Effect of Volume Fraction on Shear Mode Properties of Fe-Co and Fe-Ni Filled Magneto-Rheological Elastomers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Material Characterization
2.2. Sample Preparations (Fabrication of MRE)
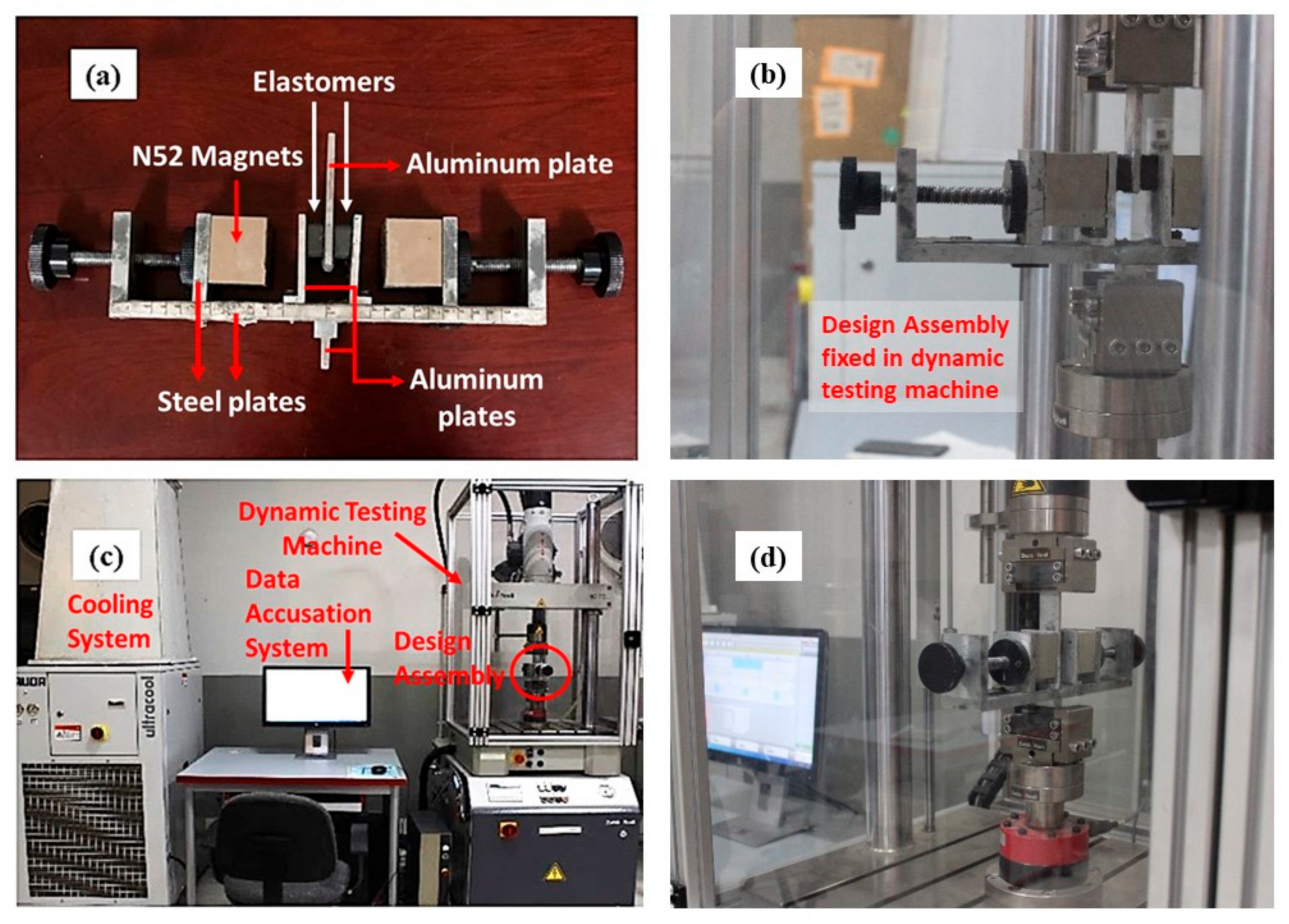
3. Experiment Setup
4. Results and Discussions
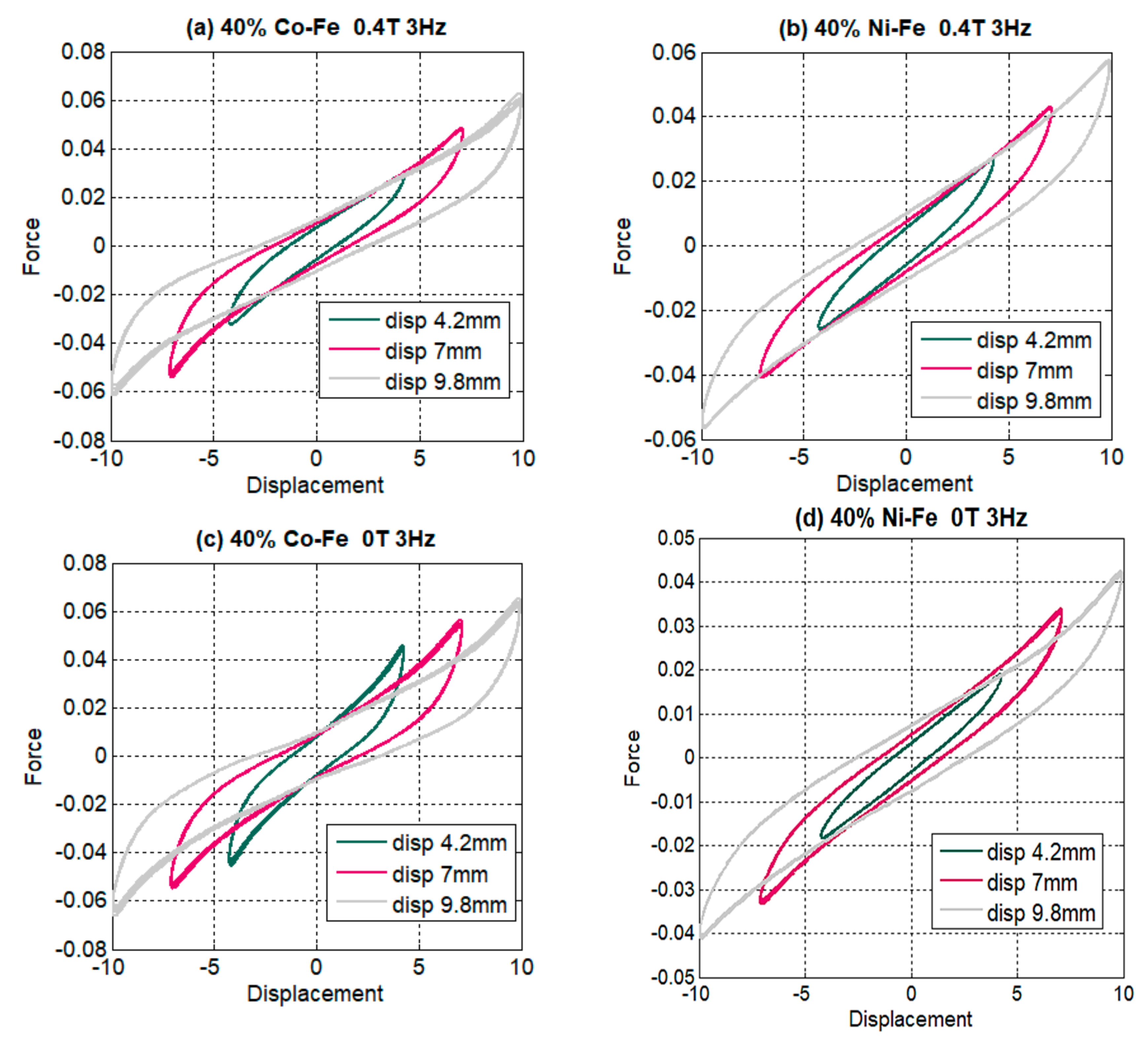
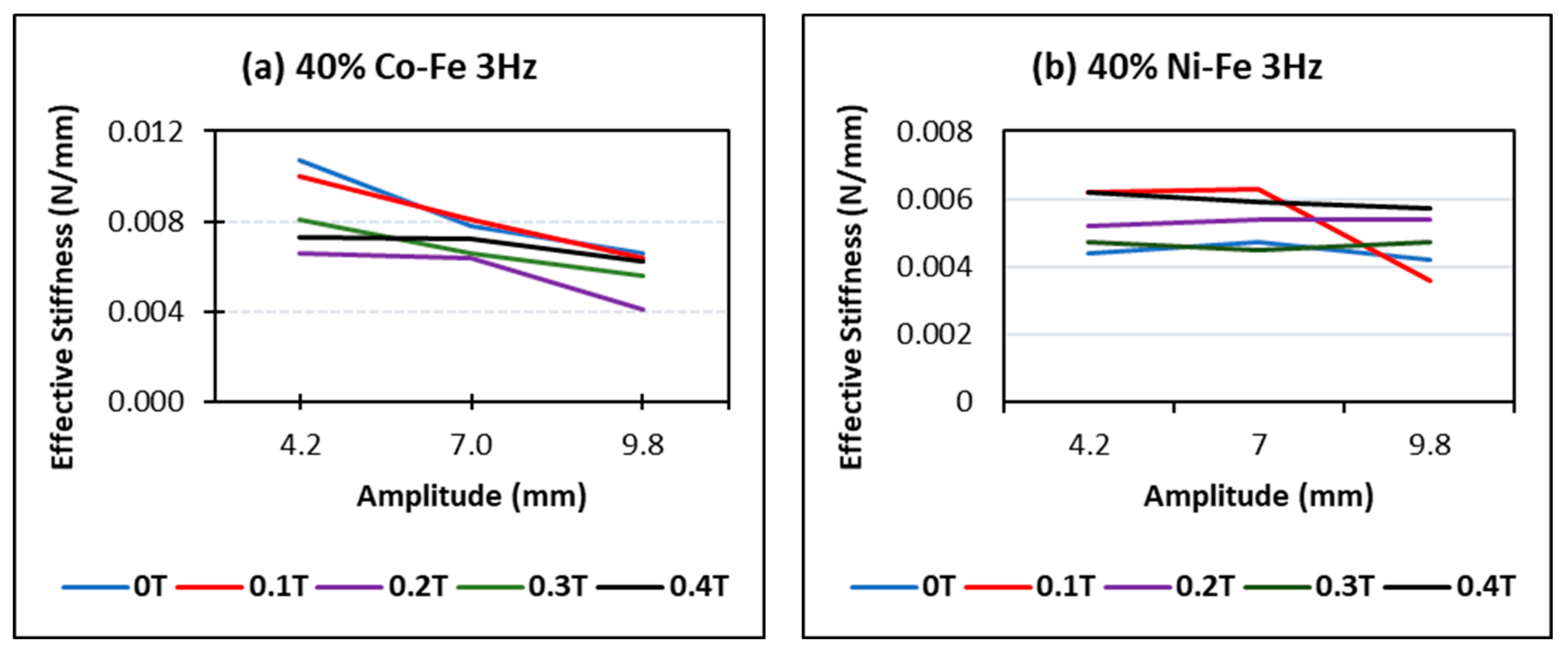
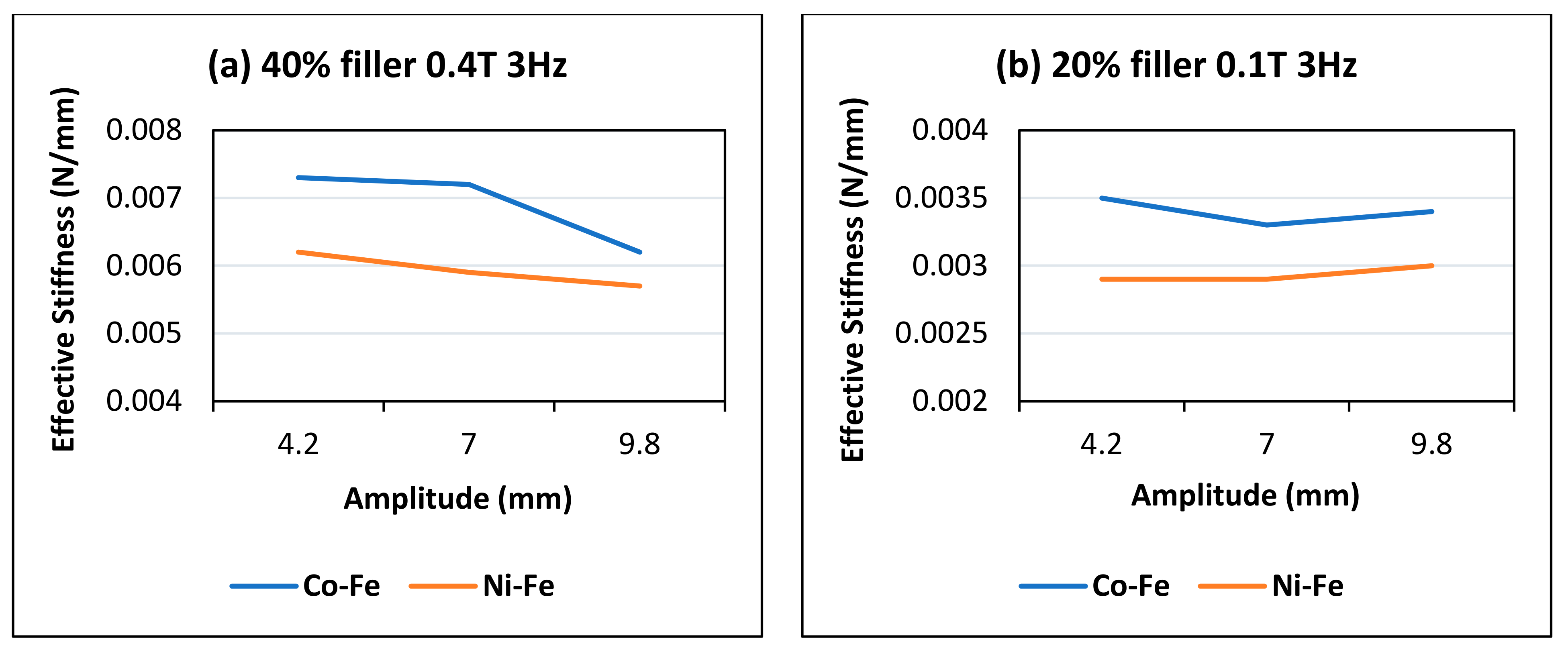
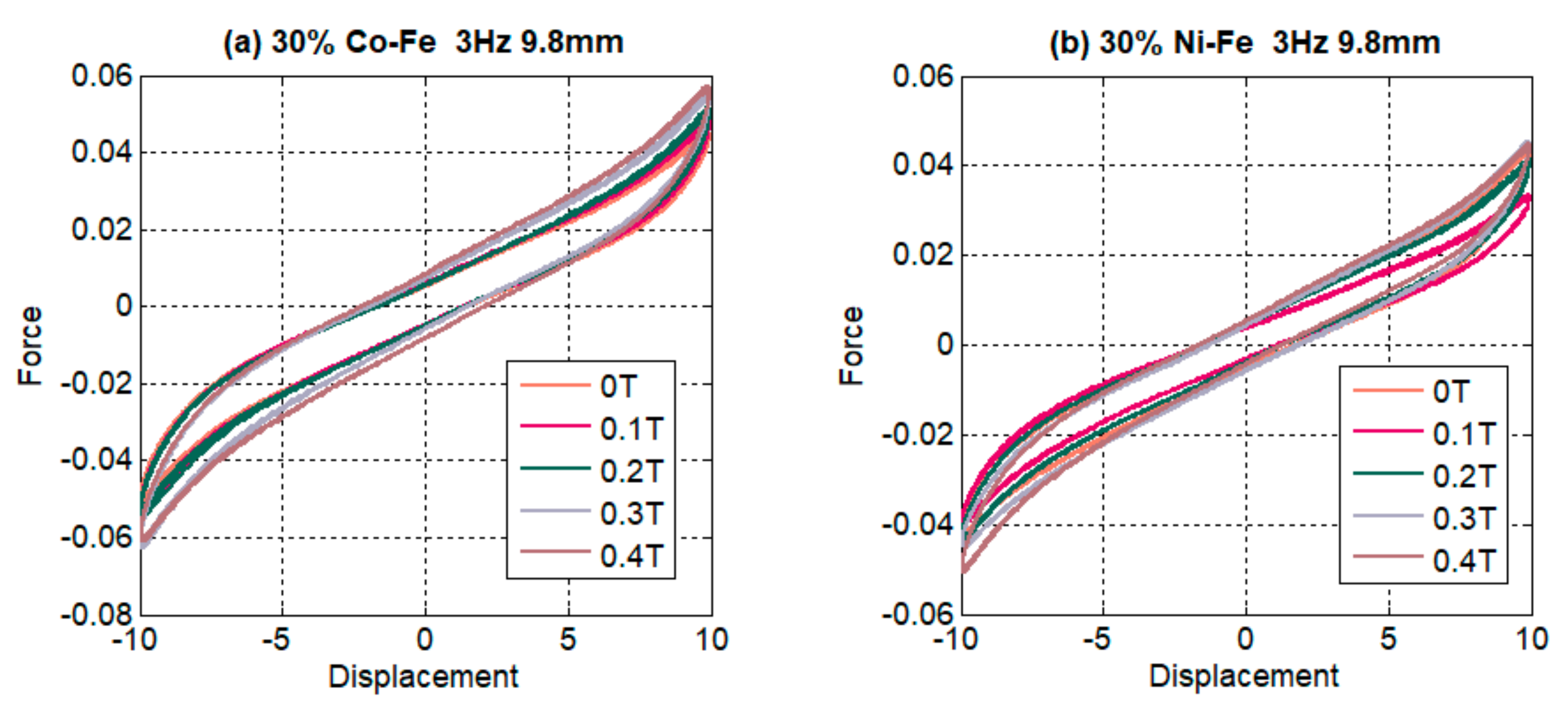
4.1. Effect of Changing Amplitudes
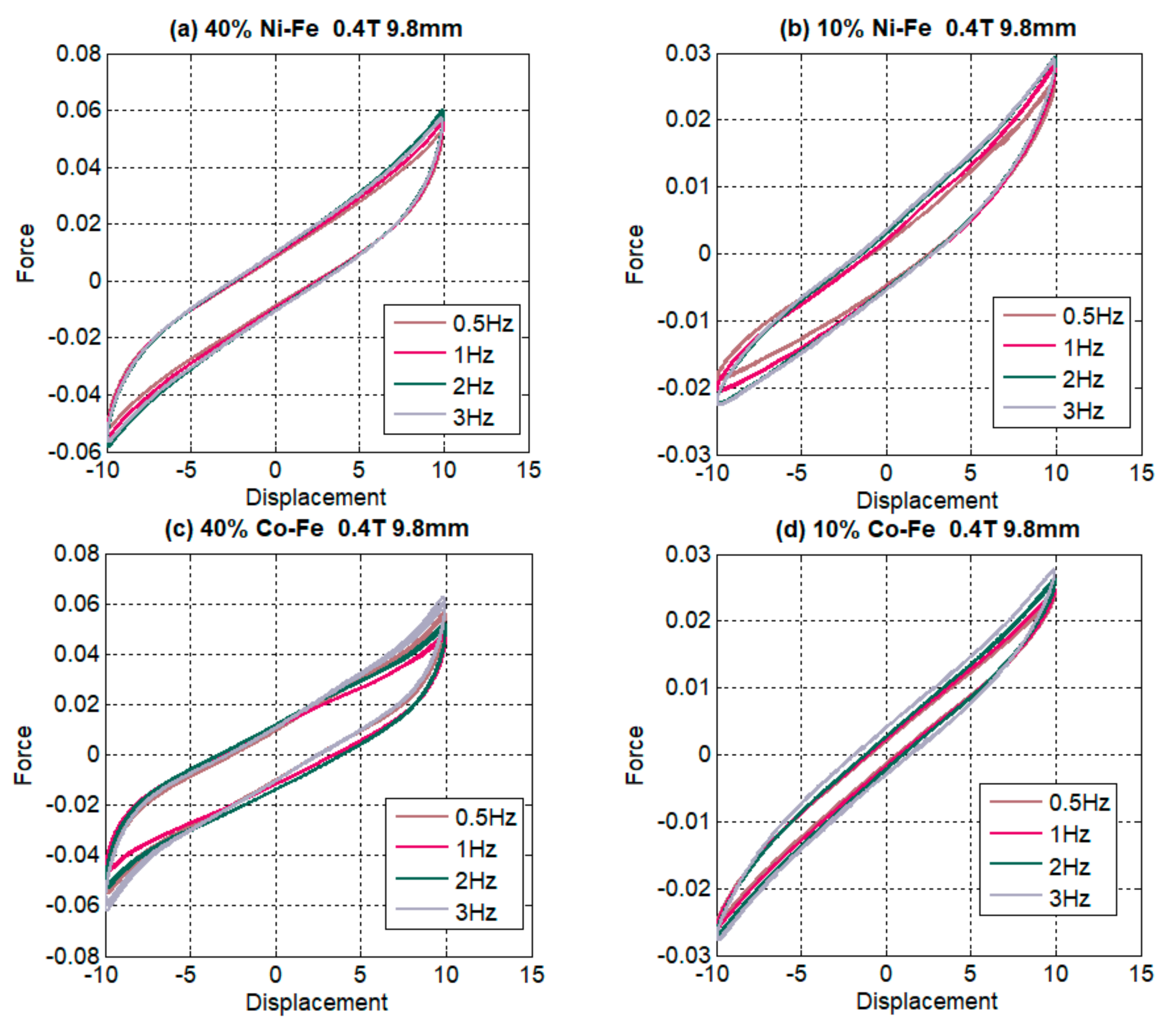
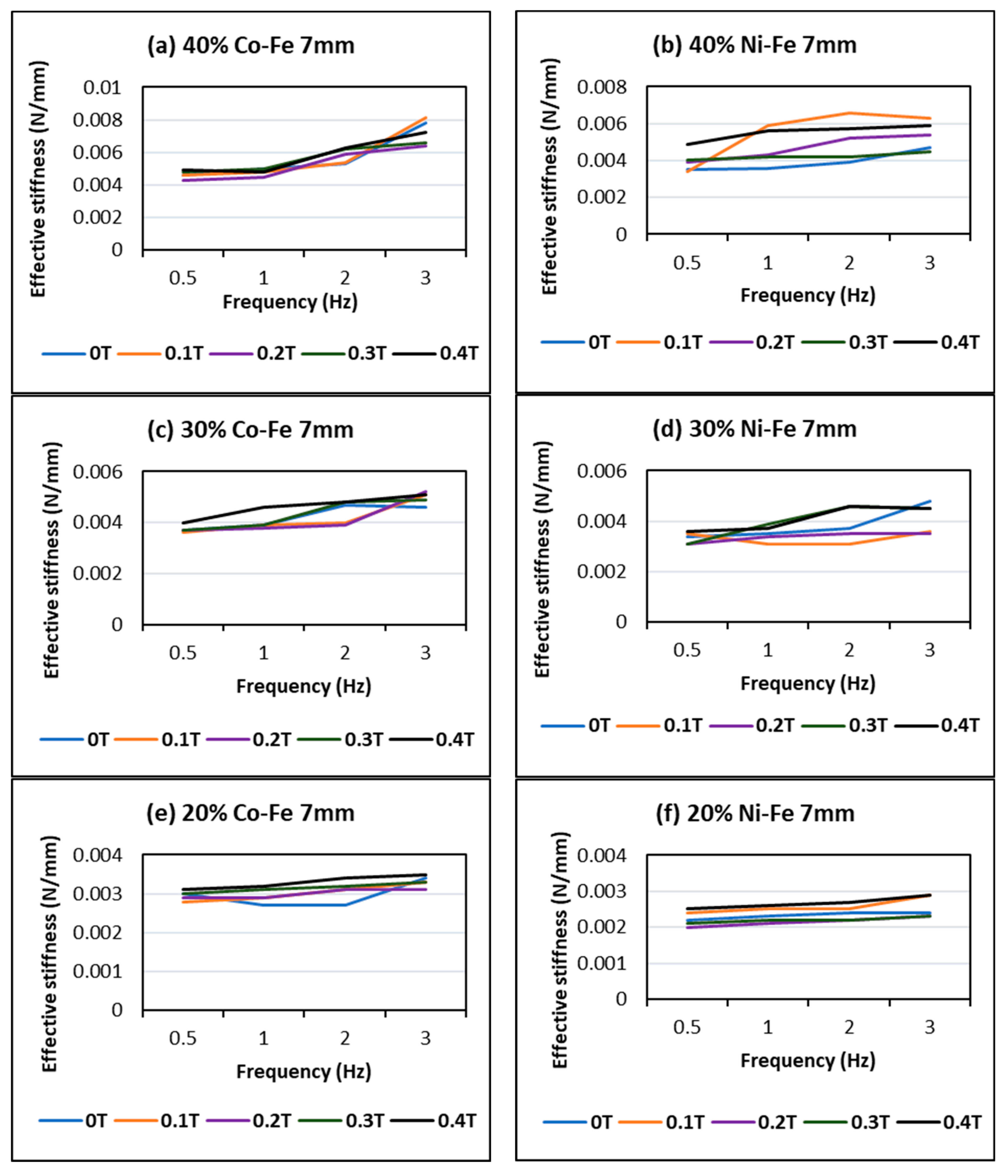
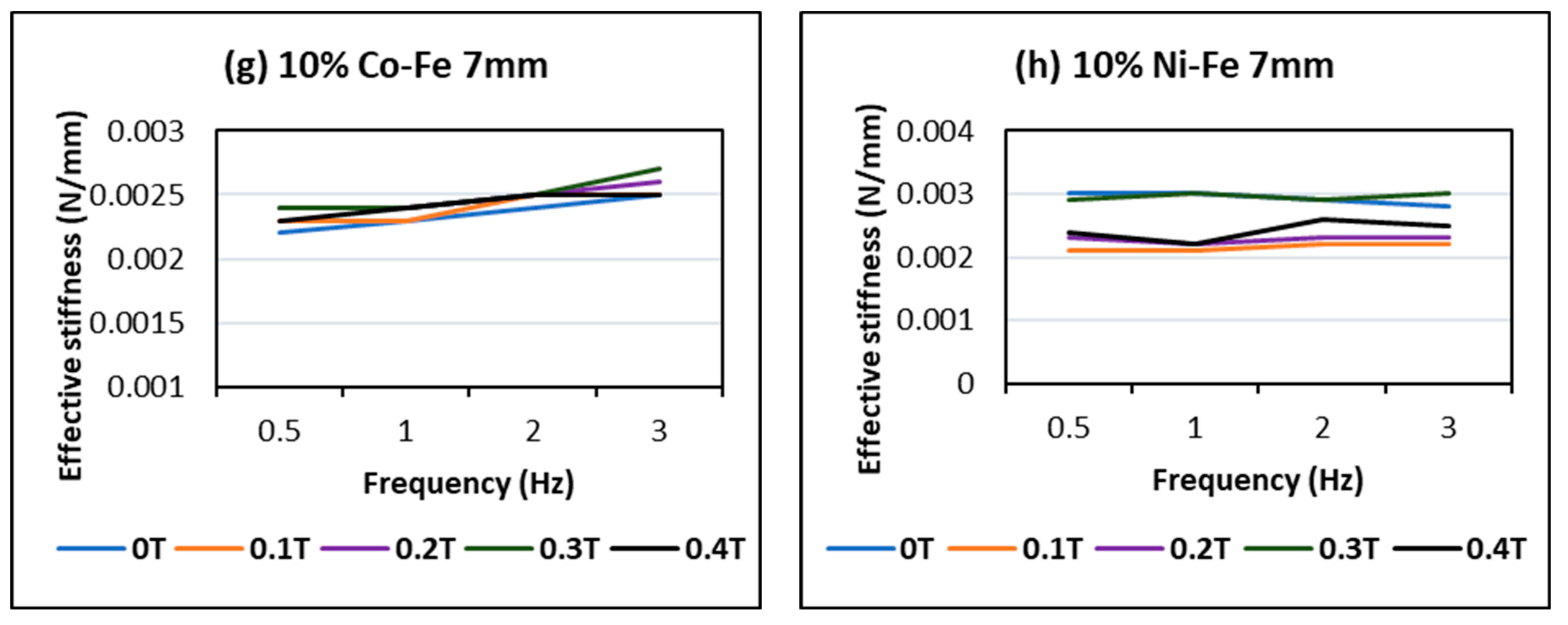
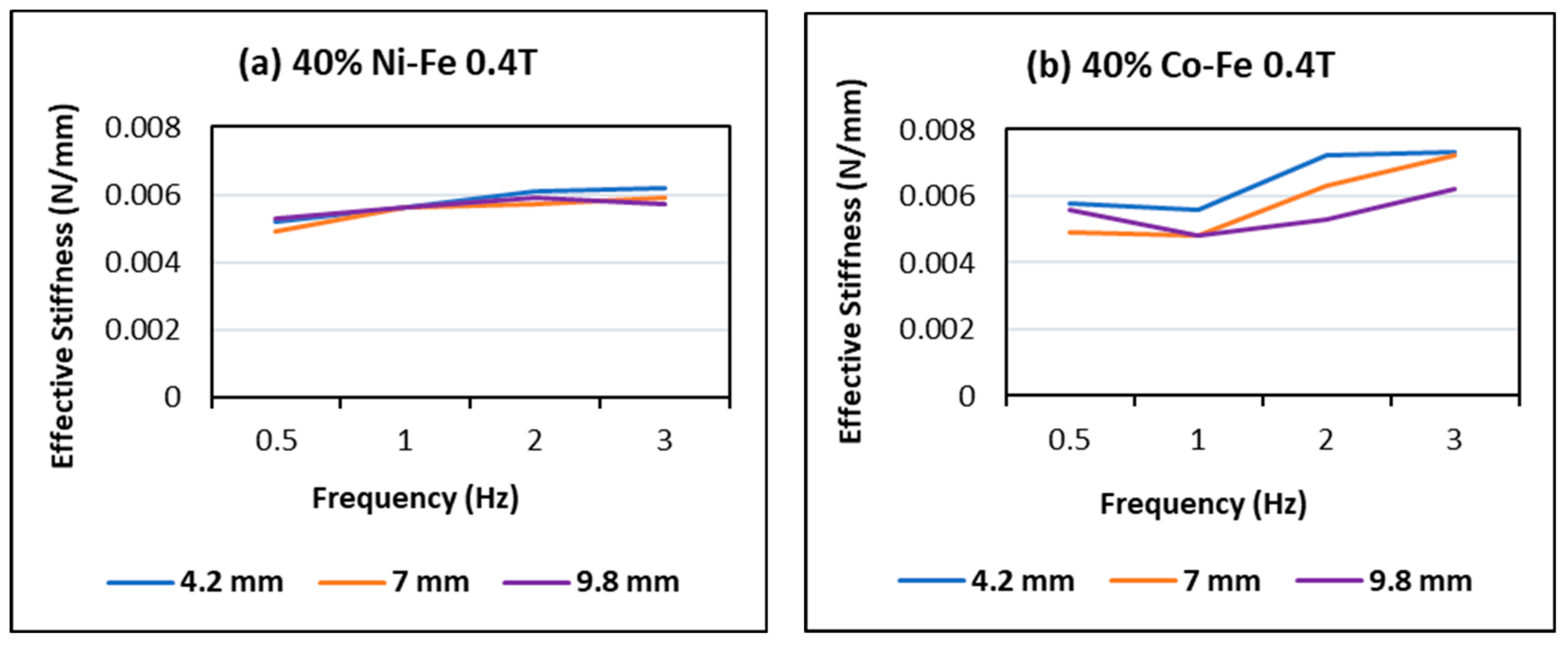
4.2. Effect of Changing Frequency
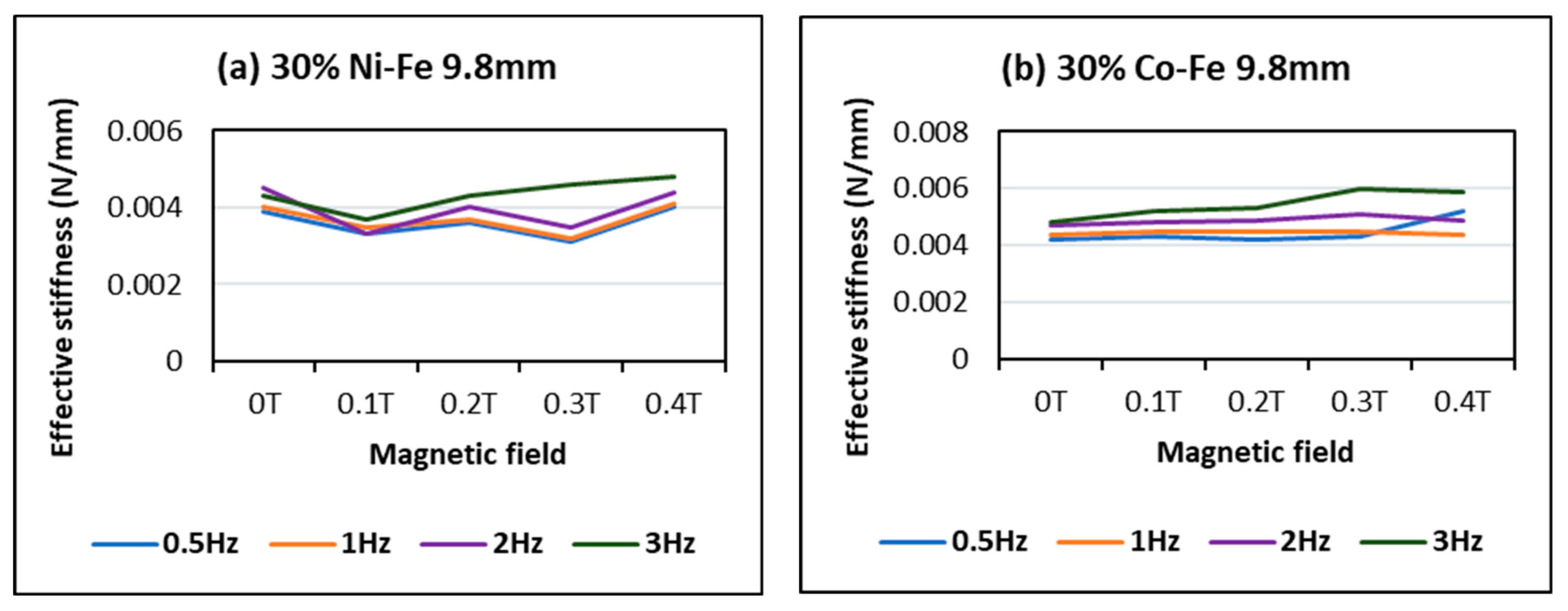
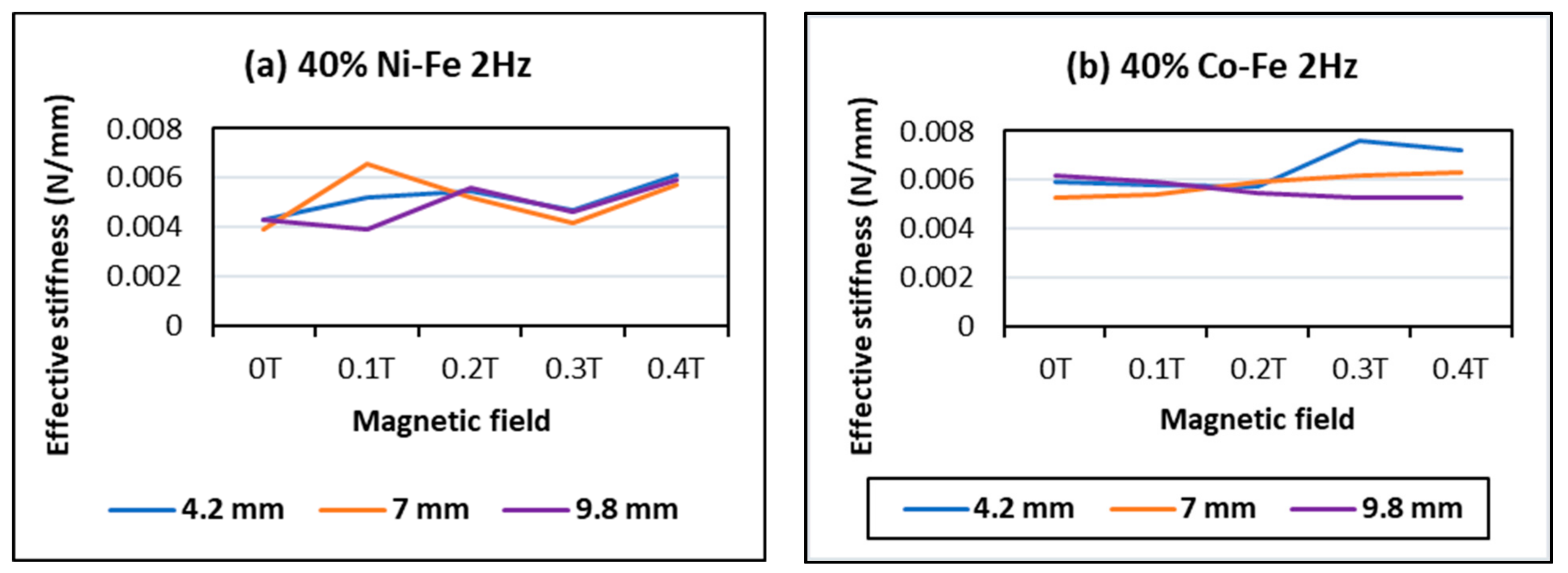
4.3. Effect of Changing Flux
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The MREs with Co-Fe as filler material have a larger Payne effect, i.e., the incremental decrease in effective stiffness of cobalt and iron filled MREs is more than nickel and iron MREs. This trend of strain-softening is intensified in the case of higher frequencies and larger magnetic fields;
- (2)
- The strain rate stiffening effect for both Ni-Fe and Co-Fe was observed to be larger at small strains. For applied magnetic fields, the incremental stiffness increase for Ni-Fe was more than Co-Fe MREs;
- (3)
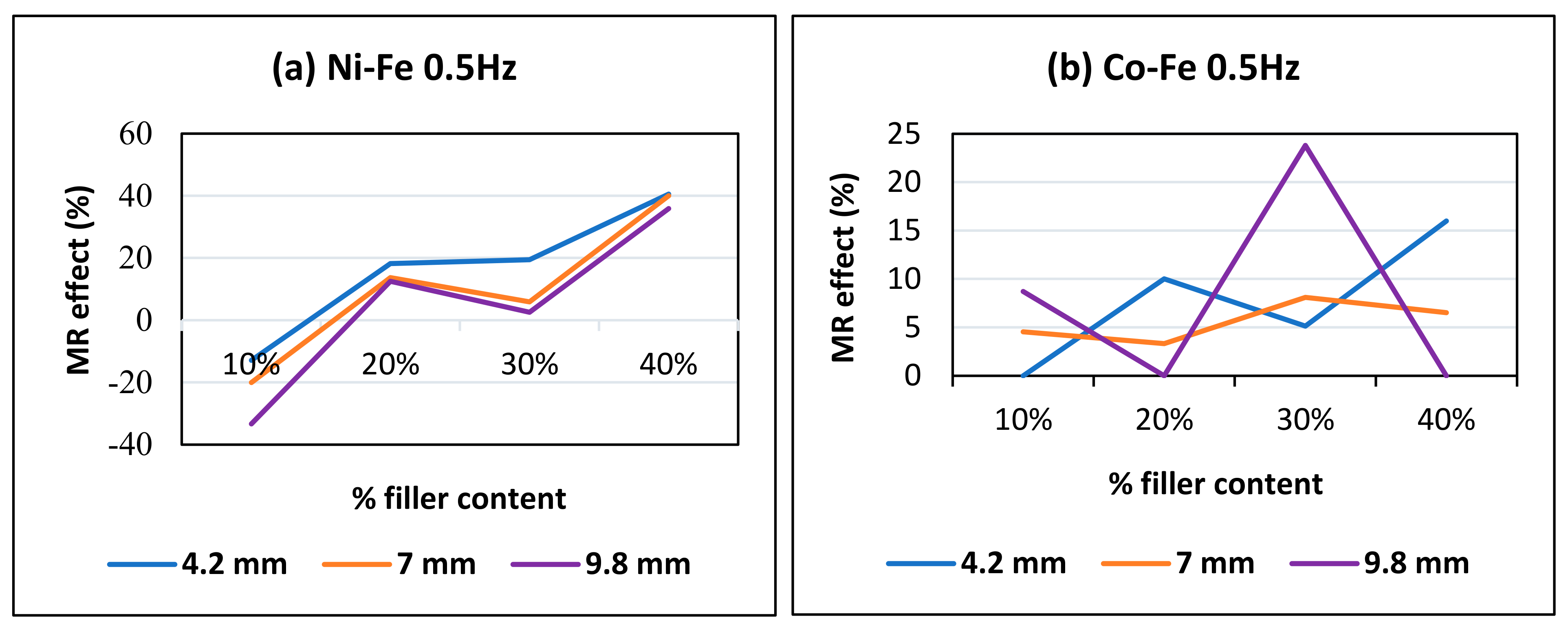
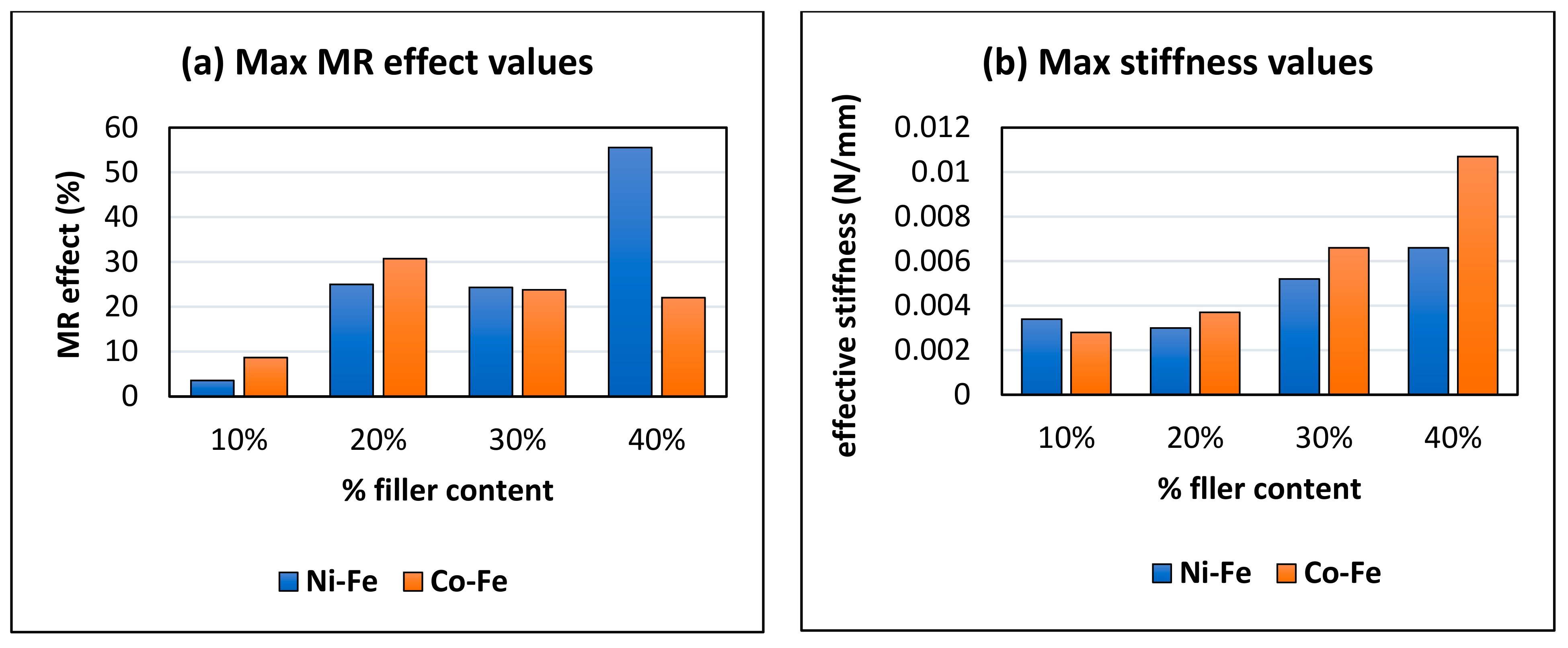
- The highest MR effect obtained was 55.56% for nickel and iron filled MRE and 30.76% for Co-Fe MRE. The MREs with nickel and iron particles showed a trend of increasing MR effect with increasing % filler content; while for Co-Fe MRE the MR effect increased up to an optimum % and then decreased;
- (4)
- The MREs with cobalt and iron particles produced higher stiffness while the MREs with nickel and iron produced a higher MR effect.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, T.; Xu, Y. Magnetorheological Elastomers: Materials and Applications. In Smart and Functional Soft Materials; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; Volume 15, p. 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.A.; Zafar, A.; Farooq, F.; Javed, M.F.; Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H. Geopolymer Concrete Compressive Strength via Artificial Neural Network, Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Interface System, and Gene Expression Programming With K-Fold Cross Validation. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 621163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.U.; Usman, M.; Farooq, S.H.; Kim, I.-H. Effect of Tuned Spring on Vibration Control Performance of Modified Liquid Column Ball Damper. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, A.A.; Stefanou, G.; Manolis, G.D. Stochastic response of structures with hybrid base isolation systems. Eng. Struct. 2018, 172, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.L.; Azeem, M.; Usman, M.; Farooq, H.; Hanif, A.; Fawad, M. Effect of near and far field earthquakes on performance of various base isolation systems. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2019, 18, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, L. Multi-resonant electromagnetic shunt in base isolation for vibration damping and energy harvesting. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 423, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tariq, M.; Usman, M.; Farooq, S.; Ullah, I.; Hanif, A. Investigation of the structural response of the mre-based mdof isolated structure under historic near- and far-fault earthquake loadings. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesmeci, S.; Gordaninejad, F.; Ryan, K.L.; Eltahawy, W. Design of a fail-safe magnetorheological-based system for three-dimensional earthquake isolation of structures. Mechatronics 2019, 64, 102296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, M.A.; Usman, M.; Umer, M.A.; Hanif, A. Recent progress in isotropic magnetorheological elastomers and their properties: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Jung, H.J. Recent developments of magneto- rheological elastomers for civil engineering applications. In Smart Material Actuators: Recent Advances in Material Characterization and Application; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Chang, K.; Cao, L.; Huang, Y. Performance of a nonlinear hybrid base isolation system under the ground motions. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 143, 106589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.D.; Usman, M.; Sung, S.H.; Moon, Y.J.; Jung, H.J. Feasibility Study of MR Elastomer-based Base Isolation System. J. Comput. Struct. Eng. Inst. Korea 2008, 21, 597–605. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Samali, B. Development and characterization of a magnetorheological elastomer based adaptive seismic isolator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 035005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Aracil, J.; Pereira, E.; Díaz, I.M.; Reynolds, P. Passive and active vibration isolation under isolator-structure interaction: Application to vertical excitations. Meccanica 2021, 56, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Ahmed, S.; Jung, H.J. State-Switched Control Algorithm fo Multi Degree of Freedom Smart Base Isolation System Employing MR Elastomer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Earthquake Engineering ans Seismology, Islamabad, Pakistan, 25–26 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, N.; Kumar, V.; Ryu, S.-R.; Choi, J.; Lee, D.-J. Magnetic response properties of natural-rubber-based magnetorhelogical elastomers with different-structured iron fillers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 513, 167106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winger, J.; Schümann, M.; Kupka, A.; Odenbach, S. Influence of the particle size on the magnetorheological effect of magnetorheological elastomers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 481, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, R.Z.A.; Johari, N.; Mazlan, S.A.; Aziz, S.A.A.; Nordin, N.A.; Nazmi, N.; Aqida, S.N.; Johari, M.A.F. Effects of silica on mechanical and rheological properties of EPDM-based magnetorheological elastomers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 30, 105033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.-H.; Jang, D.-D.; Usman, M.; Jung, H.-J. A feasibility study on smart base isolation systems using magneto-rheological elastomers. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2009, 32, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, A.; Sedaghati, R.; Rakheja, S. On the properties of magnetorheological elastomers in shear mode: Design, fabrication and characterization. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 159, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Jang, D.-D.; Kim, I.-H.; Jung, H.-J.; Koo, J.-H. Dynamic testing and modeling of magneto-rheological elastomers. In Proceedings of the ASME 2009 Conference Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems, Oxnard, CA, USA, 20–24 September 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bellelli, A.; Spaggiari, A. Magneto-mechanical characterization of magnetorheological elastomers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2019, 30, 2534–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, T.H.; Petríková, I.; Marvalová, B. Experimental characterization and viscoelastic modeling of isotropic and anisotropic magnetorheological elastomers. Polym. Test. 2020, 81, 106272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; Gonzalez-Rico, J.; Lopez-Donaire, M.; Arias, A.; Garcia-Gonzalez, D. New experimental insights into magneto-mechanical rate dependences of magnetorheological elastomers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 224, 109148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales-Martínez, I.A.; Palacios-Pineda, L.M.; Lozano-Sánchez, L.M.; Martínez-Romero, O.; Puente-Cordova, J.G.; Elías-Zúñiga, A. Enhancement of a magnetorheological PDMS elastomer with carbonyl iron particles. Polym. Test. 2017, 57, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Lee, D.-J. Iron particle and anisotropic effects on mechanical properties of magneto-sensitive elastomers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 441, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agirre-Olabide, I.; Elejabarrieta, M. A new magneto-dynamic compression technique for magnetorheological elastomers at high frequencies. Polym. Test. 2018, 66, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-J.; Lee, S.-J.; Jang, D.-D.; Kim, I.-H.; Koo, J.-H.; Khan, F. Dynamic characterization of magneto-rheological elastomers in shear mode. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 3930–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, A.K.; Hossain, M. A review on magneto-mechanical characterizations of magnetorheological elastomers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 200, 108348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatandoost, H.; Hemmatian, M.; Sedaghati, R.; Rakheja, S. Dynamic characterization of isotropic and anisotropic magnetorheological elastomers in the oscillatory squeeze mode superimposed on large static pre-strain. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 182, 107648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyeva, M.; Nagornov, D.; Orlov, G. Research on dynamic and mechanical properties of magnetoactive elastomers with high permeability magnetic filling agent at complex magneto-temperature exposure. Materials 2021, 14, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kumar, V.; Lee, D.-J. Compressive properties of magnetorheological elastomer with different magnetic fields and types of filler. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, D.; Murphy, N.; Ekins, R.; Jerrams, S. The evaluation of the effect of strain limits on the physical properties of Magnetorheological Elastomers subjected to uniaxial and biaxial cyclic testing. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 103, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khayam, S.U.; Usman, M.; Umer, M.A.; Rafique, A. Development and characterization of a novel hybrid magnetorheological elastomer incorporating micro and nano size iron fillers. Mater. Des. 2020, 192, 108748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, G.; Harrison, P. Large-strain behaviour of Magneto-Rheological Elastomers tested under uniaxial compression and tension, and pure shear deformations. Polym. Test. 2015, 42, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordaninejad, F.; Wang, X.; Mysore, P. Behavior of thick magnetorheological elastomers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2012, 23, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, M.; Alehashem, S.M.S.; Vatandoost, H.; Ni, Y.-Q.; Shahmardan, M.M. A new approach for modeling of magnetorheological elastomers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2016, 27, 1121–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanouki, M.A.; Sedaghati, R.; Hemmatian, M. Experimental characterization and microscale modeling of isotropic and anisotropic magnetorheological elastomers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 176, 107311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, N.; Kumar, V.; Lee, D.-J.; Choi, J. Magnetically active response of acrylonitrile-butadiene-rubber-based magnetorheological elastomers with different types of iron fillers and their hybrid. Compos. Commun. 2021, 24, 100657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaneyko, D.; Toshchevikov, V.; Saphiannikova, M.; Heinrich, G. Effects of particle distribution on mechanical properties of magneto-sensitive elastomers in a homogeneous magnetic field. Condens. Matter Phys. 2012, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vatandoost, H.; Rakheja, S.; Sedaghati, R. Effects of iron particles’ volume fraction on compression mode properties of magnetorheological elastomers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 522, 167552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, D.-J. The response force and rate of magneto-rheological elastomers with different fillers and magnetic fields. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 466, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.A.A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Ubaidillah, U.; Shabdin, M.K.; Yunus, N.A.; Nordin, N.A.; Choi, S.-B.; Rosnan, R.M. Enhancement of viscoelastic and electrical properties of magnetorheological elastomers with nanosized Ni-Mg cobalt-ferrites as fillers. Materials 2019, 12, 3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kramarenko, E.Y.; Chertovich, A.V.; Stepanov, G.V.; Semisalova, A.S.; Makarova, L.A.; Perov, N.S.; Khokhlov, A.R. Magnetic and viscoelastic response of elastomers with hard magnetic filler. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I. The influence of the magnetic field on the elastic properties of anisotropic magnetorheological elastomers. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 1666–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Padalka, O.; Wereley, N.; Bell, R. Impact of nanowire versus spherical microparticles in magnetorheological elastomer composites. In Proceedings of the 50th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Palm Springs, CA, USA, 4–7 May 2009; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriushchenko, P.; Nefedev, K.; Stepanov, G. Calculations of magnetoactive elastomer reactions in a uniform external magnetic field. Eur. Phys. J. B 2014, 87, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvek, M.; Kutalkova, E.; Moucka, R.; Urbanek, P.; Sedlacik, M. Lightweight, transparent piezoresistive sensors conceptualized as anisotropic magnetorheological elastomers: A durability study. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 183, 105816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berasategi, J.; Salazar, D.; Gomez, A.; Gutierrez, J.; Sebastián, M.S.; Bou-Ali, M.; Barandiaran, J.M. Anisotropic behaviour analysis of silicone/carbonyl iron particles magnetorheological elastomers. Rheol. Acta 2020, 59, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Lockette, P.R.; Kadlowec, J.; Koo, J.-H. Particle mixtures in magnetorheological elastomers (MREs). In Smart Structures and Materials 2006: Active Materials: Behavior and Mechanics; SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2006; Volume 6170, p. 61700T. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Dong, X.; Qi, M. Improved tunable range of the field-induced storage modulus by using flower-like particles as the active phase of magnetorheological elastomers. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 3504–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.R. (Ed.) ASM Specialty Handbook: Nickel, Cobalt, and Their Alloys; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.H.; Tran, T.N.; Yang, B. Investigation on the reaction of iron powder mixture as a portable heat source for thermoelectric power generators. J. Therm. Anal. 2014, 116, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zainudin, A.A.; Yunus, N.A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Shabdin, M.K.; Aziz, S.A.A.; Nordin, N.A.; Nazmi, N.; Rahman, M.A.A. Rheological and resistance properties of magnetorheological elastomer with cobalt for sensor application. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padalka, O.; Song, H.J.; Wereley, N.M.; Ii, J.A.F.; Bell, R.C. Stiffness and damping in Fe, Co, and Ni nanowire-based magnetorheological elastomeric composites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2275–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moksin, N.; Ismail, H.; Abdullah, M.K.; Shuib, R.K. Magnetorheological elastomer composites based on industrial waste nickel zinc ferrite and natural rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2019, 92, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
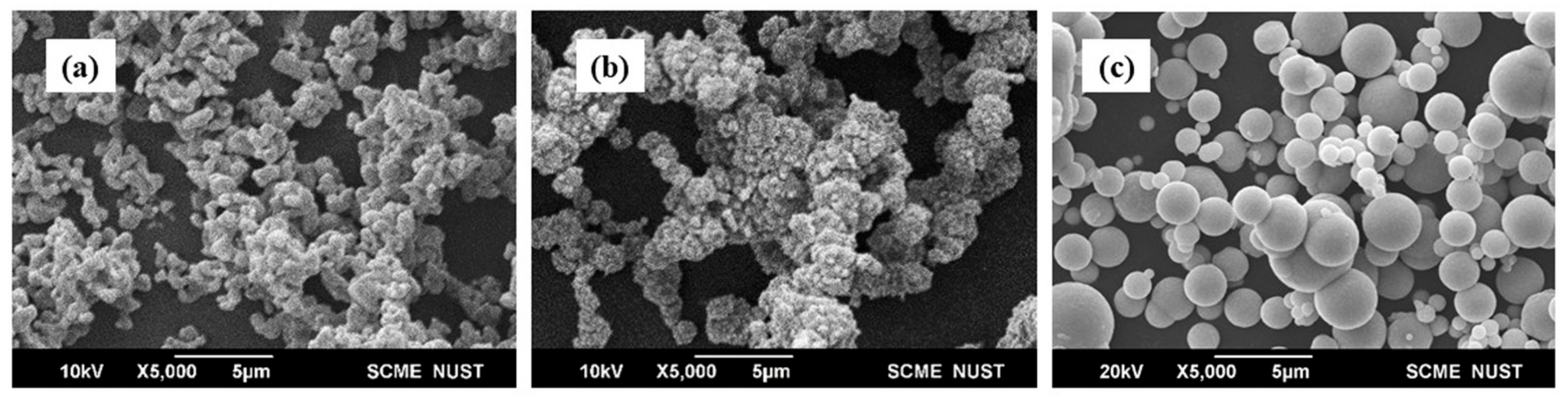
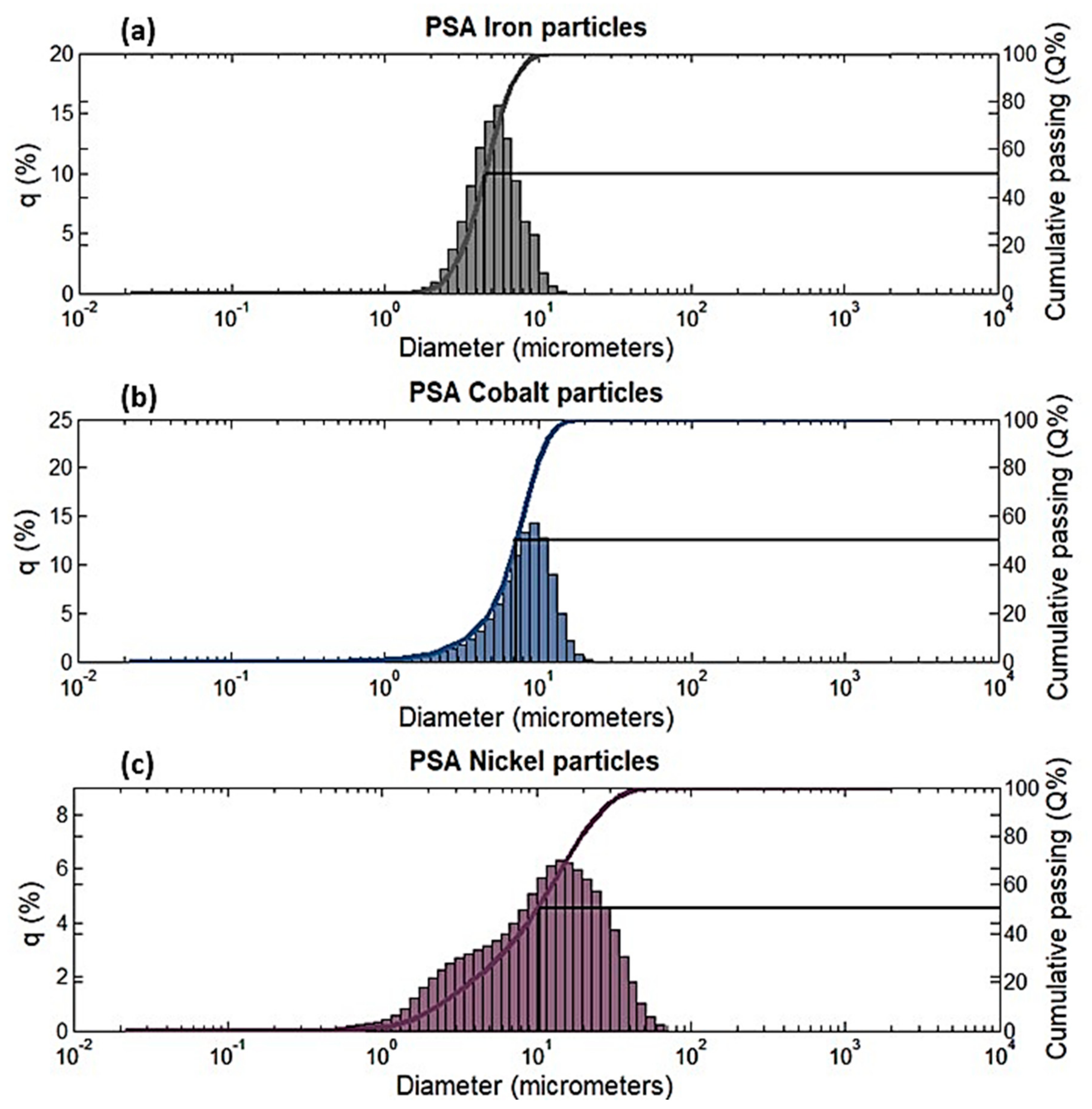

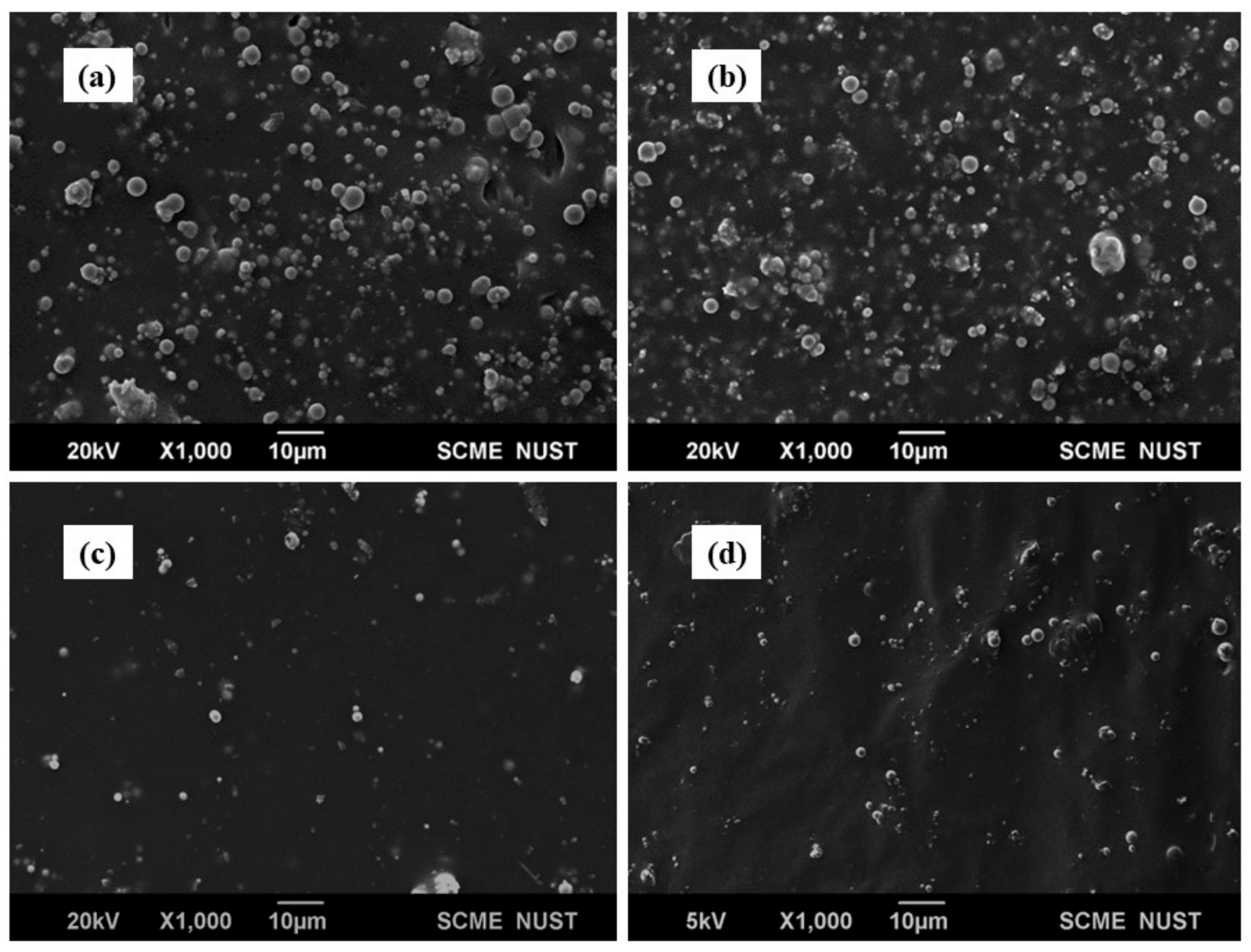
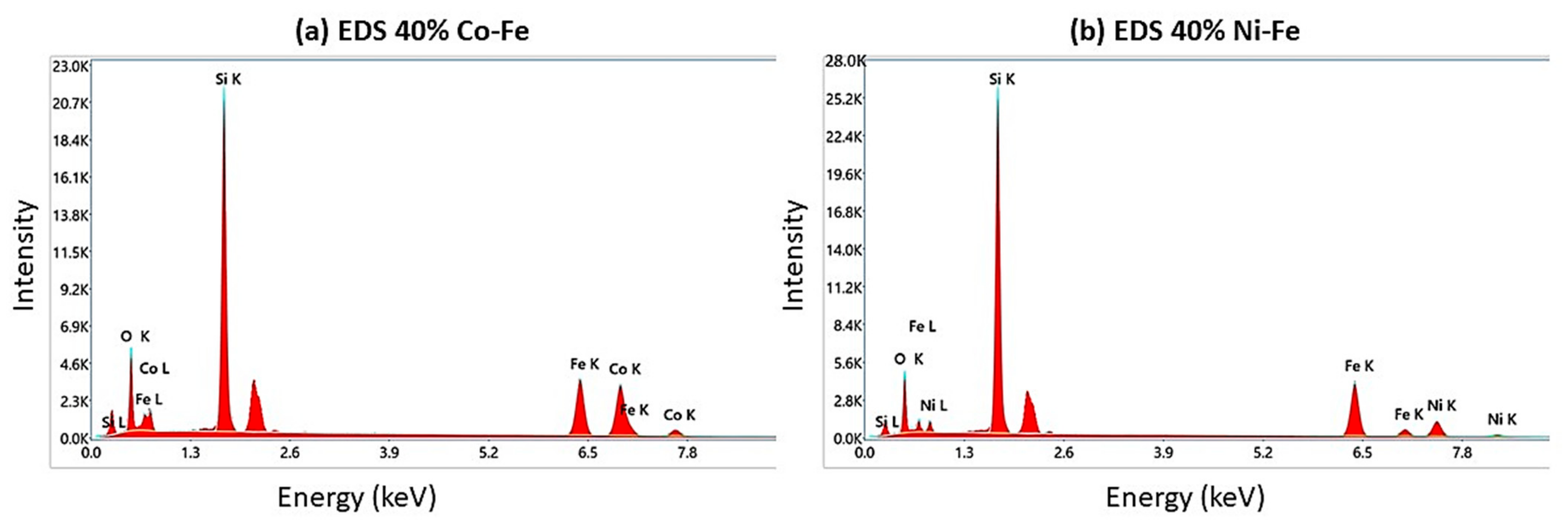
| Designation | Composition | No. of Samples | % of Particles by Vol of MRE (%) | Filler (g) (Co-Fe or Ni-Fe) | Rubber A = B (mL) | Silicone Oil by 10% Volume of MRE (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40% Co-Fe | Co & Fe | 2 | 20 & 20 | 5.89–6.08 | 2.38 | 0.95 |
| 40% Ni-Fe | Ni & Fe | 2 | 20 & 20 | 3.36–6.08 | 2.38 | 0.95 |
| 30% Co-Fe | Co & Fe | 2 | 15 & 15 | 4.42–4.56 | 2.85 | 0.95 |
| 30% Ni-Fe | Ni & Fe | 2 | 15 & 15 | 2.52–4.56 | 2.85 | 0.95 |
| 20% Co-Fe | Co & Fe | 2 | 10 & 10 | 2.95–3.04 | 3.33 | 0.95 |
| 20% Ni-Fe | Ni & Fe | 2 | 10 & 10 | 1.68–3.04 | 3.33 | 0.95 |
| 10% Co-Fe | Co & Fe | 2 | 5 & 5 | 1.47–1.52 | 3.8 | 0.95 |
| 10% Ni-Fe | Ni & Fe | 2 | 5 & 5 | 0.84–1.52 | 3.8 | 0.95 |
| Test Parameters | Cases/Variations | |
|---|---|---|
| % Filler content | iron + nickel | 10%, 20%, 30%,40% (Each having 50% iron and 50% nickel particles) |
| iron + cobalt | 10%, 20%, 30%, 40% (Each having 50% iron and 50% cobalt particles) | |
| Flux | 0 T, 0.1 T, 0.2 T, 0.3 T, 0.4 T | |
| Frequency | 0.5 Hz, 1 Hz, 2 Hz, 3 Hz, 5 Hz | |
| Disp. Amp | 4.2 mm (30% strain), 7 mm (50% strain), 9.8 mm (70% strain) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tahir, S.; Usman, M.; Umer, M.A. Effect of Volume Fraction on Shear Mode Properties of Fe-Co and Fe-Ni Filled Magneto-Rheological Elastomers. Polymers 2022, 14, 2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142968
Tahir S, Usman M, Umer MA. Effect of Volume Fraction on Shear Mode Properties of Fe-Co and Fe-Ni Filled Magneto-Rheological Elastomers. Polymers. 2022; 14(14):2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142968
Chicago/Turabian StyleTahir, Shayan, Muhammad Usman, and Malik Adeel Umer. 2022. "Effect of Volume Fraction on Shear Mode Properties of Fe-Co and Fe-Ni Filled Magneto-Rheological Elastomers" Polymers 14, no. 14: 2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142968
APA StyleTahir, S., Usman, M., & Umer, M. A. (2022). Effect of Volume Fraction on Shear Mode Properties of Fe-Co and Fe-Ni Filled Magneto-Rheological Elastomers. Polymers, 14(14), 2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142968







