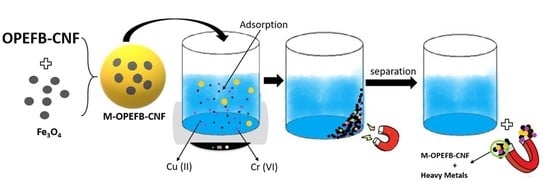
Isolation and Characterization of Magnetic Oil Palm Empty Fruits Bunch Cellulose Nanofiber Composite as a Bio-Sorbent for Cu(II) and Cr(VI) Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
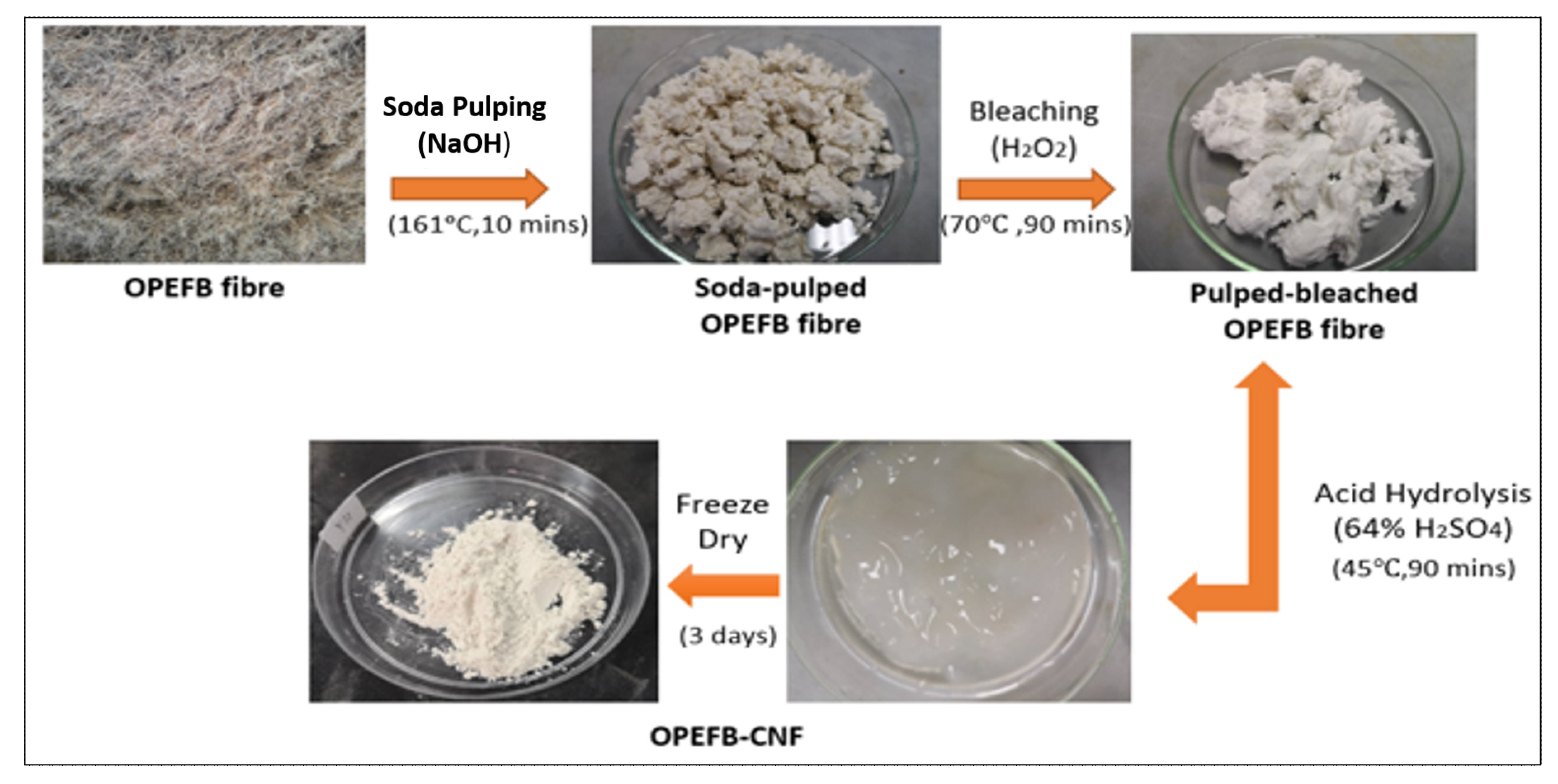
2.2. Isolation of Cellulose Nanofiber
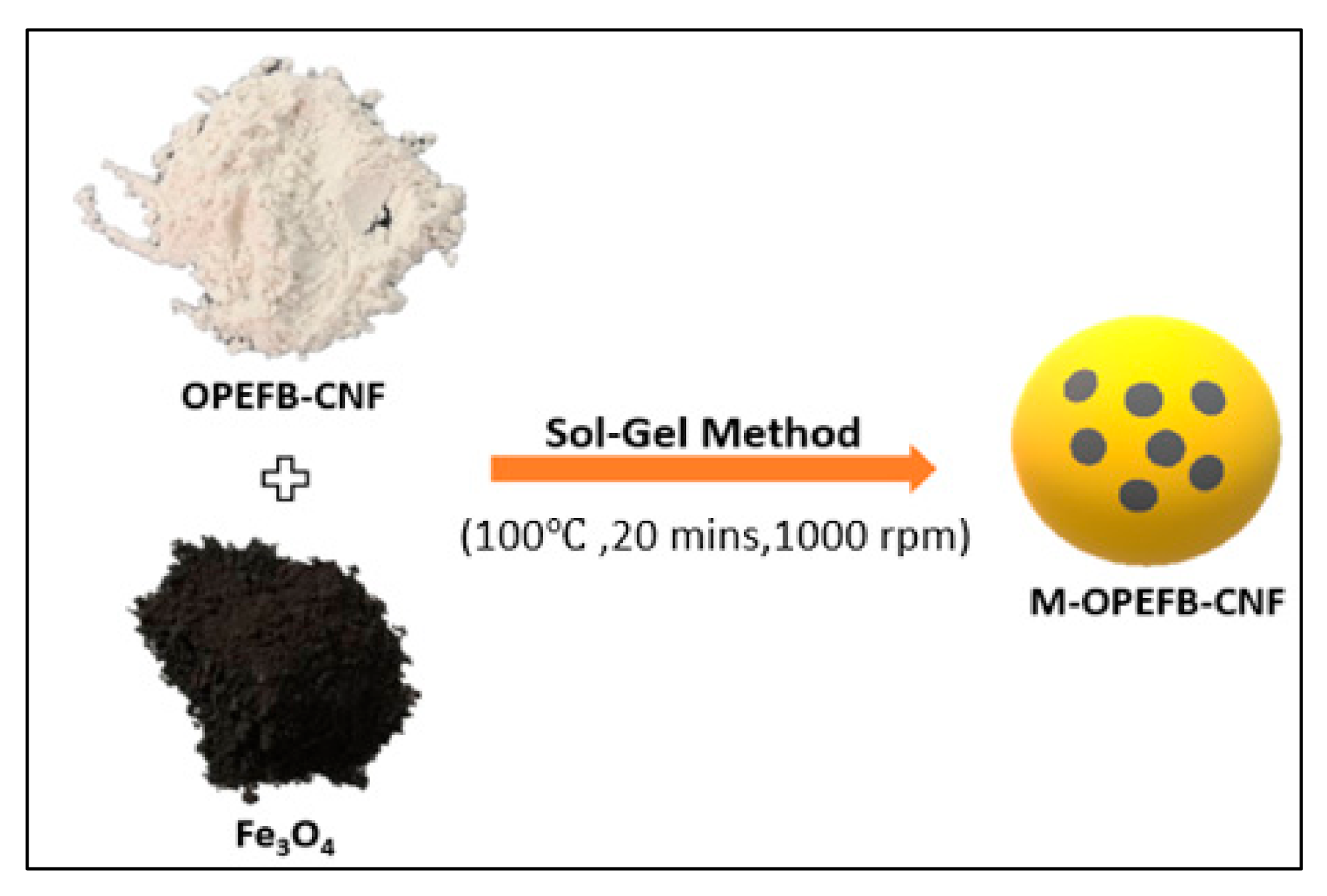
2.3. Preparation of Magnetic OP-EFB Nanofiber Composite
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Adsorption of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) Using M-OPEFB-CNF Composite
2.6. Adsorption Isotherm
2.7. Kinetics Modelling
2.8. Reusability
3. Result and Discussion
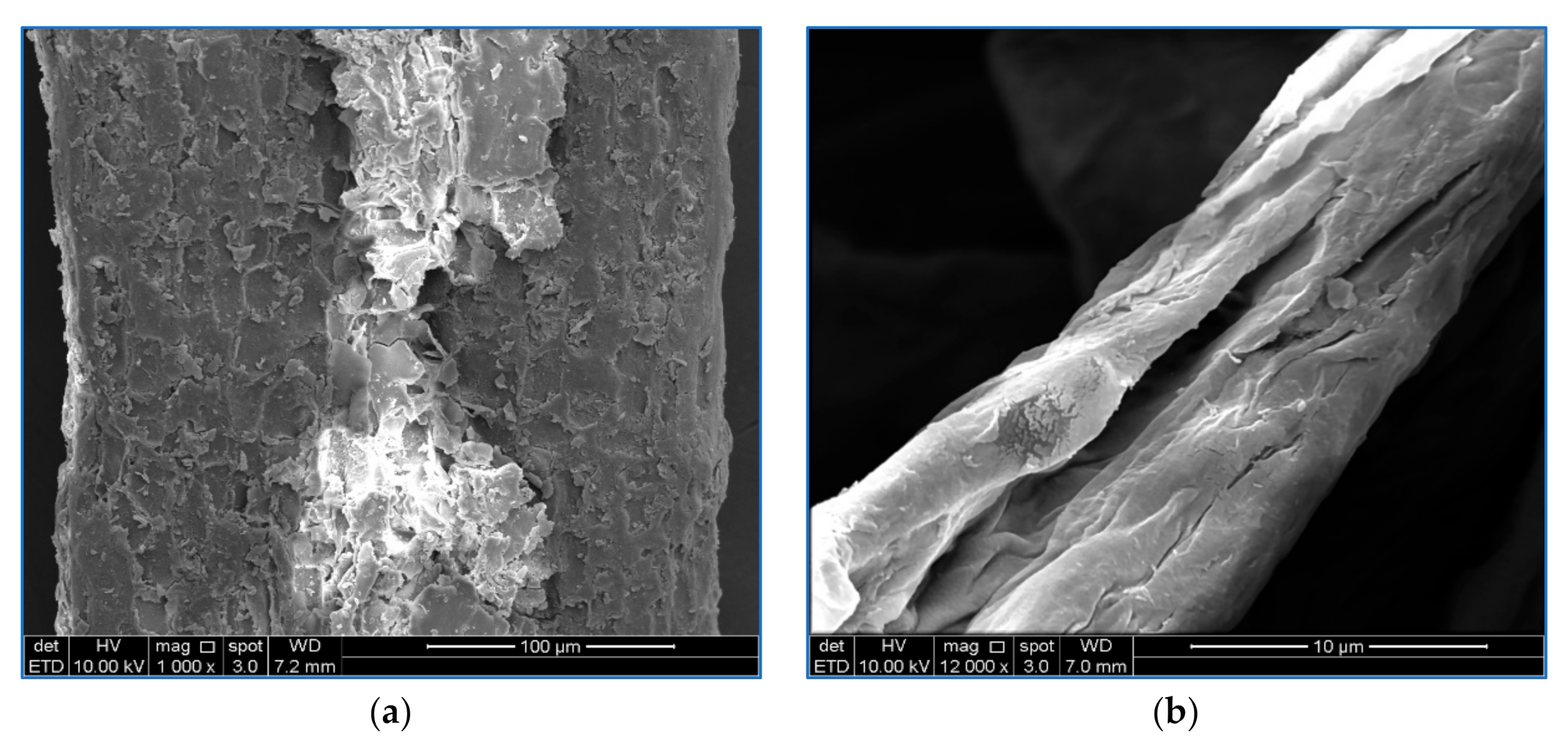
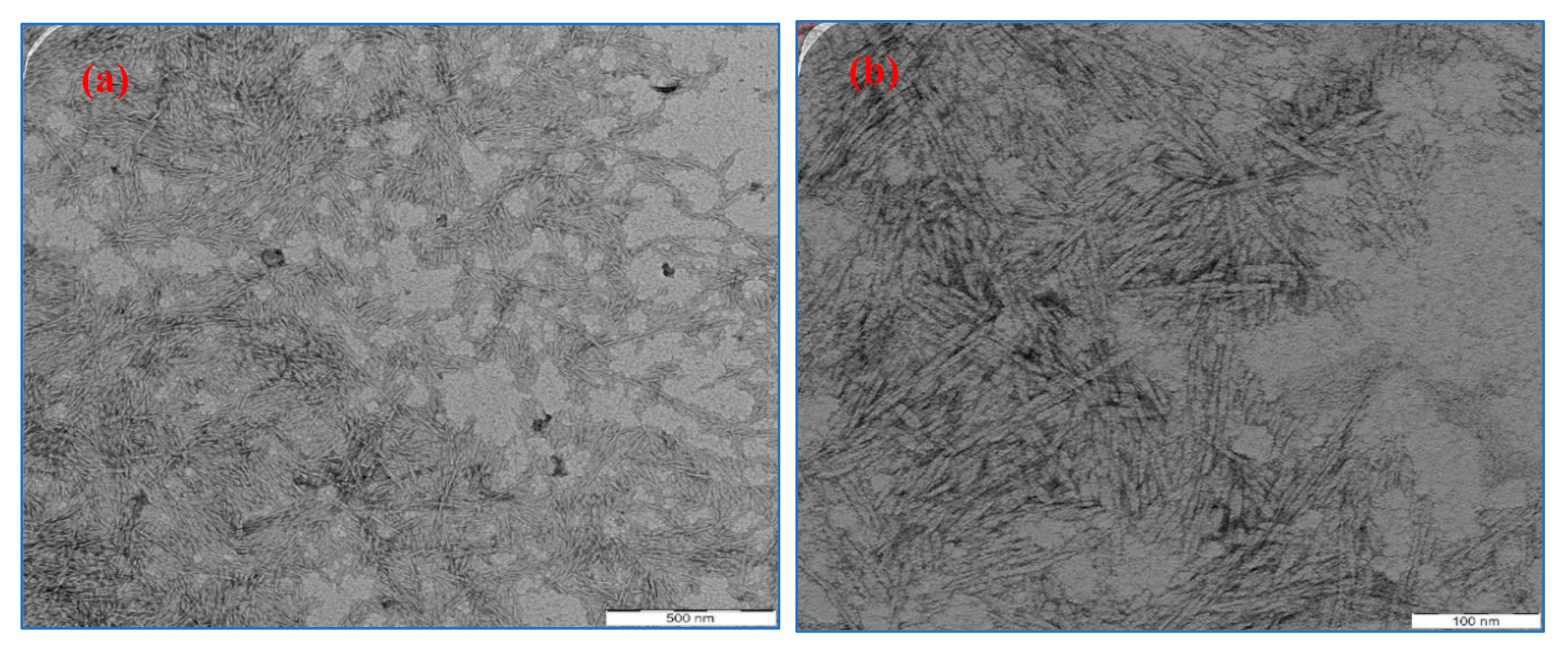
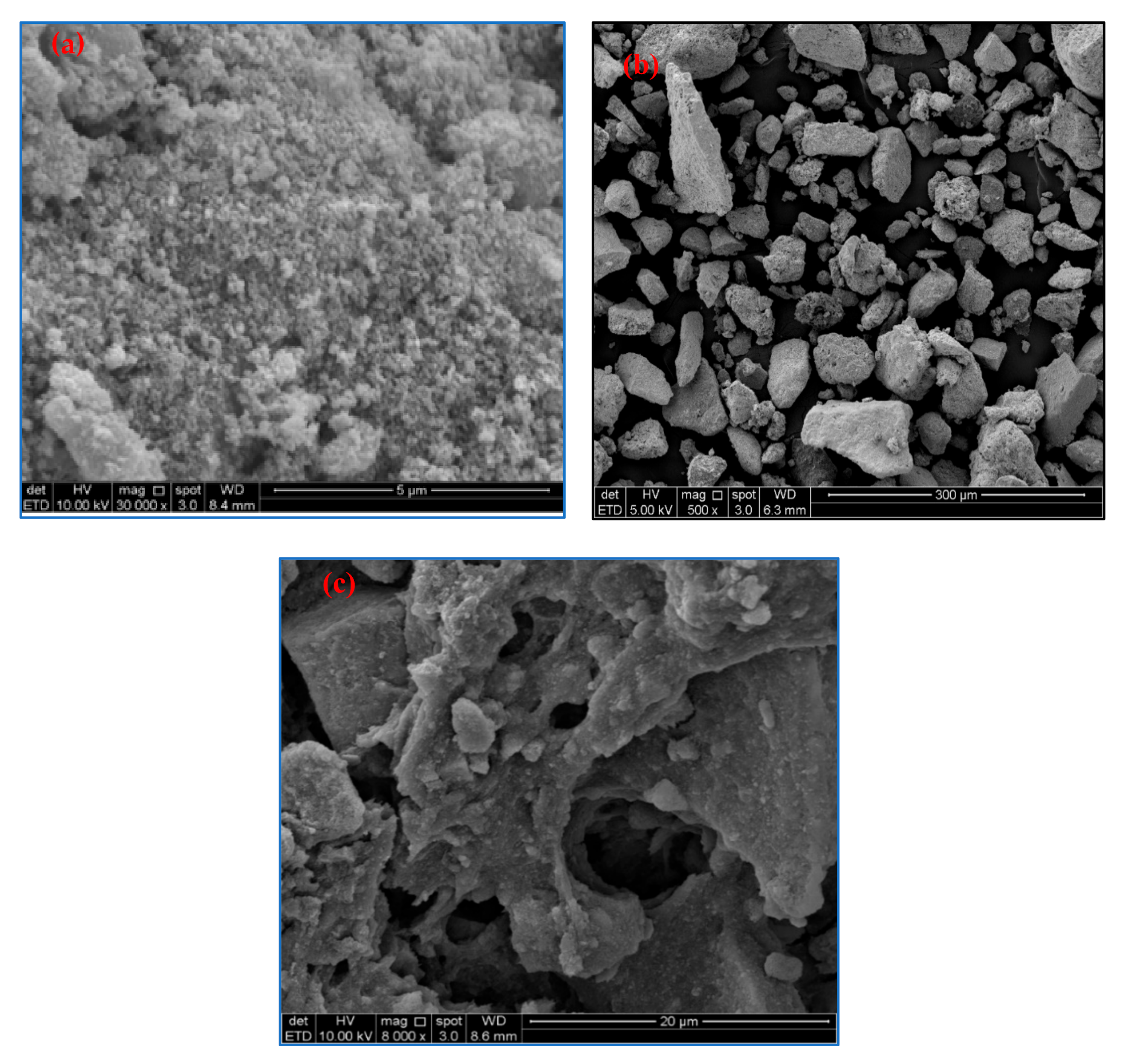
3.1. Morphological Observation of OP-EFB Cellulose and M-OPEFB-CNF
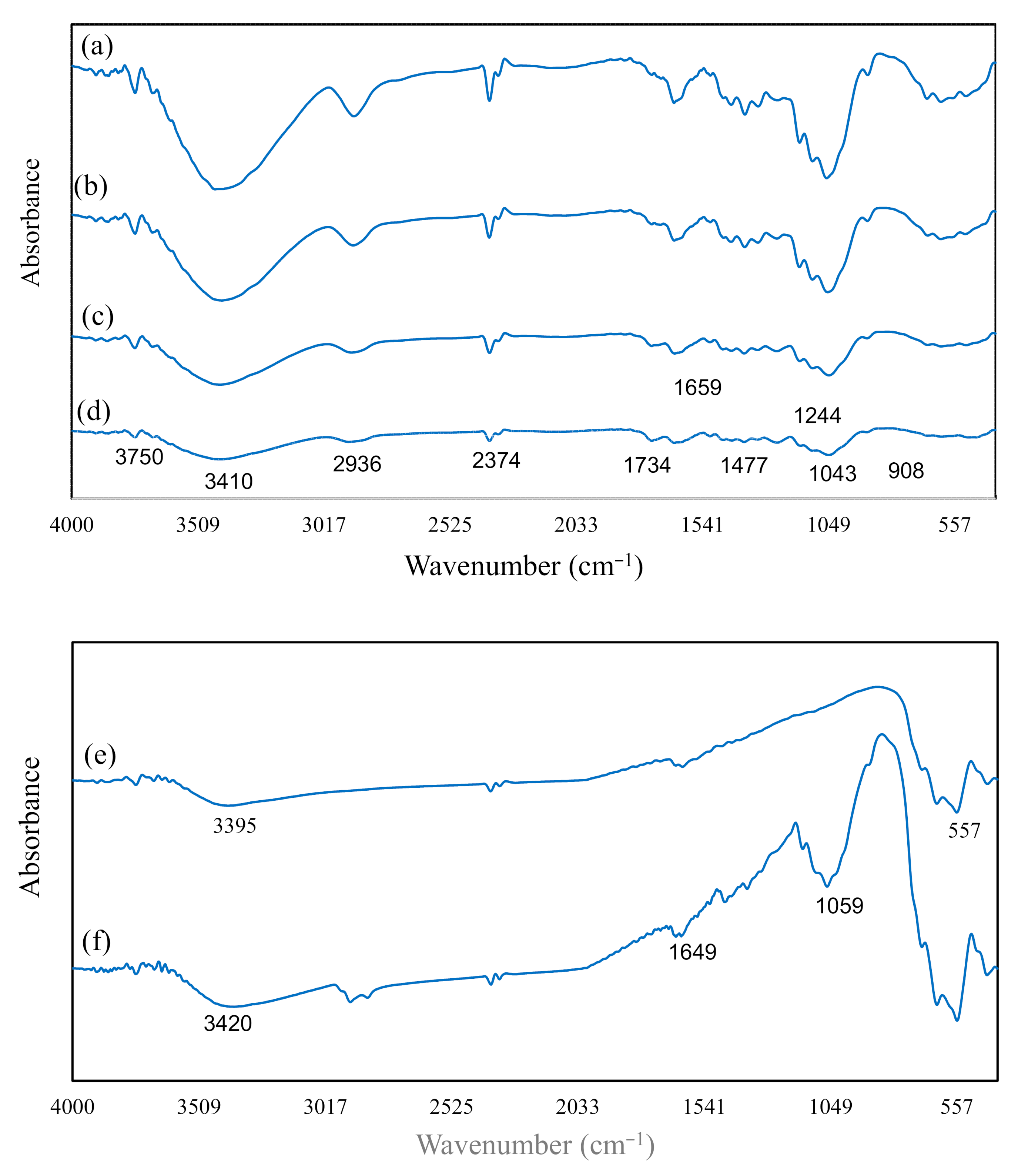
3.2. FT-IR Analyses
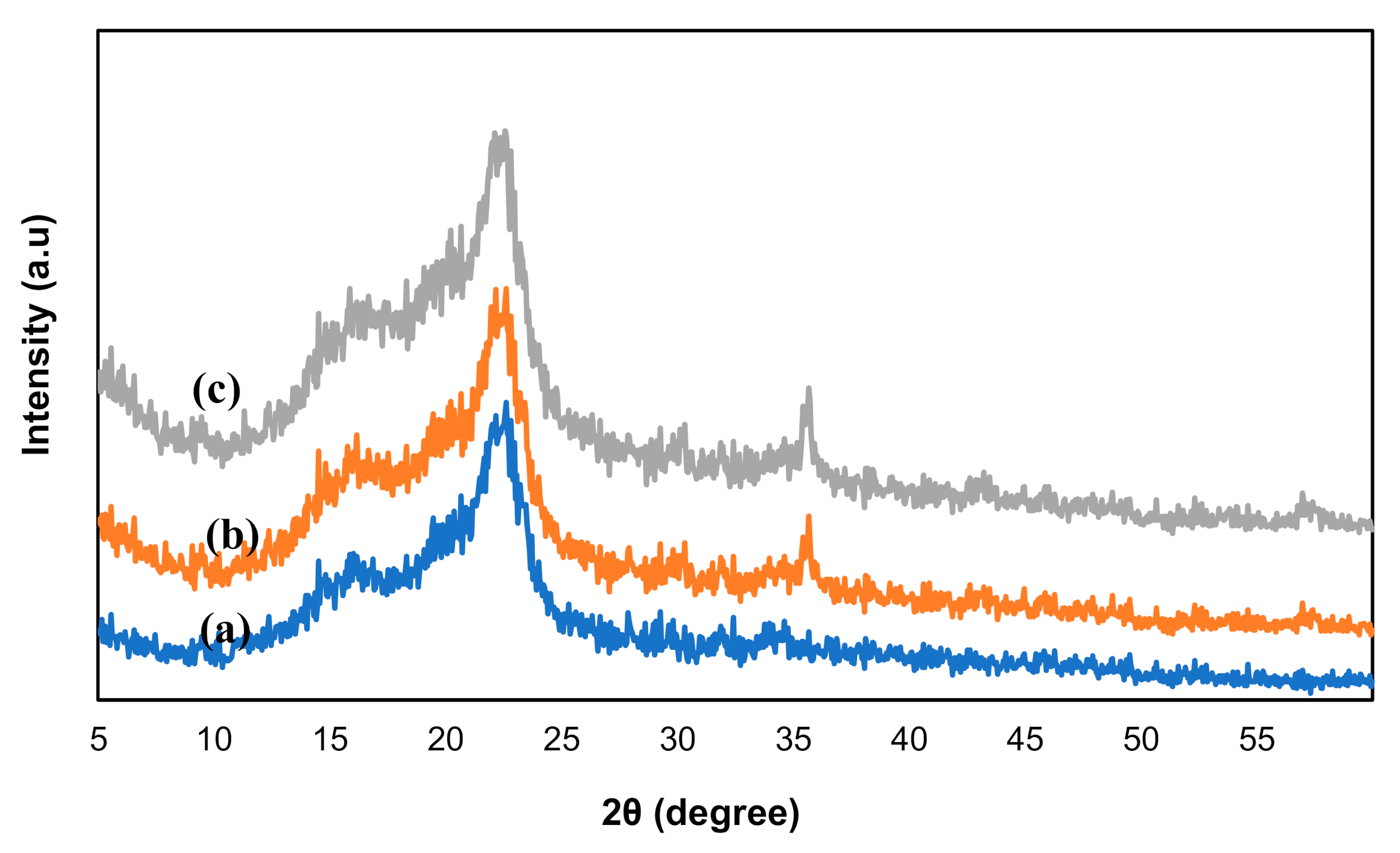
3.3. X-ray Diffraction
3.4. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis
3.5. Adsorption of Cr(VI) and Cu(II)
3.6. Adsorption Equilibrium Studies
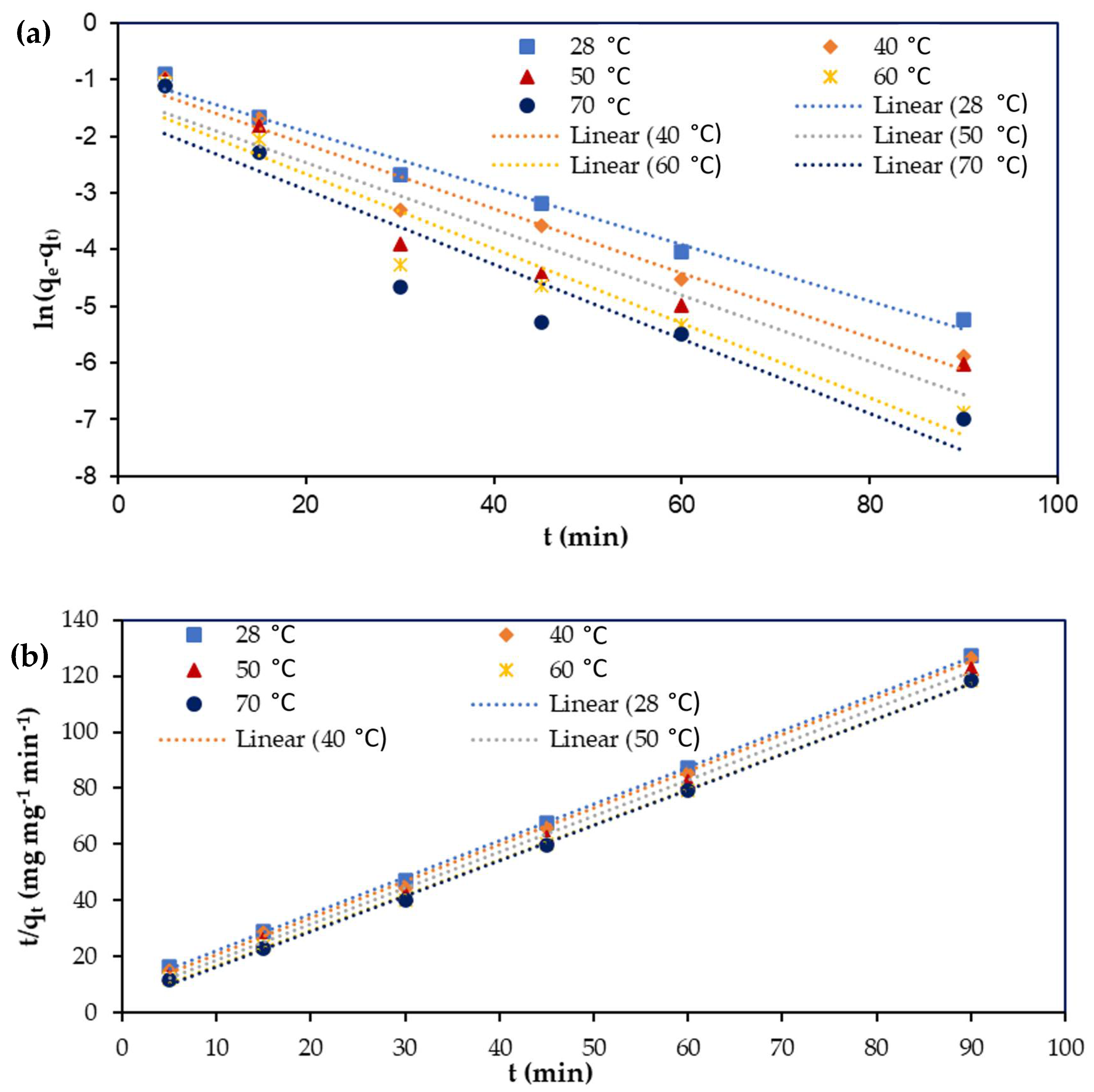
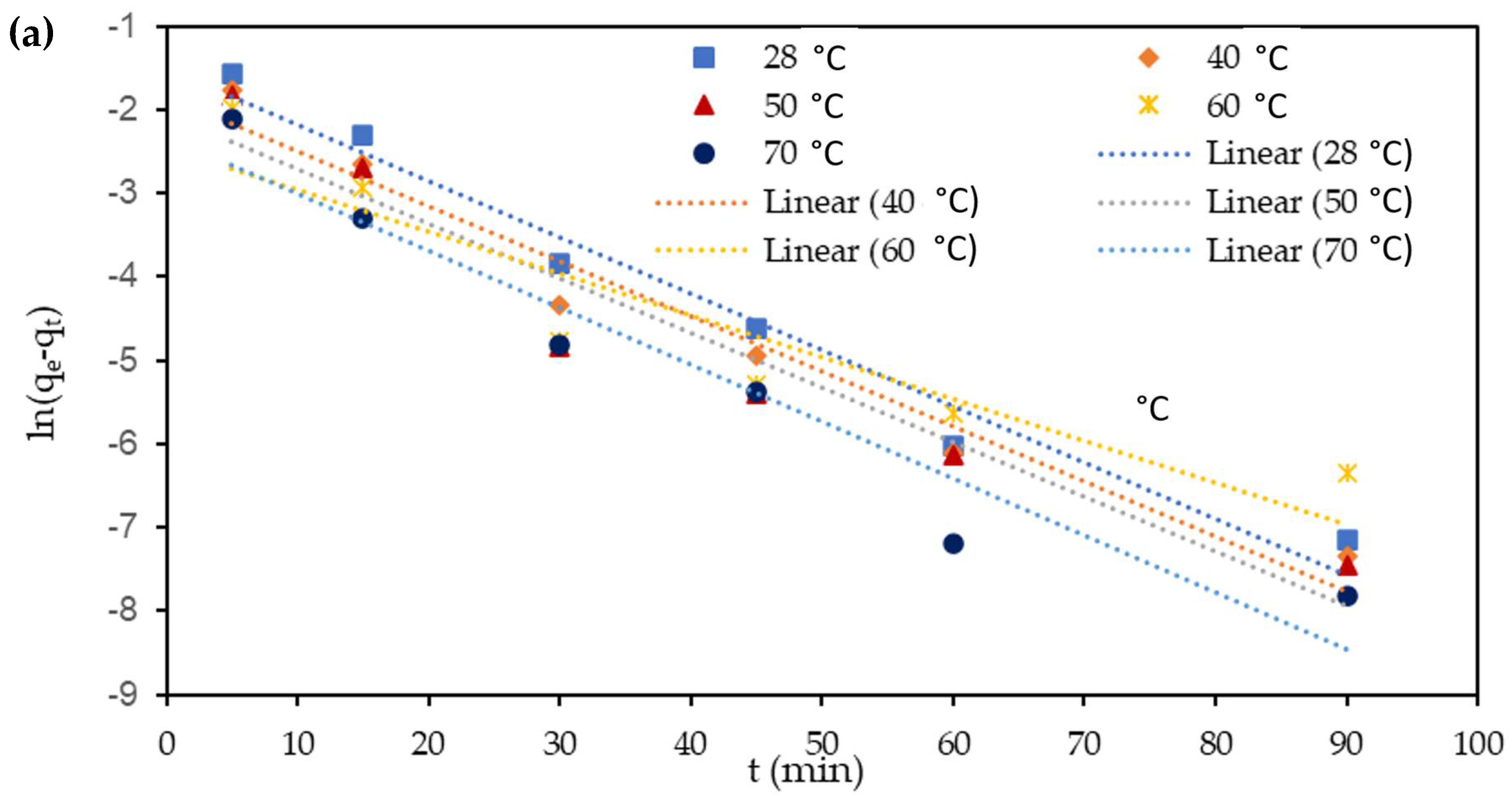
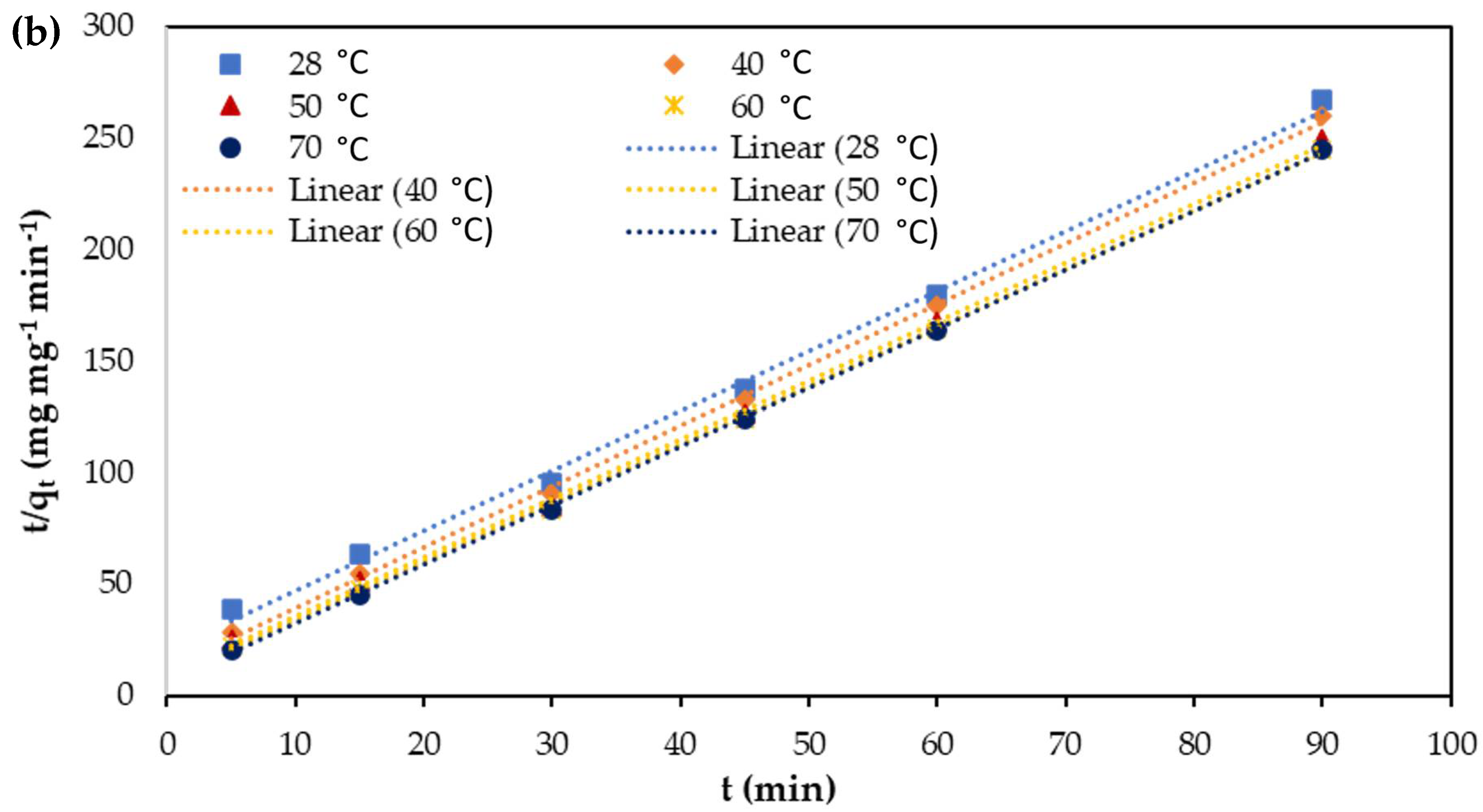
3.7. Adsorption Kinetics
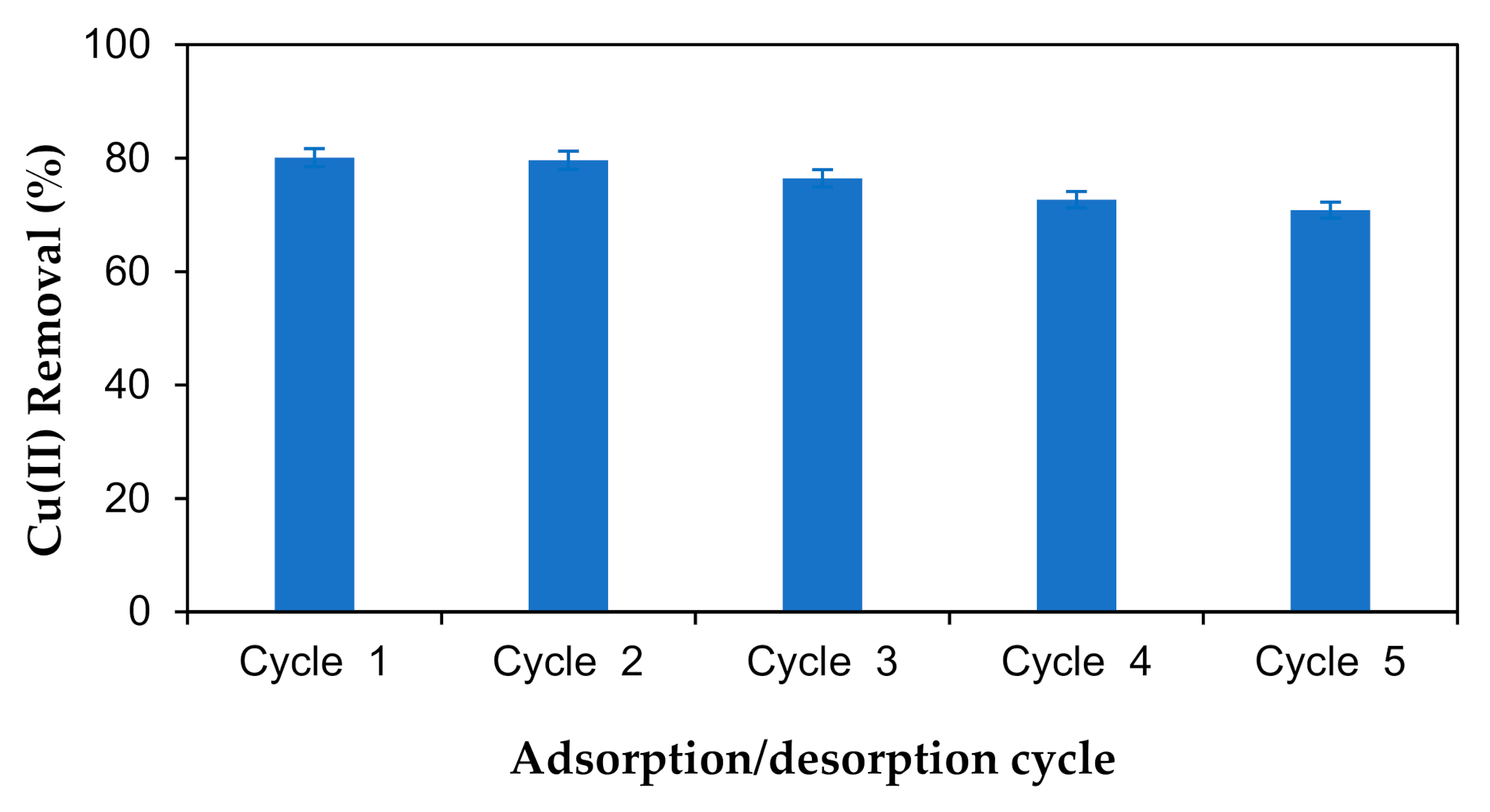
3.8. Reusability of the M-OPEFB-CNF Composite as a Biosorbent
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carolin, C.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Saravanan, A.; Joshiba, G.J.; Naushad, M. Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2782–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Meng, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Chang, J. Nanoporous Magnetic Cellulose–Chitosan Composite Microspheres: Preparation, Characterization, and Application for Cu(II) Adsorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, H. Amino-functionalized magnetic cellulose nanocomposite as adsorbent for removal of Cr(VI): Synthesis and adsorption studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 241, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, F.; Hossain, S.; Mujtaba, I.M.; Jamaluddin, S.B.; Hussin, K. Simultaneous extraction and separation of Cu(II), Zn(II), Fe(III) and Ni(II) by polystyrene microcapsules coated with Cyanex 272. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 95, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manirethan, V.; Raval, K.; Rajan, R.; Thaira, H.; Balakrishnan, R.M. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies on the adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solution by melanin nanopigment obtained from marine source: Pseudomonas stutzeri. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 214, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balladares, E.; Jerez, O.; Parada, F.; Baltierra, L.; Hernandez, C.; Araneda, E.; Parra, V. Neutralization and co-precipitation of heavy metals by lime addition to effluent from acid plant in a copper smelter. Miner. Eng. 2018, 122, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, D.; Feng, Q. Enhancement of salicylhydroxamic acid adsorption by Pb(II) modified hemimorphite surfaces and its effect on floatability. Miner. Eng. 2020, 152, 106373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Dickinson, J.; Galvin, K. Recovery and cleaning of fine hydrophobic particles using the Reflux™ Flotation Cell. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, R.; Santhanam, M.; Selvamani, V.; Sundaramoorthy, S.; Sundaram, M. A membrane electroflotation process for recovery of recyclable chromium(III) from tannery spent liquor effluent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 346, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, S.; Xia, L.; Wang, Z.; Suo, N.; Chen, H.; Long, Y.; Zhou, B.; Yu, Y. In-situ ion exchange electrocatalysis biological coupling (i-IEEBC) for simultaneously enhanced degradation of organic pollutants and heavy metals in electroplating wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efome, J.E.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Lan, C.Q. Experiment and modeling for flux and permeate concentration of heavy metal ion in adsorptive membrane filtration using a metal-organic framework incorporated nanofibrous membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnasri-Ghnimi, S.; Frini-Srasra, N. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by adsorption using single and mixed pillared clays. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 179, 105151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrokhi-Shahraki, R.; Benally, C.; El-Din, M.G.; Park, J. High efficiency removal of heavy metals using tire-derived activated carbon vs commercial activated carbon: Insights into the adsorption mechanisms. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tighadouini, S.; Radi, S.; Anannaz, M.; Bacquet, M.; Degoutin, S.; Tillard, M.; Eddike, D.; Amhamdi, H.; Garcia, Y. Engineering β-ketoenol structure functionality in hybrid silica as excellent adsorbent material for removal of heavy metals from water. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 13229–13240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Chen, J. Preparation of dialdehyde cellulose graftead graphene oxide composite and its adsorption behavior for heavy metals from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 212, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Liu, Y.; Xue, Z.; Yin, W.; Liang, X.; Li, M.; Chang, J. Modified nanoporous magnetic cellulose–chitosan microspheres for efficient removal of Pb(II) and methylene blue from aqueous solution. Cellulose 2017, 24, 4793–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Phuong, H.A.; Ayob, N.A.I.; Blanford, C.F.; Rawi, N.F.M.; Szekely, G. Nonwoven Membrane Supports from Renewable Resources: Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Poly(Lactic Acid) Composites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11885–11893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.K.A.; Lim, S.F.; Chua, S.N.D.; Salleh, S.F.; Law, P.L. Banana Fibers as Sorbent for Removal of Acid Green Dye from Water. J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Bai, S.; Zheng, X.; Huan, J.; Cao, G.; Yang, T.; Wang, M.; et al. Development of a facile and bi-functional superhydrophobic suspension and its applications in superhydrophobic coatings and aerogels in high-efficiency oil–water separation. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 7424–7434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, N.M.F.M.; Hossain, S.; Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Zulkifli, M.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Asis, A.J.; Yahaya, A.N.A. Treatment of Palm Oil Refinery Effluent Using Tannin as a Polymeric Coagulant: Isotherm, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics Analyses. Polymers 2020, 12, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewo, O.A.; Elemike, E.E.; Onwudiwe, D.C.; Onyango, M.S. Metal oxide-cellulose nanocomposites for the removal of toxic metals and dyes from wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2477–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, M.; Xiao, H. Functionalized porous magnetic cellulose/Fe3O4 beads prepared from ionic liquid for removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Zhou, X.; Lyu, S.; Pan, D.; Dong, M.; Wu, S.; Ding, T.; Wei, X.; Seok, I.; Wei, S.; et al. Magnetic nanocellulose-magnetite aerogel for easy oil adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 560, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, L.; Lu, C.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, W. Acrylic acid grafted and acrylic acid/sodium humate grafted bamboo cellulose nanofibers for Cu2+adsorption. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 55195–55201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisla, V.; Rattan, G.; Singhal, S.; Kaushik, A. Green and novel adsorbent from rice straw extracted cellulose for efficient adsorption of Hg (II) ions in an aqueous medium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, R.Z.; Chow, W.; Ismail, H. Sugarcane bagasse fiber and its cellulose nanocrystals for polymer reinforcement and heavy metal adsorbent: A review. Cellulose 2018, 25, 4303–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Danso, E.; Srivastava, V.; Sillanpää, M.; Bhatnagar, A. Pretreatment assisted synthesis and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibers from absorbent cotton. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septevani, A.A.; Rifathin, A.; Sari, A.A.; Sampora, Y.; Ariani, G.N.; Sudiyarmanto; Sondari, D. Oil palm empty fruit bunch-based nanocellulose as a super-adsorbent for water remediation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padzil, F.N.M.; Lee, S.H.; Ainun, Z.M.A.; Lee, C.H.; Abdullah, L.C. Potential of Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch Resources in Nanocellulose Hydrogel Production for Versatile Applications: A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatah, I.Y.A.; Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Hossain, S.; Aziz, A.A.; Davoudpour, Y.; Dungani, R.; Bhat, A. Exploration of a Chemo-Mechanical Technique for the Isolation of Nanofibrillated Cellulosic Fiber from Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch as a Reinforcing Agent in Composites Materials. Polymers 2014, 6, 2611–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahma, F.; Iwamoto, S.; Hori, N.; Iwata, T.; Takemura, A. Isolation, preparation, and characterization of nanofibers from oil palm empty-fruit-bunch (OPEFB). Cellulose 2010, 17, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, G.; Mu, X. Biocompatible magnetic cellulose–chitosan hybrid gel microspheres reconstituted from ionic liquids for enzyme immobilization. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 15085–15091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, Z.; Mustafa, M.; Asman, S.; Sekak, K. Preparation and Characterization of Magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles By Sol-Gel Method. Int. J. Nanoelectron. Mater. 2019, 12, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Review on porous nanomaterials for adsorption and photocatalytic conversion of CO2. Chin. J. Catal. 2017, 38, 1956–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieng, B.W.; Lee, S.H.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Then, Y.Y.; Loo, Y.Y. Isolation and Characterization of Cellulose Nanocrystals from Oil Palm Mesocarp Fiber. Polymers 2017, 9, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodeh, S.; Hamed, O.; Melhem, A.; Salghi, R.; Jodeh, D.; Azzaoui, K.; Benmassaoud, Y.; Murtada, K. Magnetic nanocellulose from olive industry solid waste for the effective removal of methylene blue from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22060–22074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, A.; Chakrabarty, D. Isolation of nanocellulose from waste sugarcane bagasse (SCB) and its characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.S.; Wahjoedi, B.A.; Yussof, A.W.; Abdullah, M.A. Eco-Friendly Extraction and Characterization of Cellulose from Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunches. Bioresources 2013, 8, 2161–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, J.; Qiu, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y. Polyethylene glycol modified magnetic nanoparticles for removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 40, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.Z.N.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Ismail, A.F.; Yusof, N.; Yusop, M.Z.M.; Aziz, F. Adsorptive removal of heavy metal ions using graphene-based nanomaterials: Toxicity, roles of functional groups and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnu, D.; Dhandapani, B.; Santhyiya, K. The symbiotic effect of integrated Muraya koenigii extract and surface-modified magnetic microspheres—A green bio-sorbent for the removal of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshfozoun, S.; Abdullah, M.; Abdullah, B. Preparation and characterization of magnetic biosorbent based on oil palm empty fruit bunch fibers, cellulose and Ceiba pentandra for heavy metal ions removal. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 105, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.H.M.A.; Azira, W.M.K.W.K.; Kasmawati, M.; Haslizaidi, Z.; Saime, W.N.W. Sequestration of toxic Pb(II) ions by chemically treated rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) leaf powder. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Oksman, K.; Mathew, A.P. Surface adsorption and self-assembly of Cu(II) ions on TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers in aqueous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 464, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, T.; Liu, Y.; Feng, B.; Zeng, G.; Yang, C.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, H.; Tan, Z.; Wang, X. Biosorption of cadmium(II), zinc(II) and lead(II) by Penicillium simplicissimum: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedin, K.C.; Souza, I.P.; Cazetta, A.L.; Spessato, L.; Ronix, A.; Almeida, V.C. CO2-spherical activated carbon as a new adsorbent for Methylene Blue removal: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 269, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngteni, R.; Hossain, S.; Omar, A.M.; Asis, A.J.; Tajudin, Z. Kinetics and Isotherm Modeling for the Treatment of Rubber Processing Effluent Using Iron (II) Sulphate Waste as a Coagulant. Water 2020, 12, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Omar, F.; Asis, A.J.; Bachmann, R.; Sarker, Z.I.; Ab Kadir, M.O. Effective treatment of palm oil mill effluent using FeSO4.7H2O waste from titanium oxide industry: Coagulation adsorption isotherm and kinetics studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljerf, L. High-efficiency extraction of bromocresol purple dye and heavy metals as chromium from industrial effluent by adsorption onto a modified surface of zeolite: Kinetics and equilibrium study. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 225, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, M.; Negm, A.; Kana, M.A.; Hefni, H.; Moneem, M.A. Adsorption of aluminum and lead from wastewater by chitosan-tannic acid modified biopolymers: Isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and process mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naushad, M.; Mittal, A.; Rathore, M.; Gupta, V. Ion-exchange kinetic studies for Cd(II), Co(II), Cu(II), and Pb(II) metal ions over a composite cation exchanger. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 2883–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ma, W.; Han, M. Biosorption of nickel and copper onto treated alga (Undaria pinnatifida): Application of isotherm and kinetic models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naushad, M. Surfactant assisted nano-composite cation exchanger: Development, characterization and applications for the removal of toxic Pb2+ from aqueous medium. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





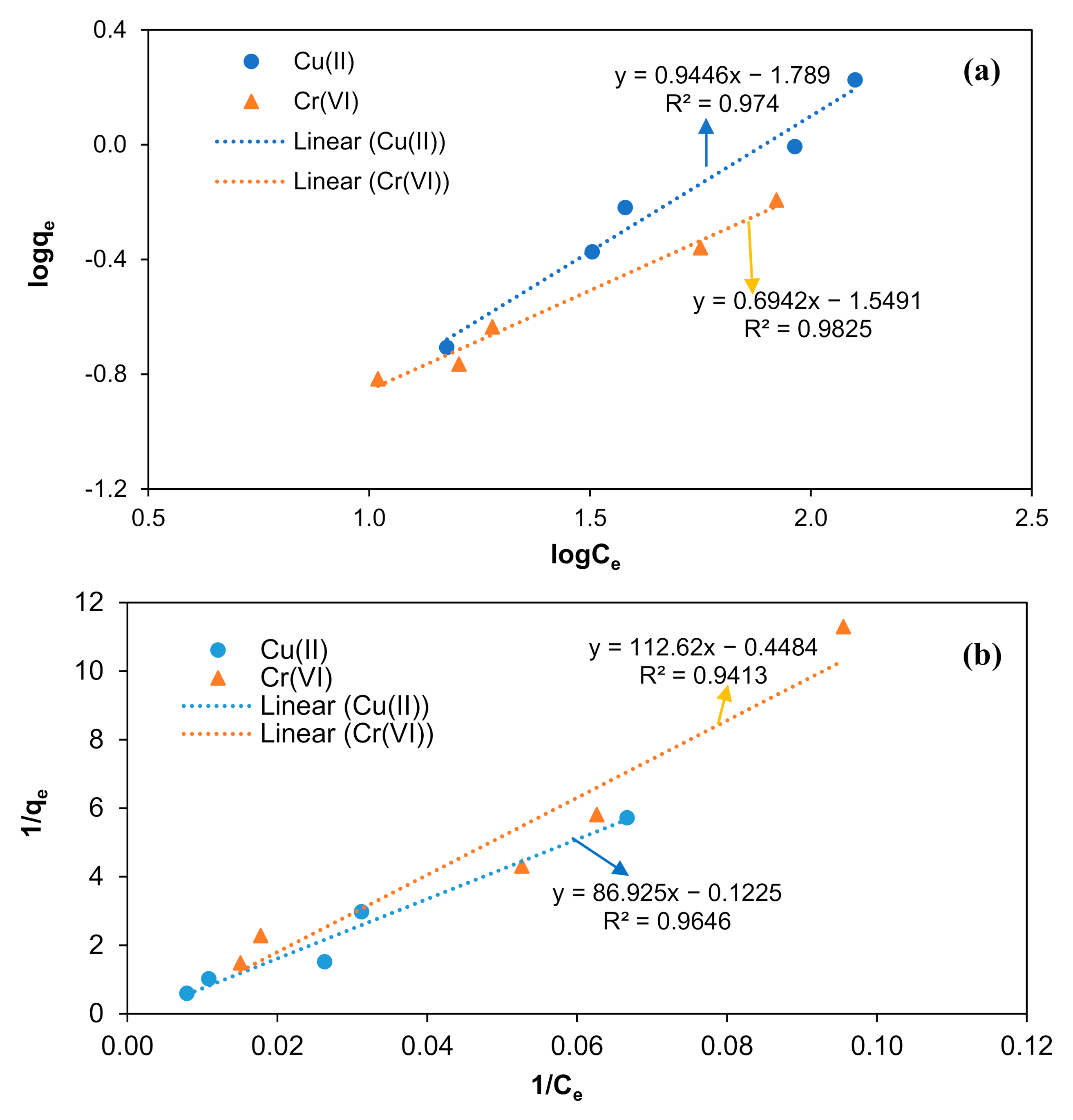
| Adsorbate | Freundlich Model | Langmuir Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | Kf (L mg−1) | n | R2 | a (L mg−1) | b(mg mg−1) | |
| Cu(II) | 0.9740 | 0.0162 | 1.0586 | 0.9646 | −0.0014 | −8.1633 |
| Cr (VI) | 0.9825 | 0.0282 | 1.4405 | 0.9413 | −0.0034 | −2.2301 |
| Parameters | Temperature (°C) | qe (exp) (mg mg−1) | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetics | Pseudo-Second Order Kinetics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg mg−1) | k1 (min−1) | R2 | qe (mg mg−1) | K2 (mg mg−1 min−1) | R2 | |||
| Cu(II) | 28 | 0.7069 | 0.4012 | 0.1152 | 0.9725 | 0.7349 | 0.1901 | 0.9996 |
| 40 | 0.7127 | 0.3678 | 0.1310 | 0.9669 | 0.7646 | 0.2287 | 0.9988 | |
| 50 | 0.7337 | 0.2722 | 0.1350 | 0.9049 | 0.7793 | 0.2812 | 0.9985 | |
| 60 | 0.7599 | 0.2600 | 0.1518 | 0.9302 | 0.7959 | 0.3660 | 0.9991 | |
| 70 | 0.7608 | 0.1993 | 0.1541 | 0.8849 | 0.7921 | 0.4323 | 0.9995 | |
| Cr(VI) | 28 | 0.33712 | 0.2225 | 0.1552 | 0.9725 | 0.3418 | 0.3583 | 0.9971 |
| 40 | 0.34612 | 0.1588 | 0.1513 | 0.9645 | 0.3670 | 0.6103 | 0.9991 | |
| 50 | 0.36104 | 0.1284 | 0.1508 | 0.9322 | 0.3789 | 0.7337 | 0.9991 | |
| 60 | 0.36772 | 0.0866 | 0.1154 | 0.8587 | 0.3808 | 0.9561 | 0.9996 | |
| 70 | 0.36808 | 0.0988 | 0.1571 | 0.9381 | 0.3785 | 1.2573 | 0.9998 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalid, A.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Ismail, N.; Khalil, N.A.; Balakrishnan, V.; Zulkifli, M.; Yahaya, A.N.A. Isolation and Characterization of Magnetic Oil Palm Empty Fruits Bunch Cellulose Nanofiber Composite as a Bio-Sorbent for Cu(II) and Cr(VI) Removal. Polymers 2021, 13, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010112
Khalid AM, Hossain MS, Ismail N, Khalil NA, Balakrishnan V, Zulkifli M, Yahaya ANA. Isolation and Characterization of Magnetic Oil Palm Empty Fruits Bunch Cellulose Nanofiber Composite as a Bio-Sorbent for Cu(II) and Cr(VI) Removal. Polymers. 2021; 13(1):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010112
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalid, Aina Mardhia, Md. Sohrab Hossain, Norli Ismail, Nor Afifah Khalil, Venugopal Balakrishnan, Muzafar Zulkifli, and Ahmad Naim Ahmad Yahaya. 2021. "Isolation and Characterization of Magnetic Oil Palm Empty Fruits Bunch Cellulose Nanofiber Composite as a Bio-Sorbent for Cu(II) and Cr(VI) Removal" Polymers 13, no. 1: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010112
APA StyleKhalid, A. M., Hossain, M. S., Ismail, N., Khalil, N. A., Balakrishnan, V., Zulkifli, M., & Yahaya, A. N. A. (2021). Isolation and Characterization of Magnetic Oil Palm Empty Fruits Bunch Cellulose Nanofiber Composite as a Bio-Sorbent for Cu(II) and Cr(VI) Removal. Polymers, 13(1), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010112