Abstract
The fabrication of skin-care products with therapeutic properties has been significant for human health trends. In this study, we developed efficient hydrophilic composite nanofibers (NFs) loaded with the folic acid (FA) by electrospinning and electrospraying processes for tissue engineering or wound healing cosmetic applications. The morphological, chemical and thermal characteristics, in vitro release properties, and cytocompatibility of the resulting composite fibers with the same amount of folic acid were analyzed. The SEM micrographs indicate that the obtained nanofibers were in the nanometer range, with an average fiber diameter of 75–270 nm and a good porosity ratio (34–55%). The TGA curves show that FA inhibits the degradation of the polymer and acts as an antioxidant at high temperatures. More physical interaction between FA and matrices has been shown to occur in the electrospray process than in the electrospinning process. A UV-Vis in vitro study of FA-loaded electrospun fibers for 8 h in artificial acidic (pH 5.44) and alkaline (pH 8.04) sweat solutions exhibited a rapid release of FA-loaded electrospun fibers, showing the effect of polymer matrix–FA interactions and fabrication processes on their release from the nanofibers. PVA-CHi/FA webs have the highest release value, with 95.2% in alkaline media. In acidic media, the highest release (92%) occurred on the PVA-Gel–CHi/sFA sample, and this followed first-order and Korsmeyer–Peppas kinetic models. Further, the L929 cytocompatibility assay results pointed out that all NFs (with/without FA) generated had no cell toxicity; on the contrary, the FA in the fibers facilitates cell growth. Therefore, the nanofibers are a potential candidate material in skin-care and tissue engineering applications.
1. Introduction
Nanofibers have played a key role in different areas of biomedical research, ranging from drug release to wound healing, and cell regeneration owing to their high specific surface area and capacity to adjust their properties by altering composition and production conditions [1,2,3,4]. The use of hydrophilic polymers in the fabrication of electrospun nanofibers has been proven to be beneficial in the development of fast-dissolving delivery systems with decreased drug–drug interactions [5,6,7]. Generally, a blended combination of natural and synthetic polymers is preferred. Synthetic polymers can offer proper mechanical strength while also enhancing electrospinnability. Natural polymers can promote cellular adhesion and thus better imitate the ECM environment [8]. Furthermore, the increased hydrophilicity supplied by natural polymers is favorable when carrying hydrophilic drugs. Nanofibrous scaffolds made of natural and synthetic polymers were shown to be suitable for designing drug release systems via the electrospinning of blended polymers or combination with bioactive agents [9,10,11,12,13,14]. Previously, electrospun nanofibers have been produced from single polymer sources, and more recently, polymer combinations have been created to develop so-called polyblend nanofibers. Polyblend nanofibers are a new type of biomaterial that can function as mimics for native tissue while presenting topographical and biochemical stimuli that support healing [15,16,17].
Scaffolds are made from a variety of polymers, including poly(vinyl alcohol), poly(ethyl oxide), poly(lactic acid), poly(glycolic acid), poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid), poly(caprolactone), and natural extracellular matrix (ECM) analogs, such as collagen, gelatin, silk, chitin, chitosan, alginate, and hyaluronic acid, because of their lack of toxicity, superior biocompatibility, cell adhesion, and proliferation capability [18]. In this context, hydrophilic PVA-based materials can be blended with natural polymers and utilized in drug delivery systems [18,19,20,21,22,23,24].
Bioactive compounds can partially lose their therapeutic efficiency during the blend–electrospinning process. It is critical to have protective agents. To ensure that drugs stay bioactive, certain procedures must be performed [8]. In this context, electrospraying can be utilized for drug release applications, especially the encapsulation of bioactive compounds [25]. Electrospraying, also referred to as electro hydrodynamic atomization (EHDA), is usually presented as a unique and simple technology capable of controlling droplet formation electrostatically [26]. Folic acid (FA) is defined as a multifunctional, active substance that is safe to use and even combine with other chemicals [27]. Moreover, folic acid has received much attention from researchers in the fields of biomedical, bioengineering, and regenerative therapies, because of its non-immunogenicity, high stability, and ability to support tissue regeneration/repair [26,27]. In this regard, an increasing number of studies on the use of folic acid in micro/nanocapsule, liposome, hydrogel and/or nanofiber forms are available in a wide range of applications [28,29,30]. However, there are no studies in the literature on the utilization of nanofibers containing FA in tissue engineering applications, formed by both blending electrospinning and simultaneous (electrospinning and electrospraying) processes.
The main objective of this study is to fabricate various PVA-based nanofibers, including FA, via two distinct processes, electrospinning and simultaneous spinning (electrospinning and e-spraying), and then to evaluate their controlled release and cell growth characteristics. The properties of PVA-based NFs in terms of morphology, thermal resistance and chemical structure were analyzed by changing the type of polymer matrix. In addition, we assessed which had better cell growth and release values.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) (density 0.4–0.6 g/cm3, purity 87.8% and Mw~30.000 g/mol) was purchased from ZAG Industrial Chemicals (Istanbul, Turkey). Gelatin from bovine skin (225 Bloom, type B, Bio Reagent) was supplied from Sigma Aldrich Chemical Company (St. Louis, MO, USA). Sodium alginate (medium molecular weight) and sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) (99.7% purity) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich Chemical Company (St. Louis, MO, USA). Acetic acid (CH3COOH) with 80% purity was also obtained from Sigma Aldrich Chemical Company (St. Louis, MO, USA), and ethanol (99.9% purity) was purchased from Tekkim Chemical Company (Bursa, Turkey). Chitosan (Mn 100,000–300,000) was supplied by Alfa Aesar Fine Chemicals and Metals (USA). Folic acid (C19H19N7O6) for biochemistry (98–102% purity) was provided by ChemSolute Company (Germany). The ethanol (99% purity) was purchased from Sigma Aldrich Chemical Company (St. Louis, MO, USA). l-Histidine mono-hydrochloride monohydrate (C6H9O2N3.HCI.H2O) (>99% purity), sodium chloride (>99.5% purity), and sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate (NaH2PO4.2H2O) were supplied by Sigma Aldrich Chemical Company (St. Louis, MO, USA) to produce the artificial sweat solutions.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Fabrication of Neat Nanofibers and FA-Loaded Hybrid Nanofiber via Blending Electrospinning
Polymer solutions were prepared as in the previous study [10]. PVA granules were dissolved in distilled water at 90 °C until a 10% (w/w) homogenous PVA solution was produced. By stirring for 2 h at room temperature, gelatin was dissolved in distilled water and acetic acid binary-solvent systems (7:3 w/w) solution to get a 20% (w/w) gelatin solution. Alginate powders were dissolved in water to make a 2% (w/w) alginate solution. Chitosan powders were dissolved in acetic acid and distilled water binary-solvent systems (9:1 w/w) solution to obtain 7% chitosan solution. The process parameters and features of the composite polymer solutions are shown in Table 1 below. The average temperature was 25 °C, the % humidity was lower than 60, and the speed of the rotating collector was 150 rpm. In all FA-loaded polymer solutions, 22 mg of FA in 1 M 1 mL of NaHCO3 was homogeneously added to the blend solutions.

Table 1.
Process parameters for electrospinning.
The electrospinning of PVA-based composite nanofibers and FA-loaded PVA-based composite nanofibers was carried out by an electrospinning process (INOVENSO Nanospinner24 Device, Turkey). Neat polymer solutions without FA were prepared as a control. In the electrospinning process, the polymer solutions were transferred into plastic syringes (10 mL) and these syringes were attached to stainless nozzles with 0.5 mm inner diameters (Figure 1). Polymer solutions were dispensed into the rotary collector. Finally, neat and FA-loaded nanofibers were deposited in the collector due to the high electrical voltage.
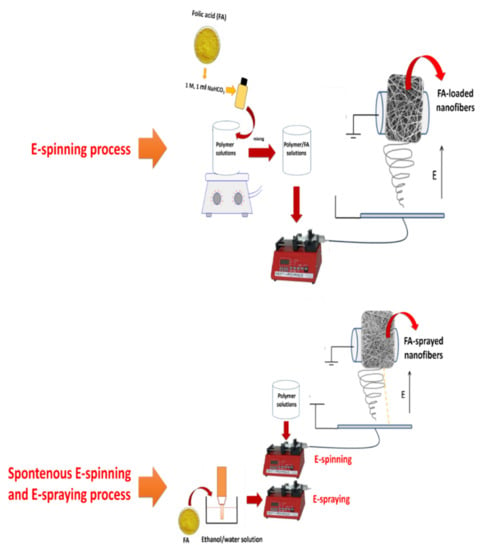
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the processes.
2.2.2. Fabrication of FA-Spraying on Hybrid Nanofibers via Simultaneous Process
The simultaneous process (electrospinning + e-spraying process) has been detailed in a previous study [10]. Two syringe pumps for polymer solution and FA dispersion were utilized in the experiments. The environmental factors and the speed of the collector were the same as in blending electrospinning process. Schematic illustrations of the two distinct processes are shown in Figure 1. In the simultaneous process, all polymer solutions were prepared. Afterwards, the sonicated FA–ethanol solution and the polymer solutions were transferred into two distinct plastic syringes. These solutions were fed into the system by two distinct syringe pumps as in the electrospinning process.
The samples are encoded as polymer blend/FA and polymer blend/sFA for the electrospinning process and simultaneous process (electrospinning + e-spraying process), respectively.
2.2.3. Microstructural Analysis of the Hybrid Nanofibers
A Carl Zeiss/Gemini 300 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) was used to examine the morphology of all nanofibers (ZEISS Ltd., Jena, Germany). Before analysis, all samples were coated with gold for 20 min. The diameters of 60 individual fibers were randomly selected for each sample and measured using ImageJ (version 1.520 software).
2.2.4. Physical Analysis of Nanofibers
The ATR-FTIR spectra of nanofibers were acquired using a ThermoNicolet iS50 FT-IR (USA) spectrometer and an ATR (Attenuated Total Reflectance) adaptor (Smart Orbit Diamond, MI, USA). Spectra in the range of 500–4000 cm−1 with automatic signal gain were collected (16 scans) at a 4 cm−1 resolution
2.2.5. Thermal Analysis of Nanofibers
The thermal analysis was performed using a TA/SDT650 TGA (USA). TGA analysis was carried out in a nitrogen (N2(g)) atmosphere with a 20 °C min−1 heating rate and a temperature range of 30–600 °C, and in an oxygen (O2(g)) atmosphere with a 20 °C min−1 heating rate and a temperature range of 600–900 °C.
2.2.6. Drug Release of Nanofibers and Kinetics
The ISO 105-E04:2013 procedure [31] was used to make the artificial sweat solutions. The total immersion procedure was performed to evaluate the vitamin-release behavior of FA-sprayed final fibers in acidic and alkaline sweat solutions at pH 5.44 and pH 8.04 [31]. Nanofibers of 30 cm2 were placed in sealed glass tubes with 100 mL of acidic and alkaline sweat solution, respectively. After this, they were placed in a shaking incubator at 36 °C with 200 rpm shaking, and we applied the folic acid release profile. Samples of 3.5 mL were taken of the sweat solutions at the specified time intervals, and the associated absorbance value was determined in a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Scinco/NEOYSY 2000, Seoul, South Korea) at max = 282 nm, which is folic acid’s typical peak. The drug concentrations were determined using the calibration curve of a model vitamin prepared with a known concentration of folic acid in acidic and alkaline solutions. For the acidic solution, the calibration curve was calculated to be Y = 0.0486X + (−0.0402) (R2 = 0.99992), and for alkaline solution, Y = 0.0551X + (−0.0422) (R2 = 0.99959), where X is the FA concentration (mg/L) and Y is the solution absorbance at 282 nm (linear range of 0.5–25 mg/L). UV-Vis spectroscopy was used to determine the amount of drug released. For each experiment, three replicates were obtained.
The kinetics of drug release were substantially controlled by polymer blends. The main mechanisms for drug release from a polymer matrix include drug diffusion and polymer relaxation/dissolution [32]. The cumulative release of FA (%) from all nanofibers was plotted with time. In this study, the kinetic mechanisms of all obtained nanofibers were calculated with zero-order, first-order, Hixson Crowell, Higuchi, and Korsmeyer–Peppas mathematical models. The different kinetic models are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Kinetic models used to calculate FA release from the nanofibers.
2.2.7. Entrapment Efficiency (EE) and FA Loading Capacity (LC) in Nanofibers
The FA entrapment efficiency (EE, %) was calculated as follows.
A previously known area of the fibrous materials (3 × 3 cm2) was completely dissolved separately in acidic and alkaline sweat solutions. Afterward, about 3 mL of these solutions was evaluated at the FA characteristic wavelength using UV-Vis spectroscopy. The FA loading capacity of the nanofibers (LC, %) was measured to specify how much FA per polymer was entrapped in them. These equations are shown as Equations (1) and (2).
2.2.8. Cytotoxicity of Nanofibers
Preparation of Cell Culture
In the cell culture laboratory of the Biotechnology Department of the Bursa Technical University, all experimental aspects of the cell culture and cytotoxicity assessments were carried out in accordance with acceptable cell culture practices (ISO Standard) [32]. The L929 cell lines (mouse fibroblasts), as a reference cell line of the UNI EN ISO 10993-5 rule: 2009, were used to test medical products and materials for cytotoxicity [33]. L929 cells were seeded in T75 bottles with the addition of 10% FBS and 1% penicillin streptomycin to RPMI 1640. The cells were cultured in a humidified cell culture incubator at 37 °C in 5% CO2 and observed daily with an inverted microscope and phase contrast (Olympus CKX41). When 80% confluence was detected, subculturing was carried out. In 96 tissue culture wells, a total of 5 cells/well were placed following disaggregation with trypsin/EDTA and the resuspension of cells in the media.
Preparation of Nanofiber Extract Solutions and MTT Assays
The ISO 10993-12: 2009 standard [34] was utilized in this study for the sample preparation of both the reference and the new nanofiber material. Both sides of standard-sized samples (3 cm2 /mL) were sterilized in a laminar flow cabinet for 1 h under a UV light. In order to obtain extract solutions, 30 cm2 (6 cm × 5 cm) sterile samples were placed in a 10 mL culture medium (RPMI 1640 with 1% Penicillin–Streptomycin, 10% serum) and cultured at 37 °C for 1 h. The samples were removed at the end of the extraction period, and the extract solutions were held at 37 °C during the cytotoxicity testing. MTT analysis was performed to determine the cytotoxicity of nanofiber extract solutions in the L929 cell line. In this regard, cells were exposed to the nanofiber extract solutions after 24 h of incubation of the cells seeded in 96-well tissue culture plates. Then, the media were aspirated to add MTT (5 mg/mL of stock of PBS) and the cells were incubated with MTT dye for a further 4 h (10 mL/well in 100 mL of cell suspension). Finally, the dye was carefully removed and 100 mL DMSO was added to each well. The absorption of the solution in each well was evaluated within a microplate reader at 570 nm. To assess cytotoxicity, the effects of 100% concentrations of original extract solutions from all reference and novel nanofiber samples on treated cells were compared to a negative control group that did not receive any chemicals. The average absorbance values and standard deviation values of living cells were calculated by averaging all the data obtained. Furthermore, cell viability in the control group was assumed to be 100%, and live cell percentages were assessed for all sample groups in comparison to the control.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis of % cell viability values obtained after the cytocompability experiments were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 22 software (IBM software, Armonk, NY, USA). The results were statistically analyzed by Student–Newman–Keuls (SNK) test to determine the importance of the difference between different groups. The significance value level was identified as p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology of the Hybrid Nanofibers
The neat blend fibers, FA-loaded composite fibers, and FA-sprayed composite fibers at the same quantities were successfully electrospun. The morphology of the fibers was characterized by SEM, as shown in Figure 2. To further analyze the diameter distributions of nanofibers, ImageJ software was used to determine the average diameter of 60 different and random nanofibers using SEM micrographs. Generally, the incorporation of FA decreases the average diameter of FA-loaded nanofibers. This could be due to the addition of FA into the polymer blend solutions, together with NaHCO3, as a result of which the viscosity decreased.
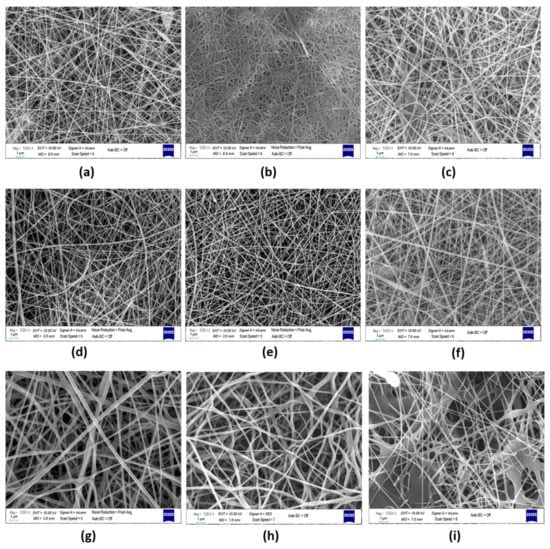
Figure 2.
(a) SEM image of PVA-Gel, (b) PVA-Gel/FA, (c) PVA-Gel/sFA, (d) PVA-CHi, (e) PVA-CHi/FA, (f)PVA-CHi/sFA, (g) PVA-Alg, (h) PVA-Alg/FA, and (i) PVA-Alg/sFA nanofibers (Magnification: 5 kX, scale bar: 1 µm).
It was noticed that the PVA-Gel, PVA-Alg, and PVA-CHi nanofibers were bead-free and smooth. Unlike PVA-Alg, which included more fiber interactivity and coarser fibers, PVA/Gel and PVA-CHi did not contain interacting or coarser fibers. An interconnected fiber structure was revealed in both neat PVA-Alg and PVA-Alg/FA fibers. However, in the PVA-Alg/FA sample, the fiber thickness was even thinner, and the porosity increased slightly (208.2 nm, 48.97%) compared to the neat one due to the FA-NaHCO3(aq) in neat PVA-Alg/FA fibers. As FA was sprayed on the fiber surfaces, morphology deteriorated (Figure 2i), and film-like structures formed on the fibers’ surfaces before the fibers dried. It is thought that this type of film formation is a consequence of the dissolution of the fiber with the solvent of the FA during the simultaneous process [10]. This heterogeneous appearance could also be an effect of controlled drug release. PVA-Gel fibers were dispersed and showed a tight structure with fewer fiber joints. On the other hand, FA-loading gave rise to larger fiber diameters and caused the fiber cross-section to adopt a flat form. After FA-loading, a partial film surface also formed, resulting from the viscosity decreasing due to the addition of the NaHCO3 (Figure 2b). As seen in Figure 2c, the simultaneous process facilitated the formation of FA beads on the PVA-Gel fibers’ surfaces, and/or layers, but the web morphology was destroyed as in the PVA-Alg/sFA and PVA-Gel/FA samples (Figure 2b,f). The SEM micrographs of the PVA-CHi nanofibers in a random spaghetti structure show that knotty fiber structures formed in some regions through a spontaneous process. Moreover, the fiber thickness increased from 96.26 nm to 101.86 nm, which occurred in parallel to porosity decline (Table 3).

Table 3.
Average diameter and porosity of the fibers.
PVA-Gel–CHi fibers have a uniform shape and are randomly oriented. As FA was incorporated into the polymer solution, the interaction of the fibers increased and a rough structure was formed. The same situation was not observed when adding FA via the electrospraying method (Figure 3c). Decreasing the viscosity due to the addition of the NaHCO3 caused a different web structure. PVA-Gel–CHi/sFA fibers were almost the same as the neat fibers. These samples showed almost no fiber entanglement. Nevertheless, the average fiber diameter of the neat PVA-Gel–CHi sample decreased from 96.15 nm to 76.82 nm (Table 3). This could be because, during the e-spray process, the FA and polymer solutions dissolve in each other before reaching the collector.
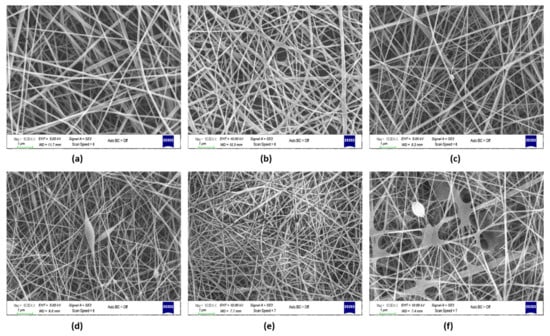
Figure 3.
(a) SEM image of PVA-Gel–CHi, (b) PVA-Gel–CHi/FA, (c) PVA-Gel–CHi/sFA, (d) PVA-Alg–CHi, (e) PVA-Alg–CHi/FA, and (f) PVA-Alg–CHi/sFA nanofibers (Magnification: 10 kX, scale bar: 1 µm).
The PVA-Alg–CHi web had a bead-on-string structure and thin and continuous fibers (Figure 3d). The PVA-Alg–CHi/FA web included discontinuous fibers and had a non-uniform web morphology, but not a bead-on-string structure. The addition of FA increased the fiber interaction and fiber breakdown due to increase secondary interactions in the electrospinning process (Figure 3e) (Li et al., 2012). In the PVA-Alg–CHi/sFA web, a PVA-Alg/sFA film formed as a web. The film formation occurred for the same reasons as in PVA-Alg/sFA.
3.2. Chemical Structure of the Hybrid Nanofibers
FT-IR spectra were acquired to investigate the physical interactions between polymer matrices and FA particles, as illustrated in Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6. It was determined that FA particles were successfully sprayed onto the surface of PVA-Gel nanofibers due to the intense and clearly defined C=O stretching of folic acid at 1651 cm−1. The band of the (–OH) group occurs at 3290 cm−1 in PVA-Gel fibers. The bands at 2938 and 2913 cm−1 are from the –CH2 stretching vibration. The typical absorption peaks of gelatin are mostly due to peptide bonds (–CONH) with amide I–III vibrations. The peak at 1643 cm−1 (amide-I) is associated with –C=O stretching vibration, while the peak at 1535 cm−1 (amide-II) is related with N-H bending and C-H stretching vibration. The (amide-III) peak was recorded at 1243 cm−1. Further, 1435 cm−1 (–CH2 bending), 1374 cm−1 (C–H wagging), 1088 cm−1 (–C–O–C), and 837 cm−1 (C–C) stretching were obtained. The disappearance of specific peaks in the FT-IR spectra of PVA-Gel/FA (Figure 5a) indicates that FA was loaded into the nanofibers. It could imply that the FA is uniformly spread throughout the blended nanofiber.
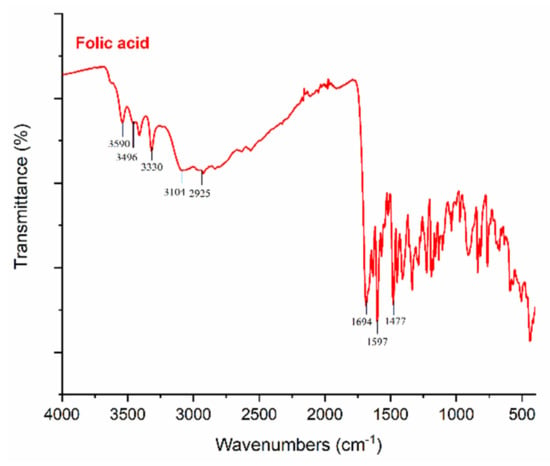
Figure 4.
FT-IR spectra of folic acid.
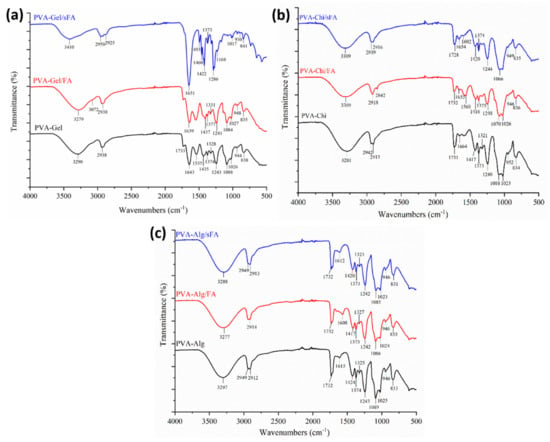
Figure 5.
FT-IR spectra of binary nanofibers, (a) shows comparison of PVA-Gel/sFA, PVA-Gel/FA, and PVA-Gel, (b) shows spectra of PVA-Chi/sFA, PVA-Chi/FA, and PVA-Chi, and (c) shows spectra of PVA-Alg/sFA, PVA-Alg/FA, and PVA-Alg.
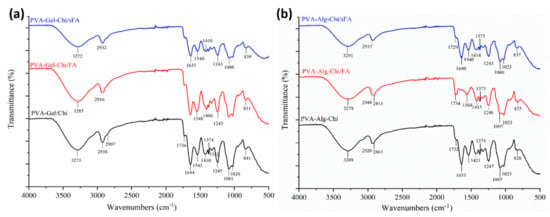
Figure 6.
FT-IR spectra of ternary nanofibers (a) shows comparison of PVA-Alg/sFA, PVA-Alg/FA, and PVA-Alg, (a) shows spectra of PVA-Gel-Chi/sFA, PVA-Gel-Chi/FA, and PVA-Gel-Chi, and (b) shows spectra of PVA-Alg-Chi/sFA, PVA-Alg-Chi/FA, and PVA-Alg-Chi.
The peaks at 3590 cm−1, 3496 cm−1, and 3330 cm−1 are linked with the (–OH) groups of folic acid in the crystalline structure. Moreover, the characteristic peaks of folic acid in the broad band between 3101 and 2400 cm−1 are caused by (–OH) groups of glutamic acid [35]. It has been found that the –NH stretching peak in the structure of the pterin ring disappeared in the broad band; however, the peak can be seen at 3101 cm−1 [36]. The (–C=O) group, related to pterin structure, can be observed at around 1694 cm−1 [35]. The peaks at 1635 cm−1 ((–C=N) stretching) and 1597 cm−1 belong to the bending of (–CONH2) [37], and 1477 cm−1 is related to the (–C=C) stretching of phenyl and pterin rings.
In PVA-CHi fibers, the band of the (–OH) group appears at about 3281 cm−1, related to –OH and –NH stretching vibrations. The FTIR spectra of the PVA/chitosan fibers (Figure 6b) show characteristic peaks of PVA and chitosan, with the exception of those associated with the ionization of the major amino groups of chitosan [38]. These peaks are signals at 1417 cm−1 and 1560 cm−1. The symmetric deformation of –NH3+ groups is responsible for the formation of the peak around 1560 cm−1, while the peak at 1417 cm−1 refers to carboxylic acid and those at 1321 cm−1 and 1240 cm−1 are connected to C-H vibration [39]. The peaks at 1731 cm−1 are typical of carboxylic acid dimers. The results are consistent with the literature [40].
The typical peaks of the PVA-Alg nanofiber were identified at 3297 cm−1, 2949 cm−1, 2912 cm−1, 1732 cm−1, and 1089 cm−1, attributed to –OH groups, asymmetric and symmetric –CH stretching, and –CO stretching, respectively (Figure 5c). The characteristic peaks of the electrospun PVA-Alg/FA nanofibers were detected at 3277 cm−1, 2949 cm−1, 2914 cm−1, 1732 cm−1 and 1086 cm−1, and are related to –OH groups, asymmetric and symmetric –CH stretching, and CO stretching, respectively. Moreover, the peaks at 1615 cm−1 and 1424 cm−1, resulting from asymmetric and symmetric (–COO) stretching, in the PVA-Alg fibers are slightly shifted to 1608 cm−1 and 1417 cm−1 in the PVA-Alg/FA fibers.
The characteristic peak of the carboxyl group of alginate, the amide group of chitosan, and the overlapping PVA peaks are similar to those in the PVA-Gel–CHi and PVA-Alg–CHi nanofibers (Figure 6a,b).
3.3. Thermal Properties and Weight-Loss of Nanofibers and Folic Acid
Figure 7 shows the thermogram of folic acid, which reveals that the bioactive powder was decomposed into four stages. In the first stage, the weight-loss of 7.54% was caused by removing moisture at temperatures from 100 to 170 °C. The 2.34% weight-loss in the second stage is related to the degradation of glutamic acid in the FA structure (between 170 and 240 °C) [41]. A slower degradation behavior occurred in the 240–600 °C range, with a weight-loss of about 49%. This was due to the degradation of the functional groups, which are pterin and p-amino benzoic acid (Janković, 2010). In the last stage, the 41.3% weight-loss was connected to the decomposition of pyrolysis products formed in the second and third steps.
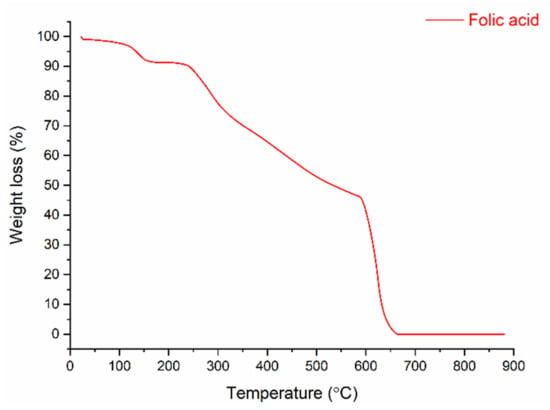
Figure 7.
TGA thermogram of folic acid.
TGA was used to assess the thermal stability of the nanofibers (Figure 8). Three main stages are seen in the TGA curves, which are linked to solvent and humidity being trapped inside (30–110 °C) the nanofiber samples; the second stage is connected to degradation of the polymers between 280 °C and 450 °C and the third stage is due to the degradation of the pyrolysis products of the polymers, which are formed during the polymer degradation stage under a N2 atmosphere [10,42]. The second weight-loss phase, related to the decomposition of the polymers, was composed of two steps according to the binary polymer mixture. The decomposition curves of PVA-Gel, PVA-Alg and PVA-CHi suggest two different decomposition behaviors. The first decomposition was related to the removal of the side group from the macromolecule chain. The last was related to the main macromolecule chain scission. Except for PVA-Alg/FA and PVA-Alg/FA, all samples gave pyrolysis products due to the inert atmosphere (N2 condition). After changing the atmosphere from N2 to O2 at 600 °C, all samples lost mass, except PVA-Alg/FA and PVA-Alg/FA, resulting from the alginate decomposition behavior in the inert atmosphere. Alginate does not create pyrolysis products when it decomposes under inert condition [43].
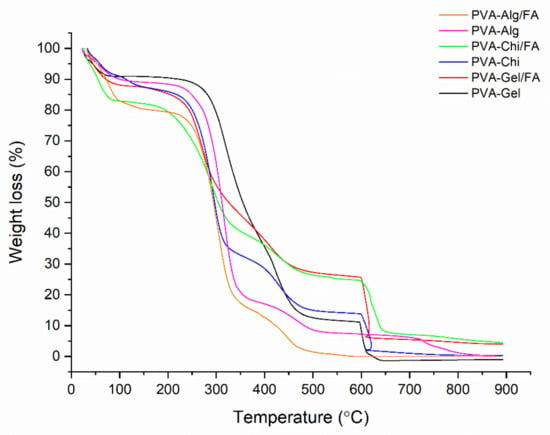
Figure 8.
TGA thermogram of nanofibers.
The decomposition of pure PVA has been discussed in the literature [31]. The thermal decomposition of the PVA mixture was hardly different from that of the pure PVA polymer, especially the last part of the curve. The first part of the polymer decomposition curve was also changed by adding FA molecules into the polymers. FA addition decreases the polymer decomposition speed due to its protective properties. This situation implies that FA could be used as an anti-oxidant in protective polymers during processing at high temperatures. FA’s conservation properties did not emerge in the case of the alginate polymers. The decomposition speed of the alginate mixture was not changed by adding FA due to the behavior of alginate decomposition in the inert atmosphere. The beginning of the first polymer decomposition stage was begun at lower temperatures by adding FA molecules. This resulted from the decomposition behavior of the FA materials [10,44]. The early decomposition of the FA molecules caused energy absorption, similar to the antioxidant running mechanism [45]. This energy absorption process preserves and delays the main polymers’ decomposition.
3.4. In Vitro Release Test and Kinetics
UV-Vis spectroscopy was utilized to analyze the FA release profile of the nanofibers, which assisted in revealing the structure–function connection of the electrospun fibers containing FA in the artificial acid (pH 5.44, 37 ℃) and alkaline (pH 8.04, 37 ℃) sweat solutions over 480 min. Figure 9 and Figure 10 depict the cumulative FA release rate profiles in the sweat solution samples, which were binary and ternary nanofibers containing FA. In Figure 9a, the release profiles of the PVA-Gel-sFA nanofibers in both acidic and alkaline media are similar, and they were released quickly in the first 30 min, then these samples continued to release FA slowly until 480 min. After 210 min, the FA release rate in alkaline media increased compared to acidic medium, and the maximum release value increased to almost 95%. The release behavior of the PVA-Gel/FA samples (in both acidic and alkaline medium) was partially different from that of PVA-Gel/sFA samples. These samples showed fast release behavior in alkaline medium for the first 30 min, while the fast release behavior in acidic medium continued until 90 min. Moreover, the amount of FA released in the alkaline medium was higher than in the acidic medium until 360 min. After this, the release rate increased in the acidic medium, and the cumulative FA release reached about 90%. It has been reported that the release media affects the polymer matrix, as well as the active drug [46].
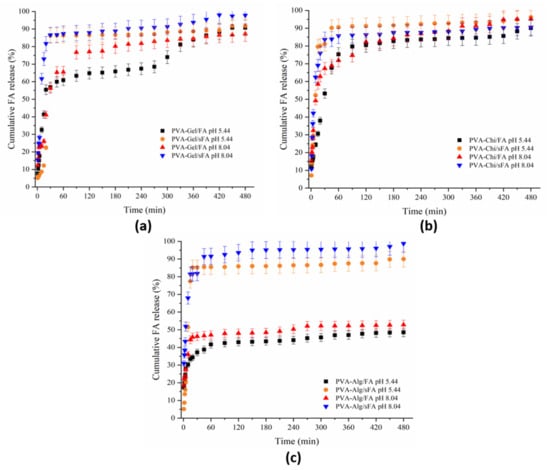
Figure 9.
UV-Vis release of binary nanofibers (a) release behavior of PVA-Gel/FA at pH 5.44, and 8.04, and PVA-Gel/sFA at pH 5.44 and 8.04, (b) release behavior of PVA-Chi/FA at pH 5.44 and 8.04, and PVA-Chi/sFA at pH 5.44 and 8.04, while (c) shows release behavior of PVA-Alg/FA at pH 5.44 and 8.04, and PVA-Alg/sFA at pH 5.44 and 8.04 respectievly.
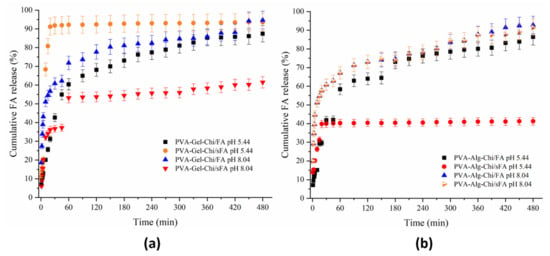
Figure 10.
UV-Vis release of ternary nanofibers (a) shows release behavior of PVA-Gel-Chi/FA at pH 5.44 and 8.04, and PVA-Gel-Chi/sFA at pH 5.44 and 8.04, while (b) shows release behavior of PVA-Alg-Chi/FA at pH 5.44 and 8.04, and PVA-Alg-Chi/sFA at pH 5.44 and 8.04.
It could be said that the fast release of FA from the samples produced via the electro- spraying process depended on the physical bond between the FA molecules and the fiber surface. It can be seen from Figure 2c that FA molecules were deposited on the fiber surface. When this type of web is immersed in acidic or alkaline media, the media breaks down the weak physical bond between fiber and FA molecules. The fast release of the samples in which FA was embedded was related to the depositing of FA on the fiber surface. Because of this, the release ratio was lower than that in the other samples produced via electrospraying. During the controlled release period, the release speed of the samples produced via electrospinning was higher than that of the others due to the removing of the embedded FA from inside the fiber.
The release behaviors of PVA-CHi/FA samples were the same in both acidic and alkaline medium (Figure 9b). After 180 min, the FA release rate increased in alkaline medium, and therefore the samples showed the highest quantity of released FA at the end of the release study. The amount released in acidic medium remained at almost 90%. Until 90 min, the release behavior of PVA-CHi/sFA was different from that of PVA-CHi/FA. A higher FA release rate occurred in the acidic medium (around 93%), while a lower FA release rate was observed in alkaline medium (around 85%).
Nair et al. (2019) performed a release study of curcumin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles by simulating skin at two distinct pH values (pH 5 and pH 7.4) [47]. In this study, the change in curcumin release observed under two different pH conditions was associated with the pH-dependent swelling behavior of chitosan. The swelling of chitosan allows the release medium to penetrate the polymer matrix and act as a plasticizer, which transforms the glassy polymer into a more rubbery structure, leading to increased drug release from the nanoparticle structure [48]. The release profiles of PVA-CHi/FA samples in both acidic and alkaline media are similar. Similarly, the release profiles of PVA-Kit/sFA in acidic and alkaline media are similar to each other. The PVA-CHi/FA samples released FA at 90% and 95% in acidic and alkaline media, respectively, due to the dissolution of PVA and chitosan. Mafenite acetate-loaded PVA-chitosan nanofibers were found to release 50% of the drug in the web structure within the first 10 min in the PBS medium [49].
The release rates of FA from the PVA-Alg/sFA nanofibers were similar in acidic and alkaline media (Figure 9c). PVA-Alg/sFA samples showed a fast release rate in the first 60 min, and then controlled release after this. It can be observed that the amount of FA released in these media during the analysis was over 90%. These findings are in agreement with the literature. Lutein-loaded sodium alginate/PVA nanofibers were found to achieve very fast lutein release, and cumulative release was completed in 7 min, at almost 92% [20]. The fast release in the first few minutes is explained by the hydrophilic character of alginate and the PVA composition. Arthanari et al. (2016) noted that gatifloxacin-loaded PVA-sodium alginate nanolyphs did not display a fast burst release tendency in the PBS (pH 7.4) for the first 1 h, but gatifloxacin was released (95% in total) during the test period [50]. The PVA-Alg/FA nanofibers in acidic and alkaline media were also similar, with almost 50% of FA released. PVA-Alg/FA had a fast release rate in the first 60 min. Unlike PVA-Alg/sFA samples, the PVA-Alg/FA samples’ FA release rate increased after 240 min. The PVA-Alg samples had the same release behavior as in PVA-Gel.
As seen Figure 10a, the ternary mixture of the PVA-Gel–CHi/FA sample had the same release profile in both acidic and alkaline media. These samples displayed fast release in the first 60 min. After this time, the release rate increased in a controlled manner. The release behaviors of PVA-Gel–CHi/sFA samples differed from those of PVA-Gel–CHi/FA samples. In addition, the release behaviors of PVA-Gel–CHi/sFA samples in acidic and alkaline media vary from each other. These samples showed fast release rates in alkaline medium in the first 60 min, and the release amount reached 60% in a controlled manner. In acidic medium, the samples showed fast release in the first 30 min and this was sustained in a controlled manner.
Apart from the PVA-Alg–CHi/sFA nanofiber structure in the acidic medium, the release rates of the other three webs were similar in both acidic and alkaline media (Figure 10b). For PVA-Alg–CHi/sFA nanofibers, the FA released in acidic medium was considerably low compared to the alkaline medium (41%). This could be related to the homogeneity of the electrospraying process. Furthermore, PVA-Alg–CHi/sFA exhibited a controlled release behavior after 30 min, while the other three samples showed gradual release to almost 90%. The PVA-Alg–CHi/FA samples showed little difference compared to the other two samples in the alkaline media.
Crosslinkers are often utilized to prepare PVA and/or gelatin-based scaffolds with physicochemical characteristics, and the obtained scaffolds are almost identical to healthy tissues. Besides this, drug release rates are advanced by crosslinkers. However, crosslinking reactions minimize the bio-based scaffolds’ in vivo degradation, and negatively affect host tissue responses [51,52]. In particular, gluteraldehyde (GA), which can be used as a crosslinker, can be considerably toxic to the body, and is typically restricted in many medicinal applications [53].
In the decision regarding the release mechanism, the choice of nanofiber matrix plays a critical role, dependent on degradation behavior and interaction with theurapeutics [54]. The diffusion mechanisms are based on both the polymer matrix properties and the processing variables, that is, whether they are Fickian or non-Fickian [55]. On the other hand, the solution matrix is more suitable for therapeutics, as these are dispersed in the electrospun fibers, resulting from the release rate and fiber morphology at which Fickian diffusion predominates. If a matrix shows considerably slow drug release, the Higuchi model (Power Law) is most often used to explain the diffusion-driven release. However, polymer degradation usually plays a substantial role in drug release, as is the case with PVA, in addition to release due to diffusion, when the matrix is biodegradable. The Korsmeyer–Peppas kinetic model typically defines such mixed release mechanisms [54].
The release profiles of the different nanofibers in two distinct release media correlated the best with different mathematical models (Table S1). The PVA-Alg–CHi/sFA nanofibers (in pH 5.44) gave the best results with zero-order, first-order, and Hixson–Crowell kinetic models. Generally, the Korsmeyer–Peppas kinetic model is used more than other models (Table S1). Moreover, the “n exponential factor” was found to be n < 1 and 0.45 < n < 0.89 for the nanofibers. For matrices in cylindrical form, the Fickian diffusion mechanism and signs of non-Fickian or abnormal transport are evident at 0.45 < n < 0.89. It was observed that both the change of release media and the use of different polymer matrices affects the release mechanism. It was found that the change in pH in the mechanism of FA release from the nanofibers obtained by the e-spraying method did not have a significant effect on the “n exponential factor”. However, the release of FA from nanofibers obtained by electrospinning was partially changed, depending on pH.
3.5. Entrapment Efficiency (EE, %) and Loading Capacity (LC, %)
The entrapment efficiency (EE, %) and also loading capacity (LC, %) have been calculated in the manuscript [56]. These values have been determined by the non-volatile FA structure using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer. The drug solubility of electrospun fibers influences the entrapment efficiency and the loading capacity of FA-loaded and FA-sprayed nanofibers (Table S2).
3.6. Cytotoxic Effects of Nanofibers by MTT Assay
The hydrophilic character of these composite fibers, which may assist in connecting the desired cells to the surfaces of the scaffolding, thus enables cell development and the improvement of viability, which is desirable in the context of applications of tissue engineering [57]. The proliferation of cells seeded on electrospun FA-loaded and FA-sprayed composite and pure nanofibers was evaluated via MTT assay after 24 h of treatment in L929 cells. The MTT results indicate that not all nanofiber scaffolds showed considerable toxicity, since their viability was no less than 70% (Figure 11) [34]. All PVA-based composite fibers with FA could be widely utilized in wound dressing and tissue engineering fields due to their ability to support cell function. The results prove that the addition of FA into PVA-based nanofibers enhances cell growth and supports cell proliferation. FA-loaded bicomponent composite fibers promoted cell proliferation during the MTT assays. In this regard, the blending process is more efficient than simultaneous processes. This could be related to the excess alcohol from the FA solution affecting the nanofibers.
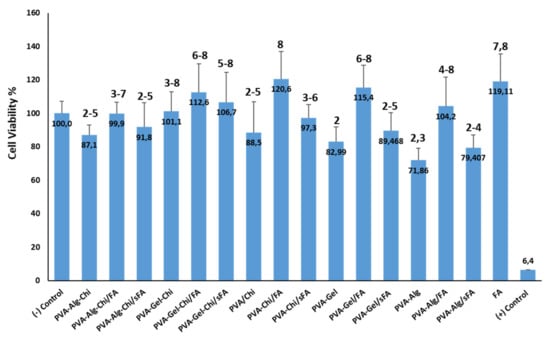
Figure 11.
Effects of all nanofibers on cell viability of L929 cells, by MTT assay.
The PVA-Gel/FA, PVA-CHi/FA, and PVA-Alg/FA samples acheved cell viability values of 115.4 ± 13.1, 120.6 ± 16.4, and 104.2 ± 17, respectively. PVA-CHi/FA fibers had the highest cell viability value of 120.6 ± 16.4.
Folic acid plays a crucial role in cell growth and repair, assisting wound healing via the biosynthesis of nucleic acids [58,59]. It is pointed out that FA can be converted into active tetrahydrofolic acid owing to the response of folic acid reductase in vivo. As a major provider of a carbon unit, tetrahydrofolic acid plays a key role in purine and pyrimidine synthesis and in amino acid mutual transformation; the absence of this in vivo vitamin may affect the transmission of the carbide unit and may affect nucleic acid synthesis bad amino acid metabolism, which are necessary to proliferate, grow and develop cells. The presence of FA in cell division throughout the wound healing process improves the healing rate due to its effect on growing cell division [60].
All the electrospun composite fibers consisting of FA exhibited more cell viability (%) compared to pure ones. This can be explained by the fact that FA has a high affinity for the folate receptor on the L929 cells [38]. Furthermore, PVA-based nanofibers have been noted as excellent drug carriers in a matrix, due to their non-toxic and biocompatible features. Therefore, PVA is utilized for a large range of medicinal applications, especially in its fibrous form, through these characteristics [61,62,63].
The ECM structure of fibroblast, osteoblast, chondrocyte and endothelial cells are the same in micro and nanofibers arranged in a random fibrous mat, which allows for quick regeneration and differentiation [64]. In recent years, various wound dressings have been developed and evaluated with similar cytotoxicity results to ours. Kalalinia et al. (2021) developed vancomycin (VCM)-loaded hybrid chitosan/poly ethylene oxide (Chi/PEO) nanofibers by blend-electrospinning [65]. There are no harmful effects of any group, according to the findings of the Alamar Blue cytotoxicity tests performed on HDFs. Çetmi et al. (2019) fabricated microalgal extract-loaded PCL nanofibers, and MTT cell growth assays revealed that the new fibers enhance the growing of cardiovascular cells by contributing significantly to cell proliferation [66]. Similarly, carbon nanofiber/gold nanoparticle (CNF/GNP)-conductive nanofibers used as scaffold have been produced by Nekounam et al. (2020) using two strategies: e-spraying simultaneously with electrospinning and blending electrospinning methods [67]. In this study, the MTT assays performed on MG63 cells did not show any toxicity, and all obtained nanofibers showed biocompatibility with cells.
These PVA-based nanofibers not only exhibited good biocompatibility in vitro, but were also found to possess many preferable wound/tissue engineering applications. In sum, PVA-based FA scaffolds offered the best nanofibers for cell development and are appropriate candidates for tissue engineering and wound healing.
According to the SNK analysis, all nanofibers ranked between the positive control (1) and PVA-CHi/FA (8), the cell viability of which was higher than FA. FA promotes the growth of cells because its cell viability values are greater than negative. PVA-Gel and PVA-Alg nanofibers are in the same group (2). The PVA-Alg sample is also placed in the third group. PVA-Alg–CHi, PVA-CHi, PVA-Gel/sFA and PVA-Alg–CHi/sFA nanofibers are in the same groups (2, 3, 4, and 5). Moreover, PVA-Alg–CHi/FA are in the same groups (3, 4, 5, 6, and 7) as the negative control. The PVA-CHi/FA, PVA-Gel/FA, PVA-Gel–CHi/FA and PVA-Gel–CHi/Sfa samples are considered to be more effective in terms of cell viability than others, based on the SNK analysis. The MTT assay results of all nanofibers show they would be acceptable for use as biocompatible materials in accordance with ISO 10993-5.
4. Conclusions
In the current study, FA-loaded and FA-sprayed PVA-based nanofibers were successfully fabricated via two distinct approaches: electrospinning and simultaneous electrospinning and electrospraying processes. The SEM micrographs indicate that spraying FA onto web layers and/or surfaces affects the nanofiber’s surface morphology. On the other hand, FA-loading did not change the morphology without phase separation, owing to the compatibility of FA with polymer matrices. The PVA gel kit samples achieved the highest porosity of 54.3 ± 3.8%, while PVA gel kit/sFA samples had the lowest fiber diameter (76.8 ± 2 nm) based on ImageJ software measurement. Based on FT-IR analysis, the resultant FA-sprayed composite fibers included the characteristic peaks of both polymer and FA. Furthermore, the TGA thermogram confirmed FA can be used as an antioxidant agent to delay the decomposition of polymer blends in the processing stage. PVA-CHi/FA webs had the highest release value of 95.2% in alkaline media, whereas PVA-Gel–CHi/sFA webs released the most FA (92%) in acidic media. The highest entrapment efficiency value was determined as 94.82 ± 4.7% for the PVA-Gel/sFA sample, while the lowest entrapment efficiency was determined for PVA-Alg/FA at 50.66 ± 2.5%. The loading capacity values of FA-loaded and FA-sprayed nanofibers were lower than 3%. Meanwhile, the MTT assays of PVA-CHi/FA samples showed that they had the highest cell viability, at 120.6 ± 16.4. Moreover, the FA release mechanism from the nanofibers was either Fickian or non-Fickian (abnormal transport) due to the change in matrices. The cytotoxicity studies of L929 cells performed via MTT assay displayed good biocompatibility, and even these hybrid nanofibers supported cell proliferation. In view of the results, nanofibrous PVA-based materials containing FA samples are recommended for tissue scaffold applications.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/polym13203594/s1. Table S1: Regression values of the FA-loaded and FA-sprayed nanofibers, Table S2: The entrapment efficiency (%) and loading capacities (%) of all nanofibers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.N.P.; methodology, F.N.P. and M.H.; software, S.U.; validation, K.Y. and I.-S.K.; formal analysis, F.N.P. and S.U.; investigation, F.N.P.; resources, F.N.P. and I.-S.K.; data curation, S.U. and M.H.; writing—original draft preparation, F.N.P. and K.Y.; writing—review and editing, S.U. and K.Y.; visualization, I.-S.K.; supervision, F.N.P. and I.-S.K.; project administration, K.Y.; funding acquisition, F.N.P. and I.-S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Scientific Research Unit of the Bursa University of Technology (SRP Project No. 190D003).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Scientific Research Unit of the Bursa University of Technology (SRP Project No. 190D003). The authors would like to thank Bursa Technical University Central Research Laboratory (Bursa, Turkey) for the SEM and TGA analysis and Gökçe Taner for MTT assays. The authors would like to thank as well the employees of the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey—Bursa Test and Analysis Laboratory (TUBİTAK-BUTAL, Turkey) for supporting the preparation of the artificial sweat solutions.
Conflicts of Interest
The author(s) declare no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
- Gupta, K.C.; Haider, A.; Choi, Y.-R.; Kang, I.-K. Nanofibrous scaffolds in biomedical applications. Biomater. Res. 2014, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashmi, M.; Ullah, S.; Ullah, A.; Akmal, M.; Saito, Y.; Hussain, N.; Ren, X.; Kim, I.S. Optimized Loading of Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) in Tri-component Electrospun Nanofibers Having Uniform Morphology. Polymers 2020, 12, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Ullah, A.; Lee, J.; Jeong, Y.; Hashmi, M.; Zhu, C.; Joo, K.I.; Cha, H.J.; Kim, I.S. Reusability Comparison of Melt-Blown vs Nanofiber Face Mask Filters for Use in the Coronavirus Pandemic. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 7231–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Hashmi, M.; Hussain, N.; Ullah, A.; Sarwar, M.N.; Saito, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, I.S. Stabilized nanofibers of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) crosslinked by unique method for efficient removal of heavy metal ions. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illangakoon, U.E.; Gill, H.; Shearman, G.C.; Parhizkar, M.; Mahalingam, S.; Chatterton, N.P.; Williams, G.R. Fast dissolving paracetamol/caffeine nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Kanjwal, M.A.; Lin, L.; Chronakis, I.S. Electrospun polyvinyl-alcohol nanofibers as oral fast-dissolving delivery system of caffeine and riboflavin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parın, F.N.; Yıldırım, K. Preparation and characterisation of vitamin-loaded electrospun nanofibres as promising transdermal patches. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2021, 29, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, J.; Yu, G.; Cardenas, R.; Wei, S.; Wujcik, E.K.; Guo, Z. Coaxial electrospun fibers: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 654–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-C.; Yu, D.-G.; Liao, Y.-Z.; Wang, X. Fast disintegrating quercetin-loaded drug delivery systems fabricated using coaxial electrospinning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21647–21659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parın, F.N.; Aydemir, Ç.İ.; Taner, G.; Yıldırım, K. Co-electrospun-electrosprayed PVA/folic acid nanofibers for transdermal drug delivery: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro cytocompatibility. J. Ind. Text. 2021, 1528083721997185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, M.; Ullah, S.; Kim, I.S. Copper oxide (CuO) loaded polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofiber membranes for antimicrobial breath mask applications. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2019, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharaghani, D.; Gitigard, P.; Ohtani, H.; Kim, K.O.; Ullah, S.; Saito, Y.; Khan, M.Q.; Kim, I.S. Design and characterization of dual drug delivery based on in-situ assembled PVA/PAN core-shell nanofibers for wound dressing application. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parin, F.N.; Terzioğlu, P.; Sicak, Y.; Yildirim, K.; Öztürk, M. Pine honey–loaded electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol)/gelatin nanofibers with antioxidant properties. J. Text. Inst. 2021, 112, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Ullah, S.; Khan, M.Q.; Hashmi, M.; Nam, P.D.; Kato, Y.; Tamada, Y.; Kim, I.S. Manuka honey incorporated cellulose acetate nanofibrous mats: Fabrication and in vitro evaluation as a potential wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, J.; Zhang, M. Polyblend nanofibers for biomedical applications: Perspectives and challenges. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Hashmi, M.; Kharaghani, D.; Khan, M.Q.; Saito, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Lee, J.; Kim, I.S. Antibacterial properties of in situ and surface functionalized impregnation of silver sulfadiazine in polyacrylonitrile nanofiber mats. Int. J. Nanom. 2019, 14, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, S.; Hashmi, M.; Khan, M.Q.; Kharaghani, D.; Saito, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Kim, I.S. Silver sulfadiazine loaded zein nanofiber mats as a novel wound dressing. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Materials, N.N.; Aktürk, A. Fabrication and Characterization of Polyvinyl Alcohol / Gelatin / Silver Nanoparticles Nanocomposite Materials. Eurasian J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2019, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Li, Y.; Nie, J. Preparation of gelatin/PVA nanofibers and their potential application in controlled release of drugs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Huo, P.; Ding, Z.; Kumar, P.; Liu, B. Preparation of lutein-loaded PVA/sodium alginate nanofibers and investigation of its release behavior. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Najafiasl, M.; Osfouri, S.; Azin, R.; Zaeri, S. Alginate-based electrospun core/shell nanofibers containing dexpanthenol: A good candidate for wound dressing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.; Netravali, A.N.; Joo, Y.L. Mechanical properties and biodegradability of electrospun soy protein Isolate/PVA hybrid nanofibers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, L.; Si, J.; Wang, Q.; Peng, X.; Chen, W. Electrospinning and crosslinking of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan composite nanofiber for transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ouyang, W.-C.; Zhou, X.-H.; Jin, T.; Wu, Z.-W. Antibacterial Activity and Drug Loading of Moxifloxacin-Loaded Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Chitosan Electrospun Nanofibers. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorani, B.; Tucker, N. Fundamentals of electrospinning as a novel delivery vehicle for bioactive compounds in food nanotechnology. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, A.; Jafari, S.M. Gum-based nanocarriers for the protection and delivery of food bioactive compounds. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 269, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Villa, D.; Gómez-Lavín, M.J.; Abradelo, C.; Román, J.S.; Rojo, L. Tissue engineering therapies based on folic acid and other vitamin B derivatives. Functional mechanisms and current applications in regenerative medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alborzi, S.; Lim, L.T.; Kakuda, Y. Release of folic acid from sodium alginate-pectin-poly(ethylene oxide) electrospun fibers under invitro conditions. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, L.M.; Crizel, R.L.; da Silva, F.T.; Fontes, M.R.V.; da Rosa Zavareze, E.; Dias, A.R.G. Starch nanofibers as vehicles for folic acid supplementation: Thermal treatment, UVA irradiation and in vitro simulation of digestion. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, J.; Shang, Y.; Hua, Y.; Ye, M.; Yang, Z.; Ou, C.; Chen, M. Folic Acid Derived Hydrogel Enhances the Survival and Promotes Therapeutic Efficacy of iPS Cells for Acute Myocardial Infarction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24459–24468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 105-E04:2013. Textiles-Tests for Colourfastness—Part E04: Colourfastness to Perspiration; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Moydeen, A.M.; Padusha, M.S.A.; Aboelfetoh, E.F.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Newehy, M.H. Fabrication of electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/dextran nanofibers via emulsion process as drug delivery system: Kinetics and in vitro release study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. UNI EN ISO 10993-12:2009. Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 12: Preparation of Samples and Reference Materials; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. UNI EN ISO 10993-5:2009. Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: In Vitro Cytotoxicity Testing; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.-Y.; Wang, X.-C.; Jin, P.-K.; Zhao, B.; Fan, X. Complexation of anthracene with folic acid studied by FTIR and UV spectroscopies. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 72, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İnce, İ.; Yıldırım, Y.; Güler, G.; Medine, E.İ.; Ballıca, G.; Kuşdemir, B.C.; Göker, E. Synthesis and characterization of folic acid-chitosan nanoparticles loaded with thymoquinone to target ovarian cancer cells. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2020, 324, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raouf, L.A.M.; Hammud, K.; Mohammed, J.M.; Mohammed, E.K.A.-D. Qualitative and Quantitative Determination of Folic acid in Tablets by FTIR Spectroscopy. Int. J. Adv. Pharm. Biol. Chem. 2014, 3, 773–780. [Google Scholar]
- Alhosseini, S.N.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Mozafari, M.; Asgari, S.; Dodel, M.; Samadikuchaksaraei, A.; Kargozar, S.; Jalali, N. Synthesis and characterization of electrospun polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous scaffolds modified by blending with chitosan for neural tissue engineering. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Gherissi, A. Synthesis and characterization of the composite material PVA/Chitosan/5% sorbitol with different ratio of chitosan. Int. J. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 2017, 17, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Pakolpakçıl, A.; Draczynski, Z. Green approach to develop bee pollen-loaded alginate based nanofibrous mat. Materials 2021, 14, 2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovi, B. Thermal stability investigation and the kinetic study of Folnak® degradation process under nonisothermal conditions. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shojaie, S.; Rostamian, M.; Samadi, A.; Alvani, M.A.S.; Khonakdar, H.A.; Goodarzi, V.; Zarrintaj, R.; Servatan, M.; Asefnejad, A.; Baheiraei, N.; et al. Electrospun electroactive nanofibers of gelatin-oligoaniline/Poly (vinyl alcohol) templates for architecting of cardiac tissue with on-demand drug release. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Gurau, G.; Block, L.E.; Hansen, L.K.; Dingee, C.; Walters, A.; Rogers, R.D. Chitin–calcium alginate composite fibers for wound care dressings spun from ionic liquid solution. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 3924–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parın, F.N. Yaşlanma Geciktirici B9 Vitamini Içeren Farklı Non-Woven Kumaşların Üretimi ve Kontrollü Salımının Incelenmesi. Ph.D. Thesis, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Bursa Teknik Üniversitesi, Bursa, Turkey, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Atteia, B.M.R.; El-Kak, A.E.-A.A.; Lucchesi, P.A.; Delafontane, P. Antioxidant activity of folic acid: From mechanism of action to clinical application. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 103.7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouazib, F.; Mokhnachi, N.B.; Haddadine, N.; Barille, R. Role of polymer/polymer and polymer/drug specific interactions in drug delivery systems. J. Polym. Eng. 2019, 39, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.S.; Morris, A.; Billa, N.; Leong, C.O. An Evaluation of Curcumin-Encapsulated Chitosan Nanoparticles for Transdermal Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinks, G.M.; Lee, C.K.; Wallace, G.G.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, S.J. Swelling behavior of chitosan hydrogels in ionic liquid-water binary systems. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9375–9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaspour, M.; Makhmalzadeh, B.S.; Rezaee, B.; Shoja, S.; Ahangari, Z. Evaluation of the antimicrobial effect of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol electrospun nanofibers containing mafenide acetate. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e24239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arthanari, S.; Mani, G.; Jang, J.H.; Choi, J.O.; Cho, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; Cha, S.E.; Oh, H.S.; Kwon, D.H.; Jang, H.T. Preparation and characterization of gatifloxacin-loaded alginate/poly (vinyl alcohol) electrospun nanofibers. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, R.T.; Mantilaka, M.M.M.G.P.G.; Goh, K.L.; Ratnayake, S.P.; Amaratunga, G.A.J.; De Silva, K.M.N. Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles Reinforced Electrospun Alginate-Based Nanofibrous Scaffolds with Improved Physical Properties. Int. J. Biomater. 2017, 2017, 1391298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xiao, Z.; Long, H.; Ma, K.; Zhang, J.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J. Assessment of the characteristics and biocompatibility of gelatin sponge scaffolds prepared by various crosslinking methods. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.-Y. Biocompatibility of chemically cross-linked gelatin hydrogels for ophthalmic use. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, T. Biomedical Textiles for Orthopaedic and Surgical Applications: Fundamentals, Applications and Tissue Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Preda, F.-M.; Alegría, A.; Bocahut, A.; Fillot, L.-A.; Long, D.R.; Sotta, P. Investigation of Water Diffusion Mechanisms in Relation to Polymer Relaxations in Polyamides. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 5730–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koudehi, M.F.; Zibaseresht, R. Synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles containing gentamicin drug as wound dressing based polyvinyl alcohol/gelatin nanofiber. Mater. Technol. 2020, 35, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadil, K.R.; Nathani, A.; Sharma, C.S.; Lenka, N.; Gupta, P. Fabrication of biocompatible alginate-poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Mater. Technol. 2018, 33, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdemirli, A.; Toksöz, F.; Karadağ, A.; Misirlioğlu, H.K.; Başbinar, Y.; Ellidokuz, H.; Açikgöz, O. Role of mesenchymal stem cell-derived soluble factors and folic acid in wound healing. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 49, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duthie, S.J.; Hawdon, A. DNA instability (strand breakage, uracil misincorporation, and defective repair) is increased by folic acid depletion in human lymphocytes in vitro. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 1491–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shen, L. Folic acid in combination with adult neural stem cells for the treatment of spinal cord injury in rats. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 10471–10480. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, P.; Ghosh, P.; Ghosh, K.; Maity, P.; Samanta, S.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Mohapatra, P.K.D.; Chatterjee, J.; Dhara, S. In vitro ALP and osteocalcin gene expression analysis and in vivo biocompatibility of N-methylene phosphonic chitosan nanofibers for bone regeneration. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarul, T.; Krishnamurithy, G.; Salih, N.D.; Ibrahim, N.S.; Raghavendran, H.R.B.; Suhaeb, A.R.; Choon, D.S.K. Biocompatibility and Toxicity of Poly(vinyl alcohol)/N,O-Carboxymethyl Chitosan Scaffold. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 905103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaji, S.; Ebrahimi, N.G.; Hosseinkhani, H. Enhancement of biocompatibility of PVA/HTCC blend polymer with collagen for skin care application. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2021, 70, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekaputra, A.K.; Prestwich, G.D.; Cool, S.M.; Hutmacher, D.W. The three-dimensional vascularization of growth factor-releasing hybrid scaffold of poly (ε-caprolactone)/collagen fibers and hyaluronic acid hydrogel. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8108–8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalalinia, F.; Taherzadeh, Z.; Jirofti, N.; Amiri, N.; Foroghinia, N.; Beheshti, M.; Bazzaz, B.S.F.; Hashemi, M.; Shahroodi, A.; Pishavar, E.; et al. Evaluation of wound healing efficiency of vancomycin-loaded electrospun chitosan/poly ethylene oxide nanofibers in full thickness wound model of rat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetmi, S.D.; Renkler, N.Z.; Kose, A.; Celik, C.; Oncel, S.S. Preparation of electrospun polycaprolactone nanofiber mats loaded with microalgal extracts. Eng. Life Sci. 2019, 19, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nekounam, H.; Allahyari, Z.; Gholizadeh, S.; Mirzaei, E.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Faridi-Majidi, R. Simple and robust fabrication and characterization of conductive carbonized nanofibers loaded with gold nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 117, 111226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).