Efficient Congo Red Removal Using Porous Cellulose/Gelatin/Sepiolite Gel Beads: Assembly, Characterization, and Adsorption Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of MGS Gel Beads
2.3. Characterization of MGS Gel Beads
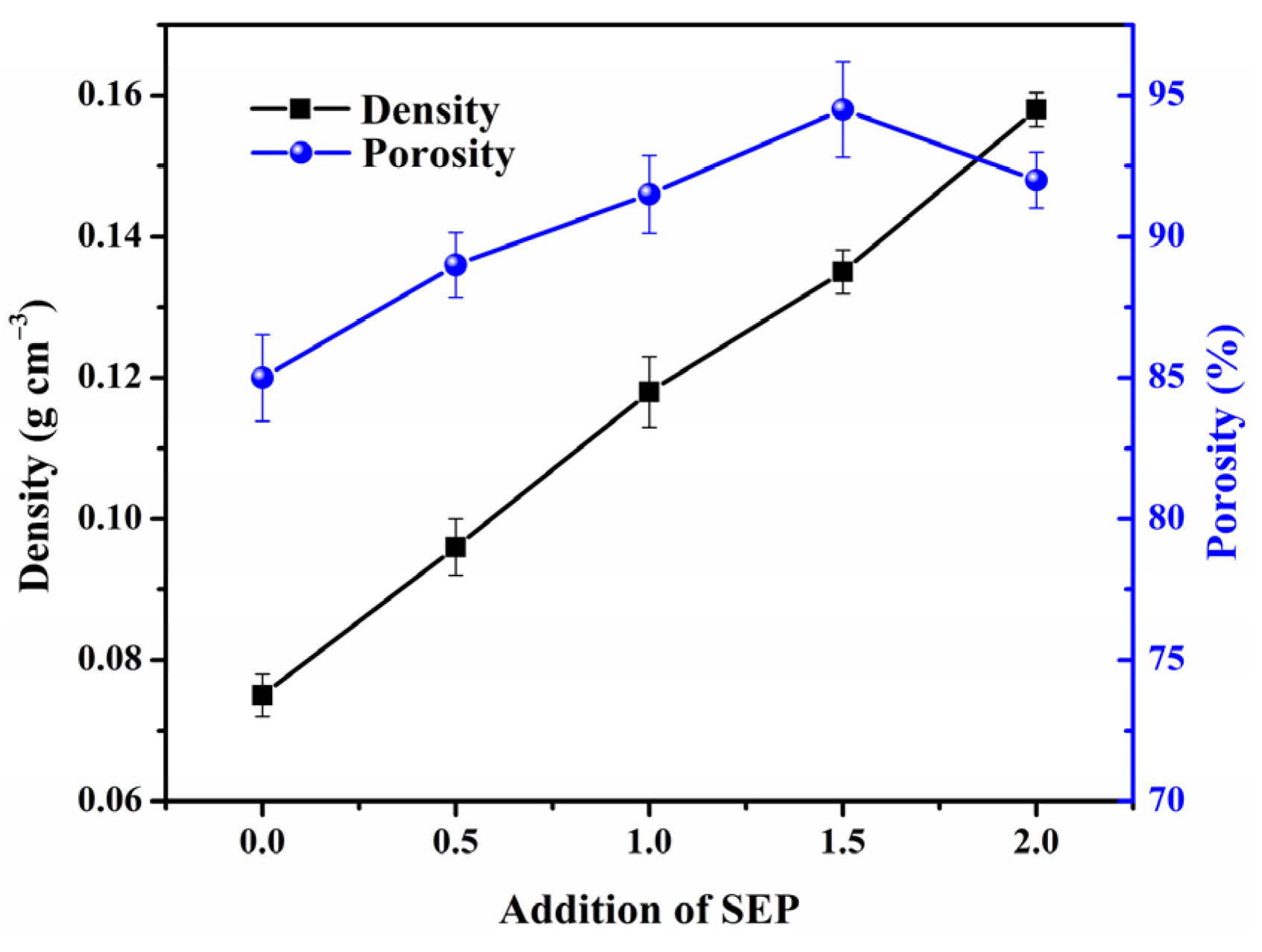
2.4. Density and Porosity Measurement
2.5. Adsorption and Desorption of CR Dye
3. Results and Discussion
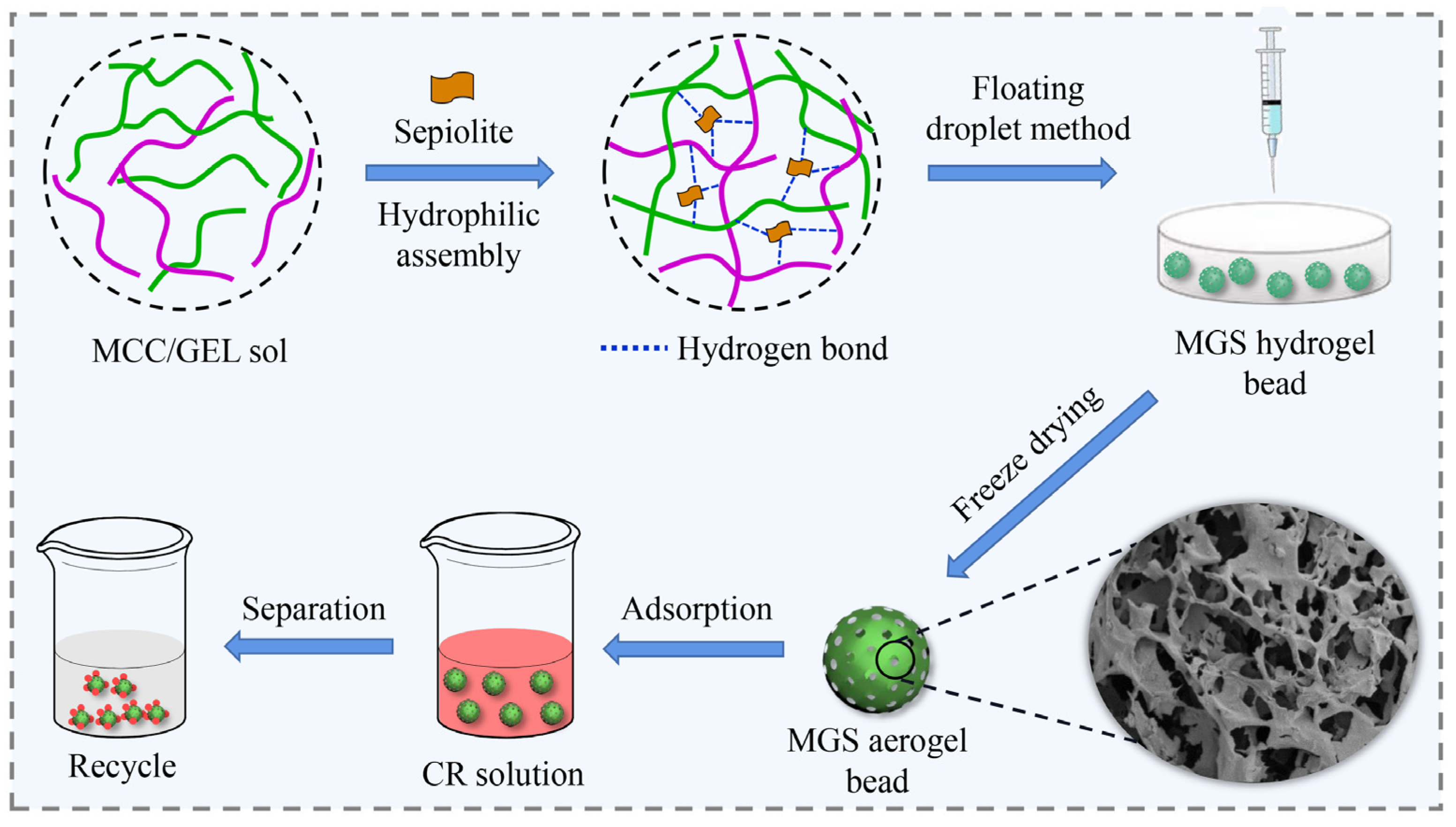
3.1. Fabrication Principle and Strategy of MGS Gel Beads
3.2. Chemical Analysis of MGS Gel Beads
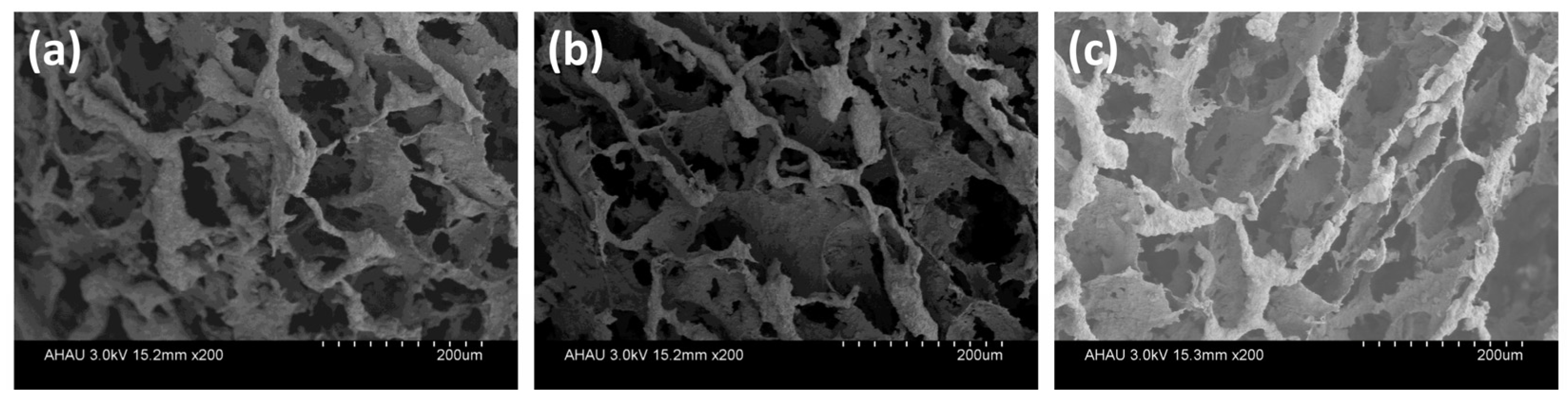
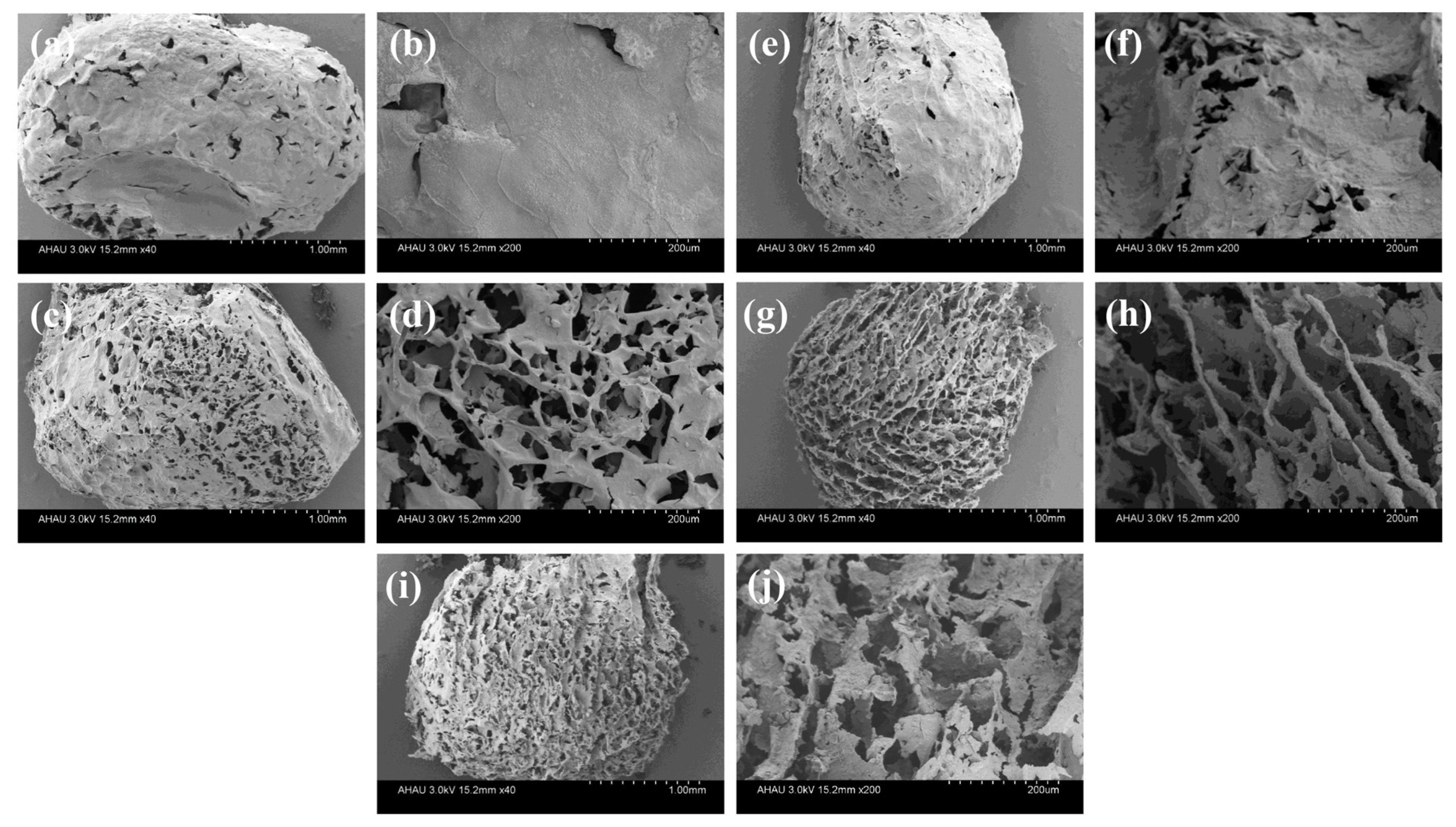
3.3. Structural Characterization of MGS Gel Beads
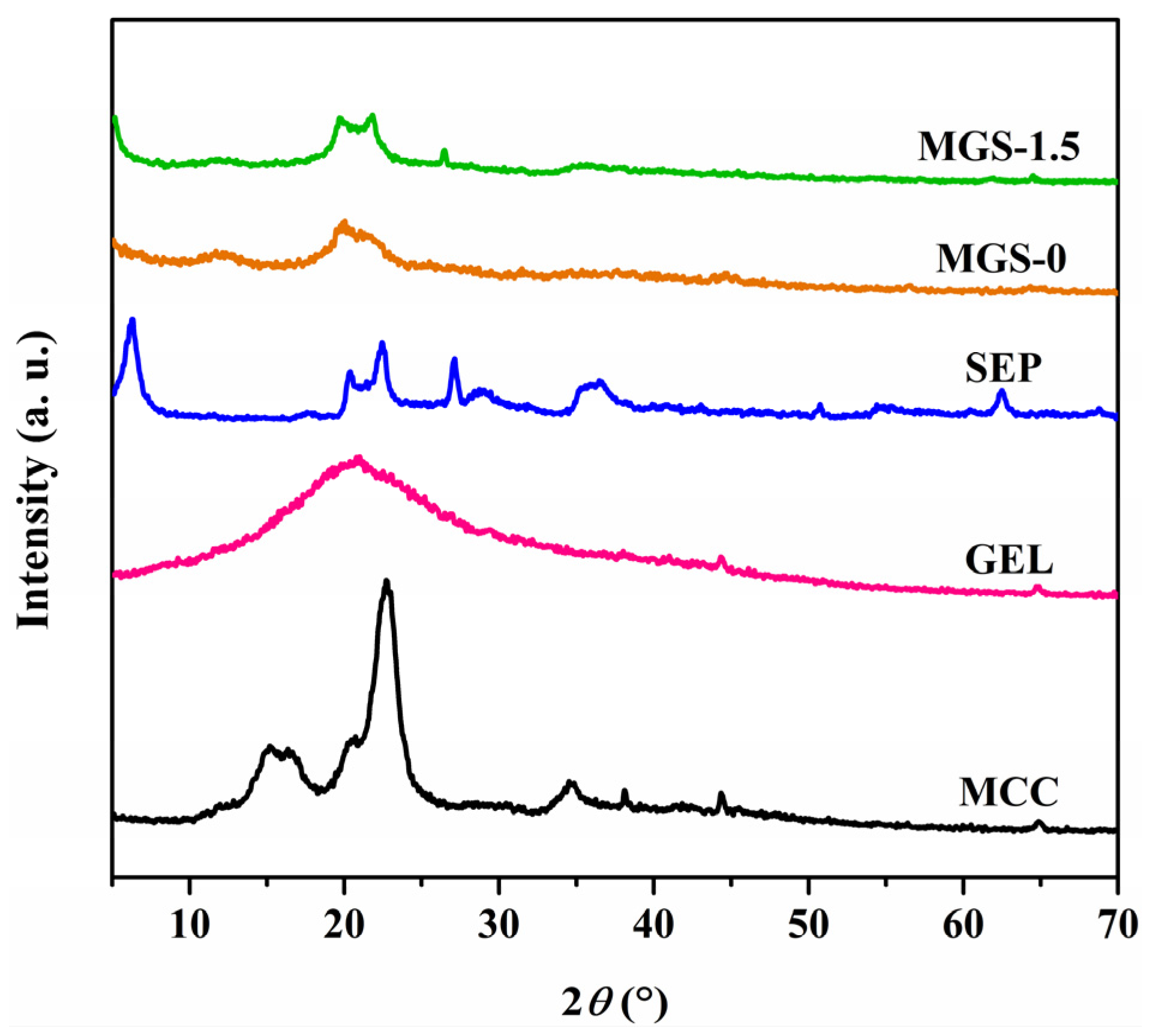
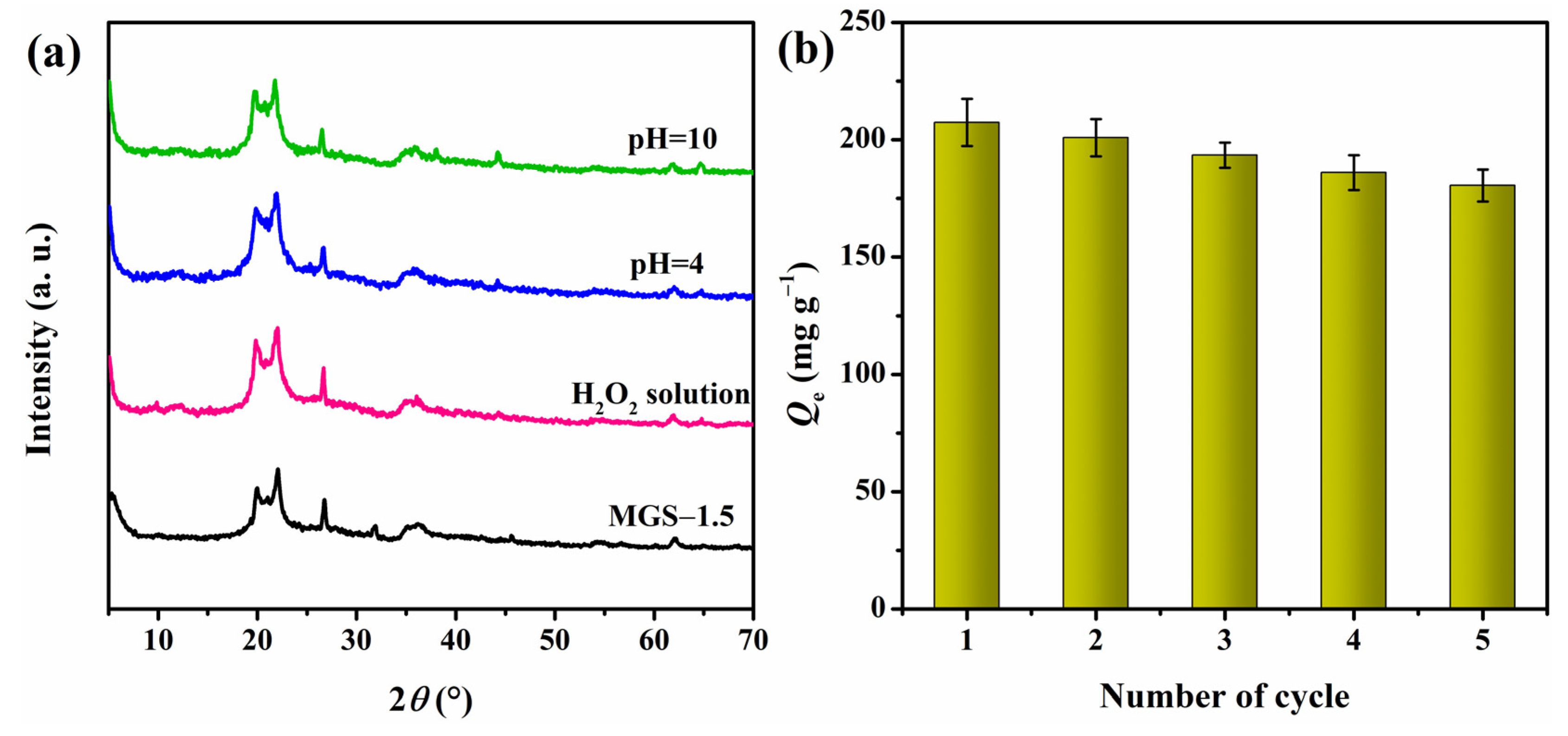
3.4. XRD Analysis of MGS Gel Beads
3.5. Thermal Property of MGS Gel Beads
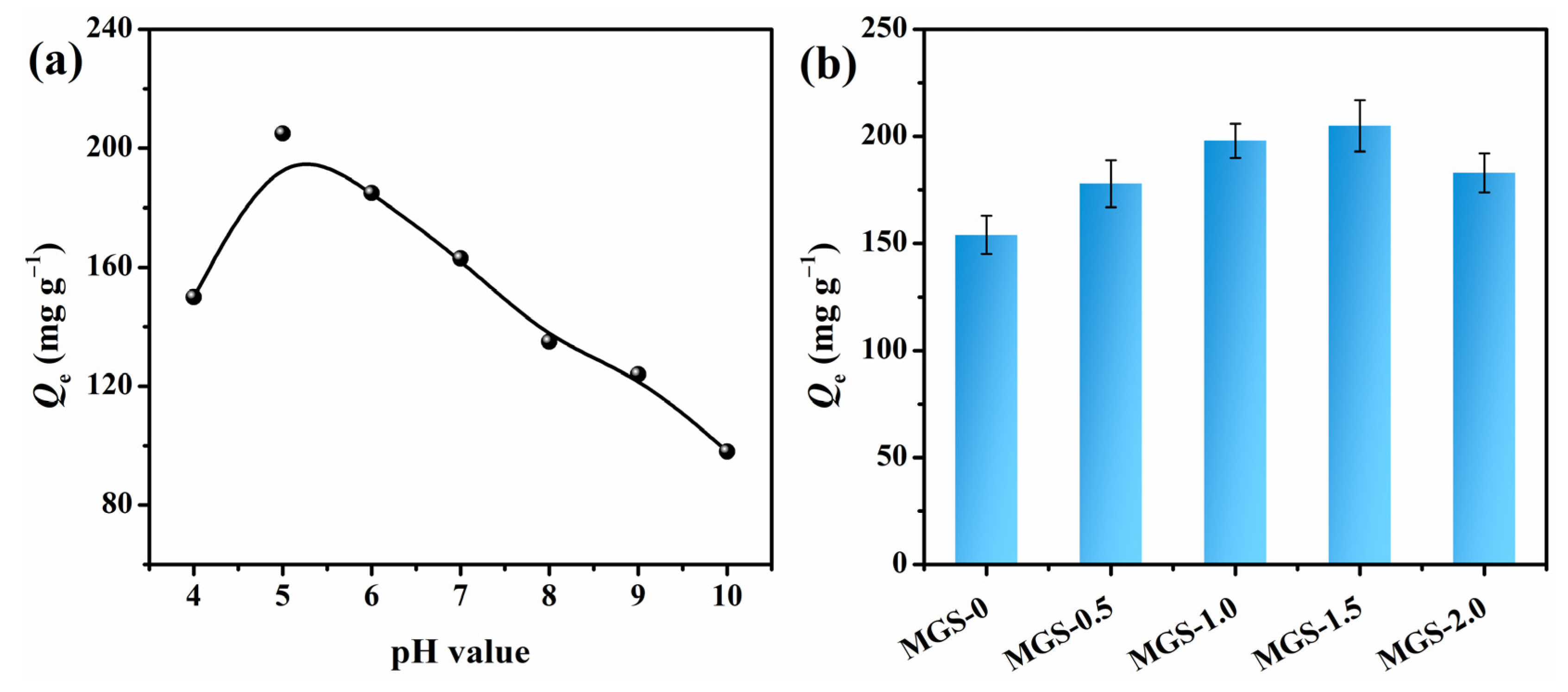
3.6. Effect of pH and SEP Content on CR Adsorption
3.7. Adsorption Kinetics
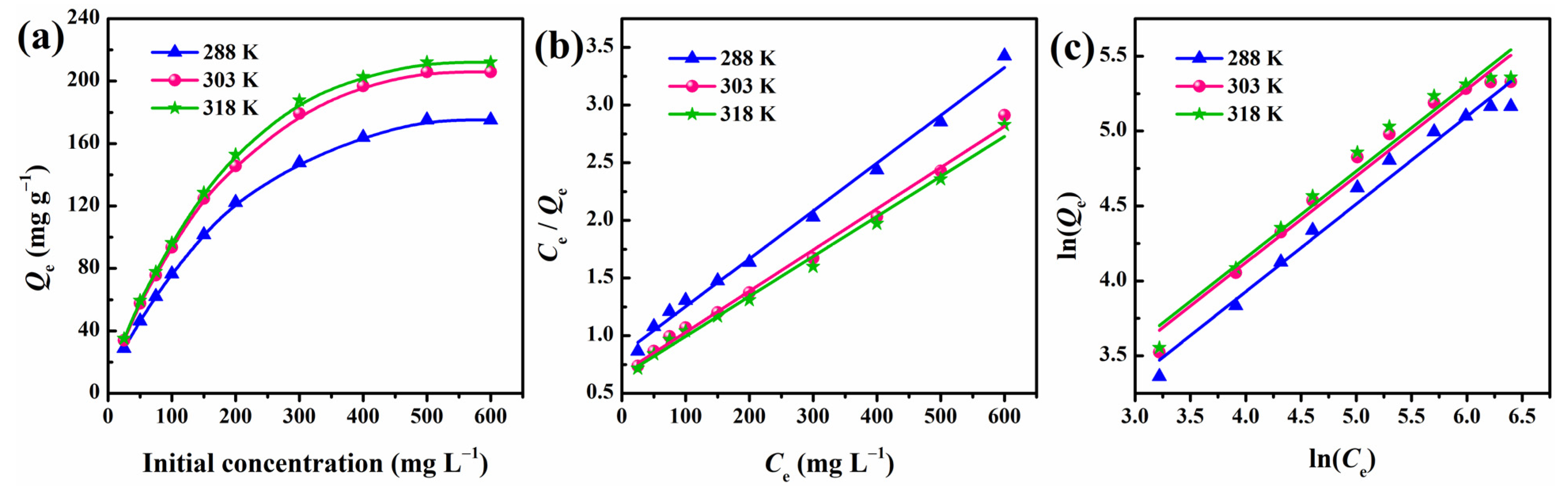
3.8. Adsorption Isotherm
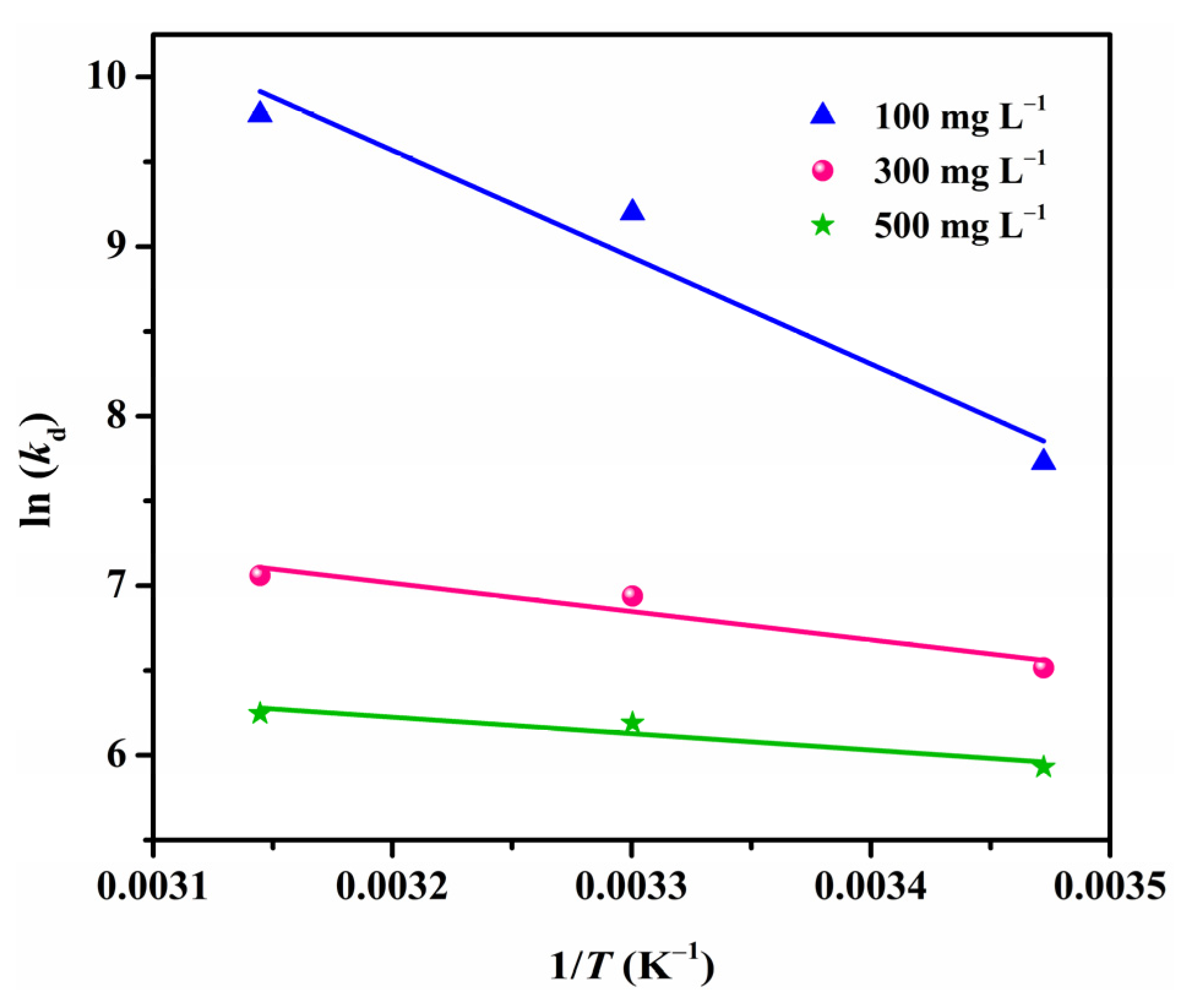
3.9. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3.10. Stability and Reusability Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kannan, R.; Peera, S.G.; Obadiah, A.; Vasanthkumar, S. MnO2 supported pom-a novel nanocomposite for dye degradation. Dig. J. Nanomater. Bios. 2011, 6, 829–835. [Google Scholar]
- Munagapati, V.S.; Kim, D.-S. Adsorption of anionic azo dye congo red from aqueous solution by cationic modified orange peel powder. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Mansha, M.; Kazi, I.W.; Ullah, N. Synthesis of a novel 3,5-diacrylamidobenzoic acid based hyper-cross-linked resin for the efficient adsorption of congo red and rhodamine B. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, N.R.; Chandanshive, V.V.; Khandare, R.V.; Gholave, A.R.; Yadav, S.R.; Govindwar, S.P. Green remediation of textile dyes containing wastewater by ipomoea hederifolia L. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 36623–36632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Guo, X.; Song, X.; Liu, X. Investigation on the degradation of acid fuchsin induced oxidation by MgFe2O4 under microwave irradiation. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2011, 335, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Xing, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.; Li, P. Facile template-free fabrication of hollow nestlike alpha-Fe2O3 nanostructures for water treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahi, R.K.; Yu, W.W.; Liu, Y.; Mejia, M.L.; Falkner, J.C.; Nolte, W.; Colvin, V.L. Photodegradation of congo red catalyzed by nanosized TiO2. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2005, 242, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudenur, C.; Sorokhaibam, L.G.; Bhandari, V.; Raja, S.; Ranade, V.V. Green approach to dye wastewater treatment using biocoagulants. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2495–2507. [Google Scholar]
- Aoopngan, C.; Nonkumwong, J.; Phumying, S.; Promjantuek, W.; Maensiri, S.; Noisa, P.; Pinitsoontorn, S.; Ananta, S.; Srisombat, L. Amine-functionalized and hydroxyl-functionalized magnesium ferrite nanoparticles for congo red adsorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 5329–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, B.; Han, J.; Meng, Y.; Yu, L.; Hou, D.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Preparation of carboxylic multiwalled-carbon-nanotube–modified poly(m-phenylene isophthalamide) hollow fiber nanofiltration membranes with improved performance and application for dye removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 453, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ding, W.; Wang, J.; Diao, G. Removal of azo dyes from water by combined techniques of adsorption, desorption, and electrolysis based on a supramolecular sorbent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 2403–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, D.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Devi, P.S. Evaluation of mechanism on selective, rapid, and superior adsorption of congo red by reusable mesoporous α-Fe2O3 nanorods. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 11255–11267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkait, M.K.; Maiti, A.; DasGupta, S.; De, S. Removal of congo red using activated carbon and its regeneration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 145, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M.; Witek-Krowiak, A. Agricultural waste peels as versatile biomass for water purification—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 244–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Fung, B.M.; Newman, J.K.; Vu, C. Organic aerogels with very high impact strength. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 644–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Pang, B.; Xu, W.; Duan, G.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, K. Recent progress on nanocellulose aerogels: Preparation, modification, composite fabrication, applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2005569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darder, M.; Matos, C.R.S.; Aranda, P.; Gouveia, R.F.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Bionanocomposite foams based on the assembly of starch and alginate with sepiolite fibrous clay. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Gao, Z.; Wu, D.; Jiang, J.; Sun, Y.; Luo, C. Efficient pb(ii) removal using sodium alginate-carboxymethyl cellulose gel beads: Preparation, characterization, and adsorption mechanism. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Du, Z.; Shang, Y.; Chen, Y. Efficient removal of dyes from aqueous solution by a porous sodium alginate/gelatin/graphene oxide triple-network composite aerogel. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soheilmoghaddam, M.; Wahit, M.U.; Yussuf, A.A.; Al-Saleh, M.A.; Whye, W.T. Characterization of bio regenerated cellulose/sepiolite nanocomposite films prepared via ionic liquid. Polym. Test. 2014, 33, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrakchi, F.; Khanday, W.A.; Asif, M.; Hameed, B.H. Cross-linked chitosan/sepiolite composite for the adsorption of methylene blue and reactive orange 16. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Knowles, J.C.; Kim, H.E. Porous scaffolds of gelatin-hydroxyapatite nanocomposites obtained by biomimetic approach: Characterization and antibiotic drug release. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 74, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Xu, A.; Tang, K.; Huang, Y.; Lu, C. In situ reduced and assembled three-dimensional graphene aerogel for efficient dye removal. J. Alloy. Compound. 2017, 714, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, X.; Chen, F. A multifunctional gelatin-based aerogel with superior pollutants adsorption, oil/water separation and photocatalytic properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, N.; Kakati, D.K. Smart porous microparticles based on gelatin/sodium alginate polyelectrolyte complex. J. Food Eng. 2013, 117, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.m.; Belleville, P.; Popalld, M.; Nicol, L. Applications of advanced hybrid organic–inorganic nanomaterials: From laboratory to market. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 40, 696–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Romero, P. Hybrid organic-inorganic materials-in search of synergic activity. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frydrych, M.; Wan, C.; Stengler, R.; O’Kelly, K.U.; Chen, B. Structure and mechanical properties of gelatin/sepiolite nanocomposite foams. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 9103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.G.; Liu, S.F.; Lu, S.X.; Kang, S.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.F. Photocatalytic degradation in aqueous solution using quantum-sized zno particles supported on sepiolite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 351, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, J.; Devi, N. Preparation, optimization, and characterization of chitosan-sepiolite nanocomposite films for wound healing. Internat. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Tang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Cui, F. Highly porous zirconium-crosslinked graphene oxide/alginate aerogel beads for enhanced phosphate removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Ge, X. Fabrication of fibrous amidoxime-functionalized mesoporous silica microsphere and its selectively adsorption property for Pb2+ in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Han, J.; Han, G.; French, A.D.; Qi, Y.; Wu, Q. Cellulose nanofibers reinforced sodium alginate-polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels: Core-shell structure formation and property characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Sokolan, N.I.; Kolotova, D.S.; Kuchina, Y.A. Interactions between gelatin and sodium alginate: Uv and ftir studies. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 2019, 41, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staroszczyk, H.; Sztuka, K.; Wolska, J.; Wojtasz-Pajak, A.; Kolodziejska, I. Interactions of fish gelatin and chitosan in uncrosslinked and crosslinked with edc films: FT-IR study. Spectrochim. Acta. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, M.; Han, Y.; Zhai, M.; Wei, S.; Li, J. A green fabrication approach of gelatin/cm-chitosan hybrid hydrogel for wound healing. Carbohyd. Polym. 2010, 82, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, Z.; Morsali, A. Synthesis and characterization of nano-sepiolite by solvothermal method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3607–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ma, Q.; Bai, Y.; Xu, D.; Wu, M.; Ma, H. Facile fabrication of gelatin/bentonite composite beads for tunable removal of anionic and cationic dyes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 134, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzi, M.; Shafagh, N.; Mohammadi, M. Assembly of gelatin biopolymer to fibrous sepiolite clay for efficient dye removal from wastewater. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González del Campo, M.M.; Darder, M.; Aranda, P.; Akkari, M.; Huttel, Y.; Mayoral, A.; Bettini, J.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Functional hybrid nanopaper by assembling nanofibers of cellulose and sepiolite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1703048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Tao, J.; Xiong, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y. In situ synthesis of mno2-loaded biocomposite based on microcrystalline cellulose for Pb2+ removal from wastewater. Cellulose 2017, 24, 2591–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Majeed, A.B.A.; Banthia, A.K. Development and characterization of pectin/gelatin hydrogel membranes for wound dressing. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 2011, 15, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhalfa, N.; Darder, M.; Boutahala, M.; Aranda, P.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Composite nanoarchitectonics: Alginate beads encapsulating sepiolite/magnetite/prussian blue for removal of cesium ions from water. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2021, 94, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turhan, Y.; Doǧan, M.; Alkan, M. Characterization and some properties of poly(vinyl chloride)/sepiolite nanocomposites. Adv. Polym. Tech. 2013, 32, E65–E82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Uniyal, V.; Naithani, S. Polymorphic transformation of cellulose i to cellulose ii by alkali pretreatment and urea as an additive. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, S.; Ge, L.; Lin, F.; Lu, Q.; Wang, T.; Huang, B.; Lu, B. Development of organic–inorganic hybrid beads from sepiolite and cellulose for effective adsorption of malachite green. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 38965–38972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldegs, Y.; Elbarghouthi, M.; Elsheikh, A.; Walker, G. Effect of solution pH, ionic strength, and temperature on adsorption behavior of reactive dyes on activated carbon. Dye. Pigment. 2008, 77, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, J.N.; Mahesh, K.; Le, N.H.; Kemp, K.C.; Timilsina, R.; Tiwari, R.N.; Kim, K.S. Reduced graphene oxide-based hydrogels for the efficient capture of dye pollutants from aqueous solutions. Carbon 2013, 56, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liao, X.; Shi, B. Hg (II) removal from aqueous solution by bayberry tannin-immobilized collagen fiber. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem 1906, 57, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.V.; Kumaran, A. Removal of methylene blue by mango seed kernel powder. Biochem. Eng. J. 2005, 27, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Ding, H.; Yang, G.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; Liao, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, D. Preparation of black-pearl reduced graphene oxide-sodium alginate hydrogel microspheres for adsorbing organic pollutants. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2017, 508, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Adhikari, B.; Majumder, S. Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies of azo dye adsorption from aqueous solution by chemically modified lignocellulosic jute fiber. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 6502–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Kinetic Model | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Concentration (mg·L−1) | Qexp (mg·g−1) | Q1e,cal (mg·g−1) | k1 (min−1) | R2 | Q2e,cal (mg·g−1) | k2 × 104 (g·(mg min)−1) | R2 |
| 100 | 69.2 | 69.4 | 0.0204 | 0.9501 | 77.6 | 3.0064 | 0.9934 |
| 300 | 164.5 | 174.9 | 0.0209 | 0.9394 | 187.6 | 1.0898 | 0.9905 |
| 500 | 205.6 | 202.8 | 0.0202 | 0.9560 | 229.9 | 1.0461 | 0.9940 |
| Isotherm | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (K) | Qmax (mg·g−1) | kL (L·mg−1) | R2 | RL | kF (L·mg−1) | n | R2 |
| 288 | 240.9 | 0.0050 | 0.9940 | 0.2500~0.8889 | 4.8914 | 1.7094 | 0.9751 |
| 303 | 279.3 | 0.0053 | 0.9938 | 0.2392~0.8830 | 6.1064 | 1.7304 | 0.9679 |
| 318 | 288.2 | 0.0054 | 0.9925 | 0.2358~0.8811 | 6.2682 | 1.7262 | 0.9657 |
| Initial Concentration (mg·L−1) | ΔH° (kJ·mol−1) | ΔS° (J·(mol K)−1) | ΔG° (kJ·mol−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 288 | 303 | 318 | |||
| 100 | 52.34 | 247.01 | −18.80 | −22.50 | −26.21 |
| 300 | 13.90 | 102.81 | −15.71 | −17.25 | −18.79 |
| 500 | 8.08 | 77.59 | −14.27 | −15.43 | −16.59 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, C.; Liu, D.; Wei, N.; Gao, J.; Fu, F.; Liu, T.; Wang, J. Efficient Congo Red Removal Using Porous Cellulose/Gelatin/Sepiolite Gel Beads: Assembly, Characterization, and Adsorption Mechanism. Polymers 2021, 13, 3890. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13223890
Jiao C, Liu D, Wei N, Gao J, Fu F, Liu T, Wang J. Efficient Congo Red Removal Using Porous Cellulose/Gelatin/Sepiolite Gel Beads: Assembly, Characterization, and Adsorption Mechanism. Polymers. 2021; 13(22):3890. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13223890
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Chenlu, Die Liu, Nana Wei, Jiannan Gao, Fan Fu, Tao Liu, and Jian Wang. 2021. "Efficient Congo Red Removal Using Porous Cellulose/Gelatin/Sepiolite Gel Beads: Assembly, Characterization, and Adsorption Mechanism" Polymers 13, no. 22: 3890. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13223890
APA StyleJiao, C., Liu, D., Wei, N., Gao, J., Fu, F., Liu, T., & Wang, J. (2021). Efficient Congo Red Removal Using Porous Cellulose/Gelatin/Sepiolite Gel Beads: Assembly, Characterization, and Adsorption Mechanism. Polymers, 13(22), 3890. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13223890






