Additive Manufacturing of Drug-Eluting Multilayer Biodegradable Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Materials
2.2. Multilayer Drug-Eluting Films Preparation
2.2.1. Polymer Film Application
2.2.2. Drug Matrix Preparation
2.2.3. Drug Deposition, Basic Print Settings
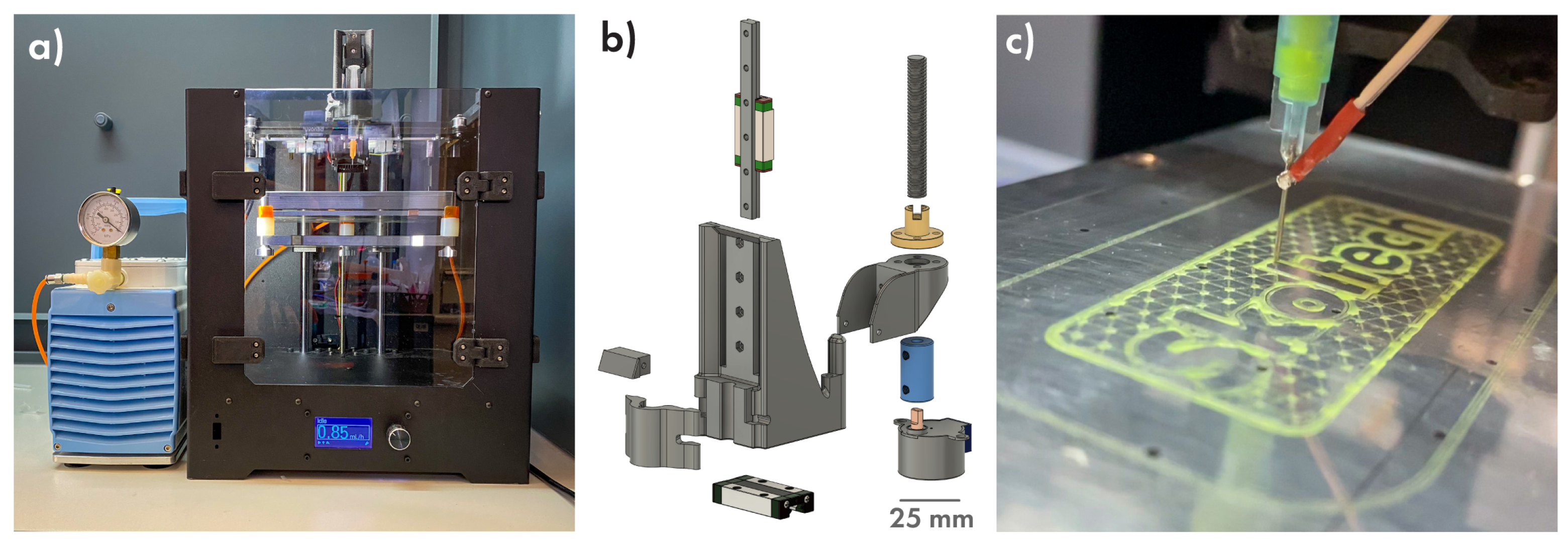
2.3. Three-Dimensional (3D) Printing Software and Hardware
2.4. DEFs Sample Characterization
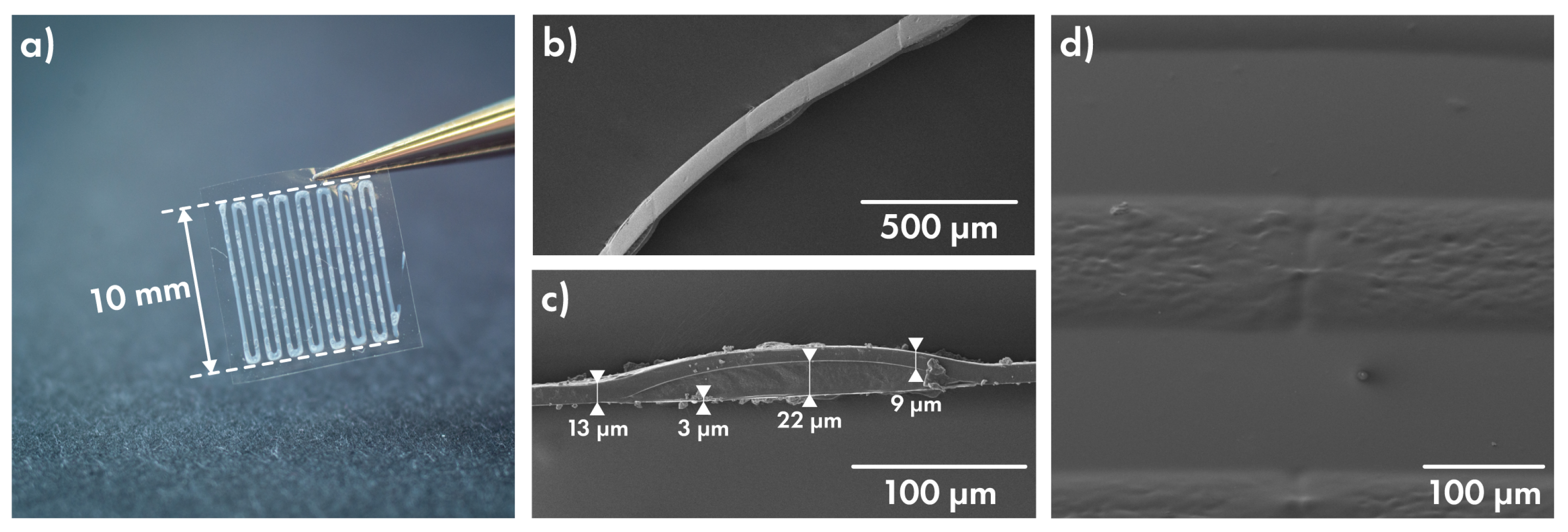
2.4.1. Polymer Film Thickness Investigation
2.4.2. Prolonged Drug Release Investigation
2.5. Characterization Technique
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Strategy Development
3.2. Printing Part
3.3. Proposed Idea of Release, Polymer Part
3.4. Characterization of Cefazolin-Loaded Films
3.5. Release of Cefazolin from Layered Films Depending on Drug Concentration
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AG | Applicator gap |
| CS | Coating speed |
| DEF | Drug-eluting film |
| DI | Deionized (water) |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| MSSA | Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| PGA | Polyglycolic acid |
| PLACE | Printed Layered Adjustable Cargo Encapsulation |
| PLGA | Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| PCL | Polycaprolactone |
| ZO | Z-offset |
Appendix A

| Manufacture Stage | Optimized Manufacture Parameters | Resulted Features |
|---|---|---|
| PLGA solution | Solvent | Acetone: Ethyl acetate = 2:8 |
| Concentration | 10 wt % | |
| Base film | CS 1 = 20 mm/s; AG 2 = 100 µm | Film thickness = 3 µm |
| Cover film | CS = 20 mm/s; AG = 400 µm | Film thickness = 12 µm |
| Drug layer | Needle size 23G; | Line width = 295 µm |
| Flow = 0.85 mL/h | Line spacing = 335 µm | |
| Printing speed = 15 mm/s | Line max. height 3 = 11 µm | |
| PVA matrix conc. = 9 wt % | Matrix viscosity = 400 mPa·s |
References
- Hong, S.J.; Hong, M.K. Drug-eluting stents for the treatment of coronary artery disease: A review of recent advances. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Chandra, S. Review on emergence of nanomaterial coatings in bio-engineered cardiovascular stents. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 70, 103224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, A.K.; Shukla, S.K.; Bhanu, S.; Kankane, S. Responsive polymers in controlled drug delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 1088–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vugt, T.A.G.; Arts, J.J.; Geurts, J.A.P. Antibiotic-Loaded Polymethylmethacrylate Beads and Spacers in Treatment of Orthopedic Infections and the Role of Biofilm Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilberman, M.; Elsner, J.J. Antibiotic-eluting medical devices for various applications. J. Control Release 2008, 130, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsuwan, N.; Dwivedi, A.; Tancharoen, S.; Nasongkla, N. Development of dental implant coating with minocycline-loaded niosome for antibacterial application. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, J.F.; Muller, O.; Heg, D.; Roffi, M.; Kurz, D.J.; Moarof, I.; Weilenmann, D.; Kaiser, C.; Tapponnier, M.; Stortecky, S.; et al. Biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stents versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (BIOSTEMI): A single-blind, prospective, randomised superiority trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, M.; Frueh, J.; Tao, T.; Petrov, A.V.; Petrov, V.V.; Shesterikov, E.V.; Tverdokhlebov, S.I.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Polylactic acid nano- and microchamber arrays for encapsulation of small hydrophilic molecules featuring drug release via high intensity focused ultrasound. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 7063–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagstrup, J.; Keller, S.; Almdal, K.; Boisen, A. 3D microstructuring of biodegradable polymers. Microelectron. Eng. 2011, 88, 2342–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, J.R.; Thamdrup, L.H.; Kamguyan, K.; Nielsen, L.H.; Nielsen, H.M.; Boisen, A.; Rades, T.; Müllertz, A. Design of a self-unfolding delivery concept for oral administration of macromolecules. J. Control Release 2021, 329, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chichareon, P.; Katagiri, Y.; Asano, T.; Takahashi, K.; Kogame, N.; Modolo, R.; Tenekecioglu, E.; Chang, C.C.; Tomaniak, M.; Kukreja, N.; et al. Mechanical properties and performances of contemporary drug-eluting stent: Focus on the metallic backbone. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2019, 16, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhardi, V.J.; Bichara, D.A.; Kwok, S.J.; Freiberg, A.A.; Rubash, H.; Malchau, H.; Yun, S.H.; Muratoglu, O.K.; Oral, E. A fully functional drug-eluting joint implant. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhu, W.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. A review of multilayer and composite films and coatings for active biodegradable packaging. NPJ Sci. Food 2022, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Gai, M.; Frueh, J.; Kudryavtseva, V.L.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Polyelectrolyte multilayer microchamber-arrays for in-situ cargo release: Low frequency vs. medical frequency range ultrasound. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 547, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindeeva, O.A.; Prikhozhdenko, E.S.; Bratashov, D.N.; Vostrikova, A.M.; Atkin, V.S.; Ermakov, A.V.; Khlebtsov, B.N.; Sapelkin, A.V.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Carbon dot aggregates as an alternative to gold nanoparticles for the laser-induced opening of microchamber arrays. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 9012–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurochkin, M.A.; Sindeeva, O.A.; Brodovskaya, E.P.; Gai, M.; Frueh, J.; Su, L.; Sapelkin, A.; Tuchin, V.V.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Laser-triggered drug release from polymeric 3-D micro-structured films via optical fibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mordovina, E.A.; Plastun, V.O.; Abdurashitov, A.S.; Proshin, P.I.; Raikova, S.V.; Bratashov, D.N.; Inozemtseva, O.A.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Sindeeva, O.A. “Smart” Polylactic Acid Films with Ceftriaxone Loaded Microchamber Arrays for Personalized Antibiotic Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, F.C. Fabrication and processing of polymer solar cells: A review of printing and coating techniques. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2009, 93, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howatt, G.N.; Breckenridge, R.G.; Brownlow, J.M. Fabrication of Thin Ceramic Sheets for Capacitors*. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1947, 30, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, T.M.; Salgado, H.R.N. Validation of Cefazolin Sodium by UV-Spectrophotometric Method. Phys. Chem. 2013, 3, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdurashitov, A.S.; Proshin, P.I.; Tuchin, V.V.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Abdurashitov, A.S.; Proshin, P.I.; Tuchin, V.V.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Integrated binary hologram to monitor cargo release from a drug-eluting film. Light. Adv. Manuf. 2022, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.N.; Park, C.; Whitesides, G.M. Solvent Compatibility of Poly(dimethylsiloxane)-Based Microfluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6544–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Ko, J.; Jeong, S.; Won, P.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Hong, S.; Jeon, N.L.; Ko, S.H. Monolithic digital patterning of polydimethylsiloxane with successive laser pyrolysis. Nat. Mater. 2020, 20, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shogren, R. Water vapor permeability of biodegradable polymers. J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 1997, 5, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laracuente, M.L.; Yu, M.H.; McHugh, K.J. Zero-order drug delivery: State of the art and future prospects. J. Control Release 2020, 327, 834–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredenberg, S.; Wahlgren, M.; Reslow, M.; Axelsson, A. The mechanisms of drug release in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-based drug delivery systems-A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, B. Final Report On the Safety Assessment of Polyvinyl Alcohol. Int. J. Toxicol. 2016, 17, 67–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Wang, B.B.; Li, W.X.; Fei, W.M.; Cui, Y.; Guo, X.D. In vivo safety assessment, biodistribution and toxicology of polyvinyl alcohol microneedles with 160-day uninterruptedly applications in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 160, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradossi, G.; Cavalieri, F.; Chiessi, E.; Spagnoli, C.; Cowman, M.K. Poly(vinyl alcohol) as versatile biomaterial for potential biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMerlis, C.C.; Schoneker, D.R. Review of the oral toxicity of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qin, B.; Xia, G.; Choi, S.H. FDA’s Poly (Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) Research Program and Regulatory Outcomes. AAPS J. 2021, 23, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murcia Valderrama, M.A.; Van Putten, R.J.; Gruter, G.J.M. PLGA Barrier Materials from CO2. The influence of Lactide Co-monomer on Glycolic Acid Polyesters. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 2706–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Velde, K.; Kiekens, P. Biopolymers: Overview of several properties and consequences on their applications. Polym. Test. 2002, 21, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.S.; Chen, Y.X.; Qi, X.Y.; Shi, H.F.; Wang, J.F.; Xiong, J. Outcomes of cement beads and cement spacers in the treatment of bone defects associated with post-traumatic osteomyelitis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffernan, A.; Alawie, J.; Wallis, S.C.; Naicker, S.; Adiraju, S.; Roberts, J.A.; Sime, F.B.; Heffernan, A.; Alawie, J.; Wallis, S.C.; et al. Pharmacodynamic Evaluation of a Single Dose versus a 24-Hour Course of Multiple Doses of Cefazolin for Surgical Prophylaxis. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phaechamud, T.; Chitrattha, S. Pore formation mechanism of porous poly(dl-lactic acid) matrix membrane. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 61, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Proshin, P.I.; Abdurashitov, A.S.; Sindeeva, O.A.; Ivanova, A.A.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Additive Manufacturing of Drug-Eluting Multilayer Biodegradable Films. Polymers 2022, 14, 4318. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204318
Proshin PI, Abdurashitov AS, Sindeeva OA, Ivanova AA, Sukhorukov GB. Additive Manufacturing of Drug-Eluting Multilayer Biodegradable Films. Polymers. 2022; 14(20):4318. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204318
Chicago/Turabian StyleProshin, Pavel I., Arkady S. Abdurashitov, Olga A. Sindeeva, Anastasia A. Ivanova, and Gleb B. Sukhorukov. 2022. "Additive Manufacturing of Drug-Eluting Multilayer Biodegradable Films" Polymers 14, no. 20: 4318. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204318
APA StyleProshin, P. I., Abdurashitov, A. S., Sindeeva, O. A., Ivanova, A. A., & Sukhorukov, G. B. (2022). Additive Manufacturing of Drug-Eluting Multilayer Biodegradable Films. Polymers, 14(20), 4318. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204318








