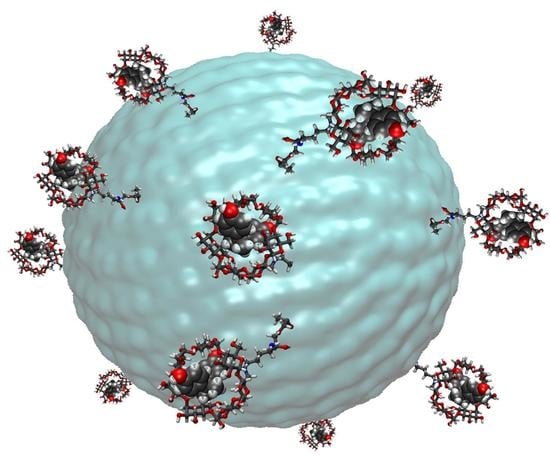
Novel Chemical Architectures Based on Beta-Cyclodextrin Derivatives Covalently Attached on Polymer Spheres
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. ST-HEMA Emulsion Polymerization
2.2.2. Seeded Emulsion Polymerization of GMA (ST-HEMA-GMA)
2.2.3. Synthesis of Diamino Butane Monosubstituted BCD (BCD-NH2)
2.2.4. The Reaction of BCD-OH with ST-HEMA-GMA
2.2.5. The Reaction of BCD-NH2 with ST-HEMA-GMA
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohore, O.E.; Zhang, S. Endocrine disrupting effects of bisphenol A exposure and recent advances on its removal by water treatment systems. A review. Sci. Afr. 2019, 5, e00135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolong, N.; Ismail, A.F.; Salim, M.R.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Tabe-Mohammadi, A. Negatively charged polyethersulfone hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane for the removal of bisphenol A from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 73, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, G.; Jiang, R.; Yan, Z.; Li, Y. Occurrence, toxicity and ecological risk of Bisphenol A analogues in aquatic environment—A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyżga, B.; Połeć, K.; Olechowska, K.; Hąc-Wydro, K. The impact of toxic bisphenols on model human erythrocyte membranes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 186, 110670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ding, T.; Luo, X.; Li, J. Toxic effect of fluorene-9-bisphenol to green algae Chlorella vulgaris and its metabolic fate. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.-p.; Liu, Z.-h.; Yuan, S.-f.; Yin, H.; Dang, Z.; Wu, P.-x. Worldwide human daily intakes of bisphenol A (BPA) estimated from global urinary concentration data (2000–2016) and its risk analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Chadha, P. Bisphenol A induced toxicity in blood cells of freshwater fish Channa punctatus after acute exposure. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdarta, J.; Staszak, M.; Jankowska, K.; Kaźmierczak, K.; Degórska, O.; Nguyen, L.N.; Kijeńska-Gawrońska, E.; Pinelo, M.; Jesionowski, T. The response surface methodology for optimization of tyrosinase immobilization onto electrospun polycaprolactone–chitosan fibers for use in bisphenol A removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y. Continuous removal of trace bisphenol A from water by high efficacy TiO2 nanotube pillared graphene-based macrostructures in a photocatalytically fluidized bed. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, P.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Zhu, N. Efficient removal of bisphenol A by superoxide radical and singlet oxygen generated from peroxymonosulfate activated with Fe0-montmorillonite. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhuang, X.; Ahmad, S.; Lee, T.; Si, H.; Cao, C.; Ni, S.-Q. Sulfate radicals based heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate system catalyzed by CuO-Fe3O4-Biochar nanocomposite for bisphenol A degradation. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahari, A.M.; Shuo, C.W.; Sathishkumar, P.; Yusoff, A.R.M.; Gu, F.L.; Buang, N.A.; Lau, W.-J.; Gohari, R.J.; Yusop, Z. A reusable electrospun PVDF-PVP-MnO2 nanocomposite membrane for bisphenol A removal from drinking water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5801–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseri, S.; Ebrahimi, S.; Abtahi, M.; Saeedi, R. Synthesis and characterization of polysulfone/graphene oxide nano-composite membranes for removal of bisphenol A from water. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 205, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Ye, L.; Xi, J.; Wang, J.; Feng, Z.-g. Cyclodextrin polymers: Structure, synthesis, and use as drug carriers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 118, 101408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; He, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.; Sang, S.; Huang, X. Cyclodextrin derivatives used for the separation of boron and the removal of organic pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaálová, J.; Michel, M.; Bourassi, M.; Ladewig, B.P.; Kasal, P.; Jindřich, J.; Izák, P. Nafion membranes modified by cationic cyclodextrin derivatives for enantioselective separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 266, 118538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omtvedt, L.A.; Dalheim, M.Ø.; Nielsen, T.T.; Larsen, K.L.; Strand, B.L.; Aachmann, F.L. Efficient Grafting of Cyclodextrin to Alginate and Performance of the Hydrogel for Release of Model Drug. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jicsinszky, L.; Martina, K.; Cravotto, G. Cyclodextrins in the antiviral therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morillo, E.; Madrid, F.; Lara-Moreno, A.; Villaverde, J. Soil bioremediation by cyclodextrins. A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 591, 119943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, L.; Liang, W.; Yang, J.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C. Effective adsorption of phenolic pollutants from water using β-cyclodextrin polymer functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 80955–80963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpatani, F.M.; Aryee, A.A.; Kani, A.N.; Guo, Q.; Dovi, E.; Qu, L.; Li, Z.; Han, R. Uptake of micropollutant-bisphenol A, methylene blue and neutral red onto a novel bagasse-β-cyclodextrin polymer by adsorption process. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cheng, G.; Chen, K.; Lu, J.; Lei, J.; Pu, S. Adsorptive removal of bisphenol A, chloroxylenol, and carbamazepine from water using a novel β-cyclodextrin polymer. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Fu, L.; Li, A. Enhanced adsorption of bisphenol A from water by acetylaniline modified hyper-cross-linked polymeric adsorbent: Effect of the cross-linked bridge. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 191, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, M.; Jia, J.; Ma, J.; Jia, Q. Design of a hyper-crosslinked β-cyclodextrin porous polymer for highly efficient removal toward bisphenol a from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 195, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.; Wen, H.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Liu, C. Fabrication of SiO2 modified biobased hydrolyzed hollow polymer particles and their applications as a removal of methyl orange dye and bisphenol-A. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 144, 110199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, S.; Zhang, B.; Fang, J.; Zhu, L. Interfacially crosslinked β-cyclodextrin polymer composite porous membranes for fast removal of organic micropollutants from water by flow-through adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Niu, D.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z. Citric acid-crosslinked β-cyclodextrin for simultaneous removal of bisphenol A, methylene blue and copper: The roles of cavity and surface functional groups. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 82, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenyvesi, É.; Barkács, K.; Gruiz, K.; Varga, E.; Kenyeres, I.; Záray, G.; Szente, L. Removal of hazardous micropollutants from treated wastewater using cyclodextrin bead polymer—A pilot demonstration case. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizro, N.; Moniri, E.; Saeb, K.; Panahi, H.A.; Ardakani, S.S. Preparation and application of grafted β-cyclodextrin/thermo-sensitive polymer onto modified Fe3O4@SiO2 nano-particles for fenitrothion elimination from aqueous solution. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, B.; Lynam, N.; O’Sullivan, T.; Ahern, C.; Darcy, R. β-Cyclodextrin-6 A-(4-methylbenzenesulfonate). Org. Synth. 2000, 77, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusen, E.; Mocanu, A.; Marculescu, B.; Somoghi, R.; Butac, L.; Miculescu, F.; Cotrut, C.; Antoniac, I.; Cincu, C. Obtaining complex structures starting from monodisperse poly(styrene-co-2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) spheres. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 375, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusen, E.; Mocanu, A.; Marculescu, B. Obtaining of monodisperse particles through soap-free and seeded polymerization, respectively, through polymerization in the presence of C60. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2010, 288, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhakov, A.; Do Thi, T.; Stappaerts, J.; Bertoletti, L.; Kimpe, K.; Sá Couto, A.R.; Saokham, P.; Van den Mooter, G.; Augustijns, P.; Somsen, G.W.; et al. Self-Assembly of Cyclodextrins and Their Complexes in Aqueous Solutions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2556–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, S.M.N.; Rey-Rico, A.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Supramolecular cyclodextrin-based drug nanocarriers. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6275–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L.; Juang, R.-S. Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, Y.; Du, J.; Huang, M. Recent advances in adsorbents for the removal of phthalate esters from water: Material, modification, and application. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Hatton, T.A.; Chung, T.-S. Effects of spacer arm length and benzoation on enantioseparation performance of β-cyclodextrin functionalized cellulose membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 339, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Agarwal, S.; Sadegh, H.; Ali, G.A.M.; Bharti, A.K.; Hamdy Makhlouf, A.S. Facile route synthesis of novel graphene oxide-β-cyclodextrin nanocomposite and its application as adsorbent for removal of toxic bisphenol A from the aqueous phase. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 237, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Lin, F.; Liu, X.; Lu, B. Removal of bisphenol A from aqueous solution via host-guest interactions based on beta-cyclodextrin grafted cellulose bead. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaoka, M.; Hayashi, K. Adsorption of Bisphenol A by Cross-Linked β-Cyclodextrin Polymer. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2002, 44, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kwak, S.-Y. Rapid adsorption of bisphenol A from wastewater by β-cyclodextrin-functionalized mesoporous magnetic clusters. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467–468, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, L.; Guo, J.; Ye, Q.; Lin, J.-M.; Yuan, J. Adsorption of environmental pollutants using magnetic hybrid nanoparticles modified with β-cyclodextrin. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Lv, J.; Liu, Q.; Nan, F.; Liu, X.; Xie, S.; Feng, J. Diatomite cross-linked β-Cyclodextrin polymers: A novel vision of diatomite adsorbent for the removal of bisphenol A. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Ahmad, I.; Zheng, Y. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of “Bisphenol A”. J. Spectrosc. 2016, 2016, 2073613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Lagergren’s Pseudo-First-Order | Ho’s Pseudo-Second-Order Model | Weber’s Intraparticles Diffusion Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe, exp (mg g−1) | k1 × 103 (min−1) | Qe (mg g−1) | R2 | k2 × 103 (g mg−1 min−1) | Qe (mg g−1) | R2 | Kp (mg g−1 min−0.5) | R2 |
| 12.57 | 4.7 | 12.36 | 0.933 | 2.1 | 8.79 | 0.9054 | 0.50873 | 0.9882 |
| Absorbent | Adsorbate | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL/ (L mg)−1 | Qmax/ (mg g−1) | R2 | KF/ (L mg−1) | n | R2 | ||
| ST-HEMA-GMA-BCD-NH2 | Bisphenol A | 0.0025 | 148.37 | 0.9431 | 0.6183 | 2.268 | 0.9244 |
| ST-HEMA-GMA-BCD-OH | Bisphenol A | 0.0195 | 37.09 | 0.9505 | 1.9179 | 1.7478 | 0.9376 |
| Adsorbent | Phenolic Pollutants | Qmax (mg g−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hyper-crosslinked β-CD porous polymer | Bisphenol A | 278 | [24] |
| Graphene oxide-β-CD nanocomposites | Bisphenol A | 373.4 | [39] |
| BCD polymer functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles | Bisphenol A | 74.63 | [20] |
| BCD grafted cellulose beads | Bisphenol A | 30.77 | [40] |
| (BCD+epichlorohydrin) polyBCD | Bisphenol A | 84 | [41] |
| BCD-Functionalized Mesoporous Magnetic Clusters | Bisphenol A | 52.7 | [42] |
| BCD-poly(glycidyl methacrylate)-SiO2- nanoparticles | Bisphenol A | 22.48 | [43] |
| Diatomite cross-linked BCD polymers | Bisphenol A | 83.57 | [44] |
| ST-HEMA-GMA-BCD-NH2 | Bisphenol A | 148.37 | This study |
| ST-HEMA-GMA-BCD-OH | Bisphenol A | 37.09 | This study |
| Sample | T10%, [°C] | Tmax, [°C] |
|---|---|---|
| ST-HEMA | 283 | 283; 355; 373 |
| ST-HEMA-GMA | 244 | 257; 409 |
| BCD-NH2 | 172 | 310 |
| BCD-OH | 306 | 318 |
| ST-HEMA-GMA-BCD-OH | 303 | 313; 425 |
| ST-HEMA-GMA-BCD-NH2 | 291 | 299; 424 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bucur, S.; Mangalagiu, I.; Diacon, A.; Mocanu, A.; Rizea, F.; Somoghi, R.; Ghebaur, A.; Boscornea, A.C.; Rusen, E. Novel Chemical Architectures Based on Beta-Cyclodextrin Derivatives Covalently Attached on Polymer Spheres. Polymers 2021, 13, 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142338
Bucur S, Mangalagiu I, Diacon A, Mocanu A, Rizea F, Somoghi R, Ghebaur A, Boscornea AC, Rusen E. Novel Chemical Architectures Based on Beta-Cyclodextrin Derivatives Covalently Attached on Polymer Spheres. Polymers. 2021; 13(14):2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142338
Chicago/Turabian StyleBucur, Stefan, Ionel Mangalagiu, Aurel Diacon, Alexandra Mocanu, Florica Rizea, Raluca Somoghi, Adi Ghebaur, Aurelian Cristian Boscornea, and Edina Rusen. 2021. "Novel Chemical Architectures Based on Beta-Cyclodextrin Derivatives Covalently Attached on Polymer Spheres" Polymers 13, no. 14: 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142338
APA StyleBucur, S., Mangalagiu, I., Diacon, A., Mocanu, A., Rizea, F., Somoghi, R., Ghebaur, A., Boscornea, A. C., & Rusen, E. (2021). Novel Chemical Architectures Based on Beta-Cyclodextrin Derivatives Covalently Attached on Polymer Spheres. Polymers, 13(14), 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142338