Fully Biodegradable Poly(hexamethylene succinate)/Cellulose Nanocrystals Composites with Enhanced Crystallization Rate and Mechanical Property
Abstract
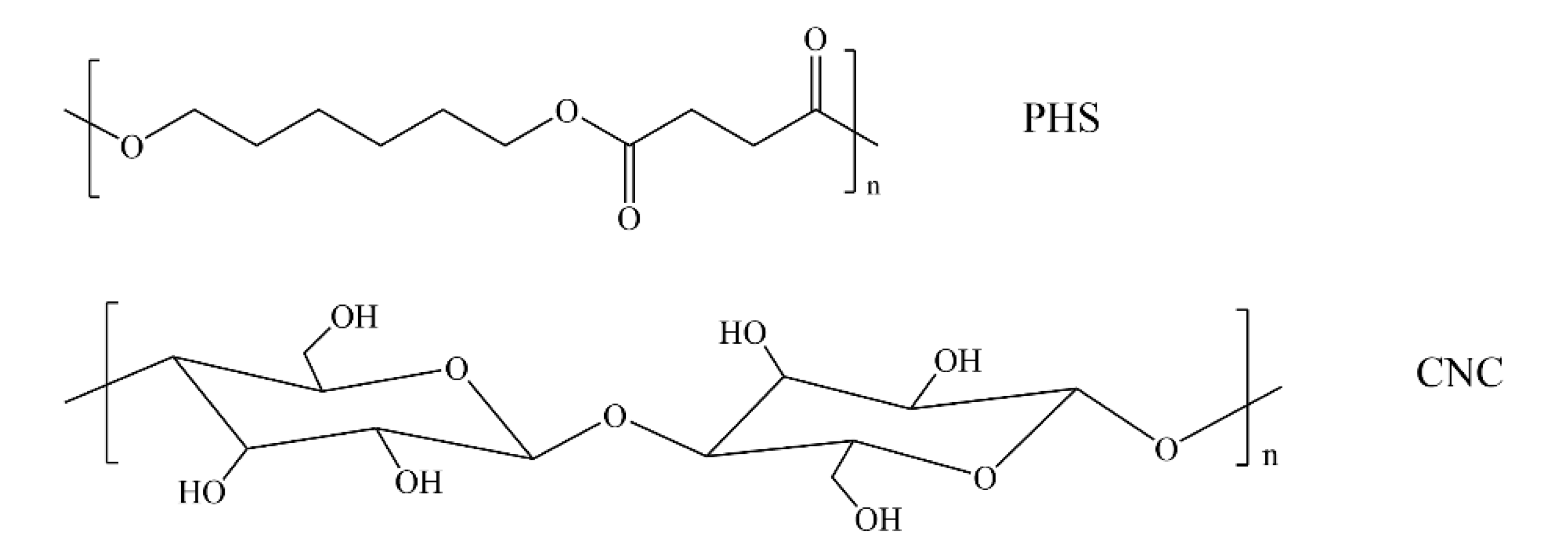
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dispersion of CNC in PHS Matrix and Thermal Stability Study
3.2. Crystallization Behavior Study
3.3. Tensile Mechanical Property Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Y.; Romain, C.; Williams, C. Sustainable polymers from renewable resources. Nature 2016, 540, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.; Vivekanandhan, S.; Misra, M.; Bhatia, S.; Mohanty, A. Biobased plastics and bionanocomposites: Current status and future opportunities. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1653–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Komura, M.; Ikehara, T.; Nishi, T. DSC and TMDSC study of melting behaviour of poly(butylene succinate) and poly(ethylene succinate). Polymer 2003, 44, 7781–7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Fujinami, S.; Komura, M.; Nakajima, K.; Ikehara, T.; Nishi, T. Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of poly(butylene succinate) and poly(ethylene succinate). Polym. J. 2004, 36, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papageorgiou, G.; Bikiaris, D. Crystallization and melting behavior of three biodegradable poly(alkylene succinates). A comparative study. Polymer 2005, 46, 12081–12092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrissafis, K.; Paraskevopoulos, K.; Bikiaris, D. Thermal degradation mechanism of poly(ethylene succinate) and poly(butylene succinate): Comparative study. Thermochim. Acta 2005, 435, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.; Jiang, Z.; Qiu, Z. Effect of different POSS structures on the crystallization behavior and dynamic mechanical properties of biodegradable poly(ethylene succinate). Polymer 2019, 163, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wei, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, Z.; Ma, H.; Yin, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, J. Biocompatible linear diamides derivative-nucleated biodegradable poly(ethylene succinate): Tailored crystallization kinetics, aggregated structure and thermal degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 183, 109428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Qiu, Z. Thermal, crystallization and mechanical properties of branched poly(butylene succinate) copolymers with 1, 2-decanediol being the comonomer. Polymer 2021, 213, 123197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Qiu, Z. Synthesis, thermal and mechanical properties of novel biobased, biodegradable and double crystalline poly(butylene succinate)-b-poly(butylene sebacate) multiblock copolymers. Polymer 2021, 214, 123248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Guo, B. Poly(butylene succinate) and its copolymers: Research, development and industrialization. Biotechnol. J. 2010, 5, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, L.; Puiggali, J. Crystallization kinetics of poly(hexamethylene succinate). Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesti, S.; Casas, M.; Puiggali, J. Crystalline structure of poly(hexamethylene succinate) and single crystal degradation studies. Polymer 2007, 48, 5088–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhou, C.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y. Poly(hexamethylene succinate) copolyesters containing phosphorus pendent group: Retarded crystallization and solid-state microstructure. Polymer 2015, 71, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hong, Z.; Sun, J.; Geng, Y.; Huang, Y. Identifying the phase behavior of biodegradable poly(hexamethylene succinate-co-hexamethylene adipate) copolymers with FTIR. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 2695–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Qiu, Z. Crystallization kinetics and morphology of novel biodegradable poly(hexamethylene succinate-co-3 mol% ethylene succinate) with low and high molecular weights. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 3537–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, H.; Qiu, Z. Thermal properties and crystallization behavior of novel biodegradable poly(hexamethylene succinate-co-6 mol% butylene succinate) and poly(hexamethylene succinate). J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gestí, S.; Zanetti, M.; Lazzari, M.; Franco, L.; Puiggalí, J. Study of clay nanocomposites of the biodegradable polyhexamethylene succinate. Application of isoconversional analysis to nonisothermal crystallization. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 2234–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, Y.; Lucia, L.A.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose Nanocrystals: Chemistry, Self-Assembly, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3479–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Hamad, W.Y. Cellulose reinforced polymer composites and nanocomposites: A critical review. Cellulose 2013, 20, 2221–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.; Dufresne, A.; Pinheiro, I.; Souza, D.; Gouveia, R.; Mei, L.; Lona, L. How do cellulose nanocrystals affect the overall properties of biodegradable polymer nanocomposites: A comprehensive review. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 108, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, M.; Noreen, A.; Sharif, A.; Majeed, A.; Hassan, A.; Tabasum, S.; Mohammadi, A.; Zia, K. A review on versatile applications of blends and composites of CNC with natural and synthetic polymers with mathematical modeling. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 591–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvino, C.; Macke, N.; Kato, R.; Rowan, S. Development, processing and applications of bio-sourced cellulose nanocrystal composites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 103, 101221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.; Khoshkava, V. Effect of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) on rheological and mechanical properties and crystallization behavior of PLA/CNC nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lv, Q.; Wu, D.; Wang, Z. Polylactide/cellulose nanocrystal composites: A comparative study on cold and melt crystallization. Cellulose 2017, 24, 2163–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiu, Z. Significantly enhanced crystallization of poly(L-lactide) by the synergistic effect of poly(diethylene glycol adipate) and cellulose nanocrystals in their fully biodegradable ternary composite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 15526–15532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, I.; Ferreira, F.; Souza, D.; Gouveia, R.; Lona, L.; Morales, A.; Mei, L. Mechanical, rheological and degradation properties of PBAT nanocomposites reinforced by functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 97, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, M.; Zeng, J. Morphology, crystallization and rheological behavior in poly (butylene succinate)/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposites fabricated by solution coagulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke, A.; Vasileiou, A.; Kontopoulou, M. Crystalline nanocellulose/thermoplastic polyester composites prepared by in situ polymerization. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, Z.; Qiu, Z. Thermal and rheological properties of fully biodegradable poly(ethylene succinate)/cellulose nanocrystals composites. Compos. Commun. 2021, 23, 100571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, Z.; Qiu, Z. Isothermal melt crystallization kinetics study of cellulose nanocrystals nucleated biodegradable poly(ethylene succinate). Polymer 2021, 227, 123869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, C.; Yu, Y.; Xiao, L. Effect of loadings of nanocellulose on the significantly improved crystallization and mechanical properties of biodegradable poly (ε-caprolactone). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wu, D.; Tam, K.C.; Pan, K.; Zheng, Z. Effect of surface modification of cellulose nanocrystal on nonisothermal crystallization of poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Qiu, Z. Effect of low loadings of cellulose nanocrystals on the significantly enhanced crystallization of biodegradable poly (butylene succinate-co-butylene adipate). Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 205, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Qiu, Z. Influence of two different nanofillers on the crystallization behavior and dynamic mechanical properties of biodegradable poly(ethylene adipate). J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2674–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Kinetics of phase change. II Transformation-time relations for random distribution of nuclei. J. Chem. Phys. 1940, 8, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Granulation, phase change, and microstructure kinetics of phase change. III. J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.; Jiang, Z.; Qiu, Z. Crystallization behavior and dynamic mechanical properties of poly(ε-caprolactone)/octaisobutyl-polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes composites prepared via different methods. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Qiu, Z. Effect of cyanuric acid as an efficient nucleating agent on the crystallization of novel biodegradable branched poly(ethylene succinate). Macromol 2021, 1, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, B. Macromolecular Physics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Larrañaga, A.; Lizundia, E. A review on the thermomechanical properties and biodegradation behaviour of polyesters. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 121, 109296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Samples | Tc (°C) | n | k (min−n) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHS | 41 | 2.9 | 3.58 × 10−2 |
| 43 | 2.8 | 3.75 × 10−3 | |
| 45 | 3.1 | 1.88 × 10−4 | |
| 47 | 3.1 | 1.22 × 10−5 | |
| PHS/CNC0.25 | 41 | 2.8 | 7.61 × 10−2 |
| 43 | 3.3 | 3.82 × 10−3 | |
| 45 | 3.0 | 8.19 × 10−4 | |
| 47 | 2.9 | 1.05 × 10−4 | |
| PHS/CNC0.5 | 41 | 2.7 | 1.07 × 10−1 |
| 43 | 2.7 | 1.39 × 10−2 | |
| 45 | 3.1 | 8.58 × 10−4 | |
| 47 | 2.7 | 3.01 × 10−4 | |
| PHS/CNC1 | 41 | 2.6 | 1.38 × 10−1 |
| 43 | 2.5 | 3.41 × 10−2 | |
| 45 | 2.8 | 2.53 × 10−3 | |
| 47 | 2.6 | 1.04 × 10−3 |
| Samples | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Yield Strain (%) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PHS | 360.2 ± 10.6 | 16.39 ± 0.01 | 9.16 ± 0.06 | 18.84 ± 0.46 | 560.0 ± 35.5 |
| PHS/CNC0.25 | 386.8 ± 10.6 | 17.18 ± 0.36 | 9.18 ± 0.34 | 16.48 ± 0.28 | 406.1 ± 15.2 |
| PHS/CNC0.5 | 430.9 ± 11.8 | 17.30 ± 0.15 | 9.67 ± 0.56 | 16.87 ± 0.43 | 398.2 ± 32.4 |
| PHS/CNC1 | 460.8 ± 14.5 | 18.35 ± 0.51 | 9.48 ± 0.46 | 18.53 ± 0.31 | 88.6 ± 6.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, S.; Qiu, Z. Fully Biodegradable Poly(hexamethylene succinate)/Cellulose Nanocrystals Composites with Enhanced Crystallization Rate and Mechanical Property. Polymers 2021, 13, 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213667
Pan S, Qiu Z. Fully Biodegradable Poly(hexamethylene succinate)/Cellulose Nanocrystals Composites with Enhanced Crystallization Rate and Mechanical Property. Polymers. 2021; 13(21):3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213667
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Siyu, and Zhaobin Qiu. 2021. "Fully Biodegradable Poly(hexamethylene succinate)/Cellulose Nanocrystals Composites with Enhanced Crystallization Rate and Mechanical Property" Polymers 13, no. 21: 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213667
APA StylePan, S., & Qiu, Z. (2021). Fully Biodegradable Poly(hexamethylene succinate)/Cellulose Nanocrystals Composites with Enhanced Crystallization Rate and Mechanical Property. Polymers, 13(21), 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213667







