Review on Electrospun Nanofiber-Applied Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Electrospinning Fundamentals
- Solution variables: concentration, degree of polymerization, viscosity and surface tension of the polymer.
- Needle variables: mono-axial, co-axial, tri-axial and needle-free.
- Collector variables: stationary collector, drum rotary collector and rotational speed.
- Electrospinning variables: voltage, feed rate, distance, temperature and humidity.
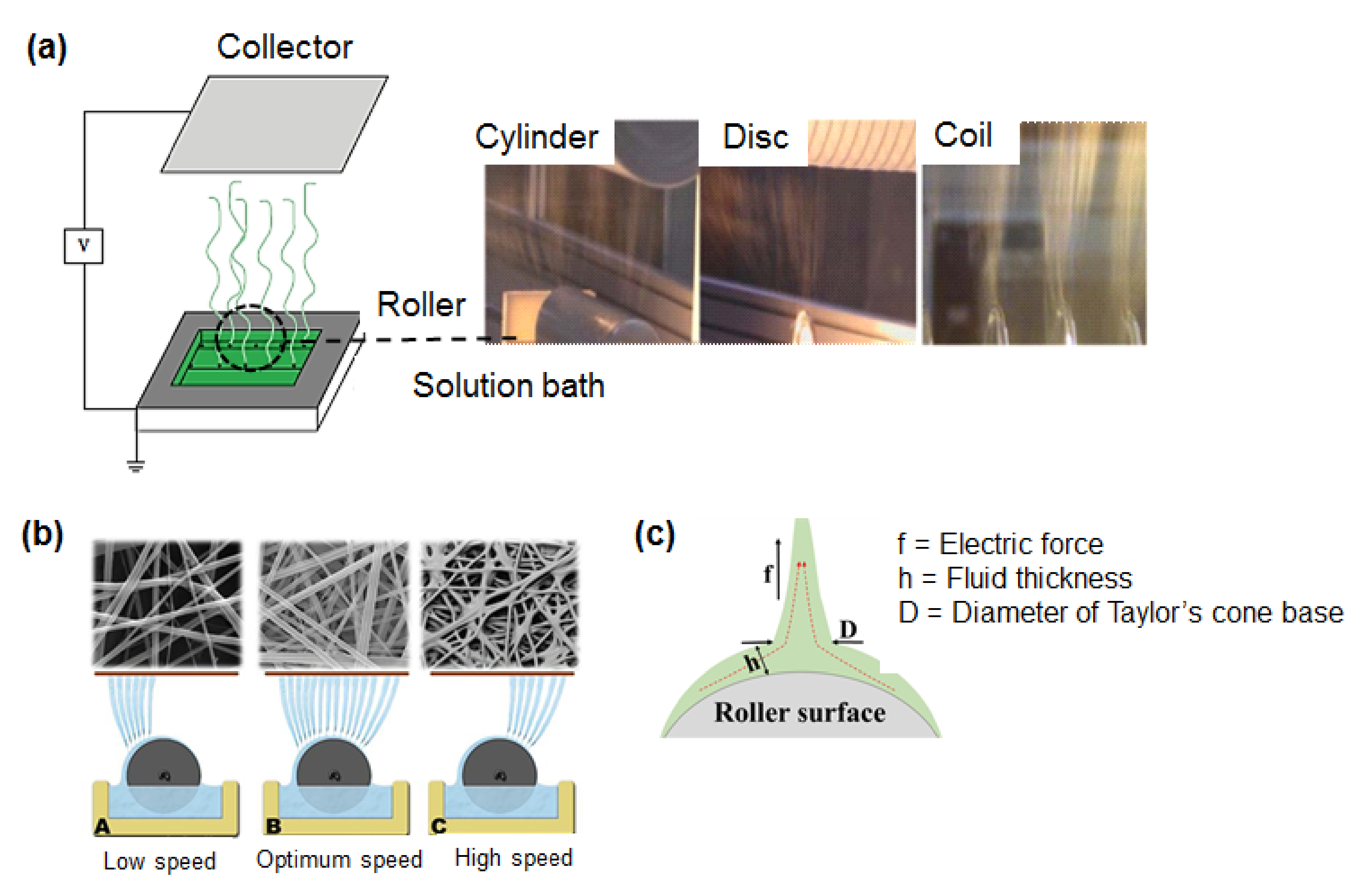
From Laboratory to Industrial Scale
3. Functional Additives in Electrospun Nanofibers
3.1. Nanoparticles Inclusion
3.2. Nanoparticles Surface Coating
4. Electrospun Nanofiber-Applied Products
4.1. Filter Media
4.2. Defense and Protection Garment
4.3. Medical Dressing
4.4. Home Furnishing
4.5. Food Packaging
4.6. Cosmetics
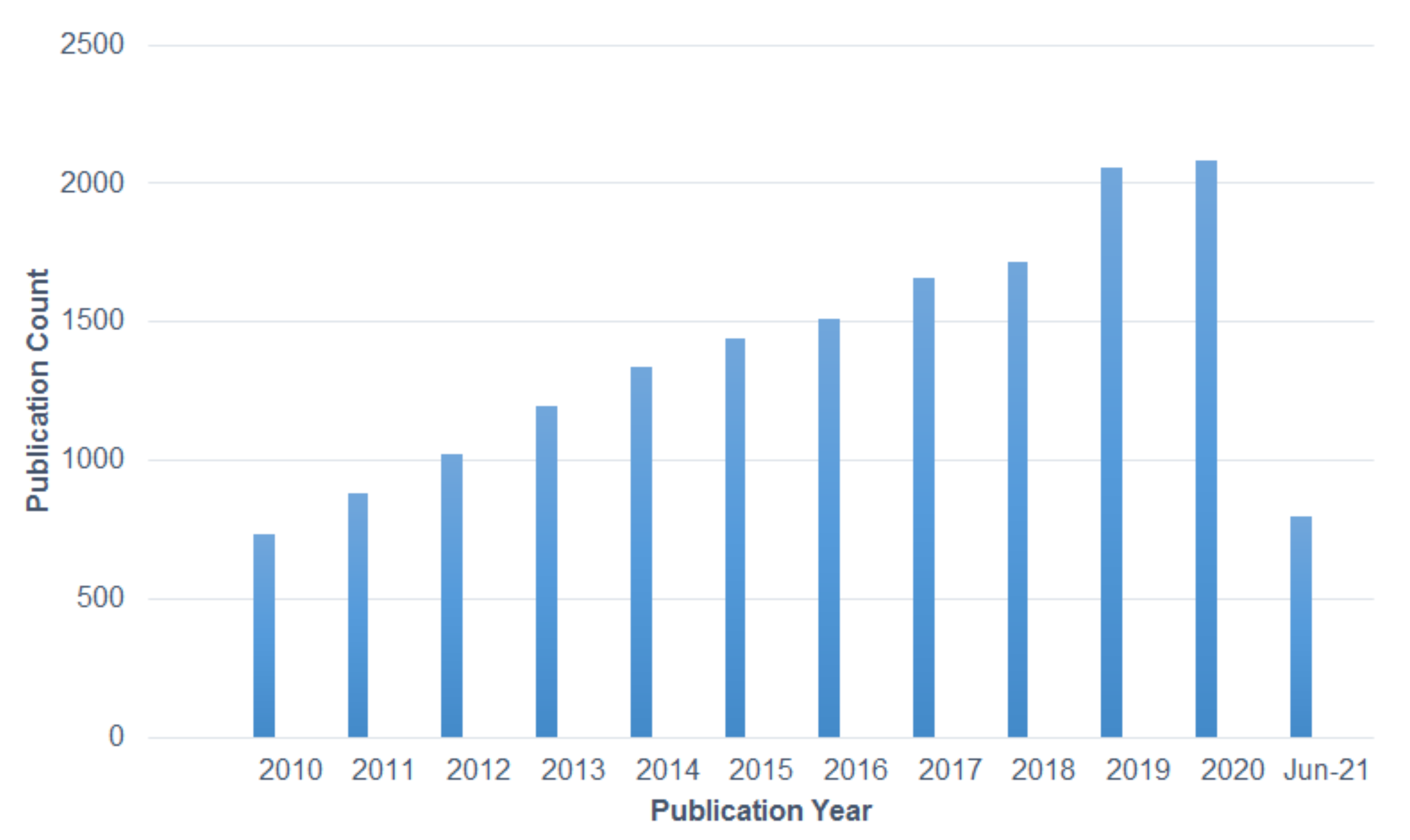
5. Global Nanofibers Industry
5.1. Nanofibers in Global Business
5.2. Market Trends of Electrospun Nanofibers
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1D | One-dimensional |
| 2D | Two-dimensional |
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
| Ag | Silver |
| CNTs | Carbon nanotubes |
| NaBH4 | Sodium borohydride |
| PAN | Polyacrylonitrile |
| PCL | Polycaprolactone |
| TiO2 | Titanium dioxide |
| SiO2 | Silicon dioxide |
| ZnO | Zinc oxide |
| PEO | Polyethylene oxide |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| TE | Thermoelectric |
| RTILs | Room temperature ionic liquids |
| SVA | Solvent vapour annealing |
| PM | Particulate matter |
| Fe2O3-Al2O3 | Iron oxide-aluminum oxide |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| SF | Separation factor |
| PVDF-TrFE | Polyvinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene |
| MgO | Magnesium oxide |
| PA6 | Polyamide 6 |
| HFIP | Hexafluoroisopropanol |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| PANI | Polyaniline |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| SPI | Soy protein isolates |
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| AITC | Allyl isothiocyanate |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| CuS | Copper monosulfide |
References
- Patra, J.K.; Gouda, S. Application of nanotechnology in textile engineering: An overview. J. Eng. Technol. Res. 2013, 5, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulrajani, M.L.; Gupta, D. Emerging techniques for functional finishing of textiles. Ind. J. Fibre Text. Res. 2011, 36, 388–397. [Google Scholar]
- Som, C.; Gallen, E.S. NanoTextiles: Functions, Nanoparticles and Commercial Applications. 2007, pp. 1–44. Available online: https://www.empa.ch/documents/56122/328606/NanoSafeTextiles_1.pdf/b2add656-265b-42df-9196-f2768d773748 (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- Wong, Y.W.H.; Yuen, C.W.M.; Leung, M.Y.S.; Ku, S.K.A.; Lam, H.L.I. Selected applications of nanotechnology in textiles. AUTEX Res. J. 2006, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, S.; Jose, S.; Sumod, U.S.; Sabitha, M. Nanotechnology in cosmetics: Opportunities and challenges. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2012, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebamalar Leavline, E.; Asir Antony Gnana Singh, D.; Prasannanayagi, S.; Kiruthika, R. A compendium of nano materials and their applications in smart nano textiles. Res. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 5, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.H.; Daoud, W.A.; Kong, Y.Y. A new approach to UV-blocking treatment for cotton fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2004, 74, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, S.H. Preparation of nanocomposite fibers for permanent antibacterial effect. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 2143–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, A.M.; Nakano, S.; Yamane, H.; Kimura, Y. Electrospinning of continuous aligning yarns with a ‘Funnel’ Target. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, C.K.S.; Sharma, C.P. Electrospinning of chitin and chitosan nanofibres. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2009, 22, 179–201. [Google Scholar]
- De Vrieze, S.; De Clerck, K. 80 years of electrospinning. In International Conference on Latest Advances in High-Tech Textiles and Textile-Based Materials; Ghent University: Ghent, Belgium, 2009; pp. 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Persano, L.; Camposeo, A.; Tekmen, C.; Pisignano, D. Industrial upscaling of electrospinning and applications of polymer nanofibers: A review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.J.; Stoyanov, S.D.; Stride, E.; Pelan, E.; Edirisinghe, M. Electrospinning versus fibre production methods: From specifics to technological. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4708–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Padhye, R.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Truong, Y.B.; Arnold, L. Recent advances in nanofibre fabrication techniques. Text. Res. J. 2012, 82, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, C.; Sheng, J. Morphology of ultrafine polysulfone fibers prepared by electrospinning. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zou, T.; Li, S.; Jing, J.; Xia, X.; Liu, X. Drug-loaded zein nanofibers prepared using a modified coaxial electrospinning process. J. Am. Assoc. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 14, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pillay, V.; Dott, C.; Choonara, Y.E.; Tyagi, C.; Tomar, L.; Kumar, P.; du Toit, L.C.; Ndesendo, V.M. A review of the effect of processing variables on the fabrication of electrospun nanofibers for drug delivery applications. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garg, K.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning jets and nanofibrous structures. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 013403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ifegwu, O.C.; Anyakora, C. The place of electrospinning in separation science and biomedical engineering. In Electrospinning Method Used to Create Functional Nanocomposites Films; Tański, T.A., Jarka, P., Matysiak, W., Eds.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2018; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, T.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Q.; Xiong, J.; Sun, D. Alignment of electrospun fibers using the whipping instability. Mater. Lett. 2017, 193, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Methods, materials, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.J.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Electrospinning process and structure relationship of biobased poly (butylene succinate) for Nanoporous Fibers. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5547–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Subianto, S. Electrospun Nanofibers, 1st ed.; Elsevier Ltd: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 449–466. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N. Applications of electrospun nanofibers in the biomedical field. SURG J. 2012, 5, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzio, A.; Canesi, E.V.; Bertarelli, C.; Caironi, M. Electrospun polymer fibers for electronic applications. Materials 2014, 7, 906–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, T.; Bhat, G.S.; Tock, R.W.; Parameswaran, S.; Ramkumar, S.S. Electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. 2005, 96, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenot, A.; Chronakis, I.S. Polymer nanofibers assembled by electrospinning. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, K.; Yoon, H.; Son, J.; Min, T.; Kim, G. Apparatus for preparing electrospun nanofibers: Designing an electrospinning process for nanofiber fabrication. Polym. Int. 2007, 56, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Klingner, A. A review on electrospun polymeric nanofibers: Production parameters and potential applications. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.-K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.P.S.; Lim, C.T. Mechanical characterization of nanofibers: A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, D.R.; Forsythe, J.S.; Shen, W.; Finkelstein, D.I.; Horne, M.K. A review of the cellular response on electrospun Nanofibers for tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 2009, 24, 347–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanani, A.G.; Bahram., S.H. Review on electrospun nanofibers scaffold and biomedical applications. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2010, 24, 93–115. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Niu, H.; Lin, T.; Wang, X. Applications of electrospun nanofibers. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 2265–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thavasi, V.; Singh, G.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun nanofibers in energy and environmental applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, S.; Maghsoodloo, S.; Noroozi, B.; Mottaghitalab, V.; Haghi, A.K. Mathematical modeling in electrospinning process of nanofibers: A detailed review. Cell. Chem. Technol. 2013, 47, 323–338. [Google Scholar]
- Angammana, C.J.; Jayaram, S.H. Analysis of the effects of solution conductivity on electrospinning process and fiber morphology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, A.S.; Mirzadeh, H.; Hajiesmaeilbaigi, F.; Bagheri-Khoulenjani, S.; Shokrgozar, M. Effect of electrospinning parameters on morphological properties of PVDF nanofibrous scaffolds. Prog. Biomater. 2017, 6, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, C.; Vidinha, R.; Botequim, D.; Borges, J.P.; Silva, J.A.M.C. A systematic study of solution and processing parameters on nanofiber morphology using a new electrospinning apparatus. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 3535–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanlou, H.M.; Sadollah, A.; Ang, B.C.; Kim, J.H.; Talebian, S.; Ghadimi, A. Prediction and optimization of electrospinning parameters for polymethyl methacrylate nanofiber fabrication using response surface methodology and artificial neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 25, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Campagne, C.; Salaün, F. Influence of solvent selection in the electrospraying process of polycaprolactone. App. Sci 2019, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L. Electrospinning jets and polymer nanofibers. Polymer 2008, 49, 2387–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H. Effects of electrospinning parameters on morphology and diameter of electrospun PLGA/MWNTs fibers and cytocompatibility in vitro. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2011, 26, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsabee, M.Z.; Naguib, H.F.; Morsi, R.E. Chitosan based nanofibers, review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1711–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadil, F.; Affandi, N.D.N.; Misnon, M.I. Mechanical behaviour of MWCNTs reinforced electrospun nanofibres. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2019, 56, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Ding, X.; Hou, X.; Wu, S. Study on the electrospun CNTs/polyacrylonitrile-based nanofiber composites. J. Nanomater 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Fu, G.; Xie, D.; Jiang, S.; Chen, Z.; Huang, B.; Zhao, Y. Preparation of carbon nanotube/polyaniline nanofiber by electrospinning. Procedia Eng. 2012, 27, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakoli, A.N.; Wan, J.; Feng, J.T.; Amirian, M.; Sui, J.H.; Cai, W. Functionalization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes for reinforcing of poly (l-lactide-co-ɛ-caprolactone) biodegradable copolymers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 256, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Truong, Y.B.; Padhye, R.; Arnold, L. Melt-electrospinning of polypropylene with conductive additives. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 6387–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.E.; Inai, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Technological advances in electrospinning of nanofibers. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2011, 12, 013002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahay, R.; Thavasi, V.; Ramakrishna, S. Design modifications in electrospinning setup for advanced applications. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.E.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on electrospinning design and nanofibre assemblies. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, R89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Lin, T. Fiber generators in needleless electrospinning. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Needleless electrospinning: Influences of fibre generator geometry. J. Text. Ins. 2012, 103, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, H.; Lin, T.; Wang, X. Needleless electrospinning. I. A comparison of cylinder and disk nozzles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 3524–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Finite Element-aided electric field analysis of needleless electrospinning. In Computational Finite Element Methods in Nanotechnology; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 333–352. [Google Scholar]
- Yalcinkaya, F.; Yalcinkaya, B.; Jirsak, O. Dependent and Independent Parameters of Needleless Electrospinning. In Electrospinning—Material, Techniques, and Biomedical Applications; Haider, S., Haider, A., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IME Technologies. Climate Controlled Electrospinning. Available online: https://www.ime-electrospinning.com/electrospinning-controlled-environmental/ (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S. Synthesis of aligned TiO2 nanofibers using electrospinning. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 309. [Google Scholar]
- Ismaya, E.P.; Diantoro, M.; Kusumaatmaja, A.; Triyana, K. Preparation of PVA/TiO2 composites nanofibers by using electrospinning method for photocatalytic degradation. IOP Conf. Ser. 2016, 202, 012011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Shafiq, M.; Liu, M.; Morsi, Y.; Mo, X. Advanced fabrication for electrospun three-dimensional nanofiber aerogels and scaffolds. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 963–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chainani, A.; Hippensteel, K.J.; Kishan, A.; Garrigues, N.W.; Ruch, D.S.; Guilak, F.; Little, D. Multilayered electrospun scaffolds for tendon tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. A 2013, 19, 2594–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, B.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Aqeel, B.M.; El-Hamshary, H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Mo, X. Fabrication and characterization of mineralized P(LLA-CL)/SF three-dimensional nanoyarn scaffolds. Iran. Polym. J. 2014, 24, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.G.; Chung, H.J.; Park, T.G. Macroporous and nanofibrous hyaluronic acid/collagen hybrid scaffold fabricated by concurrent electrospinning and deposition/leaching of salt particles. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, K.S.; Won, H.S.; Sang, Y.L.; Sang, H.L.; Seong, J.H.; Myung, C.L.; Lee, S.J. Chitosan nano-/microfibrous double-layered membrane with rolled-up three-dimensional structures for chondrocyte cultivation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2009, 90, 595–602. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Mark, A.C.; Matthew, J.T.; Hongjun, W.; Matthew, R.M.; Jingwei, X. Expanding two-dimensional electrospun nanofiber membranes in the third dimension by a modified gas-foaming technique. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, K.; Kuang, H.; You, Z.; Morsi, Y.; Mo, X. Electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering with drug loading and release. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; An, Q.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; He, L.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhu, W.; Mo, X. A novel heparin loaded poly (l-lactide-co-caprolactone) covered stent for aneurysm therapy. Mater. Lett. 2014, 116, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.N.; Dorjjugder, N.; Saito, Y.; Taguchi, G.; Ullah, A.; Kharaghani, D.; Kim, I.S. The synthesis of sil-ver-nanoparticle-anchored electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers and a comparison with as-spun silver/polyacrylonitrile nanocomposite membranes upon antibacterial activity. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 4197–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caratão, B.; Carneiro, E.; Sá, P.; Almeida, B.; Carvalho, S. Properties of electrospun TiO2 nanofibers. J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 2014, 472132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zong, X.; Cai, Y.; Sun, G.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, F.; Song, L.; Hu, Y.; Fong, H.; Wei, Q. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun SiO2 nanofibers absorbed with fatty acid eutectics for thermal energy storage/retrieval. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 132, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Shao, C.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Lu, N.; Liu, Y. Electrospun carbon nanofibers/carbon nanotubes/polyaniline ternary composites with enhanced electrochemical performance for flexible solid-state supercapacitors. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mauro, A.; Zimbone, M.; Fragalà, M.E.; Impellizzeri, G. Synthesis of ZnO nanofibers by the electrospinning process. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 42, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeesi, F.; Nouri, M.; Haghi, A.K. Electrospinning of polyaniline-polyacrylonitrile blend nanofibers. e-Polym. 2009, 9, 1350–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, H.E.; Steuber, J.G.; Du, W.; Mortazavi, M.; Bullock, D.W. Polyethylene oxide nanofiber production by electrospinning. J. Ark. Acad. Sci. 2016, 70, 211–215. [Google Scholar]
- Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Moazzez-Lalaklo, N.; Zarghami, N. An update on clinical applications of electrospun nanofibers for skin bioengineering. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 1350–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Vazirzadeh, M.; Zohaib, S.; Najeeb, B.; Sefat, F. Potential of electrospun nanofibers for biomedical and dental applications. Materials 2016, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Giner, S. Electrospun nanofibers for food packaging applications. In Multifunctional and Nanoreinforced Polymers for Food Packaging; Lagaron., J.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; pp. 108–125. [Google Scholar]
- Nejati-Koshki, K.; Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y.; Alizadeh, E.; Ebrahimi-Kalan, A.; Mortazavi, Y.; Zarghami, N. Development of Emu oil-loaded PCL/collagen bioactive nanofibers for proliferation and stemness preservation of human adipose-derived stem cells: Possible application in regenerative medicine. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 1978–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, S.B.; Zafar, M.S.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Shah, A.H.; Husain, S.; Rehman, I.U. Electrospinning of chitosan-based solutions for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xingxing, Y.; Linpeng, F.; Linlin, M.; Yunyi, W.; Si, L.; Fan, Y.; Xiaohan, P.; Gejie, L.; Dongdong, Z.; Hongsheng, W. Green electrospun Manuka honey/silk fibroin fibrous matrices as potential wound dressing. Mater. Des. 2017, 119, 76–84. [Google Scholar]
- Moreta, S.; Cahyono, E.; Affandi, N.D.N.; Fadil, F.; Kurniawan, C. Polymeric and non-polymeric nanofiber of cinnamaldehyde from cinnamon oil (Cinnamomum zeylanicum). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1567, 022035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Holtzl, T.; Szekely, G. Scavenging organic micropollutants from water with nanofibrous hypercrosslinked cy-clodextrin membranes derived from green resources. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzer, C.; Armstrong, M.; Shan, B.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Mu, B. Modeling nanoparticle dispersion in electrospun nanofibers. Langmuir 2018, 34, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsey, S.; Absar, S.; Choi, H. Investigation of simultaneous ultrasonic processing of polymer-nanoparticle solutions for electrospinning of nanocomposite nanofibers. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 34, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsey, S.; Absar, S.; Choi, H. Comparative study of polymer dissolution techniques for electrospinning. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 10, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieminen, H.J.; Laidmäe, I.; Salmi, A.; Rauhala, T.; Paulin, T.; Heinämäki, J.; Hæggström, E. Ultrasound-enhanced electrospinning. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rouxel, D.; Hadji, R.; Vincent, B.; Fort, Y. Effect of ultrasonication and dispersion stability on the cluster size of alumina nanoscale particles in aqueous solutions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 382–388. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.L.; Yu, S.H. Nanoparticles meet electrospinning: Recent advances and future prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4423–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, R.S.; Said, S.M.; Shahrir, S.R.; Abdullah, N.; Sabri, M.F.M.; Balamurugan, S.; Miyazaki, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Hashim, N.A.; Habiba, U.; et al. Ionic liquid entrapment by an electrospun polymer nanofiber matrix as a high conductivity polymer electrolyte. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48217–48223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteson, M.J.; Orr, C. Filtration: Principles and Practices, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Heyang, Y.; Zhen, H. Integrating membrane filtration into bioelectrochemical systems as next generation energy-efficient wastewater treatment technologies for water reclamation: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 195, 202–209. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S.J. Handbook of Nonwovens; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ruth, O.; Daphne, H.; Noemí, M.; Antonio, G.; Carlos, N.; Ángeles, B. Application of multi-barrier membrane filtration technologies to reclaim municipal wastewater for industrial use. J. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2014, 43, 263–310. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadzadehmoghadam, S.; Dong, Y.; Barbhuiya, S.; Guo, L.; Liu, D.; Umer, R.; Qi, X.; Tang, Y. Electrospinning: Current status and future trends. Nano-Size Polym. 2016, 89–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultra-web Media Technology. Available online: https://www.donaldson.com/en-be/industrial-dust-fume-mist/technical-articles/ultra-web-media-technology/ (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- Heikkila, P.; Taipale, A.; Lehtimaki, M.; Harlin, A. Electrospinning of polyamides with different chain compositions for filtration application. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jiao, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, B.; Peng, Q. Hierarchical electrospun nanofibers treated by solvent vapor annealing as air filtration mat for high-efficiency PM2.5 capture. Sci. China Mater. 2019, 62, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Hsu, P.-C.; Lee, H.-W.; Zheng, G.; Liu, N.; Li, W.; Cui, Y. Transparent air filter for high-efficiency PM2.5 capture. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bien, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C. Influence of fiber diameter, filter thickness, and packing density on PM2.5 removal efficiency of electrospun nanofiber air filters for indoor applications. Build. Environ. 2020, 170, 106628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaeipour, Y.; Gharehaghaji, A.A.; Bahrami, H. Filtration performance of cigarette filter tip containing nanofibrous filter. J. Ind. Text. 2015, 45, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulevicious, J.; Kliucininkas, L.; Prasauskas, T.; Buivydiene, D.; Martuzevicius, D. The comparative study of a aerosol filtration byelectrospun polyamide, polyvinyl acetate, polyacrylonitrile and cellulose acetate nanofiber media. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 92, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszczyk, T.; Petrik, S.; Donahue, K. Recent development in heavy duty engine air filtration and the role of nanofiber filter media. J. KONES 2009, 16, 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Affandi, N.D.N.; Razak, N.N.A. Removal of pigment from textile wastewater by electrospun nanofibre membrane. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 4, 190–201. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, U.A.; Khatri, Z.; Ahmed, F.; Khatri, M.; Kim, I.-S. Electrospun zein nanofiber as a green and recyclable adsorbent for the removal of reactive black 5 from the aqueous phase. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4340–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaumik, M.; McCrindle, R.I.; Maity, A.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Polyaniline nanofibers as highly effective re-usable adsorbent for removal of reactive black 5 from aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 466, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Abdulhamid, M.A.; Nunes, S.P.; Szekely, G. Hierarchically porous electrospun nanofibrous mats produced from intrinsically microporous fluorinated polyimide for the removal of oils and non-polar solvents. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso-Solares, S.; Pinto, J.; Nanni, G.; Fragouli, D.; Athanassiou, A. Enhanced oil removal from water in oil stable emulsions using electrospun nanocomposite fiber mats. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7641–7650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Z.; Tijing, L.D.; Amarjargal, A.; Park, C.H.; An, K.-J.; Shon, H.K.; Kim, C.S. Removal of oil from water using magnetic bicomponent composite nanofibers fabricated by electrospinning. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 77, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, R.; Kaur, S.; Ma, Z.; Chan, C.; Ramakrishna, S.; Matsuura, T. Electrospun nanofibrous filtration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, R.; Kaur, S.; Feng, C.; Chan, C.; Ramakrishna, S.; Tabe, S.; Matsuura, T. Electrospun nanofibrous polysulfone membranes as pre-filters: Particulate removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 289, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, A.; Mishra, B.G.; Hota, G. Electrospun Fe2O3–Al2O3 nanocomposite fibers as efficient adsorbent for removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 258–259, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Li, F.; Gu, Q.; Liang, C.; Chen, J. Heavy metal-contaminated groundwater treatment by a novel nanofiber membrane. Desalination 2008, 223, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, K.T.; Myung, N.V.; Cwiertny, D.M. Surfactant-assisted fabrication of porous polymeric nanofibers with surface-enriched iron oxide nanoparticles: Composite filtration materials for removal of metal cations. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.E.; Lalia, B.S.; Hashaikeh, R. A review on electrospinning for membrane fabrication: Challenges and applications. Desalination 2015, 356, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, M.K.; Das, B.R.; Prasad, N.; Kishore, B.; Kumar, K. Exploration of nanofibrous coated webs for chemical and biological protection. Zaštita Mater. 2018, 59, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, J.; Bastiaansen, C.W.; Peijs, T. High strength and high modulus electrospun nanofibers. Fibers 2014, 2, 158–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniasadi, M.; Huang, J.; Xu, Z.; Moreno, S.; Yang, X.; Chang, J.; Quevedo-Lopez, M.A.; Naraghi, M.; Minary-Jolandan, M. High-performance coils and yarns of polymeric piezoelectric nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5358–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhineshbabu, N.R.; Karunakaran, G.; Suriyaprabha, R.; Manivasakan, P.; Rajendran, V. Electrospun MgO/Nylon 6 hybrid nanofibers for protective clothing. Nano-Micro Lett. 2014, 6, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Foley, M.; Rowley, A. A novel approach to 3D-printed fabrics and garments. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2015, 2, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Electroloom’s Clothes-Printing Revolution Died. Available online: https://www.engadget.com/2017–09–14-electroloom-clothes-printing-startup-death-aaron-rowley.html (accessed on 28 March 2021).
- Faccini, M.; Vaquero, C.; Amantia, D. Development of protective clothing against nanoparticle based on electrospun nanofibers. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 892894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; You, M.H.; Lou, T.; Yu, M.; Zhang, J.C.; Gong, M.G.; Lv, F.Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Long, Y.Z. Colorful hydrophobic poly (vinyl butyral)/cationic dye fibrous membranes via a colored solution electrospinning process. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graham, K.; Gogins, M.; Schreuder-Gibson, H. Incorporation of electrospun nanofibers into functional structures. Int. Nonwovens J. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. A functional chitosan-based hydrogel as a wound dressing and drug delivery system in the treatment of wound healing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7533–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mengistu Lemma, S.; Bossard, F.; Rinaudo, M. Preparation of pure and stable chitosan nanofibers by electrospinning in the presence of poly (ethylene oxide). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abraham, A.; Soloman, P.A.; Rejini, V.O. Preparation of chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol blends and studies on thermal and mechanical properties. Procedia Technol. 2016, 24, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Annur, D.; Wang, Z.K.; Liao, J.D.; Kuo, C. Plasma-synthesized silver nanoparticles on electrospun chitosan nanofiber surfaces for antibacterial applications. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3248–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Guo, Y.; Wei, Y.; MacDiarmid, A.G.; Lelkes, P.I. Electrospinning polyaniline-contained gelatin nanofibers for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2705–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, A.; Izwan, S.; Wahab, I.F.; Fadil, F.; Dahli, F.N.; Khudzari, M.; Zahran, A.; Adeli, H. A review of electrospun conductive polyaniline based nanofiber composites and blends: Processing features, applications, and future directions. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 356286. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Morshed, M.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrical stimulation of nerve cells using conductive nanofibrous scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 3605–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, S.; Albukhaty, S.; Al-Karagoly, H.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Dewir, Y.H.; Soliman, D.A.; Rizwana, H. Antibacterial activity of honey/chitosan nanofibers loaded with capsaicin and gold nanoparticles for wound dressing. Molecules 2020, 25, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.-J.; Zhou, Q.-H.; Liu, Z.; Hu, P.-Y.; Yuan, Z.; Ramakrishna, S.; Yang, D.-P.; Long, Y.-Z. Bifunctional CuS composite nanofibers via in situ electrospinning for outdoor rapid hemostasis and simultaneous ablating superbug. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouthuy, P.A.; Groszkowski, L.; Ye, H. Performances of a portable electrospinningapparatus. Biotechnol. Lett. 2015, 37, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, S.C.; Qin, C.C.; Yu, M.; Dong, R.H.; Yan, X.; Zhao, H.; Han, W.P.; Zhang, H.D.; Long, Y.Z. A battery-operated portable handheld electrospinning apparatus. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 12351–12355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haik, J.; Kornhaber, R.; Blal, B.; Harats, M. The feasibility of a handheld electro-spinning device for the application of nanofibrous wound dressings. Adv. Wound Care 2017, 6, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sadri, M.; Maleki, A.; Agend, F.; Hosseini, H. Retracted: Fast and efficient electro-spinning of chitosan-Poly (ethylene oxide) nanofibers as potential wound dressingagents for tissue engineering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 126, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Stellenbosch Nanofiber Company (SNC). Available online: https://www.innovus.co.za/spin-out-companies/the-stellenbosch-nanofiber-company-snc.html (accessed on 28 March 2021).
- Bhaskar, P.; Bosworth, L.A.; Wong, R.; O’brien, M.A.; Kriel, H.; Smit, E.; McGrouther, D.A.; Wong, J.K.; Cartmell, S.H. Cell response to sterilized electrospun poly (ɛ-caprolactone) scaffolds to aid tendon regeneration in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 105, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akduman, C.; Kumbasar, E.P.A. Electrospun Polyurethane Nanofibers. In Aspects of Polyurethanes; Ylmaz, F., Ed.; Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2017; pp. 17–52. [Google Scholar]
- Knoff, A. Nanofibers Allergen Barrier Fabric. U.S. Patent 8,980,772, 29 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Phonix Nanofibre Acoustic Technology. Available online: https://www.revolutionfibres.com/products/phonix/ (accessed on 28 March 2021).
- Han, D.; Steckl, A. “Mix-and-Match”: A review of coaxial electrospinning formation of complex polymer fibers and their applications. ChemPlusChem. 2019, 84, 1453–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, B.; de Morais, M.G.; de Morais, E.G.; da Silva Vaz, B.; Costa, J.A.V. Electrospun Polymeric Nanofibers in Food Packaging. In Impact of Nanoscience in the Food Industry; Grumezescu, A.H., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 387–417. [Google Scholar]
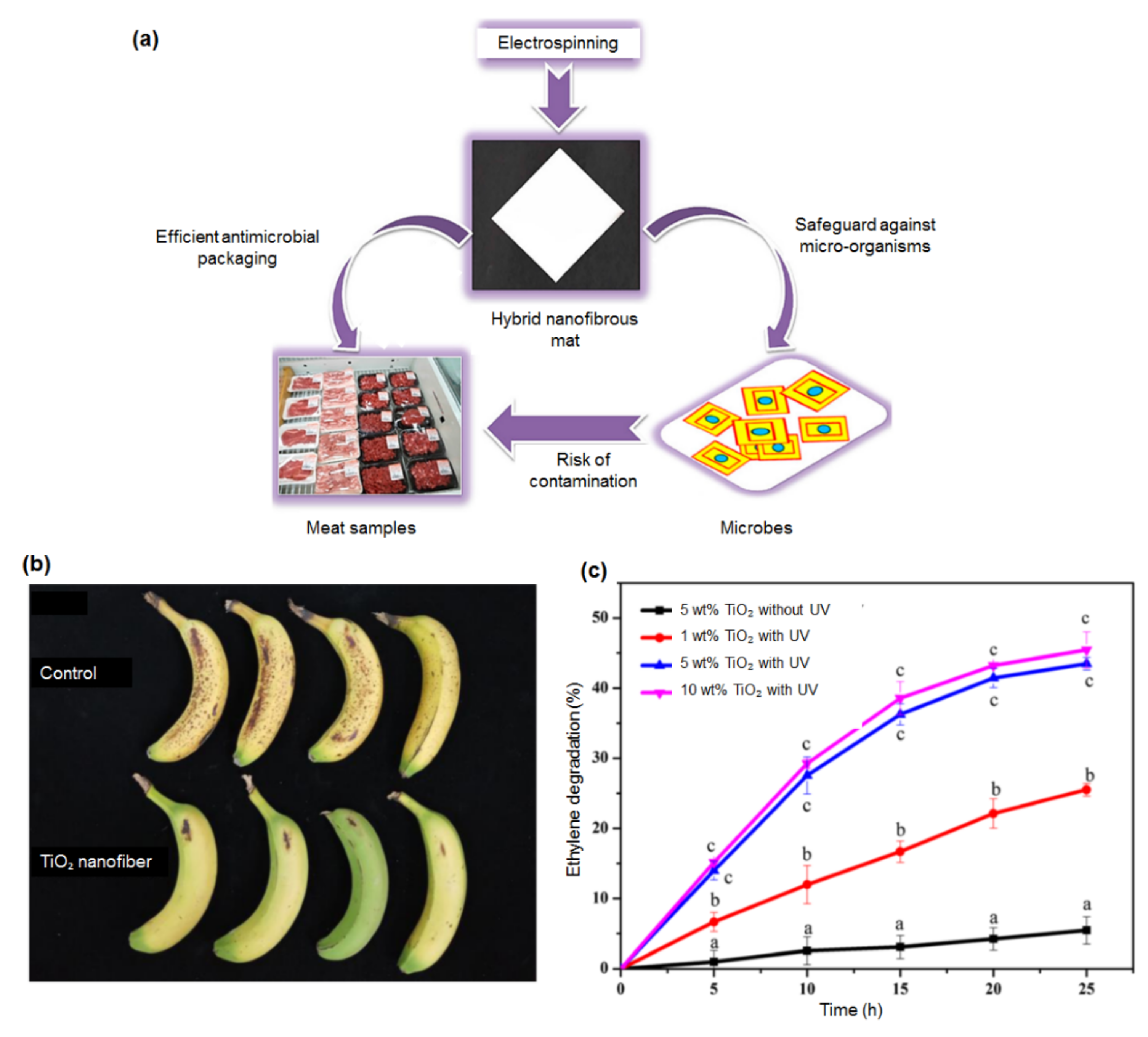
- Amna, T.; Yang, J.; Ryu, K.S.; Hwang, I.H. Electrospun antimicrobial hybrid mats: Innovative packaging material for meat and meat-products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 52, 4600–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, Y.; Wen, Y. Electrospun nanofibers containing TiO2 for the photocatalytic degradation of ethylene and delaying postharvest ripening of bananas. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2019, 12, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, S.; Tanaka, S.; Tsukamoto, H. Kinetic studies of oxidation of ethylene over a TiO2 photocatalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1999, 121, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneerat, C.; Hayata, Y. Efficiency of TiO2 photocatalytic reaction on delay of fruit ripening and removal of off-flavors from the fruit storage atmosphere. Trans. ASAE 2006, 49, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneerat, C.; Hayata, Y.; Egashira, N.; Sakamoto, K.; Hamai, Z.; Kuroyanagi, M. Photocatalytic reaction of TiO2 to decompose ethylene in fruit and vegetables storage. Trans. ASAE 2003, 46, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Zhu, D.-H.; Wu, H.; Zong, M.-H.; Jing, Y.-R.; Han, S.-Y. Encapsulation of cinnamon essential oil in electrospun nanofibrous film for active food packaging. Food Control. 2016, 59, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, A.C.; East, A.R.; Hindmarsh, J.P.; Heyes, J.A. Moisture loss is the major cause of firmness change during postharvest storage of blueberry. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2013, 79, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paull, R.E.; Gross, K.; Qiu, Y. Changes in papaya cell walls during fruit ripening. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 1999, 16, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Lugo, A.C.; Lim, L.T. Controlled release of allyl isothiocyanate using soy protein and poly (lactic acid) electrospun fibers. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi-Azarbayjani, A.; Qun, L.; Chan, Y.W.; Chan, S.Y. Novel vitamin and gold-loaded nanofiber facial mask for topical delivery. Aaps Pharmscitech 2010, 11, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camerlo, A.; Vebert-Nardin, C.; Rossi, R.M.; Popa, A.M. Fragrance encapsulation in polymeric matrices by emulsion electrospinning. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 3806–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, R.; Sundarrajan, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Recent trends in nanofibrous membranes and their suitability for air and water filtrations. Membranes 2011, 1, 232–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Research and Markets: Nanofibers Market Report 2015–2020: The Key Market Trends, Growth Drivers & Challenges. Available online: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20150922005617/en/Research-and-Markets-Nanofibers-Market-Report-2015–2020-The-Key-Market-Trends-Growth-Drivers-Challenges (accessed on 20 March 2018).



| Product | Company | Application | Description | Company Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Insert™ | 3D Biotek | Cell culture device for laboratory tissue culture | 3D cell culture insert made of PS, PCL and PDLLGA | http://www.3dbiotekstore.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Absorv™ | Zeus | Nonwoven fibrous materials | Bioabsorbable polymers made for of a wide variety of medical products for both preventive care and disease treatment | https://www.zeusinc.com (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Aeos™ | Zeus | Nonwoven fibrous materials | Composed of a number of solid nodes interconnected by a matrix of thin fibrils, which allows to excel in such diverse applications as sutures | https://www.zeusinc.com (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Antidust half-mask | Esfil Techno | Filtering materials, half-masks, analytical tapes | Produce and develop highly efficient nonwoven polymer filtering materials made of micro and nano fibres | https://www.esfiltehno.ee/en/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| AVflo™ Vascular Access Graft | Nicast Ltd. | Implantable medical devices | Is a multi-layered self-sealing vascular access graft made of electrospun polycarbonate urethane nanofibers | http://www.nicast.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Bio-Spun™ | BioSurfaces Inc. | Novel three-dimensional (3D) nanofiber scaffolds | Electrospun fibers mimic natural extracellular matrix produced from variety of polymer materials and thicknesses | https://www.biosurfaces.us/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Bioweb™ | Zeus | Nonwoven fibrous materials | Possesses a microporous nature that is similar to expanded PTFE (ePTFE) but achieves this without the nodes and fibrils associated with ePTFE | https://www.zeusinc.com (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| BreaSAFE® | PARDAM NANO4FIBERS | Nanofiber based respirator | Provides an effective protection against microbes, particles, aerosols and odors and to a limited extent, also against toxic gases and vapours | https://www.nano4fibers.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Cytoweb® Sheets | Espin Technologies | Cell culture device for laboratory tissue culture | Superior adhesion and proliferation of in vitro cell cultures, as compared to traditional lab plastic ware | http://www.espintechnologies.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Exceed® | Espin Technologies | Air filters media | A product designed to capture particulates while providing openings for un-hindered pathway for air flow | http://www.espintechnologies.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| FERENA | Koken Ltd. | Nanofiber air filter | Innovative electrospinning technology targeted to expand a clean zone through nanofibrous filter membrane | https://www.koken-ltd.co.jp/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| FiberTrap | FiberTrap | Bedding microfiber trapping material | The Fibertrap microfiber is patent-protected and manufactured with safe, green, recycled polymer materials through electrospinning, with a fluffy three-dimensional structure that immediately entangles the bed bugs upon contact | https://fibertrap.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Filter half-masks | Sorbent | Respiratory personal protective equipment (RPE) | Nanofibers filter half masks for respiratory personal protective equipment (RPE) | http://en.sorbent.su/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Filter NanoFiber | Astral Pool | Cartridge water filter | Self-cleaning cartridge filter which is able to filter particles of between 5 and 8 microns | https://www.astralpool.com/en/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| FilterLayr | NanoLayr | Air filtration media | A product made of electrospun nanofiber which can be infused with active additives designed to trap and neutralize even the smallest airborne particles for filters and masks | https://www.nanolayr.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| HealSmart™ | PolyRemedy | Wound Dressings | Wound dressing with advanced technology with personalized therapeutics to improve wound healing outcomes | https://www.polyremedy.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Microfiber separation media | Nanopareil LLC | Microfiber separation media | Nanofiber based products that provide an enormous amount of specific surface area along with a controlled porosity and offers modular, off-the- shelf installation into existing manufacturing processes | https://www.nanopareil.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Micrograde NF filter | MANN+HUMMEL | Nanofiber-coated air filters | A filtration media that consists of a cellulose carrier material coated with extremely thin layers of ultra-fine polymer fibers | https://www.mann-hummel.com/en.html (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Mimetix® scaffold | Electrospinning Company | Nanofibrous biomaterials for use in tissue-regenerative devices | Develops and manufactures variety of electrospun polymer scaffolds made from PLA, PLGA, PCL, PLCL and PAN | https://www.electrospinning.co.uk/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Naked filter | Liquidity Corporation | Nanofiber filter membranes | Nanofiber filter membranes fitted encapsulated drinking water purification cartridges | https://liquico.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Nanodream | NanoLayr | Nanofiber pillow lining | Anti-allergy bedding made of nonwoven electrospun nanofibers | https://www.nanolayr.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Nanofiber Solutions™ | Nanofiber Solutions | Novel three-dimensional (3D) nanofiber scaffolds | Provide an ideal 3D substrate uses of aligned (NanoAligned™) or randomly oriented (NanoECM™ ) polymer nanofibers integrated into standard multi-well cell culture dishes | https://nanofibersolutions.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Nanofibrous biomaterials | NanoSpun Technologies | Nanofibrous biomaterials for use in tissue-regenerative devices | Develops and produces disruptive first-of-its-kind live-active biological tissues for cosmetics, well-being and health applications | http://www.nanospuntech.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Nanotrap™ | Coway | Nanofibers Filter System | Water filter system which is effectively reduces bio-fouling materials such as cell debris, bacteria, viruses, with a patented electrospun coating | https://www.coway.com.my/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| NeoDura™ | Medprin Biotech GmbH | Dural Patch | Absorbable Dural repair patch made of degradable material poly-L-lactic acid and gelatin | http://www.medprin.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Neotherix scaffold | Neotherix | Bioresorbable scaffolds | Scaffolds possess a nonwoven three-dimensional architecture, comprising nano/micro-scale synthetic bioresorbable polymer fibres, which is highly porous scaffold structure supports the migration and proliferation of fibroblast cells from surrounding healthy skin tissue in order to facilitate healing of the wound | http://www.neotherix.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Nexture® | Lime | Technical textiles | Multi-functioning clothing with nanofiber membrane laminations which offer water and wind protection with a truly breathable difference, that can be worn during commutes, light workouts and various outdoor activities | http://limenano.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| NnF CERAM® | PARDAM NANO4FIBERS | Inorganic nanofibers | Inorganic nanofibers are special function materials in the form of thin fibers, 3D cotton like ceramic, metal and powder like materials | https://www.nano4fibers.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| NnF MBRANE® | PARDAM NANO4FIBERS | Filtration materials | A product suitable as separation membranes for many different products or filtration materials for water and air purification with very low pressure drop and very high filtration efficiency | https://www.nano4fibers.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Nonwoven nanofibers | Soft Materials and Technologies S.r.l. | Nonwoven nanofibers fibrous tissues, either in the form of nonwoven mats or as uniaxial aligned fibers | Provide nanostructured materials and nanofibers made by thermoplastic polymers, biodegradable polymers, optically active organic compounds and organic/inorganic hybrids | http://www.smtnano.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| PK Papyrus® covered coronary stent system | BIOTRONIK | Covered stent | Electrospun PU covered stent for use in the emergency treatment of acute coronary perforations | http://www.biotronik.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| ProTura® Nanofiber | United Air Specialists, Inc. | Cartridge filter | A cellulose nanofiber-based filtration media for cartridge elements for use in cartridge style dust collectors | http://www.clarcorindustrialair.com (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| ReDura™ | Medprin Biotech GmbH | Synthetic Dural Substitute | Fully degradable and absorbable, leaving no foreign body in-situ and is replaced by regenerated Dura tissue | http://www.medprin.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| ResQFoamTM | Arsenal Medical | Therapeutic foams | In-situ forming polymeric foam made up of core-shell fibers for intracavity hemorrhage treatment | http://www.arsenalmedical.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Retissue™ | Medprin Biotech GmbH | Bioresorbable Membrane | A synthetic fibrous membrane made of polylactic acid (PLA) and gelatin | http://www.medprin.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Return focus pod | IQ Commercial. | Acoustic soundproofing | Acoustic soundproofing material which has a destination touchdown point of soft walls which absorb noise in offices and offers a privacy for individual focused work | http://www.iqcommercial.co.nz/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| RIFTELEN® N15 | FILTREX and PARDAM NANO4FIBERS | Filtration media for food product | Nanofibrous filtration membrane is suitable for filtration of cooking oils as well as liqueurs, spirits, wine, beer, lemonades, fruit juices and others | https://riftelen.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Smart mask | NASK HK | Nanofiber face mask | Face mask with unique nanofiber of air purifying and bacteria killing mask | http://nask.hk/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| SNC BEST™ | Stellenbosch Nanofiber Company | Nonwoven fibrous materials | Develop and manufacture nanofiber-based materials for medical applications | https://sncfibers.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| SonoLayr | NanoLayr | Acoustic soundproofing | A lightweight sound absorption media, which is specifically designed to enhance the acoustic performance of any sound-control product | https://www.nanolayr.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| SpinCare™ | Nanomedic Technologies | Commercialized electrospinning wound treatment portable device | Utilizes proprietary Electrospun Healing Fiber (EHF™) technology to treat even the most severe and complicated wounds with a single application, eliminating the need for painful re-dressings | https://nanomedic.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| SpurTex® | SPUR | Air filter materials | Materials with high air-filter performance when separating ultrafine particles | https://www.spur.cz/cs/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| StypCel™ | Medprin Biotech GmbH | Absorbable Hemostat | For treatment in hemostasis in capillary and venous, as well as small artery, bleeding | http://www.medprin.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Technoweb™ | Lime | Nanofiber-based filters | Nanofiber filter medias that allow surface filtration to improve the efficiency and extend the lifetime of an HVAC and automotive engine and liquid and dust collectors | http://limenano.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Tubular and disc scaffold | SKE Research Equipment | Scaffold for 3D cell cultures and tissue engineering applications | Tubular and disc scaffolds made of silk fibroin and PCL | https://www.ske.it/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Ultra-Web® | Donaldson | Cartridge air filters | Cartridge air filters that offer a longer filter life, lower pressure drop and a reduction in energy usage | https://www.donaldson.com/en-sg/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| Wetlaid Nonwoven Fabrics | Hirose Paper Mfg Co., Ltd. | Nanofiber-coated paper | Manufactures wetlaid nonwoven electrospun nanofibers fabrics | https://www.hirose-paper-mfg.co.jp/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
| XantuLayr® | NanoLayr | Fiber-reinforced composite | A product consists of interleaving nanofiber veil, for use in fiber reinforced thermoset polymer composite materials | https://www.nanolayr.com/ (accessed on 17 June 2021) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fadil, F.; Affandi, N.D.N.; Misnon, M.I.; Bonnia, N.N.; Harun, A.M.; Alam, M.K. Review on Electrospun Nanofiber-Applied Products. Polymers 2021, 13, 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132087
Fadil F, Affandi NDN, Misnon MI, Bonnia NN, Harun AM, Alam MK. Review on Electrospun Nanofiber-Applied Products. Polymers. 2021; 13(13):2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132087
Chicago/Turabian StyleFadil, Fatirah, Nor Dalila Nor Affandi, Mohd Iqbal Misnon, Noor Najmi Bonnia, Ahmad Mukifza Harun, and Mohammad Khursheed Alam. 2021. "Review on Electrospun Nanofiber-Applied Products" Polymers 13, no. 13: 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132087
APA StyleFadil, F., Affandi, N. D. N., Misnon, M. I., Bonnia, N. N., Harun, A. M., & Alam, M. K. (2021). Review on Electrospun Nanofiber-Applied Products. Polymers, 13(13), 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132087







