Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Intestinal Sleeve Implants for the Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Sections
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PVDF Films
2.3. Characterization of PVDF Films
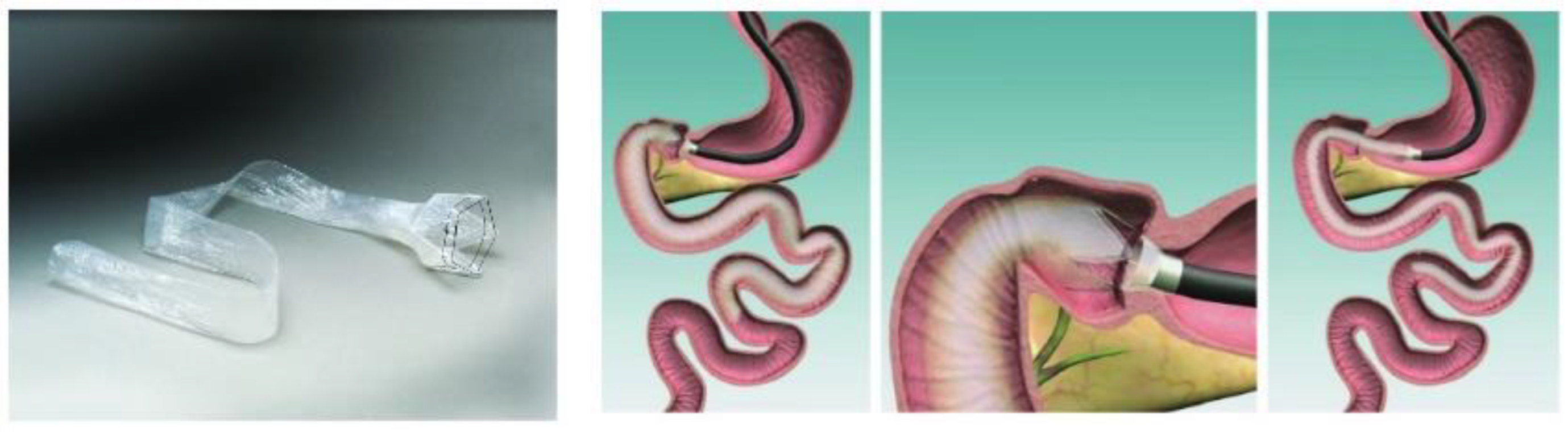
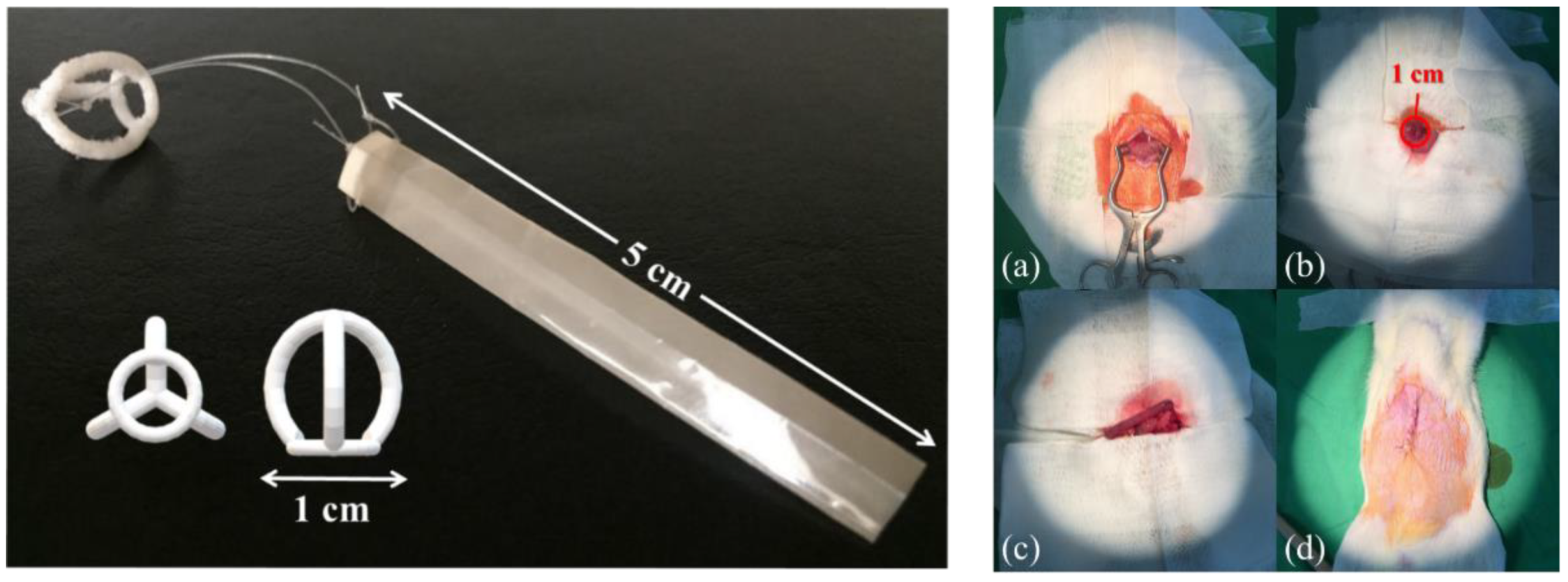
2.4. Preparation of PVDF Film Intestinal Sleeve Implants
2.5. Animal Experiments
2.6. The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
3. Result and Discussion
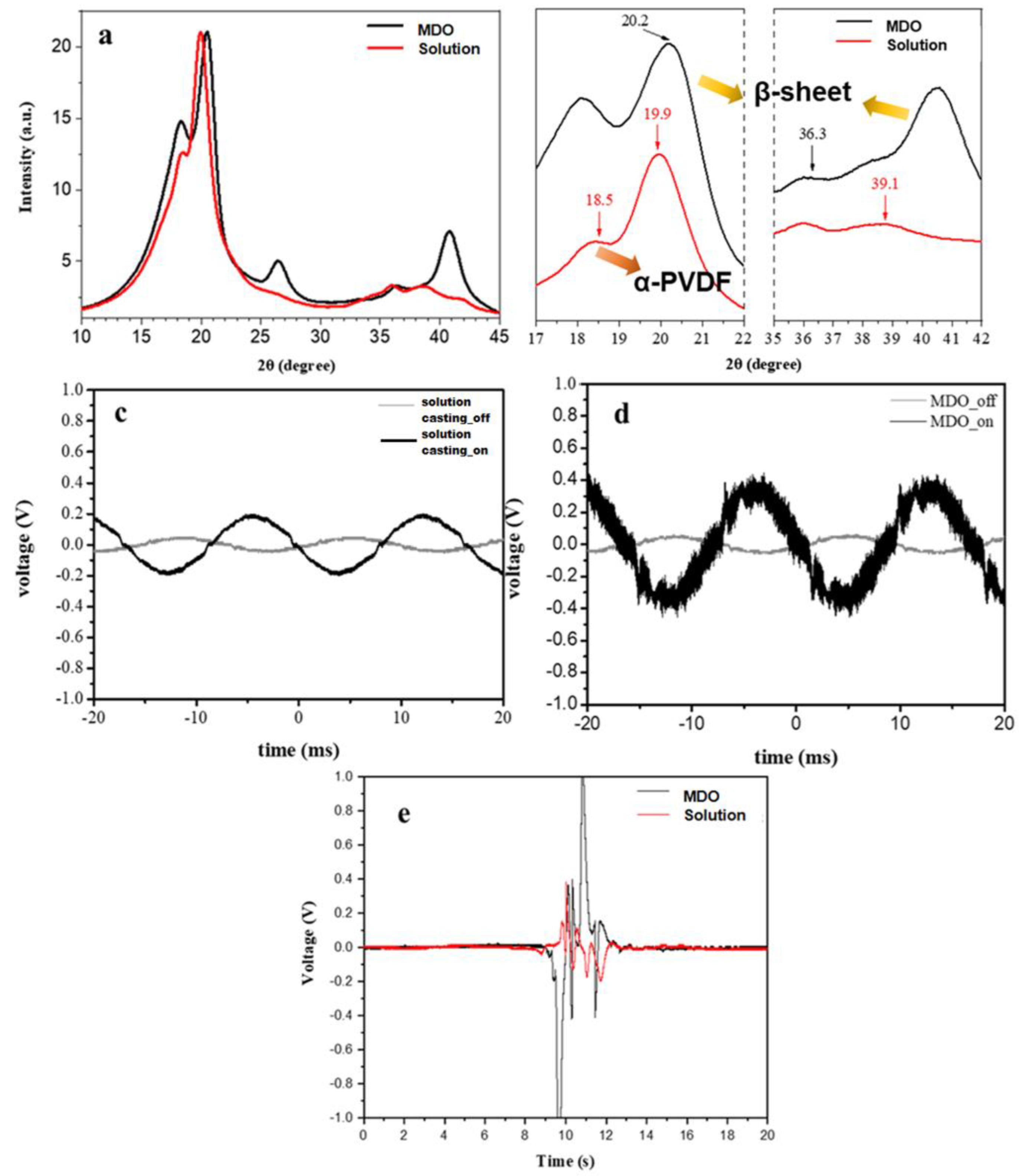
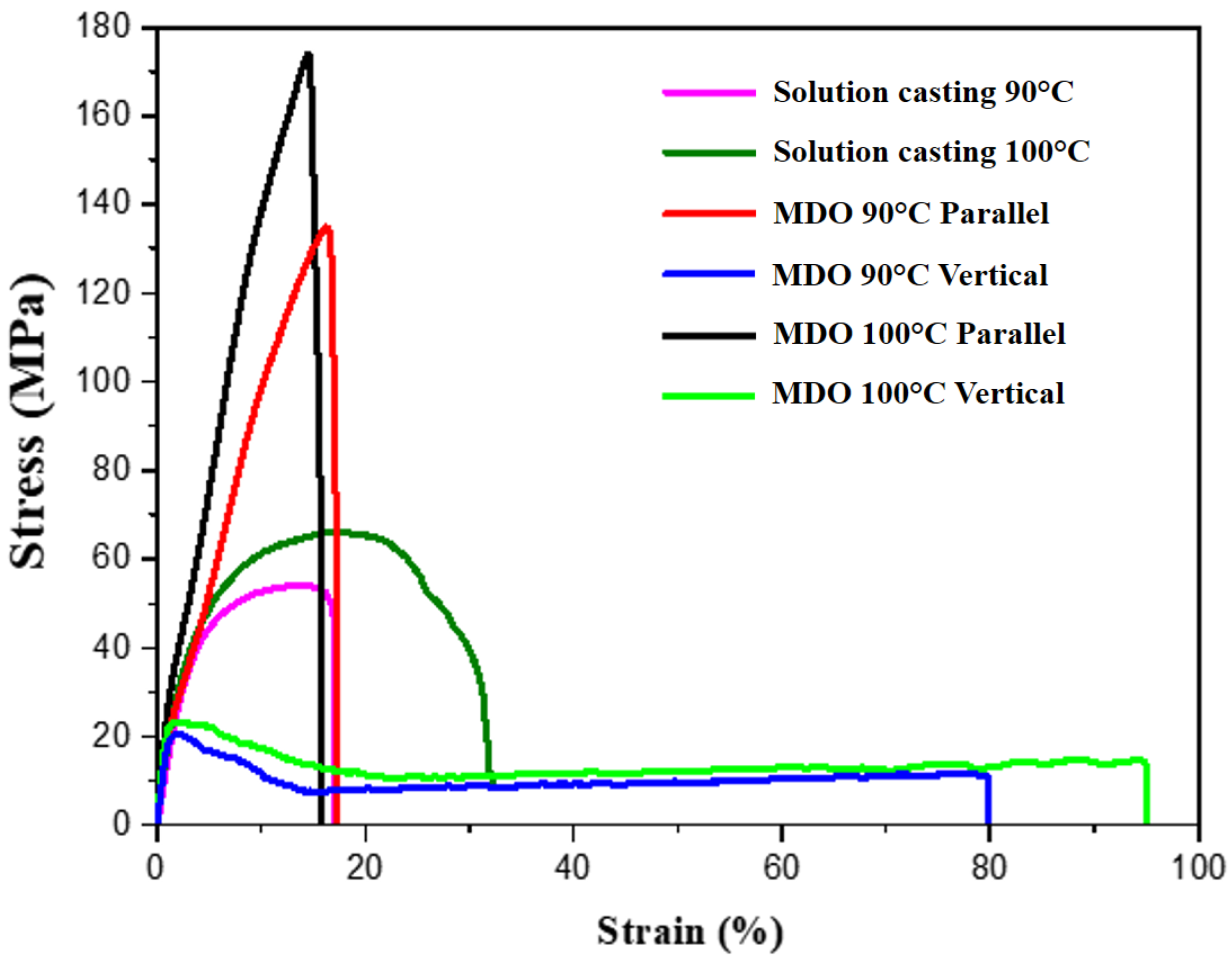
3.1. Characterization of PVDF Films
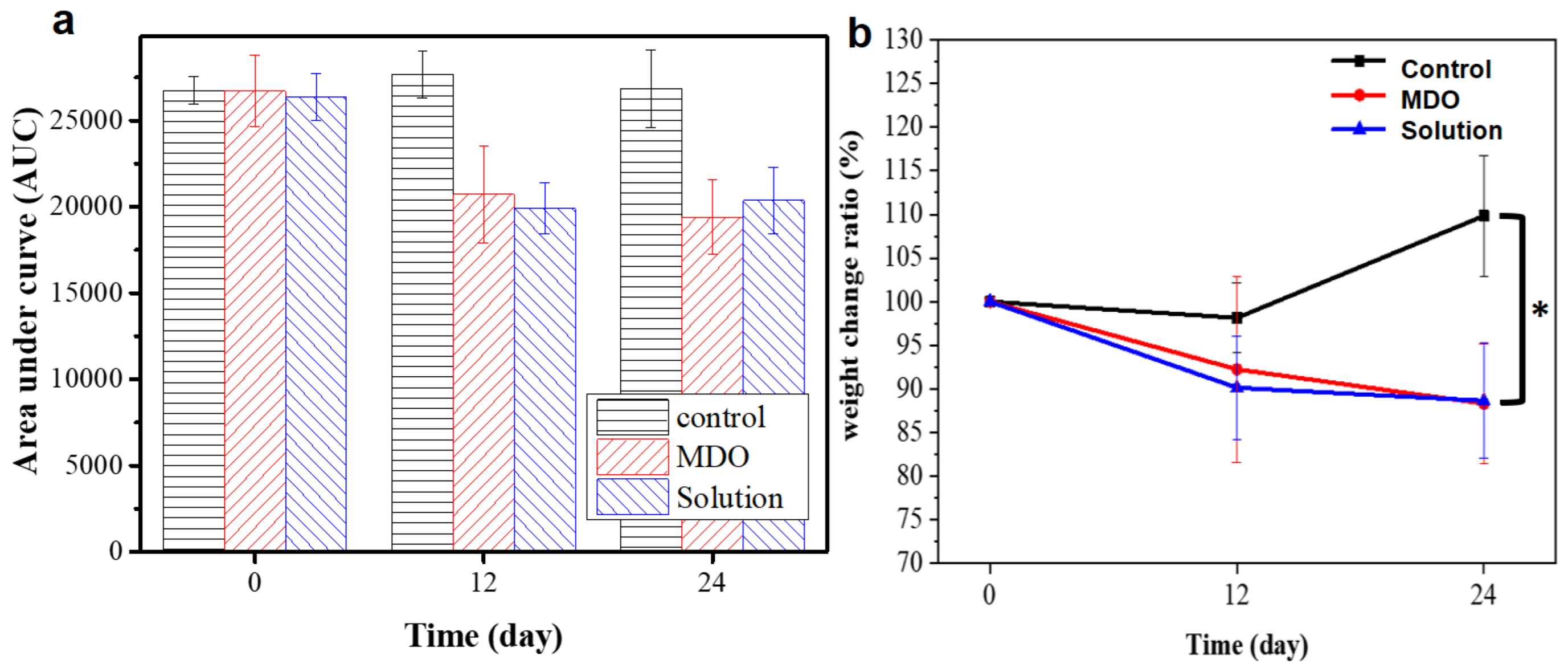
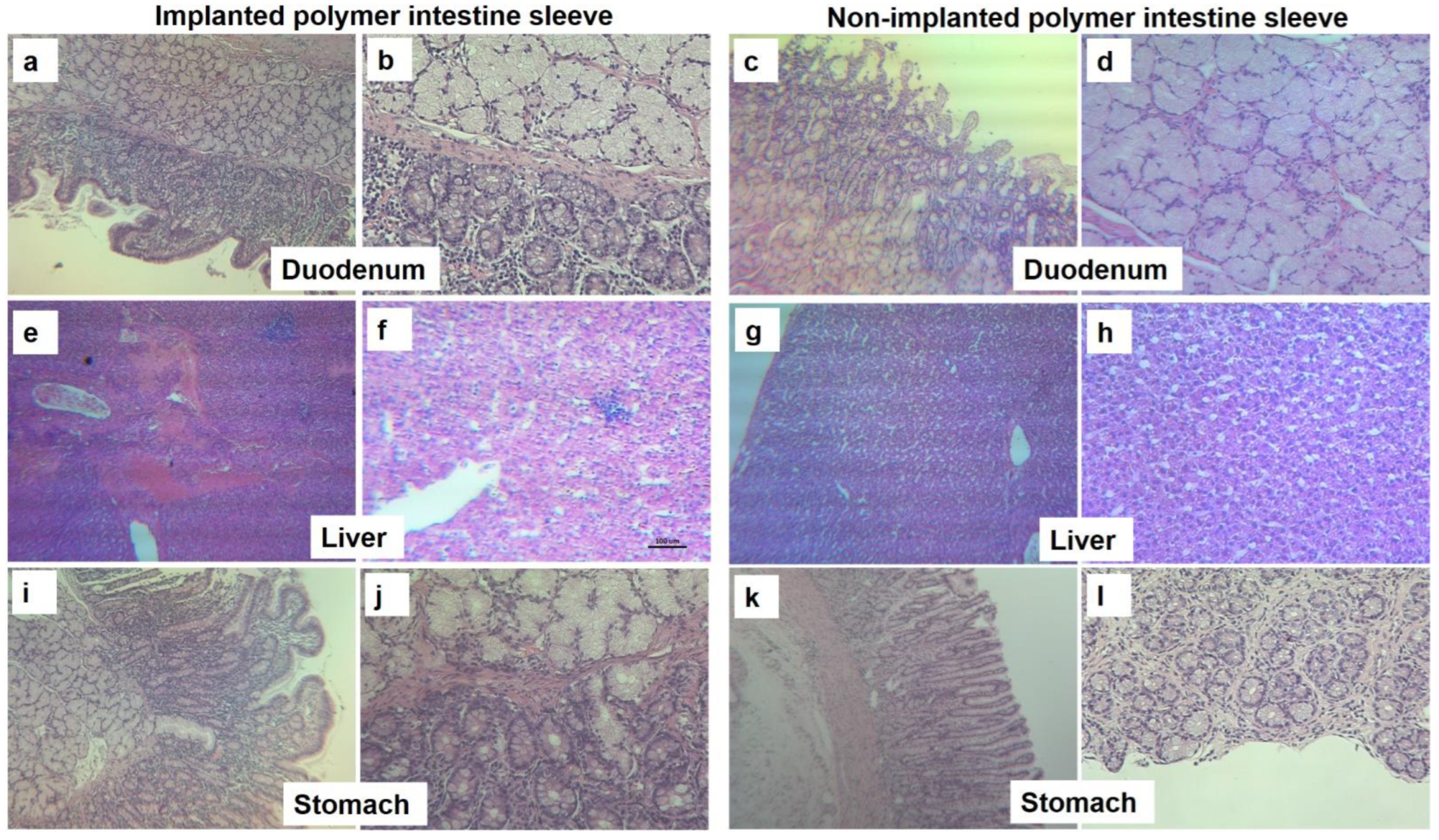
3.2. In Vivo PVDF Film Intestinal Sleeve Implantation for Glucose and Obesity Control
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roglic, G. WHO Global report on diabetes: A summary. Int. J. Noncommunicable Dis. 2016, 1, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, E.G. Trends in diabetes: Sounding the alarm. Lancet 2016, 387, 1485–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, S.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2017, 389, 2239–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Beydoun, M.A.; Liang, L.; Caballero, B.; Kumanyika, S.K. Will all Americans become overweight or obese? Estimating the progression and cost of the US obesity epidemic. Obesity 2008, 16, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bays, H.E.; Chapman, R.; Grandy, S.; The SHIELD Investigators’ Group. The relationship of body mass index to diabetes mellitus, hypertension and dyslipidaemia: Comparison of data from two national surveys. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2007, 61, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeClercq, V.; Taylor, C.; Zahradka, P. Adipose tissue: The link between obesity and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Haematol. Disord. Drug Targets 2008, 8, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElroy, S.L.; Kotwal, R.; Malhotra, S.; Nelson, E.B.; Keck, P.E.; Nemeroff, C.B. Are mood disorders and obesity related? A review for the mental health professional. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2004, 65, 634–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, C.F. Economic consequences of the obese. Diabetes 2007, 56, 2668–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stafford, R.S.; Farhat, J.H.; Misra, B.; Schoenfeld, D.A. National patterns of physician activities related to obesity management. Arch. Fam. Med. 2000, 9, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nandagopal, R.; Brown, R.J.; Rother, K.I. Resolution of type 2 diabetes following bariatric surgery: Implications for adults and adolescents. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2010, 12, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higa, K.; Ho, T.; Tercero, F.; Yunus, T.; Boone, K.B. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: 10-year follow-up. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2011, 7, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, P.R.; Ikramuddin, S.; Gourash, W.; Ramanathan, R.; Luketich, J. Outcomes after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Ann. Surg. 2000, 232, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, P.R.; Burguera, B.; Ikramuddin, S.; Cottam, D.; Gourash, W.; Hamad, G.; Eid, G.M.; Mattar, S.; Ramanathan, R.; Barinas-Mitchel, E. Effect of laparoscopic Roux-en Y gastric bypass on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann. Surg. 2003, 238, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumbs, A.A.; Gagner, M.; Dakin, G.; Pomp, A. Sleeve gastrectomy for morbid obesity. Obes. Surg. 2007, 17, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himpens, J.; Dobbeleir, J.; Peeters, G. Long-term results of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for obesity. Ann. Surg. 2010, 252, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brethauer, S.A. Sleeve gastrectomy. Surg. Clin. 2011, 91, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzampassi, K.; Grosomanidis, V.; Papakostas, P.; Penna, S.; Eleftheriadis, E. 500 intragastric balloons: What happens 5 years thereafter? Obes. Surg. 2012, 22, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, I.; Taha, A.; Azar, C. Acute pancreatitis caused by intragastric balloon: A case report. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 10, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlen, C.; Bastens, B.; Herve, J.; Malmendier, C.; Dallemagne, B.; Jehaes, C.; Markiewicz, S.; Monami, B.; Weerts, J. The BioEnterics Intragastric Balloon (BIB): How to use it. Obes. Surg. 2001, 11, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fann, C.S.; Yang, S.-H.; Chen, H.-H.; Chen, C.-Y. Weight loss and metabolic improvements in obese patients undergoing gastric banding and gastric banded plication: A comparison. Nutrition 2019, 57, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, A.E.; Kiroff, G.; Game, P.; Foster, B.; O’Brien, P.; Ham, J.; Maddern, G.J. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in the treatment of obesity: A systematic literature review. Surgery 2004, 135, 326–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee, S.G. SAGES guideline for clinical application of laparoscopic bariatric surgery. Surg. Endosc. 2008, 22, 2281–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruban, A.; Ashrafian, H.; Teare, J.P. The EndoBarrier: Duodenal-jejunal bypass liner for diabetes and weight loss. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, N.; Mohanaruban, A.; Ashrafian, H.; Le Roux, C.; Byrne, J.; Mason, J.; Hopkins, J.; Kelly, J.; Teare, J. EndoBarrier®: A Safe and Effective Novel Treatment for Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes? Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 1980–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Moura, E.G.H.; Lopes, G.S.; da Costa Martins, B.; Orso, I.R.B.; Coutinho, A.M.N.; de Oliveira, S.L.; Sakai, P.; dos Passos Galvão-Neto, M.; Santo, M.A.; Sapienza, M.T.; et al. Effects of Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass Liner (EndoBarrier®) on Gastric Emptying in Obese and Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 1618–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heness, G.; Ben, N.B. Innovative Bioceramics. Materials Forum. 2004, 27, 104–114. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.; D'hooge, D.R.; Cardon, L. Recent progress on flexible and stretchable piezoresistive strain sensors: From design to application. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 114, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, M.J.; Prashanth, N.; Abisegapriyan, K.S.; Gaurav, K.; Kim, S.J. Method for fabricating highly crystalline polyvinylidene fluoride for piezoelectric energy-harvesting and vibration sensor applications. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2022, 6, 674–681. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Na, B.; Lv, R.; Li, C.; Zhu, J.; Yu, Z. Polar phase formation in poly (vinylidene fluoride) induced by melt annealing. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2012, 50, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, T.; Kanaoka, M.; Ohigashi, H. Improved piezoelectricity in thick lamellar β-form crystals of poly (vinylidene fluoride) crystallized under high pressure. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 2016–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Sencadas, V.; Ribelles, J.L.G.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Influence of processing conditions on polymorphism and nanofiber morphology of electroactive poly (vinylidene fluoride) electrospun membranes. Soft Mater. 2010, 8, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, A.; Hagström, B. Melt spinning of β-phase poly (vinylidene fluoride) yarns with and without a conductive core. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Chen, Y. β-phase formation of poly (vinylidene fluoride) from the melt induced by quenching. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1987, 6, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradys, A.; Sajkiewicz, P.; Adamovsky, S.; Minakov, A.; Schick, C. Crystallization of poly (vinylidene fluoride) during ultra-fast cooling. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 461, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallasamy, P.; Mohan, S. Vibrational spectroscopic characterization of form II poly (vinylidene fluoride). Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2005, 42, 821–827. [Google Scholar]
- Hilczer, B.; Markiewicz, E.; Połomska, M.; Tritt-Goc, J.; Kaszyńska, J.; Pogorzelec-Glaser, K.; Pietraszko, A. Properties of PVDF-MCM41 nanocomposites studied by dielectric, Raman and NMR spectroscopy. Ferroelectrics 2014, 472, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Lei, T.; Sun, D.; Lin, L. A critical analysis of the α, β and γ phases in poly (vinylidene fluoride) using FTIR. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15382–15389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imamura, R.; Silva, A.; Gregorio, R., Jr. γ → β Phase transformation induced in poly (vinylidene fluoride) by stretching. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 3242–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhao, X.; Peng, G.; Liu, W.; Liu, K.; Zhan, Z. Investigation on crystalline structure and dielectric relaxation behaviors of hot pressed poly (vinylidene fluoride) film. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2017, 17, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnakov, Y.A.; Paul, O.; Joaquim, A.; Falconer, A.; Mu, R.; Barnakov, V.Y.; Dikin, D.; Petranovskii, V.P.; Zavalin, A.; Ueda, A. Light intensity-induced phase transitions in graphene oxide doped polyvinylidene fluoride. Opt. Mater. Express 2018, 8, 2579–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoon Kim, T.; Arias, A.C. Characterization and Applications of Piezoelectric Polymers; Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lin, H.; Li, C.; Zhou, B.; Wang, X. Effects of Room Temperature Stretching and Annealing on the Crystallization Behavior and Performance of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Hollow Fiber Membranes. Membranes 2020, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yonus, H.; Chakravartty, S.; Sarma, D.R.; Patel, A.G. Endobarrier as a pre bariatric surgical intervention in high-risk patients: A feasibility study. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 3020–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| α 795 cm−1(a.u.) | β 840 cm−1 (a.u.) | γ 812 cm−1 (a.u.) | β/(α + γ) (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solution casting 90 °C | 81.0 | 142.0 | 177.0 | 35.5 |
| Solution casting 100 °C | 78.1 | 126.2 | 163.3 | 34.3 |
| MDO 90 °C | 154.6 | 329.6 | 107.7 | 55.7 |
| MDO 100 °C | 264.0 | 519.2 | 110.6 | 58.1 |
| Sample | Yield Point (MPa) | Average Elongation (%) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solution Casting 90 °C | 54.14 | 17.01 | 22.84 |
| Solution Casting 100 °C | 66.08 | 32.17 | 38.81 |
| MDO 90 °C Parallel | 134.58 | 16.33 | 34.67 |
| MDO 90 °C Vertical | 20.29 | 79.77 | 23.48 |
| MDO 100 °C Parallel | 173.72 | 14.59 | 36.28 |
| MDO 100 °C Vertical | 22.78 | 94.89 | 26.94 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, H.-M.; Zhan, W.-P.; Tsai, H.-C.; Yang, M.-R. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Intestinal Sleeve Implants for the Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Polymers 2022, 14, 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112178
Chang H-M, Zhan W-P, Tsai H-C, Yang M-R. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Intestinal Sleeve Implants for the Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Polymers. 2022; 14(11):2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112178
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Hao-Ming, Wei-Ping Zhan, Hsieh-Chih Tsai, and Meng-Ru Yang. 2022. "Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Intestinal Sleeve Implants for the Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes" Polymers 14, no. 11: 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112178
APA StyleChang, H.-M., Zhan, W.-P., Tsai, H.-C., & Yang, M.-R. (2022). Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Intestinal Sleeve Implants for the Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Polymers, 14(11), 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112178







