Computer Simulation of Polyethylene Terephthalate Carbonated Beverage Bottle Bottom Structure Based on Manual–Automatic Double-Adjustment Optimization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principle and Experiment
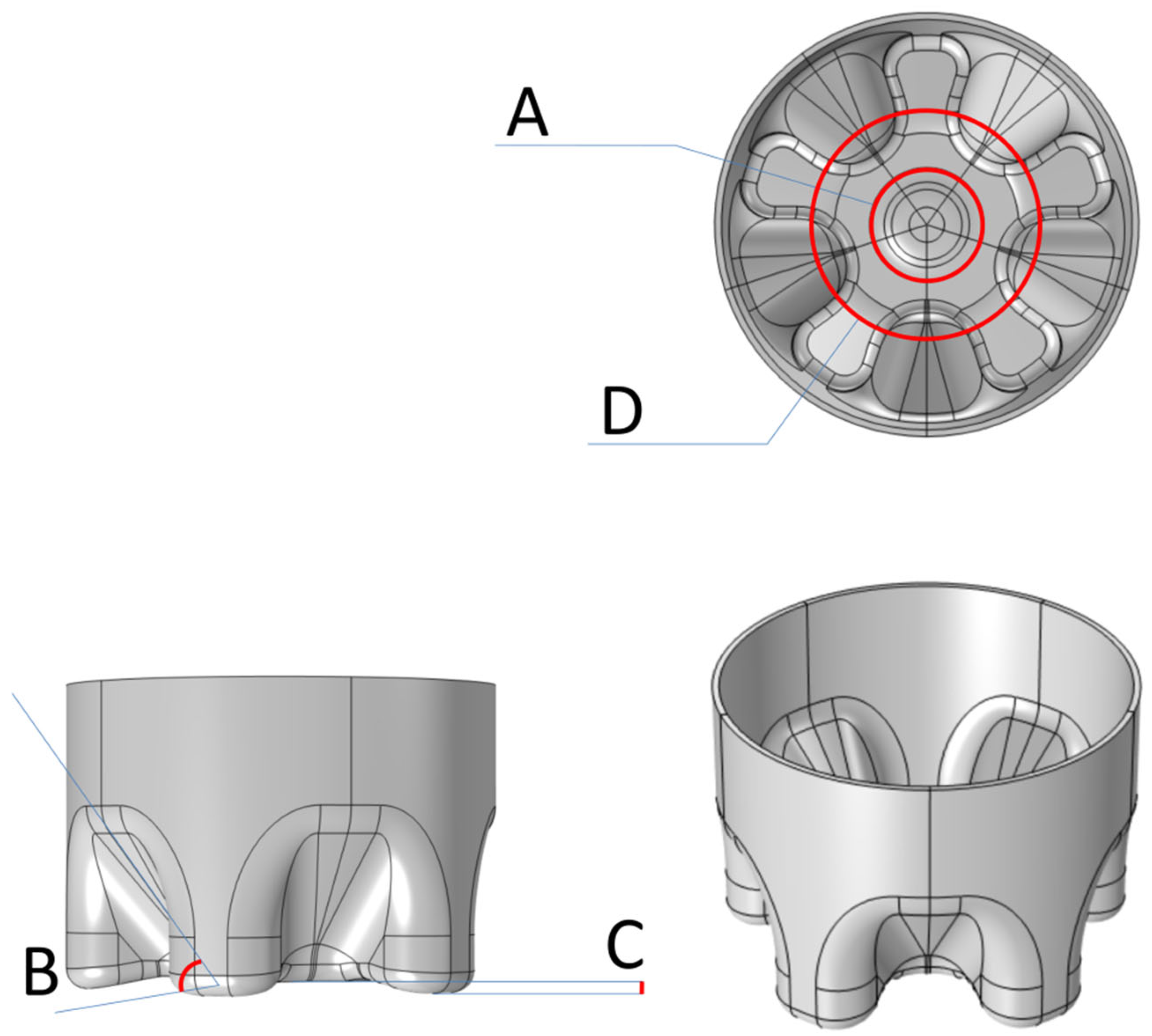
2.1. Computer-Aided Modeling of Bottle Bottom Structure
2.2. Selections of Material and Finite Element Mesh
2.3. Pressure Setting
2.4. Constraint Conditions
2.4.1. Fixed Edge
2.4.2. Free Shape Domain
2.4.3. Free Shape Boundary
2.5. Steady State Solver
2.6. Data Comparison
2.6.1. Von Mises Stress and Elastic Strain Energy
2.6.2. Deformation
2.7. Optimization
2.7.1. Optimized Content
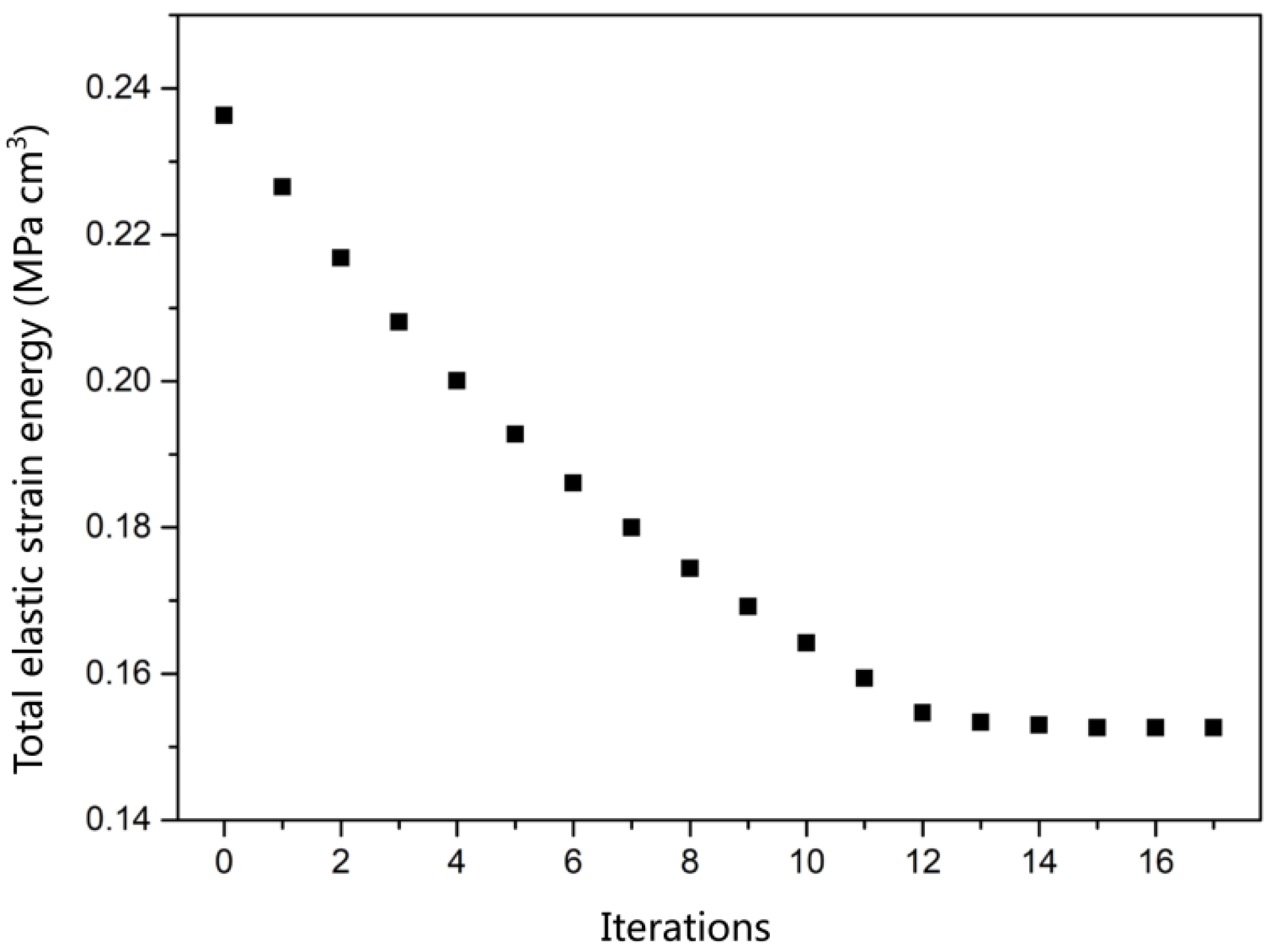
2.7.2. Optimization Method
3. Results and Discussion
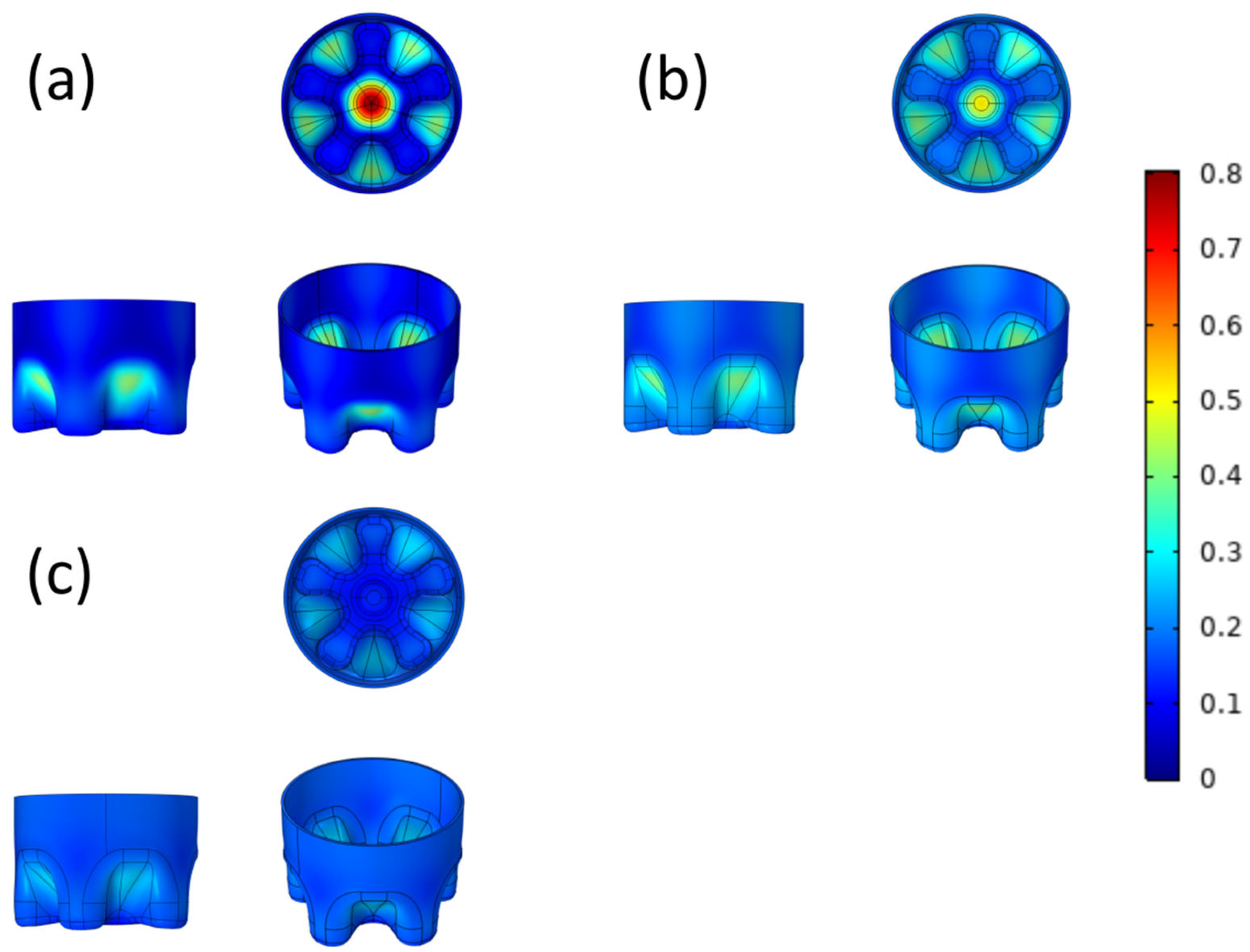
3.1. Comparison of Model Structure before and after Optimization
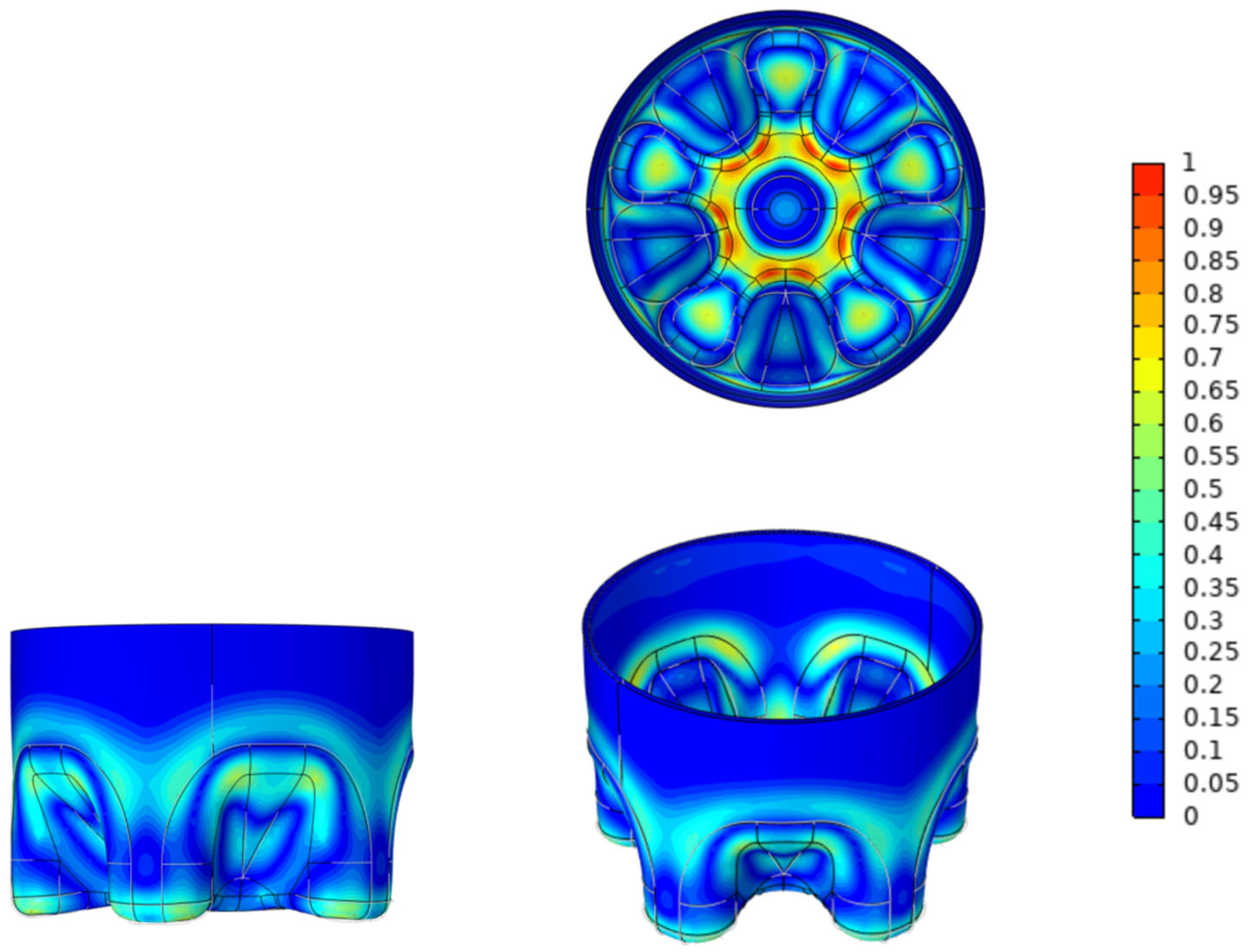
3.2. Surface Von Mises Stress
3.3. Overall Von Mises Stress
3.4. Total Elastic Strain Energy
3.5. Material Deformation
4. Conclusions
- The characteristics of high precision inautomatic optimization are maintained;
- Manual preprocessing saves computing resources.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nisticò, R. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) in the packaging industry. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiano, A.; Gallucci, T.; Pontrandolfo, A.; Crovella, T.; Lagioia, G. The Environmental Performance of Glass and PET Mineral Water Bottles in Italy. In Sustainable Packaging; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Fakirov, S. Fundamentals of Polymer Science for Engineers; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, M.H.; Rollend, G.F.; Muszynski, J.H. Self-Standing Polyester Containers for Carbonated Beverages. U.S. Patent 5,484,072, 16 January 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Karalekas, D.; Rapti, D.; Papakaliatakis, G.; Tsartolia, E. Numerical and experimental investigation of the deformational behaviour of plastic containers. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2001, 14, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lontos, A.; Gregoriou, A. The Preliminary Simulated Effect of Stretching and Blowing Combination on the Wall Thickness Distribution of 1.5 Lt PET Bottle during ISBM Process. Fibers Polym. 2021, 22, 2170–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkurt, F.; Demirel, B.; Usal, İ.A.; Şenyiğit, E. Determination of The Best Injection Stretch Blow Molding Process Parameters in Polyethylene Terephthalate Bottle Service Performance. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. 2022, 35, 1297–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, T.; Sutton, D.; Cookson, D.; Kosior, E.; Knott, R. Molecular morphology of petaloid bases of PET bottles: A small-angle X-ray scattering study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 99, 3328–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiou, V.F.; Mathioudakis, G.N.; Andrikopoulos, K.S.; Soto Beobide, A.; Voyiatzis, G.A. Poly (ethylene Terephthalate) Carbon-Based Nanocomposites: A Crystallization and Molecular Orientation Study. Polymers 2020, 12, 2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaner, N.B.; Demirel, B.; Yaras, A.; Akkurt, F.; Daver, F. Improvement of environmental stress cracking performance, load-carrying capacity, and UV light barrier property of polyethylene terephthalate packaging material. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2022, 33, 2352–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, B.; Inaner, N.B.; Gezer, D.U.; Daver, F.; Yaras, A.; Akkurt, F. Chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties and ultraviolet transmittance of novel nano-hydroxyapatite/polyethylene terephthalate milk bottles. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 61, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, M.; Combeaud, C.; Billon, N. Effects of annealing prior to stretching on strain induced crystallization of polyethylene terephthalate. Polymer 2021, 230, 124078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, B.; Daver, F. The effects on the properties of PET bottles of changes to bottle-base geometry. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 3811–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Pan, B.R.; Du, Q.G.; Li, Y.Q. The strain in the test environmental stress cracking of plastics. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Investigation of design parameters and novel design of petaloid PET bottles. Int. Polym. Process. 2002, 17, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, O.H. Some forms of the strain energy function for rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1993, 66, 754–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, M. A theory of large elastic deformation. J. Appl. Phys. 1940, 11, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, R.W. Nearly isochoric elastic deformations: Application to rubberlike solids. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1978, 26, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winslow, A.M. Magnetic Field Calculations in an Irregular Triangle Mesh; Lawrence Radiation Lab., Univ. of California: Livermore, CA, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Rivlin, R.S. Large elastic deformations of isotropic materials IV. Further developments of the general theory. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1948, 241, 379–397. [Google Scholar]
- Alappat, C.; Basermann, A.; Bishop, A.R.; Fehske, H.; Hager, G.; Schenk, O.; Thies, J.; Wellein, G. A recursive algebraic coloring technique for hardware-efficient symmetric sparse matrix-vector multiplication. ACM Trans. Parallel Comput. 2020, 7, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollhöfer, M.; Schenk, O.; Janalik, R.; Hamm, S.; Gullapalli, K. State-of-the-art sparse direct solvers. In Parallel Algorithms in Computational Science and Engineering; Birkhäuser: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 3–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bollhöfer, M.; Eftekhari, A.; Scheidegger, S.; Schenk, O. Large-scale sparse inverse covariance matrix estimation. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2019, 41, A380–A401. [Google Scholar]
- Demirel, B.; Daver, F. Effects of preform deformation behavior on the properties of the poly (ethylene terephthalate) bottles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, H.; Masood, S.; Erbulut, D.U. A study of blow moulding simulation and structural analysis for PET bottles. Aust. J. Mech. Eng. 2009, 7, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Cameron, M.R.; Jabarin, S.A. Strain energy function and stress–strain model for uniaxial and biaxial orientation of poly (ethylene terephthalate)(PET). In Biaxial Stretching Film; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; pp. 86–116. [Google Scholar]
- Svanberg, K. The method of moving asymptotes—A new method for structural optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1987, 24, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanberg, K. MMA and GCMMA–Fortran versions March 2013. R. Inst. Technol. 2013, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, M.Y.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, H.C.; Pae, Y. Causes of cracks in petaloid bottom of carbonated PET bottle. Int. Polym. Process. 2001, 16, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.Y.; Pae, Y. Bottom design of carbonated soft drink poly (ethylene terephthalate) bottle to prevent solvent cracking. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Su, T.; He, M. Gas Packaging Container Based on ANSYS Finite Element Analysis and Structural Optimization Design. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 1187, p. 032089. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; He, R.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Z. Crack Propagation on the Surface of the Bottleneck of a Pressure Vessel Considering the Initial Crack Angle. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, B.; Daver, F. Optimization of poly (ethylene terephthalate) bottles via numerical modeling: A statistical design of experiment approach. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
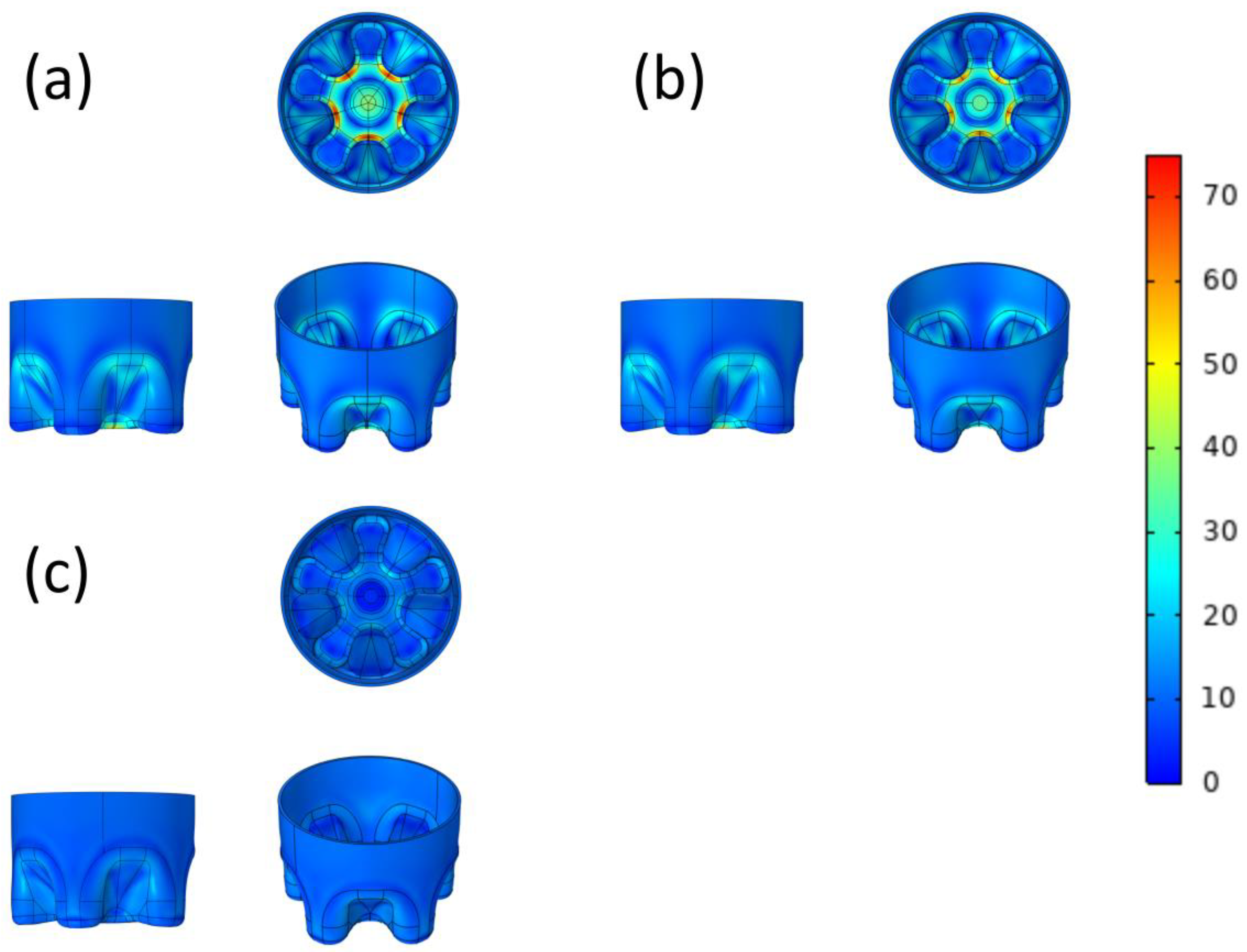
| Degree of Model Optimization | Surface Von Mises Stress | Overall Von Mises Stress | Elastic Strain Energy | Deformation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O-CF bottom | 72.8 MPa | 77.9 MPa | 0.255 MPa cm3 | 0.81 mm |
| M-CF bottom | 66.9 MPa | 69.2 MPa | 0.236 MPa cm3 | 0.56 mm |
| MA-CF bottom | 23.4 MPa | 23.8 MPa | 0.153 MPa cm3 | 0.21 mm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge-Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Zhu, H.; Song, Y.; Ding, Y.; Cui, J. Computer Simulation of Polyethylene Terephthalate Carbonated Beverage Bottle Bottom Structure Based on Manual–Automatic Double-Adjustment Optimization. Polymers 2022, 14, 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142845
Ge-Zhang S, Chen X, Zhu H, Song Y, Ding Y, Cui J. Computer Simulation of Polyethylene Terephthalate Carbonated Beverage Bottle Bottom Structure Based on Manual–Automatic Double-Adjustment Optimization. Polymers. 2022; 14(14):2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142845
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe-Zhang, Shangjie, Xiaoli Chen, Haotong Zhu, Yuan Song, Yuyang Ding, and Jingang Cui. 2022. "Computer Simulation of Polyethylene Terephthalate Carbonated Beverage Bottle Bottom Structure Based on Manual–Automatic Double-Adjustment Optimization" Polymers 14, no. 14: 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142845
APA StyleGe-Zhang, S., Chen, X., Zhu, H., Song, Y., Ding, Y., & Cui, J. (2022). Computer Simulation of Polyethylene Terephthalate Carbonated Beverage Bottle Bottom Structure Based on Manual–Automatic Double-Adjustment Optimization. Polymers, 14(14), 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142845






