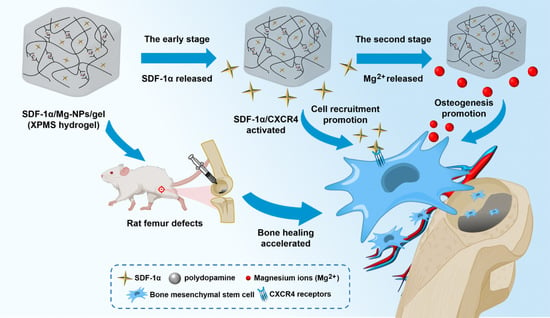
Controlled and Sequential Delivery of Stromal Derived Factor-1 α (SDF-1α) and Magnesium Ions from Bifunctional Hydrogel for Bone Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
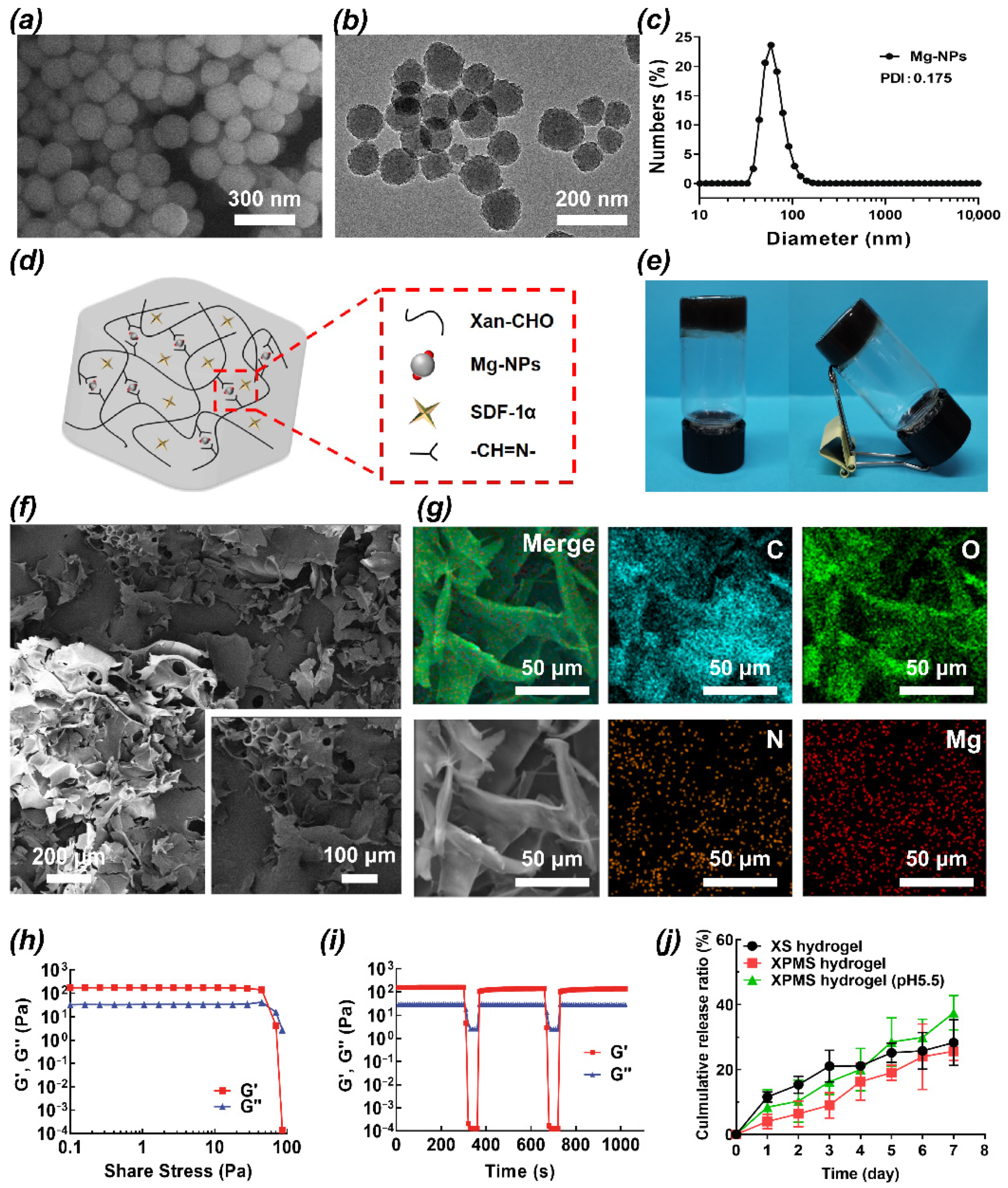
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of the SDF-1α/Mg-NPs/Gel (XPMS Hydrogel)
2.1.1. Synthesis of Mg-NPs
2.1.2. Synthesis of Xan-CHO
2.1.3. Synthesis of SDF-1α/Mg-NPs/Gel (XPMS Hydrogel)
2.1.4. Characterization
2.1.5. The SDF-1α Releasing from XPMS Hydrogel
2.2. BMSCs Isolation and Culture
2.3. The Preparation of Different Hydrogel Extraction
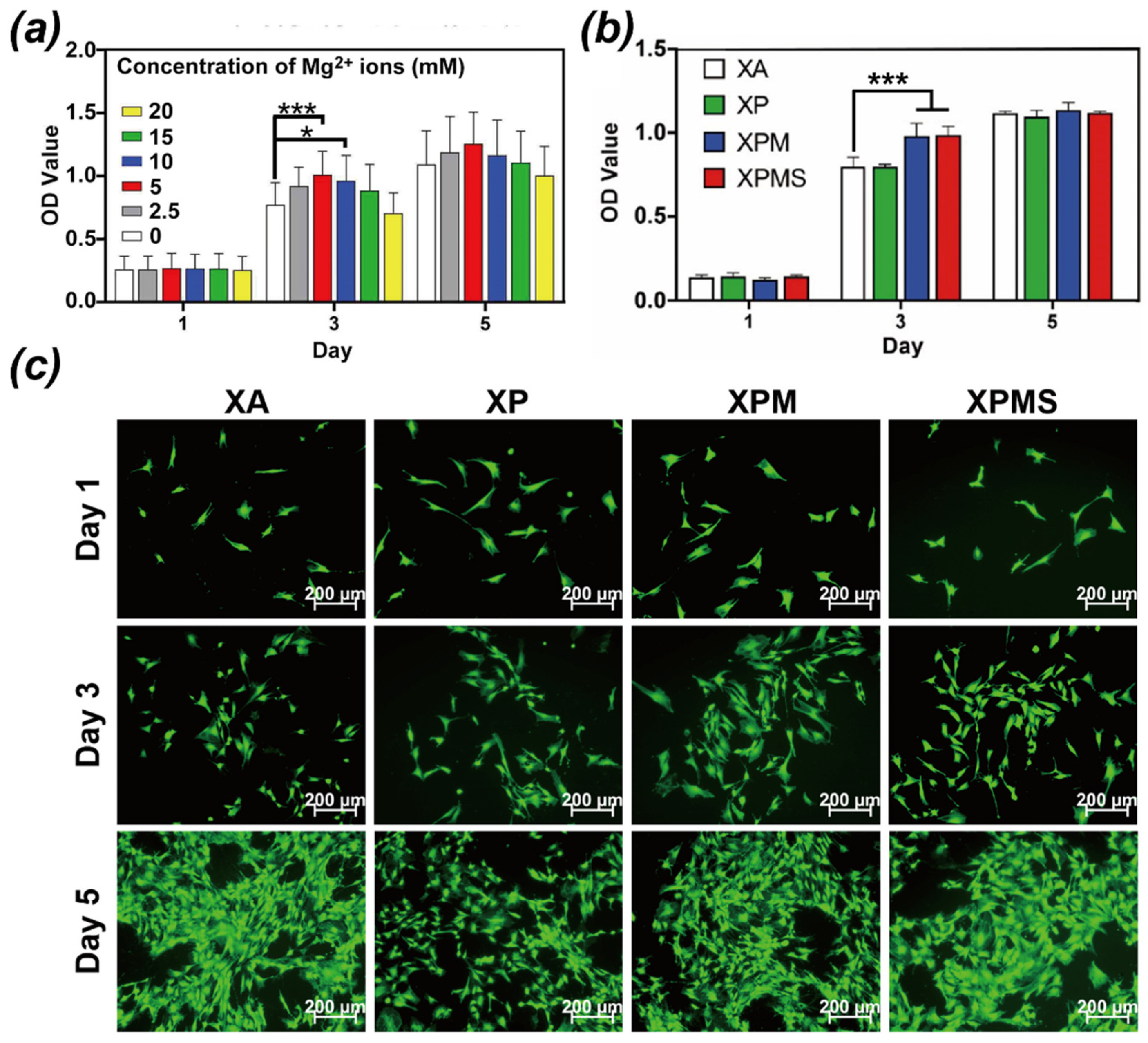
2.4. The Effect of SDF-1α Included Hydrogels on Recruitment of BMSCs In Vitro
2.4.1. Effect of SDF-1α on Chemotaxis of BMSCs
2.4.2. Functional Evaluation of Mg2+ and SDF-1α on Chemotaxis of BMSCs
2.4.3. Cell Recruitment Activity of the XPMS Hydrogels In Vitro
2.5. The Effect of Mg2+ and Hydrogels on Biocompatibility and Osteoinductivity of BMSCs In Vitro
2.5.1. Proliferation of BMSCs Stimulated with Mg2+
2.5.2. Cell Viability of the Hydrogels In Vitro
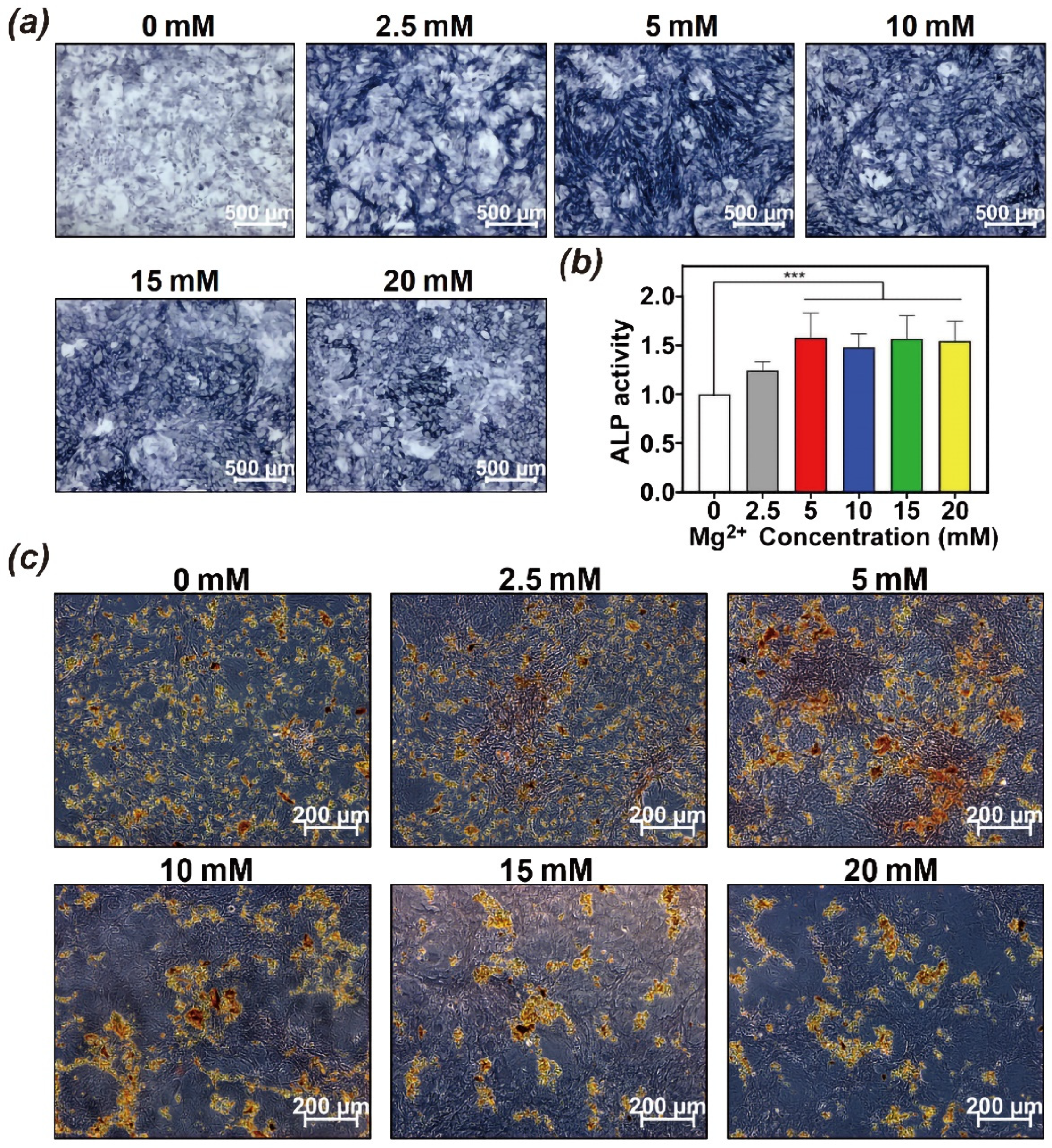
2.5.3. The Effect of Mg2+ on Osteoinductivity of BMSCs In Vitro
ALP Staining and Quantification in BMSCs Treated with Mg2+
Alizarin Red S Staining of Mineralization in Mg2+ Treated BMSCs
2.5.4. The Effect of Hydrogel Extractions on Osteoinductivity of BMSCs In Vitro
ALP Staining and Quantification in BMSCs Treated with Hydrogel Extraction
Alizarin Red S Staining of Mineralization in Hydrogel Extraction Treated BMSCs
Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Osteoinductivity of Different Hydrogels In Vivo
2.6.1. Femur Defect Model of SD Rats
2.6.2. Micro-CT Analysis
2.6.3. Histological Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of the SDF-1α/Mg-NPs/Gel (XPMS Hydrogel)
3.2. Effect of Hydrogels on Recruitment of BMSCs In Vitro
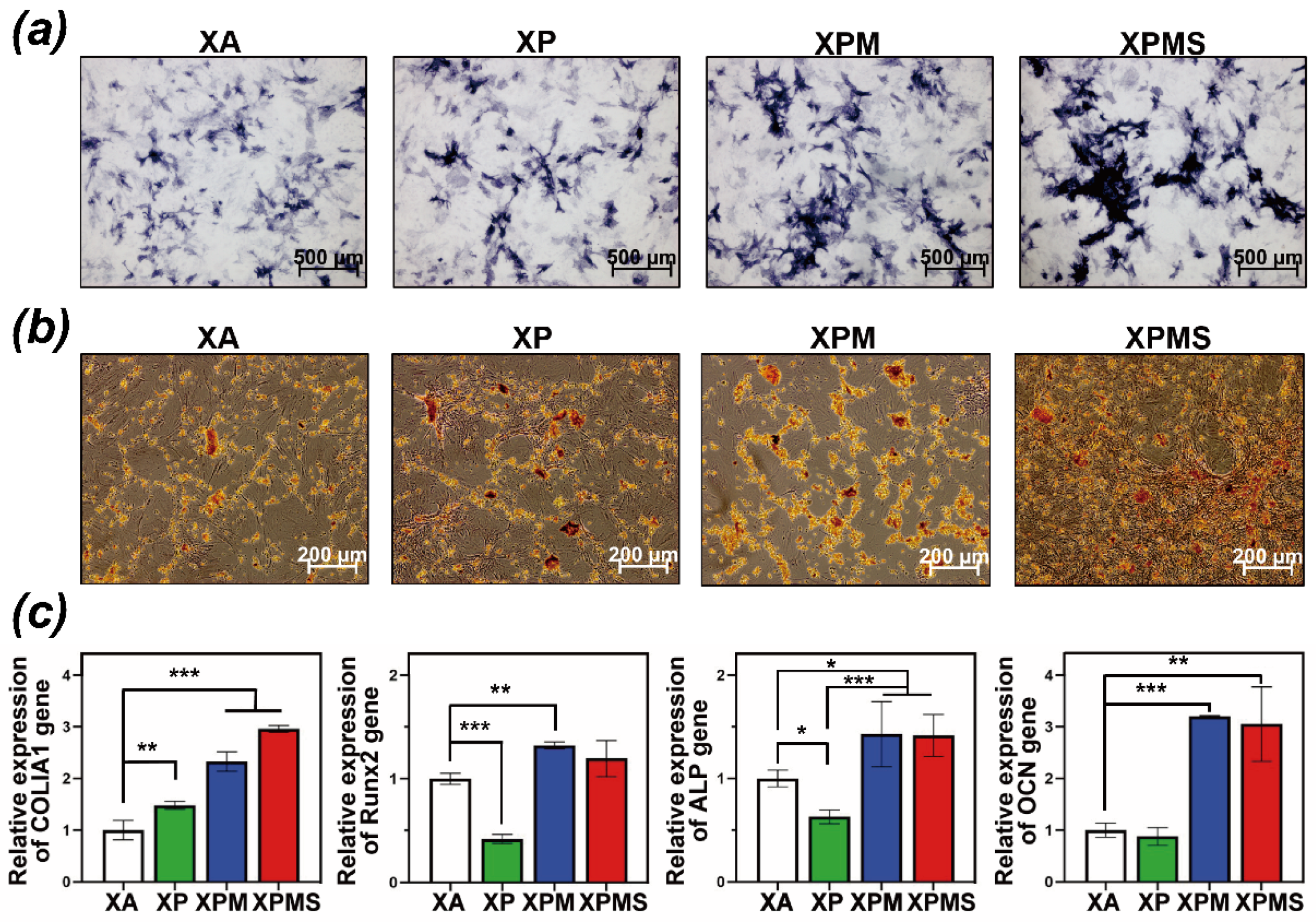
3.3. Effect of Hydrogels on Biocompatibility and Osteoinductivity In Vitro
3.4. Effect of Hydrogels on Osteoinductivity In Vivo
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kim, H.D.; Amirthalingam, S.; Kim, S.L.; Lee, S.S.; Rangasamy, J.; Hwang, N.S. Biomimetic Materials and Fabrication Approaches for Bone Tissue Engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaraju, H.; Miller, S.J.; Kohn, D.H. Dual-functioning peptides discovered by phage display increase the magnitude and specificity of BMSC attachment to mineralized biomaterials. Biomaterials 2017, 134, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho-Shui-Ling, A.; Bolander, J.; Rustom, L.E.; Johnson, A.W.; Luyten, F.P.; Picart, C. Bone regeneration strategies: Engineered scaffolds, bioactive molecules and stem cells current stage and future perspectives. Biomaterials 2018, 180, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Xing, M.M.; Zhong, W. Development of hydrogels and biomimetic regulators as tissue engineering scaffolds. Membranes 2012, 2, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortes, H.; Caballero-Florán, I.H.; Mendoza-Muñoz, N.; Escutia-Guadarrama, L.; Figueroa-González, G.; Reyes-Hernández, O.D.; González-Del Carmen, M.; Varela-Cardoso, M.; González-Torres, M.; Florán, B.; et al. Xanthan gum in drug release. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2020, 66, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rao, K.M.; Han, S.S. Application of xanthan gum as polysaccharide in tissue engineering: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombino, S.; Serini, S.; Cassano, R.; Calviello, G. Xanthan gum-based materials for Omega-3 PUFA delivery: Preparation, characterization and antineoplastic activity evaluation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 208, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ren, X.; Liu, Y. Multifunctional 3D printed porous GelMA/xanthan gum based dressing with biofilm control and wound healing activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 131, 112493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byram, P.K.; Sunka, K.C.; Barik, A.; Kaushal, M.; Dhara, S.; Chakravorty, N. Biomimetic silk fibroin and xanthan gum blended hydrogels for connective tissue regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165 Pt A, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Jin, K.; Li, J.; Qiu, X.; Li, S. Delivery of stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha for in situ tissue regeneration. J. Biol. Eng. 2017, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cencioni, C.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Napolitano, M. The SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in stem cell preconditioning. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 94, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.; Gaihre, B.; Park, S.; Li, Y.; Terzic, A.; Lu, L. SDF-1α/OPF/BP Composites Enhance the Migrating and Osteogenic Abilities of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 1938819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Du, L.; Zhang, R.; Kang, W.; Ge, S. Stromal cell-derived factor-1/Exendin-4 cotherapy facilitates the proliferation, migration and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in vitro and promotes periodontal bone regeneration in vivo. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocking, A.M. The Role of Chemokines in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Homing to Wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadinejad, R.; Kumar, A.; Ranjbar-Mohammadi, M.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Han, S.S.; Khang, G.; Roveimiab, Z. Recent Advances in Natural Gum-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, J.; Maji, B.; Moorthy, N.; Maiti, S. Xanthan gum derivatives: Review of synthesis, properties and diverse applications. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 27103–27136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, T.; Iqbal, M.W.; Jiang, B.; Chen, J. A review of the enzymatic, physical, and chemical modification techniques of xanthan gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 472–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwabebhoh, F.A.; Zandraa, O.; Patwa, R.; Saha, N.; Capakova, Z.; Saha, P. Self-crosslinked chitosan/dialdehyde xanthan gum blended hypromellose hydrogel for the controlled delivery of ampicillin, minocycline and rifampicin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1468–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yin, H.M.; Luo, E.; Zhu, S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, G.Q.; Xu, J.Z.; Li, Z.M.; Li, J.H. Accelerating Bone Healing by Decorating BMP-2 on Porous Composite Scaffolds. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 5717–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wu, G.; Dai, F.; Li, D.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Deng, H. Chitosan/polydopamine layer by layer self-assembled silk fibroin nanofibers for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maganto, H.L.C.; Ang, M.; Dizon, G.V.C.; Caparanga, A.R.; Aquino, R.R.; Huang, S.H.; Tsai, H.A.; Lee, K.R. Infusion of Silver-Polydopamine Particles into Polyethersulfone Matrix to Improve the Membrane’s Dye Desalination Performance and Antibacterial Property. Membranes 2021, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Marshall, T.; Aulin, Y.V.; Thenuwara, A.C.; Zhao, Y.; Borguet, E.; Strongin, D.R.; Ren, F. Structural evolution and electrical properties of metal ion-containing polydopamine. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 6393–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Shi, S.; Lan, X.; Quan, X.; Xu, Q.; Yao, G.; Liu, J.; Shuai, X.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; et al. Scaffold 3D-Printed from Metallic Nanoparticles-Containing Ink Simultaneously Eradicates Tumor and Repairs Tumor-Associated Bone Defects. Small Methods 2021, 5, e2100536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez-Curtis, L.A.; Janowska-Wieczorek, A. Enhancing the migration ability of mesenchymal stromal cells by targeting the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 561098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Wei, X.; Fang, J.; Xiao, L. Combination of SDF-1 and bFGF promotes bone marrow stem cell-mediated periodontal ligament regeneration. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosogane, N.; Huang, Z.; Rawlins, B.A.; Liu, X.; Boachie-Adjei, O.; Boskey, A.L.; Zhu, W. Stromal derived factor-1 regulates bone morphogenetic protein 2-induced osteogenic differentiation of primary mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, M.; Qiu, J.; Kuang, R.; Zhang, B.; Wang, W.; Yu, Q. Synergistic effects of stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha and bone morphogenetic protein-2 treatment on odontogenic differentiation of human stem cells from apical papilla cultured in the VitroGel 3D system. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 378, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, J.L.; Ma, H.; Rai, R.; Hankenson, K.D.; Burdick, J.A. Synergistic Effects of SDF-1alpha and BMP-2 Delivery from Proteolytically Degradable Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels for Bone Repair. Macromol. Biosci. 2015, 15, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhou, Y.F.; Li, W.P.; Jiang, C.; Chen, Z.; Luo, H.; Song, B. Local Administration of Magnesium Promotes Meniscal Healing Through Homing of Endogenous Stem Cells: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 954–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Deng, Y.; Lv, Y.; Chen, G. Stem cell recruitment based on scaffold features for bone tissue engineering. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 1189–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Gao, M.; Syed, S.; Zhuang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.Q. Bioactive hydrogels for bone regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 3, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, P.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, M.; Yu, F.; Dong, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qi, Y.; et al. A novel magnesium ion-incorporating dual-crosslinked hydrogel to improve bone scaffold-mediated osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 121, 111868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Kim, K.J.; Cheon, S.; Kim, E.M.; Kim, Y.A.; Park, C.; Kim, K.K. Biochemical activity of magnesium ions on human osteoblast migration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 531, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Yang, G.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, M.; Yin, S.; Tang, Y.; Tang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, X. A Magnesium-Enriched 3D Culture System that Mimics the Bone Development Microenvironment for Vascularized Bone Regeneration. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ma, X.Y.; Feng, Y.F.; Ma, Z.S.; Ma, T.C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Lei, W. Magnesium Ions Promote the Biological Behaviour of Rat Calvarial Osteoblasts by Activating the PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 179, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, L.; Qi, H.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Dual Function of Magnesium in Bone Biomineralization. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1901030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, W.; Li, T.; Jia, G.; Chang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Pei, J.; Yu, D.; Zhai, Z. Exposure to high levels of magnesium disrupts bone mineralization in vitro and in vivo. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Feng, G.; Hu, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, X.; Jin, Q. SDF Factor-1alpha Promotes the Migration, Proliferation, and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mouse Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through the Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2021, 30, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, F.M.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, C.; et al. In vitro cell behaviors of bone mesenchymal stem cells derived from normal and postmenopausal osteoporotic rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.N.; Park, C.; Kim, S.M.; Park, K.W.; Park, B.J.; Han, D.K.; Joung, Y.K. Effect of stromal cell derived factor-1 alpha release from heparin-coated Co-Cr stent substrate on the recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells. Macromol. Res. 2015, 23, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zeng, H.; Xiao, P.; Yang, A.; Situ, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Pan, W.; Wang, Y. Sustained Release of Magnesium Ions Mediated by a Dynamic Mechanical Hydrogel to Enhance BMSC Proliferation and Differentiation. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 24477–24486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cao, F.; Wu, B.; Yang, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, W.; Wei, X.; Liu, G.; Zhao, D. Immobilization of bioactive vascular endothelial growth factor onto Ca-deficient hydroxyapatite-coated Mg by covalent bonding using polydopamine. J. Orthop. Transl. 2021, 30, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Xu, J.; Mi, J.; He, X.; Pan, Q.; Zheng, L.; Zu, H.; Chen, Z.; Dai, B.; Li, X.; et al. Biodegradable magnesium combined with distraction osteogenesis synergistically stimulates bone tissue regeneration via CGRP-FAK-VEGF signaling axis. Biomaterials 2021, 275, 120984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zu, H.; Zhao, D.; Yang, K.; Tian, S.; Yu, X.; Lu, F.; Liu, B.; Yu, X.; Wang, B.; et al. Ion channel functional protein kinase TRPM7 regulates Mg ions to promote the osteoinduction of human osteoblast via PI3K pathway: In vitro simulation of the bone-repairing effect of Mg-based alloy implant. Acta Biomater. 2017, 63, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Wen, L.; Shang, F.; Wu, J.; Sui, K.; Ding, Y. Endothelial progenitors enhanced the osteogenic capacities of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in a rat alveolar bone defect model. Arch. Oral Biol. 2016, 68, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Han, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, Q. Controlled co-delivery system of magnesium and lanthanum ions for vascularized bone regeneration. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 065024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liang, G.; Xu, T.; Niu, W. Three-dimensional Printed Mg-Doped β-TCP Bone Tissue Engineering Scaffolds: Effects of Magnesium Ion Concentration on Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis In Vitro. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 16, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiva, A.L.; Raftery, R.M.; Keogh, M.B.; O’Brien, F.J. Pro-angiogenic impact of SDF-1α gene-activated collagen-based scaffolds in stem cell driven angiogenesis. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 544, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Forward Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| COL-1 | GCTGGCAAGAATGGCGAC | AAGCCACGATGACCCTTTATG |
| ALP | CAAGGATGCTGGGAAGTCCG | CTCTGGGCGCATCTCATTGT |
| Runx-2 | CAGACCAGCAGCACTCCATA | GCTTCCATCAGCGTCAACAC |
| OCN | GACAAGTCCCACACAGCAAC | CCGGAGTCTATTCACCACCT |
| GAPDH | TCTCTGCTCCTCCCTGTTC | ACACCGACCTTCACCATCT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Lin, H.; Shi, S.; Su, K.; Zheng, G.; Gao, S.; Zeng, X.; Ning, H.; Yu, M.; Li, X.; et al. Controlled and Sequential Delivery of Stromal Derived Factor-1 α (SDF-1α) and Magnesium Ions from Bifunctional Hydrogel for Bone Regeneration. Polymers 2022, 14, 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142872
Li Z, Lin H, Shi S, Su K, Zheng G, Gao S, Zeng X, Ning H, Yu M, Li X, et al. Controlled and Sequential Delivery of Stromal Derived Factor-1 α (SDF-1α) and Magnesium Ions from Bifunctional Hydrogel for Bone Regeneration. Polymers. 2022; 14(14):2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142872
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhengshi, Huimin Lin, Shanwei Shi, Kai Su, Guangsen Zheng, Siyong Gao, Xuan Zeng, Honglong Ning, Meng Yu, Xiang Li, and et al. 2022. "Controlled and Sequential Delivery of Stromal Derived Factor-1 α (SDF-1α) and Magnesium Ions from Bifunctional Hydrogel for Bone Regeneration" Polymers 14, no. 14: 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142872
APA StyleLi, Z., Lin, H., Shi, S., Su, K., Zheng, G., Gao, S., Zeng, X., Ning, H., Yu, M., Li, X., & Liao, G. (2022). Controlled and Sequential Delivery of Stromal Derived Factor-1 α (SDF-1α) and Magnesium Ions from Bifunctional Hydrogel for Bone Regeneration. Polymers, 14(14), 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142872