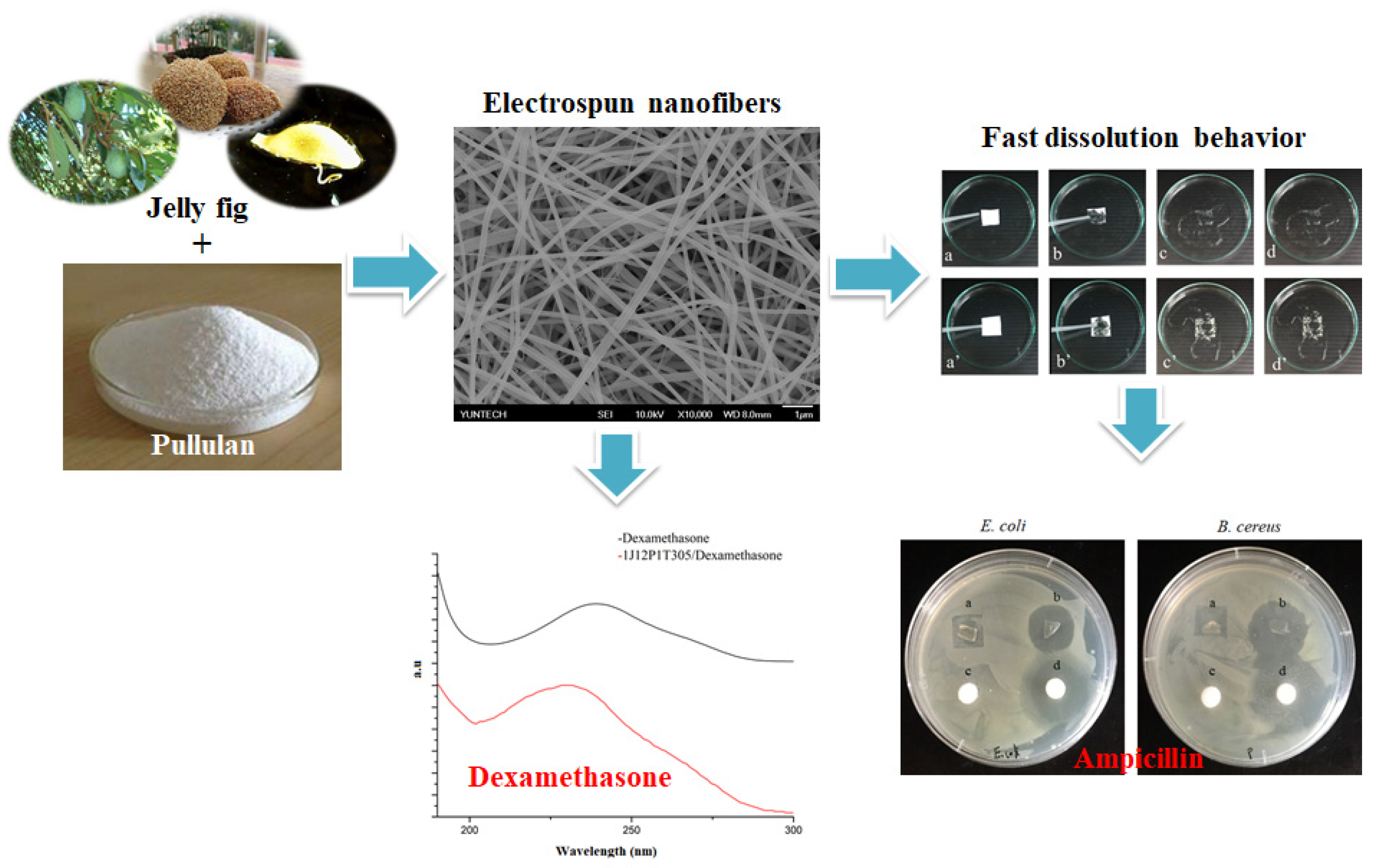
Fast Dissolving Electrospun Nanofibers Fabricated from Jelly Fig Polysaccharide/Pullulan for Drug Delivery Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction of JFP from Ficus awkeotsang Makino
2.3. Electrospinning of JFP/Pullulan Blends
2.4. Morphology of JFP/Pullulan Nanofibers
2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectrometer Analysis
2.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.7. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Study
2.8. Tensile Strength Analysis
2.9. Water Vapor Permeability (WVP) Measurement
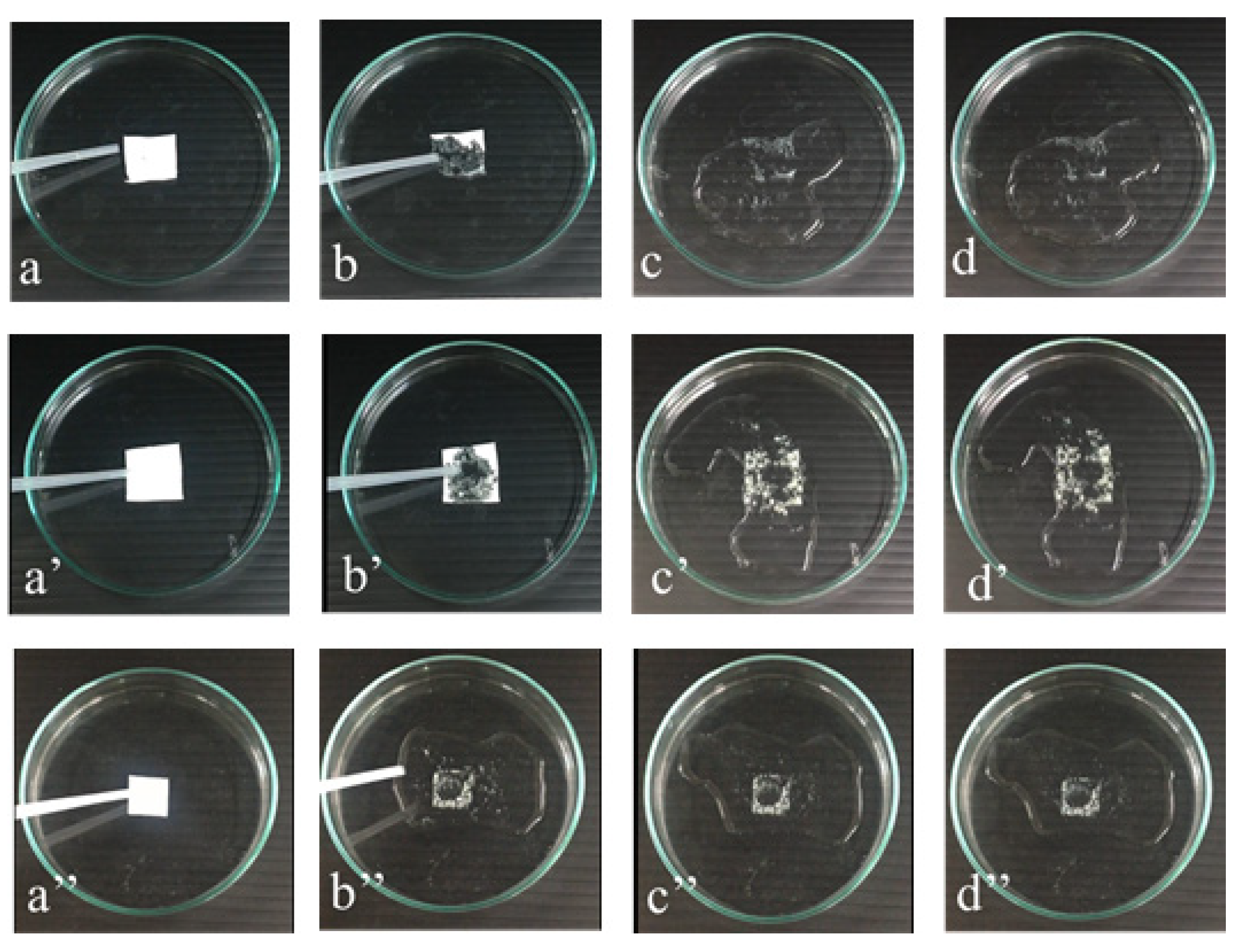
2.10. The Water Solubility or Dissolution Property of JFP/Pullulan Nanofibers
2.11. Test of In Vitro Drug Release from JFP/Pullulan Nanofibers
3. Results and Discussion
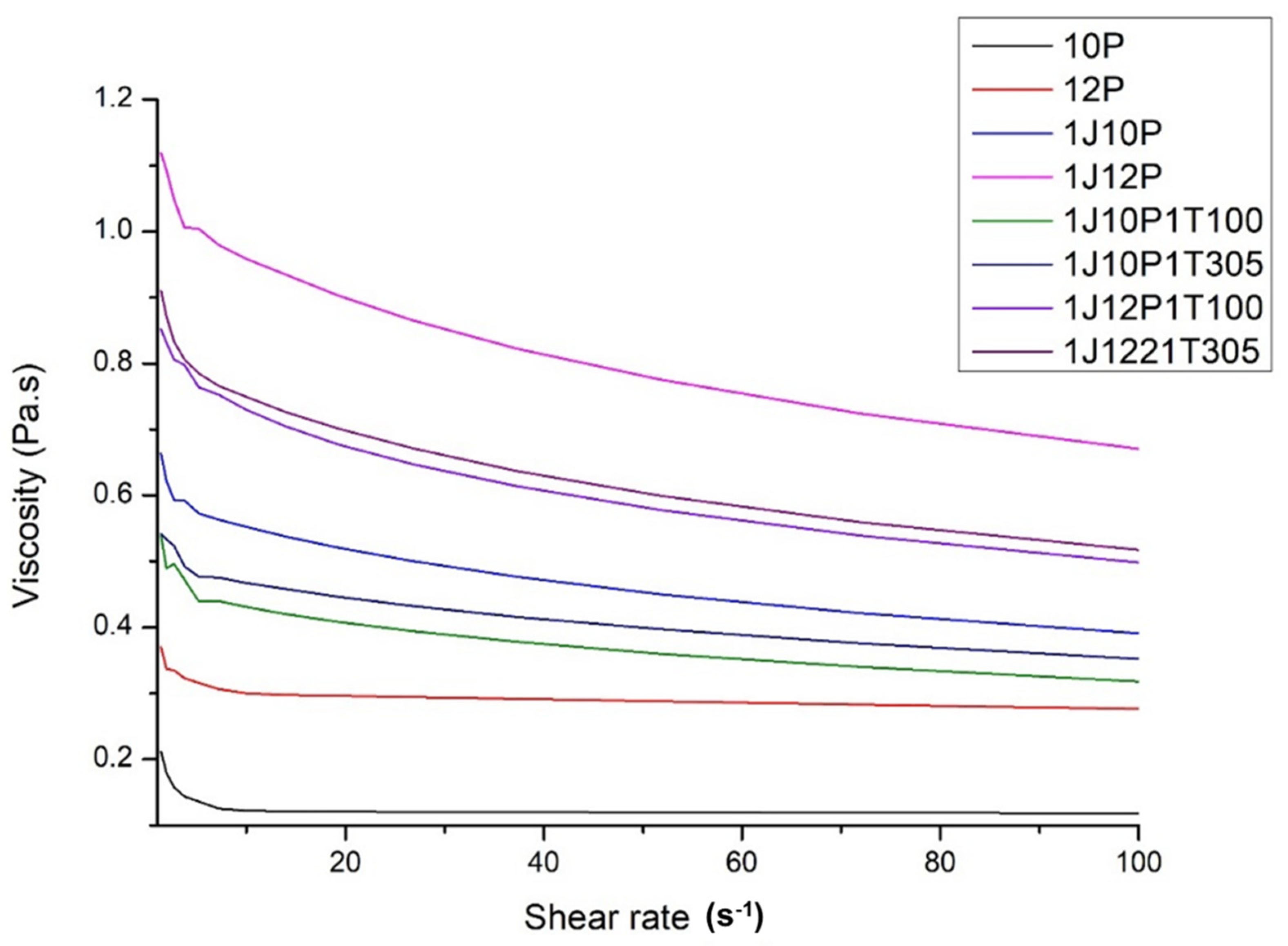
3.1. Properties of Electrospinning Solutions
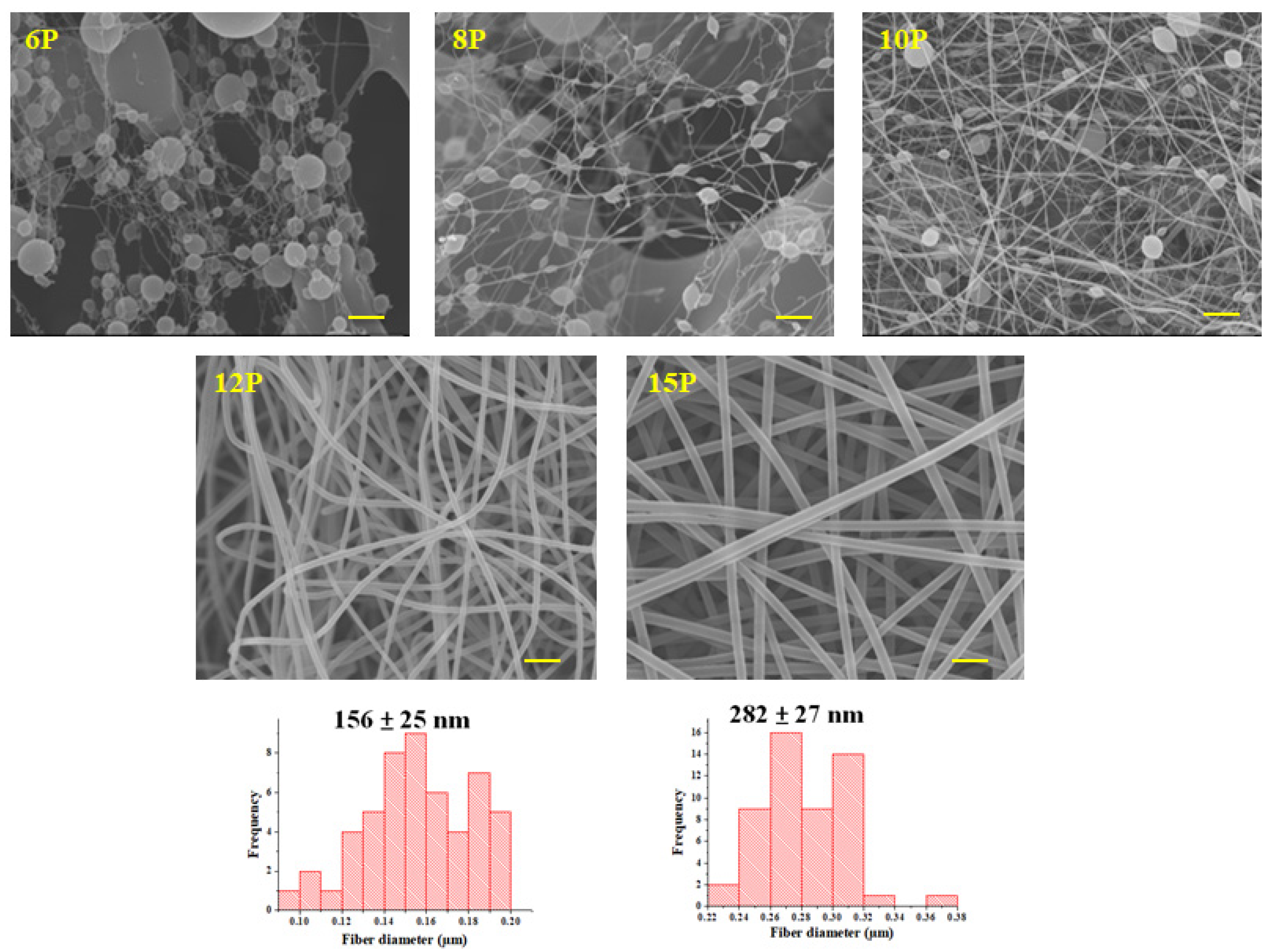
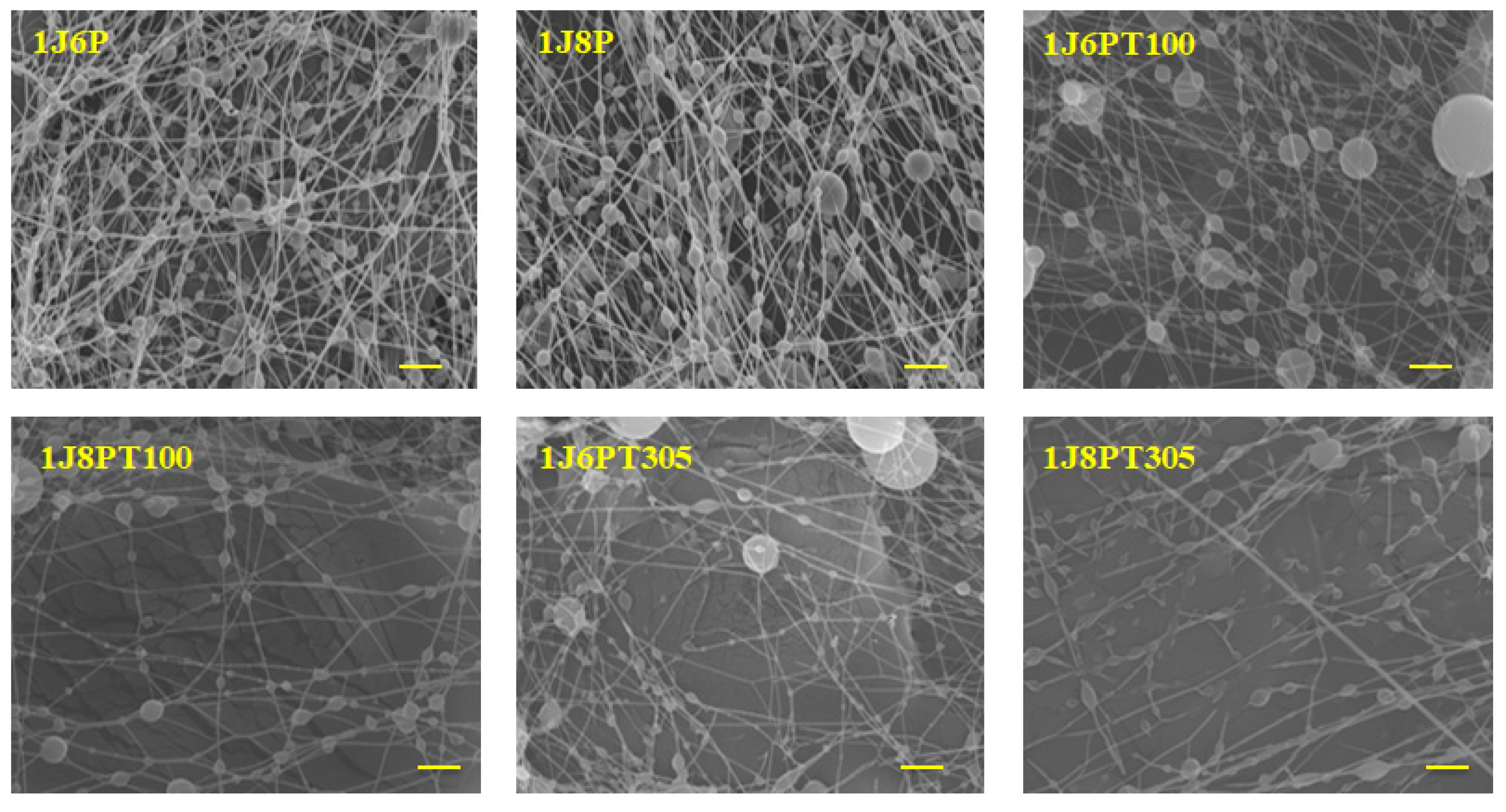
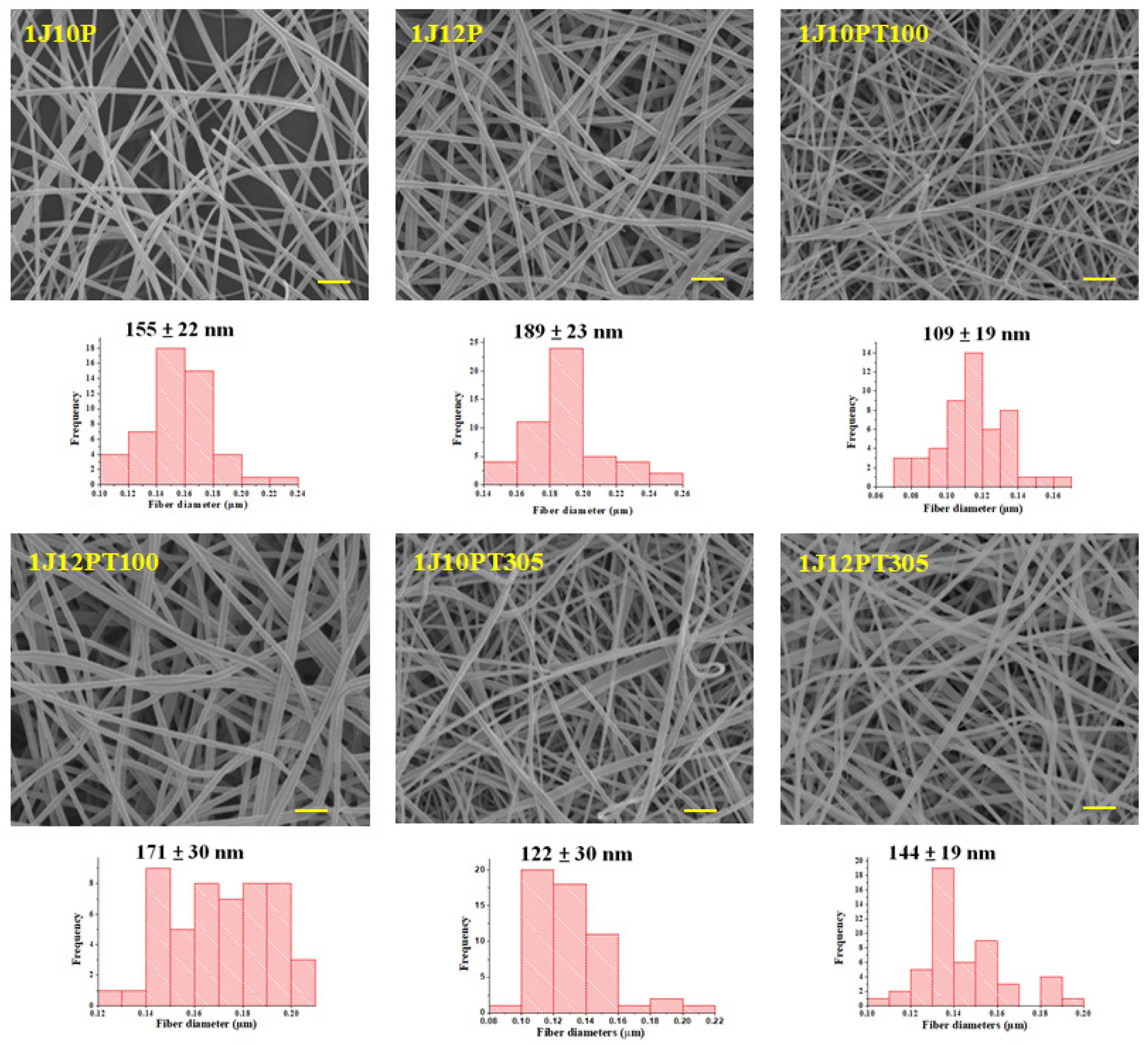
3.2. Morphology of Nanofibers
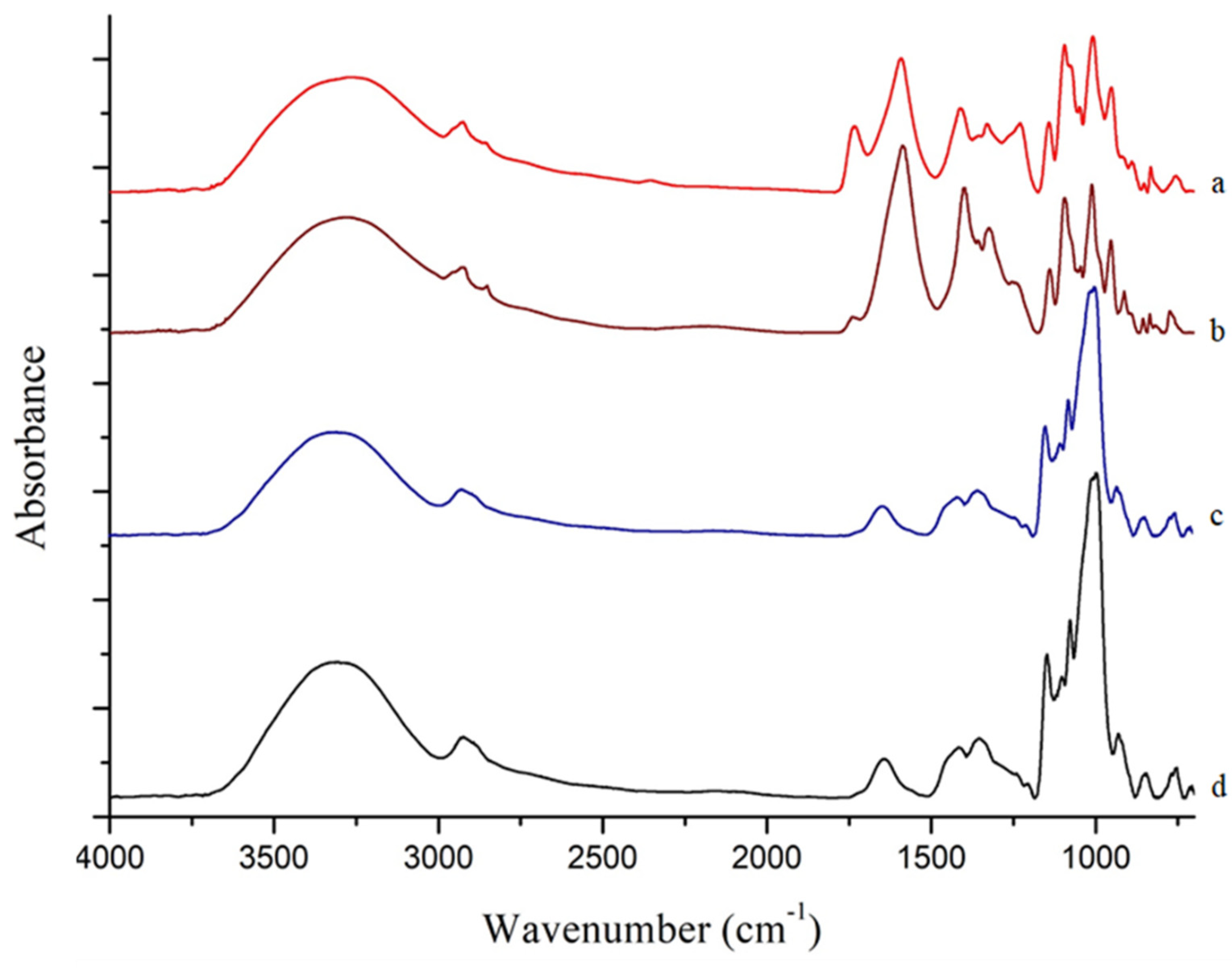
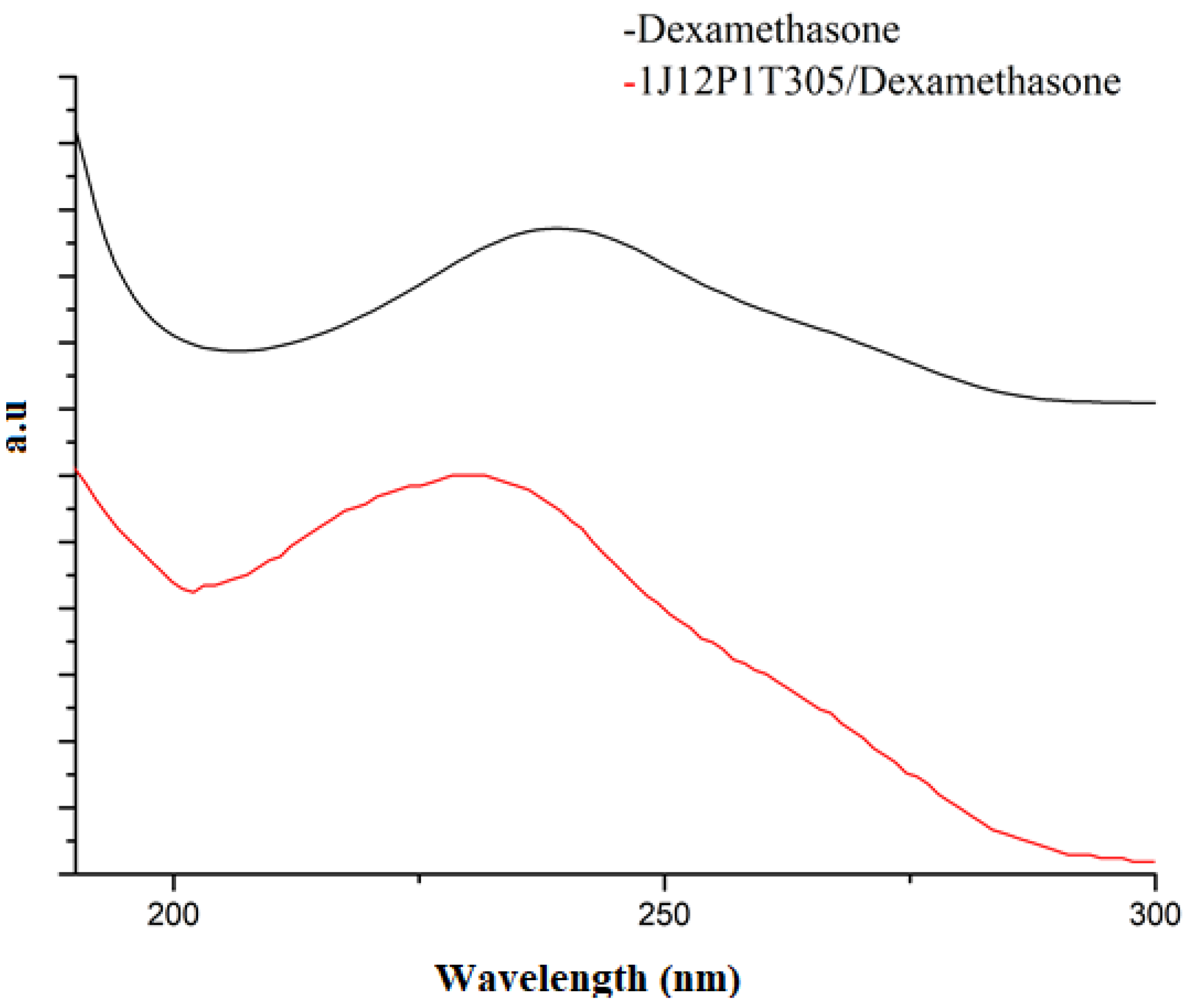
3.3. FTIR Analysis
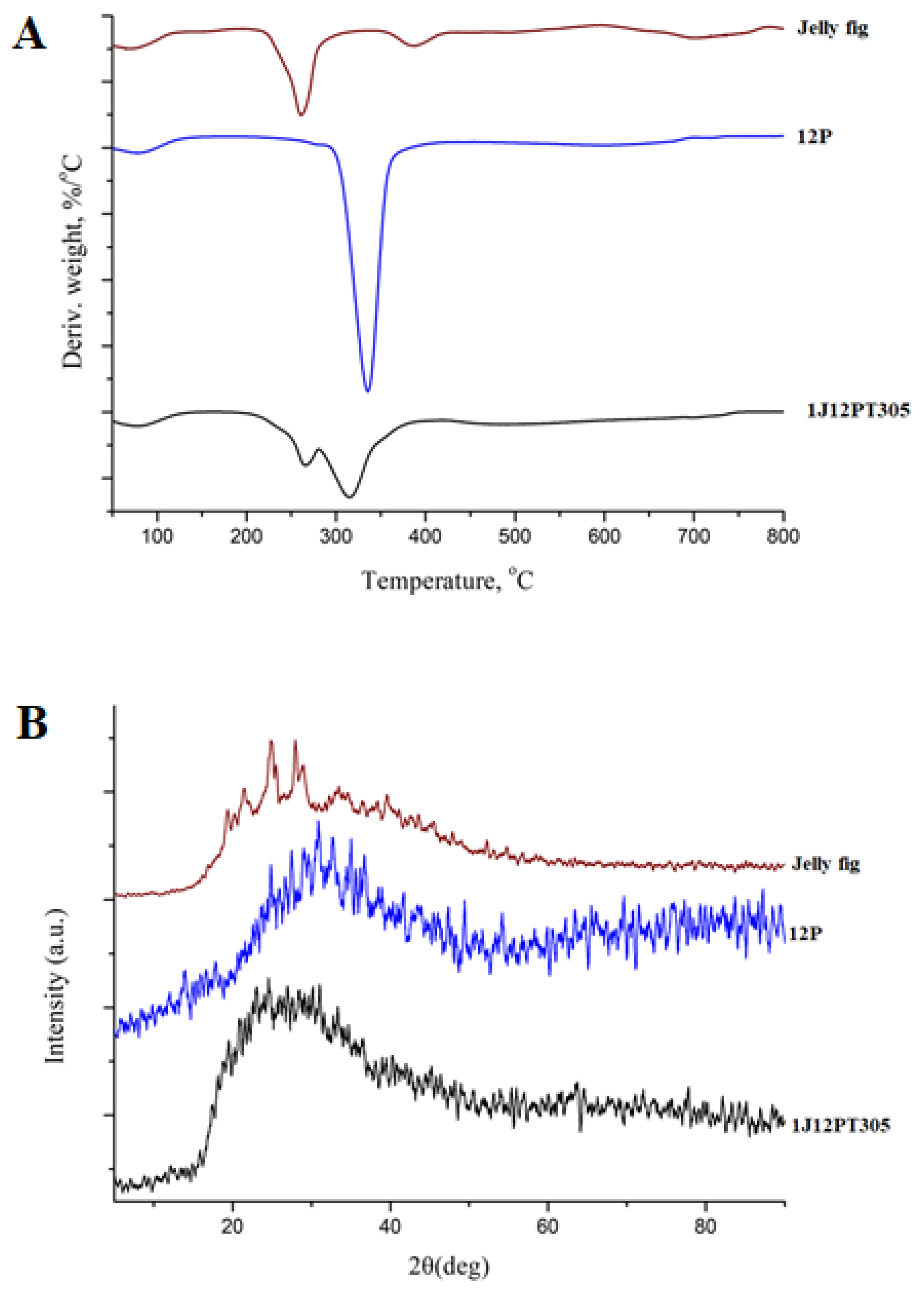
3.4. TGA Analysis
3.5. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
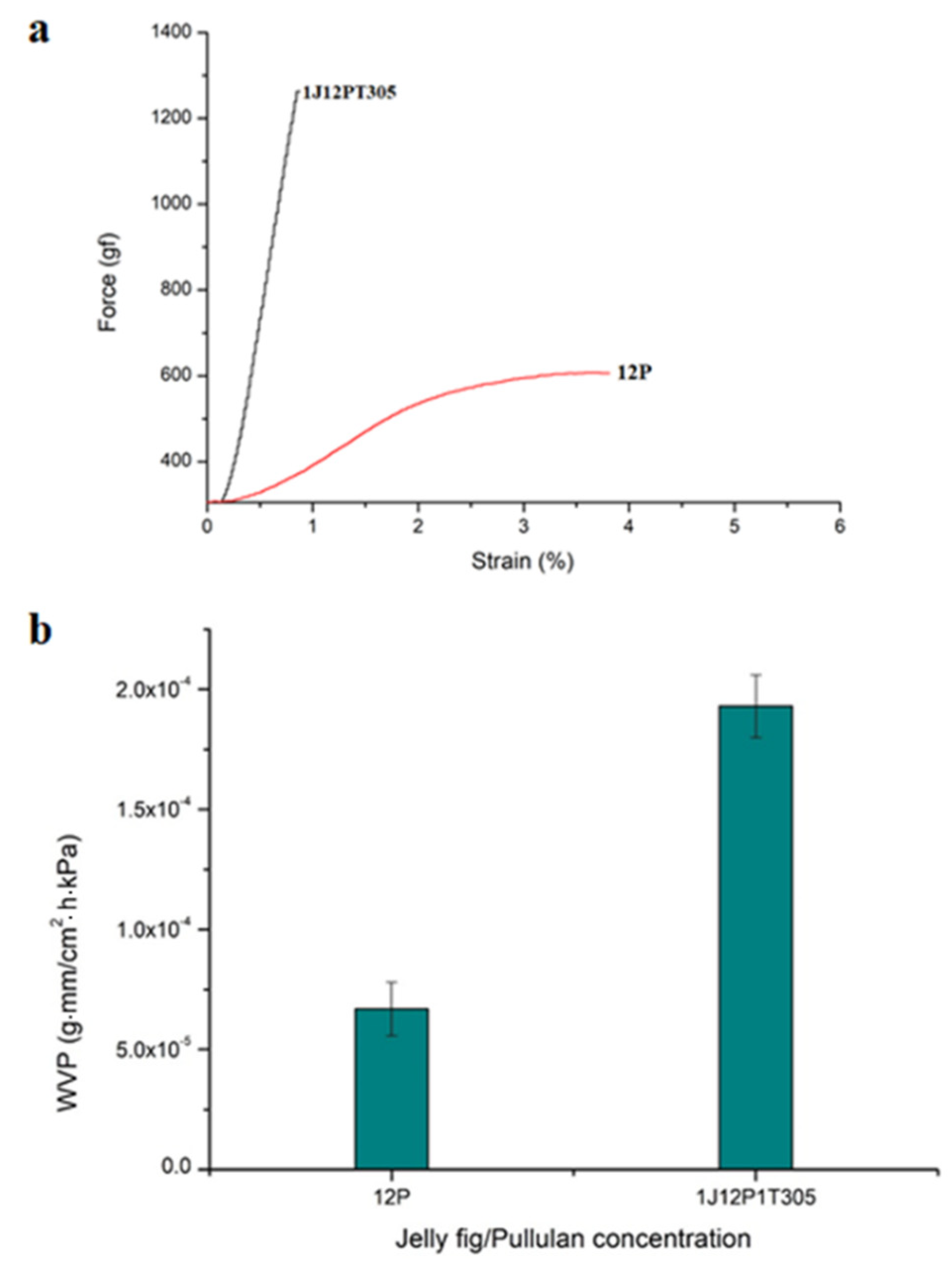
3.6. Tensile Strength
3.7. Water Vapor Permeability (WVP) Measurement
3.8. Water Solubility and Dissolution Study of Model Drug-Loaded Nanofibers
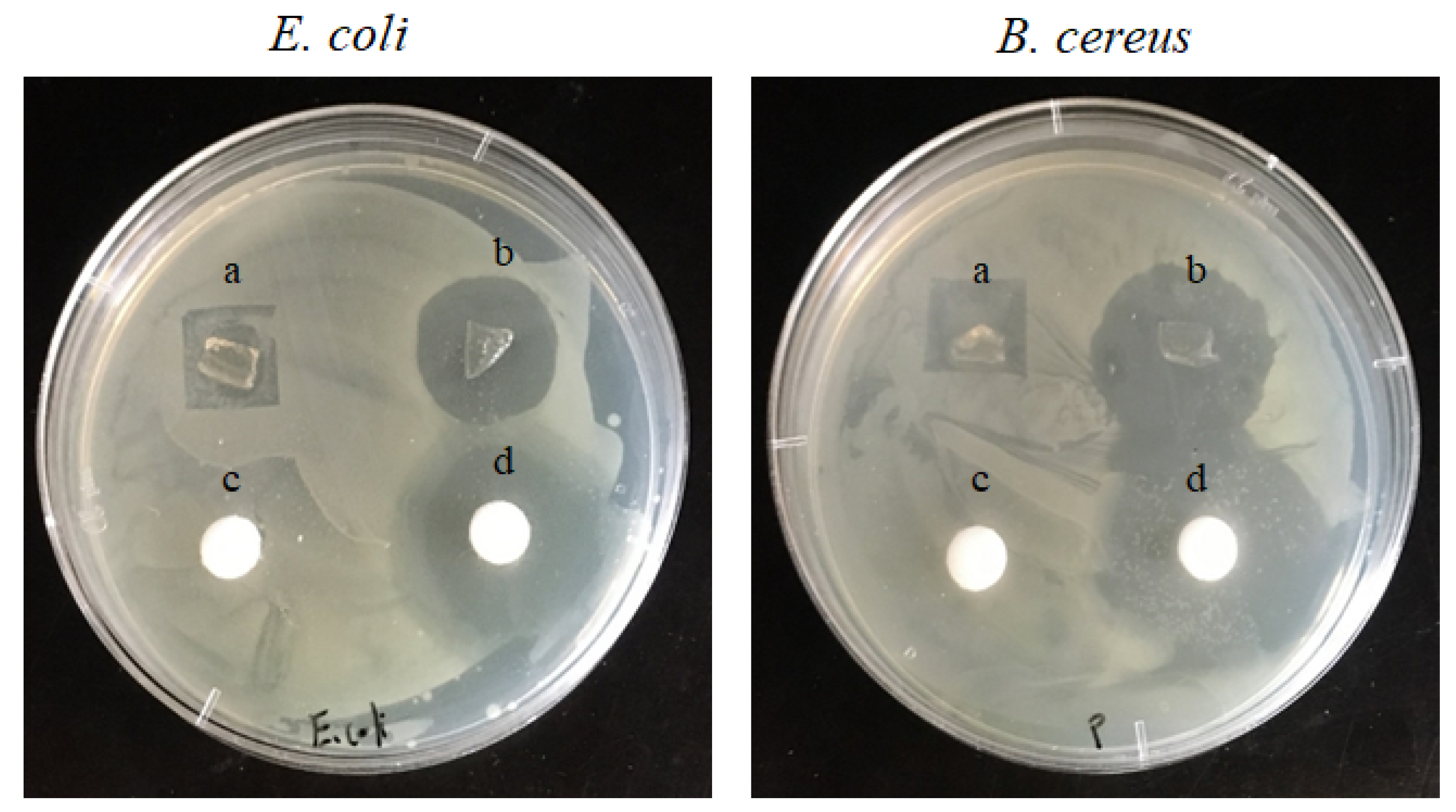
3.9. In Vitro Release Study of Drugs from Prepared Nanofibers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, D.-G.; Shen, X.-X.; Branford-White, C.; White, K.; Zhu, L.-M.; Bligh, S.A. Oral fast-dissolving drug delivery membranes prepared from electrospun polyvinylpyrrolidone ultrafine fibers. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 055104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barghi, L.; Jahangiri, A. Fast-dissolving nanofibers: As an emerging platform in pediatric and geriatric drug delivery. J. Adv. Chem. Pharm. Mater. (JACPM) 2018, 1, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Balusamy, B.; Celebioglu, A.; Senthamizhan, A.; Uyar, T. Progress in the design and development of “fast-dissolving” electrospun nanofibers based drug delivery systems—A systematic review. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 482–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Kanjwal, M.A.; Lin, L.; Chronakis, I.S. Electrospun polyvinyl-alcohol nanofibers as oral fast-dissolving delivery system of caffeine and riboflavin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okur, N.; Saricam, C.; Gocek, I.; Kalav, B.; Sahin, U.K. Functionalized polyvinyl alcohol nanofiber webs containing β–cyclodextrin/Vitamin C inclusion complex. J. Ind. Text. 2019, 1528083719866933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-C.; Yu, D.-G.; Liao, Y.-Z.; Wang, X. Fast disintegrating quercetin-loaded drug delivery systems fabricated using coaxial electrospinning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21647–21659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potrč, T.; Baumgartner, S.; Roškar, R.; Planinšek, O.; Lavrič, Z.; Kristl, J.; Kocbek, P. Electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers as a potential oromucosal delivery system for poorly water-soluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 75, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.Y.; Jia, X.W.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B.H.; Wang, H. Fast dissolving oral films for drug delivery prepared from chitosan/pullulan electrospinning nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, X.; Wang, T.; Sun, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Advances and applications of chitosan-based nanomaterials as oral delivery carriers: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciper, M.; Bodmeier, R. Modified conventional hard gelatin capsules as fast disintegrating dosage form in the oral cavity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 62, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, Z.; Ipek, S.; Erol, I.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Fast-dissolving electrospun gelatin nanofibers encapsulating ciprofloxacin/cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 178, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, Z.I.; Uyar, T. Fast-dissolving electrospun nanofibrous films of paracetamol/cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 492, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Fast Dissolving Oral Drug Delivery System Based on Electrospun Nanofibrous Webs of Cyclodextrin/Ibuprofen Inclusion Complex Nanofibers. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 4387–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Fast-dissolving antioxidant curcumin/cyclodextrin inclusion complex electrospun nanofibrous webs. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Development of ferulic acid/cyclodextrin inclusion complex nanofibers for fast-dissolving drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 584, 119395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzenis, Y. Spinning Continuous Fibers for Nanotechnology. Science 2004, 304, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, G.C.; Fridrikh, S.V. Formation of fibers by electrospinning. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cheng, S.; Lu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yao, Q. Electrospun fibers and their application in drug controlled release, biological dressings, tissue repair, and enzyme immobilization. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 25712–25729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dziemidowicz, K.; Sang, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, F.; Lagaron, J.M.; Mo, X.; Parker, G.J.M.; Yu, D.-G.; Zhu, L.-M.; et al. Electrospinning for healthcare: Recent advancements. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłowska, S.; Rinoldi, C.; Nakielski, P.; Ziai, Y.; Urbanek, O.; Li, X.; Kowalewski, T.A.; Ding, B.; Pierini, F. Ultraviolet Light-Assisted Electrospinning of Core–Shell Fully Cross-Linked P(NIPAAm-co-NIPMAAm) Hydrogel-Based Nanofibers for Thermally Induced Drug Delivery Self-Regulation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakielski, P.; Pawłowska, S.; Rinoldi, C.; Ziai, Y.; De Sio, L.; Urbanek, O.; Zembrzycki, K.; Pruchniewski, M.; Lanzi, M.; Salatelli, E.; et al. Multifunctional Platform Based on Electrospun Nanofibers and Plasmonic Hydrogel: A Smart Nanostructured Pillow for Near-Infrared Light-Driven Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 54328–54342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmetova, A.; Lanno, G.-M.; Kogermann, K.; Malmsten, M.; Rades, T.; Heinz, A. Highly Elastic and Water Stable Zein Microfibers as a Potential Drug Delivery System for Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, K.; Yu, D.-G.; Yang, Y.; Bligh, S.W.A.; Williams, G.R. Electrospun Janus nanofibers loaded with a drug and inorganic nanoparticles as an effective antibacterial wound dressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, C.; Lanno, G.-M.; Laidmäe, I.; Meos, A.; Härmas, R.; Kogermann, K. High humidity electrospinning of porous fibers for tuning the release of drug delivery systems. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sio, L.; Ding, B.; Focsan, M.; Kogermann, K.; Pascoal-Faria, P.; Petronella, F.; Mitchell, G.; Zussman, E.; Pierini, F. Personalized Reusable Face Masks with Smart Nano-Assisted Destruction of Pathogens for COVID-19: A Visionary Road. Chem. A Eur. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Cáceres, R.; Cabeza, L.; Perazzoli, G.; Díaz, A.; López-Romero, J.M.; Melguizo, C.; Prados, J. Electrospun Nanofibers: Recent Applications in Drug Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pillay, V.; Dott, C.; Choonara, Y.E.; Tyagi, C.; Tomar, L.; Kumar, P.; du Toit, L.C.; Ndesendo, V.M.K. A Review of the Effect of Processing Variables on the Fabrication of Electrospun Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 789289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres-Martinez, E.J.; Cornejo Bravo, J.M.; Serrano Medina, A.; Pérez González, G.L.; Villarreal Gómez, L.J. A Summary of Electrospun Nanofibers as Drug Delivery System: Drugs Loaded and Biopolymers Used as Matrices. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Serra, R.; Gorelick, N.; Fatima, U.; Eberhart, C.G.; Brem, H.; Tyler, B.; Steckl, A.J. Multi-layered core-sheath fiber membranes for controlled drug release in the local treatment of brain tumor. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.C.; Demirci, A.; Catchmark, J.M. Pullulan: Biosynthesis, production, and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oğuzhan, P.; Yangılar, F. Pullulan: Production and usage in food industry. Afr. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 2141–5455. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.S.; Saini, G.K.; Kennedy, J.F. Pullulan: Microbial sources, production and applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 73, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponrasu, T.; Yang, R.F.; Chou, T.H.; Wu, J.J.; Cheng, Y.S. Core-Shell Encapsulation of Lipophilic Substance in Jelly Fig (Ficus awkeotsang Makino) Polysaccharides Using an Inexpensive Acrylic-Based Millifluidic Device. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 191, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.-M.; Lai, Y.-J.; Lee, B.-H.; Chang, W.-H.; Wud, M.-C.; Chang, H.-M. Changes in physico-chemical properties of pectin from jelly fig (Ficus awkeotsang Makino) seeds during extraction and gelling. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.-W.; Wang, L.-F. Mechanical and water barrier properties of agar/κ-carrageenan/konjac glucomannan ternary blend biohydrogel films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, K.K.; Ali, N.A.; Das, D.; Mohanta, D. Thorough evaluation of sweet potato starch and lemon-waste pectin based-edible films with nano-titania inclusions for food packaging applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponrasu, T.; Gu, J.-S.; Wu, J.-J.; Cheng, Y.-S. Evaluation of jelly fig polysaccharide as a shell composite ingredient of colon-specific drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 101679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amariei, N.; Manea, L.R.; Bertea, A.P.; Bertea, A.; Popa, A. The influence of polymer solution on the properties of electrospun 3D nanostructures. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IPO Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017; p. 012092. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.-K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Bien, H.; Chung, C.-Y.; Yin, L.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B.; Entcheva, E. Electrospun fine-textured scaffolds for heart tissue constructs. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5330–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Padhye, R.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Truong, Y.B.; Arnold, L. Effect of viscosity and electrical conductivity on the morphology and fiber diameter in melt electrospinning of polypropylene. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; He, J.H.; Xu, L. Non-ionic surfactants for enhancing electrospinability and for the preparation of electrospun nanofibers. Polym. Int. 2008, 57, 1079–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziani, K.; Henrist, C.; Jérôme, C.; Aqil, A.; Maté, J.I.; Cloots, R. Effect of nonionic surfactant and acidity on chitosan nanofibers with different molecular weights. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Vázquez, G.; Loarca-Piña, G.; Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.; Mendoza, S. Electrospun fibers from blends of pea (Pisum sativum) protein and pullulan. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Lim, L.T. Pullulan-alginate fibers produced using free surface electrospinning. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.R.; Santiago, R.R.; de Souza, T.P.; Egito, E.S.; Oliveira, E.E.; Soares, L.A. Development and evaluation of emulsions from Carapa guianensis (Andiroba) oil. AAPS Pharmscitech 2010, 11, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindner, M.; Bäumler, M.; Stäbler, A. Inter-Correlation among the Hydrophilic–Lipophilic Balance, Surfactant System, Viscosity, Particle Size, and Stability of Candelilla Wax-Based Dispersions. Coatings 2018, 8, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talwar, S.; Krishnan, A.S.; Hinestroza, J.P.; Pourdeyhimi, B.; Khan, S.A. Electrospun Nanofibers with Associative Polymer−Surfactant Systems. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 7650–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Yao, B.; Sun, X.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Reducing the content of carrier polymer in pectin nanofibers by electrospinning at low loading followed with selective washing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 59, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.-Y.; Zhuang, M.-F.; Yu, Z.-J.; Zheng, G.-F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, D.-H. The Effect of Surfactants on the Diameter and Morphology of Electrospun Ultrafine Nanofiber. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulig, D.; Zimoch-Korzycka, A.; Jarmoluk, A.; Marycz, K. Study on Alginate-Chitosan Complex Formed with Different Polymers Ratio. Polymers 2016, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.-S.; Zhu, P.; Zhao, J.-C.; Zhang, C.-J.; Guo, Y.; Cui, L. Thermal degradation properties of biobased iron alginate film. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 119, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Q.; Lu, K.; Tong, Q.; Liu, C. Barrier Properties and Microstructure of Pullulan-Alginate-Based Films. J. Food Process Eng. 2015, 38, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Guo, B.; Liu, M.; Jia, D. Formation of Reinforcing Inorganic Network in Polymer via Hydrogen Bonding Self-Assembly Process. Polym. J. 2007, 39, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Ying, S.; Li, J. Hydrogen bonding and crystallization behaviour of segmented polyurethaneurea: Effects of hard segment concentration. Polymer 1992, 33, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljun, A.; Benians, T.A.S.; Goubet, F.; Meulewaeter, F.; Knox, J.P.; Blackburn, R.S. Comparative Analysis of Crystallinity Changes in Cellulose I Polymers Using ATR-FTIR, X-ray Diffraction, and Carbohydrate-Binding Module Probes. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 4121–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Li, J.J.; Williams, G.R.; Zhao, M. Electrospun amorphous solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drugs: A review. J. Control. Release 2018, 292, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lyu, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, F. Study on the Electrospinning of Gelatin/Pullulan Composite Nanofibers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burkinshaw, S.M. Physico-Chemical Aspects of Textile Coloration; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–622. Available online: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Physico+chemical+Aspects+of+Textile+Coloration-p-9781118725696 (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Okamoto, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Sakuragi, M.; Imoto, S.; Yamasaki, K.; Otagiri, M. In vivo drug delivery efficiency of albumin-encapsulated liposomes as hydrophobic drug carriers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 47, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabitha, M.; Rajiv, S. Preparation and characterization of ampicillin-incorporated electrospun polyurethane scaffolds for wound healing and infection control. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacanti, N.M.; Cheng, H.; Hill, P.S.; Guerreiro, J.D.T.; Dang, T.T.; Ma, M.; Watson, S.; Hwang, N.S.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G. Localized Delivery of Dexamethasone from Electrospun Fibers Reduces the Foreign Body Response. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3031–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birhanu, G.; Tanha, S.; Akbari Javar, H.; Seyedjafari, E.; Zandi-Karimi, A.; Kiani Dehkordi, B. Dexamethasone loaded multi-layer poly-l-lactic acid/pluronic P123 composite electrospun nanofiber scaffolds for bone tissue engineering and drug delivery. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Min, B.H.; Kim, M.S. Preparation and Evaluation of Dexamethasone-Loaded Electrospun Nanofiber Sheets as a Sustained Drug Delivery System. Materials 2016, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ponrasu, T.; Chen, B.-H.; Chou, T.-H.; Wu, J.-J.; Cheng, Y.-S. Fast Dissolving Electrospun Nanofibers Fabricated from Jelly Fig Polysaccharide/Pullulan for Drug Delivery Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020241
Ponrasu T, Chen B-H, Chou T-H, Wu J-J, Cheng Y-S. Fast Dissolving Electrospun Nanofibers Fabricated from Jelly Fig Polysaccharide/Pullulan for Drug Delivery Applications. Polymers. 2021; 13(2):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020241
Chicago/Turabian StylePonrasu, Thangavel, Bei-Hsin Chen, Tzung-Han Chou, Jia-Jiuan Wu, and Yu-Shen Cheng. 2021. "Fast Dissolving Electrospun Nanofibers Fabricated from Jelly Fig Polysaccharide/Pullulan for Drug Delivery Applications" Polymers 13, no. 2: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020241
APA StylePonrasu, T., Chen, B.-H., Chou, T.-H., Wu, J.-J., & Cheng, Y.-S. (2021). Fast Dissolving Electrospun Nanofibers Fabricated from Jelly Fig Polysaccharide/Pullulan for Drug Delivery Applications. Polymers, 13(2), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020241






