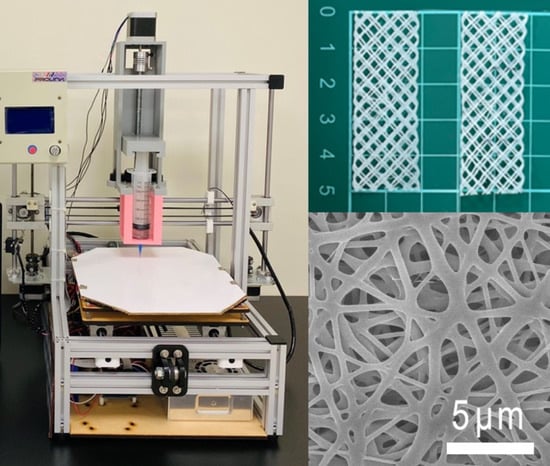
Fabrication of Drug-Eluting Polycaprolactone/poly(lactic-co-glycolic Acid) Prolapse Mats Using Solution-Extrusion 3D Printing and Coaxial Electrospinning Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. 3D-Printed Degradable Meshes
2.2. Drug/Biomolecule-Loaded Sheath-Core-Structured Nanofibrous Membranes
2.3. Mechanical Properties
2.4. Molecular Weight Variations
2.5. Fatigue Test
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Assessment
2.7. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Observation
2.8. Confocal Microscopy
2.9. Contact Angle of Water
2.10. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.11. In Vitro Release of Drugs/Growth Factors
2.12. In Vivo Animal Test
3. Results
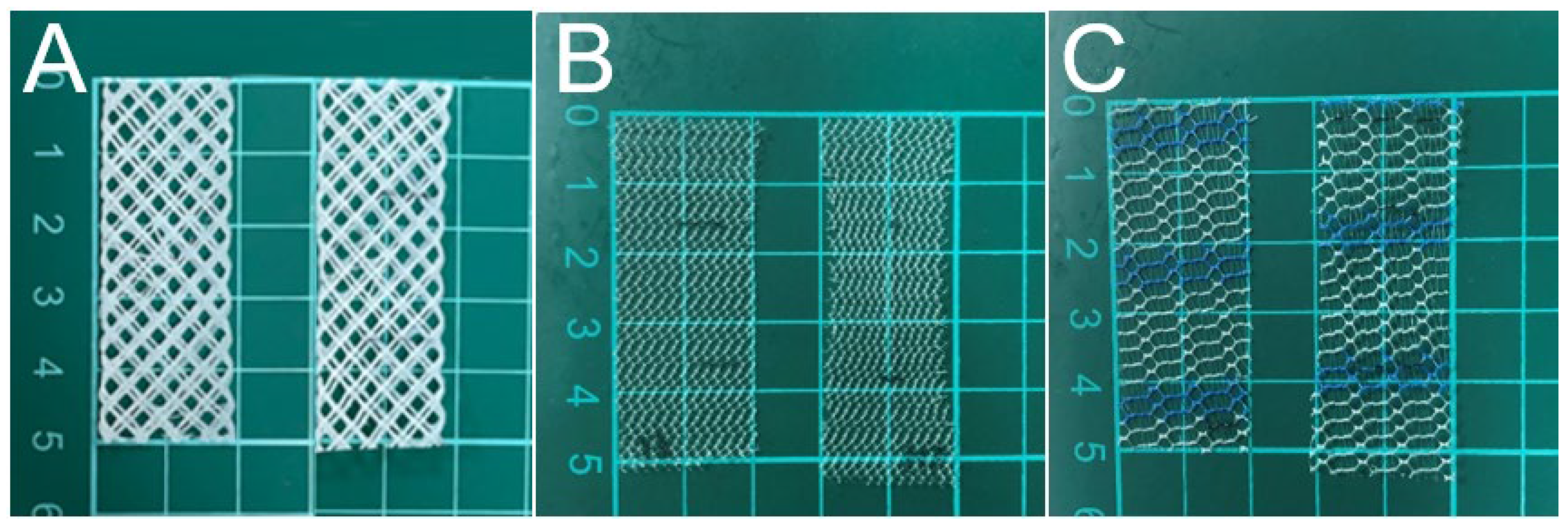
3.1. Tensile Properties of Printed PCL Mesh
3.2. Characterization of Electrospun Nanofibers
3.3. In Vitro Elution
3.4. In Vivo Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bureau, M.; Carlson, K.V. Pelvic organ prolapse: A primer for urologists. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2017, 11, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganj, F.A.; Ibeanu, O.A.; Bedestani, A.; Nolan, T.E.; Chesson, R.R. Complications of transvaginal monofilament polypropylene mesh in pelvic organ prolapse repair. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2009, 20, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubé, M.; Tu, L.M. Current trends and future perspectives in pelvic reconstructive surgery. Women Health 2018, 14, 1745506518776498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domínguez-Robles, J.; Mancinelli, C.; Mancuso, E.; García-Romero, I.; Gilmore, B.F.; Casettari, L.; Larrañeta, E.; Lamprou, D.A. 3D Printing of Drug-Loaded Thermoplastic Polyurethane Meshes: A Potential Material for Soft Tissue Reinforcement in Vaginal Surgery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dällenbach, P. To mesh or not to mesh: A review of pelvic organ reconstructive surgery. Int. J. Women Health 2015, 7, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shek, K.L.; Dietz, H.P. Assessment of pelvic organ prolapse: A review. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 48, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.-M.; Lee, D.; Yang, J.-W.; Lin, S.-H.; Lin, Y.-T.; Liu, S.-J. Solution Extrusion Additive Manufacturing of Biodegradable Polycaprolactone. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Ang, B.C.; Andriyana, A.; Afifi, A.M. A review on fabrication of nanofibers via electrospinning and their applications. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.-K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghilan, A.; Chiriac, A.P.; Nita, L.E.; Rusu, A.G.; Neamtu, I.; Chiriac, V.M. Trends in 3D Printing Processes for Biomedical Field: Opportunities and Challenges. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 1345–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Steckl, A.J. Coaxial Electrospinning Formation of Complex Polymer Fibers and their Applications. ChemPlusChem 2019, 84, 1453–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, R.; Kumar, S.; Pandey, R.; Mahajan, A.; Nandana, D.; Katti, D.S.; Mehrotra, D. Polycaprolactone as biomaterial for bone scaffolds: Review of literature. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2020, 10, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, D.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic) Acid-Controlled-Release Systems: Experimental and Modeling Insights. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2013, 30, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beecham, G.B.; Bansal, P.; Nessel, T.A. Lidocaine. [Updated 2021 Jan 26]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539881/ (accessed on 29 May 2021).
- Bodner-Adler, B.; Alarab, M.; Ruiz-Zapata, A.M.; Latthe, P. Effectiveness of hormones in postmenopausal pelvic floor dysfunction—International Urogynecological Association research and development—Committee opinion. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2020, 31, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robbie, M.O.; Sweet, R.L. Metronidazole use in obstetrics and gynecology: A review. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1983, 145, 865–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Liu, K.-S.; Cheng, C.-W.; Chan, E.-C.; Hung, K.-C.; Hsieh, M.-J.; Chang, S.-H.; Fu, X.; Juang, J.-H.; Hsieh, I.-C.; et al. Codelivery of Sustainable Antimicrobial Agents and Platelet-Derived Growth Factor via Biodegradable Nanofibers for Repair of Diabetic Infectious Wounds. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 2688–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabry, S.M.; Abdel-Hay, M.H.; Belal, T.S.; Mahgoub, A.A. Development and validation of HPLC-DAD method for the simultaneous determination of amoxicillin, metronidazole and rabeprazole sodium. Application to spiked simulated intestinal fluid samples. Ann. Pharm. Françaises 2015, 73, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekota, M.W.; Mpupa, A.; Dimpe, K.M.; Nomngongo, P.N. Preparation of ferric oxide-aluminum oxide carbon nanofiber nanocomposites for ultrasound-assisted dispersive magnetic solid phase extraction of 17-beta estradiol in wastewater. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.-W.; Tseng, Y.-Y.; Liu, K.-S.; Liu, Y.-W.; Chen, J.-C.; He, H.-L.; Kau, Y.-C.; Liu, S.-J. Anesthetics and human epidermal growth factor incorporated into anti-adhesive nanofibers provide sustained pain relief and promote healing of surgical wounds. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4007–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majumder, A.; Gupta, A.K. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of 17β-estradiol by polythiophene modified Al-doped ZnO: Optimization of synthesis parameters using multivariate optimization techniques. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holešová, S.; Hundáková, M.; Tarasiuk, Y.; Barabaszová, K.Č.; Pazdziora, E. Metronidazole/clay nanocomposites: Synthesis, structure and antibacterial efficacy. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Yu, S.; Li, X.; Ma, C.; Li, A. Evaluation of local anesthetic effects of Lidocaine-Ibuprofen ionic liquid stabilized silver nanoparticles in Male Swiss mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 178, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; He, Y.; Zong, X.; Bai, H.; Liu, Z. Antimicrobial susceptibility sesting of metronidazole and clindamycin against Gardnerella vaginalis in planktonic and biofilm formation. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 1361825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.; Babla, H.; Han, T.; Das, D.B. Lidocaine carboxymethylcellulose with gelatine co-polymer hydrogel delivery by combined microneedle and ultrasound. Drug Deliv. 2014, 23, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andersson, T.L.G.; Stehle, B.; Davidsson, B.; Höglund, P. Drug concentration effect relationship of estradiol from two matrix transdermal delivery systems: Menorest and Climara. Maturitas 2000, 35, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, T.S.; Pue, L.B.; Tan, Y.L.; Wu, P.Y. Long term outcomes of transobturator synthetic nonabsorbable anterior mesh versus anterior colporraphy in symptomatic advanced pelvic organ prolapse surgery. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2014, 25, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, T.S.; Tan, Y.L.; Pue, J.B.; Cortes, E.F.M.; Wu, P.Y.; Pue, L.B.; Al-Kharabsheh, A. Clinical outcomes of mesh exposure/extrusion: Presentation, timing and management. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2015, 55, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynkevic, R.; Martins, P.; Fernandes, A.; Vange, J.; Gallego, M.R.; Wach, R.A.; Mes, T.; Bosman, A.W.; Deprest, J. In vitro simulation of in vivo degradation and cyclic loading of novel degradable electrospun meshes for prolapse repair. Polym. Test 2019, 78, 105957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Darzi, S.; Rosamilia, A.; Kadam, V.; Truong, Y.; Werkmeister, J.A.; Gargett, C.E. Blended Nanostructured Degradable Mesh with Endometrial Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes Tissue Integration and Anti-Inflammatory Response in Vivo for Pelvic Floor Application. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Caetano, G.; Ambler, W.S.; Blaker, J.J.; Frade, M.A.; Mandal, P.; Diver, C.; Bártolo, P. Enhancing the Hydrophilicity and Cell Attachment of 3D Printed PCL/Graphene Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials 2016, 9, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.-W.; Lee, D.; Wu, M.-H.; Chen, J.-K.; He, H.-L.; Liu, S.-J. Lidocaine/ketorolac-loaded biodegradable nanofibrous anti-adhesive membranes that offer sustained pain relief for surgical wounds. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5893–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Carlo, C.; Tommaselli, G.A.; Gargano, V.; Savoia, F.; Bifulco, G.; Nappi, C. Transdermal estradiol and oral or vaginal natural progesterone: Bleeding patterns. Climacteric 2010, 13, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuğcu-Demiröz, F.; Saar, S.; Tort, S.; Acartürk, F. Electrospun metronidazole-loaded nanofibers for vaginal drug delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srithep, Y.; Akkaprasa, T.; Pholharn, D.; Morris, J.; Liu, S.-J.; Patrojanasophon, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T. Metronidazole-loaded polylactide stereocomplex electrospun nanofiber mats for treatment of periodontal disease. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrib, J.; Sirc, J.; Hobzova, R.; Hampejsova, Z.; Bosakova, Z.; Munzarova, M.; Michálek, J. Nanofibers for drug delivery—Incorporation and release of model molecules, influence of molecular weight and polymer structure. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patrojanasophon, P.; Tidjarat, S.; Opanasopit, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Rojanarata, T. Influence of nanofiber alignment on the release of a water-soluble drug from cellulose acetate nanofibers. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Week | Mn | Mw | Mz | Mz + 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 73,430 | 87,747 | 120,764 | 196,001 |
| 2 | 70,694 | 83,577 | 113,851 | 184,945 |
| 4 | 65,064 | 73,174 | 87,902 | 117,305 |
| 8 | 64,851 | 72,824 | 86,631 | 113,841 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-P.; Lo, T.-S.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chien, Y.-H.; Lu, C.-J.; Liu, S.-J. Fabrication of Drug-Eluting Polycaprolactone/poly(lactic-co-glycolic Acid) Prolapse Mats Using Solution-Extrusion 3D Printing and Coaxial Electrospinning Techniques. Polymers 2021, 13, 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142295
Chen Y-P, Lo T-S, Lin Y-T, Chien Y-H, Lu C-J, Liu S-J. Fabrication of Drug-Eluting Polycaprolactone/poly(lactic-co-glycolic Acid) Prolapse Mats Using Solution-Extrusion 3D Printing and Coaxial Electrospinning Techniques. Polymers. 2021; 13(14):2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142295
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yi-Pin, Tsia-Shu Lo, Yu-Ting Lin, Yu-Han Chien, Chia-Jung Lu, and Shih-Jung Liu. 2021. "Fabrication of Drug-Eluting Polycaprolactone/poly(lactic-co-glycolic Acid) Prolapse Mats Using Solution-Extrusion 3D Printing and Coaxial Electrospinning Techniques" Polymers 13, no. 14: 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142295
APA StyleChen, Y.-P., Lo, T.-S., Lin, Y.-T., Chien, Y.-H., Lu, C.-J., & Liu, S.-J. (2021). Fabrication of Drug-Eluting Polycaprolactone/poly(lactic-co-glycolic Acid) Prolapse Mats Using Solution-Extrusion 3D Printing and Coaxial Electrospinning Techniques. Polymers, 13(14), 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142295