Adhesion Improvement of Solvent-Free Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives by Semi-IPN Using Polyurethanes and Acrylic Polymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
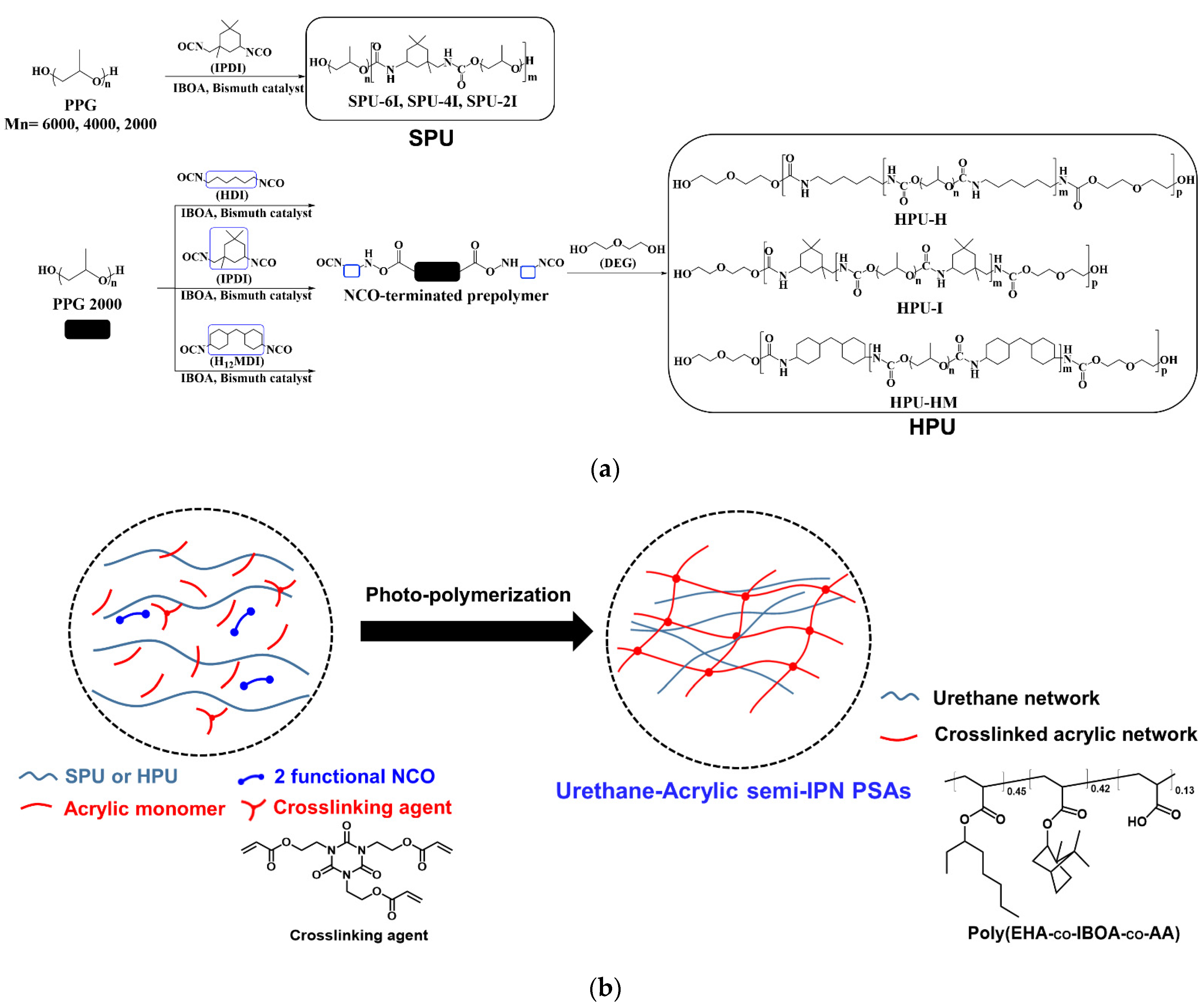
2.2. Structure of Polyurethane and Acrylic Polymers
2.3. Synthesis of SPUs
2.4. Synthesis of HPUs
2.5. Fabrication of Urethane-Acrylate Semi-IPN PSAs
2.6. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SPU and HPU Syntheses
3.2. SPU-Based Urethane-Acrylic Semi-IPN PSA
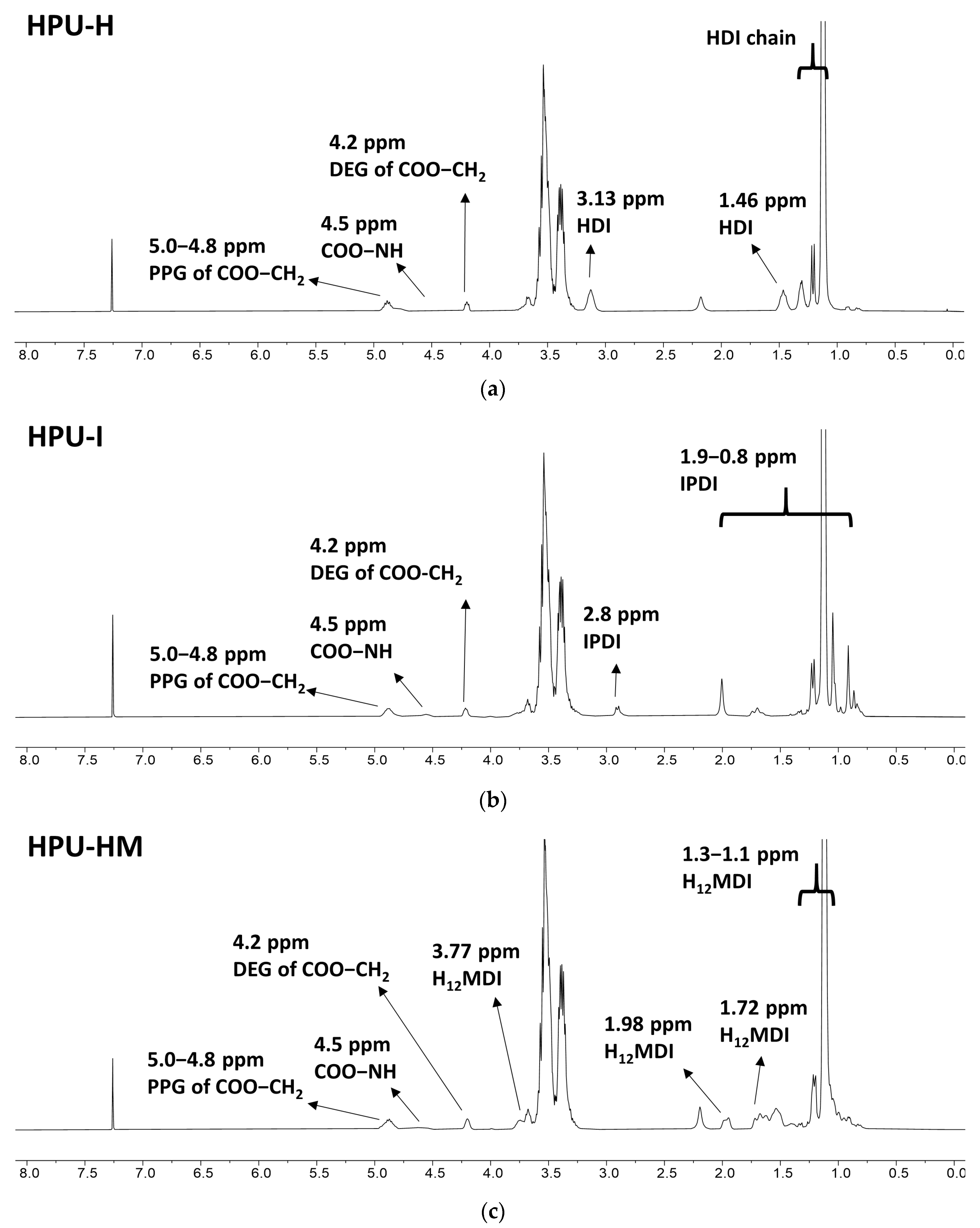
3.2.1. 1H-NMR Analysis
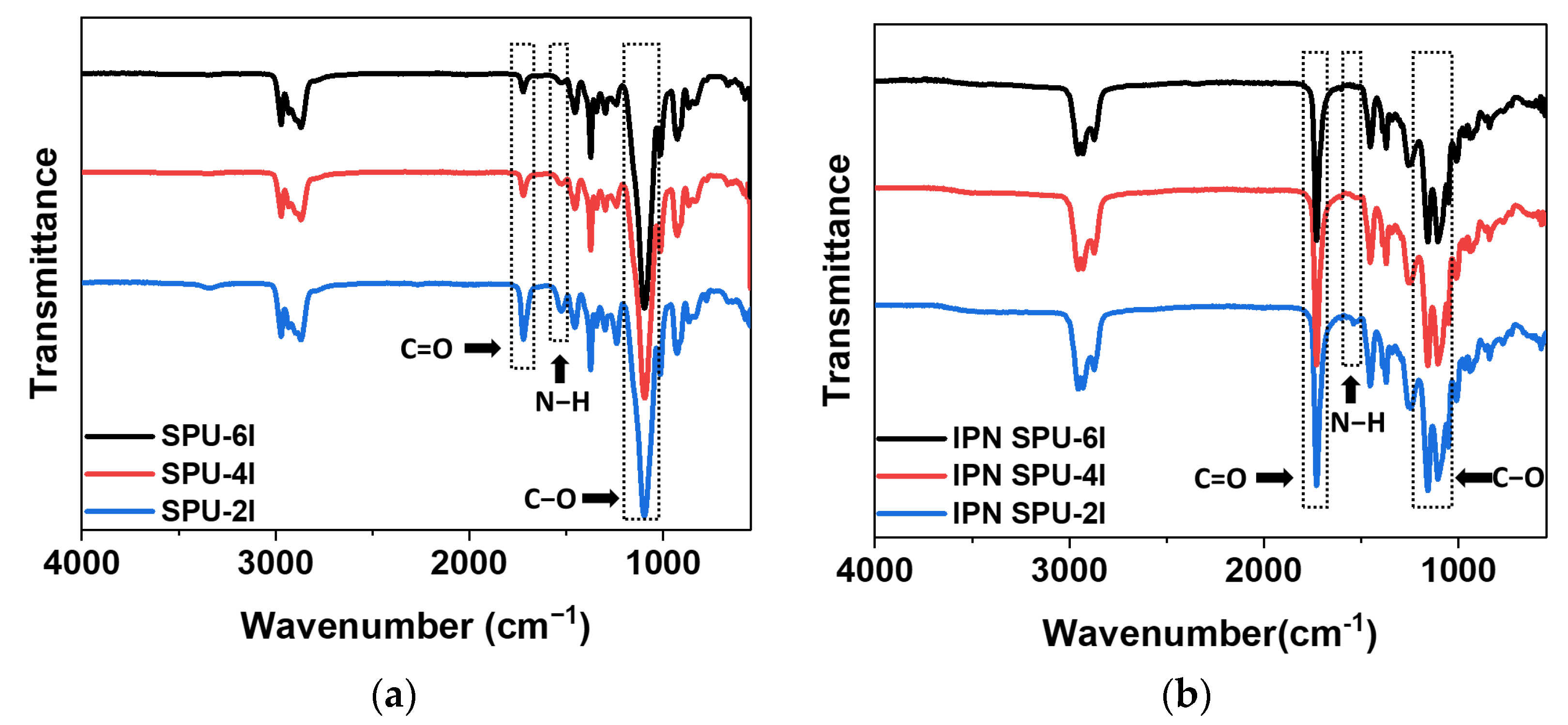
3.2.2. FT-IR Analysis
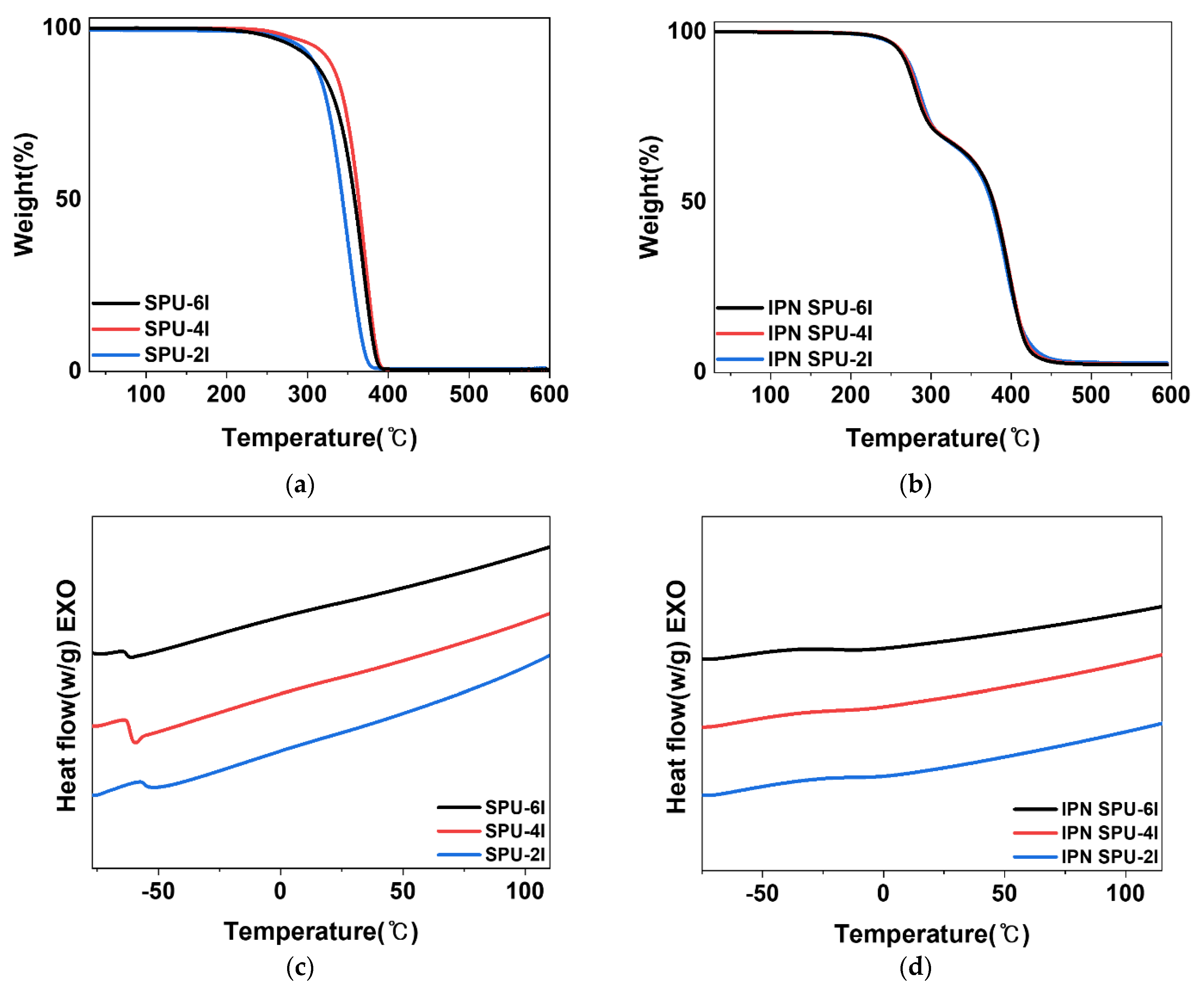
3.2.3. Thermal Analysis
3.2.4. Adhesive Properties of SPU-Based Semi-IPN PSAs
3.3. HPU-Based Urethane-Acrylic Semi-IPN PSA
3.3.1. 1H-NMR Analysis
3.3.2. FT-IR Analysis
3.3.3. Thermal Analysis
3.3.4. Adhesive Properties of HPU-Based Semi-IPN PSAs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehravar, E.; Gross, M.A.; Agirre, A.; Reck, B.; Leiza, J.R.; Asua, J.M. Importance of film morphology on the performance of thermo-responsive waterborne pressure sensitive adhesives. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 98, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapari, S.; Mestry, S.; Mhaske, S.T. Developments in pressure-sensitive adhesives: A review. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 4075–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.S.; Lee, S.-M.; Jung, S.-H.; Lee, W.-K. Study on Crosslinking Properties of Acrylic Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives. J. Adhes. Interface 2013, 14, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chang, E.P. Viscoelastic Properties of Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives. J. Adhes. 1997, 60, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.H.; Won, J.C.; Lim, W.B.; Kim, B.J.; Lee, J.H.; Min, J.G.; Seo, M.J.; Mo, Y.H.; Huh, P.H. Tacky-Free Polyurethanes Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives by Molecular-Weight and HDI Trimer Design. Materials 2021, 14, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, R.; Lee, S.H.; Park, W.H. Mechanical Properties of Acrylic Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives Containing Functional Monomers. Text. Sci. Eng. 2016, 53, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-J.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-E.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, S.D. Viscoelastic properties and peel strength of water-borne acrylic PSAs for labels. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2007, 21, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Jeong, K.; Kwak, M.J.; Choi, S.Q.; Im, S.G. Solvent-Free Deposition of Ultrathin Copolymer Films with Tunable Viscoelasticity for Application to Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 32668–32677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, J.-H.; Kwon, Y.; Roldao, J.C.; Yu, Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Gierschner, J.; Lee, W.; Kwon, M.S. Synthesis of solvent-free acrylic pressure-sensitive adhesivesviavisible-light-driven photocatalytic radical polymerization without additives. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 8289–8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuensanta, M.; Vallino-Moyano, M.A.; Martin-Martinez, J.M. Balanced Viscoelastic Properties of Pressure Sensitive Adhesives Made with Thermoplastic Polyurethanes Blends. Polymers 2019, 11, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Poh, B.T. Natural Rubber-Based Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Weisbrodt, M.; Schmidt, B.; Gziut, K. Influence of Acrylic Acid on Kinetics of UV-Induced Cotelomerization Process and Properties of Obtained Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives. Materials 2020, 13, 5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, K.-Y.; Lim, D.-H.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, H.-J.; Jeong, H.-M.; Takemura, A. Adhesion Performance and Surface Characteristics of Low Surface Energy PSAs Fluorinated by UV Polymerization. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2013, 53, 1968–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-W.; Seo, H.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Shin, S. Adhesion improvement of the acrylic pressure-sensitive adhesive to low-surface-energy substrates using silicone urethane dimethacrylates. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 137, 109949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, O. Das Di-Isocyanat-Polyadditionsverfahren (Polyurethane). Angew. Chem. 1947, 59, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Nakano, S.; Ito, K.; Imamura, K.; Fujii, S.; Sasaki, M.; Urahama, Y. Adhesion properties of polyurethane pressure-sensitive adhesive. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, N.; Zia, K.M.; Saeed, M.; Mansha, A.; Khan, W.G. Morphological studies of polyurethane based pressure sensitive adhesives by tapping mode atomic force microscopy. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuensanta, M.; Martin-Martínez, J.M. Thermoplastic polyurethane pressure sensitive adhesives made with mixtures of polypropylene glycols of different molecular weights. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2019, 88, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuensanta, M.; Martín-Martínez, J.M. Influence of the hard segments content on the structure, viscoelastic and adhesion properties of thermoplastic polyurethane pressure sensitive adhesives. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 2652–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuensanta, M.; Martín-Martínez, J.M. Thermoplastic polyurethane coatings made with mixtures of polyethers of different molecular weights with pressure sensitive adhesion property. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 118, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuensanta, M.; Martín-Martínez, J.M. Viscoelastic and Adhesion Properties of New Poly(Ether-Urethane) Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives. Front. Mech. Eng. 2020, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athawale, V.D.; Kolekar, S.L.; Raut, S.S. Recent Developments in Polyurethanes and Poly(acrylates) Interpenetrating Polymer Networks. J. Macromol. Sci. Polym. Rev. 2003, 43, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaisankar, S.N.; Lakshminarayana, Y.; Radhakrishnan, G. Polyurethane-Poly(Ethyl Hexyl Acrylate-Co-Methyl Methacrylate) Interpenetrating Polymer Networks. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2005, 44, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, D.L.; Sivasankar, B. Synthesis and characterization of semi-interpenetrating polymer networks using biocompatible polyurethane and acrylamide monomer. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenoozi, S.; Mohamad Sadeghi, G.M.; Rafiee, M. Synthesis and characterization of biocompatible semi-interpenetrating polymer networks based on polyurethane and cross-linked poly (acrylic acid). Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 140, 109974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, N.; Broughton, R.M.; Auad, M.L. Graft Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network Phase Change Materials for Thermal Energy Storage. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Zhao, T.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Tang, E.; Xu, X. IPN structured UV-induced peelable adhesive tape prepared by isocyanate terminated urethane oligomer crosslinked acrylic copolymer and photo-crosslinkable trifunctional acrylic monomer. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 137, 105281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, G.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, H.-J. Behavior and Adhesion Performance of Acrylic PSAs using Semi-IPN Structure and UV/UV Stepwise Curing. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 89, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.-S.; Lee, S.-W.; Park, J.-W.; Park, C.-H.; Kim, H.J. Kinetic and characterization of UV-curable silicone urethane methacrylate in semi-IPN-structured acrylic PSAs. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güney, A.; Gardiner, C.; McCormack, A.; Malda, J.; Grijpma, D.W. Thermoplastic PCL-b-PEG-b-PCL and HDI Polyurethanes for Extrusion-Based 3D-Printing of Tough Hydrogels. Bioengineering 2018, 5, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, A.; Chattopadhyay, D.K.; Jagadeesh, B.; Raju, K.V.S.N. Structural investigations of polypropylene glycol (PPG) and isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI)-based polyurethane prepolymer by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 1196–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Cheon, J.; Chun, J.; Mok, D.; Lee, H. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyurethane Elastomer. J. Adhes. Interface 2009, 10, 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- Trovati, G.; Sanches, E.A.; Neto, S.C.; Mascarenhas, Y.P.; Chierice, G.O. Characterization of polyurethane resins by FTIR, TGA, and XRD. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naheed, S.; Zuber, M.; Salman, M.; Rasool, N.; Siddique, Z.; Shaik, M.R.; Sharaf, M.A.F.; Abdelgawad, A.; Sekou, D.; Awwad, E.M. Impact of Macrodiols on the Morphological Behavior of H12MDI/HDO-Based Polyurethane Elastomer. Polymers 2021, 13, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, M.M.; Lee, K.H.; Skrovanek, D.J.; Painter, P.C. Hydrogen Bonding in Polymers. 4. Infrared Temperature Studies of a Simple Polyurethane. Macromoleules 1986, 19, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, M.M.; Skrovanek, D.J.; Hu, J.; Painter, P.C. Hydrogen Bonding in Polymer Blends. 1. FTIR Studies of Urethane-Ether Blends. Macromoleules 1988, 21, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y. Robust Stretchable Thermoplastic Polyurethanes with Long Soft Segments and Steric Semisymmetric Hard Segments. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 4483–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Du, X.; Cheng, X.; Wang, H.; Du, Z. Room-temperature self-healable and stretchable waterborne polyurethane film fabricated via multiple hydrogen bonds. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 151, 106081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, E.; Yurtsever, M. The role of diisocyanate and soft segment on the intersegmental interactions in urethane and urea based segmented copolymers: A DFT study. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2014, 1035, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisacariu, C. Polyurethane Elastomers, 1st ed.; Springer: Vienna, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xie, D.; Zhang, X. The structure, microphase-separated morphology, and property of polyurethanes and polyureas. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 7339–7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eceiza, A.; Martin, M.D.; de la Caba, K.; Kortaberria, G.; Gabilondo, N.; Corcuera, M.A.; Mondragon, I. Thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers based on polycarbonate diols with different soft segment molecular weight and chemical structure: Mechanical and thermal properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Pang, Y.; Liang, X. Mechanism of Adhesion of Polyurethane/ Polymethacrylate Simultaneous Interpenetrating Networks Adhesives to Polymer Substrates. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 1994, 32, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Kalita, H.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Degradation Study of Biobased Polyester–Polyurethane and its Nanocomposite Under Natural Soil Burial, UV Radiation and Hydrolytic-Salt Water Circumstances. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1528–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Gao, H.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.L.; Yang, Y.W.; Wu, G.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Ma, J. Temperature- and pH-responsive nanoparticles of biocompatible polyurethanes for doxorubicin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Król, P.; Uram, Ł.; Król, B.; Pielichowska, K.; Walczak, M. Study of chemical, physico-mechanical and biological properties of 4,4′-methylenebis(cyclohexyl isocyanate)-based polyurethane films. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 93, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Urethane Prepolymer | Polyol | Diisocyanate | Molar Ratio (PPG/Diisocyanate/DEG) | Mw (g/mol) | PDI | OHV (KOH mg/g) | Hard Segment Content (HS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPU-6I | PPG 6000 | IPDI | 1.30:1:0 | 46,100 | 1.73 | 2.20 | 2.9% |
| SPU-4I | PPG 4000 | 1.10:1:0 | 49,400 | 1.89 | 1.73 | 5.1% | |
| SPU-2I | PPG 2000 | 1.02:1:0 | 46,100 | 1.95 | 1.55 | 11.0% | |
| HPU-H | PPG 2000 | HDI | 0.71:1:0.3 | 137,000 | 1.71 | 0.73 | 12.4% |
| HPU-I | IPDI | 0.71:1:0.3 | 105,000 | 1.93 | 1.43 | 15.2% | |
| HPU-HM | H12MDI | 0.71:1:0.3 | 111,000 | 1.86 | 1.15 | 17.2% |
| Sample | N-H Peak Area | Relative Absorbance of C=O Groups in Polyurethane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free C=O (AF, 1720 cm−1) | Disordered H-Bond C=O (AD, 1700 cm−1) | Ordered H-Bond C=O (AO, 1685 cm−1) | ||
| SPU-6I | 119.5 | 67.6% | 32.4% | - |
| SPU-4I | 151.6 | 64.6% | 35.4% | - |
| SPU-2I | 347.5 | 56.0% | 32.0% | 12.0% |
| TH (°C) | TS (°C) | Tg (°C) | TU (°C) | TA (°C) | Urethane (%) | Acrylate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPU-6I | - | 369.6 | −61.7 | - | - | - | - |
| SPU-4I | - | 371 | −61.5 | - | - | - | - |
| SPU-2I | - | 349 | −58.4 | - | - | - | - |
| IPN SPU-6I | - | - | −19.7 | 279.9 | 397.8 | 32.1 | 64.9 |
| IPN SPU-4I | - | - | −17.5 | 282.4 | 397.7 | 32.6 | 64.1 |
| IPN SPU-2I | - | - | −12 | 285.8 | 394.3 | 32.1 | 64.4 |
| Sample | Ball Tack | Peel Strength (g/inch) | Holding Time (25 °C × 1 kg × 1 h) | Holding Time (120 °C × 1 kg × 1 h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPN SPU-6I | #4 | 2190 | Non-creep | 6 min |
| IPN SPU-4I | #4 | 2070 | Non-creep | 8 min |
| IPN SPU-2I | #4 | 2120 | Non-creep | 8 min |
| Sample | N-H Peak Area | Relative Absorbance of C=O Groups in Polyurethane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free C=O (AF, 1720 cm−1) | Disordered H-Bond C=O (AD, 1700 cm−1) | Ordered H-Bond C=O (AO, 1685 cm−1) | ||
| HPU-H | 426.6 | 63.0% | 20.7% | 16.3% |
| HPU-I | 443.5 | 71.1% | 21.9% | 8.0% |
| HPU-HM | 486.3 | 64.1% | 21.4% | 14.5% |
| Sample | TH (°C) | TS (°C) | Tg (°C) | TU (°C) | TA (°C) | Urethane (%) | Acrylate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPU-H | 281.6 | 368.0 | −55.8 | - | - | - | - |
| HPU-I | 286.0 | 369.0 | −52.7 | - | - | - | - |
| HPU-HM | 283.0 | 385.0 | −50.3 | - | - | - | - |
| IPN HPU-H | - | - | −16.0 | 290.1 | 393.9 | 33.1 | 62.7 |
| IPN HPU-I | - | - | −7.8 | 286.5 | 392.5 | 32.0 | 61.0 |
| IPN HPU-HM | - | - | −5.0 | 286.0 | 393.9 | 32.6 | 64.0 |
| Sample | Ball Tack | Peel Strength (g/inch) | Holding Time (25 °C × 1 kg × 1 h) | Holding Time (120 °C × 1 kg × 1 h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPN HPU-H | #4 | 2030 | Non-creep | 51 min |
| IPN HPU-I | #4 | 1990 | Non-creep | 11 min |
| IPN HPU-HM | #4 | 1750 | Non-creep | Non-creep |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, K.H.; Lee, D.Y.; Yoon, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Han, M.S.; Jeon, S.; Kim, Y.; Lim, Y.K.; Hwang, D.-H.; Jung, S.-H.; et al. Adhesion Improvement of Solvent-Free Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives by Semi-IPN Using Polyurethanes and Acrylic Polymers. Polymers 2022, 14, 3963. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193963
Park KH, Lee DY, Yoon SH, Kim SH, Han MS, Jeon S, Kim Y, Lim YK, Hwang D-H, Jung S-H, et al. Adhesion Improvement of Solvent-Free Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives by Semi-IPN Using Polyurethanes and Acrylic Polymers. Polymers. 2022; 14(19):3963. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193963
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Kwang Hun, Dong Yeob Lee, Sung Ha Yoon, Seong Hun Kim, Min Su Han, Seungju Jeon, Yejin Kim, Yong Kwan Lim, Do-Hoon Hwang, Seo-Hyun Jung, and et al. 2022. "Adhesion Improvement of Solvent-Free Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives by Semi-IPN Using Polyurethanes and Acrylic Polymers" Polymers 14, no. 19: 3963. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193963
APA StylePark, K. H., Lee, D. Y., Yoon, S. H., Kim, S. H., Han, M. S., Jeon, S., Kim, Y., Lim, Y. K., Hwang, D.-H., Jung, S.-H., & Lim, B. (2022). Adhesion Improvement of Solvent-Free Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives by Semi-IPN Using Polyurethanes and Acrylic Polymers. Polymers, 14(19), 3963. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193963








