A Study on Highly Effective Electromagnetic Wave Shield Textile Shell Fabrics Made of Point Polyester/Metallic Core-Spun Yarns
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Testing
2.3.1. Tensile Performances of the Core-Spun Yarns
2.3.2. Tensile Performances of the Non-Woven Fabrics
2.3.3. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness (EMI SE) of Non-Woven Fabrics
2.3.4. Air Permeability of Non-Woven Fabrics
2.3.5. Negative Ion Release of Non-Woven Fabrics
3. Results and Discussion
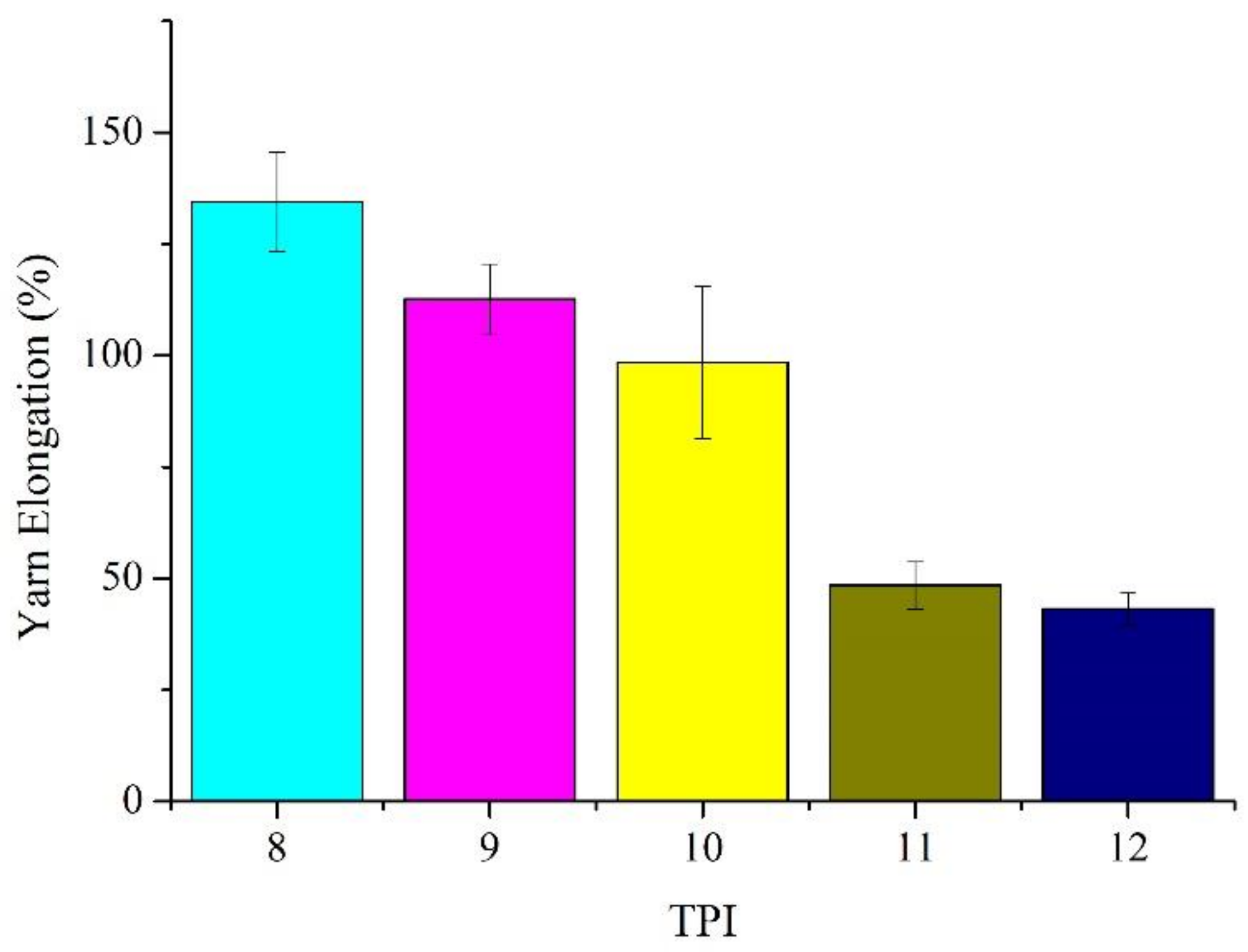
3.1. Tensile Strength and Elongation of Ge/SS Core-Spun Yarns as Related to TPI
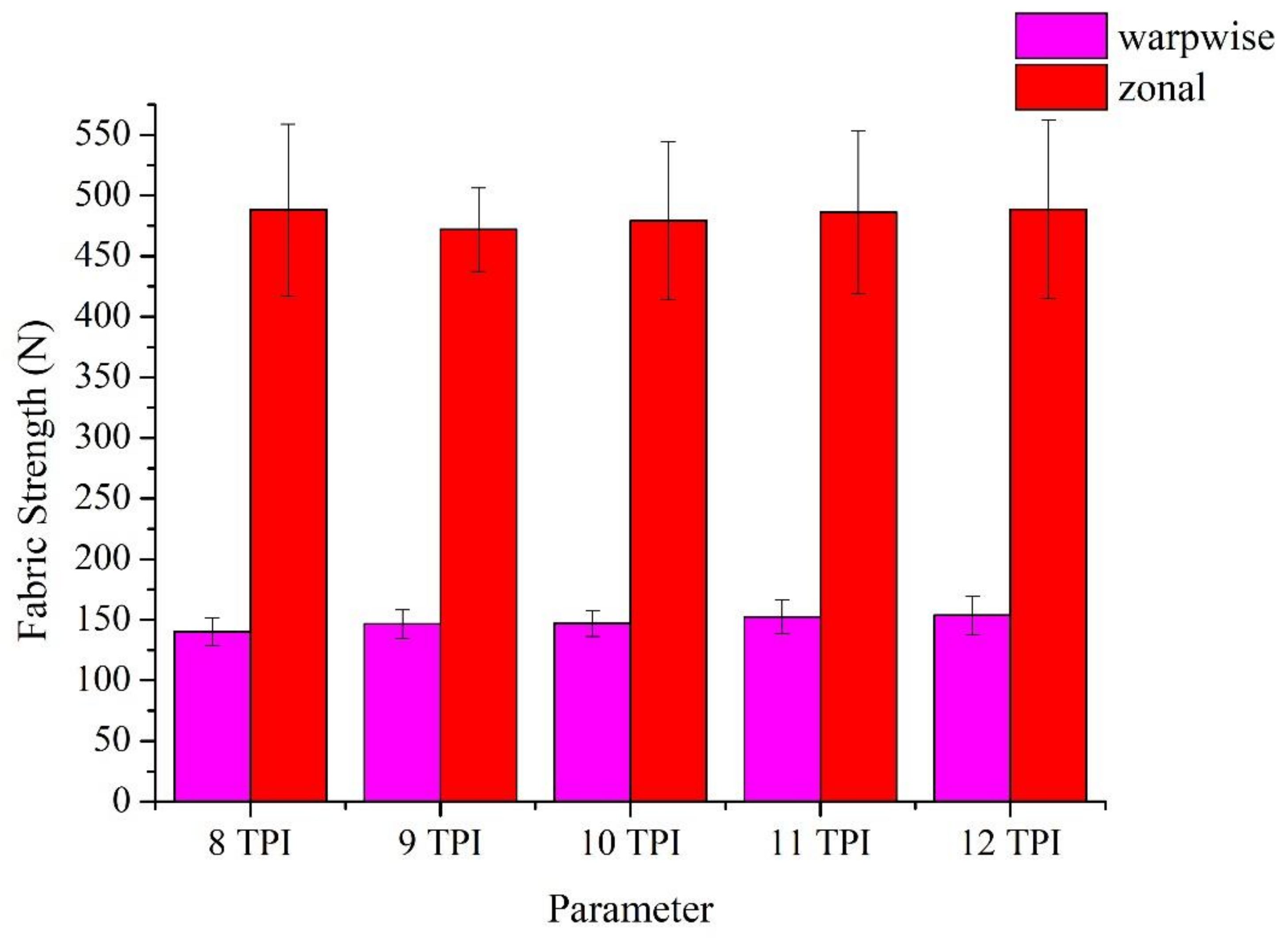
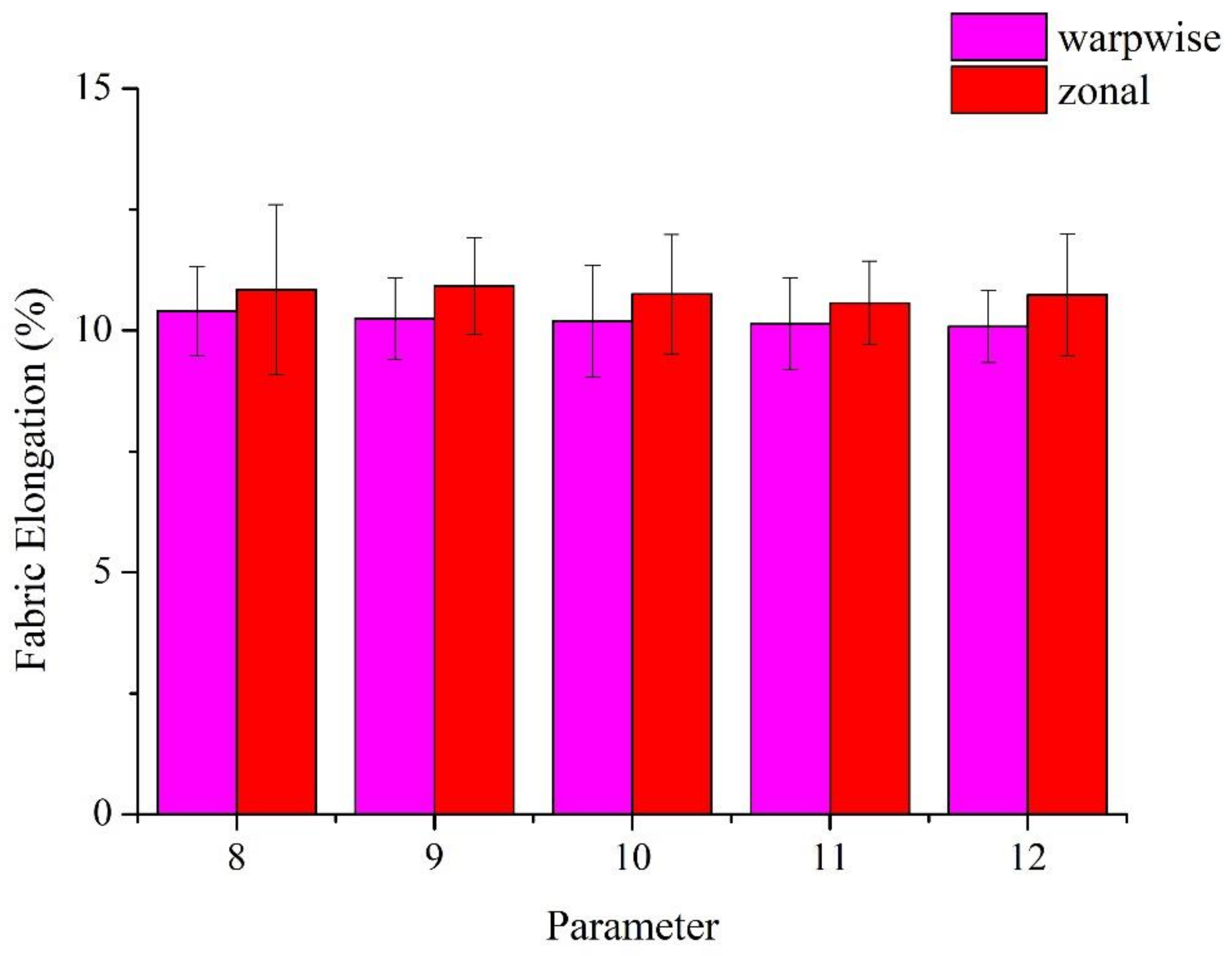
3.2. Tensile Strength and Elongation of Woven Fabrics as Related to TPI of Constituent Ge/SS Core-Spun Yarns
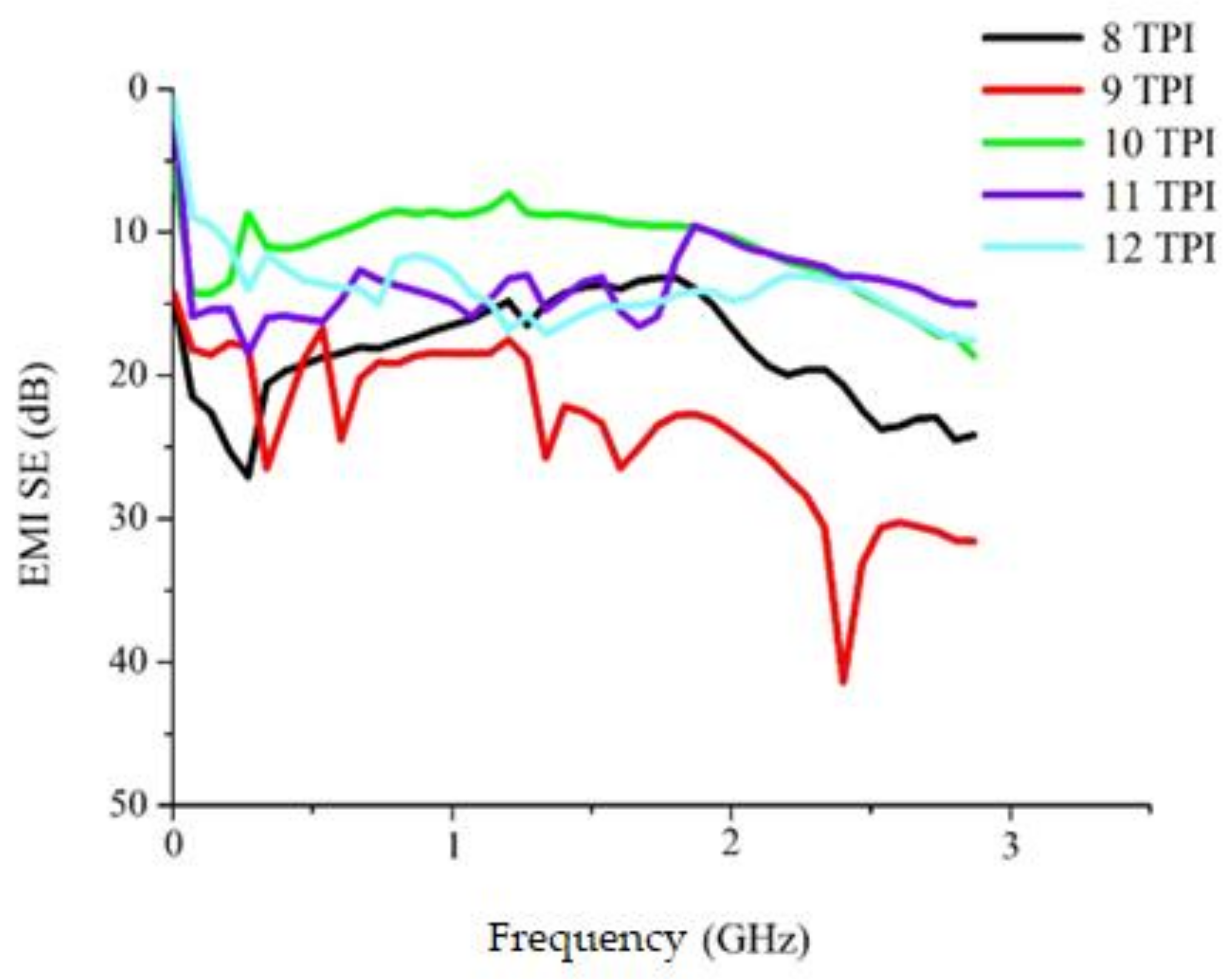
3.3. Electromagnetic Wave Shielding of Woven Fabrics as Related to the TPI of Constituent Ge/SS Core-Spun Yarns
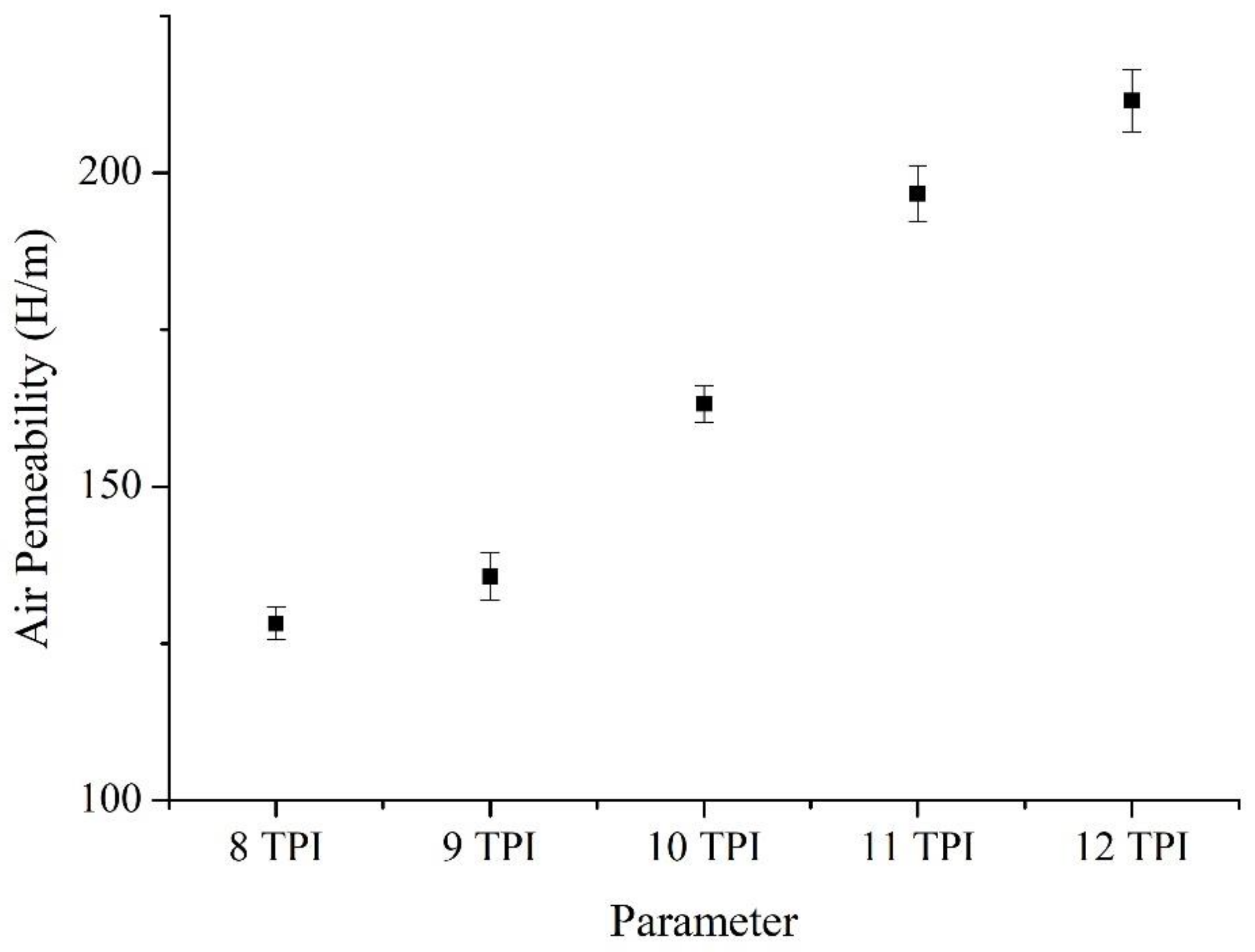
3.4. Air Permeability of Woven Fabrics as Related to TPI of Constituent Ge/SS Core-Spun Yarns
3.5. Negative Ion Release of Woven Fabrics as Related to TPI of Constituent Ge/SS Core-Spun Yarns
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berg-Beckhoff, G.; Kowall, B.; Breckenkamp, J. Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields: Health Effects. In Encyclopedia on Environmental Health Elsevier; Elsevier Editora: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2011; pp. 721–727. [Google Scholar]
- Feyyaz, O.; Aysegul, K. Electromagnetic Waves and Human Health, Electromagnetic Waves; Zhurbenko, V., Ed.; InTech: West Palm Beach, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortazavi, S.; Parsanezhad, M.E.; Kazempour, M.; Ghahramani, P.; Mortazavi, A.; Davari, M. Male reproductive health under threat: Short term exposure to radiofrequency radiations emitted by common mobile jammers. J. Hum. Reprod. Sci. 2013, 6, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wdowiak, A.; Mazurek, P.A.; Wdowiak, A.; Bojar, I. Effect of electromagnetic waves on human reproduction. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2017, 24, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Kang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Ding, Y.; Ma, M.; Gao, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y. Electromagnetic shielding hybrid nanogenerator for health monitoring and protection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1703801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Nath, R.; Mathur, A.K.; Sharma, R.S. Effect of radiofrequency radiation on reproductive health. Indian J. Med. Res. 2018, 148, S92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.; Abbas, S.; Abhyankar, A. Ultra-lightweight hybrid woven fabric containing stainless steel/polyester composite yarn for total EMI shielding in frequency range 8–18 GHz. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2015, 29, 1454–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, C.-W.; Li, T.-T.; Hwang, P.-W.; Chen, A.-P.; Lin, J.H. Preparation technique and EMI shielding evaluation of flexible conductive composite fabrics made by single and double wrapped yarns. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2017, 12, 155892501701200410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, M.-F.; Lou, C.-W.; Lin, T.A.; Wang, C.-H.; Lin, J.-H. High-strength conductive yarns and fabrics: Mechanical properties, electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness, and manufacturing techniques. J. Text. Inst. 2021, 112, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-H.; Huang, Y.-T.; Li, T.-T.; Lin, C.-M.; Lou, C.-W. Manufacture technique and performance evaluation of electromagnetic-shielding/far-infrared elastic warp-knitted composite fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2016, 107, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardanuy, M.; Rodríguez-Perez, M.; Algaba, I. Electrical conductivity and mechanical properties of vapor-grown carbon nanofibers/trifunctional epoxy composites prepared by direct mixing. Compos. Part B Eng. 2011, 42, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Y.; Liao, S.-Y.; Wan, Y.-J.; Huang, H.-P.; Li, X.-M.; Hu, Y.-G.; Zhu, P.-L.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.-P. Near-field and far-field EMI shielding response of lightweight and flexible MXene-decorated polyester textiles. Mater. Today Phys. 2022, 23, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, W.; Tong, X.; Lu, S.; Wang, B.; Ma, K.; Yang, C.; Li, Q. Hydroiodic acid and microwave reduced graphene oxide/PES-C films for flexible EMI shielding materials. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2021, 120, 108645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Song, L.; Jie, G.; Hu, Y. Durable electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding ramie fabric with excellent flame retardancy and Self-healing performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 602, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.H.; Han, Y.K.; Kwon, S.J.; Kim, T.; Jung, B.M.; Lee, S.-B.; Park, B. Absorption-dominant, low reflection EMI shielding materials with integrated metal mesh/TPU/CIP composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthi, N.; Faisal, M.; Raghavendra, N. Conducting polymer based composites as efficient EMI shielding materials: A comprehensive review and future prospects. Synth. Met. 2021, 272, 116664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, P.; Mi, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Engineering multilayered MXene/electrospun poly (lactic acid) membrane with increscent electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding for integrated Joule heating and energy generating. Compos. Commun. 2021, 26, 100770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.K.; Noorbakhsh, B.; Nazari, B.; Ranjbar, Z. Preparation and EMI shielding performance of epoxy/non-metallic conductive fillers nano-composites. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 145, 105674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Cui, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, G.; Liu, S.; He, Y.; Yu, Y.; Qi, D. Integrated hierarchical macrostructures of flexible basalt fiber composites with tunable electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and rapid electrothermal response. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 224, 109193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-I.; Chern, J.-T. Effect of stainless steel-containing fabrics on electromagnetic shielding effectiveness. Text. Res. J. 2004, 74, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-Y.; Lee, S.-E.; Kim, C.-G.; Han, J.-H. Application of MWNT-added glass fabric/epoxy composites to electromagnetic wave shielding enclosures. Compos. Struct. 2007, 81, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendrakumar, K.; Thilagavathi, G. A study on the effect of construction parameters of metallic wire/core spun yarn based knitted fabrics on electromagnetic shielding. J. Ind. Text. 2013, 42, 400–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzeziński, S.; Rybicki, T.; Karbownik, I.; Malinowska, G.; Rybicki, E.; Szugajew, L.; Lao, M.; Śledzińska, K. Textile multi-layer systems for protection against electromagnetic radiation. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2009, 2, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Perumalraj, R.; Dasaradhan, B.; Nalankilli, G. Copper, stainless steel, glass core yarn, and ply yarn woven fabric composite materials properties. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2010, 29, 3074–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedeloglu, A. Electrical, electromagnetic shielding, and some physical properties of hybrid yarn-based knitted fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2013, 104, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Krishnasamy, J.; Alagirusamy, R.; Basu, A. Analysis of the electromagnetic shielding behavior of stainless steel filament and PET/SS hybrid yarn incorporated conductive woven fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 2423–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, H.; Uğurlu, Ş.S.; Özkurt, A. The electromagnetic shielding of textured steel yarn based woven fabrics used for clothing. J. Ind. Text. 2015, 45, 416–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.; Mondal, S.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.; Huh, Y.-I.; Nah, C. Flexible thermoplastic polyurethane-carbon nanotube composites for electromagnetic interference shielding and thermal management. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Ravindren, R.; Bhawal, P.; Shin, B.; Ganguly, S.; Nah, C.; Das, N.C. Combination effect of carbon nanofiber and ketjen carbon black hybrid nanofillers on mechanical, electrical, and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of chlorinated polyethylene nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 197, 108071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Remanan, S.; Mondal, S.; Ganguly, S.; Das, P.; Singha, N.; Das, N.C. An approach to prepare mechanically robust full IPN strengthened conductive cotton fabric for high strain tolerant electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 344, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-H.; Hsu, P.-W.; Huang, C.-H.; Lai, M.-F.; Shiu, B.-C.; Lou, C.-W. A Study on Carbon Fiber Composites with Low-Melting-Point Polyester Nonwoven Fabric Reinforcement: A Highly Effective Electromagnetic Wave Shield Textile Material. Polymers 2022, 14, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X. A Flexible Sandwich Structure Carbon Fiber Cloth with Resin Coating Composite Improves Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Performance at Low Frequency. Polymers 2022, 14, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Wang, Y.; He, J. Effects of carbonyl iron powder (CIP) content on the electromagnetic wave absorption and mechanical properties of CIP/ABS composites. Polymers 2020, 12, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Vecchia, A.; Mucci, F.; Pozza, A.; Marazziti, D. Negative air ions in neuropsychiatric disorders. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 2521–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.-Y.; Ma, A.; Ramachandran, S. Negative air ions and their effects on human health and air quality improvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ge, M. Negative air ion release and far infrared emission properties of polyethylene terephthalate/germanium composite fiber. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2017, 12, 155892501701200107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajwin, A.J.; Giridev, V.; Renukadevi, M. Effect of yarn twist on mechanical properties of glass fibre reinforced composite rods. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2012, 37, 343–346. [Google Scholar]
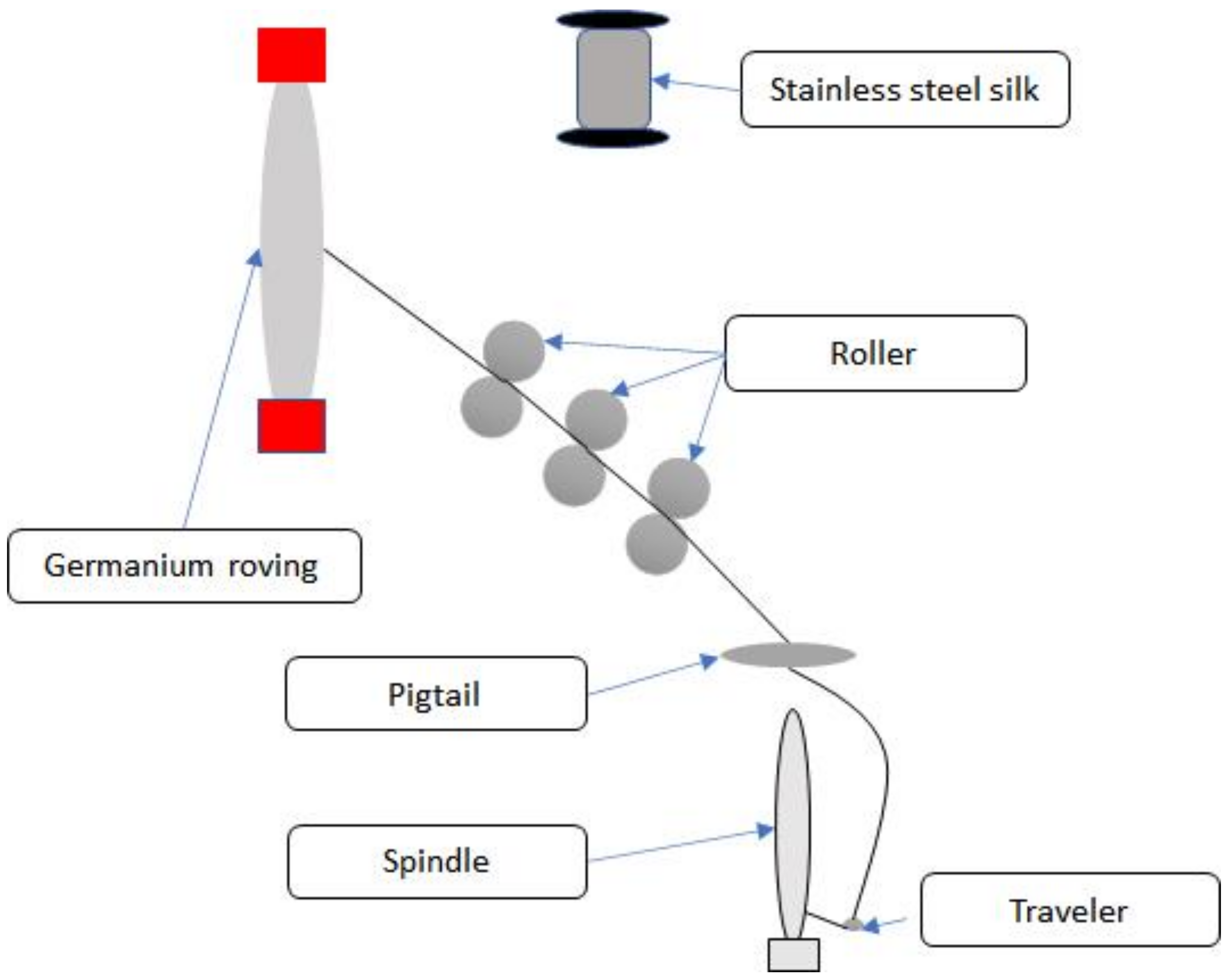
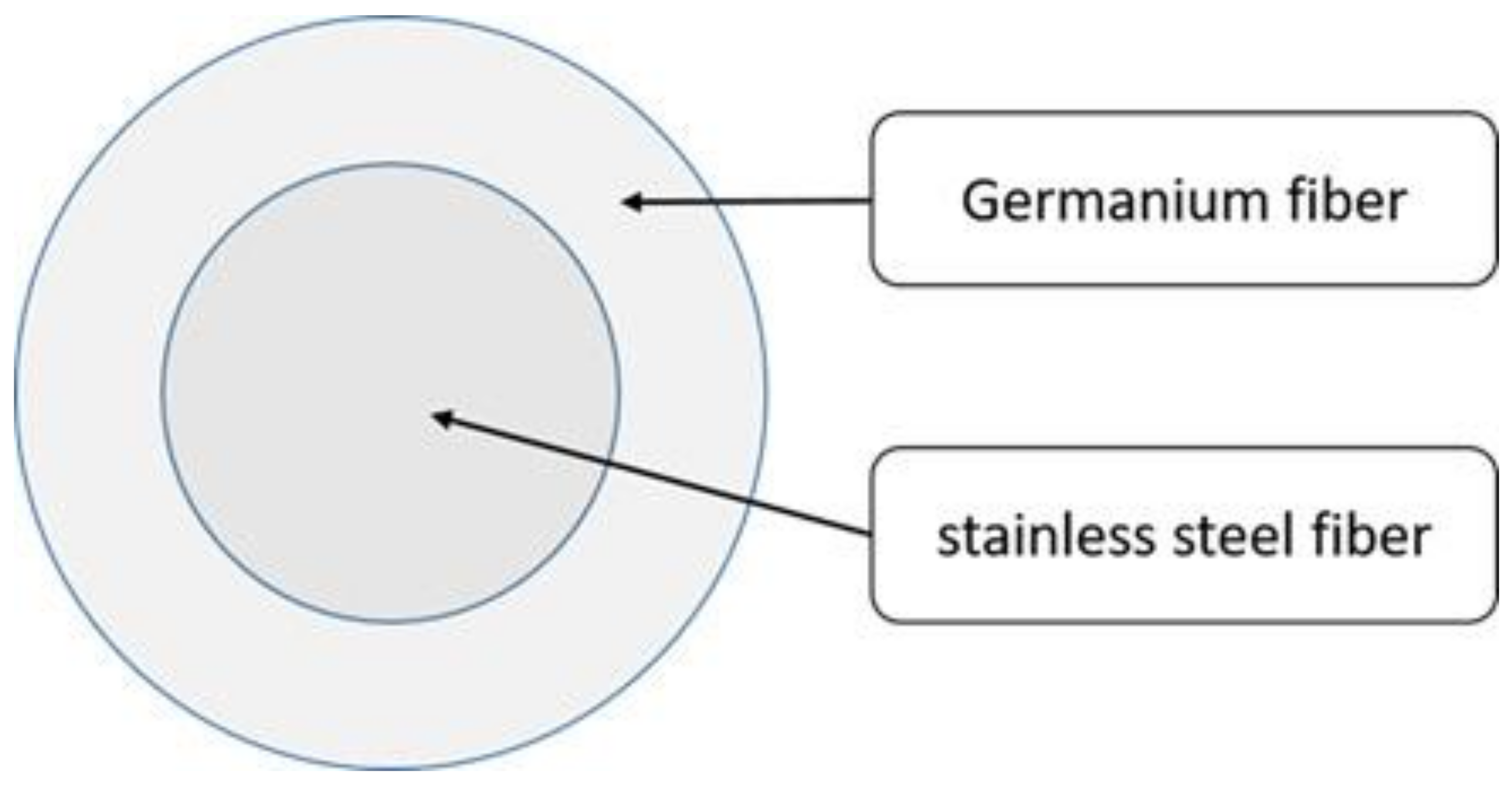


| Yarn Twist (TPI) | Yarn Strength (N) | Yarn Elongation (%) | Yarn Diameter (mm) | Yarn Strength CV% | Yarn Tenacity (N/mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 3.0 ± 0.18 | 134.4 ± 11.2 | 0.327 | 6.0% | 35.7 ± 2.1 |
| 9 | 3.8 ± 0.15 | 112.7 ± 7.79 | 0.304 | 4.0% | 52.4 ± 2.0 |
| 10 | 4.3 ± 0.23 | 98.4 ± 17.04 | 0.288 | 5.4% | 66.0 ± 3.5 |
| 11 | 4.5 ± 0.28 | 48.5 ± 5.27 | 0.275 | 6.2% | 75.8 ± 4.7 |
| 12 | 5.0 ± 0.26 | 43.2 ± 3.51 | 0.245 | 5.3% | 106.1 ± 5.5 |
| Parameter | Yarn Strength (N) | Fabric Strength along the Warp Direction (N) | Fabric Strength along the Weft Direction (N) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 TPI | 3.0 ± 0.18 | 140.0 ± 11.5 | 488.1 ± 70.6 |
| 9 TPI | 3.8 ± 0.15 | 146.6 ± 11.7 | 471.9 ± 34.4 |
| 10 TPI | 4.3 ± 0.23 | 147.0 ± 10.8 | 479.0 ± 65.1 |
| 11 TPI | 4.5 ± 0.28 | 152.4 ± 13.9 | 486.2 ± 66.9 |
| 12 TPI | 5.0 ± 0.26 | 153.6 ± 15.9 | 488.7 ± 73.8 |
| Parameter | Yarn Elongation (%) | Fabric Elongation (%) (Warpwise) | Fabric Elongation (%) (Zonal) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 TPI | 3.0 ± 0.18 | 10.40 ± 0.92 | 10.84 ± 1.76 |
| 9 TPI | 3.8 ± 0.15 | 10.25 ± 0.84 | 10.92 ± 1.00 |
| 10 TPI | 4.3 ± 0.23 | 10.20 ± 1.15 | 10.75 ± 1.23 |
| 11 TPI | 4.5 ± 0.28 | 10.14 ± 0.96 | 10.57 ± 0.86 |
| 12 TPI | 5.0 ± 0.26 | 10.08 ± 0.75 | 10.74 ± 1.25 |
| PI | Air Permeability (H/m) |
|---|---|
| 8 | 128 |
| 9 | 136 |
| 10 | 163 |
| 11 | 197 |
| 12 | 212 |
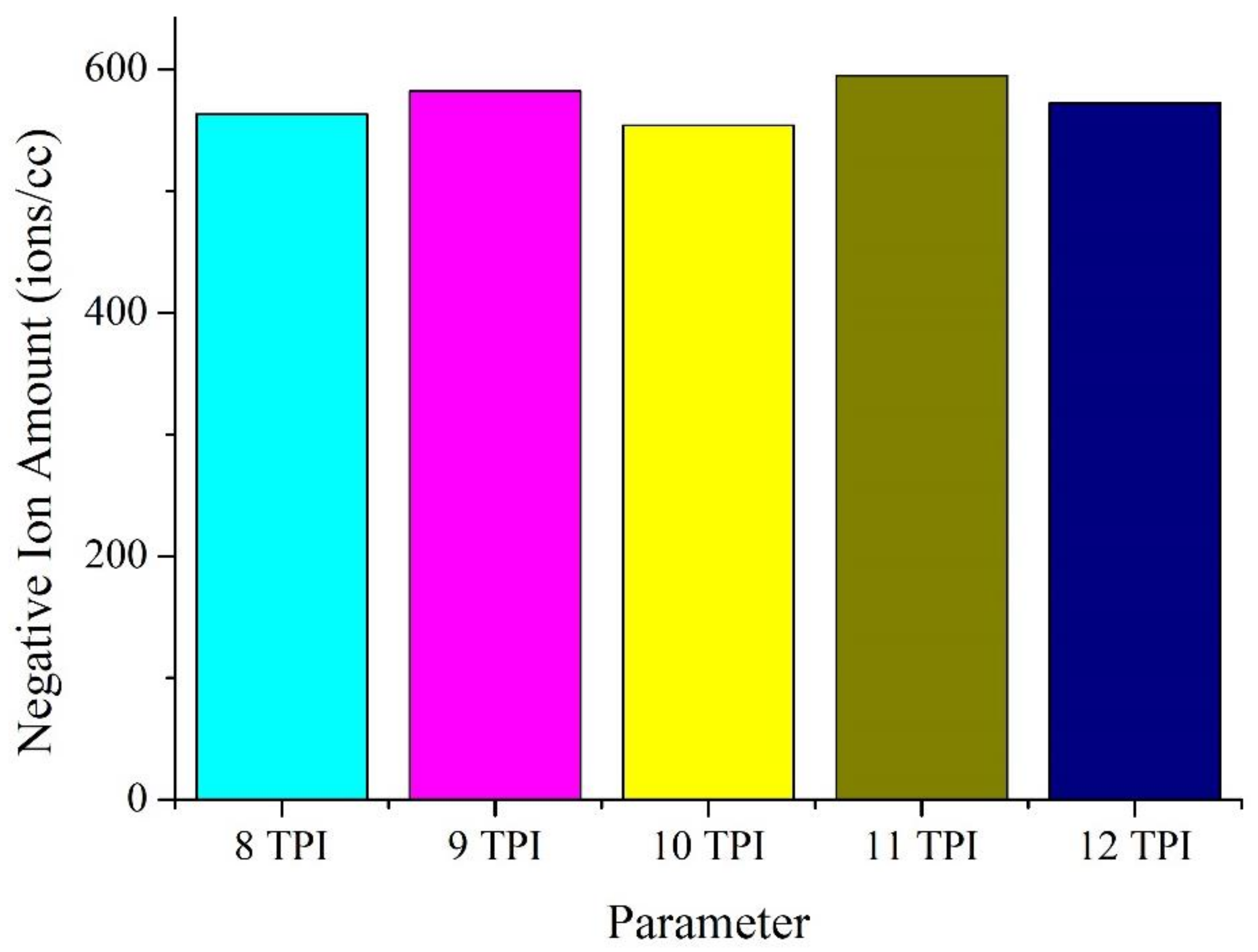
| TPI | Negative Ion Amount (Ions/cc) |
|---|---|
| 8 | 563 |
| 9 | 582 |
| 10 | 554 |
| 11 | 595 |
| 12 | 572 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.-H.; Hsu, P.-W.; Ke, Z.-W.; Lin, J.-H.; Shiu, B.-C.; Lou, C.-W.; Lin, J.-H. A Study on Highly Effective Electromagnetic Wave Shield Textile Shell Fabrics Made of Point Polyester/Metallic Core-Spun Yarns. Polymers 2022, 14, 2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132536
Huang C-H, Hsu P-W, Ke Z-W, Lin J-H, Shiu B-C, Lou C-W, Lin J-H. A Study on Highly Effective Electromagnetic Wave Shield Textile Shell Fabrics Made of Point Polyester/Metallic Core-Spun Yarns. Polymers. 2022; 14(13):2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132536
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chen-Hung, Po-Wen Hsu, Zhao-We Ke, Jian-Hong Lin, Bing-Chiuan Shiu, Ching-Wen Lou, and Jia-Horng Lin. 2022. "A Study on Highly Effective Electromagnetic Wave Shield Textile Shell Fabrics Made of Point Polyester/Metallic Core-Spun Yarns" Polymers 14, no. 13: 2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132536
APA StyleHuang, C.-H., Hsu, P.-W., Ke, Z.-W., Lin, J.-H., Shiu, B.-C., Lou, C.-W., & Lin, J.-H. (2022). A Study on Highly Effective Electromagnetic Wave Shield Textile Shell Fabrics Made of Point Polyester/Metallic Core-Spun Yarns. Polymers, 14(13), 2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132536








