Compression and Bending Properties of Short Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers Sandwich Structures Produced via Fused Filament Fabrication Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
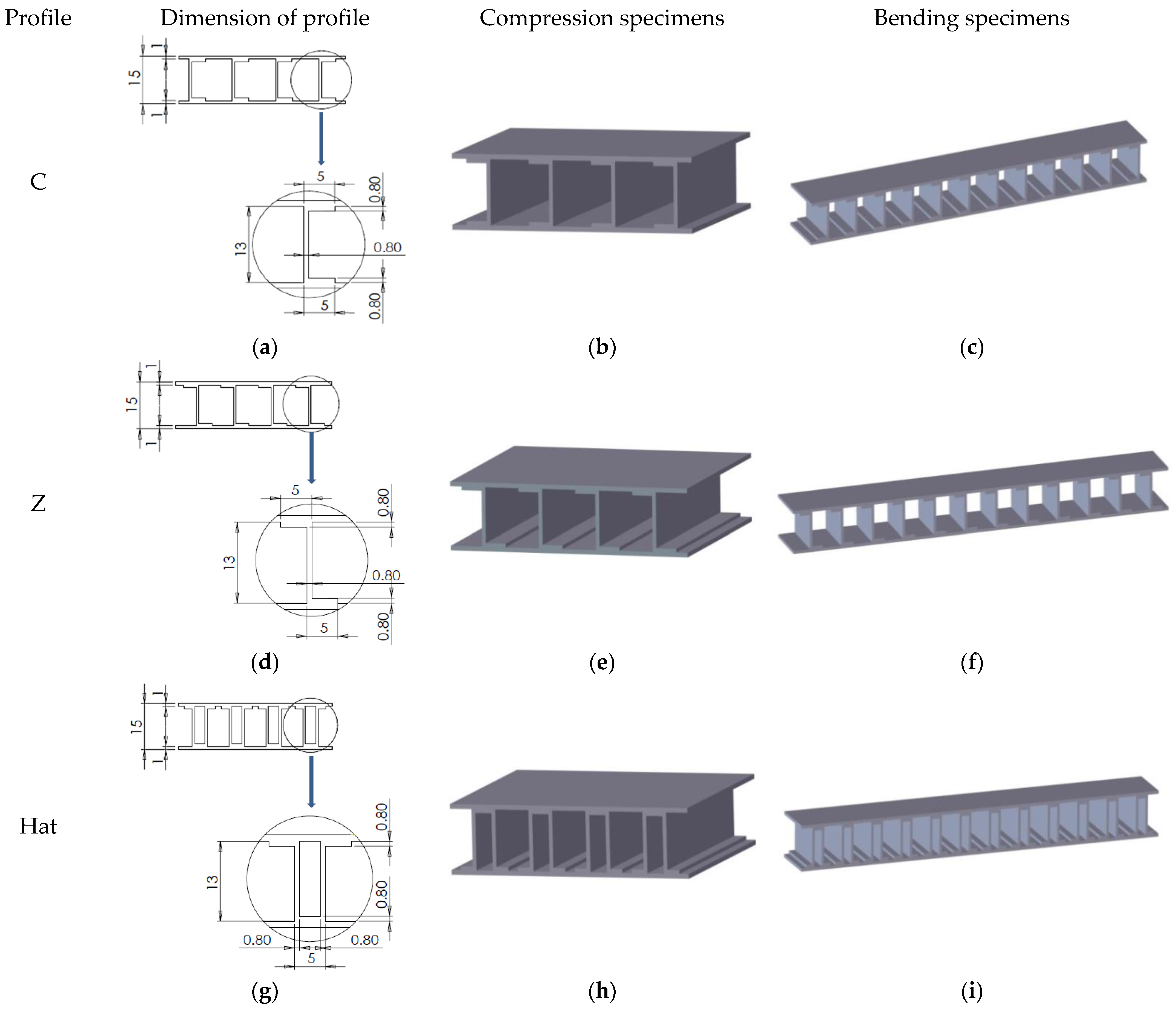
2.1. Design of Composite Sandwich Structures
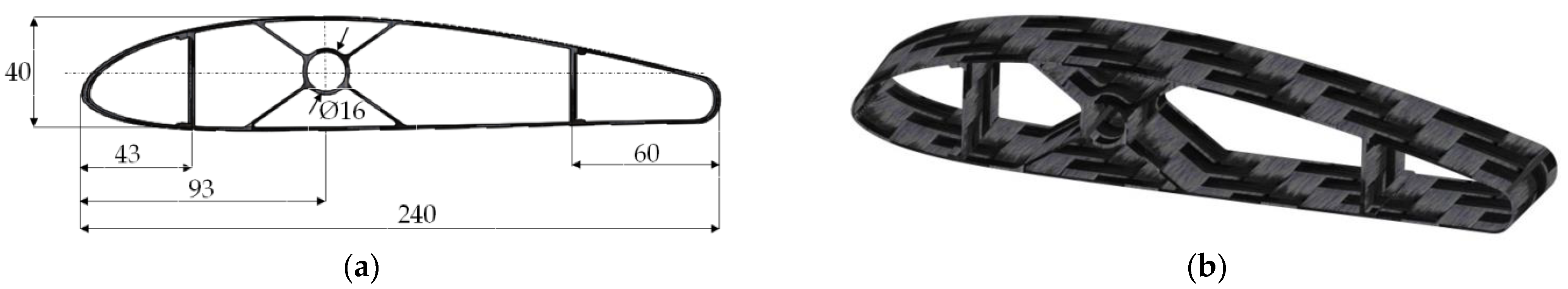
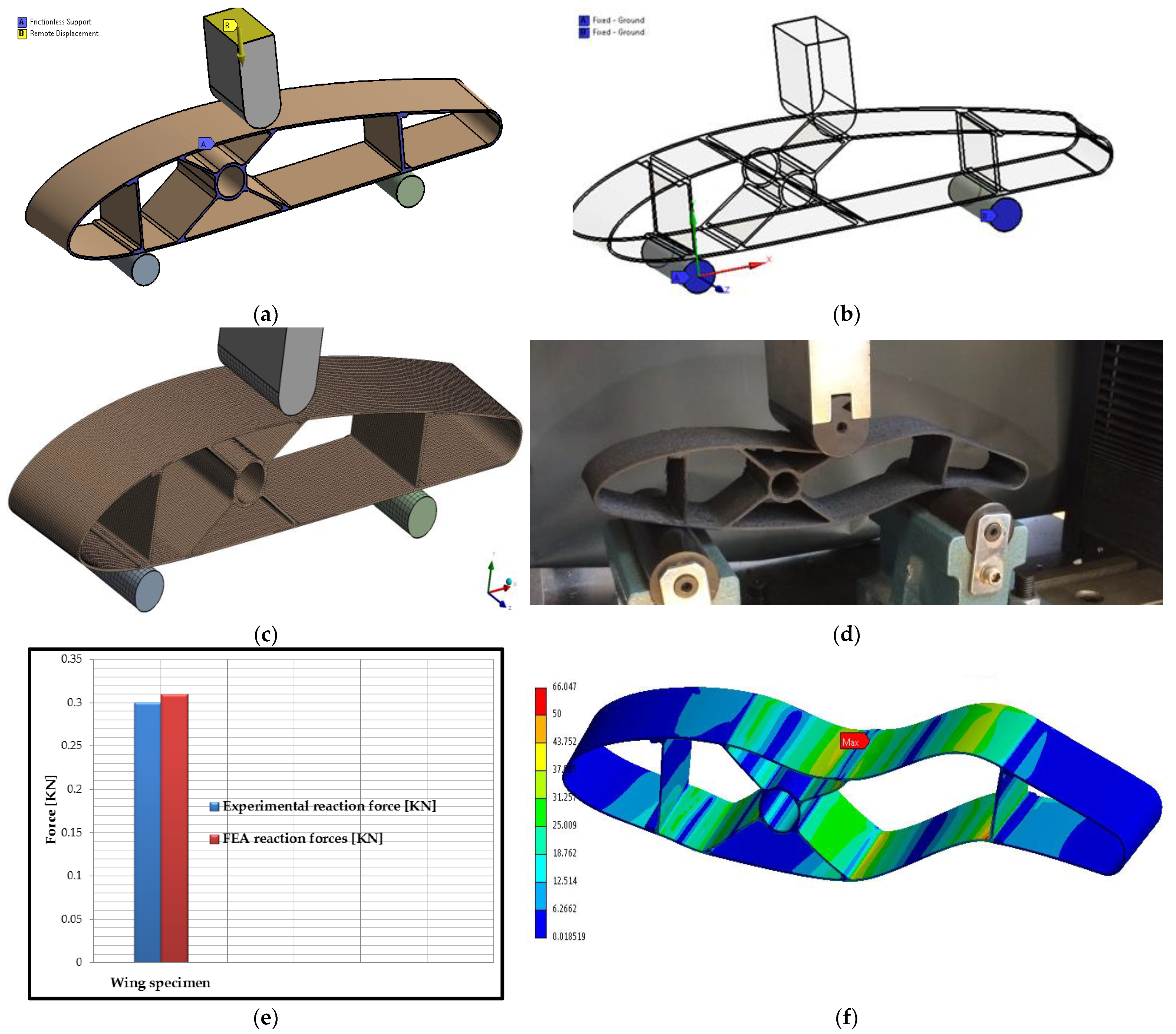
2.2. Design of Wing Sections
2.3. Manufacture of Sandwich Specimens and Wing Sections Using the FFF Process
2.3.1. Materials
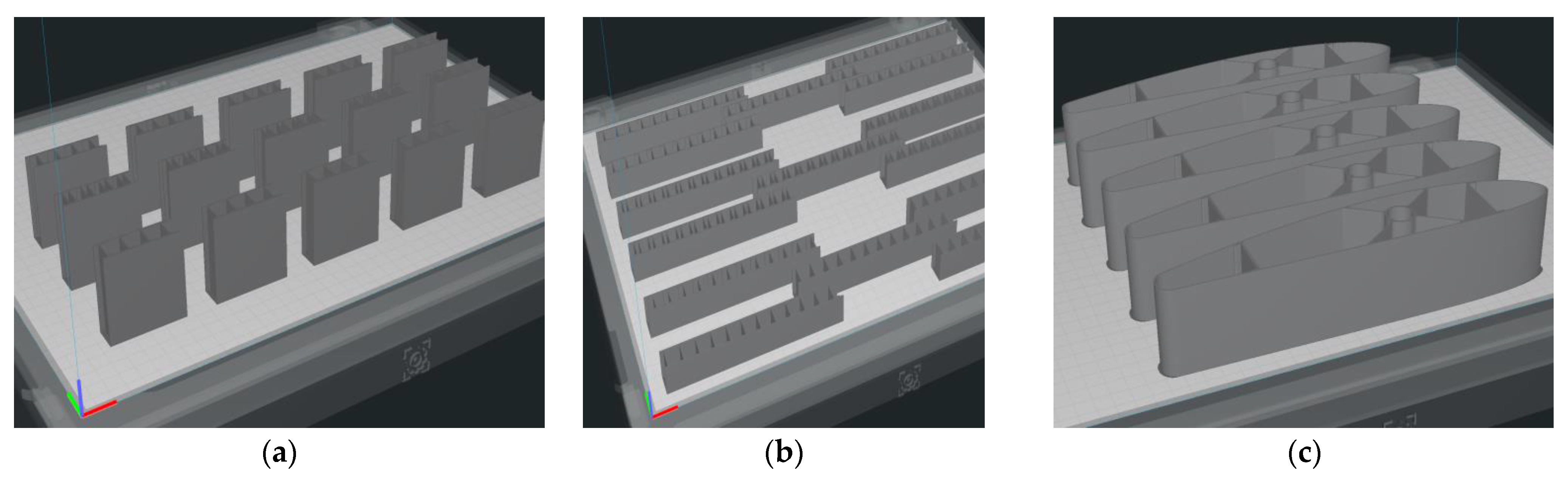
2.3.2. Manufacture of Composite Sandwich Specimens
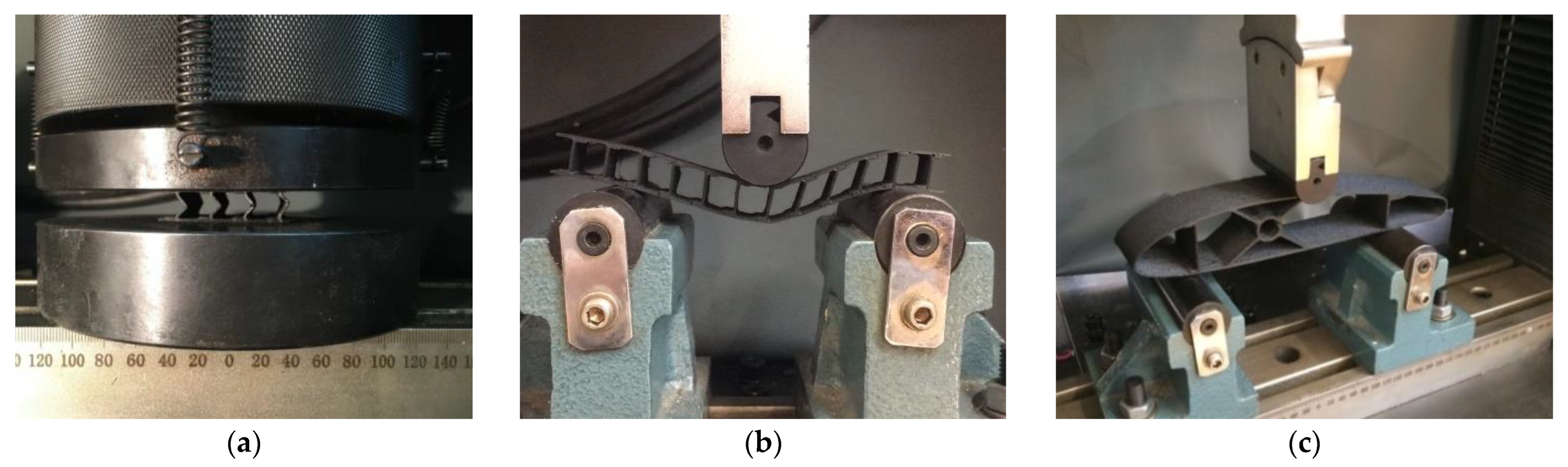
2.4. Testing of Composite Sandwich Specimens
3. Results and Discussion
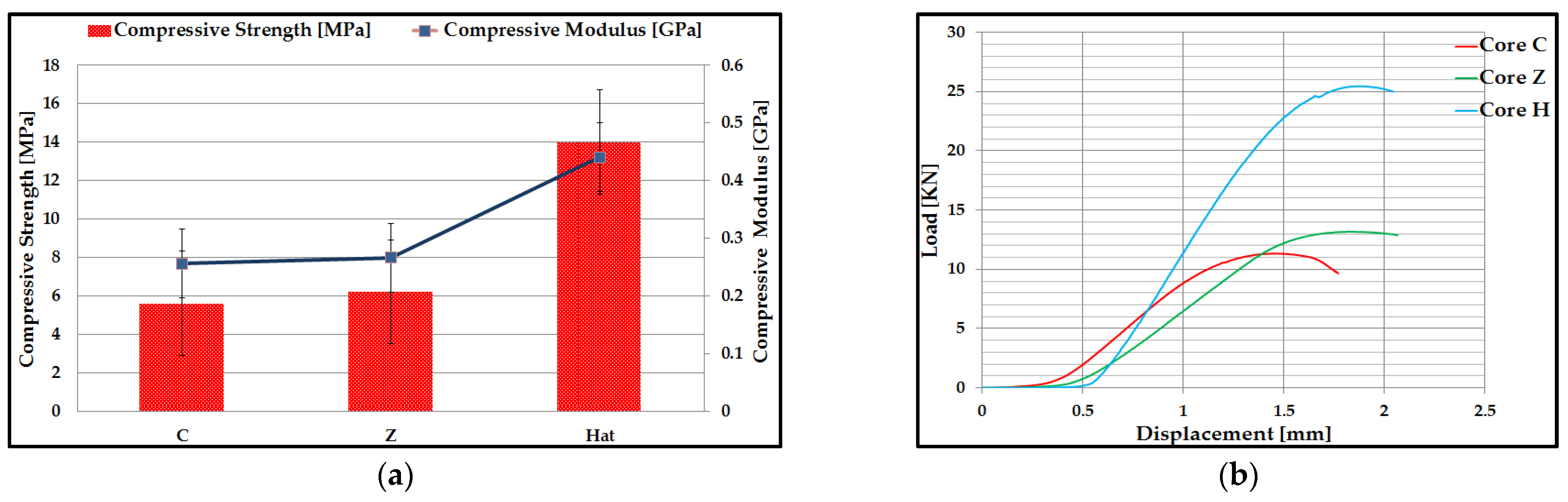
3.1. Flatwise Compression Performance of Carbon Fiber Sandwich Structures
3.2. Three-Point Bending Behavior of Carbon Fiber Sandwich Structures
- In the first domain, a linear elastic behavior of composite sandwich structures was observed. At the beginning of this domain, for Hat core specimens, the force increases and corresponds to a smaller displacement. This clearly demonstrates that the bending stiffness of this sandwich structure is enhanced by the shear stiffness of the Hat core;
- The second domain comprises the final range of the curve and corresponds to the nonlinear behavior of the material until the sudden rupture of the composite sandwich specimens. The end of this area highlights the failure mode of the composite sandwich structures. The core is shear loaded, and its failure occurs as the critical value (shear strength) of the core material is reached by the maximum shear stress.
3.3. Bending Performance of Wing Sections
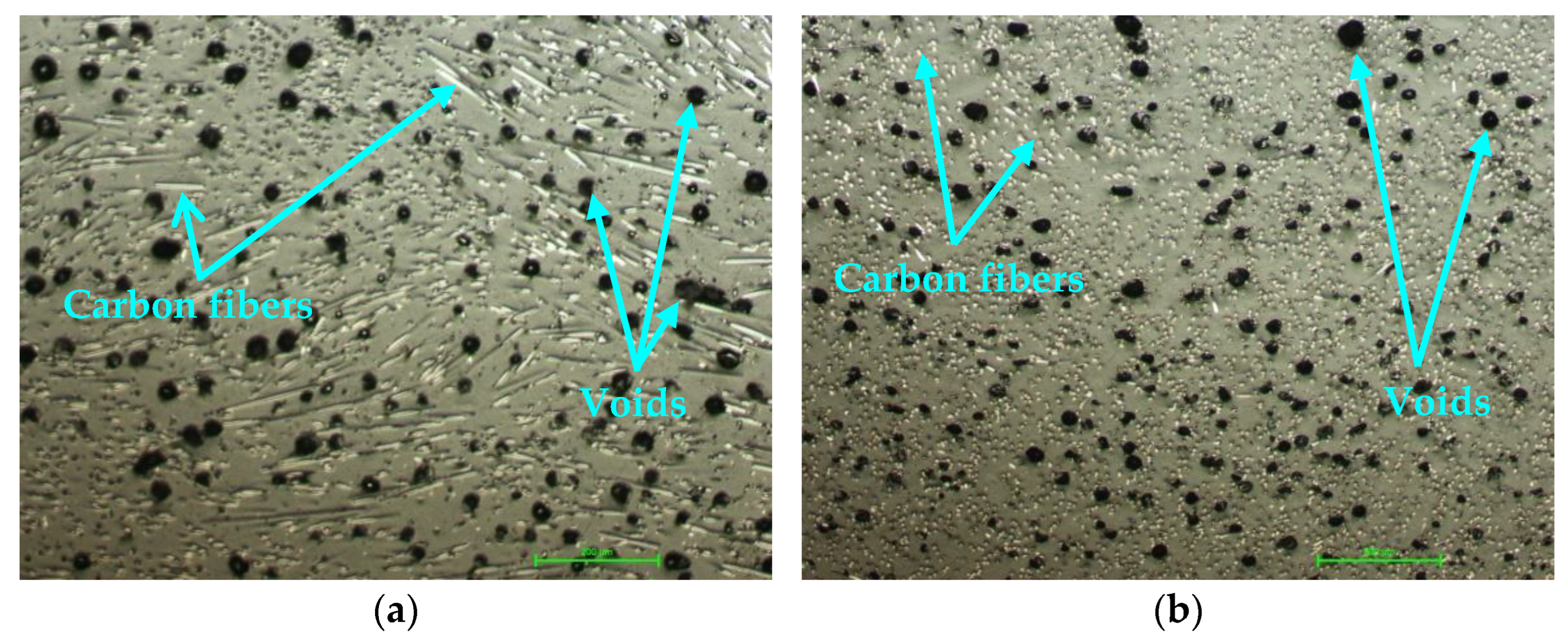
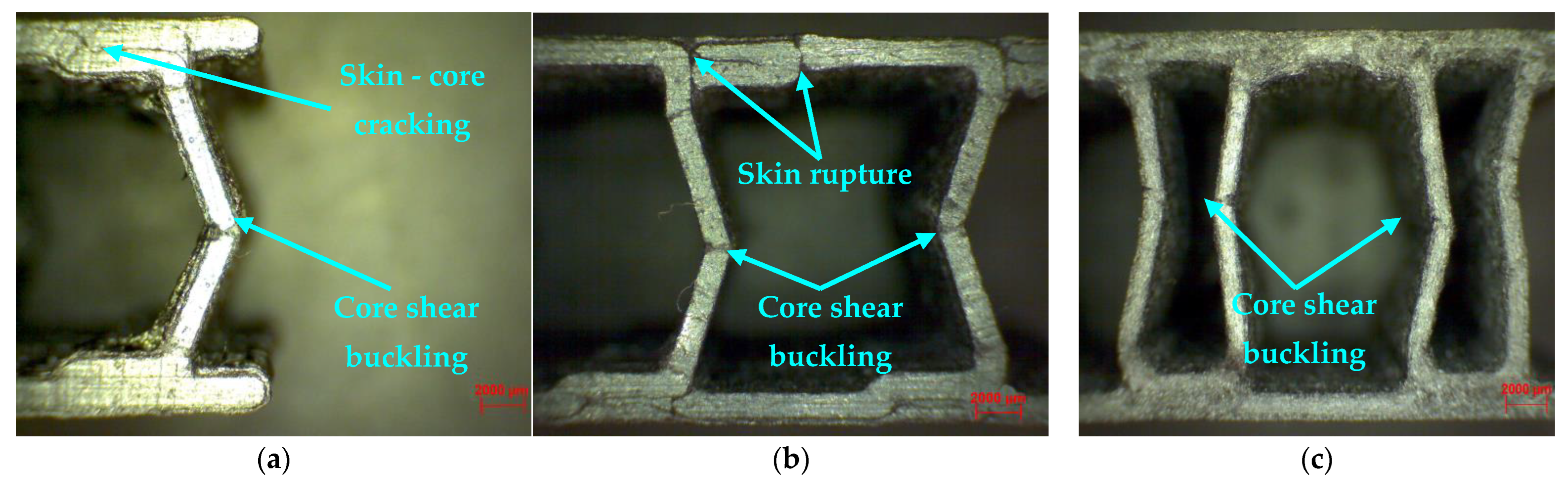
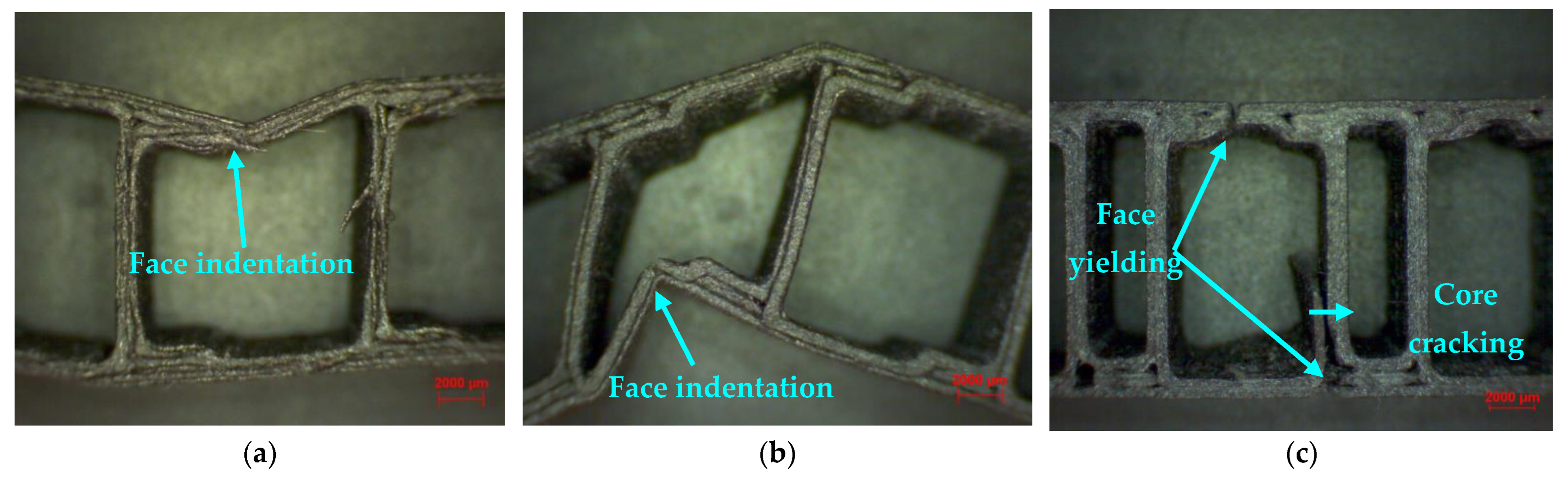
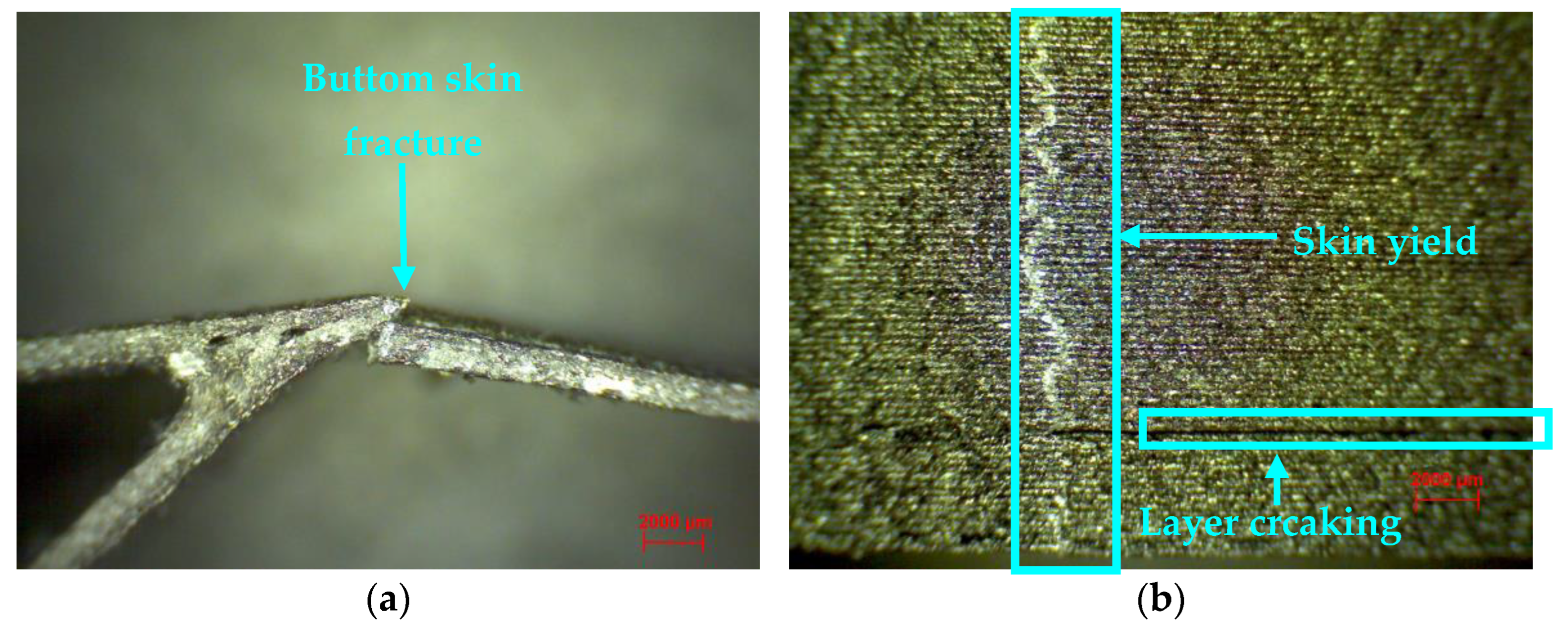
3.4. Microscopic Analysis of Composite Sandwich Structures
3.5. Analysis of the Specific Strength-to-Mass Ratio of Composite Specimens
- For compression tests, H core composite sandwich structures have the highest value; it turns out that this structure can be used for aeronautical components whose main requirement is compression. It can also be seen that the specimens with the Z-core sandwich structure have a higher ratio compared to the C-core structures. This is due to the fact that the Z-core, through the flanges positioned to the left and right of the core, absorbs the compression force much better.
- For the three-point bending tests, the sandwich structures showed a very close strength-to-mass ratio. However, C-core sandwich structures showed the highest strength-to-mass ratio, as confirmed by the frequent use of this structure in the wing airframes for small aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles.
3.6. Bending Finite Element Analysis of Composite Wing Sections
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Yan, G.; Wang, Z. Experimental and Numerical Study on Residual Strength of Honeycomb Sandwich Composite Structure after Lightning Strike. Aerospace 2022, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.V.; Pinheiro, I.F.; de Souza, S.F.; Mei, L.H.I.; Lona, L.M.F. Polymer Composites Reinforced with Natural Fibers and Nanocellulose in the Automotive Industry: A Short Review. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubino, F.; Nisticò, A.; Tucci, F.; Carlone, P. Marine Application of Fiber Reinforced Composites: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, V.V.; Le, V.S.; Louda, P.; Szczypiński, M.M.; Ercoli, R.; Růžek, V.; Łoś, P.; Prałat, K.; Plaskota, P.; Pacyniak, T.; et al. Low-Density Geopolymer Composites for the Construction Industry. Polymers 2022, 14, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, A.C.; Piedade, A.P. Sandwich Multi-Material 3D-Printed Polymers: Influence of Aging on the Impact and Flexure Resistances. Polymers 2021, 13, 4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Gou, J.; Hui, D. 3D printing of polymer matrix composites: A review and prospective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 110, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, S.; Do, T.; Tran, P. FDM-Based 3D Printing of Polymer and Associated Composite: A Review on Mechanical Properties, Defects and Treatments. Polymers 2020, 12, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, K.; Gao, G.; Ahzi, S. Synergistic reinforcement of polyamide-based composites by combination of short and continuous carbon fibers via fused filament fabrication. Compos. Struct. 2019, 207, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, P.; Li, S.; Ashcroft, I.A.; Jones, A.I. Material extrusion additive manufacturing of continuous fibre reinforced polymer matrix composites: A review and outlook. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 224, 109143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, F.; Cong, W.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H. Additive manufacturing of carbon fiber-reinforced plastic composites using fused deposition modeling: Effects of process parameters on tensile properties. J. Compos. Mater. 2017, 51, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Cheng, Y.; Ye, W.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Miao, Z.; Rudykh, S. Effect of Process Parameters on Tensile Mechanical Properties of 3D Printing Continuous Carbon Fiber-Reinforced PLA Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, R.T.L.; Amatte, I.C.; Dutra, T.A.; Bürger, D. Experimental characterization and micrography of 3D printed PLA and PLA reinforced with short carbon fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 124, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasa, E.; Ersoy, K. Dimensional Accuracy and Mechanical Properties of Chopped Carbon Reinforced Polymers Produced by Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2019, 12, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calignano, F.; Lorusso, M.; Roppolo, I.; Minetola, P. Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of a Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Nylon Filament for 3D Printing. Machines 2020, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Wang, K.; Chen, C.-B.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zeng, D.; Su, X.; Yang, H. Process-structure-property analysis of short carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite via fused filament fabrication. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 64, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.H.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z.; Song, L.; Li, Z. Short fiber reinforced composites for fused deposition modeling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 301, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, A.N.; Barry, J.N.; McDonnell, K.A.; Dowling, D.P. Fabrication of continuous carbon, glass and Kevlar fibre-reinforced polymer composites using additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 16, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Mori, K.I.; Maeno, T. 3D printing of carbon fibre-reinforced plastic parts. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 2811–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, T.; Tanaka, T.; Nomura, T.; Yuasa, R. Comparison of strength of 3D printing objects using short fiber and continuous long fiber. Proc. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 406, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadizadeh, M.; Gupta, A.; Fidan, I. Mechanical benchmarking of additively manufactured continuous and short carbon fiber reinforced nylon. J. Compos. Mater. 2021, 55, 3629–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo-Lozada, J.; Ahuett-Garza, H.; Orta-Castañón, P.; Verbeeten, W.M.; Sáiz-González, D. Tensile properties and failure behavior of chopped and continuous carbon fiber composites produced by additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 26, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Calvo, M.; López-Gómez, I.; Chamberlain-Simon, N.; León-Salazar, J.L.; Guillén-Girón, T.; Corrales-Cordero, J.S.; Sánchez-Brenes, O. Evaluation of compressive and flexural properties of continuous fiber fabrication additive manufacturing technology. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupone, F.; Padovano, E.; Venezia, C.; Badini, C. Experimental Characterization and Modeling of 3D Printed Continuous Carbon Fibers Composites with Different Fiber Orientation Produced by FFF Process. Polymers 2022, 14, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justo, J.; Távara, L.; García-Guzmán, L.; París, F. Characterization of 3D printed long fibre reinforced composites. Compos. Struct. 2018, 185, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iragi, M.; Pascual-González, C.; Esnaola, A.; Lopes, C.S.; Aretxabaleta, L. Ply and interlaminar behaviours of 3D printed continuous carbon fibre-reinforced thermoplastic laminates; effects of processing conditions and microstructure. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chacón, J.M.; Caminero, M.A.; Núñez, P.J.; García-Plaza, E.; García-Moreno, I.; Reverte, J.M. Additive manufacturing of continuous fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites using fused deposition modelling: Effect of process parameters on mechanical properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 181, 107688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowski, A.; Vogel, C.; Behnisch, T.; Geske, V.; Gude, M.; Modler, N. Additive Manufacturing-Based In Situ Consolidation of Continuous Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Polycarbonate. Materials 2021, 14, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Sun, Q.; Li, Z.; Su, X.; Yan, W. Longitudinal compression failure of 3D printed continuous carbon fiber reinforced composites: An experimental and computational study. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 146, 106416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dul, S.; Fambri, L.; Pegoretti, A. High-Performance Polyamide/Carbon Fiber Composites for Fused Filament Fabrication: Mechanical and Functional Performances. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 5066–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blok, L.G.; Longana, M.L.; Yu, H.; Woods, B.K.S. An investigation into 3D printing of fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Klift, F.; Koga, Y.; Todoroki, A.; Ueda, M.; Hirano, Y.; Matsuzaki, R. 3D Printing of Continuous Carbon Fibre Reinforced Thermo-Plastic (CFRTP) Tensile Test Specimens. Open J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 6, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammadizadeh, M.; Fidan, I. Tensile Performance of 3D-Printed Continuous Fiber-Reinforced Nylon Composites. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Song, S.; Bai, Y.; Wu, D. Tensile and flexural behaviors of additively manufactured continuous carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Struct. 2019, 225, 111147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Yan, B.; Peng, F. Manufacturing and 3D printing of continuous carbon fiber prepreg filament. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K.; Todoroki, A.; Mizutani, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Koga, Y.; Matsuzaki, R.; Ueda, M.; Hirano, Y. Bending fracture rule for 3D-printed curved continuous-fiber composite. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2019, 28, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekoi, E.J.; Dickson, A.N.; Dowling, D.P. Investigating the fatigue and mechanical behaviour of 3D printed woven and nonwoven continuous carbon fibre reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 212, 108704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, H.; Tyas, D.; Molony, S. Tensile and fatigue failure of 3D printed parts with continuous fibre reinforcement. Int. J. Rapid Manuf. 2017, 6, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminero, M.A.; Chacón, J.M.; García-Moreno, I.; Rodríguez, G.P. Impact damage resistance of 3D printed continuous fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites using fused deposition modelling. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 148, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, S.F.; Mathur, K.; Seyam, A.-F.M. Impact resistance and failure mechanism of 3D printed continuous fiber-reinforced cellular composites. J. Text. Inst. 2021, 112, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, S.M.; Enescu, L.A.; Pop, M.A. Mechanical Performances of Lightweight Sandwich Structures Produced by Material Extrusion-Based Additive Manufacturing. Polymers 2020, 12, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.W.; Hussain, G.; Al-Ghamdi, K.A.; Altaf, K. Mechanical properties of an additive manufactured CF-PLA/ABS hybrid composite sheet. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2019, 34, 1577–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D.M.B.; Ahmad, R. Tensile mechanical behaviour of multi-polymer sandwich structures via fused deposition modelling. Polymers 2020, 12, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, C.; Liu, L.; Bian, W.; Leng, J.; Liu, Y. Bending performance and failure behavior of 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced composite corrugated sandwich structures with shape memory capability. Compos. Struct. 2021, 262, 113626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, H.S.; Bonthu, D.; Gururaj, S.; Prabhakar, P.; Doddamani, M. Flexural response of 3D printed sandwich composite. Compos. Struct. 2021, 263, 113732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galatas, A.; Hassanin, H.; Zweiri, Y.; Seneviratne, L. Additive manufactured sandwich composite/ABS parts for unmanned aerial vehicle applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azarov, A.V.; Antonov, F.K.; Golubev, M.; Khaziev, A.; Ushanov, S.A. Composite 3D printing for the small size unmanned aerial vehicle structure. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 169, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultrafuse PAHT CF15. Available online: https://www.ultrafusefff.com/product-category/innopro/paht-cf/ (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Belei, C.; Joeressen, J.; Amancio-Filho, S.T. Fused-Filament Fabrication of Short Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polyamide: Parameter Optimization for Improved Performance under Uniaxial Tensile Loading. Polymers 2022, 14, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, F.; Cong, W.; Qiu, J.; Wei, J.; Wang, S. Additive Manufacturing of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 80, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papon, E.A.; Haque, A. Fracture Toughness of Additively Manufactured Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composites. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 26, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Werken, N.; Tekinalp, H.; Khanbolouki, P.; Ozcan, S.; Williams, A.; Tehrani, M. Additively Manufactured Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Composites: State of the Art and Perspective. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 31, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C365-03; Standard Test Method for Flatwise Compressive Properties of Sandwich Core. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.
- ASTM C393-C393M-06; Standard Test Method for Core Shear Properties of Sandwich Constructions by Beam Flexure. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006.
- Nath, S.D.; Nilufar, S. Performance Evaluation of Sandwich Structures Printed by Vat Photopolymerization. Polymers 2022, 14, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Liu, L.; Bian, W.; Leng, J.; Liu, Y. Compression Behavior and Energy Absorption of 3D Printed Continuous Fiber Reinforced Composite Honeycomb Structures with Shape Memory Effects. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 38, 101842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F. Cellular Solids: Structure and Properties; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Jia, Z.; Scarpa, F.; Yao, C.W.; Wang, L. 3D printed hierarchical honeycombs with shape integrity under large compressive deformations. Mater. Des. 2018, 137, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelanconi, M.; Ortona, A. Nature-Inspired, Ultra-Lightweight Structures with Gyroid Cores Produced by Additive Manufacturing and Reinforced by Unidirectional Carbon Fiber Ribs. Materials 2019, 12, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayrilmis, N.; Nagarajan, R.; Kuzman, M.K. Effects of the Face/Core Layer Ratio on the Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Wood/Polylactic Acid (PLA) Green Biocomposite Panels with a Gyroid Core. Polymers 2020, 12, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buican, G.R.; Zaharia, S.-M.; Pop, M.A.; Chicos, L.-A.; Lancea, C.; Stamate, V.-M.; Pascariu, I.S. Fabrication and Characterization of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Sandwich Structures Obtained by Fused Filament Fabrication Process. Coatings 2021, 11, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, G.D.; Dikshit, V.; Nagalingam, A.P.; Goh, G.L.; Agarwala, S.; Sing, S.L.; Wei, J.; Yeong, W.Y. Characterization of mechanical properties and fracture mode of additively manufactured carbon fiber and glass fiber reinforced thermoplastics. Mater. Des. 2018, 137, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicos, L.-A.; Pop, M.A.; Zaharia, S.-M.; Lancea, C.; Buican, G.R.; Pascariu, I.S.; Stamate, V.-M. Infill Density Influence on Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Short Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polyamide Composites Manufactured by FFF Process. Materials 2022, 15, 3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncius, T.; Rimašauskas, M.; Rimašauskienė, R. Interlayer Adhesion Analysis of 3D-Printed Continuous Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.; Wetmore, N.; Czabaj, M. Interlayer fracture toughness of additively manufactured unreinforced and carbon-fiber-reinforced acrylonitrile butadiene styrene. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 508–515. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.; Fan, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Du, Y.; Zhao, H. Failure mechanism of brass with three V-notches characterized by acoustic emission in in situ three-point bending tests. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2016, 18, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebretinsae, F.; Mikkelsen, O.; Akessa, A.D. Strength analysis of 3D printed carbon fibre reinforced thermoplastic using experimental and numerical methods. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 700, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuganti, S.; Soliman, E.; Reda Taha, M. 3D-Printed Pseudo Ductile Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Composite Using Discrete Fiber Orientations. Fibers 2020, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, M.J. Evaluation of the Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Carbon Fiber Composites. Ph.D. Thesis, South Dakota State University, Brookings, SD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]




| FFF Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Infill density [%] | 100 |
| Layer height [mm] | 0.2 |
| Printing speed [mm/sec] | 50 |
| Extrusion temperature [°C] | 260 |
| Bed Temperature [°C] | 100 |
| Nozzle diameter [mm] | 0.6 |
| Composite Sandwich Specimens | Mean (m) | Standard Deviation (s) | Coefficient of Variation (CV)% |
|---|---|---|---|
| C core—Compressive Strength (MPa) | 5.60 | 0.55 | 9.78 |
| Z core—Compressive Strength (MPa) | 6.20 | 0.45 | 7.21 |
| Hat core—Compressive Strength (MPa) | 14.00 | 1.22 | 8.75 |
| C core—Compressive Modulus (GPa) | 0.25 | 0.02 | 8.99 |
| Z core—Compressive Modulus (GPa) | 0.26 | 0.02 | 8.00 |
| Hat core—Compressive Modulus (GPa) | 0.44 | 0.03 | 6.81 |
| Composite Sandwich Specimens | Mean (m) | Standard Deviation (s) | Coefficient of Variation (CV)% |
|---|---|---|---|
| C core—Bending Strength (MPa) | 12.40 | 0.55 | 4.43 |
| Z core—Bending Strength (MPa) | 12.20 | 1.10 | 9.01 |
| Hat core—Bending Strength (MPa) | 17.00 | 0.71 | 4.17 |
| C core—Bending Modulus (GPa) | 0.49 | 0.01 | 2.04 |
| Z core—Bending Modulus (GPa) | 0.48 | 0.02 | 4.16 |
| Hat core—Bending Modulus (GPa) | 0.60 | 0.01 | 1.66 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaharia, S.M.; Pop, M.A.; Chicos, L.-A.; Buican, G.R.; Lancea, C.; Pascariu, I.S.; Stamate, V.-M. Compression and Bending Properties of Short Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers Sandwich Structures Produced via Fused Filament Fabrication Process. Polymers 2022, 14, 2923. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142923
Zaharia SM, Pop MA, Chicos L-A, Buican GR, Lancea C, Pascariu IS, Stamate V-M. Compression and Bending Properties of Short Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers Sandwich Structures Produced via Fused Filament Fabrication Process. Polymers. 2022; 14(14):2923. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142923
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaharia, Sebastian Marian, Mihai Alin Pop, Lucia-Antoneta Chicos, George Razvan Buican, Camil Lancea, Ionut Stelian Pascariu, and Valentin-Marian Stamate. 2022. "Compression and Bending Properties of Short Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers Sandwich Structures Produced via Fused Filament Fabrication Process" Polymers 14, no. 14: 2923. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142923
APA StyleZaharia, S. M., Pop, M. A., Chicos, L.-A., Buican, G. R., Lancea, C., Pascariu, I. S., & Stamate, V.-M. (2022). Compression and Bending Properties of Short Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers Sandwich Structures Produced via Fused Filament Fabrication Process. Polymers, 14(14), 2923. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142923






