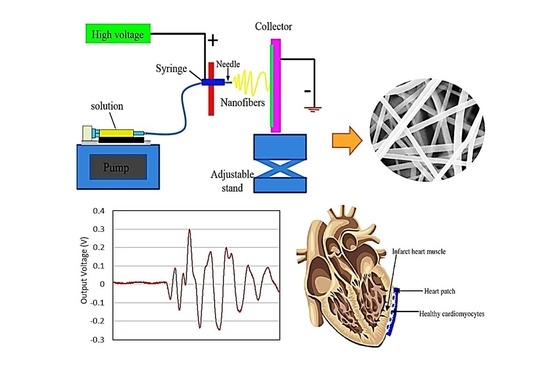
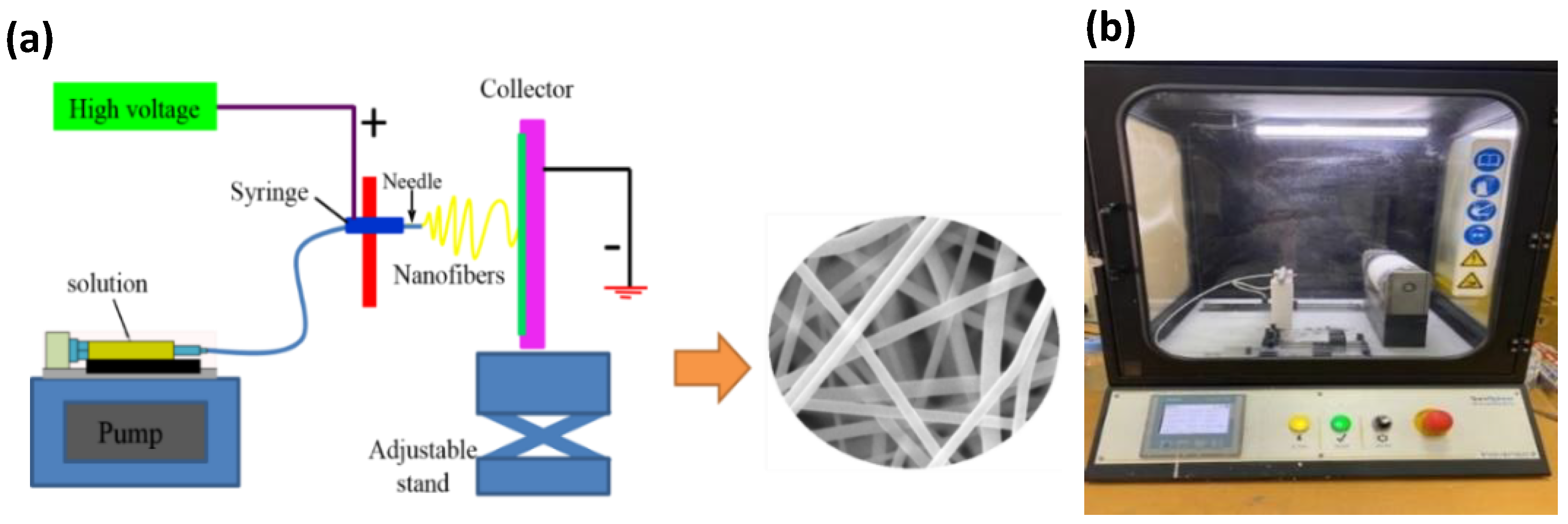
Development of New Bio-Composite of PEO/Silk Fibroin Blends Loaded with Piezoelectric Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Blends
2.2. Characterization
2.2.1. Zeta Potential
2.2.2. XRD, SEM, and FTIR Evaluation
2.2.3. Piezoelectric Characteristics
3. Results and Discussion
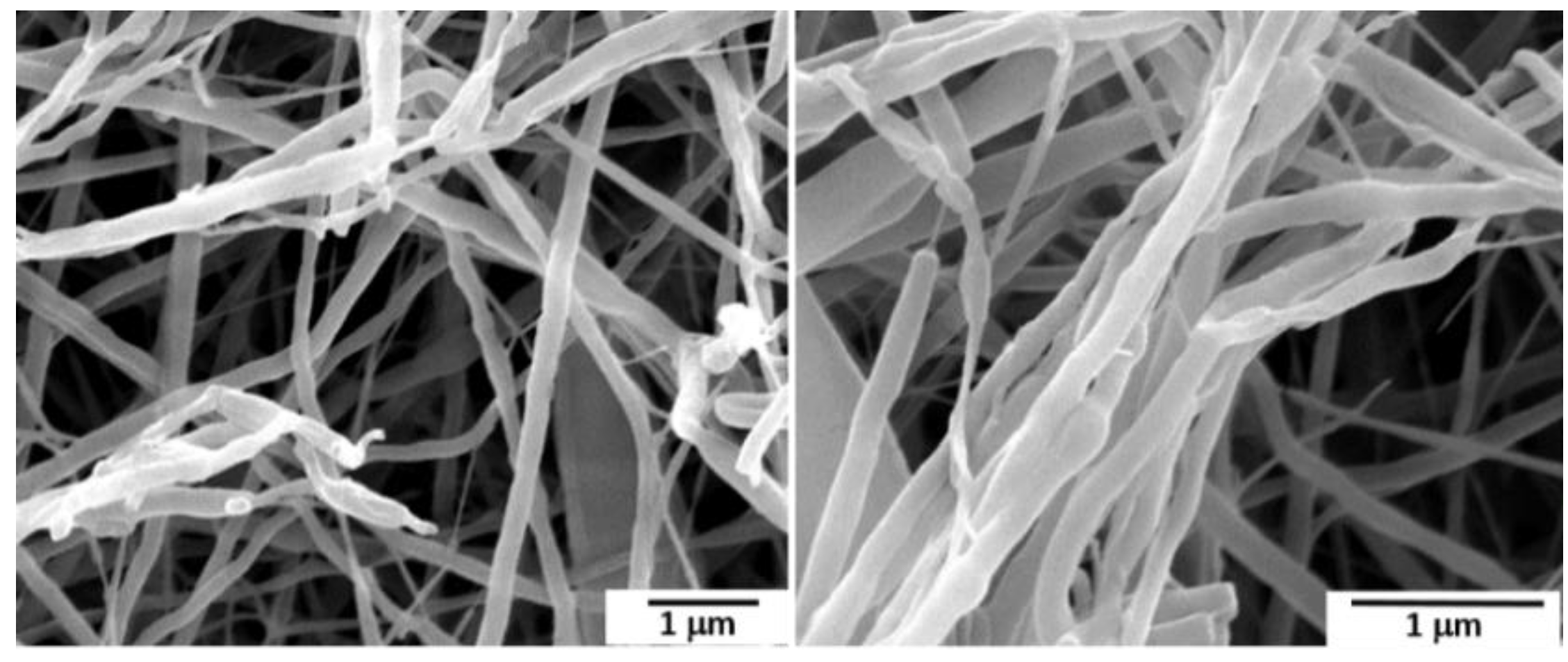
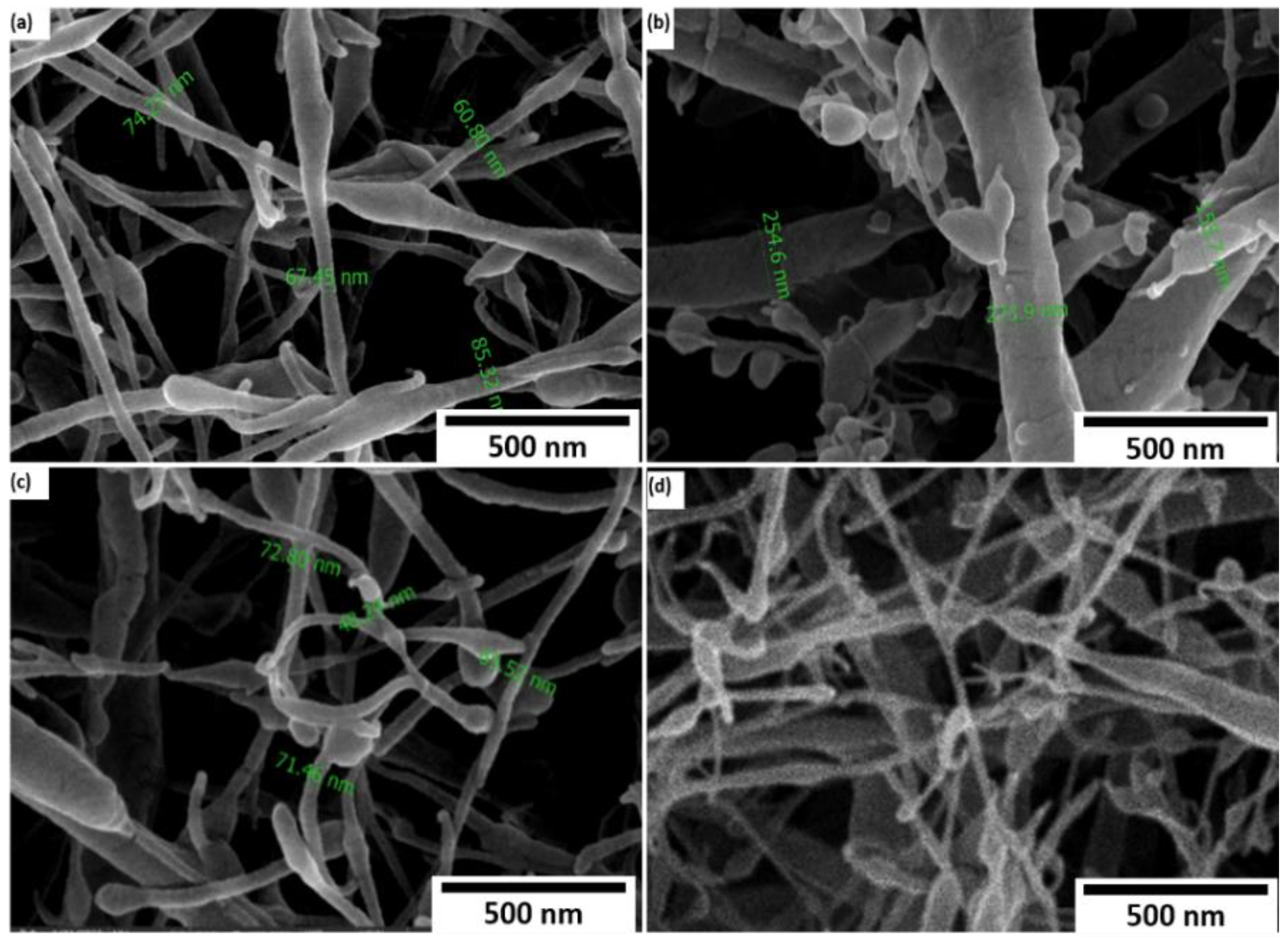
3.1. Zeta Potential and Fiber Morphology
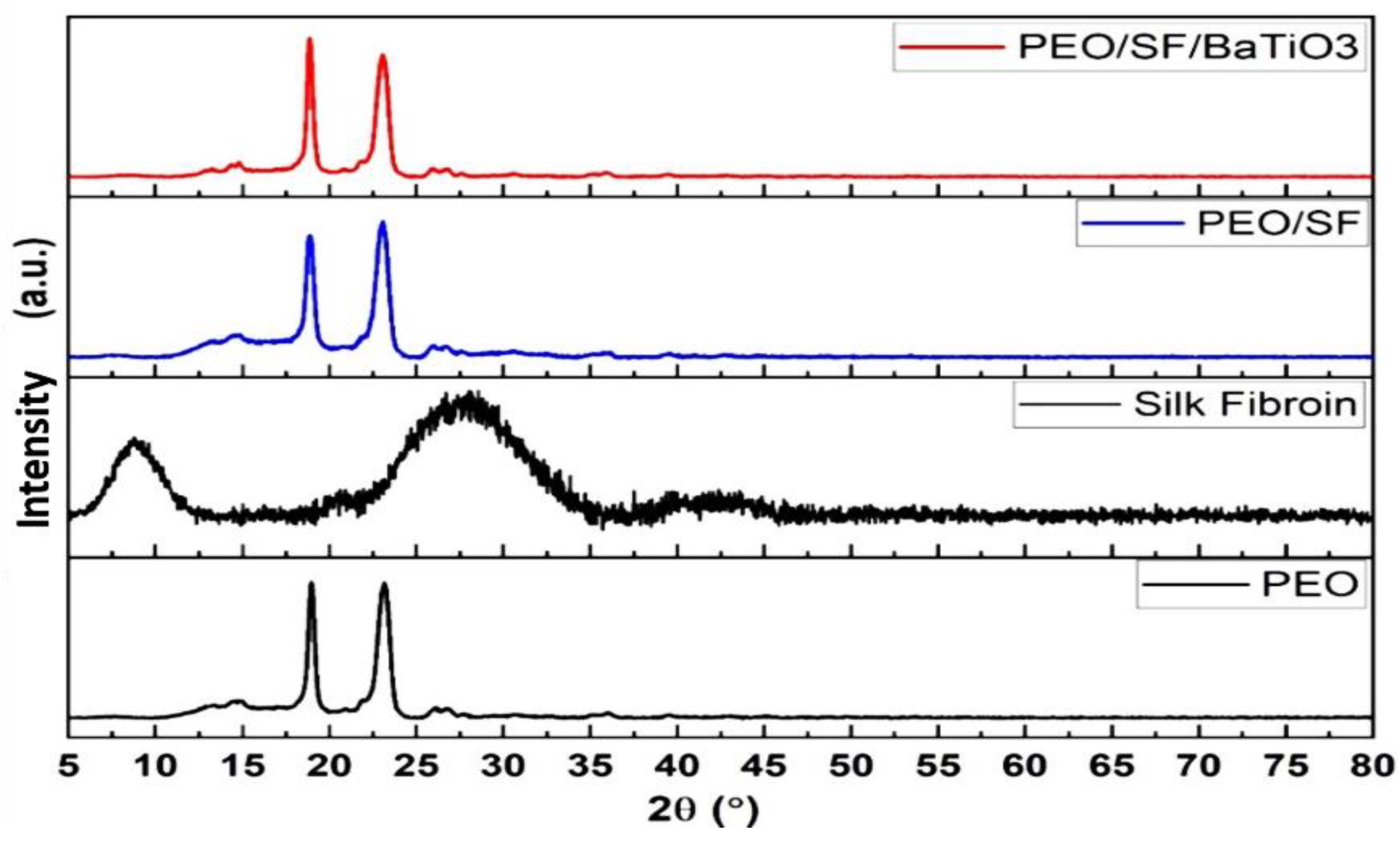
3.2. FTIR, XRD, and Raman Characterizations
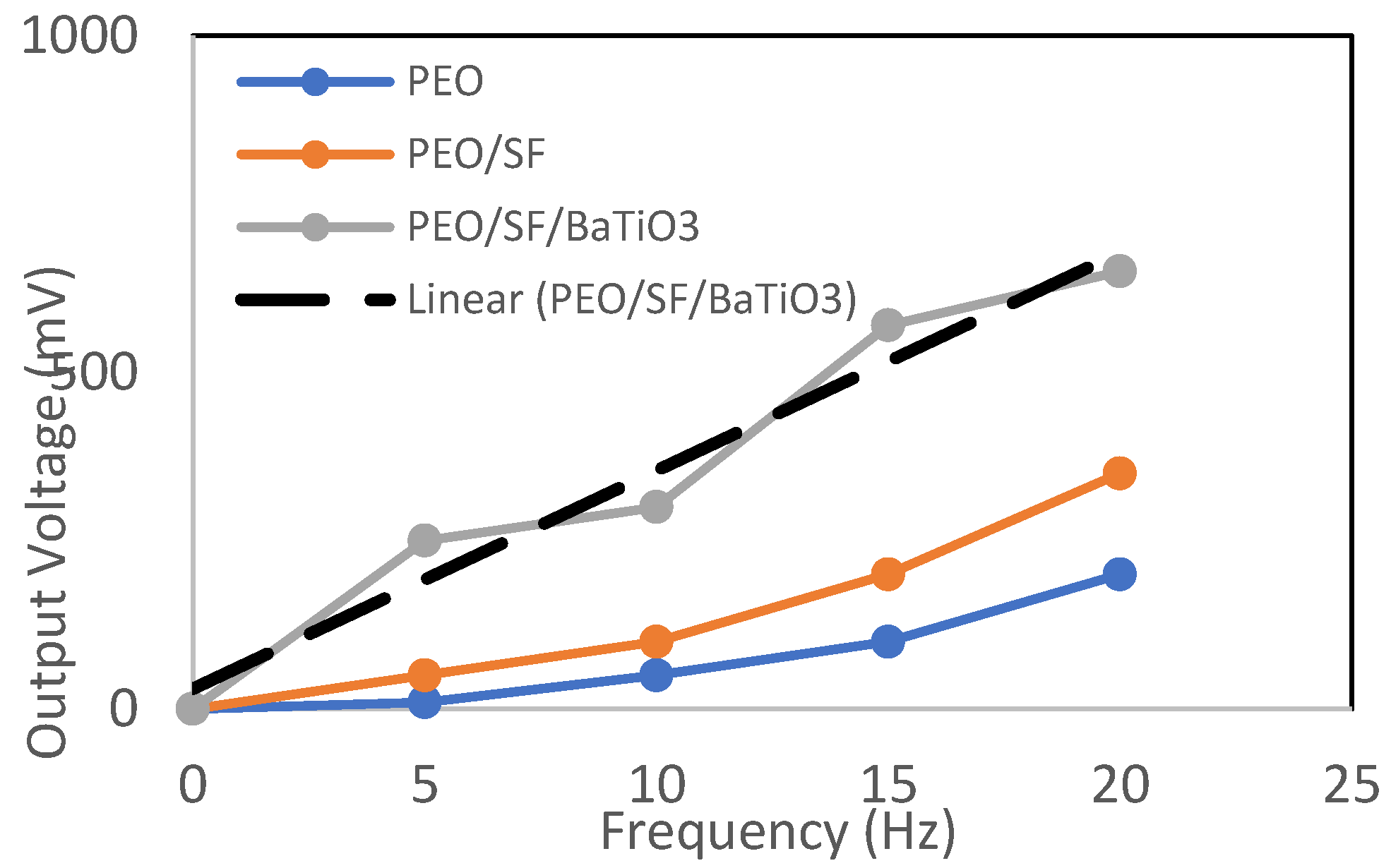
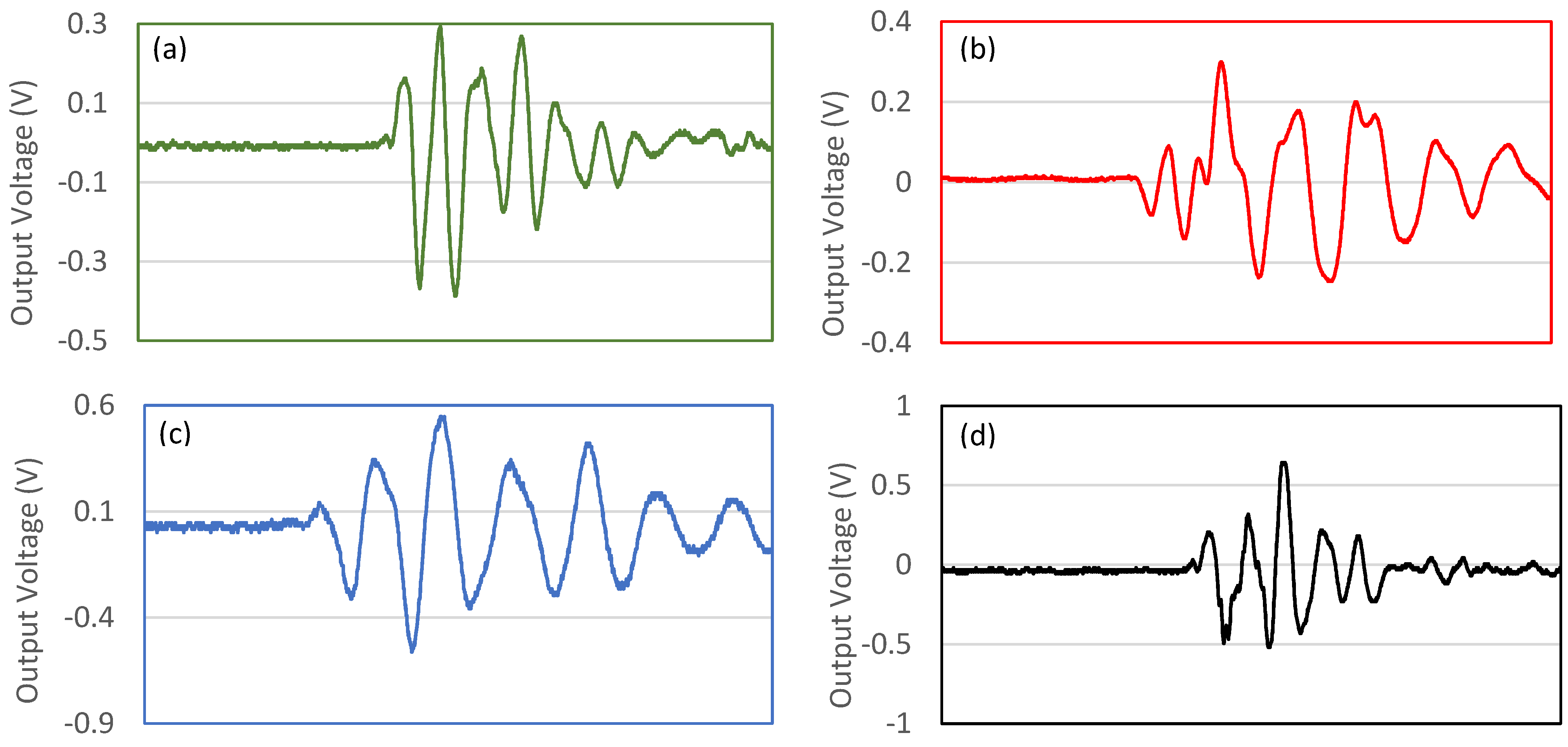
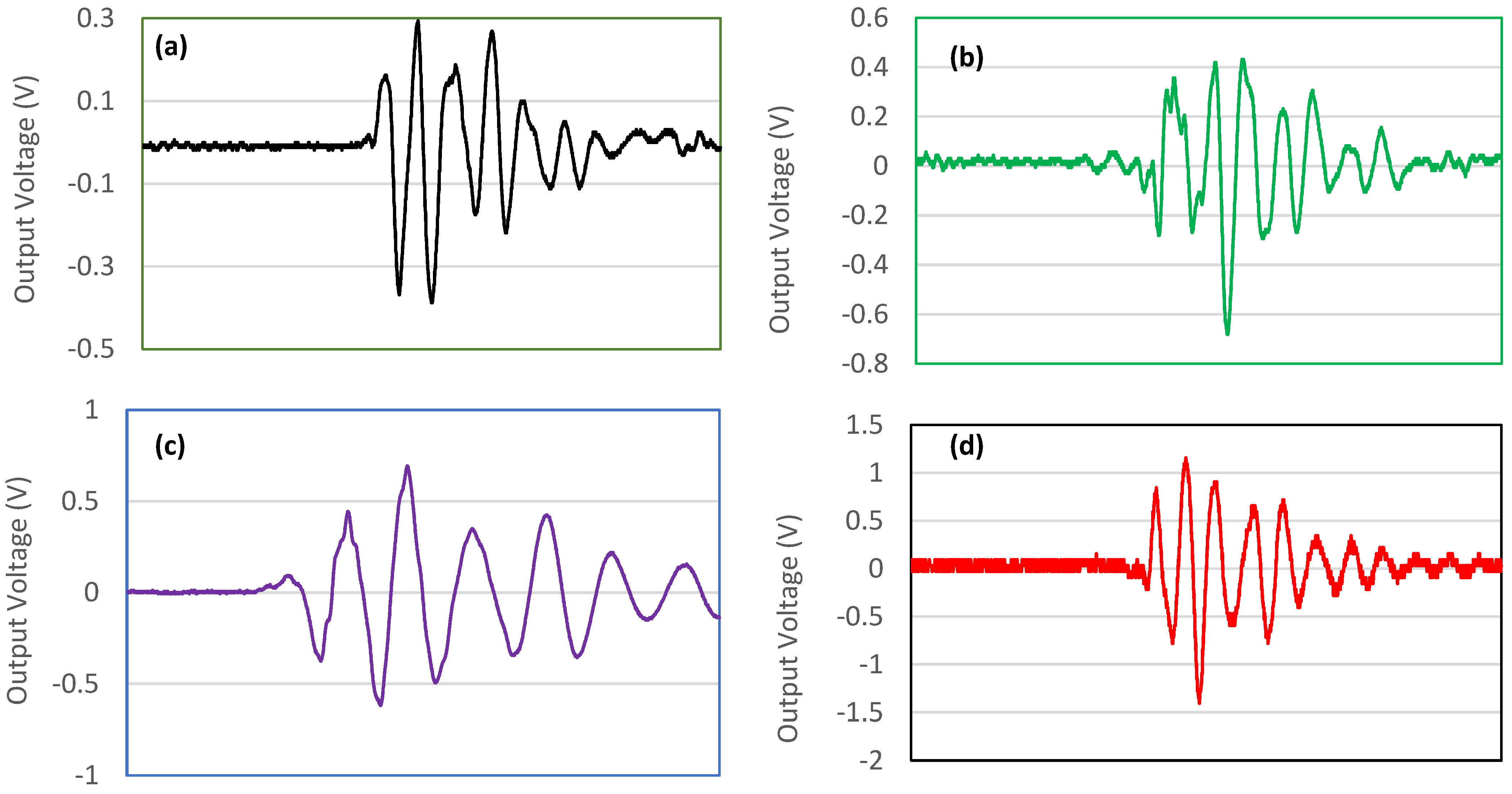
3.3. Piezoelectric Properties Evaluation
4. Conclusions
- ○
- Different weight percentages of SF solution were added to the PEO solution to form a PEO/SF blend with uniform nanofibers. An optimum amount of 15 wt.% of SF that produces nanofibers with a minimum amount of beads was achieved. BaTiO3 piezoelectric nanoparticles were added to the PEO/15 wt.% silk fibroin blend solution, and the obtained suspensions were introduced to an electrospinning device.
- ○
- Well-organized smooth nanofibers with low bead content were obtained in the PEO/15 wt.% SF/0.2 wt.% BaTiO3 composite.
- ○
- Piezoelectric characteristics were assessed by the piezotester mechanism, designed and manufactured in our lab.
- ○
- Electrospun PEO/15 wt.% SF/0.2 wt.% BaTiO3 fibers increased the output voltage (1150 mV) compared to pristine PEO and PEO/SF composite fibers (410 and 290 mV, respectively) upon applying 20 N force at 5 Hz frequency, which is much higher than PVDF-BaTiO3-Ag fibers that were reported in the literature.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gurunathan, T.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. A review of the recent developments in biocomposites based on natural fibres and their application perspectives. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 77, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, C.; Demuth, C.; Lange, A.; Stoick, P.; Pruszko, R. Biobased Automobile Parts Investigation. A Report Developed for the USDA Office of Energy Policy and New Uses; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Auras, R.; Harte, B.; Selke, S. An Overview of Polylactides as Packaging Materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 835–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.-P.; Sain, M. Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1552–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Hinrichsen, G. Biofibers, Biodegradable Polymers, and Biocomposites: An Overview. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2000, 276, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.J.; Thomas, S. Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E.; Deepa, B.; Pothan, L.A.; Jacob, M.; Thomas, S.; Cvelbar, U.; Anandjiwala, R. Extraction of nanocellulose fibrils from lignocellulosic fibres: A novel approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1468–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zini, E.; Scandola, M. Green composites: An overview. Polym. Compos. 2011, 32, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Antaya, H.; Pellerin, C. Characterization of the stable and metastable poly(ethylene oxide)-urea complexes in electrospun fibers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Antaya, H.; Pellerin, C. Structure and Phase Behavior of the Poly(ethylene oxide)−Thiourea Complex Prepared by Electrospinning. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 2373–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Allen, E.; Tonelli, A.E. Study of the inclusion compounds formed between α-cyclodextrin and high mo-lecular weight poly (ethylene oxide) and poly (ε-caprolactone). Polymer 1998, 39, 4857–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Goh, S.H.; Valiyaveettil, S. Inclusion complexes end-capped C60-end-capped poly (ethylene oxide) with cy-clodextrins. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 1399–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard-Lacroix, M.; Pellerin, C. Electrospinning of supramolecular polymer complexes. Sci. China Ser. B: Chem. 2012, 56, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, M.; Sarazin, D. Properties of PEO in Dilute Solution under Stirring. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serôdio, R.; Schickert, S.L.; Costa-Pinto, A.R.; Dias, J.R.; Granja, P.L.; Yang, F.; Oliveira, A.L. Ultrasound soni-cation prior to electrospinning tailors silk fibroin/PEO membranes for periodontal regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukseloglu, S.M.; Sokmen, N.; Canoglu, S. Biomaterial applications of silk fibroin electrospun nanofibres. Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 146, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, P.; Peer, P. Characterization of Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Nanofibers—Mutual Relations between Mean Diameter of Electrospun Nanofibers and Solution Characteristics. Processes 2019, 7, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.E.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on electrospinning design and nanofibre assemblies. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, R89–R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, H.; Izzati, A.B.N.F.; Inani, S.M.S.N.; E’Zzati, M.A.S.N.; Salimah, A.B.S.M.; Ali, F.B.; Manshor, M.R. Impregnation of Cinnamon Essential Oil into Plasticised Polylactic Acid Biocomposite Film for Active Food Packaging. J. Packag. Technol. Res. 2017, 1, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macha, I.J.; Muna, M.M.; Magere, J.L. In Vitro Study and Characterization of Cotton Fabric PLA Composite as a Slow Antibi-otic Delivery Device for Biomedical Applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 43, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, R.; Shen, L.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Fu, F.; Fu, Y.; Liu, X. Enhancing the surface affinity with silver nano-particles for antibacterial cotton fabric by coating carboxymethyl chitosan and l-cysteine. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 497, 143673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouro, C.; Gouveia, I.C. Antimicrobial functionalization of wool: Assessment of the effect of Cecropin-B and [Ala5]-Tritrp7 antimicrobial peptides. J. Text. Inst. 2016, 107, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulié, S.; Bilem, I.; Chevallier, P.; Elkoun, S.; Robert, M.; Naudé, N.; Laroche, G. Milkweed scaffold: A new candidate for bone cell growth. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2020, 69, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, G.M.; Rodas, A.C.; Leite, C.A.; Giles, C.; Higa, O.Z.; Polakiewicz, B.; Beppu, M.M. Preparation and characterization of ethanol-treated silk fibroin dense membranes for biomaterials application using waste silk fibers as raw material. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8446–8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.-J.; Li, Y.; Yao, S.-W.; He, J.-H. Silkworm-based silk fibers by electrospinning. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, G.R.; Corsini, P.; Pérez-Rigueiro, J.; Marsano, E.; Guinea, G.V.; Elices, M. Effect of water onBombyx mori regenerated silk fibers and its application in modifying their mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vepari, C.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk as a Biomaterial. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Cho, D.; Park, W.H.; Lee, S.G.; Han, S.O.; Drzal, L.T. Novel Silk/Poly (Butylene Succinate) Biocomposites: The Ef-fect of Short Fibre Content on Their Mechanical and Thermal Properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, G.H.; Diaz, F.; Jakuba, C.; Calabro, T.; Horan, R.L.; Chen, J.; Lu, H.; Richmond, J.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk-Based Bio-materials. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, I.C.; Kweon, H.Y.; Lee, K.G.; Park, Y.H. The role of formic acid in solution stability and crystallization of silk protein polymer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2003, 33, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.-Z.; Confalonieri, F.; Jacquet, M.; Perasso, R.; Li, Z.-G.; Janin, J. Silk fibroin: Structural implications of a remarkable amino acid sequence. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2001, 44, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal-Egaña, A.; Scheibel, T. Silk-based materials for biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2010, 55, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogovina, S.Z.; Prut, E.V.; Berlin, A.A. Composite Materials Based on Synthetic Polymers Reinforced with Natural Fibers. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2019, 61, 417–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katashima, T.; Malay, A.D.; Numata, K. Chemical modification and biosynthesis of silk-like polymers. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2019, 24, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Venkatesan, H.; Hu, J. Chemically Modified Silk Proteins. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.R.; Kaplan, D.L. Biomedical applications of chemically-modified silk fibroin. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6443–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-G.; Mo, X.-M. Current Research on Electrospinning of Silk Fibroin and Its Blends with Natural and Synthetic Bio-degradable Polymers. Front. Mater. Sci. 2013, 7, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Shao, Z. Electrospinning of reconstituted silk fiber from aqueous silk fibroin solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 2270–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, H.; Hu, X. Electrospun ultra-fine silk fibroin fibers from aqueous solutions. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 5359–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, Y.; Morikawa, H.; Yamanaka, S.; Tamada, Y. Electrospinning of silk fibroin from all aqueous solution at low concentration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.J.; Fridrikh, S.V.; Rutledge, G.C.; Kaplan, D.L. Electrospinning Bombyx mori silk with poly (ethylene ox-ide). Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Chen, J.; Karageorgiou, V.; Altman, G.H.; Kaplan, D.L. Human bone marrow stromal cell responses on electrospun silk fibroin mats. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacanti, J.P.; Langer, R. Tissue Engineering: The Design and Fabrication of Living Replacement Devices for Surgical Recon-struction and Transplantation. The Lancet 1999, 354, S32–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtari, K.; Nazari, H.; Ko, H.; Tebon, P.; Akhshik, M.; Akbari, M.; Alhosseini, S.N.; Mozafari, M.; Mehravi, B.; Soleimani, M.; et al. Electrically conductive nanomaterials for cardiac tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 144, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.R.; Ferreira, F.C.; Sanjuan-Alberte, P. Electrospun piezoelectric scaffolds for cardiac tissue engineering. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 137, 212808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, D.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Jin, G.; Ramakrishna, S. Guided orientation of cardiomyocytes on electrospun aligned nanofibers for cardiac tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2011, 98, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydarkhan-Hagvall, S.; Schenke-Layland, K.; Dhanasopon, A.P.; Rofail, F.; Smith, H.; Wu, B.M.; Shemin, R.; Beygui, R.E.; MacLellan, W.R. Three-dimensional electrospun ECM-based hybrid scaffolds for cardiovascular tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2907–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, M.A.; Pourmand, G.; Ai, J.; Ghanbari, H.; Dinarvand, R.; Naji, M.; Faridi-Majidi, R. Electrospun PLLA nanofiber scaffolds for bladder smooth muscle reconstruction. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2016, 48, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, G.C.; Fridrikh, S.V. Formation of fibers by electrospinning. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafqi, M.S.S.; Sadeghi, A.H.; Latifi, M.; Bagherzadeh, R. Design and fabrication of a piezoelectric output evaluation system for sensitivity measurements of fibrous sensors and actuators. J. Ind. Text. 2021, 50, 1643–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fawal, G.; Marwa, M.A.-S.; Mo, X.; Wang, H. Diethyldithiocarbamate/silk fibroin/polyethylene oxide nanofibrous for cancer therapy: Fabrication, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenot, A.; Chronakis, I.S. Polymer nanofibers assembled by electrospinning. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Yang, D.Z.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Z.P.; Yin, R.X.; Nie, J. Electrospun core-shell structure nanofibers from a homogeneous solution of poly(ethylene oxide)/chitosan. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 5278–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtizad, S.; Alizadeh, P.; Yourdkhani, A. Improving piezoelectric properties of PVDF fibers by compositing with BaTiO3-Ag particles prepared by sol-gel method and photochemical reaction. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 883, 160810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, A.; McNamee, E.; Slade, D. Piezoelectric Nanofibers as Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration and Wound Healing. Diploma Thesis, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sencadasa, V.; Garveyd, C.; Mudie, S.; Kirkensgaard, J.J.K.; Gouadec, G.; Hauser, S. Electroactive properties of electrospun silk fibroin for energy harvesting ap-plications. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fouad, H.; Khalil, K.A.; Alshammari, B.A.; Abdal-hay, A.; Abd El-salam, N.M. Development of New Bio-Composite of PEO/Silk Fibroin Blends Loaded with Piezoelectric Material. Polymers 2022, 14, 4209. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194209
Fouad H, Khalil KA, Alshammari BA, Abdal-hay A, Abd El-salam NM. Development of New Bio-Composite of PEO/Silk Fibroin Blends Loaded with Piezoelectric Material. Polymers. 2022; 14(19):4209. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194209
Chicago/Turabian StyleFouad, Hassan, Khalil Abdelrazek Khalil, Basheer A. Alshammari, Abdalla Abdal-hay, and Nasser M. Abd El-salam. 2022. "Development of New Bio-Composite of PEO/Silk Fibroin Blends Loaded with Piezoelectric Material" Polymers 14, no. 19: 4209. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194209
APA StyleFouad, H., Khalil, K. A., Alshammari, B. A., Abdal-hay, A., & Abd El-salam, N. M. (2022). Development of New Bio-Composite of PEO/Silk Fibroin Blends Loaded with Piezoelectric Material. Polymers, 14(19), 4209. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194209