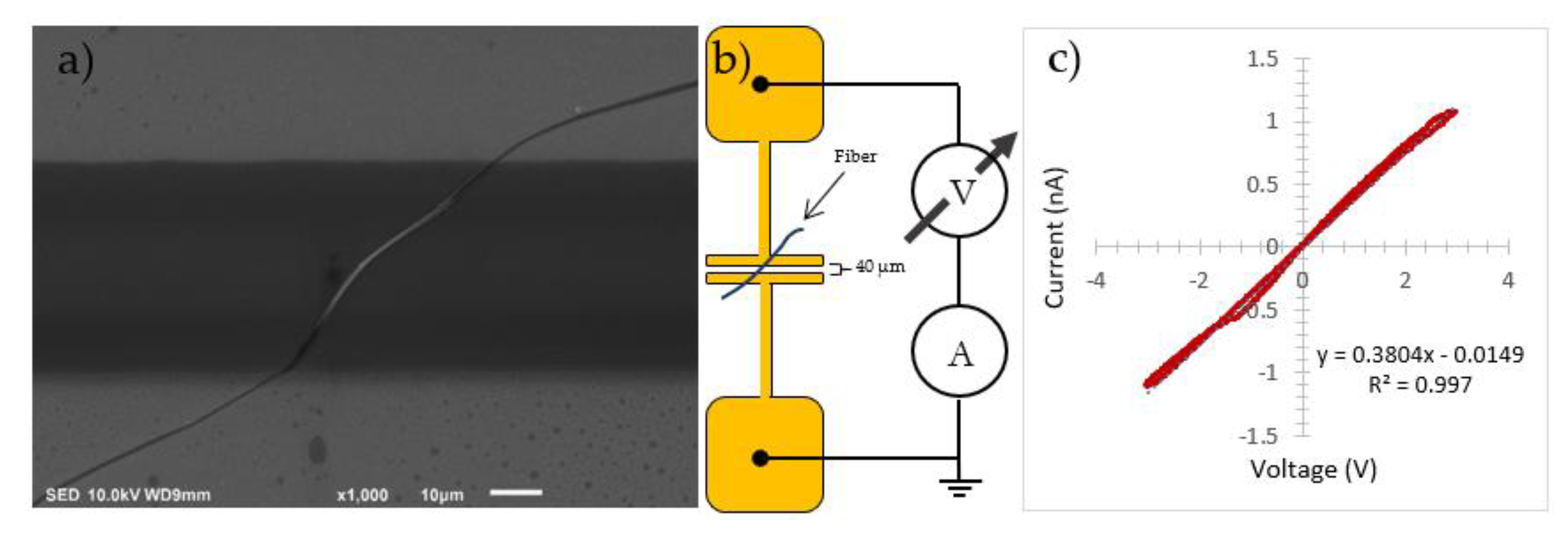
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, S.; Si, Y.; Han, Y.; Wu, T.; Iqbal, M.I.; Fei, B.; Li, R.K.Y.; Hu, J.; Qu, J. Recent Progress in Protective Membranes Fabricated via Electrospinning: Advanced Materials, Biomimetic Structures, and Functional Applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 34, 2107938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Kang, S.; Park, J.; Hwang, J.J. Fabrication of silver nanowire coated fibrous air filter medium via a two-step process of electrospinning and electrospray for anti-bioaerosol treatment. Haz. Mat. 2021, 411, 125043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, D.; Liu, Y.; Zou, Q.; Xu, S.; Luo, S.; Ye, C. Coaxial bioelectrospinning of P34HB/PVA microfibers biomimetic scaffolds with simultaneity cell-laden for improving bone regeneration. Mat. Des. 2022, 213, 110349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Steckl, A.J. Coaxial electrospinning formation of complex polymer fibers and their applications. Chem. Plus Chem. 2019, 84, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Abdelhakim, H.E. Drug Delivery Applications of Coaxial Electrospun Nanofibres in Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Garcia, W.; Jayathilaka, W.A.D.M.; Chinnappan, A.; Tran, T.Q.; Baskar, C.; Thomas, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Nanocomposites for electronic applications that can be embedded for textiles and wearables. Sci. China. Tech. Sci. 2019, 62, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilaka, W.A.D.M.; Qi, K.; Qin, Y.; Chinnappan, A.; Serrano-Garcia, W.; Chinnappan, B.; Wang, H.; He, J.; Cui, S.; Thomas, S.; et al. Significance of nanomaterials in wearables: A review on wearable actuators and sensors. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayan, M.A.H.; Taromi, F.A.; Lanzi, M.; Pierini, F. Enhanced efficiency in hollow core electrospun nanofiber-based organic solar cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Yang, C.; Gong, X.; Lee, K.; Heeger, A.J. Thermally stable, efficient polymer solar cells with nanoscale control of the interpenetrating network morphology. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Takeda, Y.; Mizukami, M.; Kumaki, D.; Tokito, S. Fully solution-processed flexible organic thin film transistor arrays with high mobility and exceptional uniformity. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzio, A.; Canesi, E.V.; Bertarelli, C.; Caironi, M. Electrospun polymer fibers for electronic applications. Materials 2014, 7, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinschmidt, A.T.; Root, S.E.; Lipomi, D.J. Poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT): Fruit fly or outlier in organic solar cell research? Mater. Chem. 2017, 5, 11396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Liu, C.L.; Chen, W.C. Flexible nonvolatile transistor memory devices based on One-Dimensional electrospun P3HT: Au hybrid nanofibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimia-Vladu, M. “Green” electronics: Biodegradable and biocompatible materials and devices for sustainable future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Kai, D.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun photosensitive nanofibers: Potential for photocurrent therapy in skin regeneration. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2012, 12, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, V.; Altobelli, R.; Cirillo, V.; Cummaro, A.; Ambrosio, L. Additive electrospraying: A route to process electrospun scaffolds for controlled molecular release. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2015, 26, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moge, A.K.; Gupta, B.S. Co-axial electrospinning for nanofiber structures: Preparation and applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ding, S.; Zhu, W.; Feng, L.; Dong, H.; Hu, W.J. Recent advances in one-dimensional organic p-n heterojunctions for optoelectronic device applications. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleshin, A.N. Polymer Nanofibers and Nanotubes: Charge Transport and Device Applications. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, R.; Pinto, N.J. Electrospun poly (3-hexylthiophene-2, 5-diyl) fiber field effect transistor. Synth. Met. 2005, 151, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.F.; Sun, B.; Breiby, D.W.; Nielsen, M.M.; Sölling, T.I.; Giles, M.; McCulloch, I.; Sirringhaus, H. Enhanced mobility of poly (3-hexylthiophene) transistors by spin-coating from high-boiling-point solvents. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, J.A.; Frisbie, C.D.J. Field effect transport and trapping in regioregular polythiophene nanofibers. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 19169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, A.; Jenekhe, S.A. High electron mobility in ladder polymer field-effect transistors. JACS 2003, 125, 13656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briseno, A.L.; Mansfeld, S.C.B.; Shamberger, P.J.; Ohuchi, F.S.; Bao, Z.; Jenekhe, S.A.; Xia, Y. Self-assembly, molecular packing, and electron transport in n-type polymer semiconductor nanobelts. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, W.; Pinto, N.J. Electrospun fibers of poly (vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene)/poly (3-hexylthiophene) blends from tetrahydrofuran. Ferroelectrics 2012, 432, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, W.; Meléndez, A.; Ramos, I.; Pinto, N.J. Poly (lactic acid)/poly (3-hexylthiophene) composite nanofiber fabrication for electronic applications. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.S.; Kim, T.G.; Park, T.G. Surface-functionalized electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, M.O.; Morfa, A.J.; White, M.S.; Kopidakis, N.; Shaheen, S.E.; Rumbles, G.; Ginley, D.S. Pathways for the degradation of organic photovoltaic P3HT:PCBM based devices. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2008, 92, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briseno, A.L.; Kim, F.S.; Babel, A.; Xia, Y.; Jenekhe, S.A. n-Channel polymer thin film transistors with long-term air-stability and durability and their use in complementary inverters. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 16461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, J.E. Addressing challenges. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Garcia, W. Advanced Organic Polymers for the Nanoscale Fabrication of Fiber-Based Electronics Using the Electrospinning Technique. USF Tampa Graduate Theses and Dissertations. 2021. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usf.edu/etd/9228 (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Sundarrajan, S.; Murugan, R.; Nair, A.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Fabrication of P3HT/PCBM solar cloth by electrospinning technique. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, P.; Schiffman, J.D. Beyond the single-nozzle: Coaxial electrospinning enables innovative nanofiber chemistries, geometries, and applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, N.J.; Carrasquillo, K.V.; Rodd, C.M.; Agarwal, R. Rectifying junctions of tin oxide and poly (3-hexylthiophene) nanofibers fabricated via electrospinning. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 083504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Meguro, H.; Okamoto, S.; Kimura, M. Flexible tactile sensor using the reversible deformation of poly (3-hexylthiophene) nanofiber assemblies. Langmuir 2012, 28, 17593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Moon, G.D.; Jeong, U.J. Continuous production of uniform poly (3-hexylthiophene)(P3HT) nanofibers by electrospinning and their electrical properties. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, J.H.; Koh, W.G.; Myoung, J.M.; Hur, J.H.; Park, J.J.; Cho, J.H.; Jeong, U. Periodic array of polyelectrolyte-gated organic transistors from electrospun poly (3-hexylthiophene) nanofibers. Nano. Lett. 2010, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, A.; Wind, J.D.; Jenekhe, S.A. Ambipolar charge transport in air-stable polymer blend thin-film transistors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenekhe, S.A.; Yi, S. Efficient photovoltaic cells from semiconducting polymer heterojunctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Jenekhe, S.A. Efficient solar cells from layered nanostructures of donor and acceptor conjugated polymers. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, X.; Lee, W.H.; Lim, J.A.; Kim, J.S.; Kwak, D.; Cho, K. Organic thin-film transistors based on blends of poly (3-hexylthiophene) and polystyrene with a solubility-induced low percolation threshold. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Lim, J.A.; Wang, X.; Lee, W.H.; Hwang, M.; Cho, K. Versatile use of vertical-phase-separation-induced bilayer structures in organic thin-film transistors. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Cha, S.N.; Im, K.; Lee, S.W.; Jeong, U.; Kim, J.; Park, J.J. P3HT-PS blend nanofiber FET based on electrospinning. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Nanotechnology: Joint Symposium with NANO Korea 2010, Ilsan, Republic of Korea, 17–20 August 2010; pp. 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, W.; Meléndez, A.; Ramos, I.; Pinto, N.J. Electrospun composite poly (lactic acid)/polyaniline nanofibers from low concentrations in CHCl3: Making a biocompatible polyester electro-active. Polymer 2014, 55, 5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenekhe, S.A.; de Paor, L.R.; Chen, X.L.; Tarkka, R.M. Photoinduced electron transfer in binary blends of conjugated polymers. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Park, K.; Dai, L.J. Liquid crystalline polymers for efficient bilayer-bulk-heterojunction solar cells. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 7892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, K.S.; Taylor-Hamilton, B.E.; Spry, R.J.; Ferguson, J.B. Photoconducting properties of a ladder polymer. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 77, 3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serrano-Garcia, W.; Ramakrishna, S.; Thomas, S.W. Electrospinning Technique for Fabrication of Coaxial Nanofibers of Semiconductive Polymers. Polymers 2022, 14, 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235073
Serrano-Garcia W, Ramakrishna S, Thomas SW. Electrospinning Technique for Fabrication of Coaxial Nanofibers of Semiconductive Polymers. Polymers. 2022; 14(23):5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235073
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerrano-Garcia, William, Seeram Ramakrishna, and Sylvia W. Thomas. 2022. "Electrospinning Technique for Fabrication of Coaxial Nanofibers of Semiconductive Polymers" Polymers 14, no. 23: 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235073
APA StyleSerrano-Garcia, W., Ramakrishna, S., & Thomas, S. W. (2022). Electrospinning Technique for Fabrication of Coaxial Nanofibers of Semiconductive Polymers. Polymers, 14(23), 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235073