Dispersed Conducting Polymer Nanocomposites with Glucose Oxidase and Gold Nanoparticles for the Design of Enzymatic Glucose Biosensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
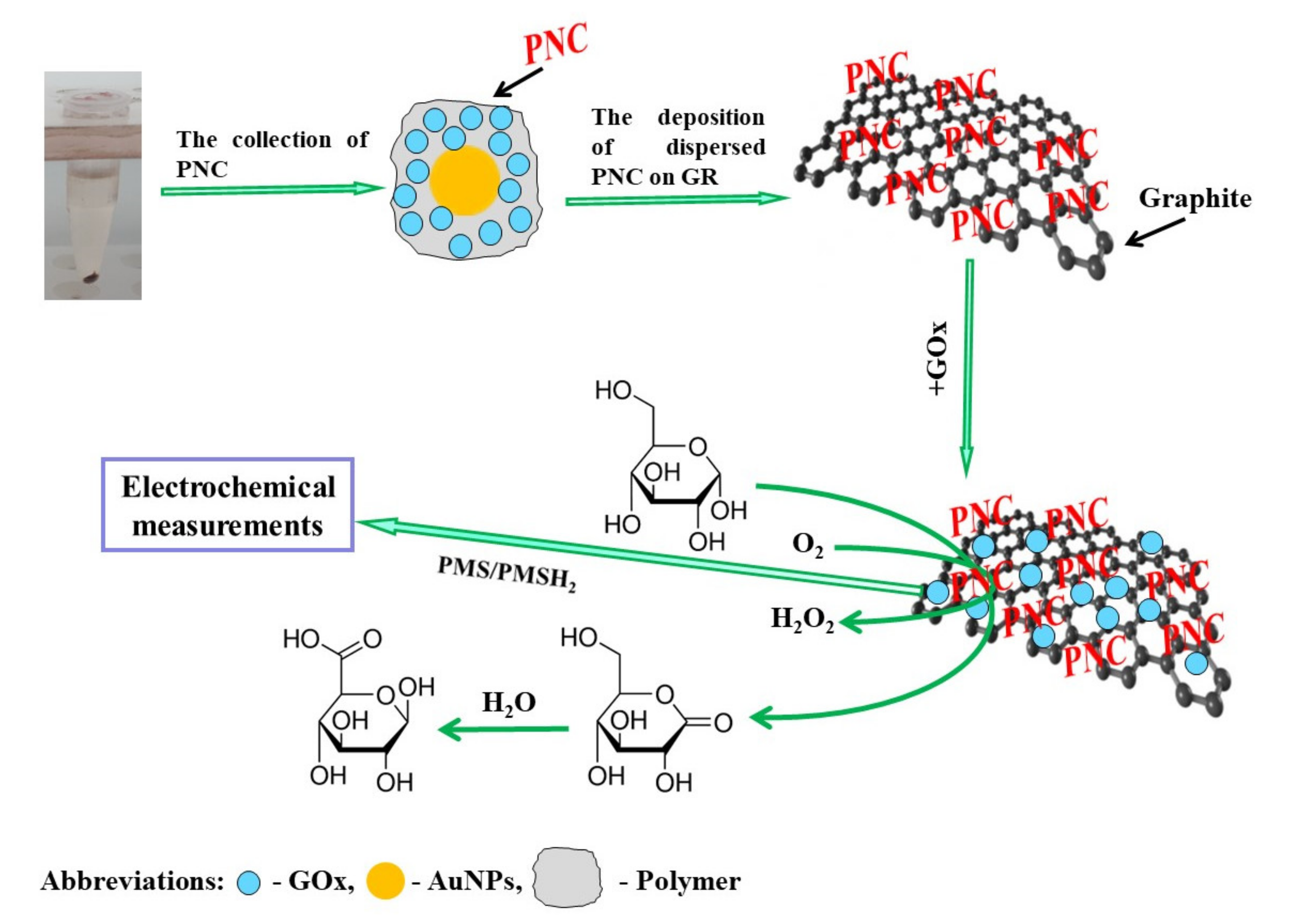
2.2. The Polymerization, Separation and Dispersion of Polymer-Based Nanocomposites
2.3. The Preparation of Graphite Rod Electrode and Modification by Polymer-Based Nanocomposites
2.4. Application of Glucose Biosensor Based on GR/PANI-AuNPs(6 nm)-GOx/GOx Electrode for Glucose Detection in the Serum Sample
2.5. Electrochemical and Statistical Evaluations of GR/PANI-GOx/GOx, GR/Ppy-GOx/GOx, GR/PANI-AuNPs(6 nm)-GOx/GOx or GR/Ppy-AuNPs(6 nm)-GOx/GOx Electrodes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Biosensors Based on GR/PANI-GOx/GOx, GR/Ppy-GOx/GOx, GR/PANI-AuNPs(6 nm)-GOx/GOx or GR/Ppy-AuNPs(6 nm)-GOx/GOx Electrodes by Cyclic Voltammetry
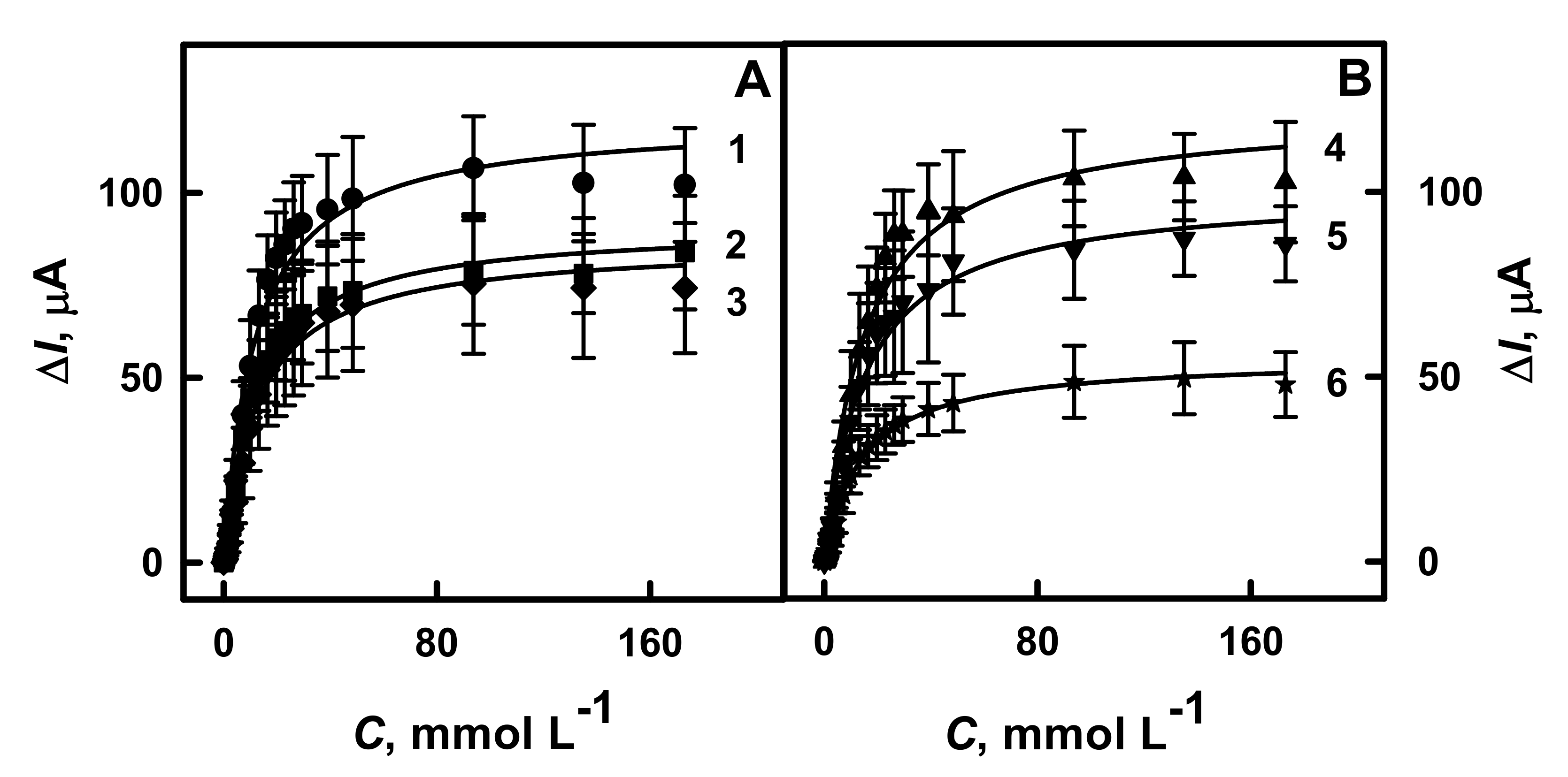
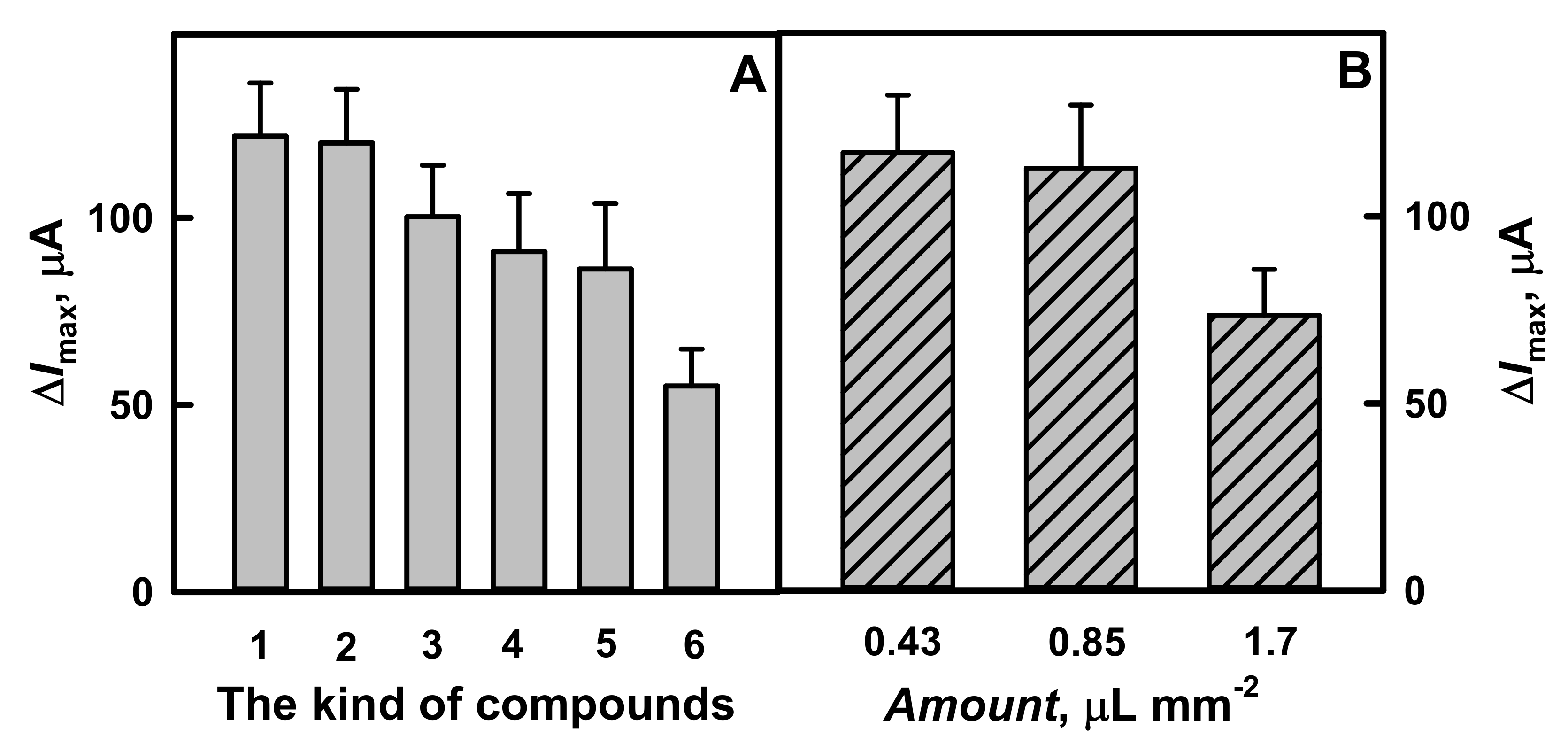
3.2. The Influence of Polymer Nanocomposites Composition and Layer Thickness on the Current Response Registered by Amperometry
3.3. The Evaluation of the Analytical Characteristics of GR Electrodes Modified by PANI-AuNPs(6 nm)-GOx/GOx, Ppy-AuNPs(6 nm)-GOx/GOx, PANI-GOx/GOx or Ppy-GOx/GOx
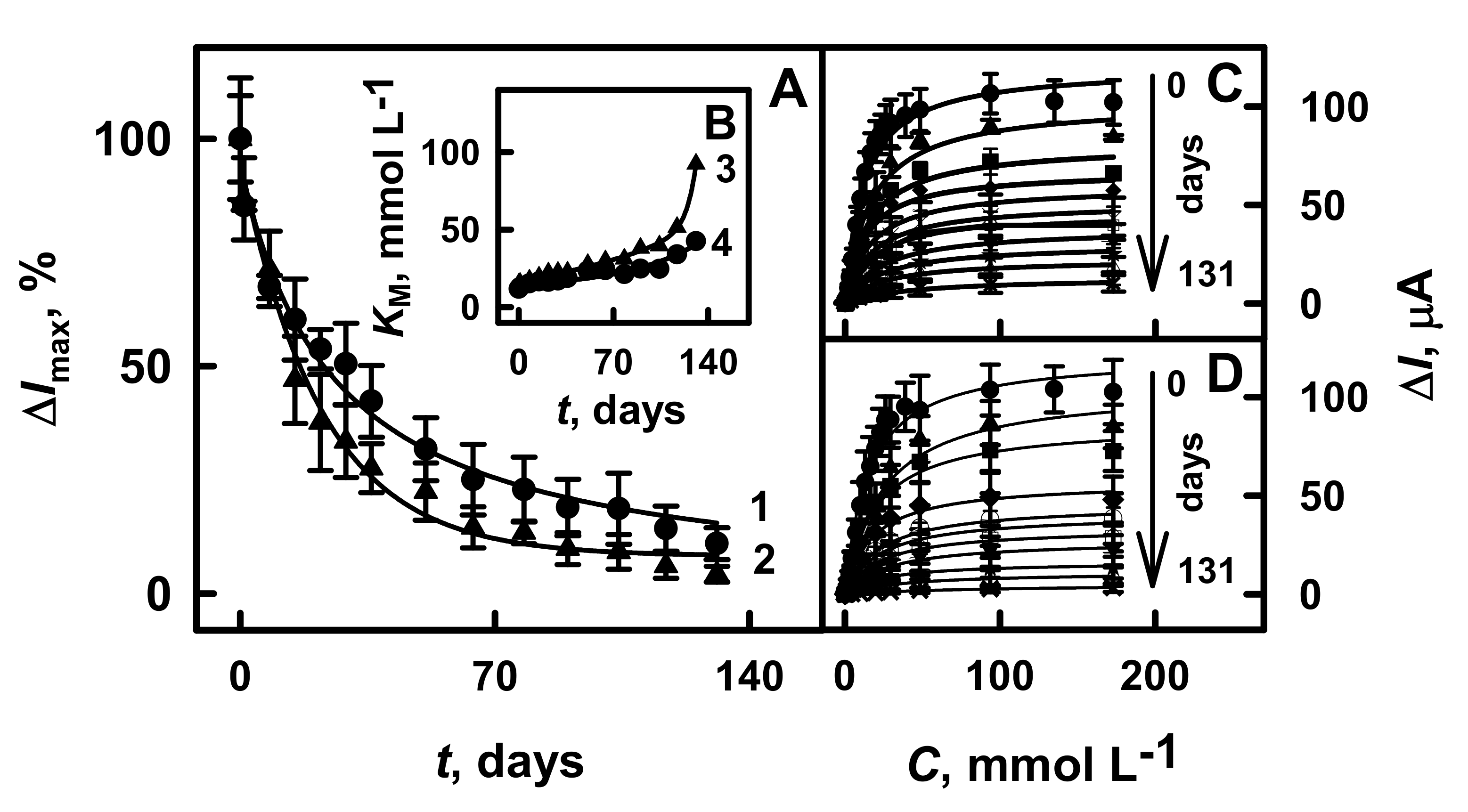
3.4. The Stability of Glucose Biosensors Based on GR Electrodes Modified by PANI-AuNPs(6 nm)-GOx/GOx or Ppy-AuNPs(6 nm)-GOx/GOx
3.5. The Application of Biosensor Based on GR/PANI-AuNPs(6 nm)-GOx/GOx for Determination of Glucose in Serum Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Batool, R.; Rhouati, A.; Nawaz, M.H.; Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. A review of the construction of nano-hybrids for electrochemical biosensing of glucose. Biosensors 2019, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.C.; Lee, A.R. Recent developments in blood glucose sensors. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heller, A.; Feldman, B. Electrochemical glucose sensors and their applications in diabetes management. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2482–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocchitta, G.; Spanu, A.; Babudieri, S.; Latte, G.; Madeddu, G.; Galleri, G.; Nuvoli, S.; Bagella, P.; Demartis, M.I.; Fiore, V.; et al. Enzyme biosensors for biomedical applications: Strategies for safeguarding analytical performances in biological fluids. Sensors 2016, 16, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Labib, M.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Electrochemical methods for the analysis of clinically relevant biomolecules. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 9001–9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Orazio, P. Biosensors in clinical chemistry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 334, 41–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.; Julkapli, N.M.; Yehye, W.A.; Basirun, W.J.; Bhargava, S.K. Graphene-gold nanoparticles hybrid-synthesis, functionalization, and application in a electrochemical and surface-enhanced raman scattering biosensor. Materials 2016, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bo, X.; Zhou, M.; Guo, L. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on less aggregated graphene. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S.; Cheemalapati, S.; Chen, S.M. Amperometric glucose biosensor based on glucose oxidase dispersed in multiwalled carbon nanotubes/graphene oxide hybrid biocomposite. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 34, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Carolina, N.; Pines, B.; Squibb, B.M.; Nordisk, N.; Nordisk, N.; Nordisk, N.; Nordisk, N.; Dickinson, B. La asociación española de la carretera entrega sus premios de periodismo. Carreteras 2006, 4, 120. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, H.; Cao, L.; Chang, G.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y. Direct electrodeposition of gold nanostructures onto glassy carbon electrodes for non-enzymatic detection of glucose. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 132, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, F.G.; Neves, A.C.O.; de Lima, D.F.; Lourenço, S.D.; da Silva, L.C.; de Lima, K.M.G. Bioorganic concepts involved in the determination of glucose, cholesterol and triglycerides in plasma using the enzymatic colorimetric method. Quim. Nova 2015, 38, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Toit, H.; Di Lorenzo, M. Continuous power generation from glucose with two different miniature flow-through enzymatic biofuel cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 69, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Babadi, A.A.; Bagheri, S.; Hamid, S.B.A. Progress on implantable biofuel cell: Nano-carbon functionalization for enzyme immobilization enhancement. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Conducting polymers in the design of biosensors and biofuel cells. Polymers 2021, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Charge transfer and biocompatibility aspects in conducting polymer-based enzymatic biosensors and biofuel cells. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Progress and insights in the application of MXenes as new 2d nano-materials suitable for biosensors and biofuel cell design. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama, E.C.; Costa-García, A.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T. Pin-based electrochemical glucose sensor with multiplexing possibilities. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 88, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulbari, H.A.; Basheer, E.A.M. Electrochemical biosensors: Electrode development, materials, design, and fabrication. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017, 4, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galant, A.L.; Kaufman, R.C.; Wilson, J.D. Glucose: Detection and analysis. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on nanomaterials and nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilian, A.T.E.; Chen, S.M.; Ali, M.A.; Al-Hemaid, F.M.A. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase immobilized on ZrO2 nanoparticles-decorated reduced graphene oxide sheets for a glucose biosensor. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 30358–30367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Electrochemical co-reduction synthesis of graphene/nano-gold composites and its application to electrochemical glucose biosensor. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 112, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, P.N.; Al-Lolage, F.A. There is no evidence to support literature claims of direct electron transfer (DET) for native glucose oxidase (GOx) at carbon nanotubes or graphene. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 819, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luckarift, H.R.; Ivnitski, D.; Rincón, R.; Atanassov, P.; Johnson, G.R. Glucose oxidase catalyzed self-assembly of bioelectroactive gold nanostructures. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z. Electrochemical glucose sensor based on one-step construction of gold nanoparticle-chitosan composite film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 138, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, N.; Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Ramanavicius, A.; Semashko, T.; Mikhailova, R.; Ramanaviciene, A. The use of different glucose oxidases for the development of an amperometric reagentless glucose biosensor based on gold nanoparticles covered by polypyrrole. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 169, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, B.; Tabrizi, M.A. Direct electron transfer from glucose oxidase immobilized on an overoxidized polypyrrole film decorated with Au nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Leech, D.; Ju, H. Application of colloidal gold in protein immobilization, electron transfer, and biosensing. Anal. Lett. 2003, 36, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, Z.; Ma, M.; Du, X.; Lin, J.; Han, B.; Takahashi, S.; Anzai, J.I.; Chen, Q. Dual-function amperometric sensors based on poly(diallydimethylammoniun chloride)-functionalized reduced graphene oxide/manganese dioxide/gold nanoparticles nanocomposite. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2016, 222, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, M.S.; Deore, B.A. Self-Doped Conducting Polymers; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NK, USA, 2007; Volume 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Oztekin, Y.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Yazicigil, Z.; Solak, A.O.; Ramanavicius, A. Direct electron transfer from glucose oxidase immobilized on polyphenanthroline-modified glassy carbon electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2541–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.H.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, H. Electrical and electrochemical properties of conducting polymers. Polymers 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanaviciene, A.; Schuhmann, W.; Ramanavicius, A. AFM study of conducting polymer polypyrrole nanoparticles formed by redox enzyme — glucose oxidase — initiated polymerisation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2006, 48, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, N.; Popov, A.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Evaluation of enzymatic formation of polyaniline nanoparticles. Polymer 2017, 115, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Gu, S.X.; Jin, L.; Zhou, Y.E.; Yang, Z.; Wang, W.; Hu, X. Graphene/polyaniline/gold nanoparticles nanocomposite for the direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase and glucose biosensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, N.; Ramanavicius, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. Amperometric glucose biosensor based on electrochemically deposited gold nanoparticles covered by polypyrrole. Electroanalysis 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, N.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Formation and electrochemical evaluation of polyaniline and polypyrrole nanocomposites based on glucose oxidase and gold nanostructures. Polymers 2020, 12, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, N.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Formation of Polyaniline and Polypyrrole Nanocomposites with Embedded Glucose Oxidase and Gold Nanoparticles. Polymers 2019, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- German, N.; Popov, A.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Formation and electrochemical characterisation of enzyme-assisted formation of polypyrrole and polyaniline nanocomposites with embedded glucose oxidase and gold nanoparticles. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 165501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, N.; Popov, A.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Enzymatic formation of polyaniline, polypyrrole, and polythiophene nanoparticles with embedded glucose oxidase. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Solanki, P.R.; Pandey, M.K.; Malhotra, B.D. Covalent immobilization of cholesterol esterase and cholesterol oxidase on polyaniline films for application to cholesterol biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 568, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, U.; Seçkin, A.İ.; Temur, E.; Torul, H. Fabrication of biosensor based on polyaniline/gold nanorod composite. Int. J. Electrochem. 2011, 2011, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amor-Gutiérrez, O.; Costa Rama, E.; Costa-García, A.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T. Paper-based maskless enzymatic sensor for glucose determination combining ink and wire electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.; Kwon, D.; Lee, D.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, G.; Yoon, D.S. A highly permselective electrochemical glucose sensor using red blood cell membrane. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psychogios, N.; Hau, D.D.; Peng, J.; Guo, A.C.; Mandal, R.; Bouatra, S.; Sinelnikov, I.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Eisner, R.; Gautam, B.; et al. The human serum metabolome. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sautin, Y.Y.; Johnson, R.J. Uric acid: The oxidant-antioxidant paradox. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2008, 27, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.; Ahn, S.; Yim, J.; Cheon, Y.; Jeong, H.; Lee, S.-G.; Kim, J.-H. Letter to the editor clinical chemistry influence of vitamin C and maltose on the accuracy of three models of glucose meters. Ann. Lab. Med. 2016, 36, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, P.; Sidloi, M.; Tonks, D.B. Estimation of serum ascorbic acid in patients and the effect of ascorbic acid and its oxidation products on SMA 12/60 parameters. Clin. Biochem. 1980, 13, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.Q.; Yang, C.; Qian, Q.Y.; Xia, X.H. Study of the nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on highly dispersed Pt nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes. Talanta 2007, 72, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Song, Y.Y.; Yang, C.; Xia, X.H. Hydrogen bubble dynamic template synthesis of porous gold for nonenzymatic electrochemical detection of glucose. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| The Composition of Polymer Nanocomposites on GR | LOD, mmol L−1 | Sensitivity, μA mM−1 cm−2 | Linear Detection, mmol L−1 | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PANI-AuNPs(6 nm)-GOx/GOx | 0.070 | 65.4 | 0.10–16.5 | 0.9968 |
| Ppy-AuNPs(6 nm)-GOx/GOx | 0.071 | 55.4 | 0.10–16.5 | 0.9961 |
| PANI-GOx/GOx | 0.084 | 52.0 | 0.10–16.5 | 0.9936 |
| Ppy-GOx/GOx | 0.10 | 48.0 | 0.10–16.5 | 0.9977 |
| Added Concentration, mmol L−1 | Detected Concentration, mmol L−1 | RSD, % | Recovery Ratio, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | 0.095 (4) | 8.13 | 95.0 |
| 0.30 | 0.291 (4) | 7.80 | 97.0 |
| 0.50 | 0.490 (4) | 4.99 | 98.0 |
| 0.70 | 0.676 (4) | 4.31 | 96.6 |
| 1.00 | 0.972 (4) | 5.42 | 97.2 |
| 2.00 | 1.92 (5) | 7.42 | 96.0 |
| 4.48 | 4.40 (4) | 7.09 | 98.2 |
| 7.21 | 7.10 (4) | 7.67 | 98.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
German, N.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Dispersed Conducting Polymer Nanocomposites with Glucose Oxidase and Gold Nanoparticles for the Design of Enzymatic Glucose Biosensors. Polymers 2021, 13, 2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132173
German N, Ramanaviciene A, Ramanavicius A. Dispersed Conducting Polymer Nanocomposites with Glucose Oxidase and Gold Nanoparticles for the Design of Enzymatic Glucose Biosensors. Polymers. 2021; 13(13):2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132173
Chicago/Turabian StyleGerman, Natalija, Almira Ramanaviciene, and Arunas Ramanavicius. 2021. "Dispersed Conducting Polymer Nanocomposites with Glucose Oxidase and Gold Nanoparticles for the Design of Enzymatic Glucose Biosensors" Polymers 13, no. 13: 2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132173
APA StyleGerman, N., Ramanaviciene, A., & Ramanavicius, A. (2021). Dispersed Conducting Polymer Nanocomposites with Glucose Oxidase and Gold Nanoparticles for the Design of Enzymatic Glucose Biosensors. Polymers, 13(13), 2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132173








