Properties of Fiber-Reinforced One-Part Geopolymers: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Two-Part Geopolymer (TPG) and One-Part Geopolymer (OPG)
3. Properties of Different Fibers
4. Properties of FOPGs
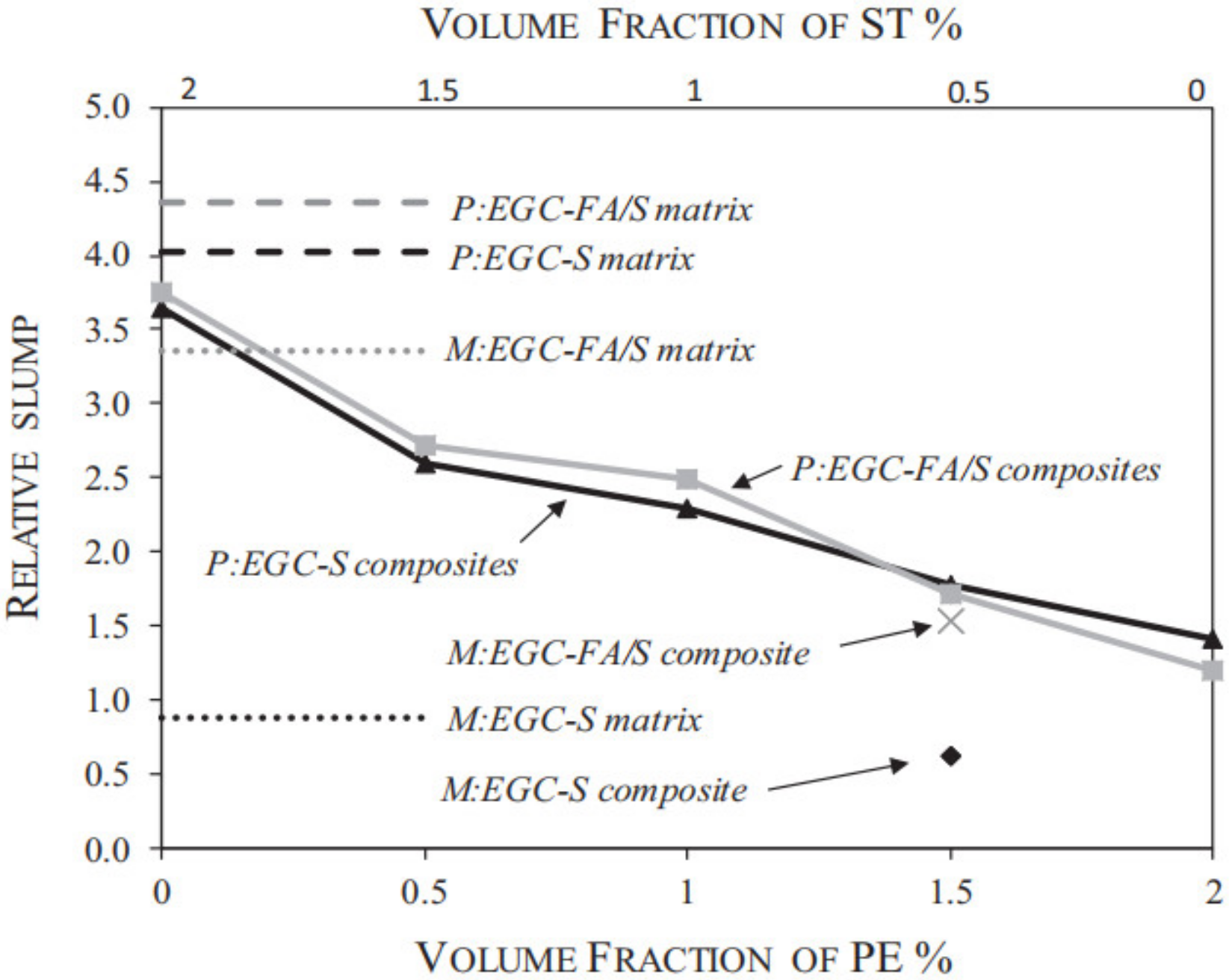
4.1. Workability of FOPGs
4.2. Mechanical Properties of FOPGs
4.2.1. Compressive Properties of FOPGs
4.2.2. Flexural Strength of FOPGs
4.2.3. Adhesion Mechanism between Fibers and Geopolymer Matrix
4.3. Durability of FOPGs
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers: Inorganic polymeric new materials. J. Therm. Anal. 1991, 37, 1633–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacobello, F.; Ielo, I.; Belhamdi, H.; Plutino, M.R. Geopolymers and Functionalization Strategies for the Development of Sustainable Materials in Construction Industry and Cultural Heritage Applications: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Jia, Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Cementitious Composites. Minerals 2022, 12, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeni, O.; Mahamat, A.A.; Bih, N.L.; Stanislas, T.T.; Isah, I.; Savastano Junior, H.; Boakye, E.; Onwualu, A.P. Effect of Coir Fiber Reinforcement on Properties of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Composite. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, I.; Luhar, S. A Comprehensive Review on Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Ma, C.; Long, G.; Xie, Y. A novel non-Portland cementitious material: Mechanical properties, durability and characterization. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; He, F.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Krivenko, V.; Palomo, A. Classification and Characteristics of Alkali-Activated Cements. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 1, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Mourak, A.; Hajjaji, M.; Alagui, A. Cured alkali-activated heated clay-cellulose composites: Microstructure, effect of glass addition and performances. Boletín Soc. Española Cerámica Vidr. 2021, 20, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Fang, C.; Jiao, Y.; Kang, D.; Yan, C.; Zhang, J. Hydration Mechanisms of Alkali-Activated Cementitious Materials with Ternary Solid Waste Composition. Materials 2022, 15, 3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, V.; Prasad, B. Strength development and flexural behavior of reinforced concrete beam using one-part alkali-activated binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 281, 122619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, F.U.A.; Patel, A. Flexural Behavior of Hybrid PVA Fiber and AR-Glass Textile Reinforced Geopolymer Composites. Fibers 2018, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lv, C. Properties of 3D-Printed Polymer Fiber-Reinforced Mortars: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Lee, B.; Ranade, R.; Li, V.C.; Lee, Y. Ultra-high-ductile behavior of a polyethylene fber-reinforced alkali-activated slagbased composite. Cement. Concr. Compos. 2016, 70, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas, F.; Amat, T.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Vázquez, T. Mechanical and durable behaviour of alkaline cement mortars reinforced with polypropylene fbres. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lv, C. Research Progress on Durability of Cellulose Fiber-Reinforced Cement-Based Composites. Int. J. Polymer Sci. 2021, 2021, 1014531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Chen, B.; Haque, M.; Oderji, S. Multiproperty characterization of cleaner and energy-efficient vegetal concrete based on one-part geopolymer binder. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaplana, J.L.; Baeza, F.J.; Galao, O.; Alcocel, E.G.; Zornoza, E.; Garcés, P. Mechanical properties of alkali activated blast furnace slag pastes reinforced with carbon fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 116, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S. Anisotropic Heat Transfer in Plane of Carbon Fabrics Reinforced Geopolymer Composite. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopika, M.; Ganesan, N.; Indira, P.V.; Sathish Kumar, V.; Murali, G.; Vatin, N.I. Influence of Steel Fibers on the Interfacial Shear Strength of Ternary Blend Geopolymer Concrete Composite. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomayri, T.; Raza, A.; Shaikh, F. Effect of nano SiO2 on mechanical properties of micro-steel fibers reinforced geopolymer composites. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 33444–33453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łach, M.; Kluska, B.; Janus, D.; Kabat, D.; Pławecka, K.; Korniejenko, K.; Guigou, M.D.; Choińska, M. Effect of Fiber Reinforcement on the Compression and Flexural Strength of Fiber-Reinforced Geopolymers. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas, F.; Gil-Maroto, A.; Palacios, M.; Amat, T. Alkali-activated slag mortars reiforced with ar glassfbre. Performance and properties. Mater. Constr. 2006, 56, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Liu, Y.; Le, H. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Phosphoric Acid Activated Geopolymer Materials Reinforced with Mullite Fibers. Materials 2022, 15, 4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomayri, T. Performance evaluation of basalt fiber-reinforced geopolymer composites with various contents of nano CaCO3. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 29949–29959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, M.; Ranjith, P.; Hui, D.; Haque, A.; Chen, B. Extensive use of waste glass in one-part alkali-activated materials: Towards sustainable construction practices. Waste Manag. 2021, 130, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, S.; Strecker, K. Kaolin, fly-ash and ceramic waste based alkali-activated materials production by the “one-part” method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesanya, E.; Ohenoja, K.; Maria, A.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. Alternative alkali-activator from steel-making waste for one-part alkali-activated slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 123020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wu, J. Early Strength Development of Soft Clay Stabilized by One-Part Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag and Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 616430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrefaei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; Xu, Q. Effect of superplasticizers on properties of one-part Ca(OH)2/Na2SO4 activated geopolymer pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 241, 117990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.B. Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Binder: A Future Construction Material. Minerals 2018, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, A.; Hot, J.; Habert, G.; Roussela, N.; Lacaillerie, J. Flow properties of mk-based geopolymer pastes: A comparative study with standard portland cement pastes. Soft Matter 2013, 10, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.U.; Mohammed, A.A.; Rafiq, S.; Mohammed, A.S.; Mosavi, A.; Sor, N.H.; Qaidi, S.M.A. Compressive Strength of Sustainable Geopolymer Concrete Composites: A State-of-the-Art Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.S.; Patil, A.A. Properties of Polypropylene Fiber Reinforced Geopolymer Concrete. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2015, 5, 2909–2912. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Jang, J. Environmentally benign production of one-part alkali-activated slag with calcined oyster shell as an activator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobili, A.; Tittarelli, F.; Rahier, H. One-Part Alkali-Activated Pastes and Mortars Prepared with Metakaolin and Biomass Ash. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Cheng, Y. Advances in geopolymer materials: A comprehensive review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2021, 8, 283–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkareem, M.; Havukainen, J.; Nuortila-Jokinen, J.; Horttanainen, M. Environmental and economic perspective of waste-derived activators on alkali-activated mortars. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, B.; Sanjayan, J. Effect of different superplasticizers and activator combinations on workability and strength of fly ash based geopolymer. Mater. Design 2014, 57, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, A.; Sadique, M.; Al-Mufti, R.; Hashim, K. Long-term performance of novel high-calcium one-part alkali-activated cement developed from thermally activated lime kiln dust. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, P.; Sreenivasan, H.; Luukkonen, T.; Kantola, A.M.; Telkki, V.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. High strength one-part alkali-activated slag blends designed by particle packing optimization. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 124004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, P.; Gluth, G.J.G.; Jäger, C.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Kühne, H.-C. Sulfuric acid resistance of one-part alkali-activated mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 109, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, I.K.; Ryou, J.S.; Jakhrani, S.H.; Kim, H.G. Effects of Light-Burnt Dolomite Incorporation on the Setting, Strength, and Drying Shrinkage of One-Part Alkali-Activated Slag Cement. Materials 2019, 12, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, H.; Kang, S.; Zhang, T.; Song, S. Eco-friendly geopolymer prepared from solid wastes: A critical review. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Elchalakani, M.; Karrech, A. Development of high strength one-part geopolymer mortar using sodium metasilicate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 236, 117611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhao, X.; Bu, M.; Niu, D. The microstructure and durability of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete: A review. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 29550–29566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haha, M.B.; Le Saout, G.; Winnerfeld, F. Influence of activator type on hydration kinetics, hydrate assemblage and microstructural development of alkali activated blast-furnace slags. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, F.; Farina, I.; Travaglioni, M.; Salzano, C.; Cioffi, R.; Petrillo, A. Eco-efficient industrial waste recycling for the manufacturing of fibre reinforced innovative geopolymer mortars: Integrated waste management and green product development through LCA. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarian, M.; Tao, Z.; Samali, B.; Adam, G.; Shuaibu, R. Mix composition and characterisation of one-part geopolymers with different activators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oderji, S.; Chen, B.; Ahmad, M.; Shah, S. Fresh and hardened properties of one-part fly ash-based geopolymer binders cured at room temperature: Effect of slag and alkali activators. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.H.; Song, J.K.; Ashour, A.F. Properties of cementless mortars activated by sodium silicate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Chen, L.; Komarneni, S.; Zhou, C.; Tong, D.; Yang, H.; Yu, W.; Wang, H. Fly ash-based geopolymer: Clean production, properties and applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 125, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M. An exploratory study on sodium sulfate activated slag modified with Portland cement. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 4085–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Yu, Q.; Brouwers, H. Reaction kinetics, reaction products and compressive strength of ternary activators activated slag designed by Taguchi method. Mater. Design 2015, 86, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humur, G.; Çevik, A. Mechanical characterization of lightweight engineered geopolymer composites exposed to elevated temperatures. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 13634–13650. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.; Choi, J.; Song, J.; Lee, B. Rheological and mechanical properties of fber-reinforced alkali-activated composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, A.; Borges, P.H.R.; Zanotti, Z.; Farooq, M.; Banthia, N. Flexural behavior of geopolymer composites reinforced with steel and polypropylene macro fibers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 80, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Abdollahnejad, Z.; Yliniemi, J.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. One-part alkali-activated materials: A review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 103, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna, S.; Mohammed, B.; Wahab, M.; Liew, M. Effect of paste aggregate ratio and curing methods on the performance of one-part alkali-activated concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 120024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.; Vilarinho, I.S.; Capela, M.; Caetano, A.; Novais, R.M.; Labrincha, J.A.; Seabra, M.P. Waste-Based One-Part Alkali Activated Materials. Materials 2021, 14, 2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Provis, J.; Van Deventer, S. Thermal activation of Albite for the synthesis of one-part mix geopolymers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Wang, S.; Quan, X.; Liu, Y. Behavior of polyvinyl alcohol fiber reinforced geopolymer composites under the coupled attack of sulfate and freeze-thaw in a marine environment. Ocean Eng. 2021, 238, 109734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lv, C. Durability of Cellulosic-Fiber-Reinforced Geopolymers: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merta, I.; Poletanovic, B.; Dragas, J.; Carevic, V.; Ignjatovic, I.; Komljenovic, M. The Influence of Accelerated Carbonation on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Hemp-Fibre-Reinforced Alkali-Activated Fly Ash and Fly Ash/Slag Mortars. Polymers 2022, 14, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahnejad, Z.; Mastali, M.; Falah, M.; Mohammad Shaad, K.; Luukkonen, T.; Illikainen, M. Durability of the Reinforced On-Part Alkali-Activated Slag Mortars with Diferent Fibers. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2021, 12, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahnejad, Z.; Mastali, M.; Woof, B.; Illikainen, M. High strength fiber reinforced one-part alkali activated slag/fly ash binders with ceramic aggregates: Microscopic analysis, mechanical properties, drying shrinkage, and freeze-thaw resistance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 241, 118129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Chen, B.; Oderji, S.; Haque, M.; Ahmad, M. Comparative study on the effect of fiber type and content on the performance of one-part alkali-activated mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 243, 118221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, B.; Sanjayan, J.; Qiu, J.; Yang, E.-H. High ductile behavior of a polyethylene fiber-reinforced one-part geopolymer composite: A micromechanics-based investigation. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2017, 17, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrefaei, Y.; Dai, J. Deflection hardening behavior and elastic modulus of one-part hybrid fiber-reinforced geopolymer composites. J. Asian Concr. Fed. 2019, 5, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrfaei, Y.; Dai, J. Tensile behavior and microstructure of hybrid fiber ambient cured one-part engineered geopolymer composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 184, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Flexural Strength and Flexural Toughness of Fiber/Hybrid Fibers and Slag-geopolymers Composites. Mater. Rev. 2017, 31, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Nematollahi, B.; Sanjayan, J. Influence of Type of Fiber on Tensile Performance of One-Part “Dry-Mix” Strain Hardening Geopolymer Composite (SHGC). In Proceedings of the 11th Fib International PhD Symposium in Civil Engineering, Tokyo, Japan, 29–31 August 2016; pp. 831–838. [Google Scholar]
- Nematollahi, B.; Sanjayan, J.; Ahmed, S.F.U. Tensile strain hardening behavior of PVA fiber-reinforced engineered geopolymer composite. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, B.; Sanjayan, J.; Shaikh, F.U.A. Comparative deflection hardening behavior of short fiber reinforced geopolymer composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 70, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimohammadi, A.; Deventer, J. Deventer. Characterisation of One-Part Geopolymer Binders Made from Fly Ash. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2017, 8, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.; Bejarano, J.; Garzón, C.; Mejía de Gutiérrez, R.; Delvasto, S.; Rodríguez, E. Performance of refractory aluminosilicate particle/fber-reinforced geopolymer composites. Compos. Part B 2012, 43, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozub, B.; Bazan, P.; Mierzwiński, D.; Korniejenko, K. Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymers Reinforced by Melamine Fibers. Materials 2021, 14, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumal, P.; Nguyen, H.; Carvelli, V.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. High strength fiber reinforced one-part alkali activated slag composites from industrial side streams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 319, 126124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, D.; Hossain, K.M.A. Strength, Shrinkage and Early Age Characteristics of One-Part Alkali-Activated Binders with High-Calcium Industrial Wastes, Solid Reagents and Fibers. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhao, B.; Guo, S.; Long, G.; Xie, Y. Properties and characterization of green one-part geopolymer activated by composite activators. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Jang, S.-J.; Kang, D.-H.; Ahn, K.-L.; Yun, H.-D. Mechanical Properties and Eco-Efficiency of Steel Fiber Reinforced Alkali-Activated Slag Concrete. Materials 2015, 8, 7309–7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B.; Singh, G.; Unluer, C.; Tan, M. Synthesis and characterization of one-part geopolymers for extrusion based 3D concrete printing. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazan, P.; Kozub, B.; Łach, M.; Korniejenko, K. Evaluation of Hybrid Melamine and Steel Fiber Reinforced Geopolymers Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nematollahi, B.; Sanjayan, J.; Qiu, J.; Yang, E.-H. Micromechanics-based investigation of a sustainable ambient temperature cured one-part strain hardening geopolymer composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.; Shirai, K.; Lim, J.H. Influence of Precursor Materials on the Mechanical Behavior of Ambient-Cured One-Part Engineered Geopolymer Composites. Eng. Proc. 2022, 17, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Carvelli, V.; Adesanya, E.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. High performance cementitious composite from alkali-activated ladle slag reinforced with polypropylene fibers. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2018, 90, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Kinnunen, P.; Carvelli, V.; Illikainen, M. Durability of ettringite-based composite reinforced with polypropylene fibers under combined chemical and physical attack. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2019, 102, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.; Gutierrez, R.; Delvasto, S.; Rodriguez, E. Performance of an alkali-activated slag concrete reinforced with steel fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, N.; Mehrali, M.; Behnia, A.; Javadi Pordsari, A.; Mehrali, M.; Alengaram, U. A Comprehensive Study of the Polypropylene Fiber Reinforced Fly Ash Based Geopolymer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuaiter, M.; El-Hassan, H.; El-Maaddawy, T.; El-Ariss, B. Properties of Slag-Fly Ash Blended Geopolymer Concrete Reinforced with Hybrid Glass Fibers. Buildings 2022, 12, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali, A.; Manzi, S.; Bignozzi, M.C. Novel fiber-reinforced composite materials based on sustainable geopolymer matrix. Procedia Eng. 2011, 21, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Abdollahnejad, Z.; Mastali, M. Fiber-reinforced one-part alkali-activated slag/ceramic binders. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 8963–8976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Ghazali, N.B.; Yusoff, S.; Bashar, I.I. Influence of steel fibers on the mechanical properties and impact resistance of lightweight geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 152, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yan, C.; Li, L.; Khan, M. Assessment of fiber factor for the fracture toughness of polyethylene fiber reinforced geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Cao, H.; Song, S. Tensile behavior contrast of basalt and glass fibers after chemical treatment. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4244–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhand, V.; Mittal, G.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.J.; Hui, D. A short review on basalt fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 73, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, H.; Gelbrich, S.; Kroll, L. The durability and performance of short fbers for a newly developed alkali-activated binder. Fibers 2016, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna, S.; Mohammed, B.S.; Wahab, M.M.A.; Kankia, M.U.; Amran, M.; Gora, A.M. Long-Term Strength Development of Fly Ash-Based One-Part Alkali-Activated Binders. Materials 2021, 14, 4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzaza, A.; Ohenoja, K.; Illikainen, M. Enhancing the mechanical and durability properties of subzero-cured one-part alkali-activated blast furnace slag mortar by using submicron metallurgical residue as an additive. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2021, 122, 104128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.S. Durability Performance of Geopolymer Concrete: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.; Kim, G.; Lee, B.; Hasegawa, R.; Hama, Y. Frost resistance of polyvinyl alcohol fiber and polypropylene fiber reinforced cementitious composites under freeze thaw cycling. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 90, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, L.; Coffetti, D.; Crotti, E.; Gazzaniga, G.; Pastore, T. The Durability of One-Part Alkali-Activated Slag-Based Mortars in Different Environments. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, X.; Haque, M.; Chen, B. Engineering properties and microstructure analysis of magnesium phosphate cement mortar containing bentonite clay. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procházka, L.; Boháčová, J.; Vojvodíková, B. Effect of Admixtures on Durability and Physical-Mechanical Properties of Alkali-Activated Materials. Materials 2022, 15, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Chen, B.; Shah, S. Influence of different admixtures on the mechanical and durability properties of one-part alkali-activated mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Fiber Type | Aspect Ratio | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Density (g/cm3) | Elongation (%) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | Polyvinyl alcohol | 200 | 41 | 1600 | 1.30 | - | [64] |
| 40–450 | - | - | [65] | ||||
| 308 | 40 | 6.42 | [66] | ||||
| 200 | 41 | 6 | [67] | ||||
| Polyethylene | 765 | 114 | 3000 | 0.97 | [68,69] | ||
| 1000 | 123 | 3500 | 3–5 | [67] | |||
| Polypropylene | 538 | - | 220–340 | 0.91 | - | [65] | |
| Steel | 72 | 200 | 2850 | 7.8 | - | [68,69] | |
| 47 | 200 | 3000 | - | [66] | |||
| 47 | 200 | 1300 | - | [64] | |||
| 50 | 210 | 850 | 4.2 | [70] | |||
| Basalt | 333 | 100 | 4500 | 2.63 | - | [64] | |
| 1389 | - | 4100–4840 | 2.8 | - | [65] | ||
| 1385 | 105 | 3500 | 2.4 | 2.5 | [66] | ||
| 750 | 45 | 1360 | 2.7 | 1.2 | [70] | ||
| Carbon | 1000 | 218 | 3500 | 1.75 | 1.5 | [70] | |
| Cellulose | 117 | 8.5 | 750 | 1.10 | - | [64] | |
| Precursors | Solid Activators | Fibers | Fiber Content (%) | Fine Aggregate | Curing Condition * | Water Solid Ratio | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground granulated blast furnace slag | Anhydrous sodium metasilicate | Steel | 1.0 | Standard sand | A, 23 °C 35% (RH) | 0.45 | [64] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol | |||||||
| Basalt | |||||||
| Cellulose | |||||||
| Ground granulated blast furnace slag | Anhydrous sodium metasilicate | Polyvinyl alcohol | 0.5–1.5 | Porcelain ceramic waste | A, 23 °C 60% (RH) | 0.35 | [65] |
| Polypropylene | |||||||
| fly ash | Basalt | ||||||
| Fly ash and slag | Anhydrous sodium silicate grains | Micro-steel | 0.5–2.0 | Fine sand | A, 25 ± 2 °C 70 ± 10% (RH) | 0.3 | [66] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol | |||||||
| Basalt | |||||||
| Fly ash and slag | Anhydrous sodium metasilicate powder | Polyvinyl alcohol | 2.0 | - | H | 0.35 | [67] |
| Polyethylene | A, 23 ± 3 °C | ||||||
| Activating slag | Anhydrous sodium metasilicate powder | Steel | 1.5 PE and 0.5 ST | Fine silica sand | W | 0.45 | [68,69] |
| Fly ash and slag | Polyethylene | ||||||
| Plain slag | Sodium silicate | Steel | 1.0 | Standard sand | A, 20 °C 100% (RH) | 0.3 | [77] |
| Ternary blended slag | Glass | ||||||
| Basalt | |||||||
| Fly ash and Ground granulated blast furnace slag | Ca(OH)2/Na2SO4 | Polyvinyl alcohol | 2.0 | - | W | 0.35–0.375 | [78] |
| Ca(OH)2/Na2SiO3·5H2O | A, 23 ± 3 °C 95 ± 5% (RH) |
| Mix ID | Fly Ash | Slag | Solid Activator | Water | Fiber | First-Crack Strength (MPa) | Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strain Capacity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE-H | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.08 | 0.35 | PE | 2.1 ± 0.24 | 3.3 ± 0.50 | 5.5 ± 0.52 |
| PE-A | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.08 | 0.35 | PE | 2.8 ± 0.66 | 4.2 ± 0.66 | 4.9 ± 0.68 |
| PVA-A | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.08 | 0.35 | PVA | 4.1 ± 0.095 | 4.6 ± 0.26 | 4.2 ± 0.71 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, G.; Lv, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, L. Properties of Fiber-Reinforced One-Part Geopolymers: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 3333. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163333
Guo G, Lv C, Liu J, Wang L. Properties of Fiber-Reinforced One-Part Geopolymers: A Review. Polymers. 2022; 14(16):3333. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163333
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Guoliang, Chun Lv, Jie Liu, and Li Wang. 2022. "Properties of Fiber-Reinforced One-Part Geopolymers: A Review" Polymers 14, no. 16: 3333. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163333
APA StyleGuo, G., Lv, C., Liu, J., & Wang, L. (2022). Properties of Fiber-Reinforced One-Part Geopolymers: A Review. Polymers, 14(16), 3333. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163333






