Preparation and Properties of Wet-Spun Microcomposite Filaments from Various CNFs and Alginate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Characteristics of PCNF, LCNF, and TOLCNF
3.2. Viscosity of the Wet-Spinning Suspension
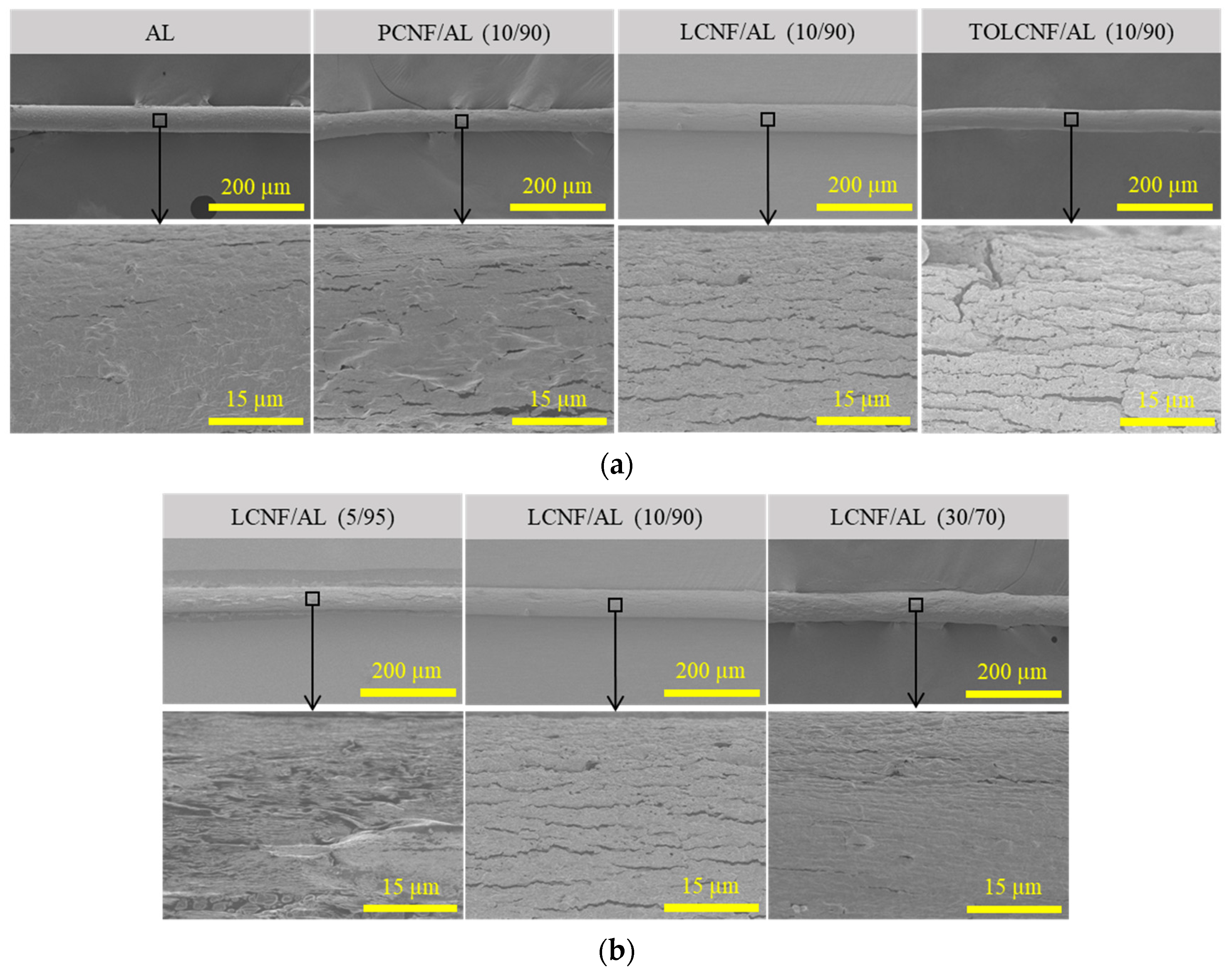
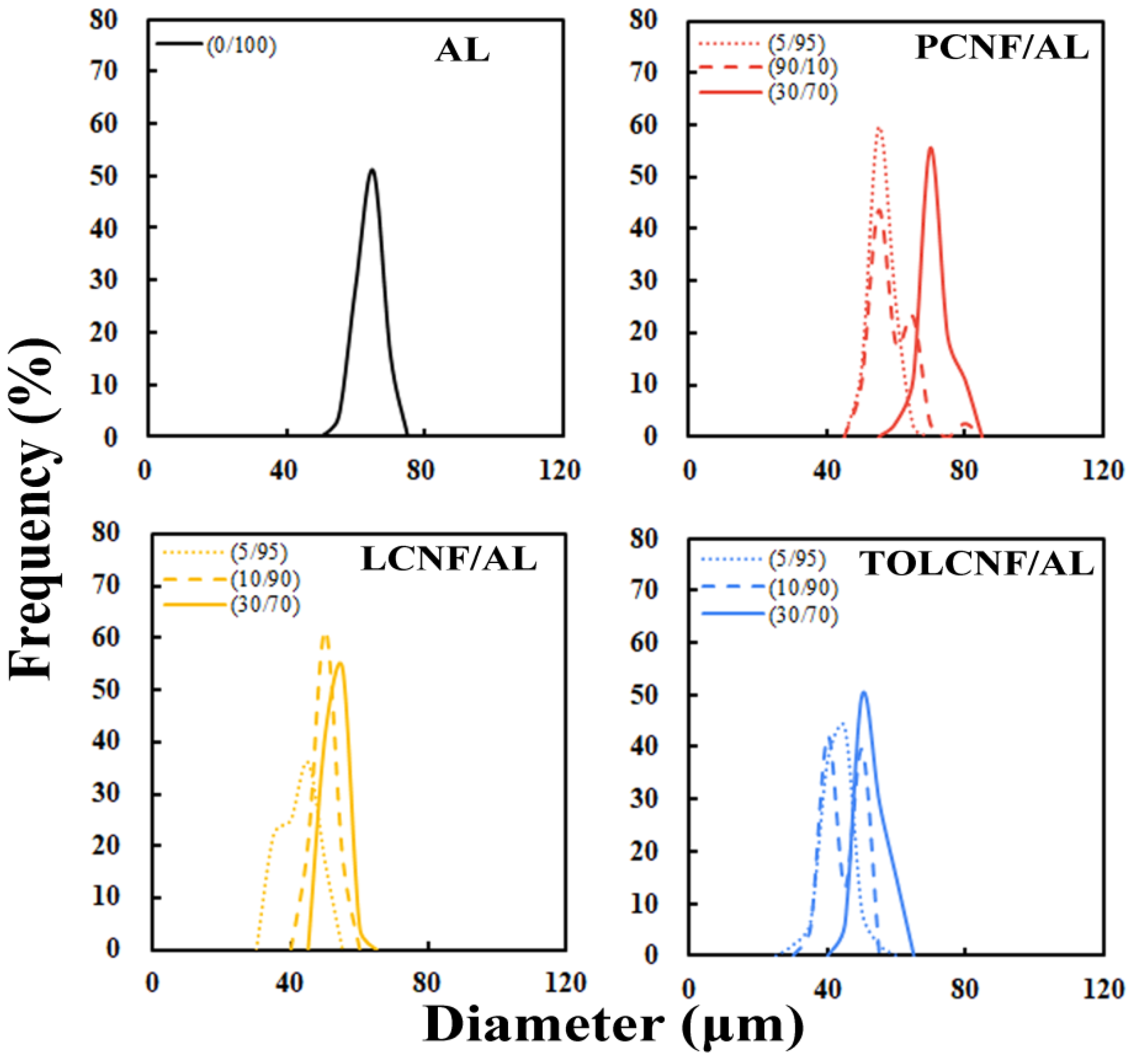
3.3. Morphological Characteristics of Wet-Spun Filaments
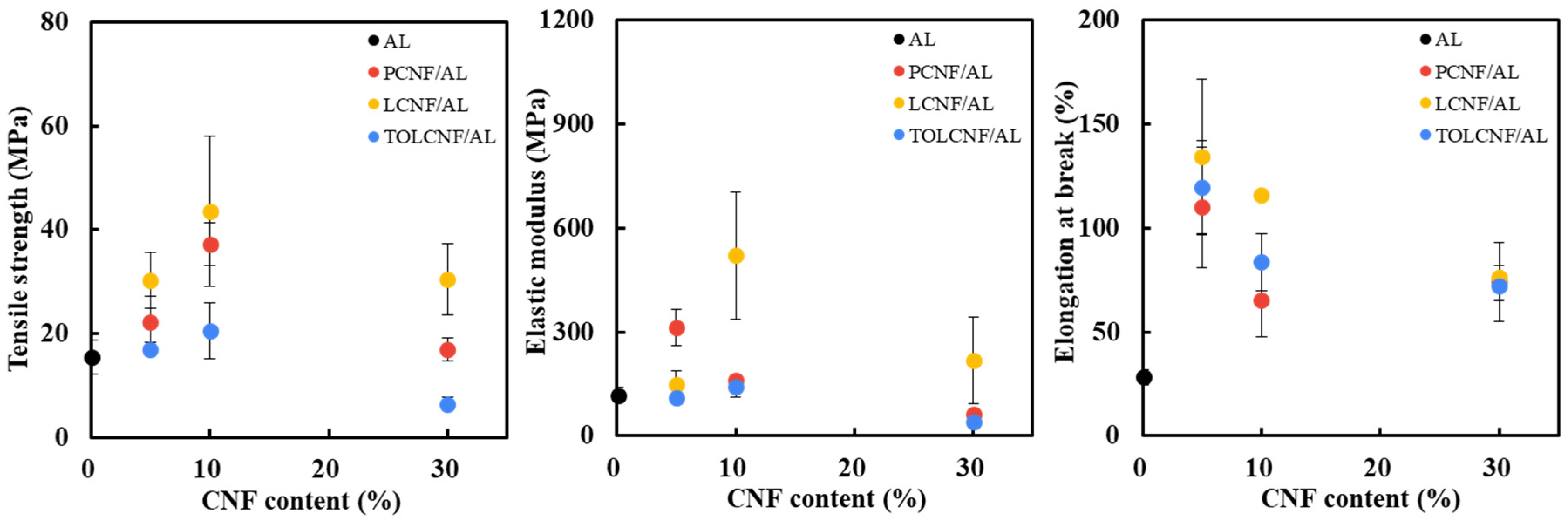
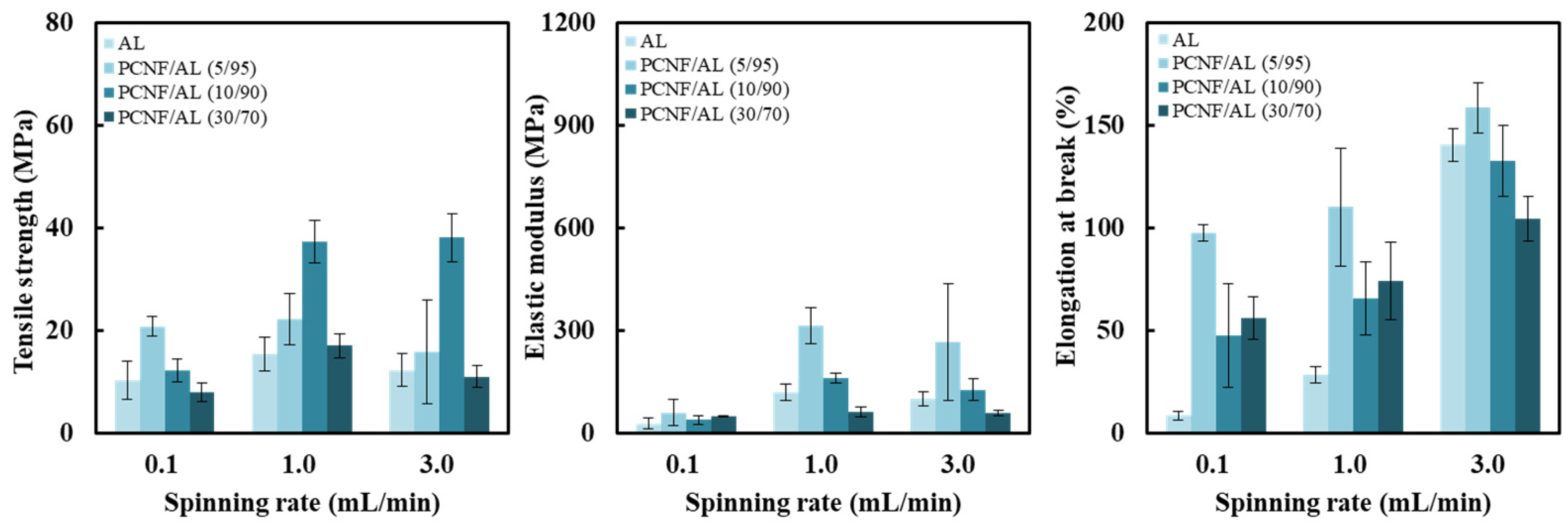
3.4. Tensile Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, X.; Li, R.; Zhao, X.; Ji, Q.; Xing, Y.; Sunarso, J.; Xia, Y. Biopolymer composite fibres composed of calcium alginate reinforced with nanocrystalline cellulose. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 96, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.K.; Liu, L.; Yao, J.M. Fabrication and Characterization of Alginate Fibers by Wet-Spinning. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 796, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y. Alginate fibres: An overview of the production processes and applications in wound management. Polym. Int. 2007, 57, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Q.; Ma, X.; Quan, F.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y. The preparation of alginate-AgNPs composite fiber with green approach and its antibacterial activity. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 24, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Ci, M.; Sui, S.; Zhu, P. Sodium alginate/cellulose nanocrystal fibers with enhanced mechanical strength prepared by wet spinning. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2019, 14, 155892501984755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedê, P.M.; Da Silva, M.H.P.; Figueiredo, A.B.-H.D.S.; Finotelli, P.V. Nanostructured magnetic alginate composites for biomedical applications. Polímeros 2017, 27, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, M.; Alboofetileh, M.; Rezaei, M.; Behrooz, R. Comparing physico-mechanical and thermal properties of alginate nanocomposite films reinforced with organic and/or inorganic nanofillers. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.-W. Physical and mechanical properties of water resistant sodium alginate films. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 37, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureña-Benavides, E.E.; Brown, P.J.; Kitchens, C.L. Effect of Jet Stretch and Particle Load on Cellulose Nanocrystal−Alginate Nanocomposite Fibers. Langmuir 2010, 26, 14263–14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Bugnicourt, E.; Latorre, M.; Jorda, M.; Sanz, Y.E.; Lagaron, J.M.; Miesbauer, O.; Bianchin, A.; Hankin, S.; Bölz, U.; et al. Review on the Processing and Properties of Polymer Nanocomposites and Nanocoatings and Their Applications in the Packaging, Automotive and Solar Energy Fields. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Luo, J.; Gulgunje, P.V.; Kumar, S. Structural and Functional Fibers. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2017, 47, 331–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, B.; Abraham, E.; Pothan, L.A.; Cordeiro, N.; Faria, M.; Thomas, S. Biodegradable Nanocomposite Films Based on Sodium Alginate and Cellulose Nanofibrils. Materials 2016, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B.; Huang, Q.; Yu, B.; Long, G.; Chen, H. A fractal model for predicting oxygen effective diffusivity of porous media with rough surfaces under dry and wet conditions. Fractals 2021, 29, 2150076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Liang, M.; Chen, X.; Long, G. A fractal model for kozeny–Carman constant and dimensionless permeability of fibrous porous media with roughened surfaces. Fractals 2019, 27, 1950116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Huang, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Long, G. A fractal model for capillary flow through a single tortuous capillary with roughened surfaces in fibrous porous media. Fractals 2021, 29, 2150017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Iwamoto, A.S.; Yano, H. Obtaining Cellulose Nanofibers with a Uniform Width of 15 nm from Wood. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3276–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alle, M.; Bandi, R.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.-C. Recent trends in isolation of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils from various forest wood and nonwood products and their application. In Nanomaterials for Agriculture and Forestry Applications; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 41–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.-C. Nanocellulose Applications for Drug Delivery: A Review. J. For. Environ. Sci. 2019, 35, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, G.-J.; Han, S.-Y.; Park, C.-W.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, E.-A.; Kim, N.-H.; Alle, M.; Bandi, R.; Lee, S.-H. Adsorption Characteristics of Ag Nanoparticles on Cellulose Nanofibrils with Different Chemical Compositions. Polymers 2020, 12, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.; Balcells, M.; Cequier, E.; Canela-Garayoa, R. Effect of Four Novel Bio-Based DES (Deep Eutectic Solvents) on Hardwood Fractionation. Molecules 2020, 25, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Fu, H.; Tan, Y.; Sui, K.; Xia, Y. Functionalized alginate with liquid-like behaviors and its application in wet-spinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.R.; Lee, K.H.; Kang, E.; Kim, D.-S.; Lee, S.-H. Microfluidic wet spinning of chitosan-alginate microfibers and encapsulation of HepG2 cells in fibers. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 022208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.J.; Huang, P.L.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, Y.Y.; Liu, Q.Y.; Sun, R.C. Comparison of acid-hydrolyzed and TEMPO-oxidized nanocellulose for reinforcing alginate fibers. BioResources 2017, 12, 8180–8198. [Google Scholar]
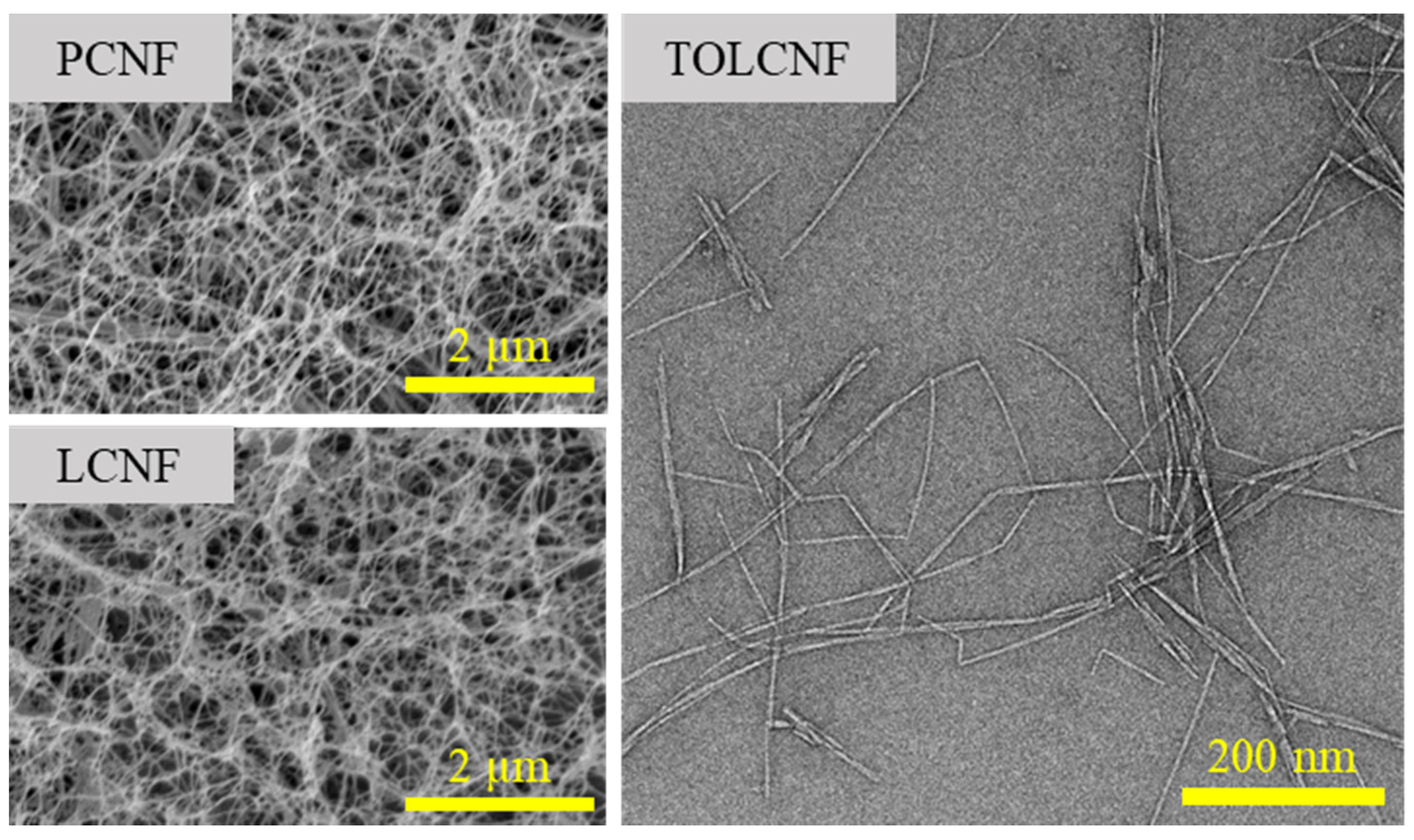



| Sample | Average Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|
| PCNF | 17.4 ± 2.1 |
| LCNF | 16.5 ± 1.2 |
| TOLCNF | 3.5 ± 1.0 |
| Ratio of CNF/AL | Viscosity (mPa·s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNF | AL | SR 0.40 s−1 | SR 0.66 s−1 | SR 1.32 s−1 | |
| AL | - | 100 | 1856 | 1818 | 1727 |
| PCNF/AL | 5 | 95 | 1843 | 1667 | 1515 |
| 10 | 90 | 1693 | 1652 | 1485 | |
| 30 | 70 | 2223 | 1909 | 1455 | |
| LCNF/AL | 5 | 95 | 1570 | 1142 | 970 |
| 10 | 90 | 2168 | 1992 | 1769 | |
| 30 | 70 | 4425 | 3258 | 2371 | |
| TOLCNF/AL | 5 | 95 | 1970 | 1689 | 1371 |
| 10 | 90 | 3475 | 2424 | 1640 | |
| 30 | 70 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Ratio of CNF/AL | Spinning Rate (mL/min) | Average Diameter (µm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNF | AL | |||
| AL | - | 100 | 0.1 | 50.68 ± 3.08 |
| 1.0 | 61.27 ± 3.20 | |||
| 3.0 | 66.22 ± 6.28 | |||
| PCNF/AL | 5 | 95 | 1.0 | 53.25 ± 3.10 |
| 10 | 90 | 1.0 | 56.15 ± 6.09 | |
| 30 | 70 | 0.1 | 51.01 ± 5.15 | |
| 1.0 | 69.06 ± 4.34 | |||
| 3.0 | 73.70 ± 9.42 | |||
| LCNF/AL | 5 | 95 | 1.0 | 40.20 ± 4.80 |
| 10 | 90 | 1.0 | 47.44 ± 2.63 | |
| 30 | 70 | 0.1 | 50.08 ± 3.45 | |
| 1.0 | 50.36 ± 2.65 | |||
| 3.0 | 64.08 ± 3.70 | |||
| TOLCNF/AL | 5 | 95 | 1.0 | 40.17 ± 4.41 |
| 10 | 90 | 1.0 | 42.19 ± 5.46 | |
| 30 | 70 | 0.1 | 44.21 ± 4.89 | |
| 1.0 | 49.89 ± 3.92 | |||
| 3.0 | 70.37 ± 5.62 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.-S.; Park, C.-W.; Han, S.-Y.; Lee, E.-A.; Cindradewi, A.W.; Kim, J.-K.; Kwon, G.-J.; Seo, Y.-H.; Yoo, W.-J.; Gwon, J.; et al. Preparation and Properties of Wet-Spun Microcomposite Filaments from Various CNFs and Alginate. Polymers 2021, 13, 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111709
Park J-S, Park C-W, Han S-Y, Lee E-A, Cindradewi AW, Kim J-K, Kwon G-J, Seo Y-H, Yoo W-J, Gwon J, et al. Preparation and Properties of Wet-Spun Microcomposite Filaments from Various CNFs and Alginate. Polymers. 2021; 13(11):1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111709
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Ji-Soo, Chan-Woo Park, Song-Yi Han, Eun-Ah Lee, Azelia Wulan Cindradewi, Jeong-Ki Kim, Gu-Joong Kwon, Young-Ho Seo, Won-Jae Yoo, Jaegyoung Gwon, and et al. 2021. "Preparation and Properties of Wet-Spun Microcomposite Filaments from Various CNFs and Alginate" Polymers 13, no. 11: 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111709
APA StylePark, J.-S., Park, C.-W., Han, S.-Y., Lee, E.-A., Cindradewi, A. W., Kim, J.-K., Kwon, G.-J., Seo, Y.-H., Yoo, W.-J., Gwon, J., & Lee, S.-H. (2021). Preparation and Properties of Wet-Spun Microcomposite Filaments from Various CNFs and Alginate. Polymers, 13(11), 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111709







