Nanofiber Scaffold Based on Polylactic Acid-Polycaprolactone for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Functional Group Test Using Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectrophotometer
2.3.2. Diameter Measurement of the PLA-PCL Nanofiber Scaffold with Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.3.3. Mechanical Properties Measurement of PLA-PCL Nanofiber Scaffolds
2.3.4. Degradation Test of PLA-PCL Nanofiber Scaffold
2.3.5. Cytotoxicity Test (MTT Assay) PLA-PCL Nanofiber Scaffold
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Amin, S.F. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tissue Engineering: A Review of Current Investigations. J. Nanotechnol. Mater. Sci. 2016, 3, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Duthon, V.B.; Barea, C.; Abrassart, S.; Fasel, J.H.; Fritschy, D.; Ménétrey, J. Anatomy of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2006, 14, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everhart, J.S.; Sojka, J.H.; Kaeding, C.C.; Bertone, A.L.; Flanigan, D.C. The ACL Injury Response: A Collagen-Based Analysis. Knee 2017, 24, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, J.W.; Woods, M.D.; Laurencin, C.T. Tissue Engineering of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament Using a Braid–Twist Scaffold Design. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurlek, A.C.; Sevinc, B.; Bayrak, E.; Erisken, C. Synthesis and Characterization of Polycaprolactone for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengsteab, P.Y.; Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. The Past, Present and Future of Ligament Regenerative Engineering. Regen. Med. 2016, 11, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, A.; Maurice, E.; Viateau, V.; Migonney, V. Feasibility Study of the Elaboration of a Biodegradable and Bioactive Ligament Made of Poly(ε-Caprolactone)-PNaSS Grafted Fibers for the Reconstruction of Anterior Cruciate Ligament: In Vivo Experiment. IRBM 2019, 40, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Chueh, J.-Y.; Tseng, H.; Huang, H.-M.; Lee, S.-Y. Preparation and Characterization of Biodegradable PLA Polymeric Blends. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Satapathy, B.K. Performance Evaluation of Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats of Polylactic Acid (PLA)/Poly (ε-Caprolactone) (PCL) Blends. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 19, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeStefano, V.; Khan, S.; Tabada, A. Applications of PLA in Modern Medicine. Eng. Regen. 2020, 1, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Yang, F.; Goh, J.C.H.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lee, E.H. Biomaterials and Scaffolds for Ligament Tissue Engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2006, 77A, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, E.M.; Athanasiou, K.A. Bioactive Scaffold Design for Articular Cartilage Engineering. Biomed. Technol. Devices Handb. 2004, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, C.P.; Durville, D.; Mainard, D.; Ganghoffer, J.-F.; Rahouadj, R. A Multilayer Braided Scaffold for Anterior Cruciate Ligament: Mechanical Modeling at the Fiber Scale. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 12, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Cid, P.; Rubio-Valle, J.F.; Jiménez-Rosado, M.; Pérez-Puyana, V.; Romero, A. Effect of Solution Properties in the Development of Cellulose Derivative Nanostructures Processed via Electrospinning. Polymers 2022, 14, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gao, S.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. The Application of Electrospinning Used in Meniscus Tissue Engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoidy, W.H.; Ahmad, M.B.; Al-Mulla, E.A.J.; Ibrahim, N.A.B. Preparation and Characterization of Polylactic Acid/Polycaprolactone Clay Nanocomposites. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Chen, X.; Sovani, S.; Jin, S.; Grogan, S.P.; D’Lima, D.D. Meniscus Tissue Engineering Using a Novel Combination of Electrospun Scaffolds and Human Meniscus Cells Embedded within an Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel: Biomimetic Scaffolds for Meniscus Engineering. J. Orthop. Res. 2015, 33, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Ferreira, F.N.; Alves, N.M.; Paiva, M.C. Biodegradable Polymer Nanocomposites for Ligament/Tendon Tissue Engineering. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, M.A.; Hutmacher, D.W. The Return of a Forgotten Polymer—Polycaprolactone in the 21st Century. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1217–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockert, J.C.; Blázquez-Castro, A.; Cañete, M.; Horobin, R.W.; Villanueva, Á. MTT Assay for Cell Viability: Intracellular Localization of the Formazan Product Is in Lipid Droplets. Acta Histochem. 2012, 114, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, M.; Chambers, M.C.; Sheean, A.J.; Fu, F.H. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Anatomy. In ACL Injuries in Female Athletes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 25–30. ISBN 978-0-323-54839-7. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, A.C.; Vieira, J.C.; Ferra, J.M.; Magalhães, F.D.; Guedes, R.M.; Marques, A.T. Mechanical Study of PLA–PCL Fibers during in Vitro Degradation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenoun, D.; Vaccaro, J.; Le Corroller, T.; Barral, P.-A.; Lagier, A.; Pauly, V.; Coquart, B.; Coste, J.; Champsaur, P. A Dynamic Study of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament of the Knee Using an Open MRI. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2017, 39, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, F.; Pagès, P.; Gámez-Pérez, J.; Santana, O.O.; Maspoch, M.L. Kinetics of the Thermal Decomposition of Processed Poly(Lactic Acid). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2508–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Peng, X.; Zhang, S.W. Synthetic Biodegradable Medical Polymers. In Science and Principles of Biodegradable and Bioresorbable Medical Polymers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 217–254. ISBN 978-0-08-100372-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.T.; Tan, M.H.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.M.; Yang, F.W. Morphological Structure and Thermal Property of PLA/PCL Nanofiber by Electrospinning. AMR 2014, 1048, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Shin, H.J.; Cho, I.H.; Kang, Y.-M.; Kim, I.A.; Park, K.-D.; Shin, J.-W. Nanofiber Alignment and Direction of Mechanical Strain Affect the ECM Production of Human ACL Fibroblast. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, H.M.; Kelly, D.J.; Popat, K.C.; Trujillo, N.A.; Dunne, N.J.; McCarthy, H.O.; Haut Donahue, T.L. Mechanical Properties and Cellular Response of Novel Electrospun Nanofibers for Ligament Tissue Engineering: Effects of Orientation and Geometry. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 61, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Jiang, H.B.; Kim, J.-E.; Zhang, S.; Kim, K.-M.; Kwon, J.-S. Bioresorbable Magnesium-Reinforced PLA Membrane for Guided Bone/Tissue Regeneration. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 112, 104061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
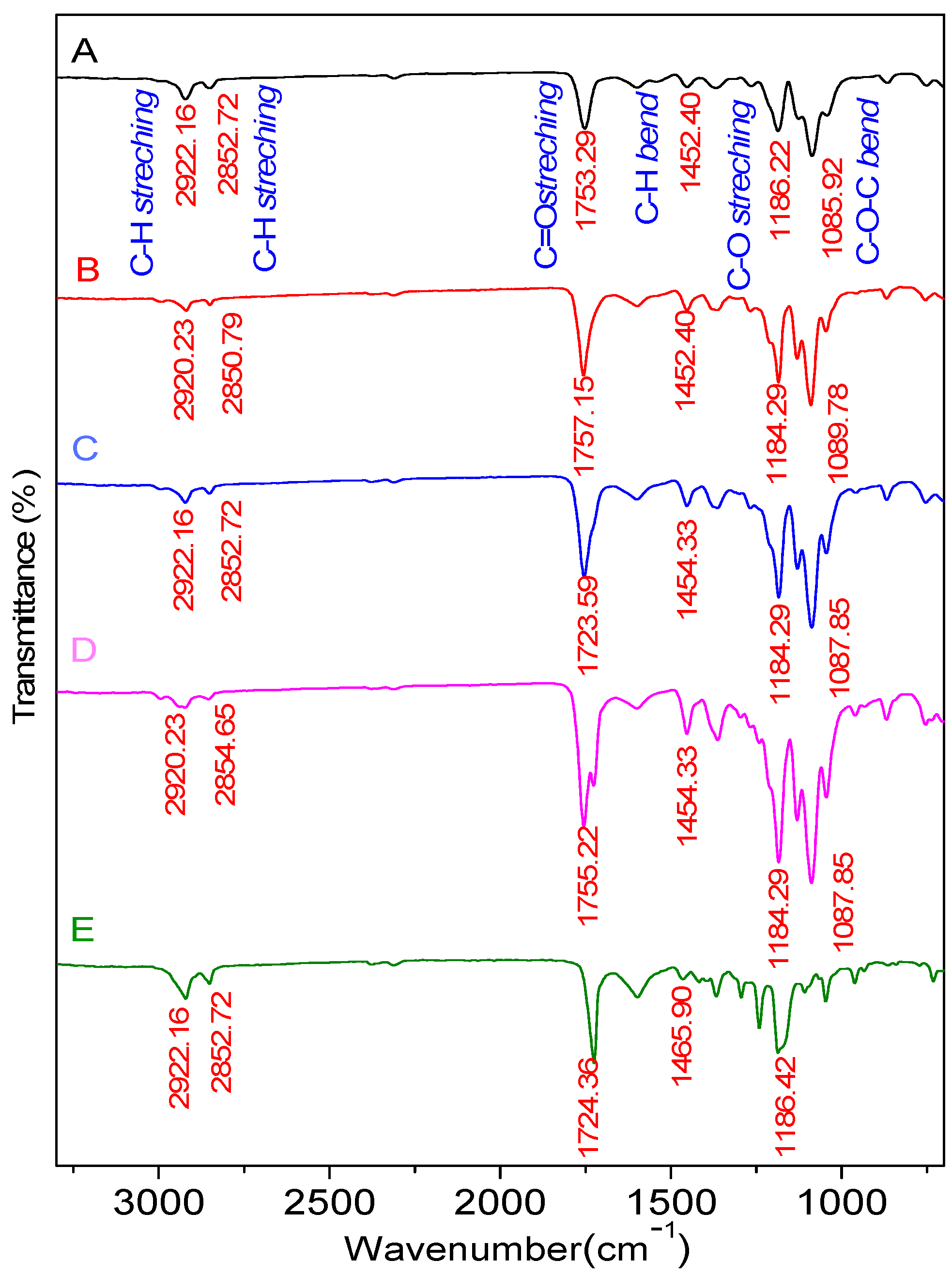
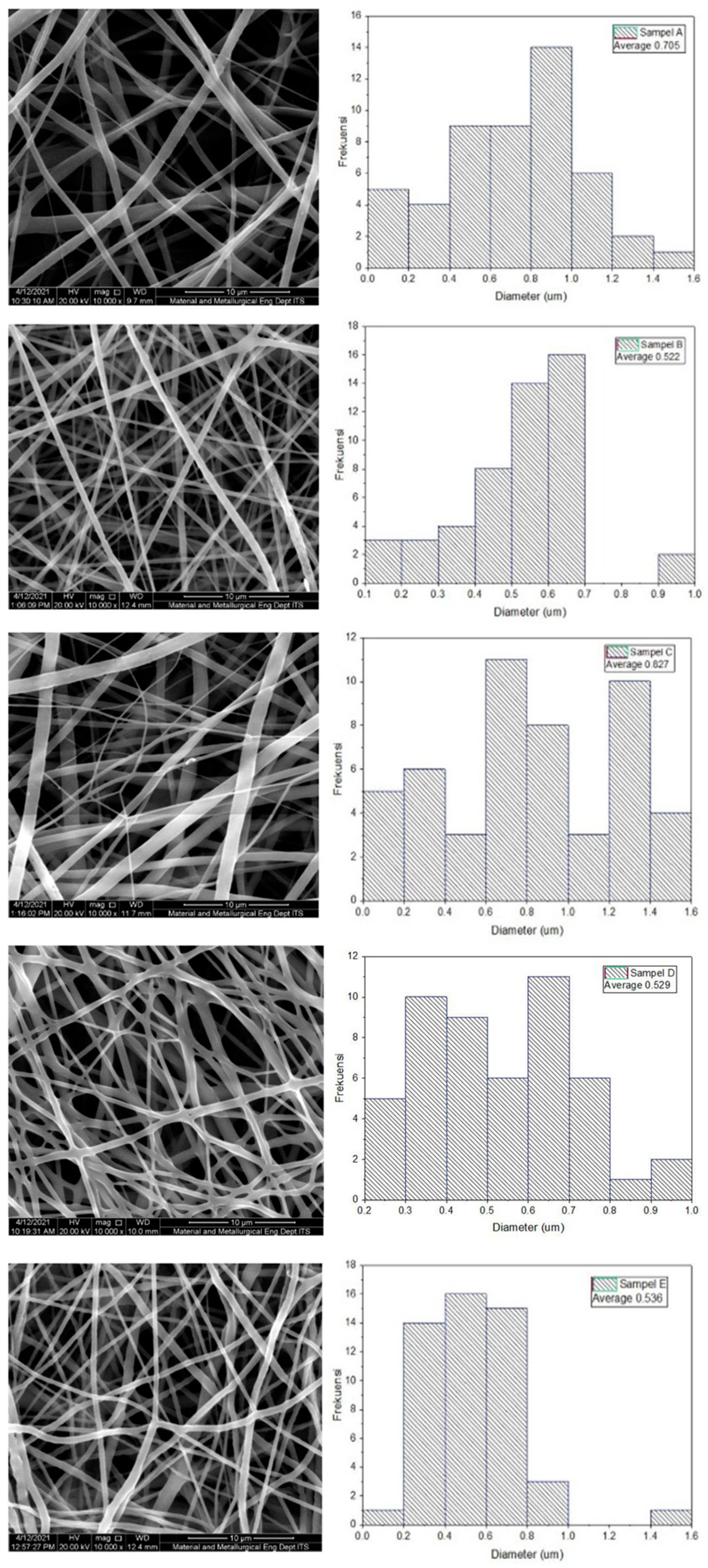



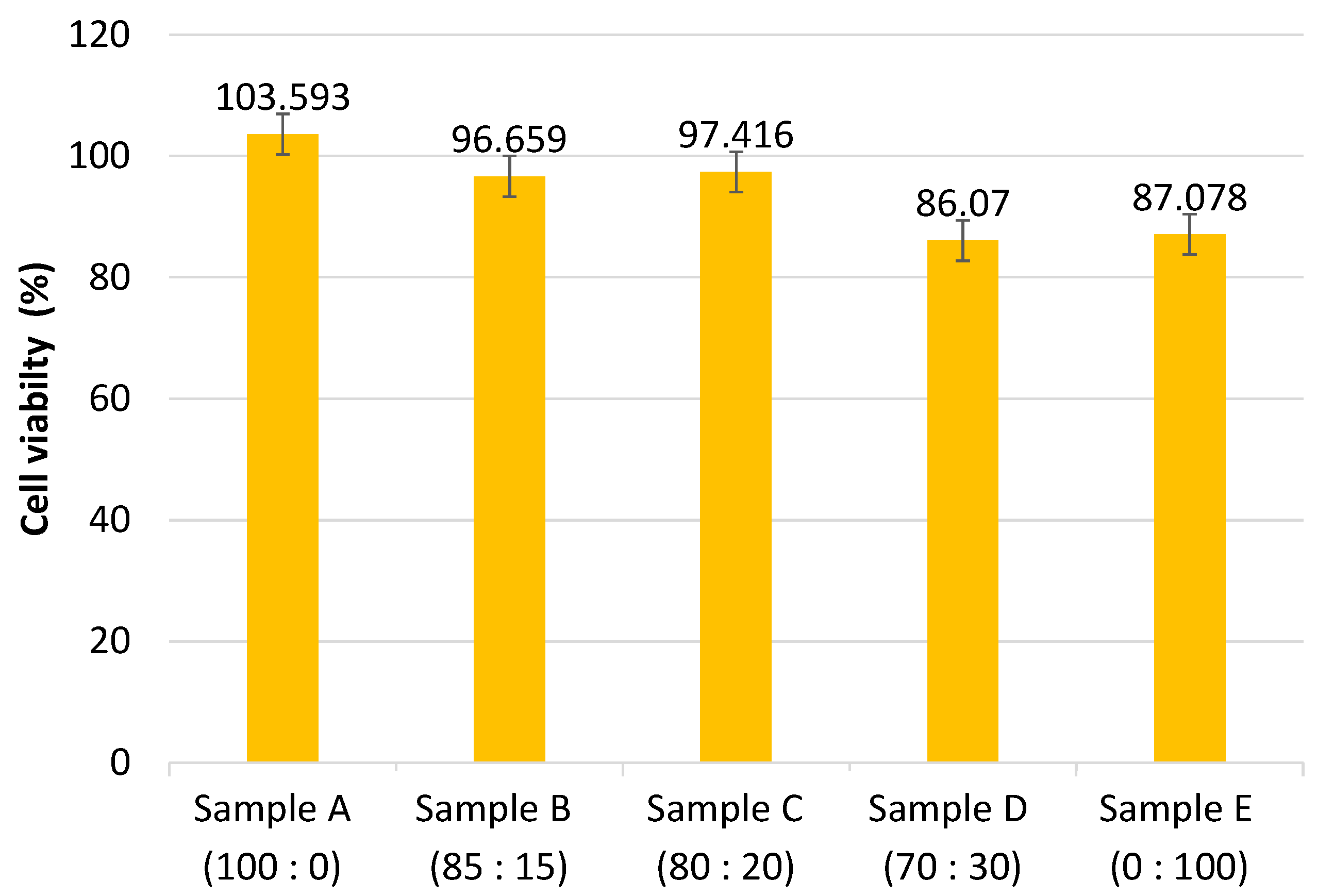
| Bond | Standard Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A PLA-PCL (100:0) | B PLA-PCL (85:15) | C PLA-PCL (80:20) | D PLA-PCL (70:30) | E PLA-PCL (0:100) | ||
| C-O stretch | 1300–1100 | 1186.22 | 1184.29 | 1184.29 | 1184.29 | 1186.22 |
| C-O-C bend | 1150–1050 | 1085.92 | 1089.78 | 1087.85 | 1087.85 | - |
| C-H bend | 1485–1445 | 1452.40 | 1452.40 | 1454.33 | 1454.33 | 1465.90 |
| C=O stretch | 1750–1730 | 1753.29 | 1757.15 | 1753.29 | 1755.22 | 1724.36 |
| C-H2stretch | 2935–2915 | 2922.16 | 2920.23 | 2922.16 | 2920.23 | 2922.16 |
| O-H stretch | 3570–3200 | - | - | - | - | 3525.88 |
| Sample | PLA-PCL Composition (wt%) | Minimum Diameter (nm) | Maximum Diameter (nm) | Average Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 100:0 | 108 | 1.528 | 705 ± 328 |
| B | 85:15 | 149 | 977 | 522 ± 192 |
| C | 80:20 | 155 | 1.510 | 827 ± 271 |
| D | 70:30 | 248 | 957 | 529 ± 104 |
| E | 0:100 | 195 | 1.412 | 536 ± 154 |
| Sample | Composition of PLA:PCL (wt%) | Unbraided | Braided | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTS (MPa) | Modulus of Elasticity (MPa) | UTS (MPa) | Modulus of Elasticity (MPa) | ||
| A | 100:0 | 4.387 ± 1.90 | 141.901 ± 36.96 | 0.879 ± 0.15 | 4.523 ± 1.32 |
| B | 85:15 | 2.660 ± 0.35 | 121.373 ± 25.39 | 1.149 ± 0.28 | 2.739 ± 1.24 |
| C | 80:20 | 1.578 ± 0.37 | 93.698 ± 31.53 | 1.014 ± 0.48 | 4.746 ± 2.51 |
| D | 70:30 | 1.621 ± 0.05 | 76.908 ± 5.83 | 1.025 ± 0.31 | 3.095 ± 1.29 |
| E | 0:100 | 1.739 ± 1.30 | 8.351 ± 2.10 | 1.863 ± 0.45 | 3.042 ± 1.35 |
| Sample | Composition of PLA-PCL (wt%) | Degradation Rate (g/day) | Estimated Sample Time Out (days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 100:0 | 104 | |
| B | 85:15 | 176 | |
| C | 80:20 | 219 | |
| D | 70:30 | 354 | |
| E | 0:100 | 534 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aminatun; Huriah, R.; Hikmawati, D.; Hadi, S.; Amrillah, T.; Abdullah, C.A.C. Nanofiber Scaffold Based on Polylactic Acid-Polycaprolactone for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury. Polymers 2022, 14, 2983. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14152983
Aminatun, Huriah R, Hikmawati D, Hadi S, Amrillah T, Abdullah CAC. Nanofiber Scaffold Based on Polylactic Acid-Polycaprolactone for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury. Polymers. 2022; 14(15):2983. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14152983
Chicago/Turabian StyleAminatun, Rifqha Huriah, Dyah Hikmawati, Sofijan Hadi, Tahta Amrillah, and Che Azurahanim Che Abdullah. 2022. "Nanofiber Scaffold Based on Polylactic Acid-Polycaprolactone for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury" Polymers 14, no. 15: 2983. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14152983
APA StyleAminatun, Huriah, R., Hikmawati, D., Hadi, S., Amrillah, T., & Abdullah, C. A. C. (2022). Nanofiber Scaffold Based on Polylactic Acid-Polycaprolactone for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury. Polymers, 14(15), 2983. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14152983





