Sodium Silicate from Rice Husk Ash and Their Effects as Geopolymer Cement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
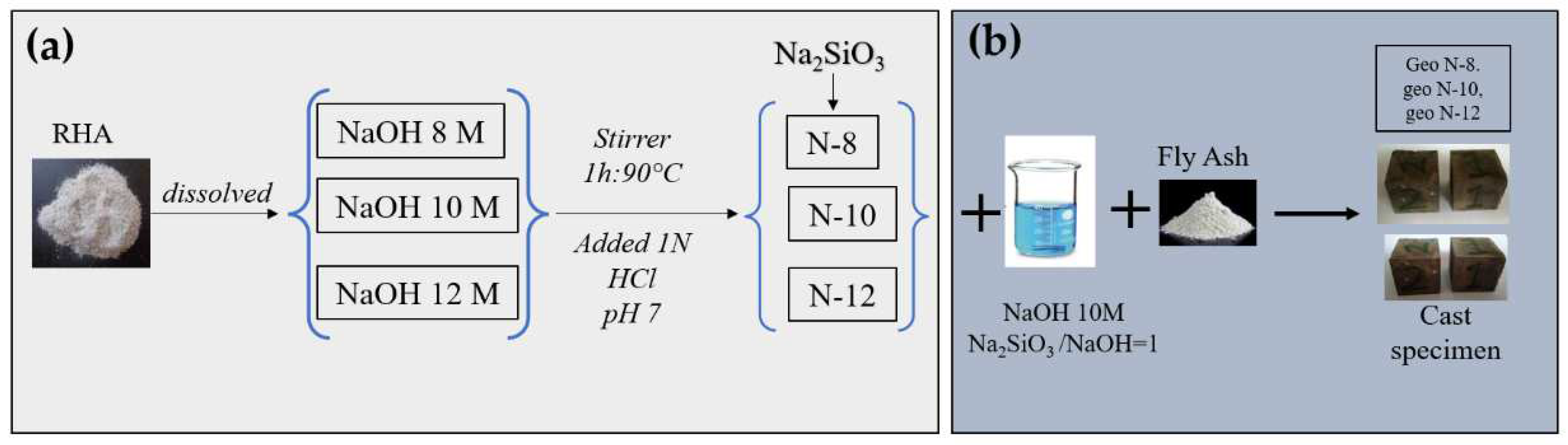
2.2. Synthesis of Sodium Silicate
2.3. Preparation of Geopolymer Paste
2.4. Microstructure Characterization
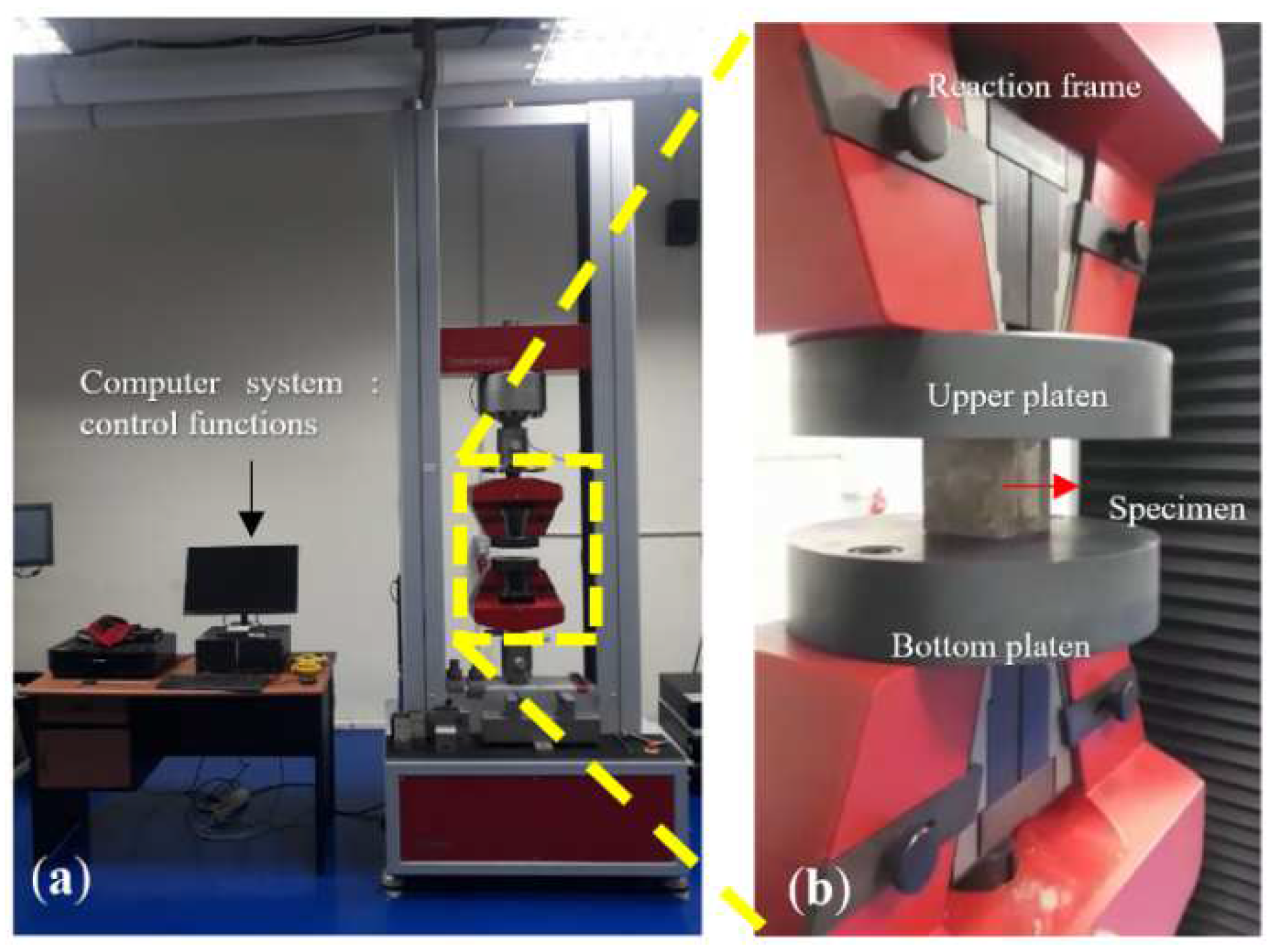
2.5. Testing Procedure
2.5.1. Water Absorption, Bulk Density, and Compressive Strength
2.5.2. Flexural Strength and Fracture Toughness
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mechanical Properties of Geopolymer Cement
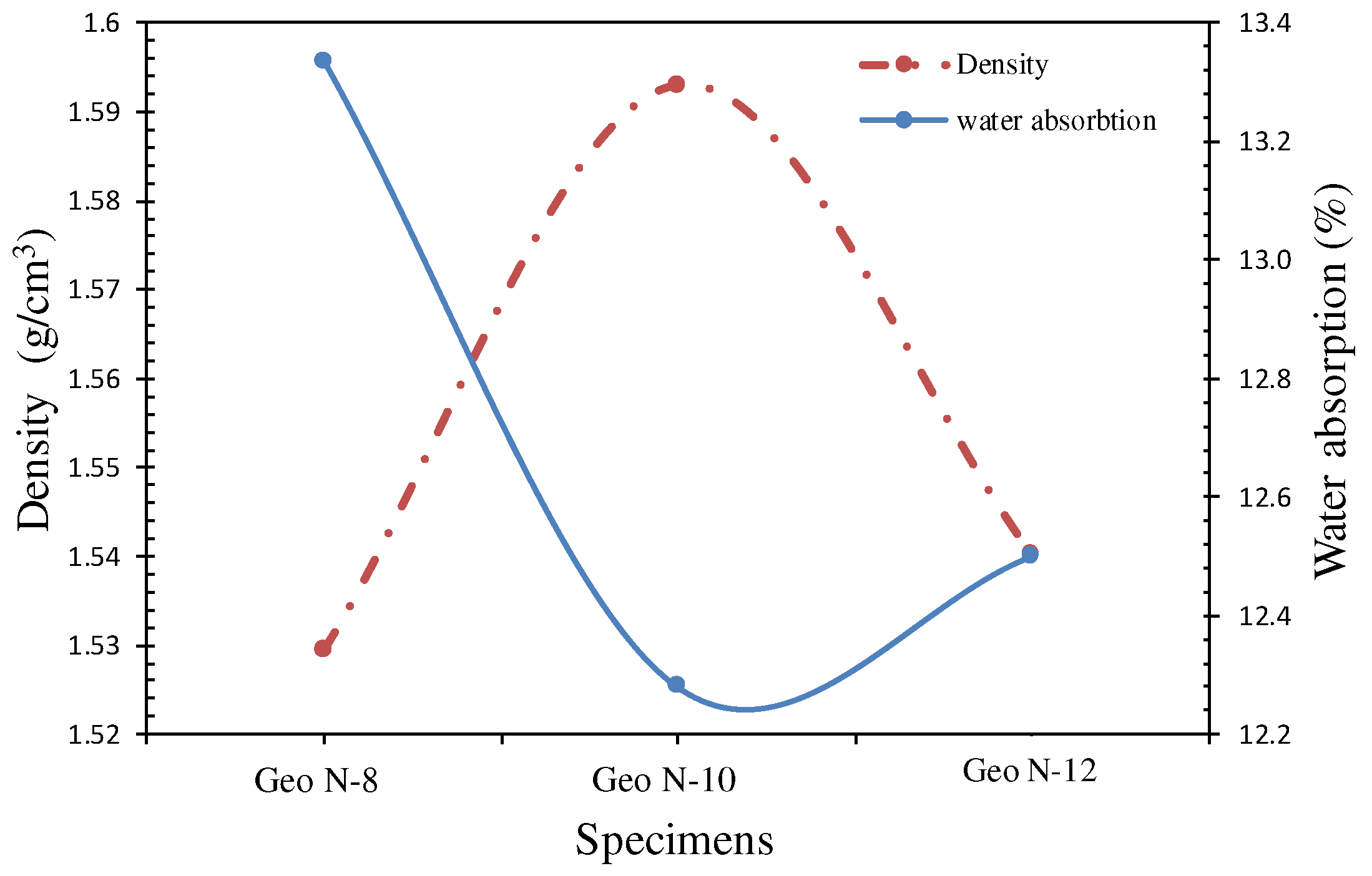
3.1.1. Bulk Density
3.1.2. Water Absorption
3.1.3. Compressive Strength
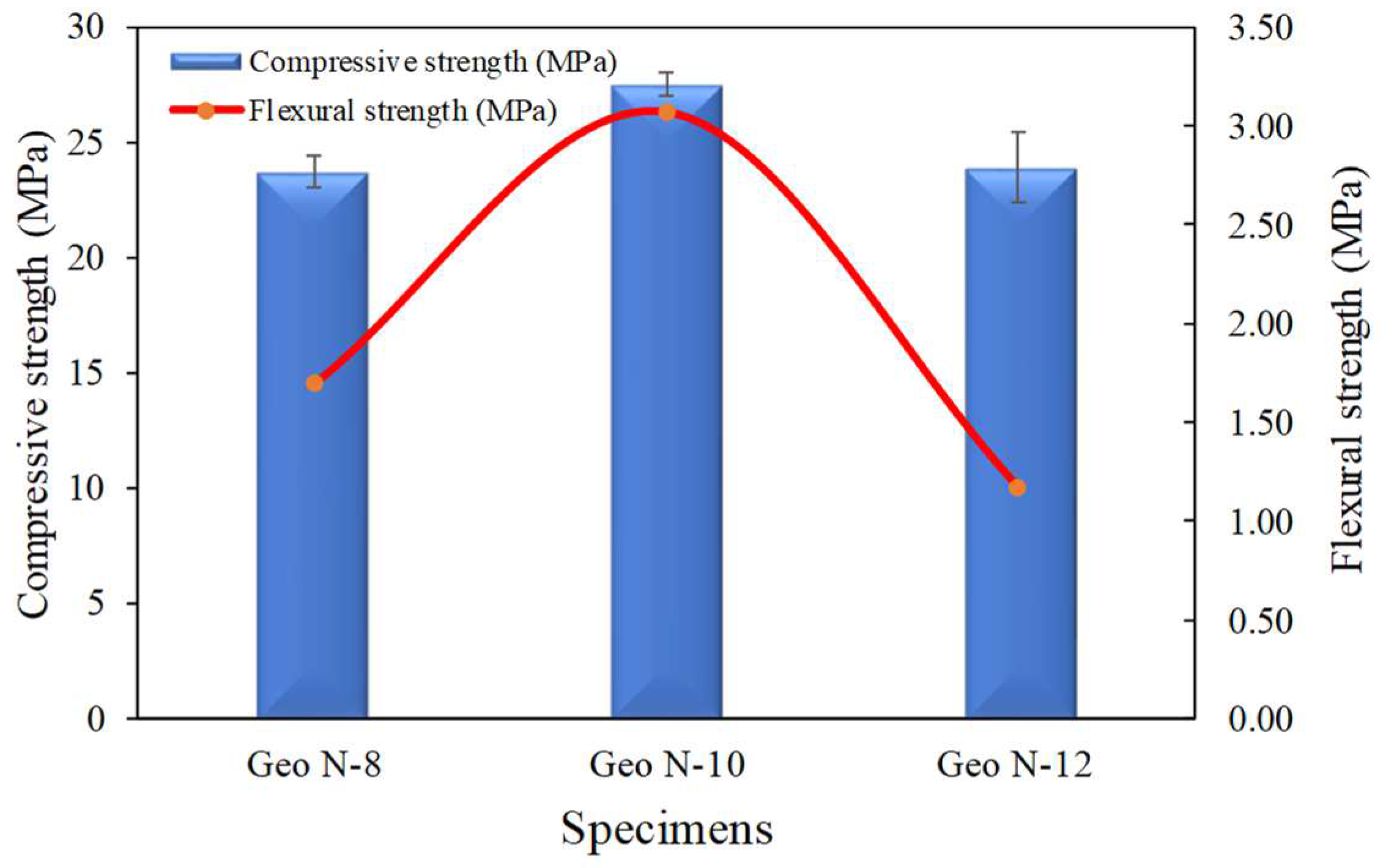
3.1.4. Compressive Strength and Flexural Strength
3.1.5. Fracture Toughness
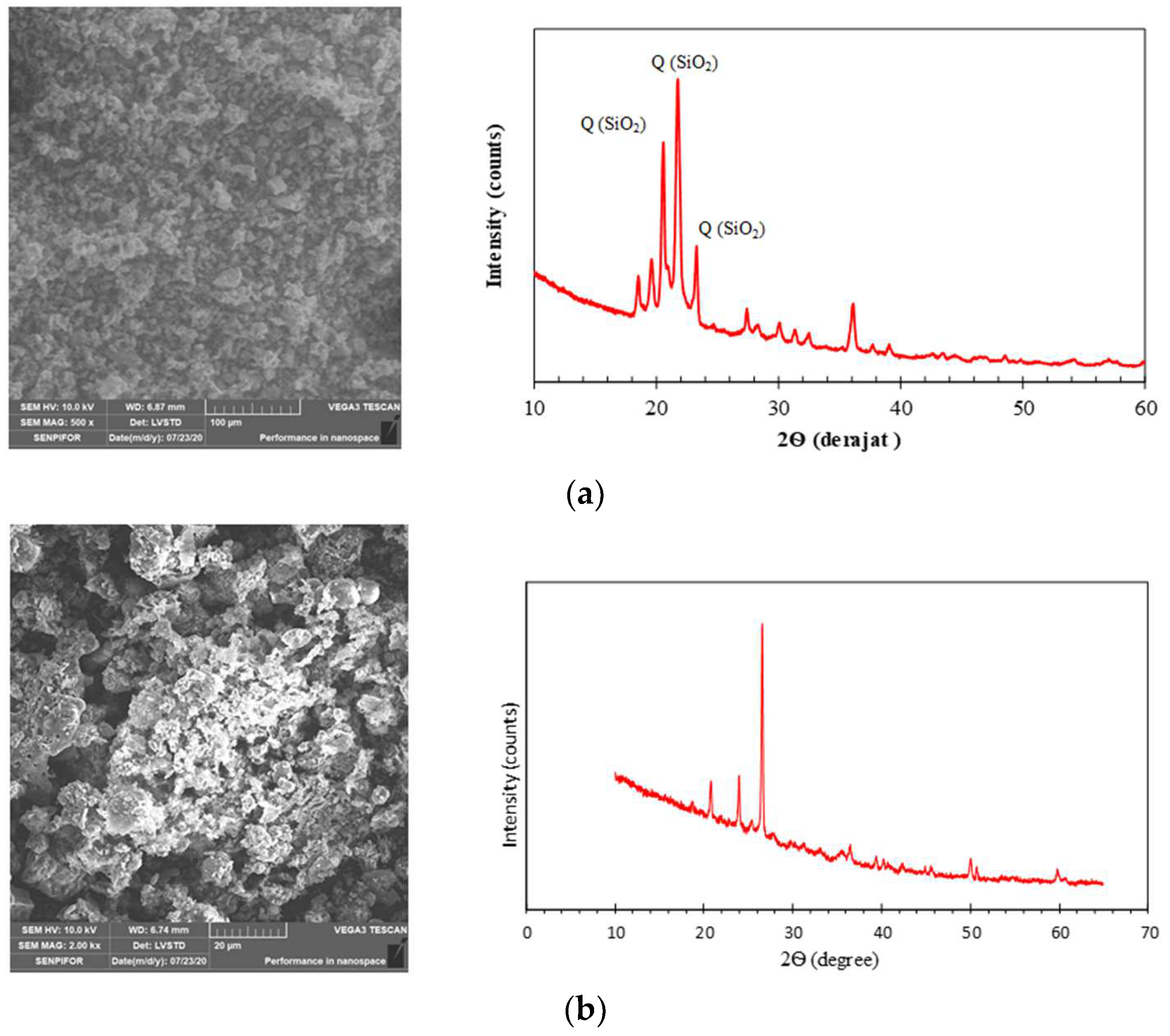
3.1.6. XRD Patterns of Geopolymers
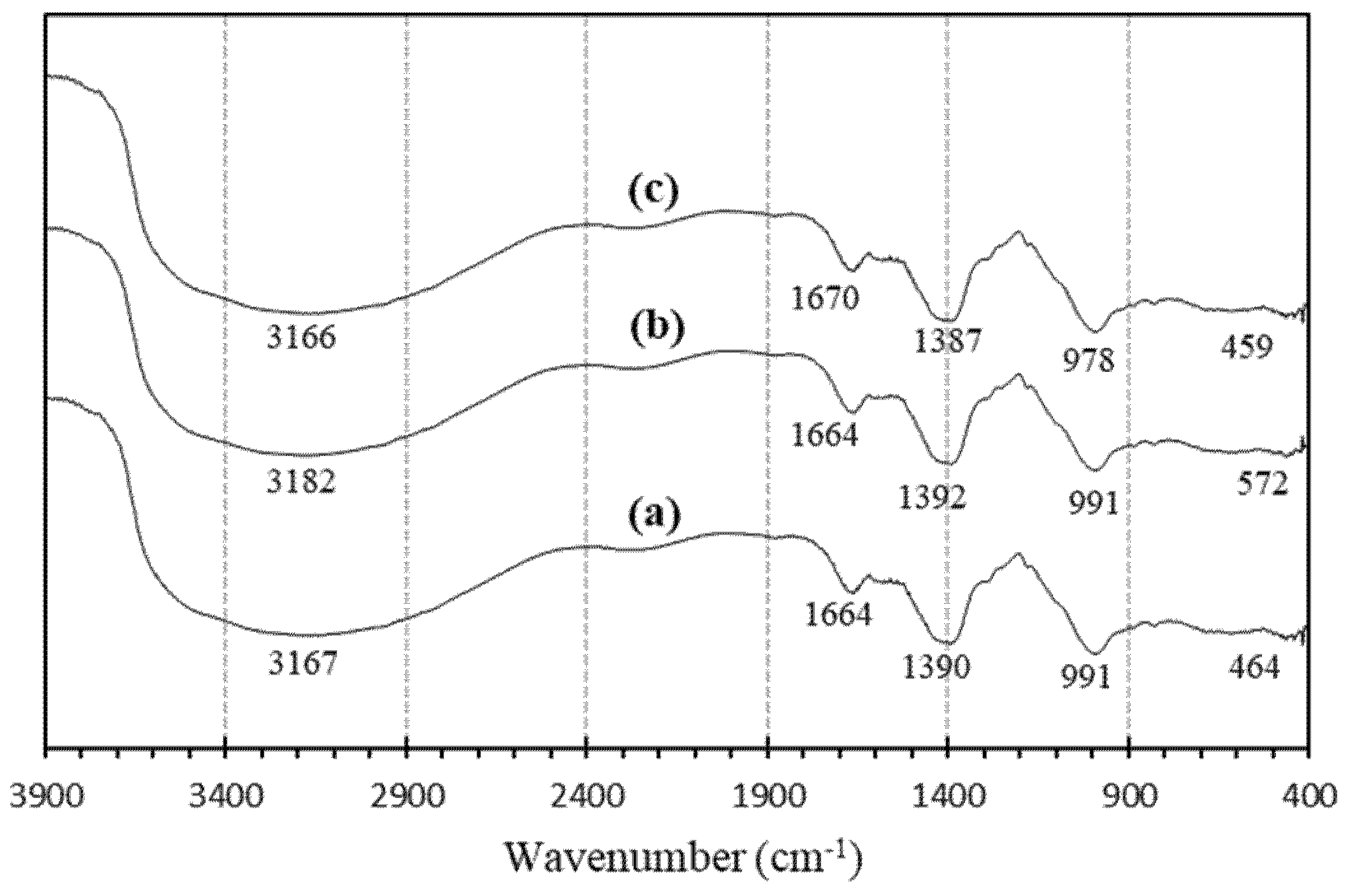
3.1.7. FTIR Spectra of Geopolymers
3.1.8. Microstructure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Habert, G. Assessing the environmental impact of conventional and “green” cement production. In Eco-Efficient Construction and Building Materials: Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), Eco-Labelling and Case Studies; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Babaee, M.; Castel, A. Chloride-induced corrosion of reinforcement in low-calcium fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 88, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaissi, A.; Li, L.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Bui, Q.-B. Mechanical properties and microstructure analysis of FA-GGBS-HMNS based geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 210, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbabi, M.S.; Carrigan, C.; McKenna, S. Trends and developments in green cement and concrete technology. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2012, 1, 194–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Zuo, L.; Zhu, Q.; Ma, W. Physical and mechanical properties and micro characteristics of fly ash-based geopolymers incorporating soda residue. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 98, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Nie, Q.; Huang, B.; Shu, X.; He, Q. Mechanical and microstructural characterization of geopolymers derived from red mud and fly ashes. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Bai, G. Micro-cable reinforced geopolymer composite for extrusion-based 3D printing. Mater. Lett. 2019, 235, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers. J. Therm. Anal. 1991, 37, 1633–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.K.; Collins, F.G. Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2-e) emissions: A comparison between geopolymer and OPC cement concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rêgo, J.H.S.; Nepomuceno, A.A.; Figueiredo, E.P.; Hasparyk, N.P.; Borges, L.D. Effect of Particle Size of Residual Rice-Husk Ash in Consumption of Ca(OH)2. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, P.; Gluth, G.J.; Brouwers, H.J.; Kühne, H.-C. Synthesizing one-part geopolymers from rice husk ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, L.; Aprilia, S.; Abdullah, A.; Rahmawati, C.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Aziz, I.H.; Azimi, E.A. Synthesis of Sodium Silicate from Rice Husk Ash as an Activator to Produce Epoxy-Geopolymer Cement. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Britol, UK, 2021; Volume 1845, p. 012072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakouté, H.K.; Rüscher, C.H.; Hinsch, M.; Djobo, J.N.Y.; Kamseu, E.; Leonelli, C. Utilization of sodium waterglass from sugar cane bagasse ash as a new alternative hardener for producing metakaolin-based geopolymer cement. Chem. Erde 2017, 77, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, Y.; Pei, X.; Huang, R.; Lin, J. Simple process for synthesis of layered sodium silicates using rice husk ash as silica source. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 683, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, C.; Aprilia, S.; Saidi, T.; Aulia, T.B.; Hadi, A.E. The Effects of Nanosilica on Mechanical Properties and Fracture Toughness of Geopolymer Cement. Polymers 2021, 13, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthu Kumar, E.; Ramamurthy, K. Influence of production on the strength, density and water absorption of aerated geopolymer paste and mortar using Class F fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Mu, J. Effects of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin on the morphology and mechanical properties of metakaolin-based geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 173, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, C.; Aprilia, S.; Saidi, T.; Aulia, T.B.; Ahmad, I. Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from Typha sp. as a reinforcing agent. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuun Reddy, S.R.; Bala Murugan, S. Experimental and microstructural assessment of ternary blended geopolymer concrete with different Na2SiO3-to-NaOH volume ratios. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2020, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamseu, E.; Beleuk à Moungam, L.M.; Cannio, M.; Billong, N.; Chaysuwan, D.; Melo, U.C.; Leonelli, C. Substitution of sodium silicate with rice husk ash-NaOH solution in metakaolin based geopolymer cement concerning reduction in global warming. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3050–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, C.; Aprilia, S.; Saidi, T.; Aulia, T.B. Current development of geopolymer cement with nanosilica and cellulose nanocrystals. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Medan, Indonesia, 2021; Volume 1783, p. 012056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoo-ngernkham, T.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Sata, V.; Pangdaeng, S.; Sinsiri, T. Properties of high calcium fly ash geopolymer pastes with Portland cement as an additive. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2013, 20, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; De Silva, P.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K.; Hanjitsuwan, S. Effect of SiO2 and Al2O3 on the setting and hardening of high calcium fly ash-based geopolymer systems. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4876–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvee, A.R.; Malinda, R.; Akbar, A.M.; Ashar, R.D.; Rahmawati, C.; Alomayri, T.; Raza, A.; Shaikh, F.U.A. Experimental study of the mechanical properties and microstructure of geopolymer paste containing nano-silica from agricultural waste and crystalline admixtures. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.; Huang, R. Binding mechanism and properties of alkali-activated fly ash/slag mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Majidi, M.H.; Lampropoulos, A.; Cundy, A.; Meikle, S. Development of Sustainable Geopolymer Mortar using Industrial Waste Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 120, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naenudon, S.; Vilaivong, A.; Zaetang, Y.; Tangchirapat, W.; Wongsa, A.; Sata, V.; Chindaprasirt, P. High flexural strength lightweight fly ash geopolymer mortar containing waste fiber cement. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e01121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong-Sing, N.; Yun-Ming, L.; Cheng-Yong, H.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Chan, L.W.L.; Hui-Teng, N.; Shee-Ween, O.; Wan-En, O.; Yong-Jie, H. Evaluation of flexural properties and characterisation of 10-mm thin geopolymer based on fly ash and ladle furnace slag. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaedi, H.; Shaikh, F.U.A.; Low, I.M. Influence of mixing methods of nano silica on the microstructural and mechanical properties of flax fabric reinforced geopolymer composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakouté, H.K.; Rüscher, C.H.; Kong, S.; Ranjbar, N. Synthesis of sodium waterglass from white rice husk ash as an activator to produce metakaolin-based geopolymer cements. J. Build. Eng. 2016, 6, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyoko, D.; Ramli, Z.; Endud, S.; Hamdan, H.; Sulikowski, B. Conversion of rice husk ash to zeolite beta. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakouté, H.K.; Rüscher, C.H.; Kong, S.; Kamseu, E.; Leonelli, C. Comparison of metakaolin-based geopolymer cements from commercial sodium waterglass and sodium waterglass from rice husk ash. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 78, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Lin, K.-L.; Wang, D.; Hwang, C.-L.; Shiu, H.-S.; Chang, Y.-M.; Cheng, T.-W. Effects SiO2/Na2O molar ratio on mechanical properties and the microstructure of nano-SiO2 metakaolin-based geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 53, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollah, M.Y.A.; Hess, T.R.; Cocke, D.L. Surface and bulk studies of leached and unleached fly ash using XPS, SEM, EDS and FTIR techniques. Cem. Concr. Res. 1994, 24, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lodeiro, I.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Blanco, M.T.; Palomo, A. FTIR study of the sol–gel synthesis of cementitious gels: C–S–H and N–A–S–H. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 45, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Chemical Composition (%) | Fly Ash | Rice Husk Ash |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 21.07 | 93.27 |
| Fe2O3 | 27.23 | 0.15 |
| CaO | 32.58 | 1.03 |
| Mno | 0.44 | 0.17 |
| K2O | 1.17 | 3.41 |
| SO3 | 5.69 | 0.26 |
| Cl | 0.22 | 0.35 |
| Ag2O | 0.23 | 0.10 |
| Al2O3 | 9.65 | - |
| TiO2 | 1.68 | - |
| Yb2O3 | 0.06 | - |
| Specimens | Fly Ash (g) | NaOH (g) | Na2SiO3 (g); Was Prepared in Three Variations with | Water (l) | Ratio Na2SiO3/NaOH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geo N-8 | 100 | 14 | 35; NaOH 8 M | 35 | 2.5 |
| Geo N-10 | 100 | 14 | 35; NaO 10 M | 35 | 2.5 |
| Geo N-12 | 100 | 14 | 35; NaOH 12 M | 35 | 2.5 |
| Reference | Alkaline Activator | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Water Absorption (%) | Fracture Toughness (MPa·m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study | NaOH + Na2SiO3 | 23.69–27.53 | 1.17–1.69 | 12.3–13.3 | 0.32–0.86 |
| [25] | NaOH + Na2SiO3 | 88.0–110.6 | 2.93–9.32 | 1.1–7.5 | - |
| [26] | NaOH + K2SiO3 | 20–50 | 0.6–2 | - | - |
| [27] | NaOH + Na2SiO3 | 38.3–46.9 | 4.73–6.63 | - | - |
| [28] | NaOH + Na2SiO3 | - | 6.2–7.8 | 9.9–12.4 | - |
| [24] | NaOH + Na2SiO3 | 17.77–22.69 | 0.91–3.02 | - | 0.37–1.07 |
| [15] | NaOH + Na2SiO3 | 18.16–26.26 | 0.45–2.62 | - | 0.16–0.74 |
| [29] | NaOH + Na2SiO3 | 50.1–56.7 | 7.0–9.3 | 10 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Handayani, L.; Aprilia, S.; Abdullah; Rahmawati, C.; Aulia, T.B.; Ludvig, P.; Ahmad, J. Sodium Silicate from Rice Husk Ash and Their Effects as Geopolymer Cement. Polymers 2022, 14, 2920. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142920
Handayani L, Aprilia S, Abdullah, Rahmawati C, Aulia TB, Ludvig P, Ahmad J. Sodium Silicate from Rice Husk Ash and Their Effects as Geopolymer Cement. Polymers. 2022; 14(14):2920. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142920
Chicago/Turabian StyleHandayani, Lia, Sri Aprilia, Abdullah, Cut Rahmawati, Teuku Budi Aulia, Péter Ludvig, and Jawad Ahmad. 2022. "Sodium Silicate from Rice Husk Ash and Their Effects as Geopolymer Cement" Polymers 14, no. 14: 2920. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142920
APA StyleHandayani, L., Aprilia, S., Abdullah, Rahmawati, C., Aulia, T. B., Ludvig, P., & Ahmad, J. (2022). Sodium Silicate from Rice Husk Ash and Their Effects as Geopolymer Cement. Polymers, 14(14), 2920. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142920







