Abstract
Magnetic polymer composites are used in a variety of applications in many industries. Their production methods are usually time-consuming and solvent-intensive as they are performed in liquid phase processes, such as emulsion polymerization or precipitation. In this work, a quick, easy, and solvent-free method is presented to coat polymer particles with a discrete, non-coherent coating of superparamagnetic nanoparticles. The results of the dry coating process are evaluated optically, by means of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), via powder X-ray diffraction and thermally by means of differential scanning calorimetry, before finally demonstrating the effectiveness of dry coating by means of a vibrating sample magnetometer.
1. Introduction
Magnetic polymer composites are being investigated and used for a wide variety of applications in the medical technology, for example magnetic resonance spectroscopy [1,2], pharmaceutical [3,4,5,6,7], and (bio-)chemical industries [8,9,10] as gas and humidity sensors [11,12] or for urea sensing [13]. The sensing abilities of iron oxides are always of interest, as recently iron oxide—based supra-particles were used to track the temperature [14] or to create a magnetic fingerprint [15]. Therefore, the functionalization and production of magnetic polymers has been the topic of research for several years. A number of processes have been developed, all taking place in the liquid phase, where the polymerization occurs in a liquid or emulsion containing the magnetic particles [16,17,18,19,20,21] as well as the deposition of nanoscale iron oxid within the liquid phase [22]. This not only entails the use of various solvents, which can be problematic for both humans and the environment, but this process route is always followed by a drying step, which also takes time and resources.
To create a magnetizable polymer composite, various substances are currently used; most of them are iron-based, since iron has the highest saturation magnetization at ambient temperatures [23]. Iron oxides, especially Fe3O4 [21,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32] and γ-γ-Fe2O3, are the most popular. The benefits of iron oxides in comparison with other iron compounds are their stability, their environmental friendliness, and their inexpensiveness [33], which makes them easy-to-use and to prepare [34,35,36,37,38,39]. Their combination with polymers can yield completely new functionalities such as the recently reported magnetic indication of elapsed temperature events [33]. Another large group of magnetic particles with which the polymer is modified during polymerization are the carbonyl iron compounds such as shown in [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49]. As well as some rarer compounds containing zinc [50], copper [51], or cobalt [52].
Compared to the wet chemical methods mentioned, dry coating (DC) offers several advantages, especially the absence of solvents, possible stabilizers within the liquid phase, and therefore the non-required drying step, making dry coating a sustainable and cost-efficient method of functionalization. Dry coating has been used for some time to improve the flowability [53,54] and fluidizability [55] of powders, e.g., by uniform deposition of silica nanoparticles on the surface of the particles. Research has also been conducted to use DC for the production of customized advanced materials, for example to control the powder charge [56,57], improve the humidity resistance [58] or to increase the electrical conductivity [59]. The influencing factors for dry coating can be found on the process side as well as on the material side. On the process side, the following variables should be mentioned: the filling level of the mixer, the ratio of HP to GP to mixing aids, the process temperature [60], and the mechanical energy input (stirrer speed). On the material side, the particle sizes of the materials used, as well as the differentiation between conductive and non-conductive materials and the densities have an influence on the process result [61].
The process, inherently designed to deposit nanoparticles (guest particles—GP) on host particles (HP), is based on the adhesion between those resulting from van-der-Waals forces and consists of several steps that transition into each other as can be seen in Figure 1. In step (a) host and guest particles are added to the mixing device and brought into contact. (b) Guest particles are dispersed (c) and deagglomerated (d) by assistance of mixing aids. Due to the impact and shear between the mixing aids, the nanoparticle agglomerates are exposed to constant mechanical energy. The agglomerates are broken down by the mechanical energy so that increasingly smaller aggregates can attach to the host particles. Ideally, single nanoparticles are obtained during deagglomeration. (d) The different results which can be obtained by dry coating are schematically described in (e): ideal hexagonal coating is a purely theoretical ideal condition (1). The random coating occurs during a non-optimized process, where the product already has the desired properties (2). The ideal random coating occurs in an optimized process, where the smallest possible amount of additive achieves the desired product properties due to a close-to-ideal coating quality. It is important to notice, that powder dry coating can be performed in several kinds of mixing devices and is not limited to a shaker mixer, as used in this work and therefore even big batches can be produced.
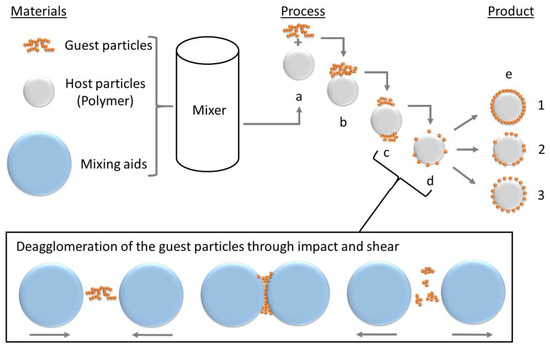
Figure 1.
Process of dry coating, described by Alonso et al. [62,63,64]. (a) addition of GP to HP and first contact (b); (c) deagglomeration and (d) dispersion of the GP; (e) different product qualities to achieve.
For an ideal random single-layer coating, as in Figure 1 (e-1), Yang et al. [53] gave the approximate additive content in weight percent:
with the diameter of the host particles dhost and the guest particle diameter dg as well as the density of the host particles ρhost and the guest particles ρg, as well as N (cf. Equation (2)), which represents the number of guest particles to achieve the surface coverage.
The dry coating process will therefore form a discrete core—shell coating around on the particle surface. When the process is optimized a uniformly distributed coating, which is near Figure 1 (e-3), is achievable. The difficulties in dry coating are primarily the de-agglomeration of the nanoparticulate GP, selecting the process time so that de-coating does not occur, and observing the yield, since triboelectric effects have a massive influence on this.
The aim of this work is therefore to showcase a sustainable, solvent-free, scalable, and easy-to-use method to create discrete magnetic core-shell structures on polypropylene (PP) particle surfaces by use of dry particle coating. PP is a widely used thermoplast with high chemical resistance and good thermal properties which is used in additive manufacturing or injection moulding. A magnetisable PP-composite would, for example, be perfect to produce magnetically responsive sensors. The composite is analyzed by use of scanning electron microscopy to showcase the coating and the differences in the two additives used, as well as to evaluate the degree of coverage on the polymer surface. Furthermore, the powder is analyzed by powder X-ray diffraction to evaluate polymorphs in the coating material and differential scanning calorimetry to determine the crystallinity of the polymer- super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (SPION) composite. Finally, the magnetizability of the newly made composites is determined and results are compared to each other.
2. Materials and Methods
Polypropylene, type Coathylene PD0580 (Axalta, Bulle, Switzerland) with a density of 0.907 g cm−3 and particle sizes of x10.3 = 32 ± 3 µm, x50.3 = 93 ± 5 µm and x90.3 = 182 ± 4 µm (measured by laser diffraction (Mastersizer 2000, Malvern, UK)) is used. Magnetic γ-Fe2O3 powder, 98%, (NanoArc®, APS Powder, S.A, Singapore) with a particle diameter between 20–40 nm and a specific surface area (BET) of 32.188 m2 g−1 is used as an additive and compared with self-synthesized Fe3O4, with a mean particle size between 10 to 20 nm and a specific surface area (BET) of 79.138 m2 g−1, stabilized with oleic acid according to [14]. The synthesis of Fe3O4 is achieved by a co-precipitation reaction. Therefore, FeCl3 6 H2O (total: 10.80 g, 40 mmol, Sigma Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany, >99%) and FeCl2 4 H2O (total: 3.98 g, 20 mmol, Fluka—obtained by Sigma Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany, >99%) were dissolved in deionized water (225 mL) at room temperature (ca. 20 °C) and mixed with 30% aqueous ammonia solution NH3 (aq.) (25 mL). After 60 s of stirring, the black precipitate was magnetically separated, and the overlaying water decanted. In this manner, the particles were washed with deionized water (250 mL) three times before dispersing them in water (250 mL). The self-synthesized nanoparticle dispersion is dried with a vacuum oven and pre-crushed before use via mortar and pestle. The commercial γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles as well as the self-synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles are displayed in Figure 2. It is important to note, that the Fe3O4 powder is difficult to deagglomerate and most Fe3O4 particles are present in agglomerates larger than 100 nm.
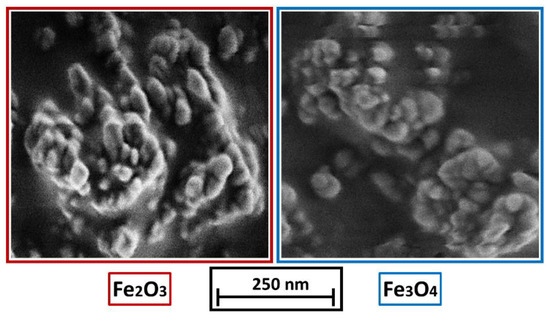
Figure 2.
(left): γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles, (right): Fe3O4 nanoparticles.
2.1. Dry Coating
A Turbula mixer (T2f, Willy A. Bachofen AG, Muttenz, Switzerland) is used for the coating experiments. The polymer coating takes place in borosilicate snap-on lid glasses with a volume of 25 mL. To ensure reproducibility, each experiment is performed 3 times. The mixer is operated in all experiments at 49 rpm with a coating time of 60 min.
In each experiment 3 g of polymer powder were used. To achieve deagglomeration of the guest particles, 9 g of glass spheres (Sili S, Sigmund Lindner GmbH, Warmensteinach, Germany) with particle size ranging between 1.0–1.25 mm and a bulk density of 1.5 g cm−1 were added as mixing aids. The glass beads were separated with a 0.8 mm sieve after the coating process.
2.2. Nitrogen Sorption
Nitrogen sorption measurements (77.4 K) were performed to determine the properties of the nanoparticles using a NovaTouch LXII (Anton Paar, Graz, Austria). Before each measurement, the samples were gassed out at 200 °C for 12 h at vacuum and weighted in an inert atmosphere.
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
The polymer particles have been characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) using a Gemini Ultra 55 (Zeiss, Jena, Germany) device equipped with a SE2 detector. An acceleration voltage of 1 kV has been applied.
2.4. X-ray Diffraction
For structural analysis of the product, powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed with an AXS D8 Advance diffractometer in the Bragg–Brentano geometry (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA). The device is equipped with a VANTEC-1 detector and a Ni filter and uses Cu Kα radiation (154 pm). The step size for collecting the diffractograms was set to 0.014° with a measuring time of 1 s per step for the range of 2Θ = 10–60°.
2.5. Dynamic Scanning Calorimetry
The crystallinity and the crystallization temperature of the coated powders are determined by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). For this purpose, a Polyma 214 (Netzsch, Selb, Germany) is used. The samples with a weight of 10 mg ± 0.1 mg are measured with covered aluminum pans type Concavus Lids (Al), NGB817526 (Netzsch, Germany) with dry nitrogen gas purging at 40 mL min−1. As the melting temperature of the PP is at 186 °C, the temperature profile to measure the thermogram is as following: (1) Start at 20 °C, (2) heating to 200 °C by a gradient of 10 K min−1, (3) isothermal step of 60° s, (4) cooling by a gradient of 10 K min−1.
2.6. Virbating Sample Magnetometer
Magnetic properties of the nanoparticles as well as the product particles were determined with a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) type VersaLabTM 3T from Quantum Design Inc., San Diego, CA, USA. Field dependent magnetization measurements were conducted between −30 to +30 kOe with a measurement speed of 50 Oe s−1 and 5 Oe s−1 between −5 and 5 kOe.
3. Results
3.1. Degree of Coverage
The effect of dry coating can be observed visually in Figure 3. The surface coating noticeably changes the color of the powder to the color of the iron oxide used. Inside the red box (top row), the powders functionalized with Fe2O3 are displayed; in the blue box (bottom row) results of functionalization with Fe3O4 are displayed.

Figure 3.
Change in color of the coated powders. From left to right, increase of iron oxide content from 0.05 to 5 wt.% according to experiments listed in Table 1. The last beaker in each row (most right position) shows the pure SPIONs.
The evaluation of the particle surface by means of SEM shows, an increase in the degree of coverage with an increase of the SPION content. Figure 4 shows the change in the degree of coverage of Fe2O3 (red box) and Fe3O4 (blue box). The coating with Fe3O4 is not as uniform as in the samples with γ-Fe2O3. The reason is found in the production process of the SPIONs by spray drying: The Fe3O4 formulation has not been stabilized against aggregation of the primary particles while drying. Nevertheless, the images show a homogeneous, discrete distribution of the guest particles on the polymer surface. Due to the van der Waals forces acting between the GP and the HP, the two materials are almost inseparably bonded, which makes the process stand out. Due to the surface deposition of the GP on the HP, their effect, such as magnetization in this case, is not hindered by any polymer layers, as often occurs in liquid phase processes, where the GP preferentially accumulate inside a polymer matrix. In that case, the polymer would act as a spacer between the nano particles and the external magnetic field.
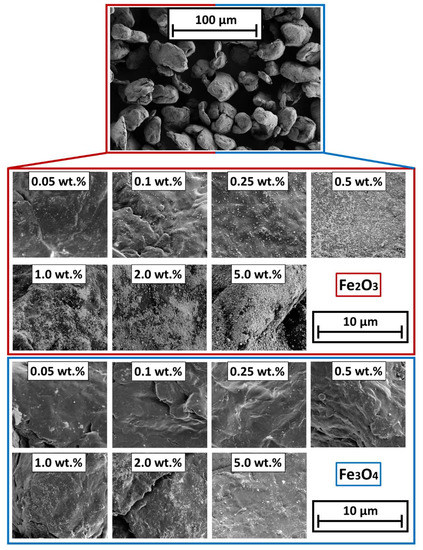
Figure 4.
SEM micrographs of the different SPION coated polymer surfaces. (Top): Overview of the particle bulk; (Bottom): coated surfaces.
Corresponding to the SEM-images from Figure 5, the degrees of coverage (see Figure 4) are determined. Image analysis via MATLAB, due to binarization of the SEM images by use of Otsu’s method [65] to determine the threshold. After binarization, the guest particles are displayed in white and the polymer surface is displayed in black. The degree of coverage is the amount of white area within the image. It is easy to observe that the degree of coverage increases continuously and flattens around 2 wt.% additive content onwards. The lower degree of coverage of the Fe3O4 samples is also evident here. The higher degree of coverage when using the γ-Fe2O3 is related to the easier deagglomeration of the commercial product. The Fe3O4 particles from our own production, were hydrophobized by the oleic acid but not functionalized against aggregation. Results indicate that the interparticulate forces between the Fe3O4 primary particles are stronger than the forces needed to deagglomerate them sufficiently during the coating process, leading to a non-ideal coating result and even spread on the HP surface.
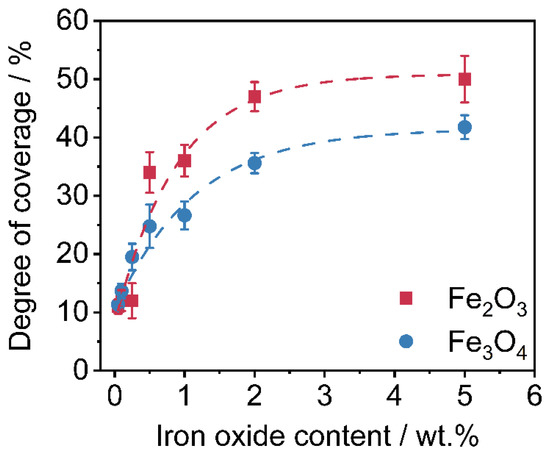
Figure 5.
Degrees of coverage of the nanoparticles on the polymer surface (n = 3).
To confirm the lower degree of coverage of Fe3O4, a thermo-gravimetrical experiment to determine the amount of SPIONs on the polymer powder has been carried out. For this purpose, around 1 g of polymer-iron oxide powder is weighed into a ceramic bowl. Afterwards, the polymer is burned at 900 °C for 10 min within an oven. Subsequently, the residual mass (the inorganic iron oxide) is weighed, and the measured iron oxide content is calculated. The results are shown in Figure 6. As displayed, the residual mass of Fe3O4 within the polymer-iron oxide composite is lower in comparison with the easily-dispersible commercial product.
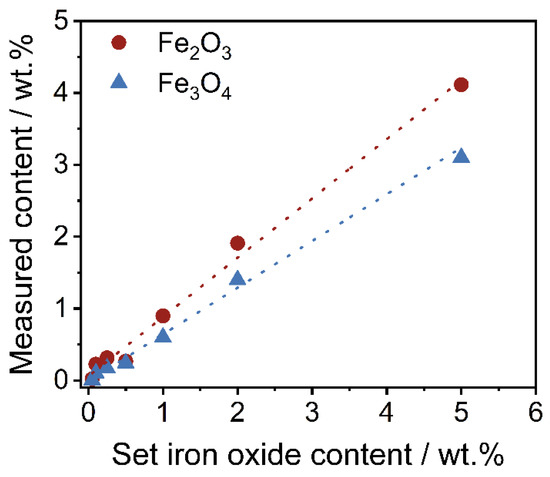
Figure 6.
Measured iron oxide content in regard to the set iron oxide content of both formulations.
It is not surprising that the measured iron oxide content is lower than the set content in this work, as losses always occur on the wall of the mixing device. For the purpose of this work and better comparability, further results are displayed in regard to the set iron oxide content.
3.2. X-ray Diffraction
The measurements are intensity min-max-normalized for all values obtained within a sample according to:
In all diffractogramms (Figure 7), the increase in the reflexes, characteristic of the iron oxides used, can be clearly observed. As can be seen in the diffractograms from the reflexes 2Θ = 31°, 2Θ = 38°, 2Θ = 47°, and 2Θ = 55°, the iron oxide nanoparticles are not one pure polymorph, but exhibit both alpha (hematite) and gamma (maghemite) reflexes [66,67]. The reflexes correspond to those of the raw material used, which proves the gentle processing conditions during dry coating, as otherwise a change in the polymorphy [66] would have occurred. Although not as distinct, the same behavior can be seen in the polymer particles coated with Fe3O4. The polymorphy is detectable on the surface. The reason for this is that there is often a slight transformation on the nanoparticle surface where γ-Fe3O4 converts to Fe2O3, but the Fe3O4 is still present in the core [68].
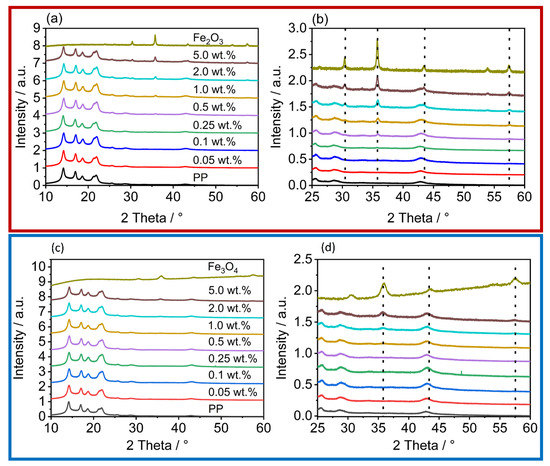
Figure 7.
XRD of the iron oxides, the unfunctionalized PP, and the coated powders; the red box contains the diffractograms of the γ-Fe2O3 coated powders, the blue box the diffractograms of the powders with Fe3O4. (a,c) shows an overview over the measured area; (b,d) zooms inside the area, where the increase of the iron oxide reflexes are observed.
3.3. Thermal Analysis
Thermal analysis by DSC shows the influence of the iron oxide nanoparticles on the crystallization temperature (Figure 8a) as well as the relative crystallinity (Figure 8b). Further processing, e.g., in additive manufacturing or injection moulding, strongly depends on the melting and crystallization behavior. Figure 8 shows the determined crystallization temperatures (Figure 8a) and the corresponding relative crystallinities (Figure 8b). The nanoparticles act as crystallization nuclei and, thus, shift the crystallization temperature as expected to higher temperatures [69,70,71]. This effect is further enhanced by the higher heat transfer ability of the iron oxides. The more rapid heat transfer also explains the reduced relative crystallinity, since colder temperatures are also passed.
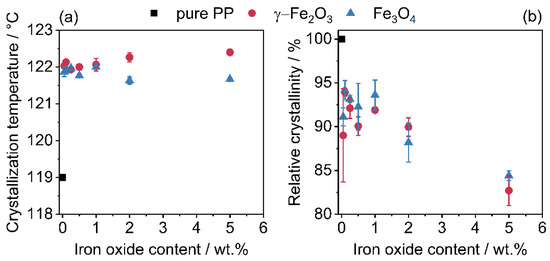
Figure 8.
Change in crystallization temperature (a) and relative crystallinity (b) due to additivation with iron oxide nanoparticles. The relative crystallinity refers solely to the weight of the polymer, the SPIONs have been excluded.
3.4. Vibrating Sample Magnetometer
The results of the magnetometer measurements (Figure 9) show the full spectrum of magnetization measurements of the γ-Fe2O3 (a-1) and Fe3O4 (b-1) samples, showing that the maximum magnetization of the commercial Fe2O3 SPIONs does not differ from that of the synthesized Fe3O4 SPIONs. In the enlarged plot of the data (a-2) for γ-Fe2O3 and (b-2) for Fe3O4 functionalization, it is shown that the magnetization by the commercially available SPIONs is higher than with the self-synthesized Fe3O4. In this case, this is in line with expectations, since it has already been shown in the determination of the degree of coverage (Figure 4) that the coating process using Fe3O4 cannot be performed optimally. A stabilization of the SPIONs that keeps the Fe3O4 nanoparticles separated during the drying step will solve this problem. Since the functionalization, unlike in liquid-phase processes, only takes place on the surface of the polymer, the resulting value of the magnetization is comparatively low. During dry coating, much less iron oxide is required to functionalize the polymer. For example, in [26], in which the ration between polymer and SPIONs is around 1:3, or in [28] where SPION contents up to 80% are used. For the iron oxides used, the more additive is applied to the surface, the higher the magnetization.
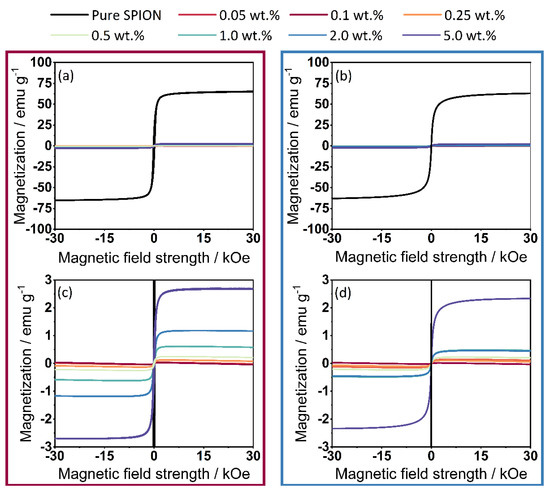
Figure 9.
Measurement results from VSM. (a) Results from the complete measurement spectrum of γ-Fe2O3, (b) Results from the complete measurement spectrum of Fe3O4, (c) Magnification; (d) Magnification of the magnetization—(values displayed in cgs units).
If the maximum magnetizations are extracted from the measurements (Figure 9) and plotted against the set iron oxide content (Figure 10), an expected linear relationship can be seen as the magnetization scales with the amount of iron oxide available. Again, the maximum values of Fe3O4 are slightly lower than those of Fe2O3, which is again due to the different coating quality.
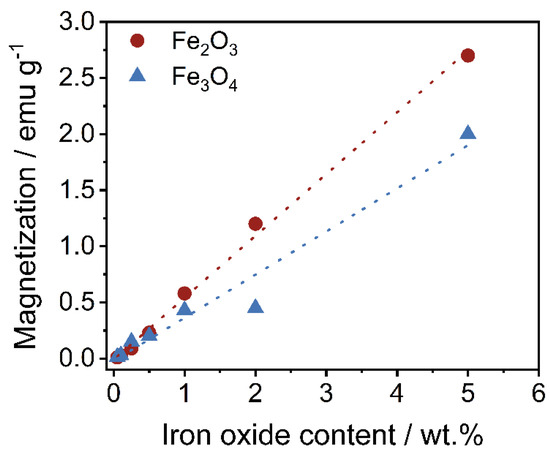
Figure 10.
Relationship between the maximum magnetization as regards the set iron oxide content.
4. Conclusions
In this work, a solvent-free dry coating process for producing magnetic polymer particles is introduced. Seven different additive concentrations of γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 were used to show the versatility of this process as it is possible to coat commercially available host particles quickly and sufficiently. The discrete coating is evenly distributed on the polymer particle surface and adjustable by the additive concentration. The additive content controls the magnetization directly. Dry coating is therefore a simple, sustainable coating method for the production of magnetizable polymer composites with commercially available products and a low need for resources.
Author Contributions
B.D.: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, visualization, writing—original draft preparation; P.G.: investigation; S.M.: writing—review and editing; J.S.: investigation, writing—review and editing; A.B.: supervision, funding, writing—review and editing, project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
German research foundation (DFG) is acknowledged for funding of this study within the framework of the Collaborative Research Center (CRC) 814 “Additive Manufacturing”—Project-ID 61375930—subproject A2 and Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg within the funding programme “Open Access Publication Funding”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Karl Mandel for his support and discussion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lin, X.-M.; Samia, A.C.S. Synthesis, assembly and physical properties of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 305, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Huang, J.; Dufresne, A. Preparation, properties and applications of polysaccharide nanocrystals in advanced functional nanomaterials: A review. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3274–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorodov, V.V.; Kostrov, S.A.; Kamyshinskii, R.A.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Muzafarov, A.M. Modification of carbonyl iron particles by carboxyl-containing polydimethylsiloxanes. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2018, 67, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Jia, W.; Zheng, W.; Liu, H.; Jiang, D.; Li, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J. Hierarchically magnetic Ni–Al binary layered double hydroxides: Towards tunable dual electro/magneto-stimuli performances. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 58, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.A.; Hauser, J.L.; Allen, A.C.; Lindquist, K.P.; Ramirez, A.P.; Oliver, S.; Zhang, J.Z. Fe3O4@ SiO2 nanoparticles functionalized with gold and poly (vinylpyrrolidone) for bio-separation and sensing applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arief, I.; Mukhopadhyay, P.K. Yielding behavior and temperature-induced on-field oscillatory rheological studies in a novel MR suspension containing polymer-capped Fe3Ni alloy microspheres. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 429, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Kocaefe, D.; Chen, C.; Kocaefe, Y. Review of research on template methods in preparation of nanomaterials. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Kostopoulou, A.; LaGrow, A.P. Magnetic nanoparticle composites: Synergistic effects and applications. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.V.; Stepanov, G.V.; Shamonin, M.; Monkman, G.J.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Hysteresis of the viscoelastic properties and the normal force in magnetically and mechanically soft magnetoactive elastomers: Effects of filler composition, strain amplitude and magnetic field. Polymer 2015, 76, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Lee, J.S.H.; Zhang, M. Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1252–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Široký, K.; Jirešová, J.; Hudec, L. Iron oxide thin film gas sensor. Thin Solid Film. 1994, 245, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, K.; Annapoorni, S.; Sarkar, A.K.; Tandon, R.P. Gas and humidity sensors based on iron oxide–polypyrrole nanocomposites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 81, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Solanki, P.R.; Ansari, A.A.; Sumana, G.; Ahmad, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Iron oxide-chitosan nanobiocomposite for urea sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 138, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müssig, S.; Reichstein, J.; Prieschl, J.; Wintzheimer, S.; Mandel, K. A Single Magnetic Particle with Nearly Unlimited Encoding Options. Small 2021, 17, 2101588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müssig, S.; Fidler, F.; Haddad, D.; Hiller, K.-H.; Wintzheimer, S.; Mandel, K. Supraparticles with a Magnetic Fingerprint Readable by Magnetic Particle Spectroscopy: An Alternative beyond Optical Tracers. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Kawaguchi, H. Impact of initiators in preparing magnetic polymer particles by miniemulsion polymerization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 56, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natour, S.; Levi-Zada, A.; Abu-Reziq, R. Magnetic polyurea nano-capsules synthesized via interfacial polymerization in inverse nano-emulsion. Molecules 2019, 24, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ramos, J.; Forcada, J. Self-stabilized magnetic polymeric composite nanoparticles by emulsifier-free miniemulsion polymerization. Langmuir 2007, 23, 12893–12900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Qu, R.; Forcada, J. Preparation of magnetic polymeric composite nanoparticles by seeded emulsion polymerization. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 770–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, A.; Kamura, H.; Higashitani, K. Development and application of thermo-sensitive magnetic immunomicrospheres for antibody purification. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1994, 41, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothberg, H.S.; Pietsch-Braune, S.; Spahr, L.; Kanina, Y.; Heinrich, S. Production of magnetite-polyvinyl butyral composites using a Nano Spray Dryer. Powder Technol. 2021, 394, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupfeld, T.; Salamon, S.; Landers, J.; Sommereyns, A.; Doñate-Buendía, C.; Schmidt, J.; Wende, H.; Schmidt, M.; Barcikowski, S.; Gökce, B. 3D printing of magnetic parts by laser powder bed fusion of iron oxide nanoparticle functionalized polyamide powders. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 12204–12217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Choi, K.; Nam, J.-D.; Choi, H.J. Magnetic polymer composite particles: Design and magnetorheology. Polymers 2021, 13, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yi, C.; Liu, C.; Hu, X.; Chuang, S.; Gong, X. Effects of magnetic nanoparticles and external magnetostatic field on the bulk heterojunction polymer solar cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Han, S.; Kim, H.; Sohn, E.-H.; Choi, H.J.; Seo, Y. Suspensions of hollow polydivinylbenzene nanoparticles decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles as magnetorheological fluids for microfluidics applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 6939–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.Z.; Choi, H.J. Synthesis of smart poly (diphenylamine)/magnetic particle composites and their electric/magnetic stimuli-response. Macromol. Res. 2018, 26, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lu, Q.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, H.J. Polymer-magnetic composite particles of Fe3O4/poly (o-anisidine) and their suspension characteristics under applied magnetic fields. Polymers 2019, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.W.; Bae, D.H.; Kwon, S.H.; Choi, H.J. Magnetite embedded mini-emulsion polymerized polystyrene particles and their magnetorheology. Macromol. Res. 2018, 26, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.S.; Piao, S.H.; Han, W.J.; Choi, H.J. Core/shell polystyrene/magnetite hybrid nanoparticles fabricated by pickering emulsion polymerization and their magnetorheological response. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2018, 219, 1700408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.Y.; Kim, M.W.; Bae, D.H.; Dong, Y.Z.; Piao, S.H.; Choi, H.J. Fe3O4 nanoparticle-embedded polystyrene composite particles fabricated via a Shirasu porous glass membrane technique and their magnetorheology. Polymer 2017, 125, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.H.; Sim, B.; Choi, H.J. Magnetorheological characteristics of nano-sized iron oxide coated polyaniline composites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Watson, B.W.; Qin, Y. Hybrid conjugated polymer/magnetic nanoparticle composite nanofibers through cooperative non-covalent interactions. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 2462–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichstein, J.; Müssig, S.; Bauer, H.; Wintzheimer, S.; Mandel, K. Recording Temperature with Magnetic Supraparticles. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2202683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audonnet, V.; Malaquin, L.; Viovy, J.-L. Polymeric coatings on micro-and nanometric particles for bioapplications. Bioanal. Rev. 2011, 3, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, A.J.; Yang, V.C.; David, A.E. Cancer theranostics: The rise of targeted magnetic nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijs, M.A.M.; Lacharme, F.; Lehmann, U. Microfluidic applications of magnetic particles for biological analysis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1518–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Misra, R.; Sahoo, S.K. Nanoparticles: A boon to drug delivery, therapeutics, diagnostics and imaging. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Sharma, A.; Chen, C.J. State of art on bioimaging by nanoparticles in hyperthermia and thermometry: Visualization of tissue protein targeting. Open Nanomed. J. 2011, 3, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubayev, V.I.; Pisanic II, T.R.; Jin, S. Magnetic nanoparticles for theragnostics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrlik, M.; Sedlacik, M.; Pavlinek, V.; Bazant, P.; Saha, P.; Peer, P.; Filip, P. Synthesis and magnetorheological characteristics of ribbon-like, polypyrrole-coated carbonyl iron suspensions under oscillatory shear. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 2977–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrlik, M.; Pavlinek, V. Magnetorheological suspensions based on modified carbonyl iron particles with an extremely thin poly (n-butyl acrylate) layer and their enhanced stability properties. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 85011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvek, M.; Mrlík, M.; Mosnáček, J.; Babayan, V.; Kuceková, Z.; Humpolíček, P.; Pavlínek, V. The chemical stability and cytotoxicity of carbonyl iron particles grafted with poly (glycidyl methacrylate) and the magnetorheological activity of their suspensions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 72816–72824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrlík, M.; Ilčíková, M.; Pavlínek, V.; Mosnáček, J.; Peer, P.; Filip, P. Improved thermooxidation and sedimentation stability of covalently-coated carbonyl iron particles with cholesteryl groups and their influence on magnetorheology. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 396, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.H.; Kwon, S.H.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, N.H.; You, C.Y. Polyindole-Coated Soft-Magnetic Particles and their Viscoelastic Behaviors under Applied Magnetic Field. J. Magn. 2019, 24, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, H.J. Synthesis of core-shell formed carbonyl iron/polydiphenylamine particles and their rheological response under applied magnetic fields. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, T.H.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, N.-H.; Park, K.; You, C.-Y. Effects of surface treatment on magnetic carbonyl iron/polyaniline microspheres and their magnetorheological study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 531, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Ahn, W.J.; Choi, H.J.; Seo, Y. Fabrication and magnetic stimuli-response of polydopamine-coated core–shell structured carbonyl iron microspheres. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2016, 294, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.S.; Lim, S.T.; Jang, I.B.; Choi, H.J.; Jhon, M.S. Encapsulation of spherical iron-particle with PMMA and its magnetorheological particles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2004, 40, 3036–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.Y.; Piao, S.H.; Choi, H.J. Pickering emulsion polymerized magnetite-poly (methyl methacrylate) composite particles and their magnetorheology. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.N.; Dong, Y.Z.; Choi, H.J. Pickering emulsion polymerized polyaniline/zinc-ferrite composite particles and their dual electrorheological and magnetorheological responses. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 7675–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, J.; Bettge, M.; Haik, Y.; Chen, C.J. Synthesis and characterization of polymer encapsulated Cu–Ni magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korth, B.D.; Keng, P.; Shim, I.; Bowles, S.E.; Tang, C.; Kowalewski, T.; Nebesny, K.W.; Pyun, J. Polymer-coated ferromagnetic colloids from well-defined macromolecular surfactants and assembly into nanoparticle chains. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6562–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Sliva, A.; Banerjee, A.; Dave, R.N.; Pfeffer, R. Dry particle coating for improving the flowability of cohesive powders. Powder Technol. 2005, 158, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümel, C.; Sachs, M.; Laumer, T.; Winzer, B.; Schmidt, J.; Schmidt, M.; Peukert, W.; Wirth, K.-E. Increasing flowability and bulk density of PE-HD powders by a dry particle coating process and impact on LBM processes. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2015, 21, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Dave, R.N.; Pfeffer, R. Fluidization of coated group C powders. AIChE J. 2008, 54, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejat, L.A.; Johnson, J.E.; Jones, R.O.; Livengood, B.P.; Srinivasan, K.R.; Strain, D.J.V. Toner Formulations with Tribocharge Control and Stability. U.S. Patent 20100040969A1, 18 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Düsenberg, B.; Kopp, S.-P.; Tischer, F.; Schrüfer, S.; Roth, S.; Schmidt, J.; Schmidt, M.; Schubert, D.W.; Peukert, W.; Bück, A. Enhancing Photoelectric Powder Deposition of Polymers by Charge Control Substances. Polymers 2022, 14, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujumdar, A.; Wei, D.; Dave, R.N.; Pfeffer, R.; Wu, C.-Y. Improvement of humidity resistance of magnesium powder using dry particle coating. Powder Technol. 2004, 140, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockholt, H.; Haselrieder, W.; Kwade, A. Intensive powder mixing for dry dispersing of carbon black and its relevance for lithium-ion battery cathodes. Powder Technol. 2016, 297, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düsenberg, B.; Tischer, F.; Valayne, E.; Schmidt, J.; Peukert, W.; Bück, A. Temperature influence on the triboelectric powder charging during dry coating of polypropylene with nanosilica particles. Powder Technol. 2022, 399, 117224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümel, C. Charakterisierung der Trockenen Beschichtung zur Herstellung von Maßgeschneiderten Kompositpartikeln; Verlag Dr. Hut: München, Germany, 2015; ISBN 3843921202. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, M.; Alguacil, F.J. Dry mixing and coating of powders. Rev. de Metal. 1999, 35, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Satoh, M.; Miyanami, K. Powder coating in a rotary mixer with rocking motion. Powder Technol. 1988, 56, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Satoh, M.; Miyanami, K. The effect of random positioning on the packing of particles adhering to the surface of a central particle. Powder Technol. 1990, 62, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimanke, G. In situ XRD study of the phase transition of nanocrystalline maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) to hematite (α-Fe2O3). Solid State Ion. 2000, 136-137, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemine, O.M. Microstructural characterisation of nanoparticles using, XRD line profiles analysis, FE-SEM and FT-IR. Superlattices Microstruct. 2009, 45, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuzio, F.; Sala, A.; Schmidt, T.; Menzel, D.; Freund, H.-J. Interconversion of α-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 thin films: Mechanisms, morphology, and evidence for unexpected substrate participation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 29068–29076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.N.; Ledbetter, H.D. DTA study of heterogeneous nucleation of crystallization in polypropylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1965, 9, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillon, B.; Thierry, A.; Lotz, B.; Wittmann, J.C. Efficiency scale for polymer nucleating agents. J. Therm. Anal. 1994, 42, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, J.I.; de Saja, J.A.; Martinez, A.B. Crystallization behavior of polypropylene filled with surface-modified talc. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 61, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
