Barrier Effects of Cellulosic Fibers with Hybrid Coating Based on Zirconium Metal-Organic Framework
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagent and Materials
2.2. Characterization Methods
2.2.1. Particle Size and Stability of Zr-MOF Homogeneous Dispersion
2.2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.2.5. Fire Test
2.3. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Zr-MOF Homogeneous Dispersion
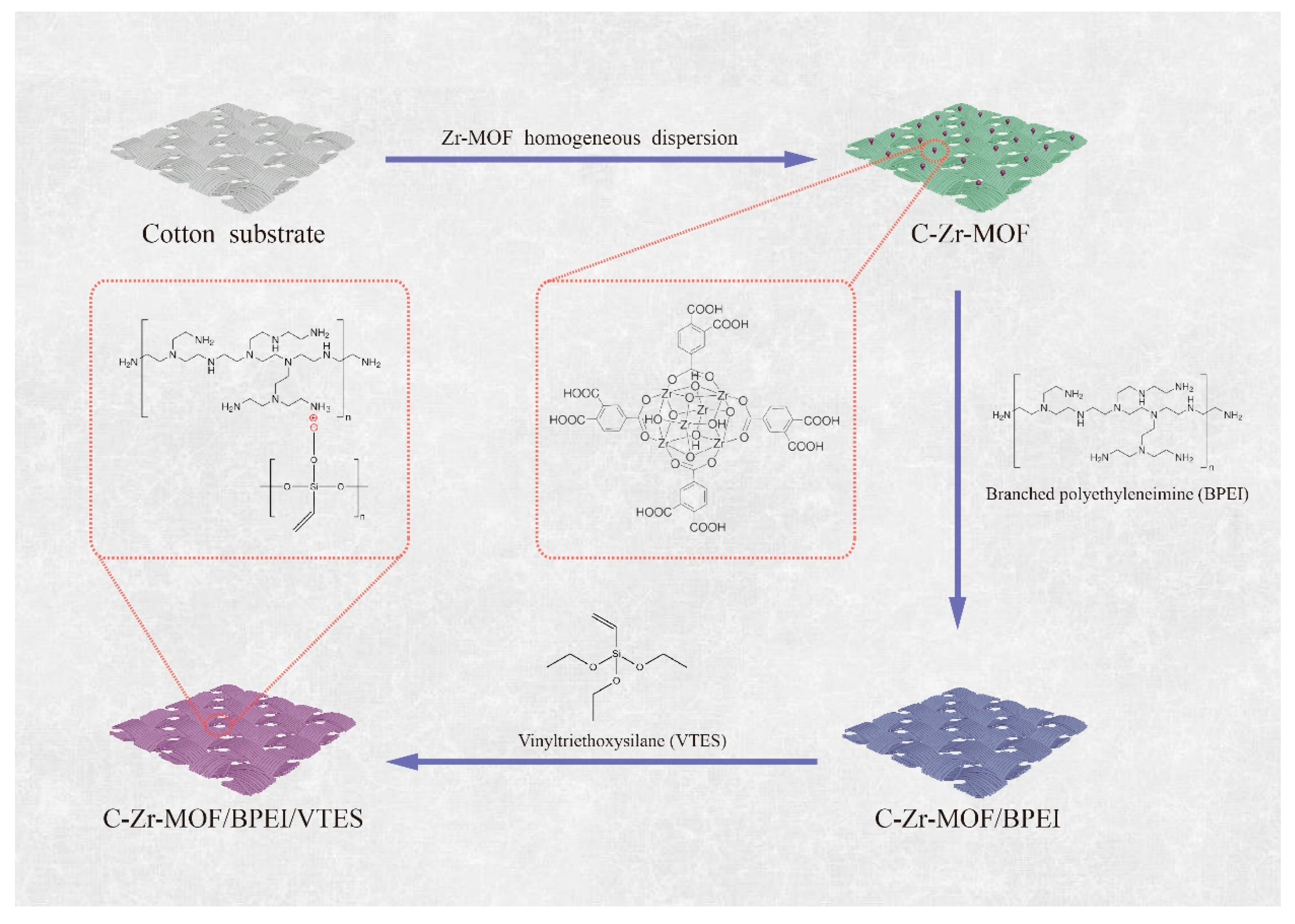
2.4. Finishing of Cotton Substrates with Zr-MOF, BPEI, and VTES
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size and Stability of Zr-MOF Homogeneous Dispersion
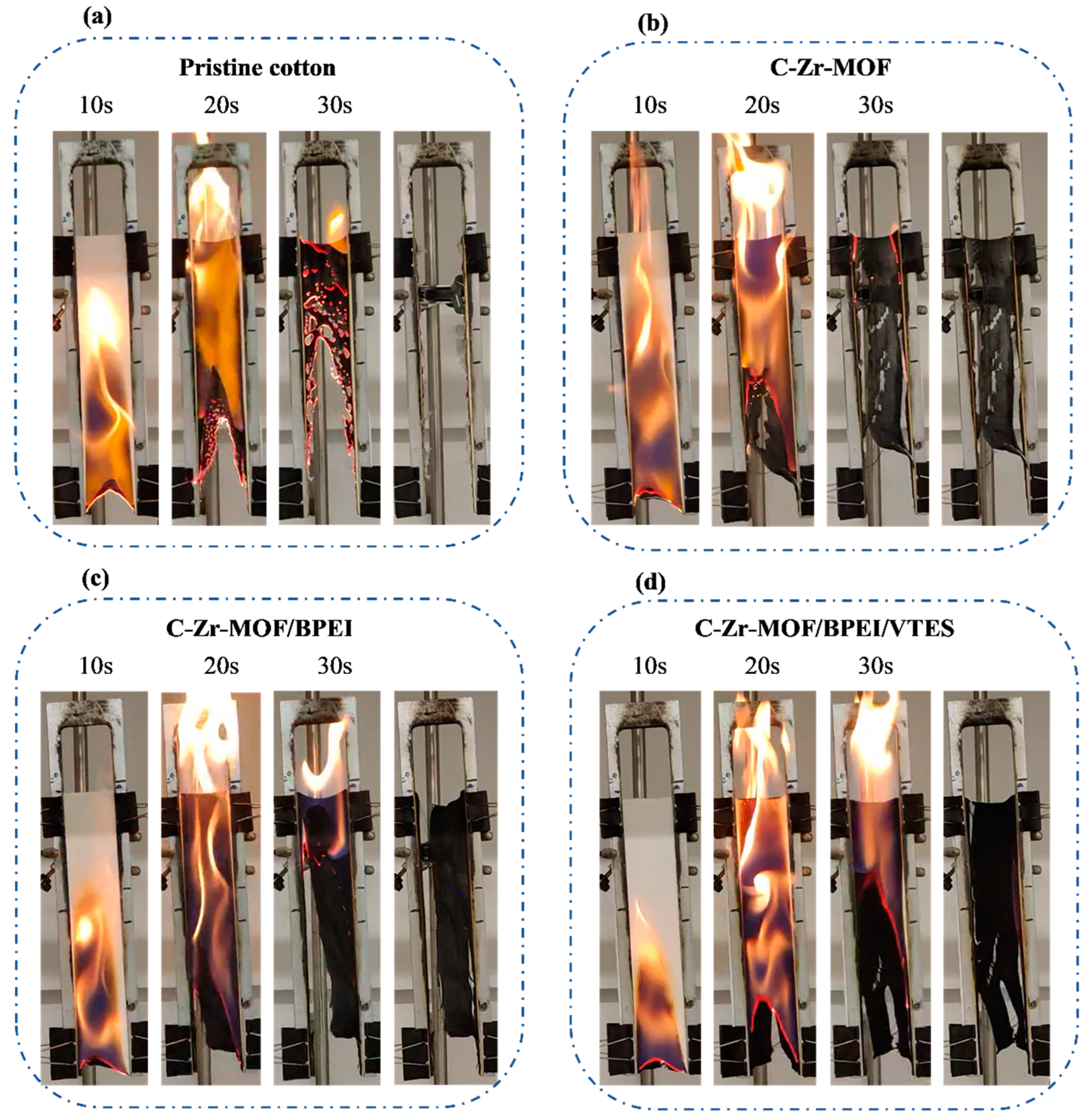
3.2. Fire Test
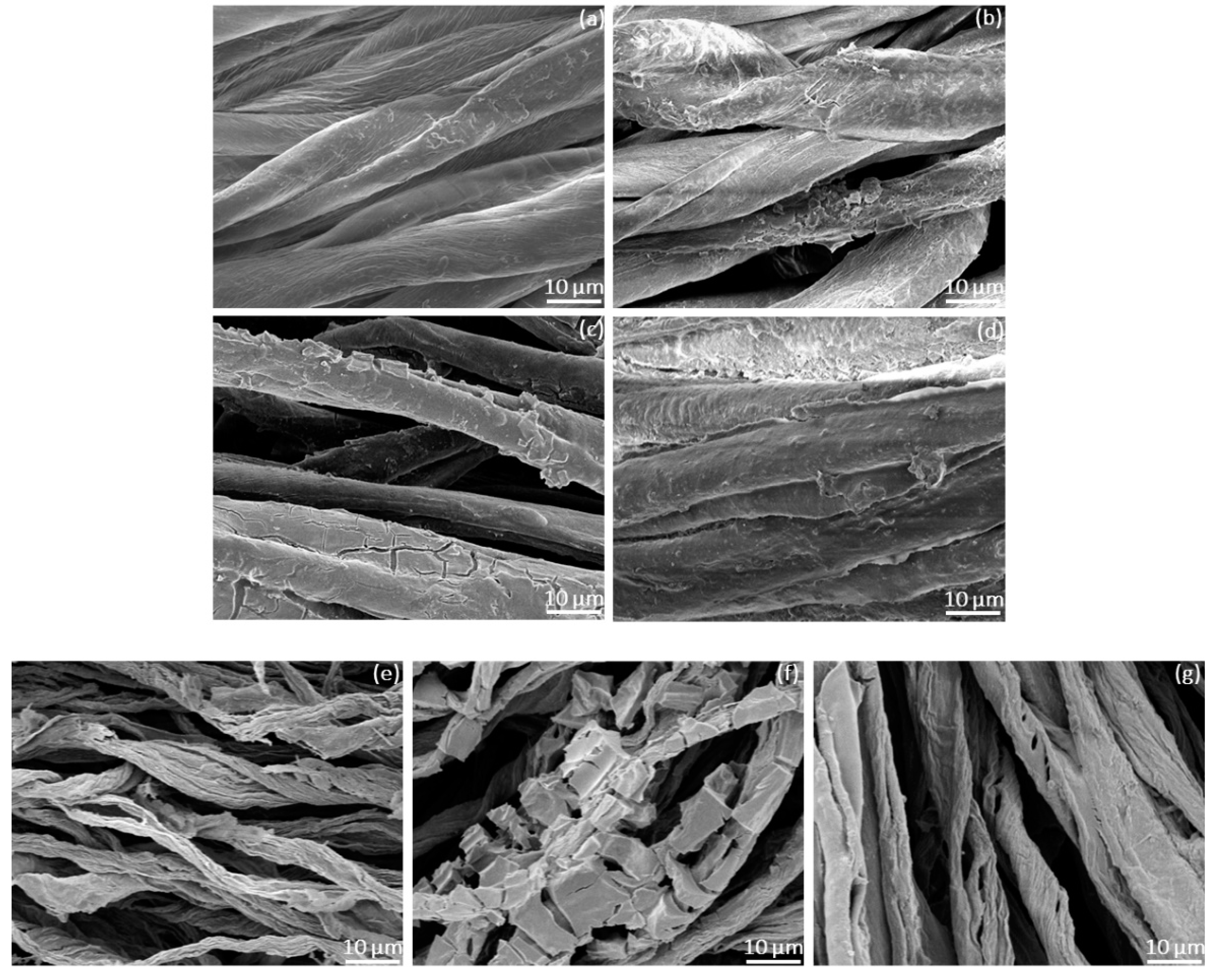
3.3. SEM
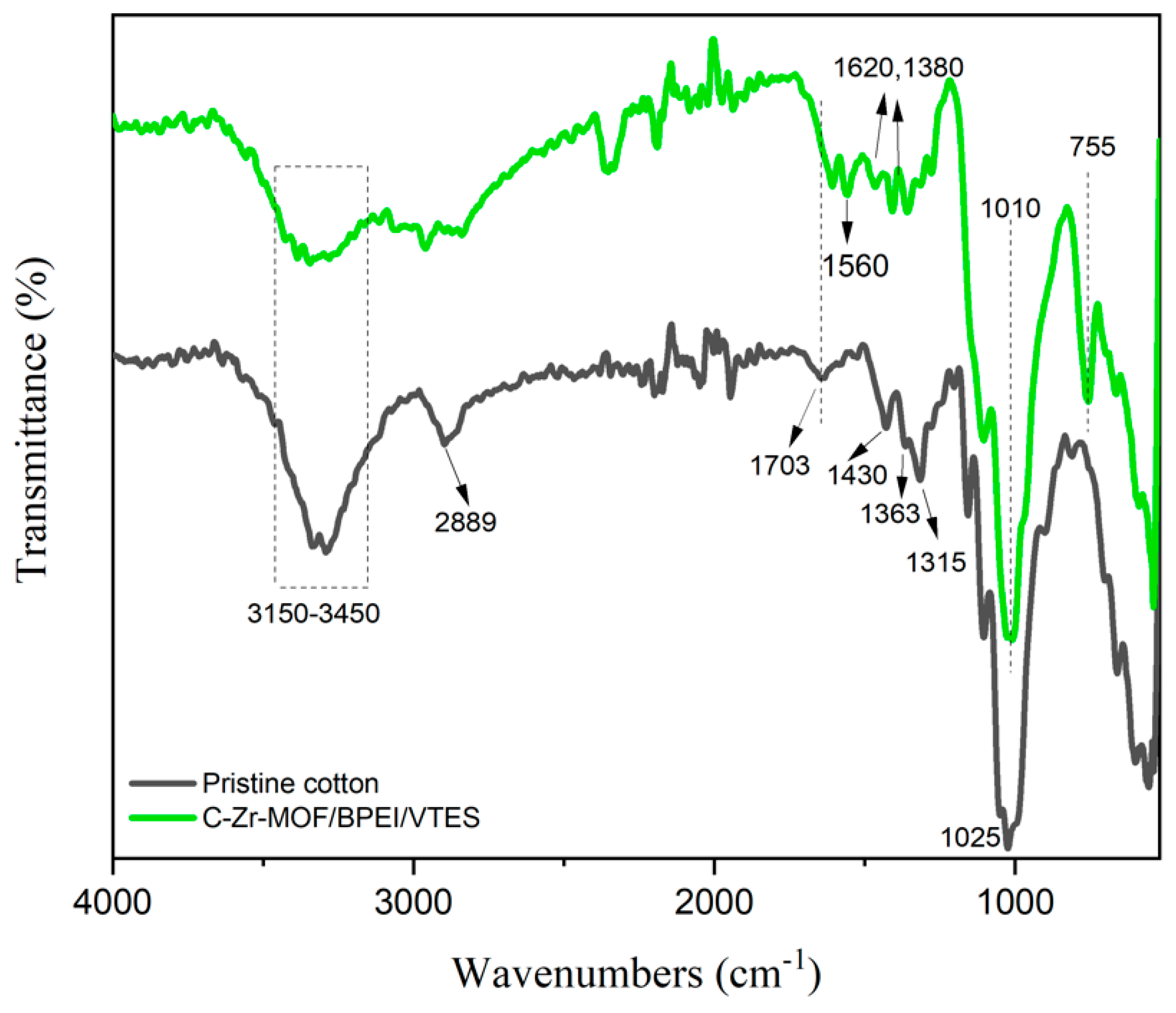
3.4. FTIR
3.5. Thermal Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciechańska, D.; Wesołowska, E.; Wawro, D. An Introduction to Cellulosic Fibres. In Handbook of Textile Fibre Structure; Eichhorn, S.J., Hearle, J.W.S., Jaffe, M., Kikutani, T., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009; Volume 2, pp. 3–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, H.; El-Shafei, A.; Hauser, P.J. Conferring flame retardancy on cotton using novel halogen-free flame retardant bifunctional monomers: Synthesis, characterizations and applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, R.E.; Borch, J.; Habeger, C. Handbook of Physical Testing of Paper; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, S.; Samanta, K.K.; Chattopadhyay, S. Fire retardant property of cotton fabric treated with herbal extract. J. Text. Inst. 2014, 106, 1338–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Ji, S.; Yin, T.; Tao, X.; Chen, Y.; Ma, H. Phosphorus–nitrogen-type fire-retardant vinyl ester resin with good comprehensive properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazaré, S.; Davis, R.D. A review of fire blocking technologies for soft furnishings. Fire Sci. Rev. 2012, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, P.; Thomas, H.; Moeller, M.; Walther, A. Large-scale, thick, self-assembled, nacre-mimetic brick-walls as fire barrier coatings on textiles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sui, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mao, Z. Durable flame retardant finishing of cotton fabrics with organosilicon functionalized cyclotriphosphazene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 128, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. A review on flame retardant technology in China. Part II: Flame retardant polymeric nanocomposites and coatings. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusack, P.; Perrett, T. The EU RoHS Directive and its implications for the plastics industry. Plast. Addit. Compd. 2006, 8, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, S.T.; Kolibaba, T.J.; Grunlan, J.C. Flame-retardant surface treatments. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costes, L.; Laoutid, F.; Brohez, S.; Dubois, P. Bio-based flame retardants: When nature meets fire protection. Mater. Sci. Eng. Rep. 2017, 117, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.-M.; An, Q.-D.; Xiao, Z.-Y.; Zhai, S.-R.; Shi, Z. Polyethylenimine-functionalized cellulose aerogel beads for efficient dynamic removal of chromium (vi) from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 54039–54052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mercado, L.; Galià, M.; Reina, J. Silicon-containing flame retardant epoxy resins: Synthesis, characterization and properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 2588–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carosio, F.; Laufer, G.; Alongi, J.; Camino, G.; Grunlan, J.C. Layer-by-layer assembly of silica-based flame retardant thin film on PET fabric. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Su, Y.; Wan, Y. Preparation and characterization of vinyltriethoxysilane (VTES) modified silicalite-1/PDMS hybrid pervaporation membrane and its application in ethanol separation from dilute aqueous solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 360, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, S. Chemical Aspects of Rubber Reinforcement by Fillers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1996, 69, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljević, J.; Jerman, I.; Jakša, G.; Alongi, J.; Malucelli, G.; Zorko, M.; Tomšič, B.; Simončič, B. Functionalization of cellulose fibres with DOPO-polysilsesquioxane flame retardant nanocoating. Cellulose 2015, 22, 1893–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowsell, J.L.; Yaghi, O.M. Metal-organic frameworks: A new class of porous materials. Microporous Mesoporous Materials. 2004, 73, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhah, O.; Liu, J.; Fischer, R.A.; Wöll, C. MOF thin films: Existing and future applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1081–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Hu, W.; Gui, Z.; Hu, Y. Preparation of Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Application as Flame Retardants for Polystyrene. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 2036–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelling, M.; Kim, M.; Otal, E.; Hinestroza, J. Decoration of Cotton Fibers with a Water-Stable Metal-Organic Framework (UiO-66) for the Decomposition and Enhanced Adsorption of Micropollutants in Water. Bioengineering 2018, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Hong, J.; Peng, C.; Chen, G.; Yuan, C.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, B.; Dai, L. Superhydrophobic and flame retardant cotton modified with DOPO and fluorine-silicon-containing crosslinked polymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 208, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Hu, Y.; Song, L.; Lu, H. Effect of modified organic–inorganic hybrid materials on thermal properties of cotton fabrics. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 103, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-F.; Zhang, C.-J.; Cui, L.; Zhu, P.; Yan, C.; Liu, Y. Fire retardant and thermal degradation properties of cotton fabrics based on APTES and sodium phytate through layer-by-layer assembly. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 123, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Seo, S.; Kwon, H.; Kim, D.; Park, Y.T. Fire protection behavior of layer-by-layer assembled starch–clay multilayers on cotton fabric. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 11433–11443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, C.; Fu, X.; Huang, Q. Immobilization of chitosan grafted carboxylic Zr-MOF to porous starch for sulfanilamide adsorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117305. Available online: https://jglobal.jst.go.jp/en/detail?JGLOBAL_ID=202002243957798107 (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Portella, E.H.; Romanzini, D.; Angrizani, C.C.; Amico, S.; Zattera, A.J. Influence of Stacking Sequence on the Mechanical and Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Cotton/Glass Fiber Reinforced Polyester Composites. Mat. Res. Vol. 2016, 19, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, K.; Carmalt, C.; Parkin, I.P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X. Durable Fire Retardant, Superhydrophobic, Abrasive Resistant and Air/UV Stable Coatings. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 582, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Lee, M.; Choe, E.K. Characterization of cotton fabric scouring by FT-IR ATR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 58, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabzina, Y.; Dhainaut, J.; Ahlhelm, M.; Richter, H.J.; Reinsch, H.; Stock, N.; Farrusseng, D. Synthesis and Shaping Scale-up Study of Functionalized UiO-66 MOF for Ammonia Air Purification Filters. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 8200–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, B.; Huang, H. Synergistic effect of carboxyl and sulfate groups for effective removal of radioactive strontium ion in a Zr-metal-organic framework. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 2001–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Kolibaba, T.J.; Lazar, S.; Grunlan, J.C. Environmentally-benign, water-based covalent polymer network for flame retardant cotton. Cellulose 2021, 28, 5855–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Zeng, X.; Li, H.; Lai, X.; Wu, T. One-pot fabrication of superhydrophobic and flame-retardant coatings on cotton fabrics via sol-gel reaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 533, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmeia, K.A.; Jovic, M.; Ragaisiene, A.; Rukuiziene, Z. Flammability of Cellulose-Based Fibers and the Effect of Structure of Phosphorus Compounds on Their Flame Retardancy. Polymers 2016, 8, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, Y. Chemical structure and properties of cotton. Cotton Sci. Technol. 2007, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Sui, X.; Xie, R.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Mao, Z. Durable flame retardant and antibacterial finishing on cotton fabrics with cyclotriphosphazene/polydopamine/silver nanoparticles hybrid coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-L.; Zhang, T.; Yan, H.-Q.; Peng, M.; Fang, Z.-P.; Li, Y.; Hao, W. Flame-retardant coating by alternate assembly of poly (vinylphosphonic acid) and polyethylenimine for ramie fabrics. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 32, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdani, S.; Longuet, C.; Perrin, D.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.-M.; Ganachaud, F. Flame retardancy of silicone-based materials. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 465–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, J.; Adibki, K. Application of Cellulose and Cellulose Derivatives in Pharmaceutical Industries; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uddin, A.; Khatoon, R.; Estevez, D.; Salem, M.; Ali, A.; Attique, S.; Lu, J.; Qin, F. Waste paper cellulose based-MoS2 hybrid composites: Towards sustainable green shielding. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | T10% (°C) | Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Residue at 800 °C (wt%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tmax (°C) | Rmax (wt%/min) | Tmax (°C) | Rmax (wt%/min) | |||
| Pristine cotton | 318.5 | 341.6 | 37.6 | 479 | 93.4 | −1.21 |
| C-Zr-MOF | 310.8 | 325.7 | 40.8 | 500.9 | 92.8 | 0.0573 |
| C-Zr-MOF/BPEI | 303.5 | 326.2 | 25.6 | 499 | 88.1 | 0.9052 |
| C-Zr-MOF/BPEI/VTES | 319.3 | 330.8 | 17.2 | 523.3 | 84.6 | 7.2355 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Q.; Lis, M.J. Barrier Effects of Cellulosic Fibers with Hybrid Coating Based on Zirconium Metal-Organic Framework. Polymers 2022, 14, 3071. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153071
Wu Q, Lis MJ. Barrier Effects of Cellulosic Fibers with Hybrid Coating Based on Zirconium Metal-Organic Framework. Polymers. 2022; 14(15):3071. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153071
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Qiuyue, and Manuel Jose Lis. 2022. "Barrier Effects of Cellulosic Fibers with Hybrid Coating Based on Zirconium Metal-Organic Framework" Polymers 14, no. 15: 3071. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153071
APA StyleWu, Q., & Lis, M. J. (2022). Barrier Effects of Cellulosic Fibers with Hybrid Coating Based on Zirconium Metal-Organic Framework. Polymers, 14(15), 3071. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153071







