Immobilization of Phospholipase A1 Using a Protein-Inorganic Hybrid System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PLA1 and Enzyme Activity Determination
2.3. Preparation of PLA1–Metal Hybrid Nanostructures
2.4. The Encapsulation Yield of PLA1
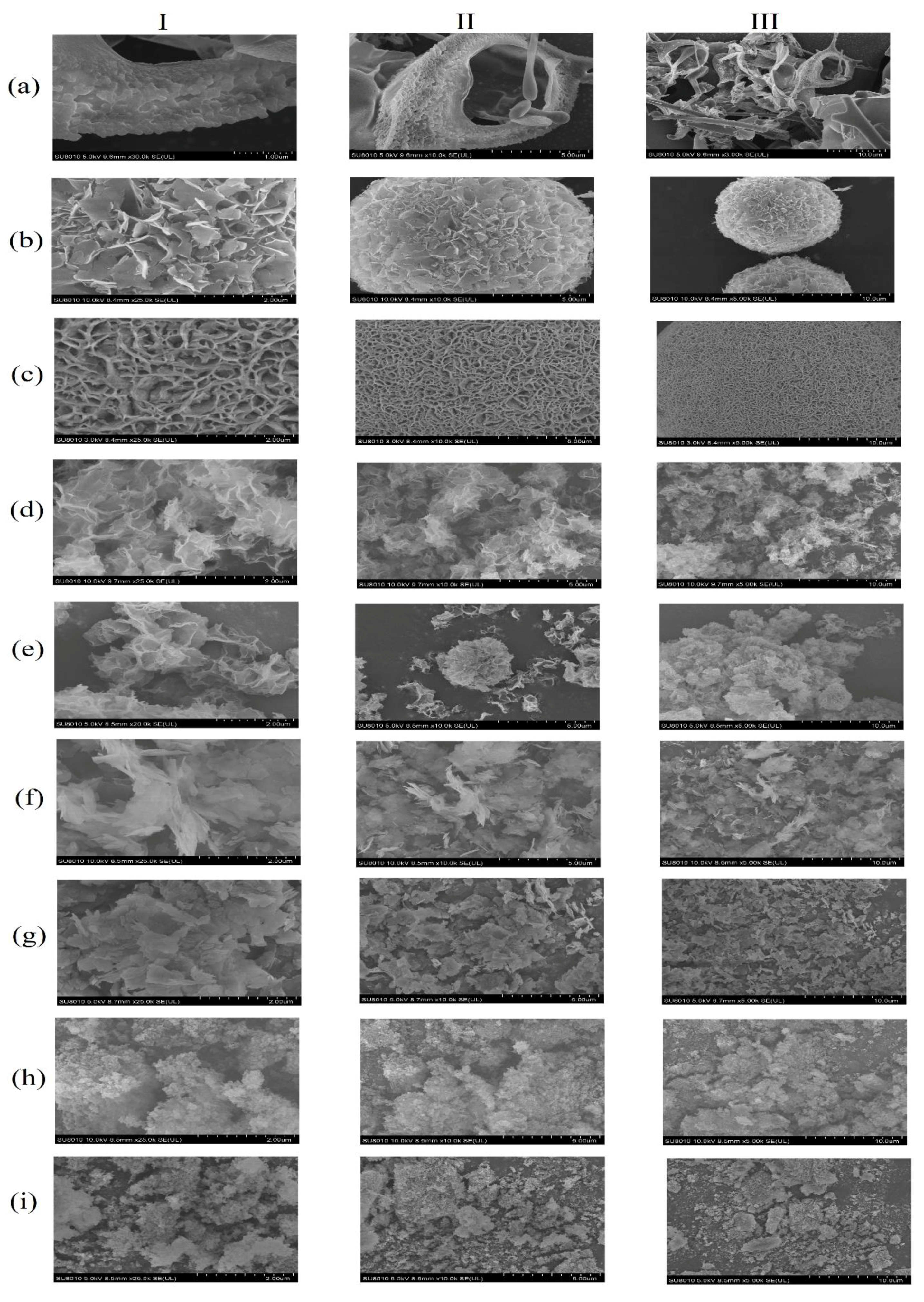
2.5. Field Emission Electron Microscope (FE-SEM)
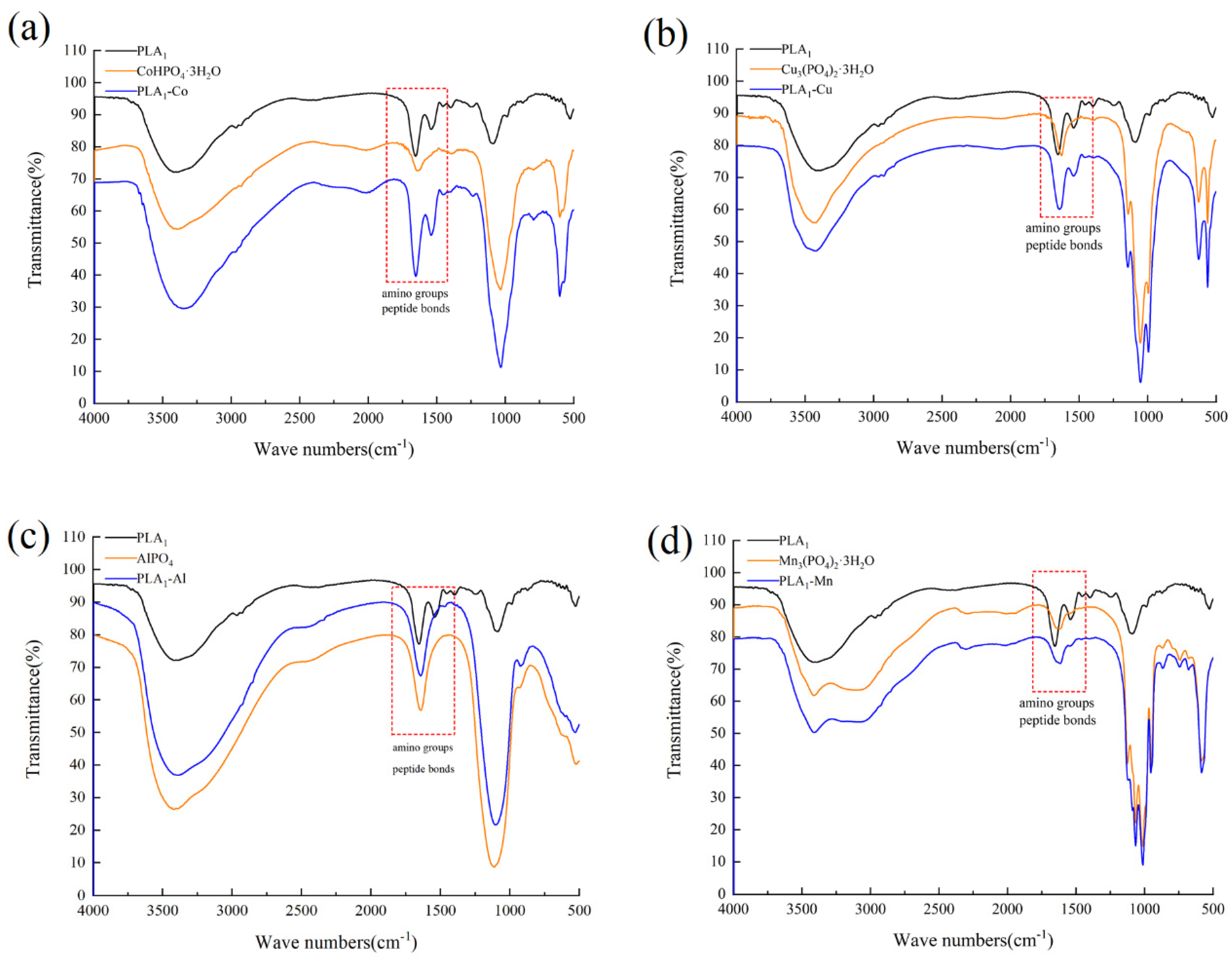
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
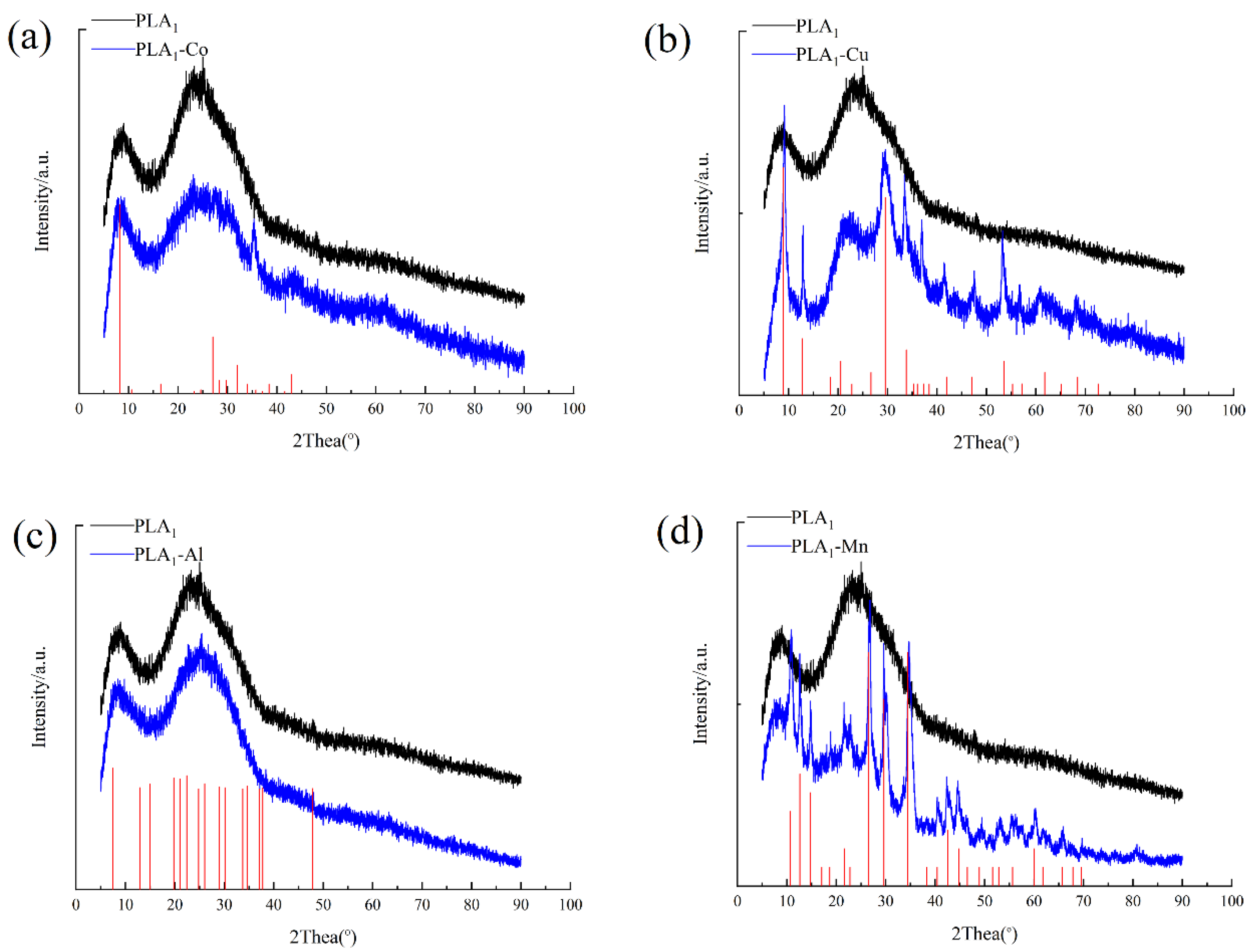
2.7. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.8. Enzymatic Properties of PLA1–Metal Hybrid Nanostructures
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of PLA1–Metal Hybrid Nanostructures
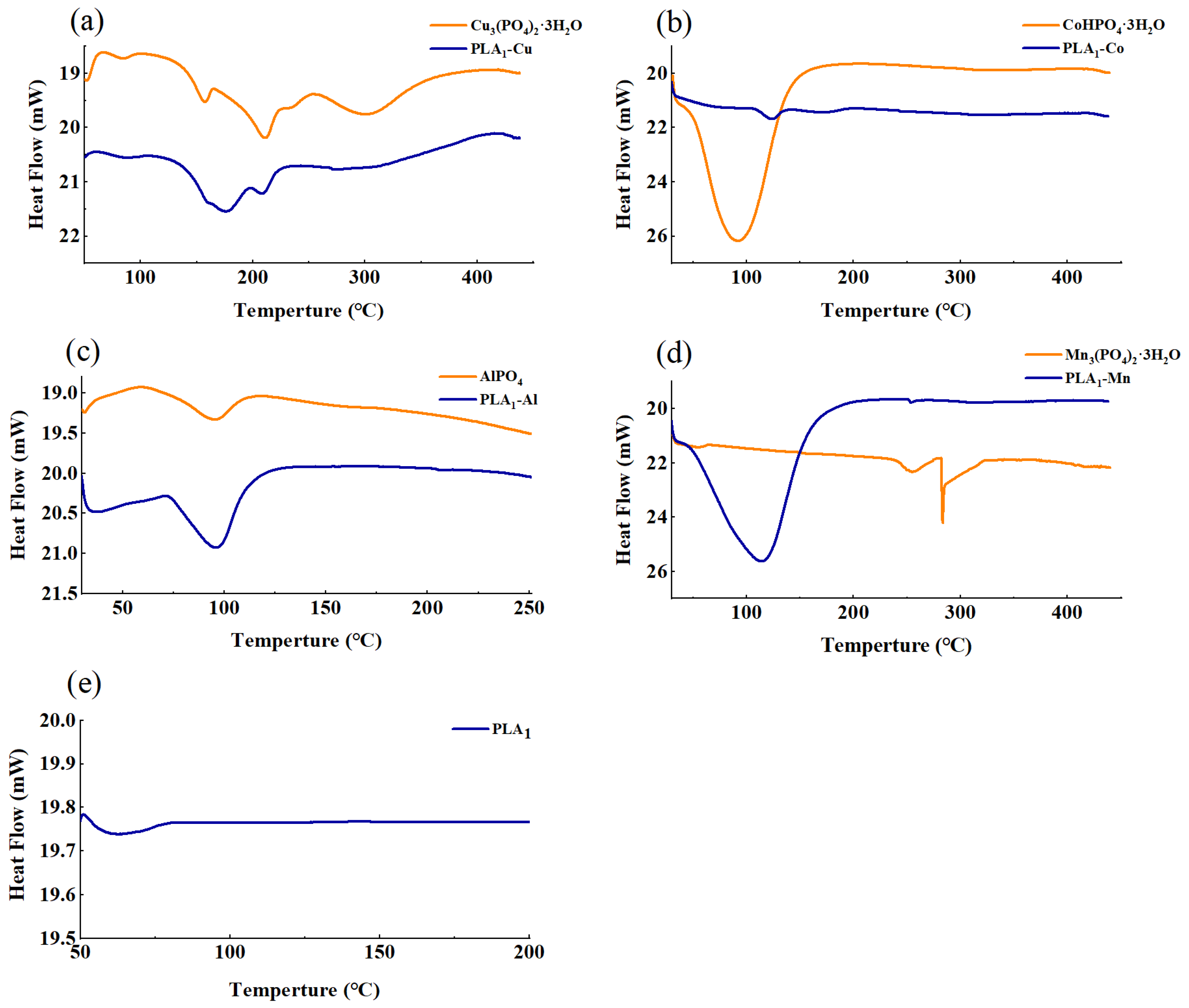
3.2. Characterization of Metal–PLA1 Hybrid Nanostructures
3.3. Analysis of the Properties of Immobilized Nanostructures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Virgen-Ortíz, J.J.; dos Santos, J.C.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Barbosa, O.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Lecitase ultra: A phospholipase with great potential in biocatalysis. Mol. Catal. 2019, 473, 110405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, A.M. Histamine release by bee venom phospholipase a and mellitin in the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 1965, 25, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Phospholipases A2: Unveiling the secrets of a functionally versatile group of snake venom toxins. Toxicon 2013, 62, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecucco, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Cellular pathology induced by snake venom phospholipase A2 myotoxins and neurotoxins: Common aspects of their mechanisms of action. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2897–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naglik, J.; Rodgers, C.A.; Shirlaw, P.J.; Dobbie, J.L.; Fernandes-Naglik, L.L.; Greenspan, D.; Agabian, N.; Challacombe, S. Differential Expression ofCandida albicansSecreted Aspartyl Proteinase and Phospholipase B Genes in Humans Correlates with Active Oral and Vaginal Infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Shi, G. Secretory expression of a phospholipase A2 from Lactobacillus casei DSM20011 in Kluyveromyces lactis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 120, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimuta, K.; Ohnishi, M.; Iyoda, S.; Gotoh, N.; Koizumi, N.; Watanabe, H. The hemolytic and cytolytic activities of Serratia marcescens phospholipase A (PhlA) depend on lysophospholipid production by PhlA. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimasa, M.; Shiobara, M. Purification and some properties of soluble phospholipase B from baker’s yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). Agric. Biol. Chem. 1985, 49, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoko-O, T.; Matsui, Y.; Yagisawa, H.; Nojima, H.; Uno, I.; Toh-E, A. The putative phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C gene, PLC1, of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is important for cell growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, K.W. Enzymatic Properties of an Extracellular Phospholipase C Purified from a Marine Streptomycete. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 2136–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohata, H.; Tanaka, K.-I.; Maeyama, N.; Ikeuchi, T.; Kamada, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Momose, K. Physiological and Pharmacological Role of Lysophosphatidic Acid as Modulator in Mechanotransduction. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 87, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sheelu, G.; Kavitha, G.; Fadnavis, N.W. Efficient Immobilization of Lecitase in Gelatin Hydrogel and Degumming of Rice Bran Oil Using a Spinning Basket Reactor. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2008, 85, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, M.R.; Park, C.S.; Auh, J.H.; Cho, B.M.; Yang, N.S.; Park, K.H. Phospholipid Hydrolysate and Antistaling Amylase Effects on Retrogradation of Starch in Bread. J. Food Sci. 1994, 59, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.H.; Høier, E. Environmental assessment of yield improvements obtained by the use of the enzyme phospholipase in mozzarella cheese production. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2008, 14, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Buxmann, W.; Bindrich, U.; Heinz, V.; Knorr, D.; Franke, K. Influencing emulsifying properties of egg yolk by enzymatic modification by phospholipase D from Streptomyces chromofuscus: Part 1: Technological properties of incubated egg yolk. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, M.; Kamata, M.; Koyama, T.; Yazawa, K. New Phospholipase A1-producing Bacteria from a Marine Fish. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, S.; Christena, R.; Rajaram, Y.R.S. Enzyme immobilization: An overview on techniques and support materials. 3 Biotech 2013, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, R.A. Enzyme Immobilization: The Quest for Optimum Performance. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 1289–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.R.C.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; Alcantara, A.R.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Enzyme-Coated Micro-Crystals: An Almost Forgotten but Very Simple and Elegant Immobilization Strategy. Catalysts 2020, 10, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Bhatt, K.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Chen, S. Esterase is a powerful tool for the biodegradation of pyrethroid insecticides. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.F.; Jiang, S.T.; Pan, L.J. Immobilization of phospholipase a1 using a polyvinyl alcohol-alginate matrix and evaluation of the effects of immobilization. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Ma, Y.; Xue, S.J.; Jiang, L.; Shi, J. Characterization of immobilized phospholipase A1 on magnetic nanoparticles for oil degumming application. LWT 2013, 50, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, J.-F.; Yang, B.; Li, D.-M.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, W.-F. Production of Structured Phosphatidylcholine with High Content of DHA/EPA by Immobilized Phospholipase A1-Catalyzed Transesterification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 15244–15258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Lei, J.; Zare, R.N. Protein–inorganic hybrid nanoflowers. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Domínguez, C.M.; Christ, S.; Niemeyer, C.M. Postsynthetic Functionalization of DNA-Nanocomposites withProteins Yields Bioinstructive Matrices for Cell Culture Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 19178–19182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cui, X.; Liu, N.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. Structural engineering of graphene for high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy. SmartMat 2021, 2, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batule, B.S.; Park, K.S.; Kim, M.I.; Park, H.G. Ultrafast sonochemical synthesis of proteininorganic nanoflowers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhong, C.; Jia, S. Surfactant-activated lipase hybrid nanoflowers with enhanced enzymatic performance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Tian, L.; Ali, N.; Ali, Z.; Zhang, Q. Preparation of lipase/Zn3(PO4)2 hybrid nanoflower and its catalytic performance as an immobilized enzyme. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 291, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.R.; Chung, M.; Kim, M.I.; Ha, S.H. Preparation of glutaraldehyde-treated lipase-inorganic hybrid nanoflowers and their catalytic performance as immobilized enzymes. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2017, 105, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, G. Using Laccases in the Nanoflower to Synthesize Viniferin. Catalysts 2017, 7, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Li, H.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lei, M.; Zhang, T.; Xiao, Y.; Chu, B.; Qian, Z. Uricase and Horseradish Peroxidase Hybrid CaHPO₄ Nanoflower Integrated with Transcutaneous Patches for Treatment of Hyperuricemia. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2019, 15, 951–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydemir, D.; Gecili, F.; Özdemir, N.; Ulusu, N.N. Synthesis and characterization of a triple enzyme-inorganic hybrid nanoflower (TrpE@ihNF) as a combination of three pancreatic digestive enzymes amylase, protease and lipase. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 129, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Cai, C.; Chen, G.; Ma, L. Nitroxide-Modified Protein-Incorporated Nanoflowers with Dual Enzyme-Like Activities. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Elfeky, N.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Bao, Y. Self-assembly of lipase hybrid nanoflowers with bifunctional Ca2+ for improved activity and stability. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2020, 132, 109408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Liang, C.; Geng, P.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, G. Affinity adsorption of phospholipase A1 with designed ligand binding to catalytic pocket. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1159, 122402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Fan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, L. Preparation and characterization of copper-Brevibacterium cholesterol oxidase hybrid nanoflowers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Gao, Q.; Gu, Y.; Hao, M.; Fan, G.; Zhang, L. Self-assembly of metal-cholesterol oxidase hybrid nanostructures and application in bioconversion of steroids derivatives. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Z.; Xin, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Gu, Z.; Zhong, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L. Preparation of efficient, stable, and reusable copper-phosphotriesterase hybrid nanoflowers for biodegradation of organophosphorus pesticides. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 146, 109766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altinkaynak, C.; Tavlasoglu, S.; Ÿzdemir, N.; Ocsoy, I. A new generation approach in enzyme immobilization: Organic-inorganic hybrid nanoflowers with enhanced catalytic activity and stability. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2016, 93-94, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudrant, J.; Woodley, J.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Parameters necessary to define an immobilized enzyme preparation. Process. Biochem. 2020, 90, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Bade, R.; Oh, S.; Shin, W.S. Immobilization of heavy metals in a contaminated soil using organic sludge char and other binders. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 29, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colina, F.G.; Abellan, M.N.; Caballero, I. High-temperature reaction of kaolin with ammonium sulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Patel, S.K.S.; Mardan, B.; Pagolu, R.; Lestari, R.; Jeong, S.-H.; Kim, T.; Haw, J.R.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, I.-W.; et al. Immobilization of Xylanase Using a Protein-Inorganic Hybrid System. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| EC (mg/mL) | Co2+ (mM) | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EY % | SEA (U/mg) | EY % | SEA (U/mg) | EY % | SEA (U/mg) | ||
| 0.05 | 1 | 84 ± 1 | 6.84 ± 0.05 | 100 ± 3 | 4.41 ± 0.08 | 100 ± 9 | 4.80 ± 0.07 |
| 0.10 | 1 | 46 ± 6 | 3.05 ± 0.04 | 99 ± 4 | 4.99 ± 0.01 | 83 ± 7 | 4.50 ± 0.04 |
| 0.15 | 1 | 24 ± 5 | 7.47 ± 0.15 | 82 ± 5 | 3.98 ± 0.06 | 88 ± 8 | 3.88 ± 0.02 |
| 0.05 | 2 | 100 ± 1 | 1.58 ± 0.12 | 100 ± 7 | 1.32 ± 0.01 | 99 ± 5 | 2.24 ± 0.03 |
| 0.10 | 2 | 89 ± 7 | 4.72 ± 0.36 | 100 ± 1 | 0.79 ± 0.01 | 28 ± 16 | 2.19 ± 0.04 |
| 0.15 | 2 | 68 ± 3 | 6.30 ± 0.25 | 92 ± 7 | 1.05 ± 0.01 | 74 ± 10 | 1.63 ± 0.05 |
| 0.05 | 3 | 100 ± 2 | 0.53 ± 0.01 | 100 ± 2 | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 82 ± 9 | 1.49 ± 0.01 |
| 0.10 | 3 | 85 ± 2 | 2.60 ± 0.06 | 100 ± 1 | 0.45 ± 0.01 | 78 ± 1 | 4.07 ± 0.07 |
| 0.15 | 3 | 73 ± 1 | 1.08 ± 0.01 | 98 ± 11 | 0.37 ± 0.04 | 38 ± 1 | 1.65 ± 0.02 |
| EC (mg/mL) | Cu2+ (mM) | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EY % | SEA (U/mg) | EY % | SEA (U/mg) | EY % | SEA (U/mg) | ||
| 0.05 | 1 | 100 ± 6 | 1.80 ± 0.08 | 100 ± 1 | 0.93 ± 0.01 | 100 ± 2 | 0.88 ± 0.02 |
| 0.1 | 1 | 98 ± 2 | 1.33 ± 0.03 | 99 ± 1 | 1.05 ± 0.01 | 74 ± 4 | 0.72 ± 0.03 |
| 0.15 | 1 | 62 ± 7 | 1.55 ± 0.17 | 68 ± 8 | 1.34 ± 0.15 | 55 ± 1 | 0.85 ± 0.02 |
| 0.05 | 2 | 100 ± 1 | 1.14 ± 0.01 | 100 ± 6 | 1.42 ± 0.03 | 100 ± 1 | 0.86 ± 0.01 |
| 0.1 | 2 | 91 ± 4 | 1.44 ± 0.06 | 100 ± 0 | 0.65 ± 0.04 | 78 ± 1 | 1.19 ± 0.01 |
| 0.15 | 2 | 67 ± 1 | 1.26 ± 0.02 | 80 ± 9 | 0.69 ± 0.08 | 76 ± 10 | 0.70 ± 0.09 |
| 0.05 | 3 | 100 ± 4 | 0.80 ± 0.02 | 100 ± 3 | 0.57 ± 0.01 | 100 ± 1 | 0.46 ± 0.01 |
| 0.1 | 3 | 99 ± 1 | 0.78 ± 0.01 | 100 ± 1 | 0.52 ± 0.01 | 90 ± 4 | 0.30 ± 0.01 |
| 0.15 | 3 | 86 ± 1 | 0.95 ± 0.01 | 83 ± 2 | 0.58 ± 0.02 | 72 ± 3 | 0.38 ± 0.01 |
| 0.05 | 5 | 90 ± 10 | 0.58 ± 0.04 | 100 ± 1 | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 100 ± 1 | 0.58 ± 0.01 |
| 0.1 | 5 | 51 ± 1 | 0.69 ± 0.08 | 46 ± 4 | 0.59 ± 0.06 | 48 ± 6 | 1.34 ± 0.02 |
| 0.15 | 5 | 44 ± 1 | 0.89 ± 0.01 | 47 ± 1 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 49 ± 2 | 2.27 ± 0.03 |
| 0.05 | 7 | 100 ± 1 | 2.48 ± 0.07 | 100 ± 1 | 2.24 ± 0.01 | 100 ± 1 | 1.22 ± 0.05 |
| 0.1 | 7 | 46 ± 1 | 1.51 ± 0.05 | 81 ± 6 | 2.31 ± 0.05 | 81 ± 4 | 1.63 ± 0.03 |
| 0.15 | 7 | 32 ± 1 | 1.37 ± 0.04 | 34 ± 1 | 1.26 ± 0.01 | 69 ± 1 | 2.59 ± 0.07 |
| 0.05 | 9 | 100 ± 1 | 2.47 ± 0.07 | 100 ± 1 | 1.88 ± 0.01 | 100 ± 1 | 0.74 ± 0.07 |
| 0.1 | 9 | 57 ± 3 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 81 ± 5 | 2.36 ± 0.01 | 81 ± 1 | 2.15 ± 0.04 |
| 0.15 | 9 | 51 ± 1 | 2.15 ± 0.01 | 42 ± 2 | 2.31 ± 0.03 | 46 ± 1 | 2.23 ± 0.02 |
| EC (mg/mL) | Mn2+ (mM) | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EY % | SEA (U/mg) | EY % | SEA (U/mg) | EY % | SEA (U/mg) | ||
| 0.05 | 1 | 92 ± 7 | 0.64 ± 0.05 | 100 ± 15 | 0.57 ± 0.07 | 92 ± 5 | 0.48 ± 0.03 |
| 0.1 | 1 | 43 ± 10 | 1.11 ± 0.02 | 57 ± 1 | 0.77 ± 0.01 | 30 ± 4 | 1.09 ± 0.14 |
| 0.15 | 1 | 29 ± 1 | 1.48 ± 0.07 | 29 ± 5 | 0.96 ± 0.08 | 18 ± 2 | 1.60 ± 0.20 |
| 0.05 | 2 | 74 ± 1 | 1.17 ± 0.02 | 100 ± 18 | 0.76 ± 0.05 | 72 ± 5 | 1.23 ± 0.08 |
| 0.1 | 2 | 27 ± 1 | 2.04 ± 0.07 | 45 ± 3 | 0.80 ± 0.05 | 38 ± 1 | 1.30 ± 0.03 |
| 0.15 | 2 | 15 ± 1 | 2.22 ± 0.02 | 29 ± 2 | 0.97 ± 0.05 | 24 ± 1 | 1.56 ± 0.07 |
| 0.05 | 3 | 62 ± 10 | 3.00 ± 0.02 | 100 ± 2 | 0.66 ± 0.01 | 63 ± 4 | 0.85 ± 0.05 |
| 0.1 | 3 | 28 ± 1 | 1.43 ± 0.03 | 48 ± 3 | 0.69 ± 0.05 | 32 ± 5 | 0.90 ± 0.14 |
| 0.15 | 3 | 8 ± 2 | 5.58 ± 0.04 | 32 ± 1 | 0.83 ± 0.02 | 17 ± 0 | 1.13 ± 0.01 |
| EC (mg/mL) | Al3+ (mM) | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EY % | SEA (U/mg) | EY % | SEA (U/mg) | EY % | SEA (U/mg) | ||
| 0.05 | 1 | 89 ± 7 | 0.61 ± 0.04 | 100 ± 21 | 0.38 ± 0.03 | 95 ± 2 | 0.50 ± 0.01 |
| 0.10 | 1 | 20 ± 3 | 1.01 ± 0.13 | 42 ± 6 | 0.67 ± 0.03 | 97 ± 6 | 0.37 ± 0.04 |
| 0.15 | 1 | 12 ± 1 | 1.16 ± 0.09 | 49 ± 24 | 0.90 ± 0.07 | 27 ± 3 | 0.94 ± 0.12 |
| 0.05 | 2 | 71 ± 2 | 1.20 ± 0.03 | 99 ± 16 | 0.45 ± 0.01 | 82 ± 1 | 0.79 ± 0.01 |
| 0.10 | 2 | 28 ± 3 | 1.19 ± 0.14 | 53 ± 4 | 0.40 ± 0.08 | 66 ± 1 | 0.61 ± 0.01 |
| 0.15 | 2 | 13 ± 1 | 1.95 ± 0.10 | 52 ± 12 | 0.35 ± 0.04 | 53 ± 1 | 0.64 ± 0.01 |
| 0.05 | 3 | 46 ± 5 | 1.36 ± 0.15 | 83 ± 10 | 0.54 ± 0.05 | 74 ± 1 | 0.55 ± 0.01 |
| 0.10 | 3 | 17 ± 0 | 1.80 ± 0.02 | 40 ± 4 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 28 ± 1 | 0.88 ± 0.01 |
| 0.15 | 3 | 3 ± 3 | 1.17 ± 0.02 | 21 ± 7 | 0.84 ± 0.04 | 25 ± 1 | 1.07 ± 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, S.; Guo, Z.; Liang, C.; Shi, Y.; Geng, P.; Xin, Y.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, L. Immobilization of Phospholipase A1 Using a Protein-Inorganic Hybrid System. Polymers 2021, 13, 2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172865
Cheng S, Guo Z, Liang C, Shi Y, Geng P, Xin Y, Gu Z, Zhang L. Immobilization of Phospholipase A1 Using a Protein-Inorganic Hybrid System. Polymers. 2021; 13(17):2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172865
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Shi, Zitao Guo, Chaojuan Liang, Yi Shi, Peng Geng, Yu Xin, Zhenghua Gu, and Liang Zhang. 2021. "Immobilization of Phospholipase A1 Using a Protein-Inorganic Hybrid System" Polymers 13, no. 17: 2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172865
APA StyleCheng, S., Guo, Z., Liang, C., Shi, Y., Geng, P., Xin, Y., Gu, Z., & Zhang, L. (2021). Immobilization of Phospholipase A1 Using a Protein-Inorganic Hybrid System. Polymers, 13(17), 2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13172865








