The Optimization and Evaluation of Flibanserin Fast-Dissolving Oral Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
3. Methods
3.1. Spectrophotometric Scanning of FLB
3.2. FLB Calibration Curve Construction
3.3. Preparation of Solid Inclusion Complexes
3.3.1. Physical Mixture
3.3.2. Kneading Method
3.4. Characterization of the Inclusion Complex
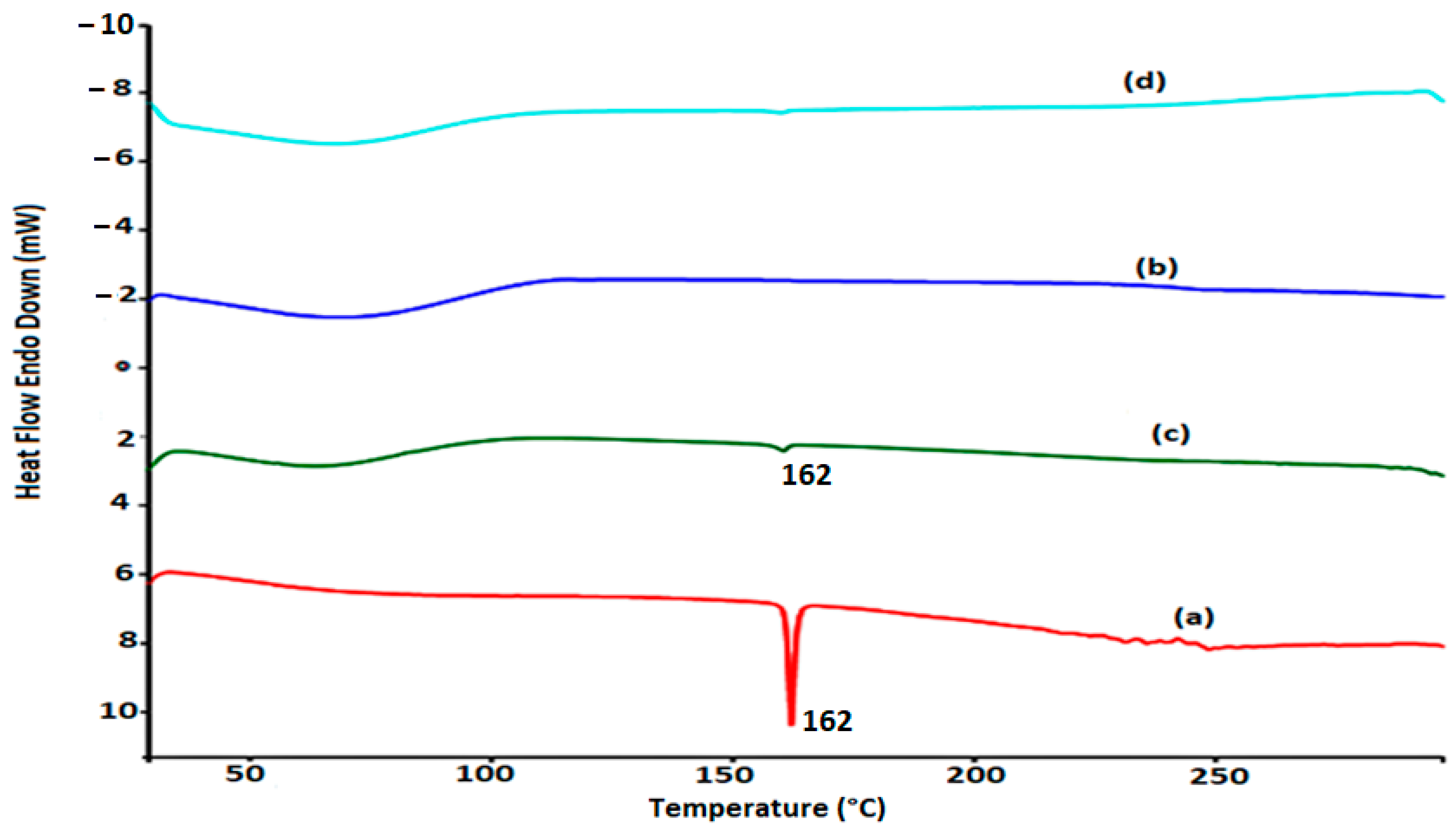
3.4.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
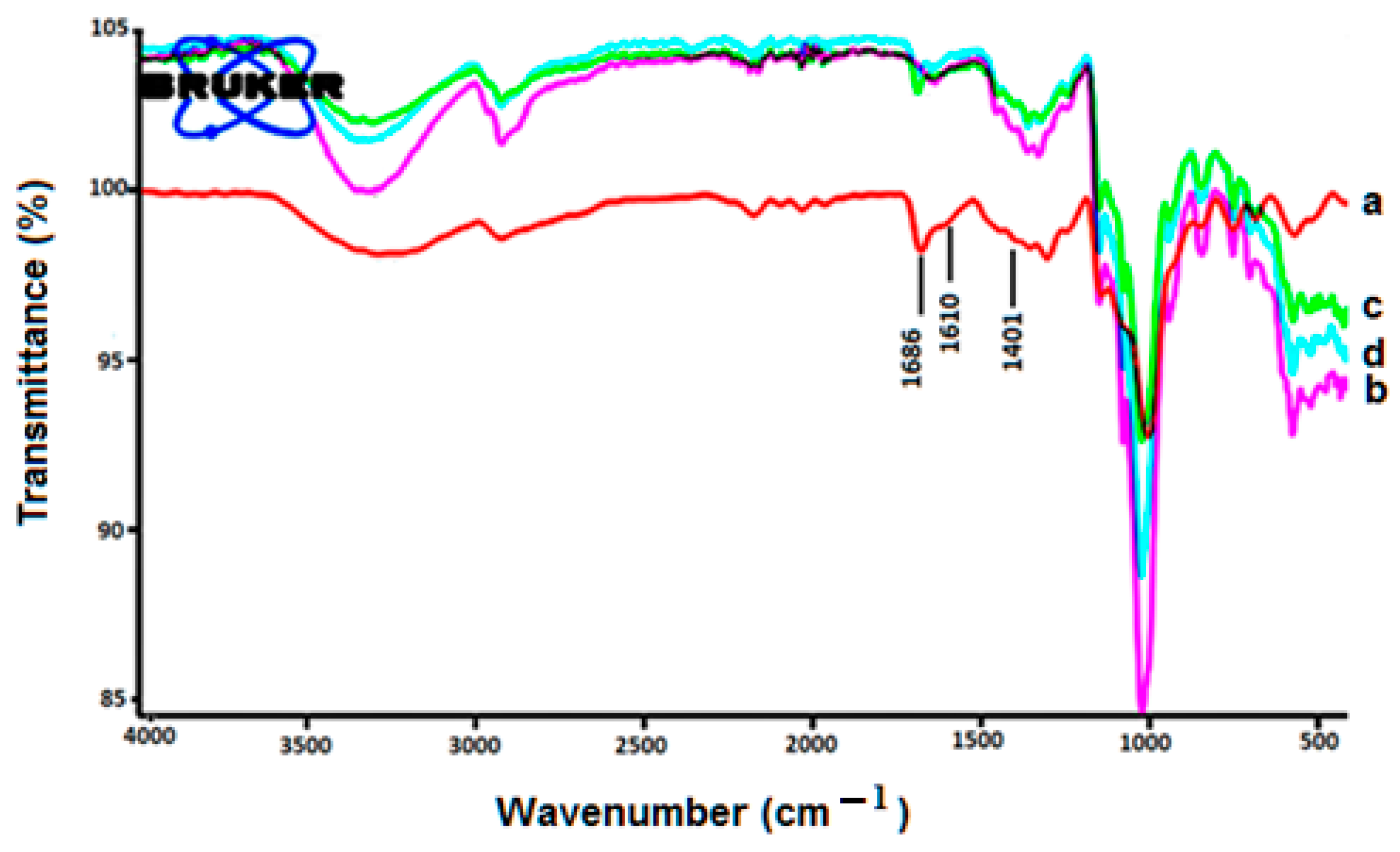
3.4.2. Fourier Transforms Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
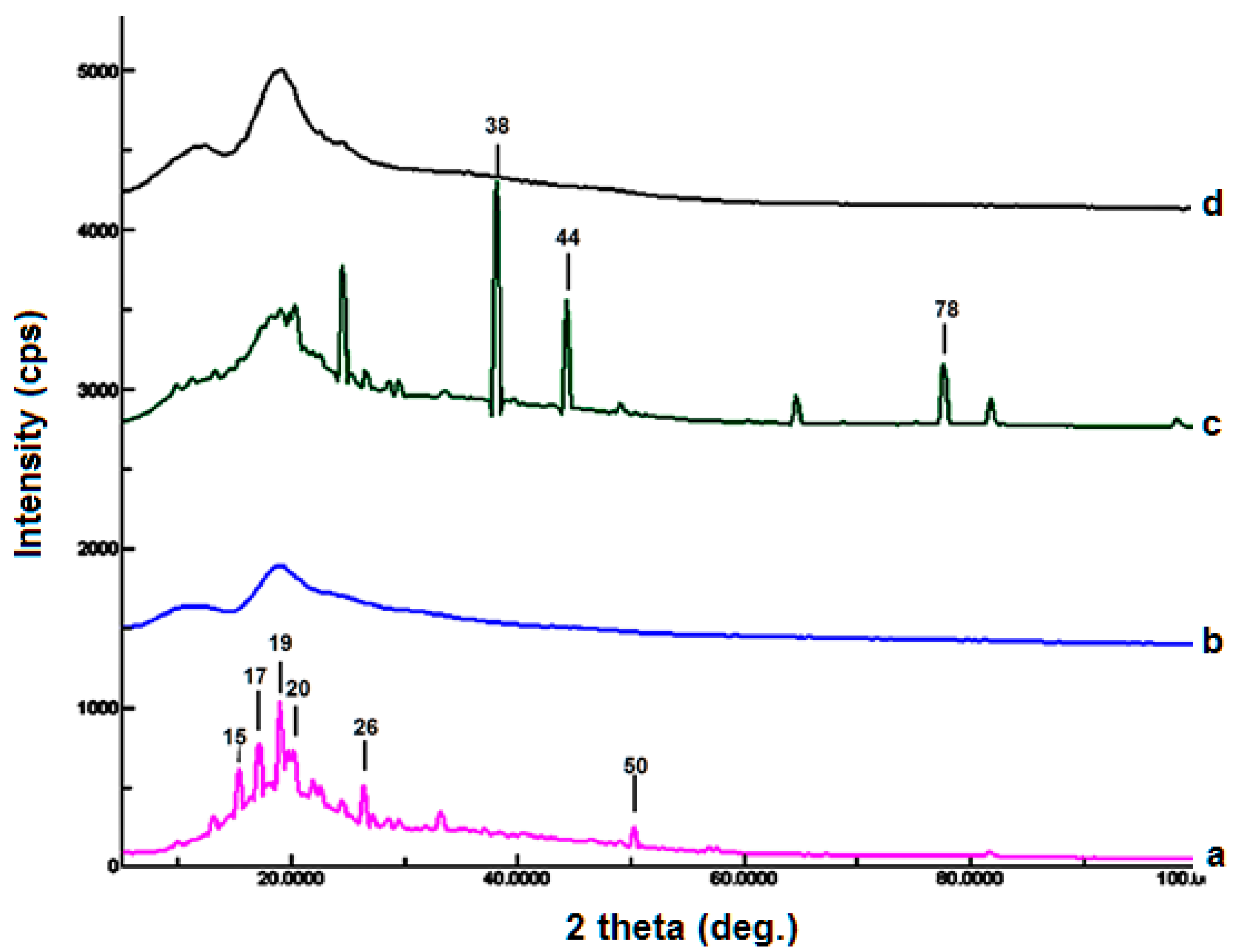
3.4.3. Powder X-ray Diffractometry (XRD)
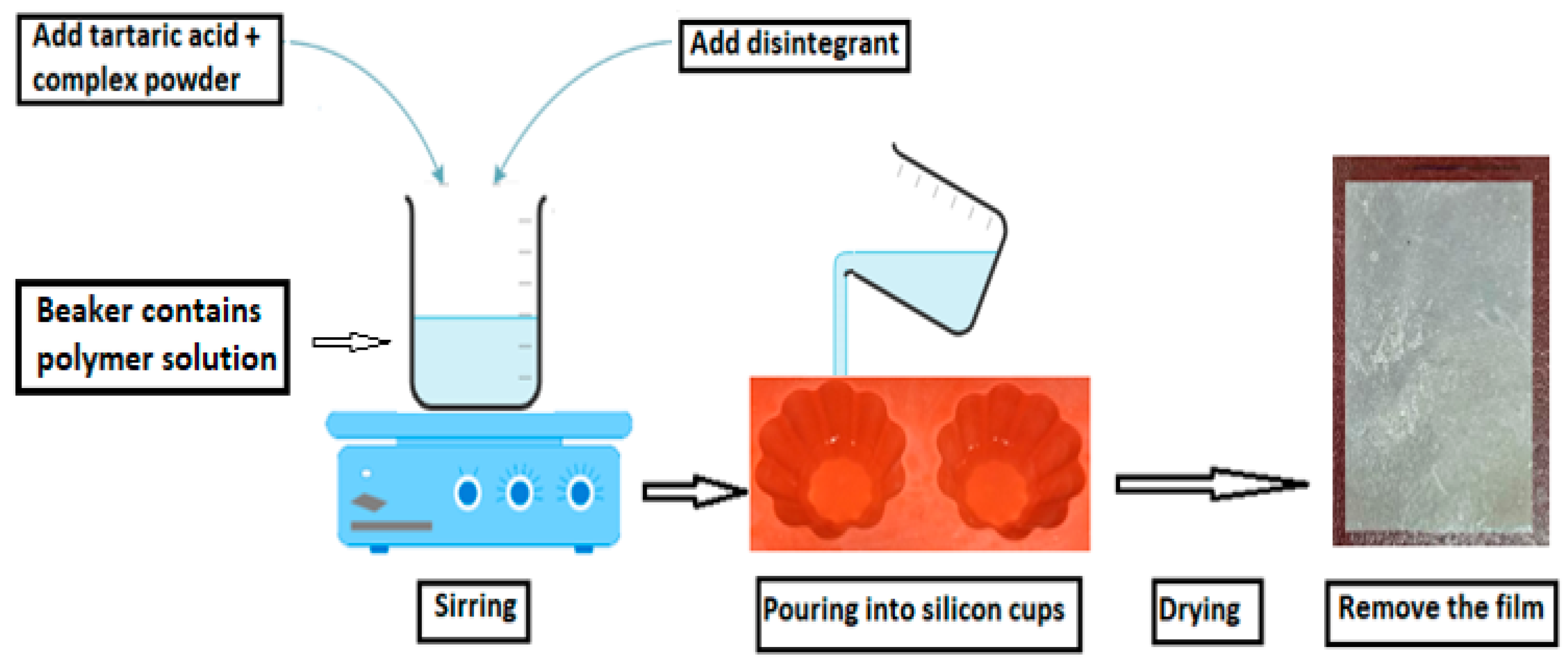
3.5. Preparation of FLB Fast-Dissolving Oral Films (FLBFDOFs)
3.6. Evaluation of the Prepared FLB Films
3.6.1. Film Thickness
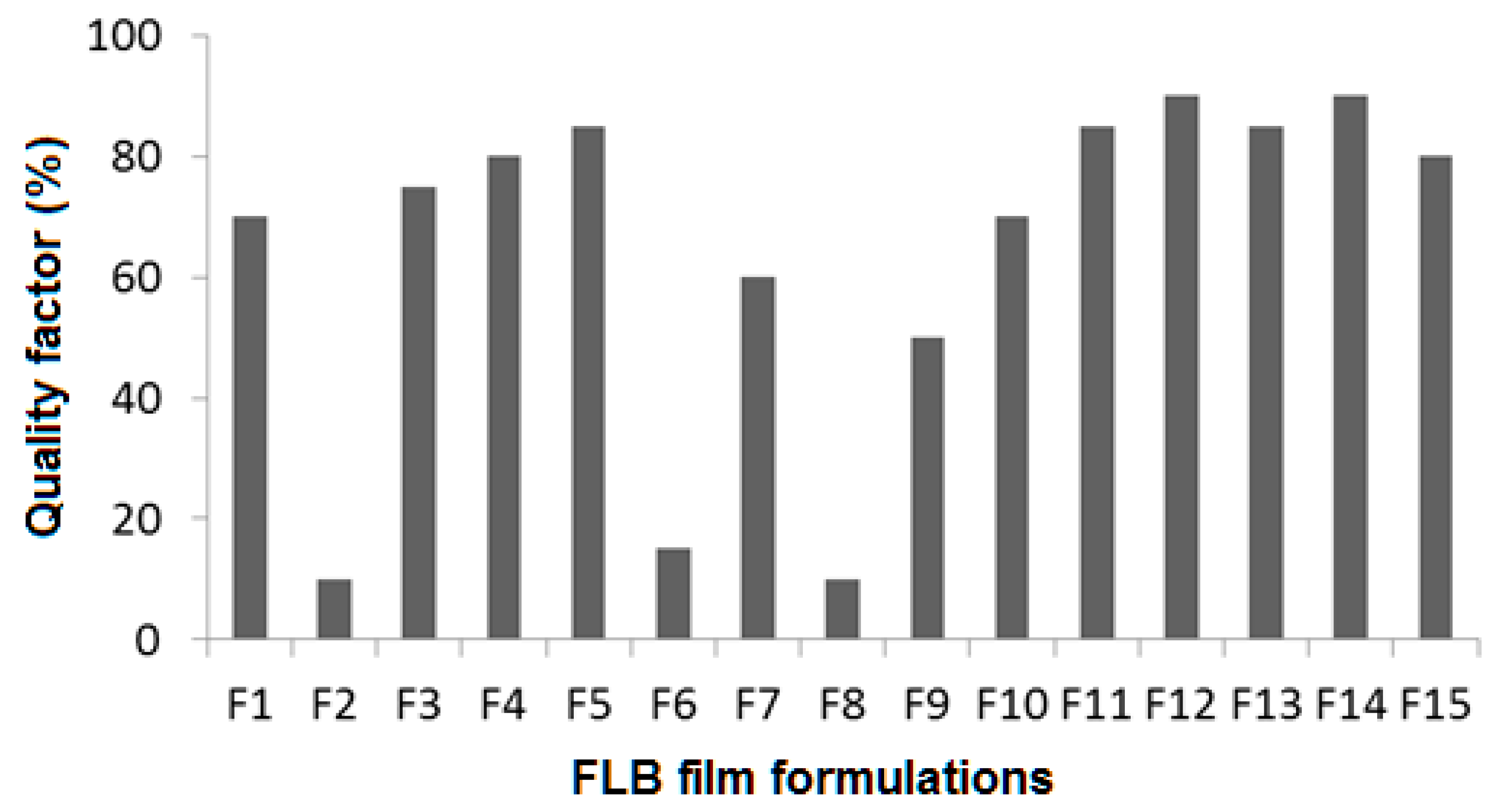
3.6.2. Film Quality
3.6.3. In Vitro Disintegration
3.6.4. FLBFDOF Content
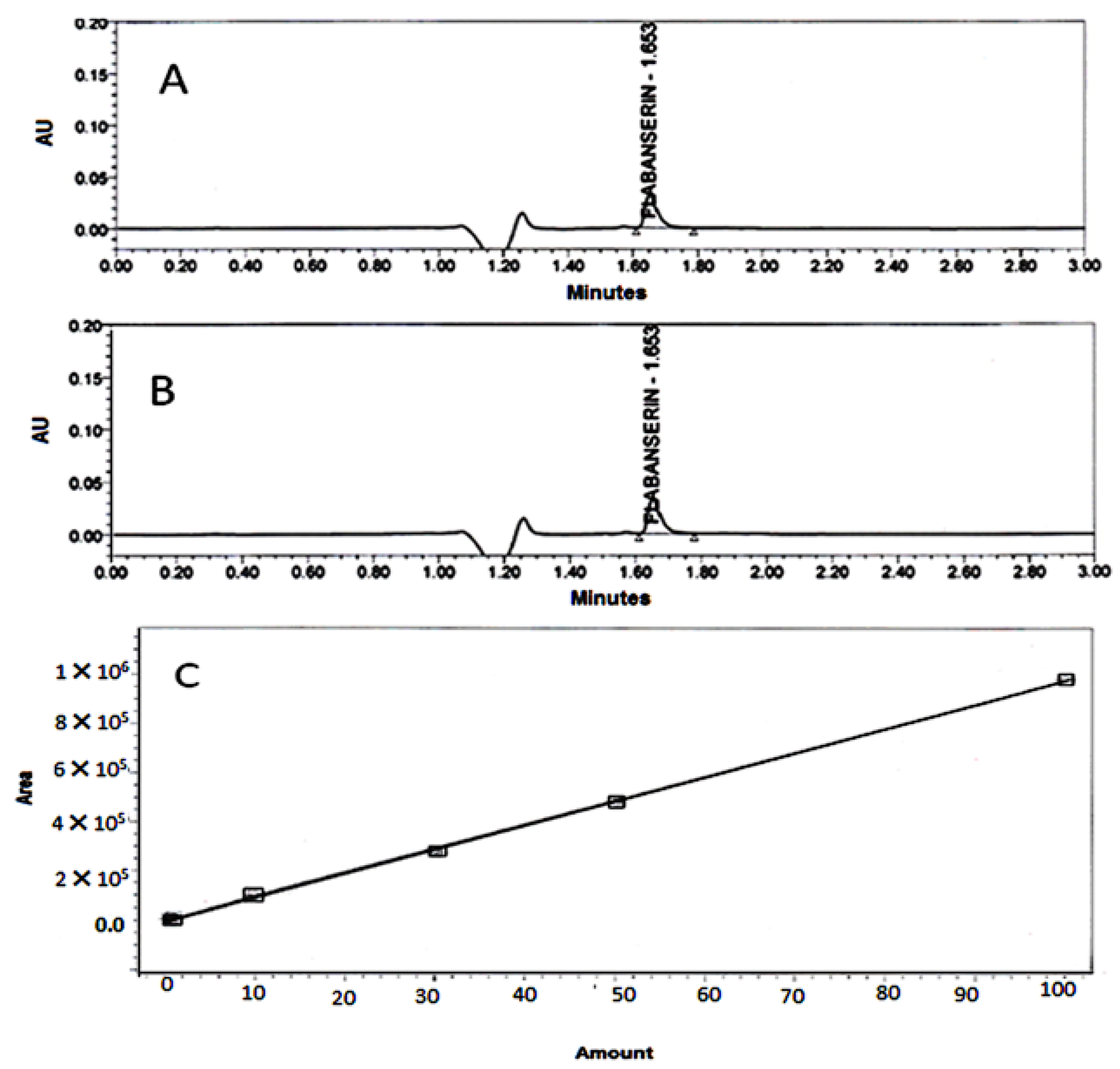
3.6.5. HPLC assay Conditions
3.6.6. In Vitro Release Studies
3.7. Response Surface Methodology for Optimization of FLBFDOFs
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. FLB Spectrophotometric Assay
4.2. DSC Studies
4.3. FTIR Studies
4.4. X-ray Diffractometry
4.5. FLB Film Formation
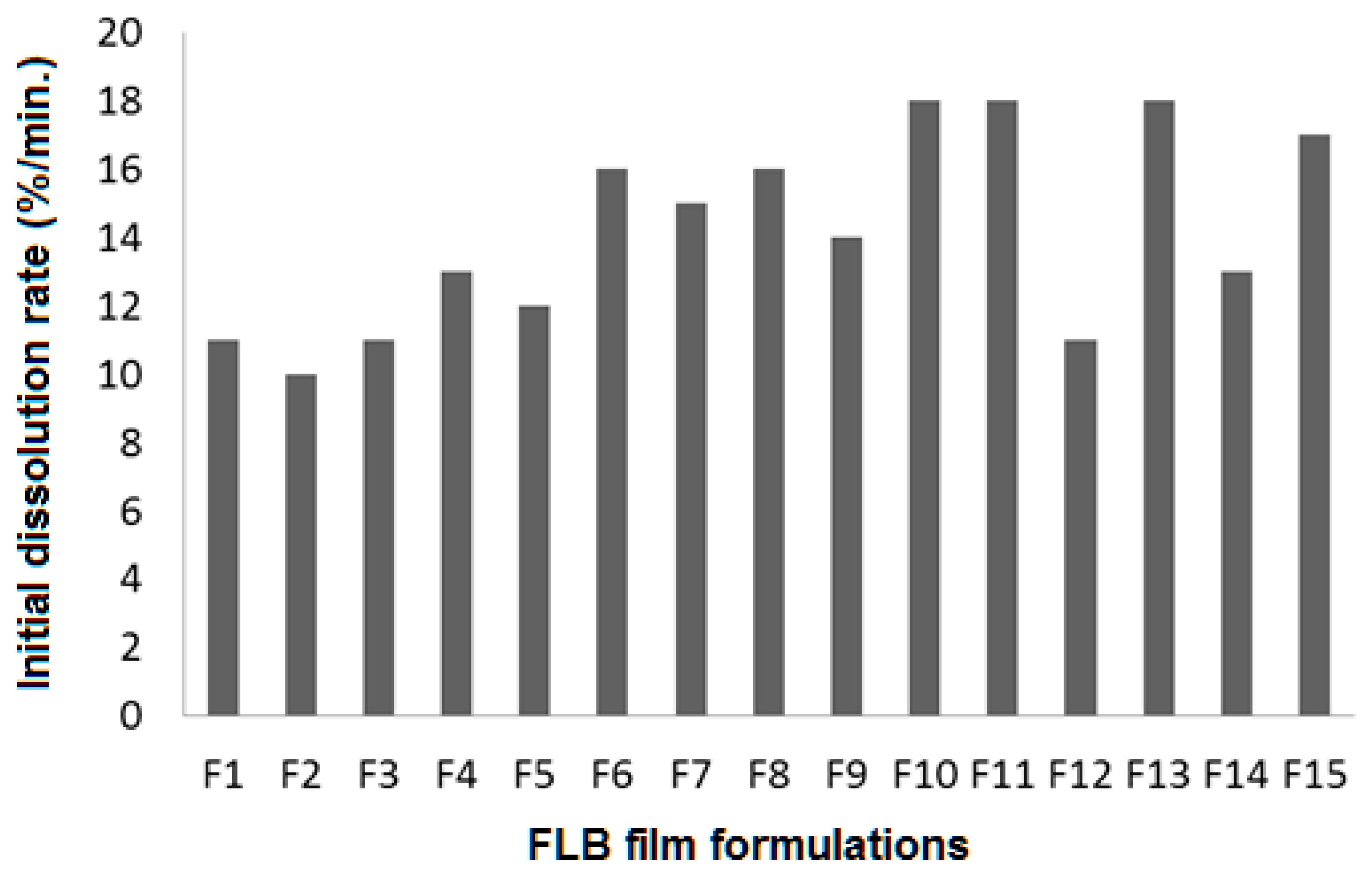
4.6. FLB Orally Fast-Dissolving Film (FLBFDOF) Evaluation
4.7. Determination of FLB Content in the Prepared Films
4.8. Response Surface Methodology for Optimization of FLBFDOFs
4.9. Statistical Analysis and Summary of Fit
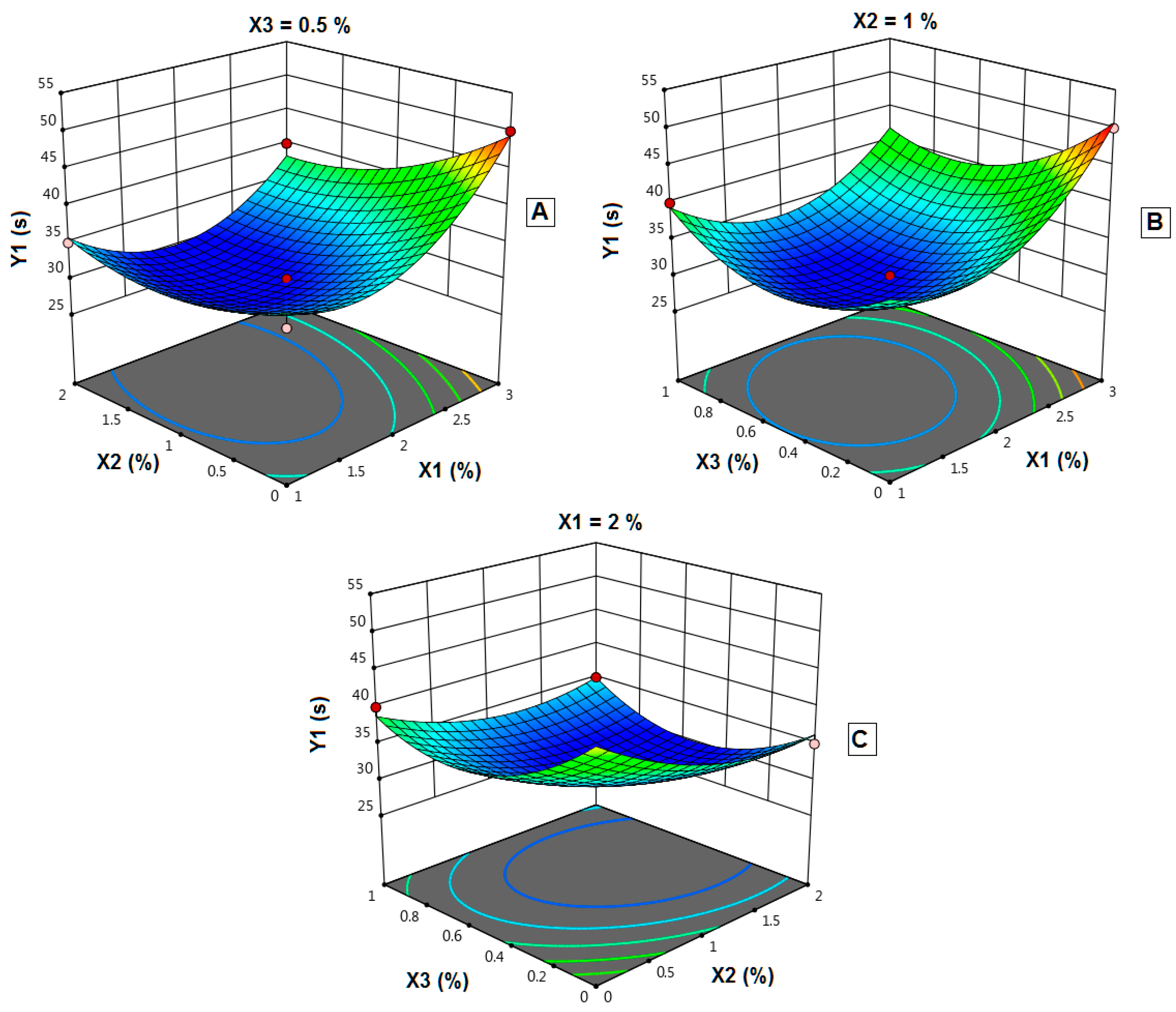
4.10. Effect of Independent Variables on the In Vitro Disintegration Time (Y1)
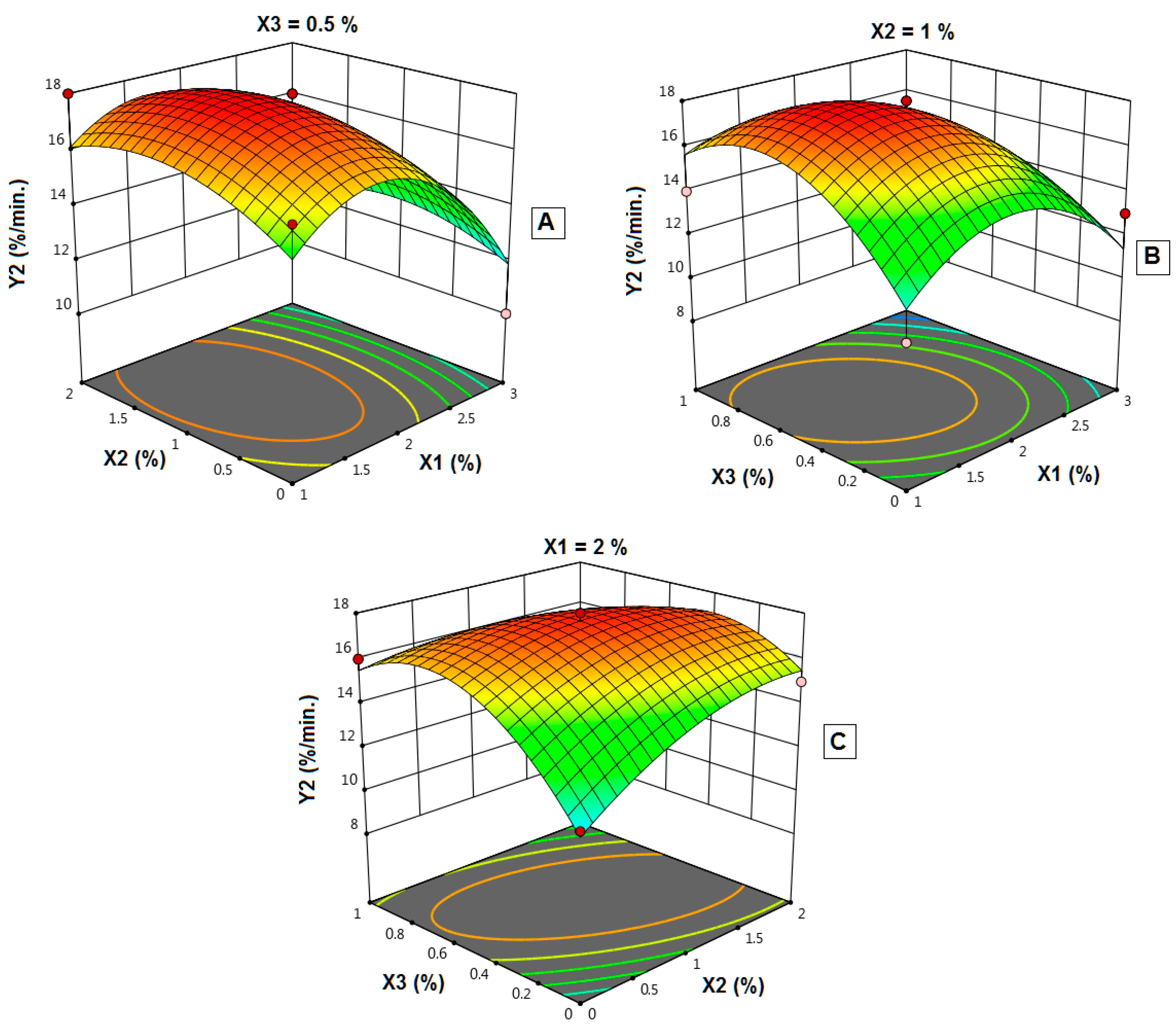
4.11. Influence of Independent Variables on the In-Vitro Initial Dissolution Rate (Y2)
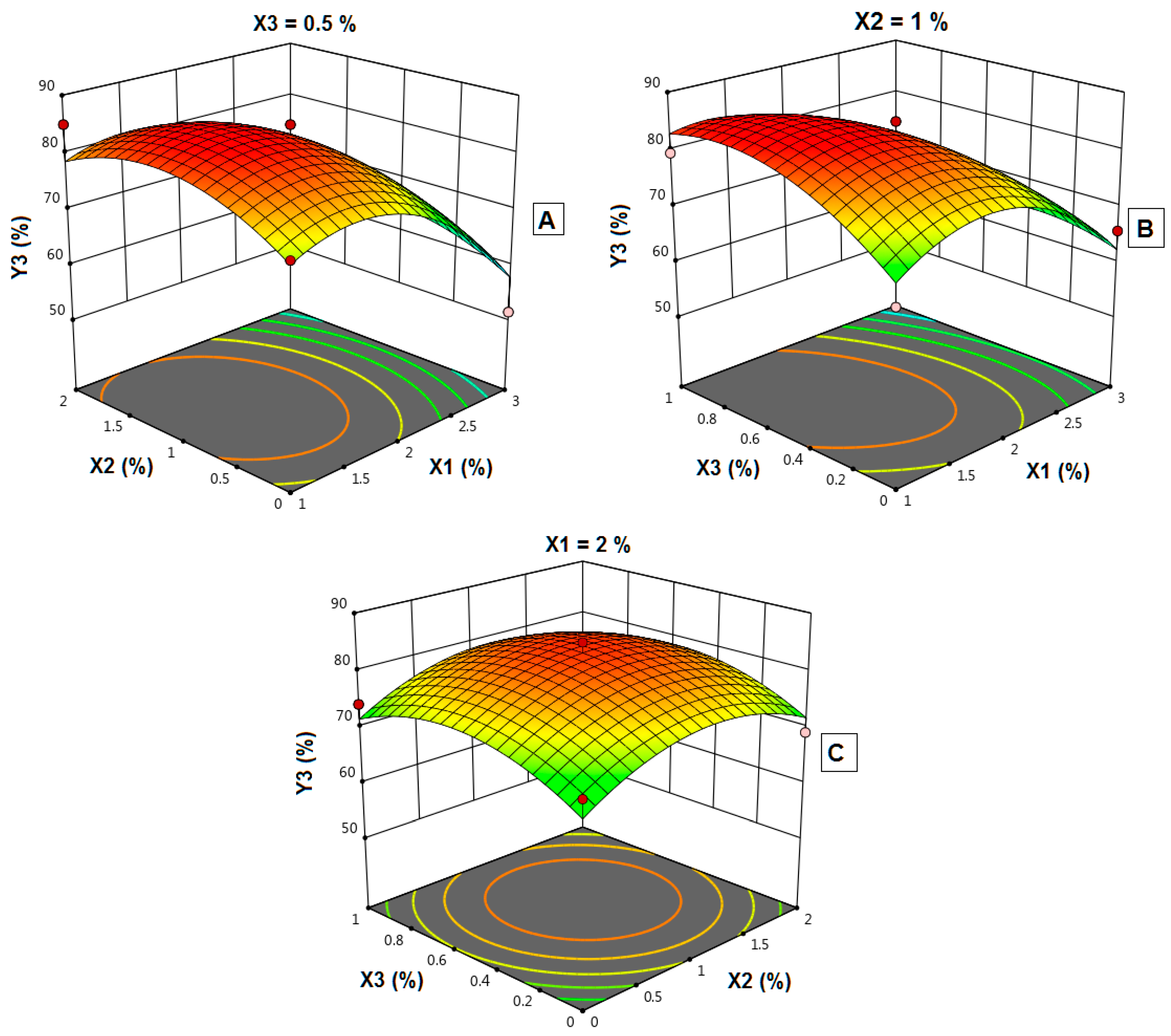
4.12. Influence of Independent Variables on the Dissolution Efficiency (Y3)
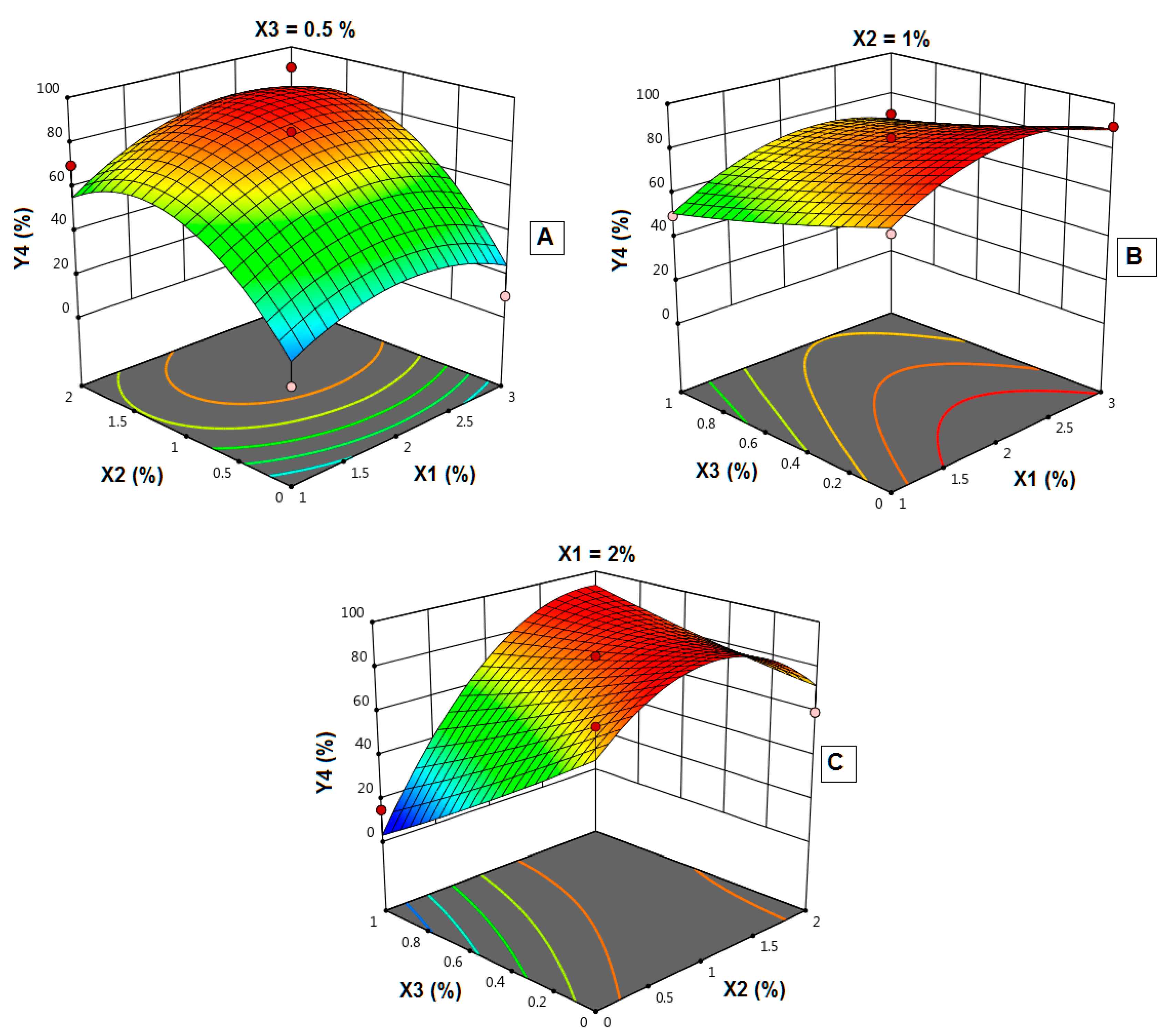
4.13. Influence of Independent Variables on the Quality Factor (Y4)
Optimization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allers, K.A.; Dremencov, E.; Ceci, A.; Flik, G.; Ferger, B.; Cremers, T.I.; Ittrich, C.; Sommer, B. Acute and repeated flibanserin administration in female rats modulates monoamines differentially across brain areas: A microdialysis study. J. Sex Med. 2010, 7, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, R.W.; Sacchetti, G.S.; Parini, S.; Acconcia, R.; Samanin, F. A potential antidepressant drug, lowers 5-HT and raises dopamine and noradrenaline in the rat prefrontal cortex dialysate: Role of 5-HT(1A) receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- English, C.; Muhleisen, A.; Rey, J.A. Flibanserin (Addyi): The First FDA-Approved Treatment for Female Sexual Interest/Arousal Disorder in Premenopausal Women. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 42, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Fahmy, U.A.; Ahmed, O.A.A.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Okbazghi, S.Z.; Awan, Z.A.; Bakhrebah, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Abdulaal, W.H.; Medina, C.; et al. Optimized Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Integrated into In Situ Nasal Gel for Enhancing Brain Delivery of Flibanserin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 5253–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, R.A.; Nair, S.S.; Harindran, J. Formulation and Evaluation of Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex Tablets of Carvedilol. Asian J. Pharm. 2016, 10, 84–94. [Google Scholar]
- Malaekeh-Nikouei, B.; Nassirli, H.; Davies, N. Enhancement of cyclosporine aqueous solubility using alpha- and hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin mixtures. J. Incl. Phenom. Macro 2007, 59, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.; Vasudevan, D. Studies on the Preparation, Characterization, and Solubility of 2-HP-beta-Cyclodextrin-Meclizine HCl Inclusion Complexes. J. Young Pharm. 2012, 4, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vikas, Y.; Sandeep, K.; Braham, D.; Manjusha, C.; Budhwar, V. Cyclodextrin Complexes: An Approach to Improve the Physicochemical Properties of Drugs and Applications of Cyclodextrin Complexes. Asian J. Pharm. 2018, 12, S394–S409. [Google Scholar]
- Carrier, R.L.; Miller, L.A.; Ahmed, M. The utility of cyclodextrins for enhancing oral bioavailability. J. Control Release 2007, 123, 78–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, R.; Pawar, P.; Khanna, S.; Arora, S. Orally dissolving strips: A new approach to oral drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2013, 3, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaturvedi, A.; Srivastava, P.; Yadav, S.; Bansal, M.; Garg, G.; Sharma, P.K. Fast dissolving films: A review. Curr Drug Deliv 2011, 8, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouda, G.I.; Dahmash, E.Z.; Alyami, H.; Iyire, A. A Novel Technique to Improve Drug Loading Capacity of Fast/Extended Release Orally Dissolving Films with Potential for Pediatric and Geriatric Drug Delivery. AAPS Pharm. SciTech. 2020, 21, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saab, M.; Mehanna, M.M. Disintegration time of orally dissolving films: Various methodologies and in-vitro/in-vivo correlation, Die Pharm. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 74, 227–230. [Google Scholar]
- Onishi, H.; Sakata, O. Preparation and evaluation of fast-dissolving films of etilefrine hydrochloride for practical buccal dosing. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.S.; Kumar, T.P.; Gowda, D.V. Orodispersible Thin Film: A new patient-centered innovation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Hassan, R.; Razzaq, S.; Mahmood, A.; Amjad, M.W.; Raja, M.A.G.; Qaisar, A.A.; Majeed, A.; Hanif, M.; Tahir, R.A. Fabrication of polyvinyl alcohol based fast dissolving oral strips of sumatriptan succinate and metoclopramide HCL. Sci. Prog. 2020, 103, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Boateng, J.S.; Mitchell, J.; Trivedi, V. Formulation, Characterisation and Stabilisation of Buccal Films for Paediatric Drug Delivery of Omeprazole. AAPS Pharm. SciTech 2015, 16, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soni, G.; Yadav, K.S. Fast-Dissolving Films of Sumatriptan Succinate: Factorial Design to Optimize In Vitro Dispersion Time. J. Pharm. Innov. 2015, 10, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahtani, M.E.; Aodah, A.H.; Abu Asab, O.A.; Basit, A.W.; Orlu, M.; Tawfik, E.A. Fabrication and Characterization of Fast-Dissolving Films Containing Escitalopram/Quetiapine for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghaith, A.F.; Mahrous, G.M.; Zidan, D.E.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Alamoudi, A.J.; Radwan, A.A. Preparation, characterization, dissolution, and permeation of flibanserin-2-HP-beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021, 29, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mogherah, A.I.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Hassan, M.A. Optimization and evaluation of venlafaxine hydrochloride fast dissolving oral films. SPJ 2020, 28, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhyan, B.; Jangra, S.; Kaur, M.; Singh, H. Orally fast dissolving films: Innovations in formulation and technology. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2011, 9, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Guinesi, L.S.; Cavalheiro, E.T.G. The use of DSC curves to determine the acetylation degree of chitin/chitosan samples. Thermochim. Acta 2006, 444, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.M.; Abdallah, I.A. Determination of flibanserin in the presence of confirmed degradation products by a third derivative emission spectrofluorometric method: Application to pharmaceutical formulation, Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 225, 117491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, S.; Zhang, L. Inclusion complexes of fluconazole with beta-cyclodextrin and 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin in aqueous solution: Preparation, characterization and a structural insight. J. Incl. Phenom. Macro. 2016, 84, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.S.; Deokule, H.A. Exploration of different polymers for use in the formulation of oral fast dissolving strips. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2010, 2, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- USP Convention, INC. 12601, USP 30; Twinbrook Parkway: Rockville, MD, USA, 2008.
- Sharma, P.; Dahiya, M.; Wakode, S.; Rani, R. HPLC Method Development and Validation: For Simultaneous Determination of Flibanserin and Caffeine. Pharm. Res. 2020, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, O.A.; El-Say, K.M.; Aljaeid, B.M.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Ahmed, T.A. Optimized vinpocetine-loaded vitamin E D-alpha-tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate-alpha lipoic acid micelles as a potential transdermal drug delivery system: In vitro and ex vivo studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Elkordy, A.A.; Tan, X.N.; Essa, E.A. Spironolactone release from liquisolid formulations prepared with Capryol™ 90, Solutol® HS-15 and Kollicoat® SR 30 D as non-volatile liquid vehicles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 83, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Kaza, R.; Sumathi, P. Design and evaluation of losartan potassium fast dissolving films. Int. J. Innov. Pharm. Res. 2014, 5, 431–439. [Google Scholar]
- Bergström, C.A.S.; Avdeef, A. Perspectives in solubility measurement and interpretation. ADMET DMPK 2019, 7, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulkarni, V.R.; Mutalik, S. Effect of plasticizers on permeability and mechanical properties of films for transdermal application. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 64, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Dahmash, E.Z.; Iyire, A.; Alyami, H.S. Development of orally dissolving films for pediatric-centric administration of anti-epileptic drug topiramate—A design of experiments (DoE) study. SPJ 2021, 29, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Formulation | Ingredients (% w/w in the Dispersions) | Average Film Weight (g) | Average Thickness (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPC | Propylene Glycol | Crospovidone | Tartaric Acid | FLB Complex (Contains 10 mg FLB) | |||
| F1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.277 ± 0.003 | 0.37 ± 0.01 |
| F2 | 3 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.203 ± 0.006 | 0.3 ± 0.01 |
| F3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.134 ± 0.004 | 0.1 ± 0.01 |
| F4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.234 ± 0.009 | 0.22 ± 0.01 |
| F5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.16 ± 0.001 | 0.13 ± 0.01 |
| F6 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.207 ± 0.006 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| F7 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.193 ± 0.015 | 0.163 ± 0.006 |
| F8 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| F9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.205 ± 0.005 | 0.24 ± 0.01 |
| F10 | 1 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.165 ± 0.007 | 0.17 ± 0.01 |
| F11 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.21 ± 0.006 | 0.303 ± 0.005 |
| F12 | 3 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.282 ± 0.004 | 0.35 ± 0.01 |
| F13 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.213 ± 0.006 | 0.3 ± 0.01 |
| F14 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.257 ± 0.012 | 0.25 ± 0.01 |
| F15 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.257 ± 0.004 | 0.203 ± 0.058 |
| Optimized (F16) | 2 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.214 ± 0.002 | 0.213 ± 0.006 |
| Independent Variables, Factor | Low (−1) | Middle (0) | High (1) |
| X1: HPC Polymer (%) | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| X2: Plasticizer concentration (PG) (%) | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| X3: Disintegrant concentration (%) | 0 | 0.5 | 1 |
| Dependent Variables, Response | |||
| Y1: Disintegration time (s) | |||
| Y2: initial dissolution rate (%) | |||
| Y3: Dissolution efficiency (%) | |||
| Y4: quality factor (%) | |||
| Runs | Independent Variable | Dependent Variables | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed Value | Predicted Value | ||||||||||
| X1 | X2 | X3 | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 | |
| 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 40 | 11.00 | 59.50 | 70 | 41.88 | 9.63 | 55.68 | 67.50 |
| 2 | 3 | 0 | 0.5 | 50 | 10.00 | 51.40 | 10 | 49.38 | 11.88 | 57.85 | 24.38 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 40 | 11.00 | 67.10 | 75 | 38.13 | 12.38 | 70.93 | 77.50 |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 35 | 13.00 | 70.90 | 80 | 35.00 | 13.25 | 74.03 | 93.13 |
| 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 12.00 | 71.70 | 85 | 45.00 | 11.75 | 68.58 | 71.88 |
| 6 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 40 | 16.00 | 74.20 | 15 | 38.75 | 15.50 | 71.58 | 13.13 |
| 7 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 35 | 15.00 | 69.20 | 60 | 36.25 | 15.50 | 71.83 | 71.88 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 35 | 16.00 | 75.00 | 10 | 36.88 | 14.88 | 74.30 | 20.63 |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 40 | 14.00 | 79.50 | 50 | 39.38 | 15.63 | 82.83 | 51.25 |
| 10 | 1 | 2 | 0.5 | 35 | 18.00 | 85.00 | 70 | 35.63 | 16.13 | 78.55 | 55.63 |
| 11 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 30 | 18.00 | 82.50 | 85 | 30.00 | 17.67 | 83.17 | 83.33 |
| 12 | 3 | 2 | 0.5 | 40 | 11.00 | 58.60 | 90 | 38.13 | 12.13 | 59.30 | 79.38 |
| 13 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 30 | 18.00 | 82.00 | 85 | 30.00 | 17.67 | 83.17 | 83.33 |
| 14 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 50 | 13.00 | 65.70 | 90 | 50.63 | 11.37 | 62.38 | 88.75 |
| 15 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 30 | 17.00 | 85.00 | 80 | 30.00 | 17.67 | 83.17 | 83.33 |
| Response | Model | Sequential p-Value | Lack of Fit p-Value | R2 | Adjusted R2 | Adequate Precision | Significant Terms | F Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disintegration time (Y1) | Quadratic | 0.0032 | 0.36 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 13.04 | X1, X12, X22, X32 | 16.73 |
| Initial dissolution rate (Y2) | Quadratic | 0.073 | 0.04 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 4.935 | X1, X12, X32 | 4.37 |
| Dissolution efficiency (Y3) | Quadratic | 0.0578 | 0.044 | 0.88 | 0.664 | 5.7 | X1, X12 | 4.99 |
| Quality factor (Y4) | Quadratic | 0.0989 | 0.019 | 0.81 | 0.6926 | 6.8415 | X2, X3, X2, X3, X22 | 3.64 |
| Optimized Formula (F16) | Predicted Formula | |
|---|---|---|
| Disintegration time (s) | 30 | 33 |
| IDR % per minute | 16.60 | 15.00 |
| DE15 % | 77.70 | 80.00 |
| QF % | 90.00 | 90.00 |
| Desirability | 0.672 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alghaith, A.F.; Mahrous, G.M.; Shazly, G.A.; Zidan, D.E.Z.; Alhamed, A.S.; Alqinyah, M.; Almutairi, M.M.; Syed, S.A. The Optimization and Evaluation of Flibanserin Fast-Dissolving Oral Films. Polymers 2022, 14, 4298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204298
Alghaith AF, Mahrous GM, Shazly GA, Zidan DEZ, Alhamed AS, Alqinyah M, Almutairi MM, Syed SA. The Optimization and Evaluation of Flibanserin Fast-Dissolving Oral Films. Polymers. 2022; 14(20):4298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204298
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlghaith, Adel F., Gamal M. Mahrous, Gamal A. Shazly, Diaa Eldin Z. Zidan, Abdullah S. Alhamed, Mohammed Alqinyah, Mohammed M. Almutairi, and Saeed A. Syed. 2022. "The Optimization and Evaluation of Flibanserin Fast-Dissolving Oral Films" Polymers 14, no. 20: 4298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204298
APA StyleAlghaith, A. F., Mahrous, G. M., Shazly, G. A., Zidan, D. E. Z., Alhamed, A. S., Alqinyah, M., Almutairi, M. M., & Syed, S. A. (2022). The Optimization and Evaluation of Flibanserin Fast-Dissolving Oral Films. Polymers, 14(20), 4298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204298






