Water Behavior of Emulsions Stabilized by Modified Potato Starch
Abstract
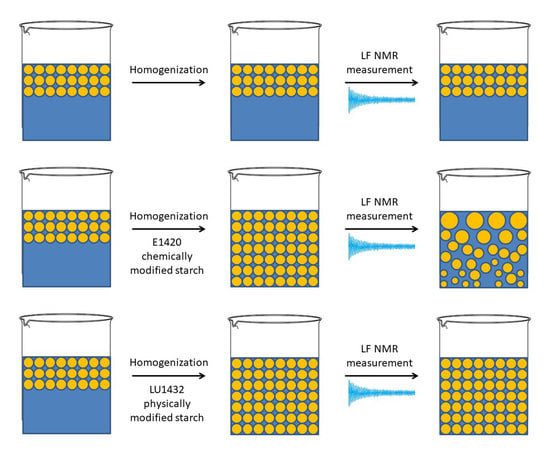
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Emulsions
2.2. Fatty Acid Profile
2.3. NMR Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, J.; Kaur, L.; McCarthy, O.J. Factors influencing the physico-chemical, morphological, thermal and rheological properties of some chemically modified starches for food applications—A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashogbon, A.O.; Akintayo, E.T. Recent trend in the physical and chemical modification of starches from different botanical sources: A review. Starch Stärke 2014, 66, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Hydrocolloids acting as emulsifying agents—How do they do it? Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 78, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Lin, Y.; Wu, H.; Zeng, S.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H. Water migration depicts the effect of hydrocolloids on the structural and textural properties of lotus seed starch. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Jane, J. Gelatinization and rheological properties of starch. Starch Stärke 2015, 67, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gao, H.; Liu, W.; Zou, L.; McClements, D.J. A review of the rheological properties of dilute and concentrated food emulsions. J. Texture Stud. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błaszczak, W.; Lewandowicz, G. Light Microscopy as a Tool to Evaluate the Functionality of Starch in Food. Foods 2020, 9, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Lewandowicz, J. Functionality of Native Starches in Food Systems: Cluster Analysis Grouping of Rheological Properties in Different Product Matrices. Foods 2020, 9, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altuna, L.; Herrera, M.L.; Foresti, M.L. Synthesis and characterization of octenyl succinic anhydride modified starches for food applications. A review of recent literature. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochaska, K.; Kędziora, P.; Le Thanh, J.; Lewandowicz, G. Surface activity of commercial food grade modified starches. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 60, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kędziora, P.; Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Lewandowicz, G.; Prochaska, K. An attempt to application of continuous recycle membrane reactor for the hydrolysis of oxidised starches. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 282, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochaska, K.; Kędziora, P.; Le Thanh, J.; Lewandowicz, G. Surface properties of enzymatic hydrolysis products of octenylsuccinate starch derivatives. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochaska, K.; Konował, E.; Sulej-Chojnacka, J.; Lewandowicz, G. Physicochemical properties of cross-linked and acetylated starches and products of their hydrolysis in continuous recycle membrane reactor. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 74, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konował, E.; Lewandowicz, G.; Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Prochaska, K. Physicochemical characterisation of enzymatically hydrolysed derivatives of acetylated starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Lewandowicz, G.; Błaszczak, W.; Prochaska, K. Starch modified by high-pressure homogenisation of the pastes—Some structural and physico-chemical aspects. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowicz, G. Physical modification of starch—really physical? In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Polysaccharides-Glycoscience, Praha, Czech Republic, 8–10 November 2017; Rapkova, R., Copikova, J., Sarka, E., Eds.; Czech Chemical Society: Prague, Czech Republic, 2017; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Małyszek, Z.; Szwengiel, A.; Zięba, T.; Lewandowicz, G. Sodium salt of starch octenylsuccinate as an emulsifier in “light” type mayonnaises. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2012, 11, 265–271. [Google Scholar]
- Ezeanaka, M.C.; Nsor-Atindana, J.; Zhang, M. Online Low-field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for Food Quality Optimization in Food Processing. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 1435–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, T.; Cheng, S.; Khan, I.A.; Nawab, K.; Zhang, T.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Nadeem, M.; Riaz, M.; Khan, M.A.U.; et al. Potential uses of LF-NMR and MRI in the study of water dynamics and quality measurement of fruits and vegetables. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Su, G.; Wang, X.; Nie, S. Rapid Assessment of Deep Frying Oil Quality as Well as Water and Fat Contents in French Fries by Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2361–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Qin, P. Simultaneous, Rapid and Nondestructive Determination of Moisture, Fat Content and Storage Time in Leisure Dried Tofu Using LF-NMR. Anal. Sci. 2021, 37, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Lewandowicz, G.G.; Krzywdzińska-Bartkowiak, M.; Piątek, M.; Baranowska, H.M.; Białas, W.; Jeziorna, M.; Kubiak, P. Finely comminuted frankfurters fortified with potato juice—Quality and structure. J. Food Eng. 2015, 167, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkowiak, K.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Kubiak, P.; Baranowska, H.M. Effect of cricket powder addition on 1H NMR mobility and texture of pork pate. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2019, 9, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Walkowiak, K.; Masewicz, Ł.; Smarzyński, K.; Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Kačániová, M.; Baranowska, H.M. LF NMR spectroscopy analysis of water dynamics and texture of Gluten-Free bread with cricket powder during storage. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2021, 108201322098791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowska, H.M.; Masewicz, Ł.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Lewandowicz, G.; Piątek, M.; Kubiak, P. Water properties in pâtés enriched with potato juice. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowalczewski, P.; Walkowiak, K.; Masewicz, Ł.; Bartczak, O.; Lewandowicz, J.; Kubiak, P.; Baranowska, H. Gluten-Free Bread with Cricket Powder—Mechanical Properties and Molecular Water Dynamics in Dough and Ready Product. Foods 2019, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewandowicz, J.; Ostrowska-Ligeza, E.; Baranowska, H.M. Gelatinization of Starch: A Comparative Study of Viscographic, Differential Scanning Calorimetry and Low Field NMR Analyses. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Polysaccharides-Glycoscience, Prague, Czech Republic, 4–6 November 2020; Rapkova, R., Copikova, J., Sarka, E., Eds.; Czech Chemical Society: Prague, Czech Republic, 2020; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Vaclavik, V.A.; Christian, E.W. Water. In Essentials of Food Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bloembergen, N.; Purcell, E.M.; Pound, R.V. Relaxation Effects in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Absorption. Phys. Rev. 1948, 73, 679–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska, H.M.; Rezler, R. Molecular dynamics of water in fat-in-water type of emulsions emulsified with potato starch. Żywność. Nauk. Technol. Jakość/Food. Sci. Technol. Qual. 2013, 20, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska, H.M.; Rezler, R. Emulsions stabilized using potato starch. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska, H.M.; Rezler, R. Water binding analysis of fat-water emulsions. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 1921–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezler, R.; Baranowska, H.M. Rheological and water binding properties of fat-in-water type emulsions stabilized by potato starch. Żywność. Nauk. Technol. Jakość/Food. Sci. Technol. Qual. 2013, 20, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Shen, Q. Discrimination of Edible Vegetable Oil Adulteration with Used Frying Oil by Low Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-G.; Xiao, Z.-G.; Chen, S.-S.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Jiang, W.; Lai, K.-G. Application of low field nuclear magnetic resonance on rapid determination of frying oil quality. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. Rapid detection of peanut oil adulteration using low-field nuclear magnetic resonance and chemometrics. Food Chem. 2017, 216, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Codex Alimentarius: General Standard for Food Additives; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2011; ISBN 9789250069630. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Codex Alimentarius: Class Names and the International Numbering System for Food Additives CXG 36-1989; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 17059:2019—Oilseeds—Extraction of Oil and Preparation of Methyl Esters of Triglyceride Fatty Acids for Analysis by Gas Chromatography (Rapid Method); International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Brosio, E.; Gianferri, R.R. An analytical tool in foods characterization and traceability. In Basic NMR in Foods Characterization; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2009; pp. 9–37. [Google Scholar]
- Weglarz, W.P.; Haranczyk, H. Two-dimensional analysis of the nuclear relaxation function in the time domain: The program CracSpin. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2000, 33, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, H.Y.; Purcell, E.M. Effects of Diffusion on Free Precession in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Experiments. Phys. Rev. 1954, 94, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiboom, S.; Gill, D. Modified Spin-Echo Method for Measuring Nuclear Relaxation Times. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1958, 29, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casperson, S.L.; Conrad, Z.; Raatz, S.K.; Derner, J.; Roemmich, J.N.; Jahns, L.; Picklo, M.J. Impact of beef consumption on saturated fat intake in the United States adult population: Insights from modeling the influences of bovine genetics and nutrition. Meat Sci. 2020, 169, 108225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chiba, L.I.; Magee, W.E.; Wang, Y.; Rodning, S.P.; Bratcher, C.L.; Bergen, W.G.; Spangler, E.A. Effect of flaxseed oil, poultry fat, and vitamin E supplementation on physical and organoleptic characteristics and fatty acid profile of pork, and expression of genes associated with lipid metabolism. Livest. Sci. 2020, 231, 103849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, L.; Scholten, E.; van Aken, G.A. Effect of fat hardness on large deformation rheology of emulsion-filled gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skendi, A.; Papageorgiou, M.; Ritzoulis, C. Physicochemical properties and emulsification properties of maize starch modified by hydrochloric, phosphoric and tartaric acid. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 3595–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.; Chang, M.J.; Goh, K.K.T.; Ban, C.; Choi, Y.J. Rheology, Microstructure, and Storage Stability of Emulsion-Filled Gels Stabilized Solely by Maize Starch Modified with Octenyl Succinylation and Pregelatinization. Foods 2021, 10, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scrimgeour, C.; Gao, Y.; Oh, W.Y.; Shahidi, F. Chemistry of Fatty Acids. In Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Marangoni, A.G.; Wesdorp, L.H. Structure and Properties of Fat Crystal Networks; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780429111150. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowicz, J.; Baranowska, H.M.; Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Makowska, A. Water binding capacity in waxy and normal rice starch pastes. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Polysaccharides-Glycoscience, Prague, Czech Republic, 7–9 October 2015; Rapkova, R., Copikova, J., Sarka, E., Eds.; Czech Chemical Society: Prague, Czech Republic, 2015; pp. 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Cheng, B.; Li, J.; Shu, Z.; Wang, P.; Zeng, X. Structure and Properties of Octenyl Succinic Anhydride-Modified High-Amylose Japonica Rice Starches. Polymers 2021, 13, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwengiel, A.; Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Lewandowicz, G. Molecular structure of acetylated starches with different degree of substitution. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Polysaccharides-Glycoscience, Prague, Czech Republic, 8–10 November 2017; Rapkova, R., Copikova, J., Sarka, E., Eds.; Czech Chemical Society: Prague, Czech Republic, 2017; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Szwengiel, A.; Lewandowicz, G.; Górecki, A.R.; Błaszczak, W. The effect of high hydrostatic pressure treatment on the molecular structure of starches with different amylose content. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Błaszczak, W.; Szwengiel, A.; Paukszta, D.; Lewandowicz, G. Molecular and Supermolecular Structure of Commercial Pyrodextrins. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, C2135–C2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Fatty acid | Beef Fat | Pork Fat |
|---|---|---|
| C 10:0 capric acid | 0.043 ± 0.001 | 0.059 ± 0.001 |
| C 12:0 lauric acid | 0.058 ± 0.001 | 0.073 ± 0.001 |
| C 13:0 tridecanoic acid | 0.012 ± 0.001 | N/D |
| C 14:0 myristic acid | 2.622 ± 0.020 | 1.365 ± 0.009 |
| C 14:1 oleomyristic acid | 0.423 ± 0.003 | 0.068 ± 0.001 |
| C 15:0 pentadecanoic acid | 0.499 ± 0.001 | 0.117 ± 0.001 |
| C 16:0 palmitic acid | 26.493 ± 1.035 | 23.761 ± 2.014 |
| C 16:1 palmitoleic acid | 2.760 ± 0.014 | 2.340 ± 0.089 |
| C 17:0 heptadecanoic acid | 1.382 ± 0.032 | 0.524 ± 0.004 |
| C 18:0 stearic acid | 21.405 ± 0.912 | 17.855 ± 1.009 |
| C 18:1 oleic acid | 38.734 ± 3.012 | 41.572 ± 2.392 |
| C 18:2 linoleic acid | 4.276 ± 0.015 | 7.375 ± 0.012 |
| C 18:3 linolenic acid | 0.678 ± 0.001 | 0.702 ± 0.003 |
| C 20:0 arachidic acid | 0.319 ± 0.001 | 0.234 ± 0.002 |
| C 20:1 gadoleic acid | 0.289 ± 0.001 | 1.033 ± 0.004 |
| Starch Concentration (g/g) | ΔEa (kJ/mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil Phase | Water Phase | |||
| Beef Fat | Pork Fat | Beef Fat | Pork Fat | |
| E 1420 | ||||
| 0.12 | 25.7 ± 0.6 | 23.5 ± 0.2 | 13.0 ± 0.3 | 12.3 ± 0.4 |
| 0.17 | 29.5 ± 0.4 | 27.3 ± 0.3 | 15.8 ± 0.5 | 19.5 ± 0.6 |
| 0.25 | 20.2 ± 0.3 | 17.4 ± 0.7 | 19.5 ± 0.2 | 13.7 ± 0.4 |
| LU 1432 | ||||
| 0.12 | 21.1 ± 0.4 | 20.4 ± 0.7 | 28.9 ± 0.5 | 22.9 ± 0.2 |
| 0.17 | 27.7 ± 0.5 | 22.2 ± 0.3 | 31.2 ± 0.7 | 24.4 ± 0.4 |
| 0.25 | 22.1 ± 0.2 | 18.8 ± 0.5 | 10.9 ± 0.6 | 23.1 ± 0.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Małyszek, Z.; Lewandowicz, J.; Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Walkowiak, K.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Baranowska, H.M. Water Behavior of Emulsions Stabilized by Modified Potato Starch. Polymers 2021, 13, 2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132200
Małyszek Z, Lewandowicz J, Le Thanh-Blicharz J, Walkowiak K, Kowalczewski PŁ, Baranowska HM. Water Behavior of Emulsions Stabilized by Modified Potato Starch. Polymers. 2021; 13(13):2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132200
Chicago/Turabian StyleMałyszek, Zuzanna, Jacek Lewandowicz, Joanna Le Thanh-Blicharz, Katarzyna Walkowiak, Przemysław Łukasz Kowalczewski, and Hanna Maria Baranowska. 2021. "Water Behavior of Emulsions Stabilized by Modified Potato Starch" Polymers 13, no. 13: 2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132200
APA StyleMałyszek, Z., Lewandowicz, J., Le Thanh-Blicharz, J., Walkowiak, K., Kowalczewski, P. Ł., & Baranowska, H. M. (2021). Water Behavior of Emulsions Stabilized by Modified Potato Starch. Polymers, 13(13), 2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132200