Novel Polymeric Nanomaterial Based on Poly(Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate-Methacryloylamidophenylalanine) for Hypertension Treatment: Properties and Drug Release Characteristics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
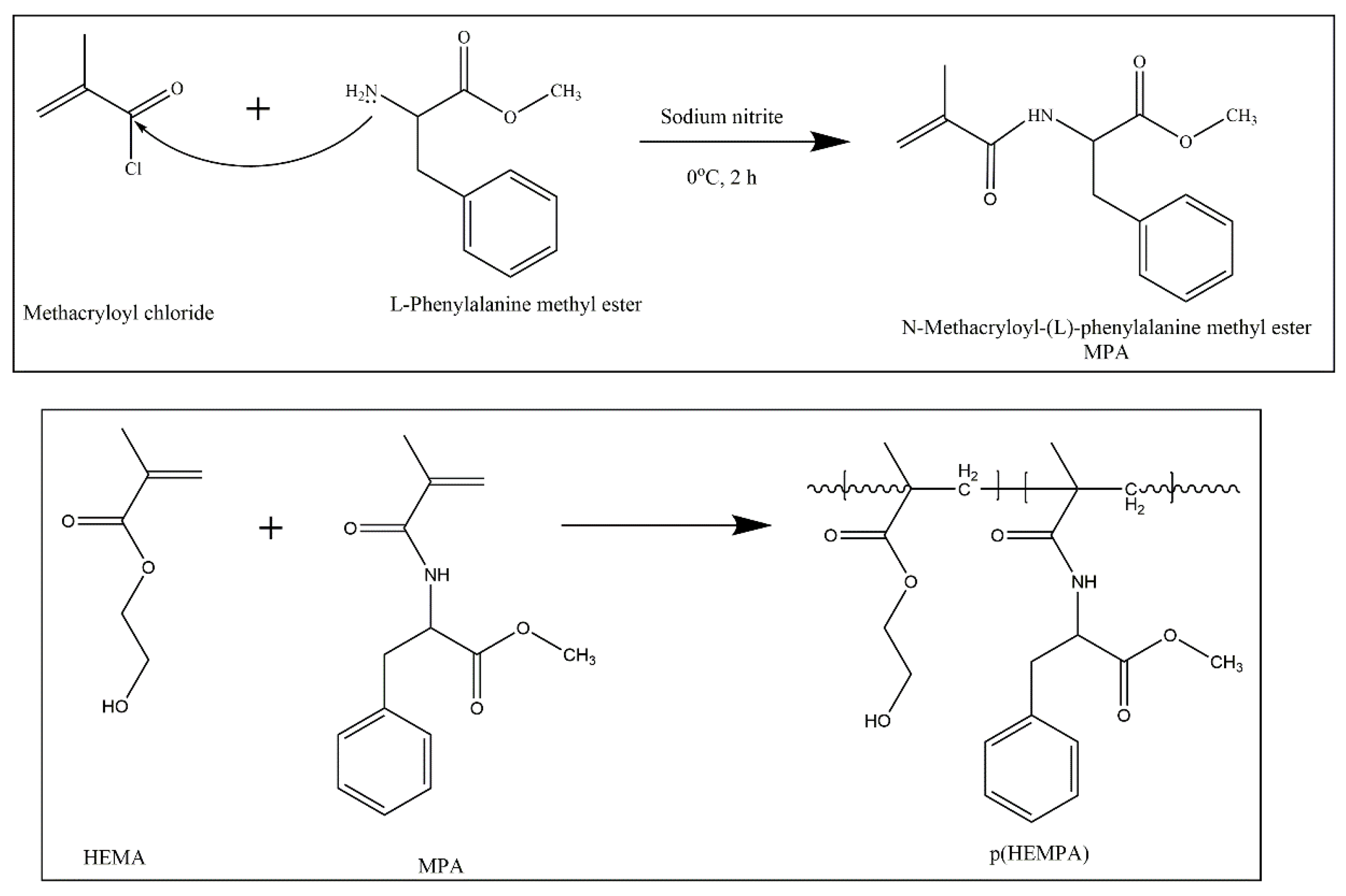
2.2.1. Preparation of p(HEMPA) Nanomaterials
Synthesis of MPA
Preparation of p(HEMPA) Nanopolymers
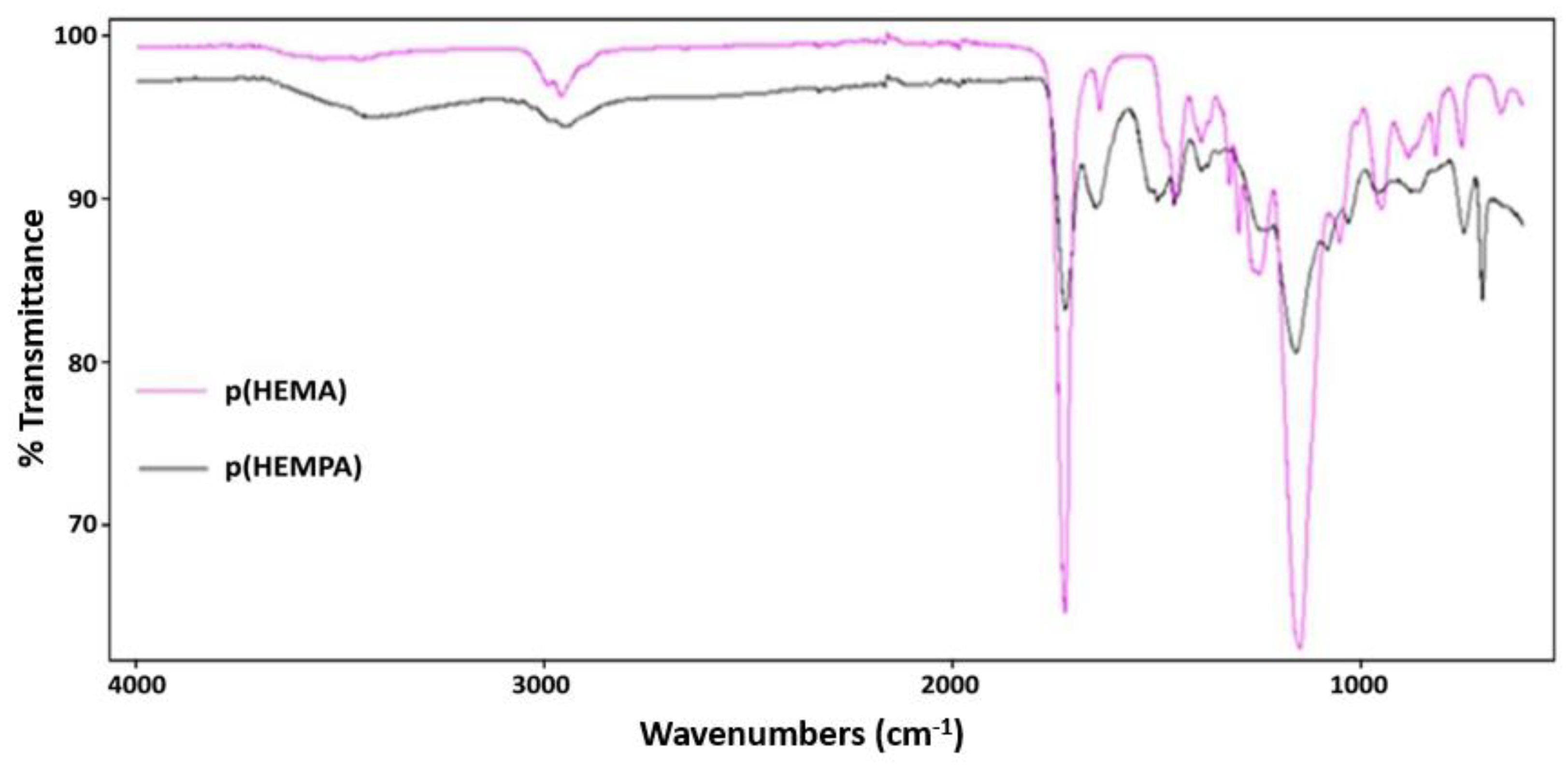
2.2.2. Characterization Studies
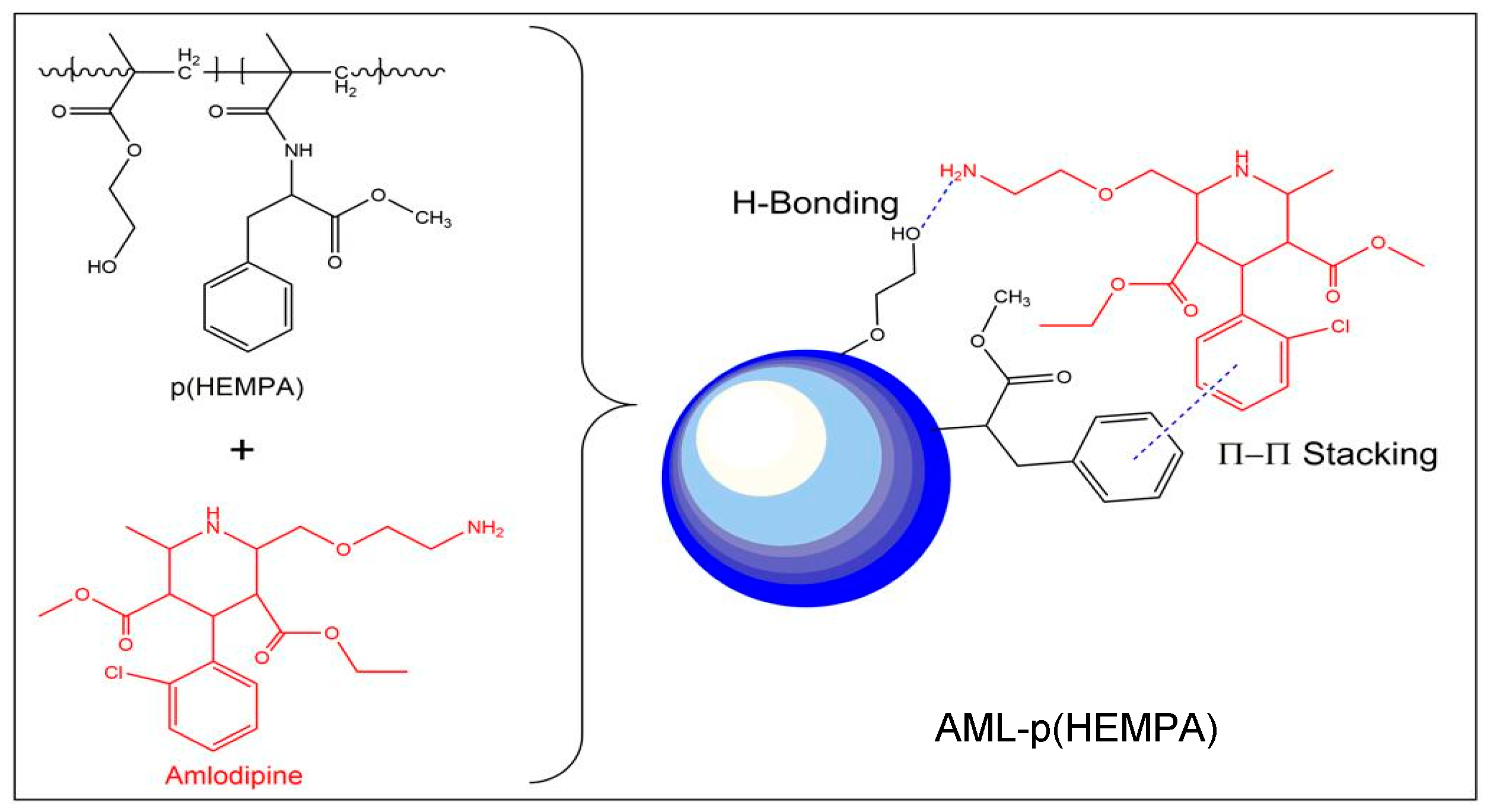
2.2.3. Binding Studies of Amlodipine
2.2.4. Effect of Nanopolymer: Drug Ratio
- Q: AML amount bound to 1 g of nanopolymer (mg/g);
- C0: AML initial concentration;
- C: AML concentration in the solution (mg/mL);
- V: solution volume (mL);
- M: nanopolymer mass (g).
2.2.5. Optimization of AML Release Conditions
2.2.6. In Vitro AML Release Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of p(HEMPA) Nanopolymer
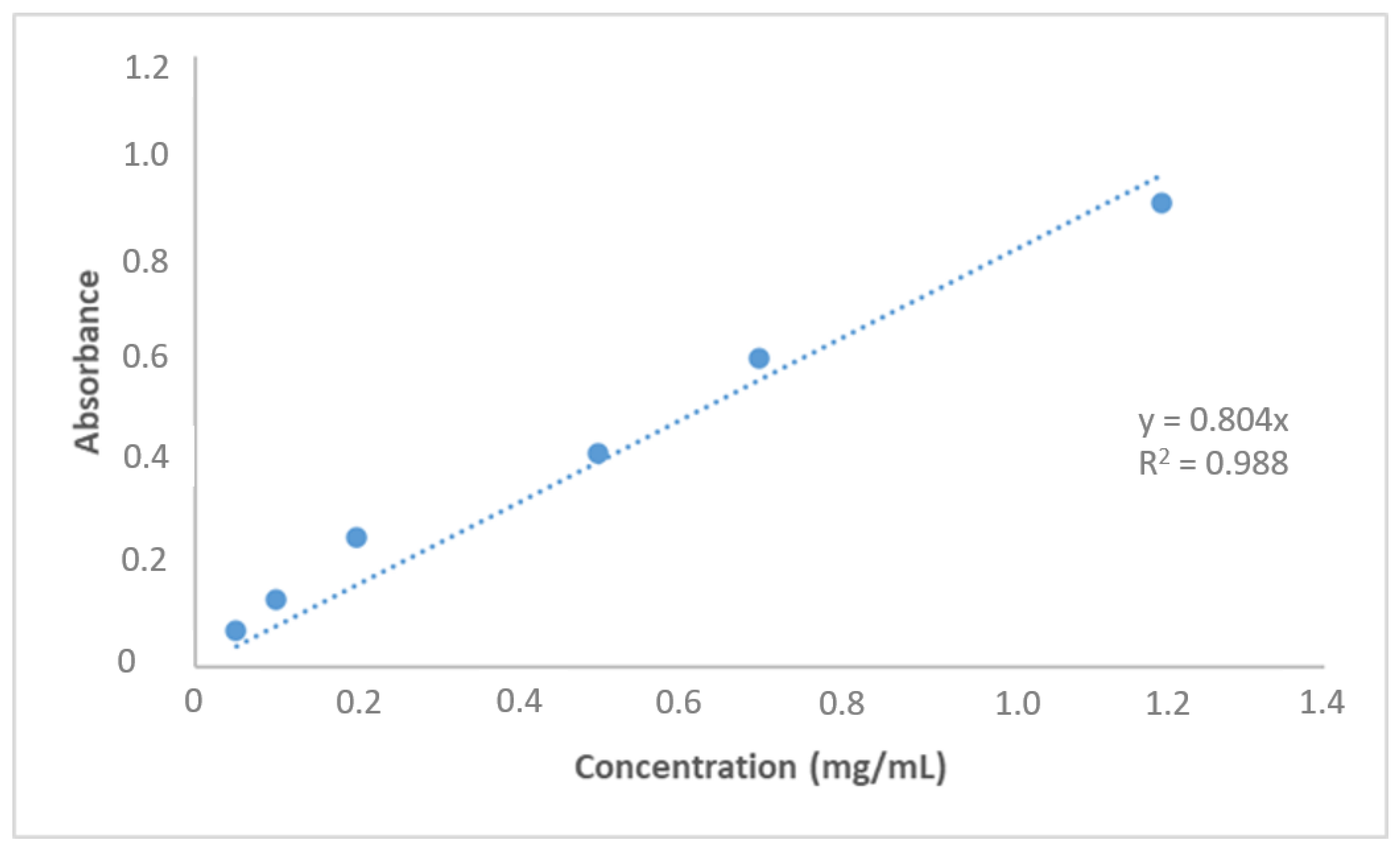
3.2. AML Binding to the Nanopolymer
3.3. In Vitro AML Release Studies and Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niaz, T.; Shabbir, S.; Manzoor, S.; Rehman, A.; Rahman, A.; Nasir, H.; Imran, M. Antihypertensive nano-ceuticales based on chitosan biopolymer: Physico-chemical evaluation and release kinetics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 142, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doadrio, A.L.; Sánchez-Montero, J.M.; Doadrio, J.C.; Salinas, A.J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as for a new carrier methodology in the controlled release of the active components in a polypill. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 97, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergler-Klein, J. What’s new in the ESC 2018 guidelines for arterial hypertension. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2019, 131, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cativo, E.H.; Lopez, P.D.; Cativo, D.P.; Atlas, S.A.; Rosendorff, C. The Effect of Calcium Channel Blockers on Moderate or Severe Albuminuria in Diabetic, Hypertensive Patients. Am. J. Med. 2021, 134, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbak, G.; Uzuner, K.; Kuşat Ol, K.; Oğlakçı, A.; Kartkaya, K.; Şentürk, H. Effect of kefir and low-dose aspirin on arterial blood pressure measurements and renal apoptosis in unhypertensive rats with 4 weeks salt diet. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2014, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocci, G.; Battistoni, A.; Passerini, J.; Musumeci, M.B.; Francia, P.; Ferrucci, A.; Volpe, M. Calcium channel blockers and hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 20, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, J. The role of existing and newer calcium channel blockers in the treatment of hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2004, 6, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, G.; Chuttani, K.; Mishra, A.K.; Pathak, K. Design and development of nanoemulsion drug delivery system of amlodipine besilate for improvement of oral bioavailability. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 37, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, R.; Hemdan, A.; Fares, N.V.; Farouk, M. Determination of amlodipine and atorvastatin mixture by different spectrophotometric methods with or without regression equations. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 210, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haria, M.; Wagstaff, A.J. Amlodipine. Drugs 1995, 50, 560–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulsara, K.G.; Cassagnol, M. Amlodipine. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- El-Kosasy, A.M.; Tawakkol, S.M.; Ayad, M.F.; Sheta, A.I. New methods for amlodipine and valsartan native spectrofluorimetric determination, with factors optimization study. Talanta 2015, 143, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, H.; Limouei-Khosrowshahi, B. Magnetic solid phase extraction with carbon-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles coupled to HPLC-UV for the simultaneous determination of losartan, carvedilol, and amlodipine besylate in plasma samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1114, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBMcBride, A.; Houtmann, S.; Wilde, L.; Vigil, C.; Eischen, C.M.; Kasner, M.; Palmisiano, N. The role of inhibition of apoptosis in acute leukemias and myelodysplastic syndrome. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.S.N.; Shaikh, S.N.; Khan, M.J.A.; Deshmukh, N.I.; Khan, M.S.A.; Khan, S.J. A Novel Derivatization Ultraviolet Spectrophotometric Method for the Determination of Amlodipine Besylate Using Benzoyl Chloride. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Duan, X.; Li, Y.; Junyaprasert, V.B.; Mao, S. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of chitosan graft glyceryl monooleate as peroral delivery carrier of enoxaparin. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlekar, N.A.; Youan, B.B.C. The quest for non-invasive delivery of bioactive macromolecules: A focus on heparins. J. Control Release 2006, 113, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Mao, S.; Mei, D.; Kissel, T. Self-assembled polyelectrolyte nanocomplexes between chitosan derivatives and enoxaparin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, H.; Akgöl, S.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. Affinity separation of immunoglobulin G subclasses on dye attached poly(hydroxypropyl methacrylate) beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2006, 39, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgöl, S.; Öztürk, N.; Denizli, A. New generation polymeric nanospheres for catalase immobilization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoc, V.; Yılmaz, E.; Türkmen, D.; Öztürk, N.; Akgöl, S.; Denizli, A. Selective separation of human serum albumin with copper (II) chelated poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) based nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 45, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcıbaşı, U.; Türkyarar, T.; Karadağ, A.; Bakan, B.; Yavaşoğlu, N.Ü.K.; Kuşat, K.K.; Akgöl, S.; Gülcemal, D.; Tekin, V.; Müftüler, F.Z.B.; et al. Preparation of a 99mTc-labeled graft polymer and its in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2021, 329, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inanan, T.; Tüzmen, N.; Akgöl, S.; Denizli, A. Selective cholesterol adsorption by molecular imprinted polymeric nanospheres and application to GIMS. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangs, L.B. Uniform Latex Particles. In 41st National Meeting; American Association for Clinical Chemistry, Seragen Diagnostics: Indianapolis, India, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kavathia, A.; Misra, M. Development and validation of RP-HPLC and UV-spectrophotometric methods for rapid simultaneous estimation of amlodipine and benazepril in pure and fixed dose combination. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3021–S3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, H.; Aqil, M.; Imam, S.S.; Sultana, Y.; Ali, A. Formulation of amlodipine nano lipid carrier: Formulation design, physicochemical and transdermal absorption investigation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyzioğlu Demir, E.; Öztürk Atay, N.; Koruyucu, M.; Kök, G.; Salman, Y.; Akgöl, S. Mannose based polymeric nanoparticles for lectin separation. Sep. Sci. Techn. 2018, 53, 2365–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Wong, H.S.; Lin, K.J.; Chen, H.L.; Wey, S.P.; Sonaje, K.; Lin, Y.H.; Chu, C.Y.; Sung, H.W. The characteristics, biodistribution and bioavailability of a chitosan-based nanoparticulate system for the oral delivery of heparin. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6629–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagre, A.P.; Jain, K.; Jain, N.K. Alginate coated chitosan core shell nanoparticles for oral delivery of enoxaparin: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, R.S.T.; Pulat, M. 5-Fluorouracil encapsulated chitosan nanoparticles for pH-stimulated drug delivery: Evaluation of controlled release kinetics. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 313961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.H.; Tazeen, J.; Merchant, H.A.; Yousuf, R.B. Evaluation of drug release kinetics from ibuprofen matrix tablets using HPMC. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 19, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Elgawish, M.S.; Soltan, M.K.; Sebaiy, M.M. Molecular modeling, spectrofluorimetric, and tandem mass spectrometric analysis reveal a competitive binding of amlodipine and rosuvastatin to plasma albumin: Insight into drug-drug interaction. Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 104014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthaman, M.; Koland, M. Investigation of Polymeric Micellar Nanoparticles of Amlodipine Besylatefor Transdermal Delivery. J. Young Pharm. 2020, 12, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; He, F.; Zhou, R.Q.; Wu, C.D.; Liang, R.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.J.; Wang, W.; Chu, L.Y. Novel intestinal-targeted Ca-alginate-based carrier for pH-responsive protection and release of lactic acid bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5962–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaz, T.; Nasir, H.; Shabbir, S.; Rehman, A.; Imran, M. Polyionic hybrid nano-engineered systems comprising alginate and chitosan for antihypertensive therapeutics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.M.; Abd-Allah, W.M.; Ibrahim, A.M. Effect of gamma irradiation on drug releasing from nano-bioactive glass. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2015, 5, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev Jindal, K. RSM-CCD optimized microwave-assisted synthesis of chitosan and sodium alginate based nanocomposite containing inclusion complexes of β-cyclodextrin and amlodipine besylate for sustained drug delivery systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


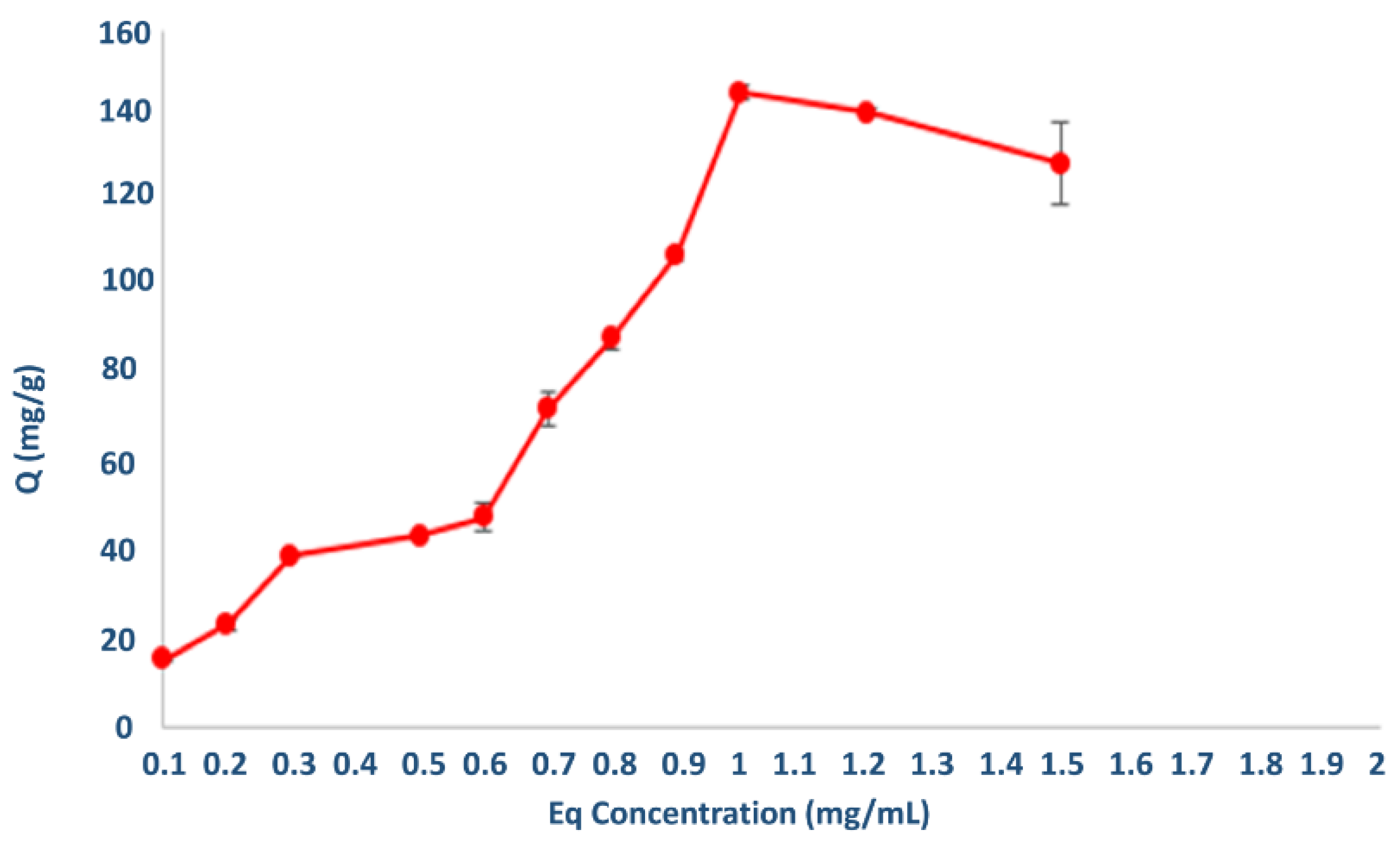
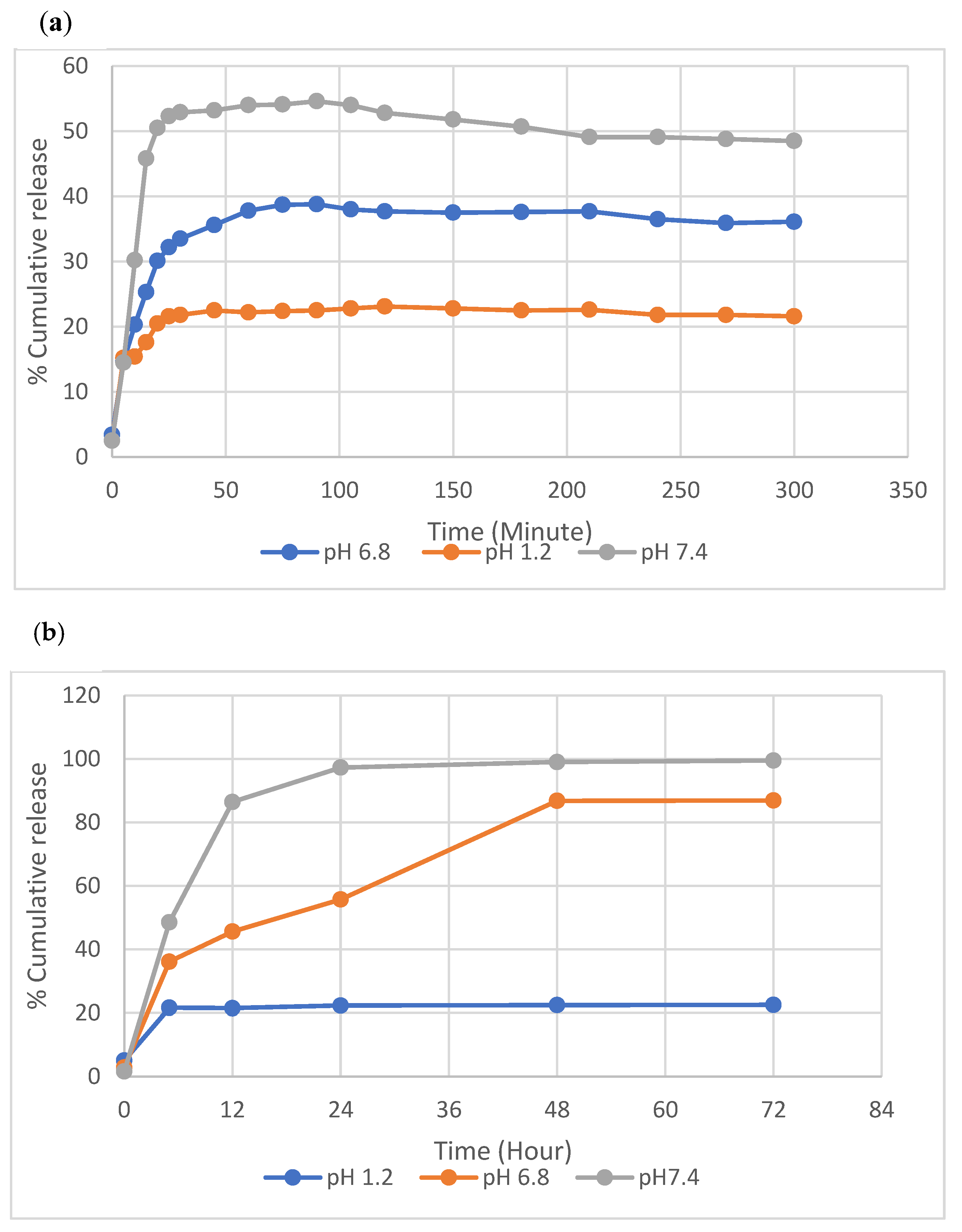
| Correlation Coefficient (R2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Zero Order | First Order | Higuchi | Korsmeyer–Peppas | Hixson–Crowell |
| p(HEMPA)/AML | 0.9751 | 0.9736 | 0.9947 | 0.9660 | 0.9634 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bardakci, F.; Kusat, K.; Adnan, M.; Badraoui, R.; Alam, M.J.; Alreshidi, M.M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Sachidanandan, M.; Akgöl, S. Novel Polymeric Nanomaterial Based on Poly(Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate-Methacryloylamidophenylalanine) for Hypertension Treatment: Properties and Drug Release Characteristics. Polymers 2022, 14, 5038. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14225038
Bardakci F, Kusat K, Adnan M, Badraoui R, Alam MJ, Alreshidi MM, Siddiqui AJ, Sachidanandan M, Akgöl S. Novel Polymeric Nanomaterial Based on Poly(Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate-Methacryloylamidophenylalanine) for Hypertension Treatment: Properties and Drug Release Characteristics. Polymers. 2022; 14(22):5038. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14225038
Chicago/Turabian StyleBardakci, Fevzi, Kevser Kusat, Mohd Adnan, Riadh Badraoui, Mohammad Jahoor Alam, Mousa M. Alreshidi, Arif Jamal Siddiqui, Manojkumar Sachidanandan, and Sinan Akgöl. 2022. "Novel Polymeric Nanomaterial Based on Poly(Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate-Methacryloylamidophenylalanine) for Hypertension Treatment: Properties and Drug Release Characteristics" Polymers 14, no. 22: 5038. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14225038
APA StyleBardakci, F., Kusat, K., Adnan, M., Badraoui, R., Alam, M. J., Alreshidi, M. M., Siddiqui, A. J., Sachidanandan, M., & Akgöl, S. (2022). Novel Polymeric Nanomaterial Based on Poly(Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate-Methacryloylamidophenylalanine) for Hypertension Treatment: Properties and Drug Release Characteristics. Polymers, 14(22), 5038. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14225038










