Halloysite Nanotubes Coated by Chitosan for the Controlled Release of Khellin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Khellin Loading within Halloysite Cavity
2.3. Chitosan Coating of Halloysite/Khellin Composite
2.4. Khellin Release Experiments
2.5. Methods
2.5.1. ζ Potential
2.5.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5.3. Thermogravimetry
2.5.4. UV-VIS Spectroscopy
2.5.5. Water Contact Angle
3. Results
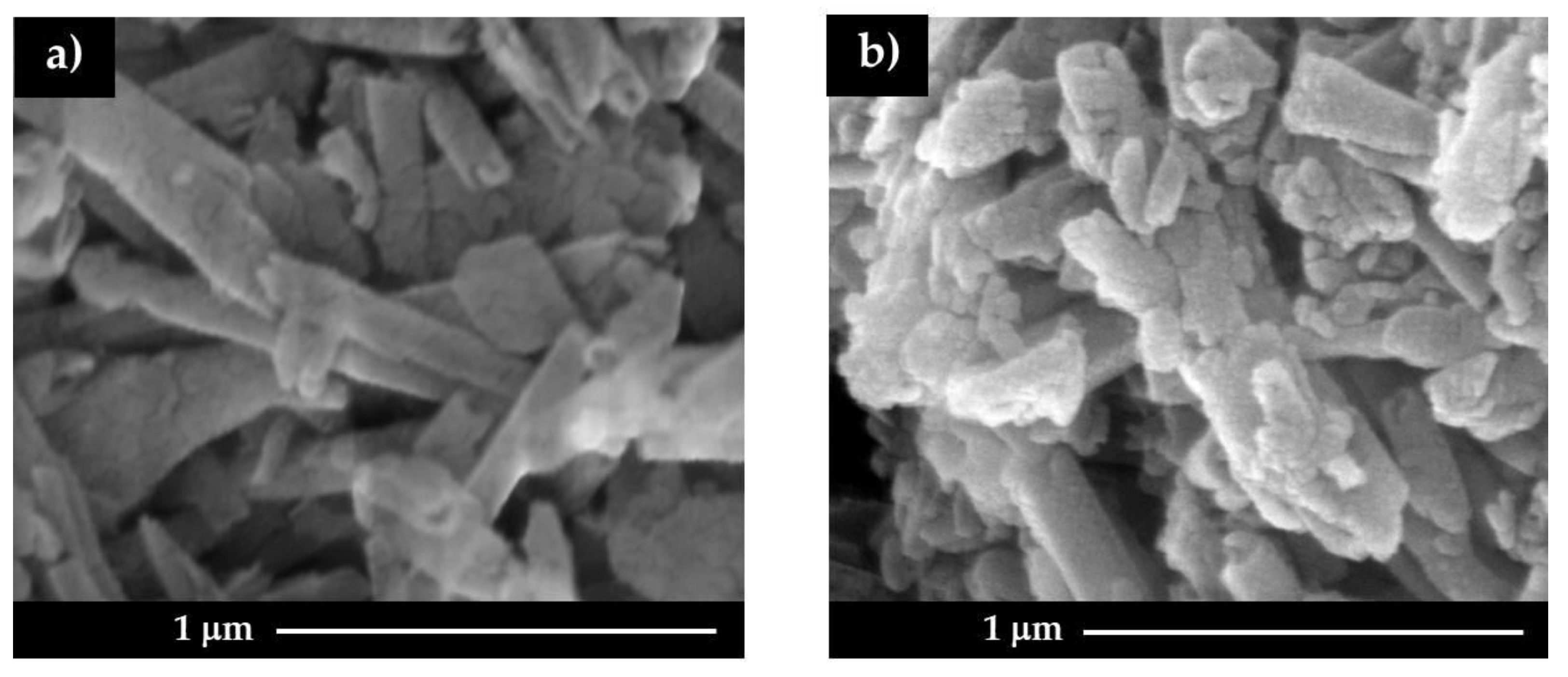
3.1. Surface Charge and Morphological Characteristics
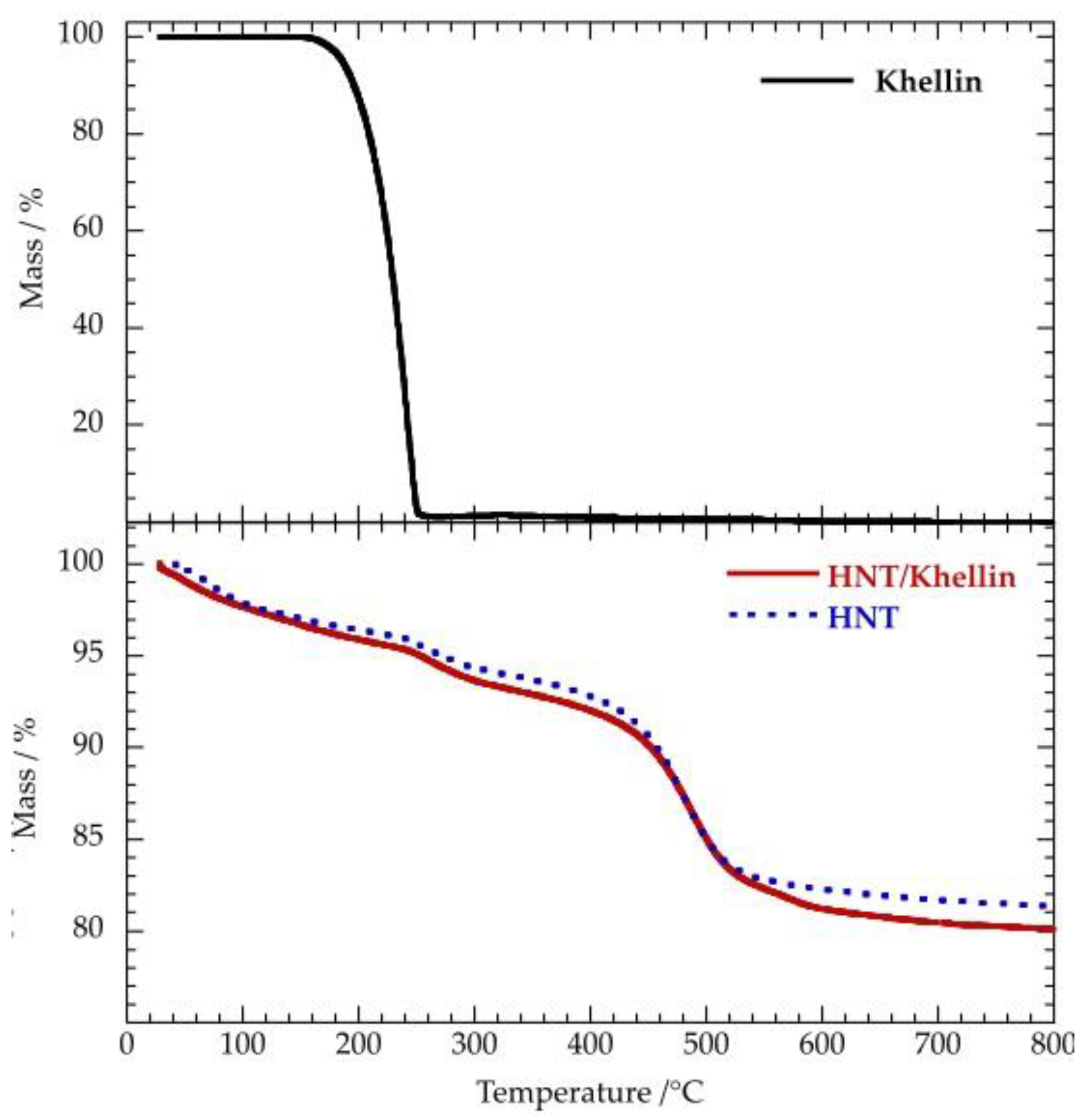
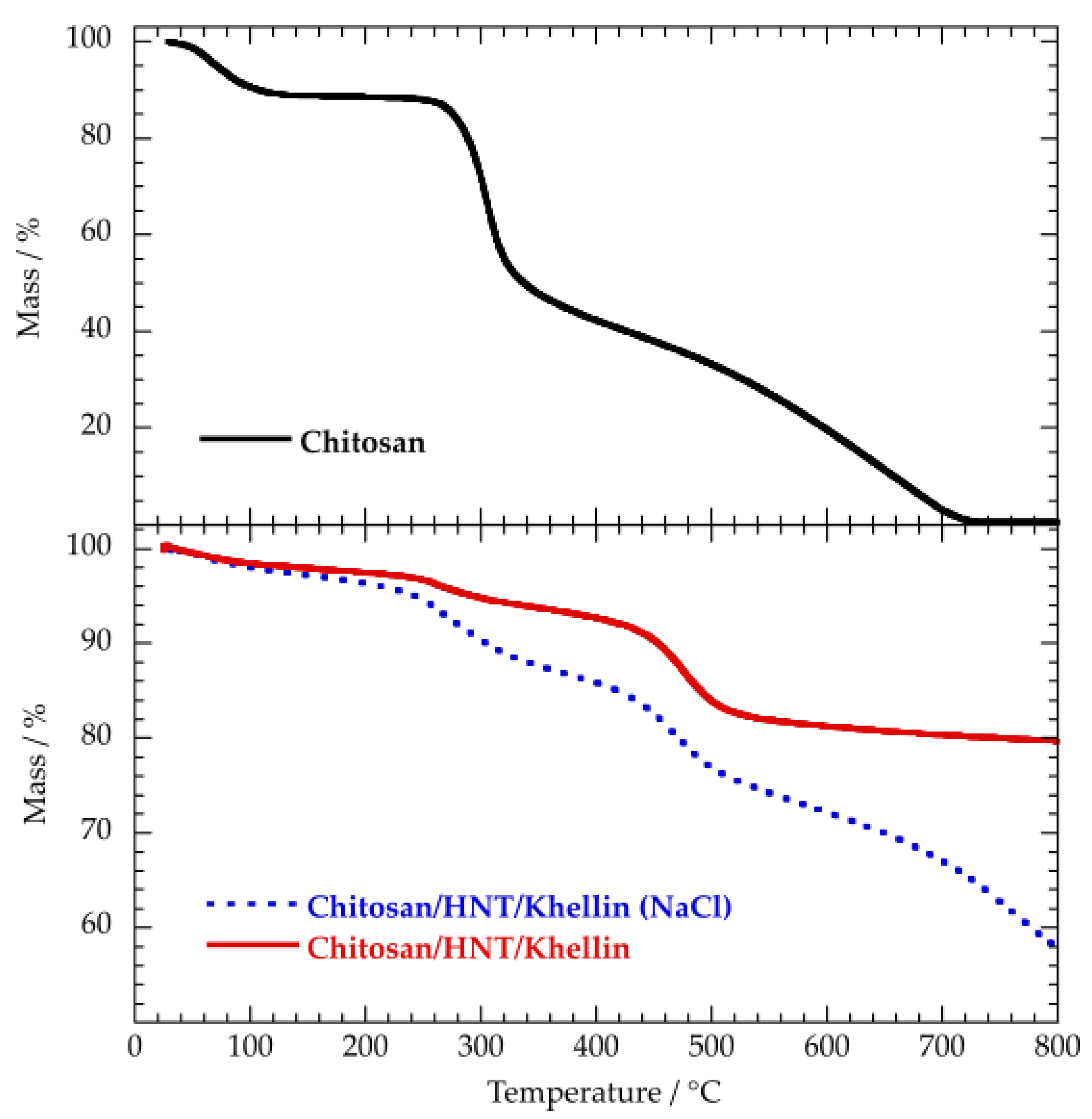
3.2. Thermal Properties
3.2.1. HNT/Khellin
3.2.2. Chitosan/HNT/Khellin
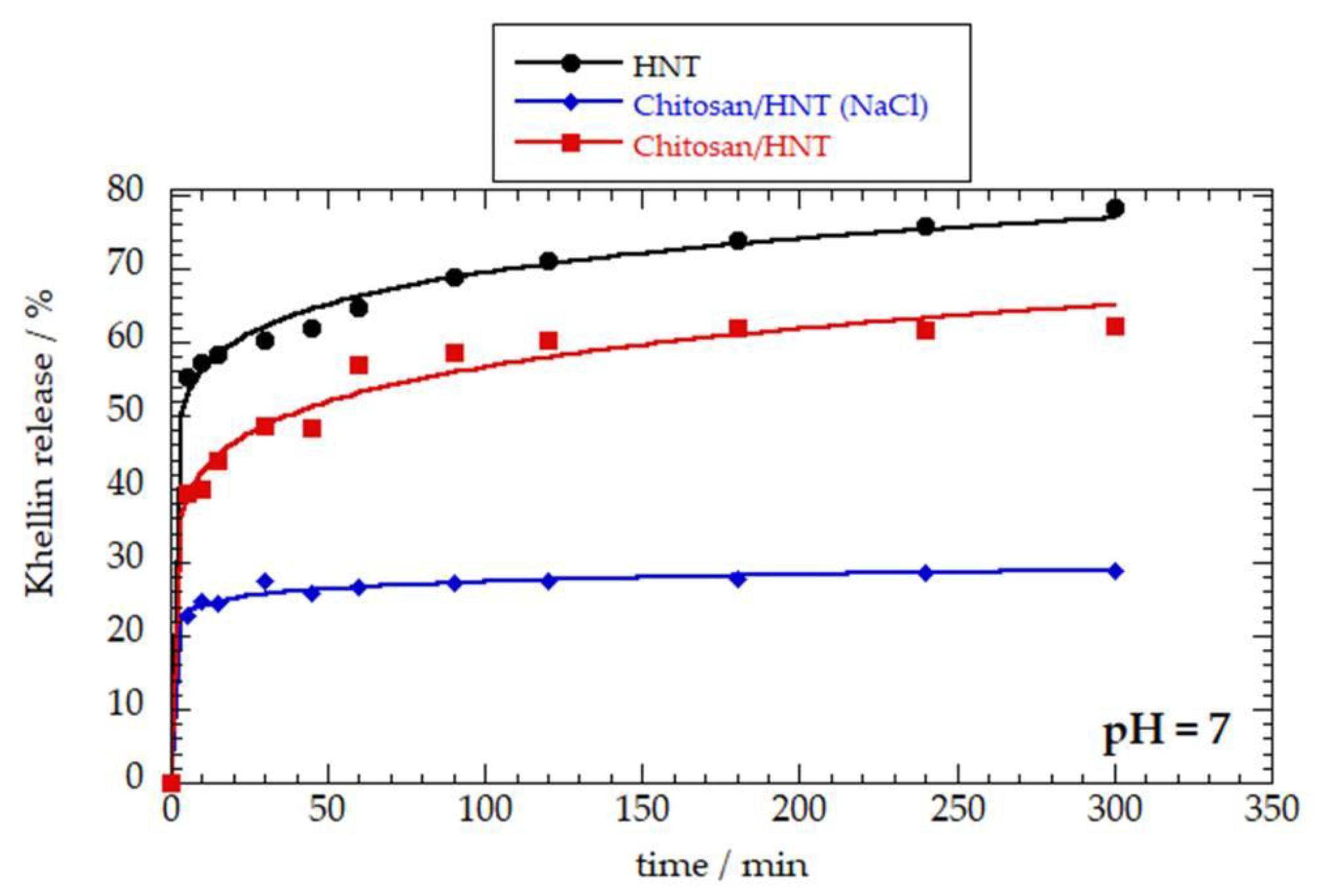
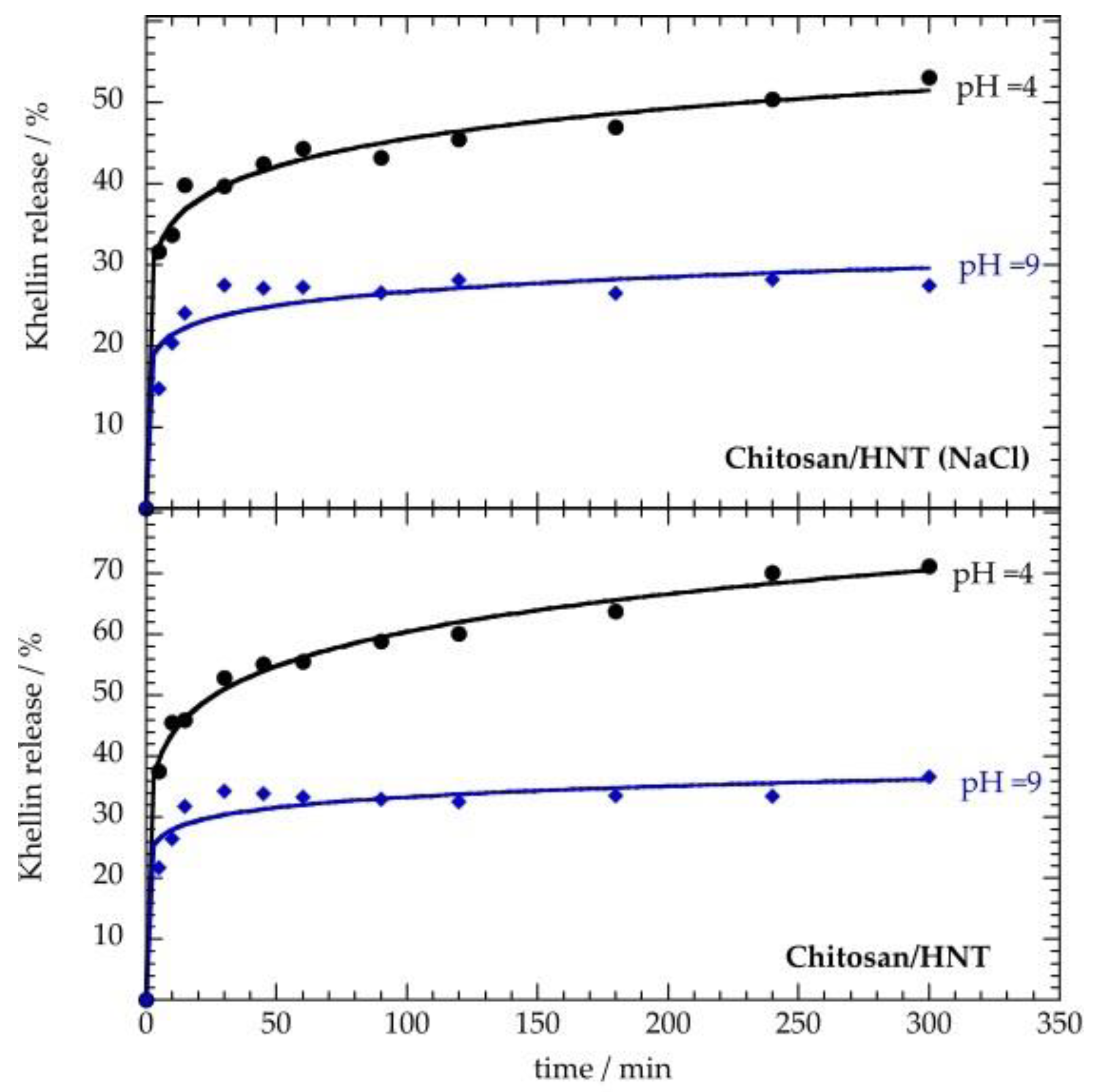
3.3. Khellin Release Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, M.; Huang, K.; Yang, F.; Wang, R.; Han, L.; Yu, H.; Ye, Z.; Wu, F. Chitosan nanocomposite films based on halloysite nanotubes modification for potential biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velmurugan, S.; Palanisamy, S.; Yang, T.C.; Gochoo, M.; Chen, S.-W. Ultrasonic assisted functionalization of MWCNT and synergistic electrocatalytic effect of nano-hydroxyapatite incorporated MWCNT-chitosan scaffolds for sensing of nitrofurantoin. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 62, 104863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan-Pragłowska, J.; Janus, Ł.; Piątkowski, M.; Bogdał, D.; Matýsek, D. Hybrid Bilayer PLA/Chitosan Nanofibrous Scaffolds Doped with ZnO, Fe3O4, and Au Nanoparticles with Bioactive Properties for Skin Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2020, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nastyshyn, S.; Raczkowska, J.; Stetsyshyn, Y.; Orzechowska, B.; Bernasik, A.; Shymborska, Y.; Brzychczy-Włoch, M.; Gosiewski, T.; Lishchynskyi, O.; Ohar, H.; et al. Non-cytotoxic, temperature-responsive and antibacterial POEGMA based nanocomposite coatings with silver nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 10155–10166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, K.; Dahlan, N.A.; Janarthanan, P.; Goh, K.L.; Chai, S.-P.; Pasbakhsh, P. Electrospun chitosan/polyethylene-oxide (PEO)/halloysites (HAL) membranes for bone regeneration applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 190, 105601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Parisi, F.; Milioto, S.; Fakhrullin, R.; Lazzara, G. Core/Shell Gel Beads with Embedded Halloysite Nanotubes for Controlled Drug Release. Coatings 2019, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koosha, M.; Hamedi, S. Intelligent Chitosan/PVA nanocomposite films containing black carrot anthocyanin and bentonite nanoclays with improved mechanical, thermal and antibacterial properties. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 127, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Rashidpour, A.; Almajano, M.-P.; Metón, I. Chitosan-Based Drug Delivery System: Applications in Fish Biotechnology. Polymers 2020, 12, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebitski, E.P.; Souza, G.P.; Santana, S.A.A.; Pergher, S.B.C.; Alcântara, A.C.S. Bionanocomposites based on cationic and anionic layered clays as controlled release devices of amoxicillin. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 173, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebitski, E.P.; Alcântara, A.C.S.; Darder, M.; Cansian, R.L.; Gómez-Hortigüela, L.; Pergher, S.B.C. Functional Carboxymethylcellulose/Zein Bionanocomposite Films Based on Neomycin Supported on Sepiolite or Montmorillonite Clays. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 13538–13550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Quiles, L.; Valdés, A.; Cuello, Á.F.; Jiménez, A.; Garrigós, M.C.; Castell, P. Reducing off-Flavour in Commercially Available Polyhydroxyalkanoate Materials by Autooxidation through Compounding with Organoclays. Polymers 2019, 11, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrasi, G. Dispersion of halloysite loaded with natural antimicrobials into pectins: Characterization and controlled release analysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrasi, G.; Pantani, R.; Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. PLA/Halloysite Nanocomposite Films: Water Vapor Barrier Properties and Specific Key Characteristics. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Chiappisi, L.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Gradzielski, M.; Lazzara, G. A structural comparison of halloysite nanotubes of different origin by Small-Angle Neutron Scattering (SANS) and Electric Birefringence. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaremi, M.; De Silva, R.T.; Pasbakhsh, P. Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes of Polyacrylonitrile/Halloysite with Superior Water Filtration Ability. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 7949–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.H.; ElSawy, M.A.; Darwish, M.S.A.; Hussein, L.I.; Abdaleem, A.H. Microwave-Assisted preparation of Chitosan/ZnO nanocomposite and its application in dye removal. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 248, 122914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Liu, M.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, C. Adsorption of dyes in aqueous solutions by chitosan–halloysite nanotubes composite hydrogel beads. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 201, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Nigamatzyanova, L.; Akhatova, F.; Fakhrullin, R.; Lazzara, G. Pickering Emulsion Gels Based on Halloysite Nanotubes and Ionic Biopolymers: Properties and Cleaning Action on Marble Surface. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 3169–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Halloysite Nanotubes: Interfacial Properties and Applications in Cultural Heritage. Langmuir 2020, 36, 3677–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Ruisi, F. Nanocomposites based on esterified colophony and halloysite clay nanotubes as consolidants for waterlogged archaeological woods. Cellulose 2017, 24, 3367–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, V.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Polysaccharides/Halloysite nanotubes for smart bionanocomposite materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of chitosan with ultra high molecular weight. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 148, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubina, M.; Shulenina, A.; Svetogorov, R.; Vasilkov, A. Metal-Chitosan Nanocomposites: A Perspective Way to Preparation, Morphology, and Structural Studies. Macromol. Symp. 2020, 389, 1900067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.I.; Mahmoud, S.T.; Awwad, F.; Greish, Y.E.; Abu-Hani, A.F. Low power consumption and fast response H2S gas sensor based on a chitosan-CuO hybrid nanocomposite thin film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benucci, I.; Liburdi, K.; Cacciotti, I.; Lombardelli, C.; Zappino, M.; Nanni, F.; Esti, M. Chitosan/clay nanocomposite films as supports for enzyme immobilization: An innovative green approach for winemaking applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 74, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, R.; Wang, H.; Sun, R.; Chen, K. Preparation and properties of a highly dispersed nano-hydroxyapatite colloid used as a reinforcing filler for chitosan. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.-C.; Chen, M.; Shi, Q.; Sun, R.; Wang, X. Chitosan/rectorite nanocomposite with injectable functionality for skin hemostasis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6544–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neji, A.B.; Jridi, M.; Kchaou, H.; Nasri, M.; Sahnoun, R.D. Preparation, characterization, mechanical and barrier properties investigation of chitosan-kaolinite nanocomposite. Polym. Test. 2020, 84, 106380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, V.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F. Biopolymer-Targeted Adsorption onto Halloysite Nanotubes in Aqueous Media. Langmuir 2017, 33, 3317–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wu, C.; Jiao, Y.; Xiong, S.; Zhou, C. Chitosan–halloysite nanotubes nanocomposite scaffolds for tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2078–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Park, S.; Sohn, D. Modification of halloysite nanotubes for enhancement of gas-adsorption capacity. Clays Clay Miner. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.; Sim, J.H.; Jeon, Y.; Lee, S.U.; Sohn, D. Opening and blocking the inner-pores of halloysite. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4519–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, S.; Heravi, M.M.; Kazemi, S.S. Ionic liquid decorated chitosan hybridized with clay: A novel support for immobilizing Pd nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Guan, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, B. Polydopamine-coated halloysite nanotubes supported AgPd nanoalloy: An efficient catalyst for hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 2754–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.-H.; Zhang, B. Preparation of bimetallic Cu-Co nanocatalysts on poly (diallyldimethylammonium chloride) functionalized halloysite nanotubes for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yang, J.-H.; Gao, X.; Yin, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B. Encapsulation of Ammonia Borane in Pd/Halloysite Nanotubes for Efficient Thermal Dehydrogenation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 2122–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Yuan, P.; Liu, D.; Du, P.; Zhou, J.; Wei, Y.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y. Effects of calcination and acid treatment on improving benzene adsorption performance of halloysite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 181, 105240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yuan, P.; Du, P.; Deng, L.; Wei, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhong, X.; Zhou, J. A novel halloysite–CeOx nanohybrid for efficient arsenic removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 186, 105450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Fakhrullin, R. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes for Loading and Sustained Release of Functional Compounds. Adv. Mater. 2015, 28, 1227–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzamukova, M.R.; Naumenko, E.A.; Lvov, Y.M.; Fakhrullin, R. Enzyme-activated intracellular drug delivery with tubule clay nanoformulation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergaro, V.; Lvov, Y.M.; Leporatti, S. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes for Resveratrol Delivery to Cancer Cells. Macromol. Biosci. 2012, 12, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Evtugyn, V.; Rozhina, E.; Fakhrullin, R. Nanohydrogel Formation within the Halloysite Lumen for Triggered and Sustained Release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 8265–8273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fizir, M.; Dramou, P.; Dahiru, N.S.; Ruya, W.; Huang, T.; He, H. Halloysite nanotubes in analytical sciences and in drug delivery: A review. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dramou, P.; Fizir, M.; Taleb, A.; Itatahine, A.; Dahiru, N.S.; Mehdi, Y.A.; Wei, L.; Zhang, J.; He, H. Folic acid-conjugated chitosan oligosaccharide-magnetic halloysite nanotubes as a delivery system for camptothecin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Bai, L.; Zhang, H.; Song, H.; Hu, L.; Wu, Y.; Ba, X. Smart H2O2-Responsive Drug Delivery System Made by Halloysite Nanotubes and Carbohydrate Polymers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 31626–31633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Gao, Y.; Song, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H. Halloysite nanotube-based H2O2-responsive drug delivery system with a turn on effect on fluorescence for real-time monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Lazzara, G. Halloysite Nanotubes Loaded with Calcium Hydroxide: Alkaline Fillers for the Deacidification of Waterlogged Archeological Woods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27355–27364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Abdullayev, E.; Vasiliev, A.; Volkova, O.; Lvov, Y. Interfacial Modification of Clay Nanotubes for the Sustained Release of Corrosion Inhibitors. Langmuir 2013, 29, 7439–7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wan, Q.; Fu, X.; Meng, X.; Ou, X.; Zhong, R.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, M. Toxicity Evaluation of One-Dimensional Nanoparticles Using Caenorhabditis elegans: A Comparative Study of Halloysite Nanotubes and Chitin Nanocrystals. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 18965–18975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrullina, G.I.; Akhatova, F.S.; Lvov, Y.M.; Fakhrullin, R. Toxicity of halloysite clay nanotubes in vivo: A Caenorhabditis elegans study. Environ. Sci. Nano 2015, 2, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryuchkova, M.; Danilushkina, A.; Lvov, Y.; Fakhrullin, R. Evaluation of toxicity of nanoclays and graphene oxide in vivo: A Paramecium caudatum study. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Wu, Y.-P.; Gao, H.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Ou, X.; He, R.-R.; Liu, M. In vitro and in vivo toxicity evaluation of halloysite nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 7204–7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gong, J.; Rong, R.; Gui, Z.; Hu, T.; Xu, X. Halloysite Nanotubes-Induced Al Accumulation and Fibrotic Response in Lung of Mice after 30-Day Repeated Oral Administration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2925–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergaro, V.; Abdullayev, E.; Lvov, Y.M.; Zeitoun, A.; Cingolani, R.; Rinaldi, R.; Leporatti, S.; Rinaldi, R. Cytocompatibility and Uptake of Halloysite Clay Nanotubes. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Chiappisi, L.; Gradzielski, M.; Lazzara, G. Effect of the supramolecular interactions on the nanostructure of halloysite/biopolymer hybrids: A comprehensive study by SANS, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and electric birefringence. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 8193–8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, J.; Yendluri, R.; Lvov, Y. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes for Enzyme Immobilization. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Konnova, S.; Fakhrullina, G.; Akhatova, F.; Lazzara, G.; Fakhrullin, R.; Lvov, Y. Halloysite/Keratin Nanocomposite for Human Hair Photoprotection Coating. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24348–24362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Grillo, I.; Gradzielski, M.; Lazzara, G. Structure of Hybrid Materials Based on Halloysite Nanotubes Filled with Anionic Surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 13492–13502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Why does vacuum drive to the loading of halloysite nanotubes? The key role of water confinement. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 547, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Layered composite based on halloysite and natural polymers: A carrier for the pH controlled release of drugs. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 10887–10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, I.; Abate, L.; Bottino, F.A.; Bottino, P. Thermal behaviour of a series of novel aliphatic bridged polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSSs)/polystyrene (PS) nanocomposites: The influence of the bridge length on the resistance to thermal degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 102, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, L.; Bottino, F.A.; Cicala, G.; Chiacchio, M.A.; Ognibene, G.; Blanco, I. Polystyrene Nanocomposites Reinforced with Novel Dumbbell-Shaped Phenyl-POSSs: Synthesis and Thermal Characterization. Polymer 2019, 11, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lvov, Y.; Decher, G.; Moehwald, H. Assembly, structural characterization, and thermal behavior of layer-by-layer deposited ultrathin films of poly (vinyl sulfate) and poly (allylamine). Langmuir 1993, 9, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morariu, S.; Brunchi, C.-E.; Bercea, M. The Behavior of Chitosan in Solvents with Different Ionic Strengths. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 12959–12966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duce, C.; Ciprioti, S.V.; Ghezzi, L.; Ierardi, V.; Tiné, M.R. Thermal behavior study of pristine and modified halloysite nanotubes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 121, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler-Borowska, M.; Chełminiak, D.; Kaczmarek, H. Thermal stability of magnetic nanoparticles coated by blends of modified chitosan and poly(quaternary ammonium) salt. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 119, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazzari, I.; Nisticò, R.; Turci, F.; Faga, M.G.; Franzoso, F.; Tabasso, S.; Magnacca, G. Advanced physico-chemical characterization of chitosan by means of TGA coupled on-line with FTIR and GCMS: Thermal degradation and water adsorption capacity. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 112, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Hu, Q.; Shen, K. Preparation and structure of chitosan soluble in wide pH range. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, H.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, H. Natural halloysite nanotubes modified as an aspirin carrier. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 44197–44202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taroni, T.; Cauteruccio, S.; Vago, R.; Franchi, S.; Barbero, N.; Licandro, E.; Ardizzone, S.; Meroni, D. Thiahelicene-grafted halloysite nanotubes: Characterization, biological studies and pH triggered release. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 520, 146351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leporatti, S. Halloysite clay nanotubes as nano-bazookas for drug delivery. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Material | ζ Potential/mV |
|---|---|
| HNT | −20.0 ± 0.6 |
| HNT/khellin | −21.5 ± 0.3 |
| Chitosan/HNT/khellin (NaCl) | +23.5 ± 0.8 |
| Chitosan/HNT/khellin | −18.5 ± 0.4 |
| Material | ML150/wt % | MR800/wt % | MD800/wt % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Khellin | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| HNT | 2.93 ± 0.04 | 81.4 ± 1.2 | 15.7 ± 0.2 |
| HNT/khellin | 3.27± 0.04 | 80.2 ± 1.1 | 16.5± 0.2 |
| Material | ML150/wt % | MR800/wt % | MD800/wt % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | 11.3 ± 0.2 | 0 | 88.7 ± 1.5 |
| Chitosan/HNT/Khellin (NaCl) | 2.88 ± 0.03 | 57.9 ± 0.6 | 33.2 ± 0.3 |
| Chitosan/HNT/Khellin | 2.11 ± 0.03 | 79.6 ± 0.9 | 18.2 ± 0.3 |
| Nanocarrier | k/min−n | n |
|---|---|---|
| HNT | 45.46 ± 1.14 | 0.092 ± 0.006 |
| Chitosan/HNT (NaCl) | 21.6 ± 0.5 | 0.052 ± 0.006 |
| Chitosan/HNT | 31.7 ± 1.6 | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
| Nanocarrier | pH | k/min−n | n |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan/HNT (NaCl) | 4 | 27.2 ± 1.1 | 0.112 ± 0.009 |
| Chitosan/HNT (NaCl) | 9 | 17.2 ± 1.9 | 0.09 ± 0.02 |
| Chitosan/HNT | 4 | 31.6 ± 1.1 | 0.141 ± 0.007 |
| Chitosan/HNT | 9 | 23 ± 2 | 0.08 ± 0.02 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Halloysite Nanotubes Coated by Chitosan for the Controlled Release of Khellin. Polymers 2020, 12, 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081766
Lisuzzo L, Cavallaro G, Milioto S, Lazzara G. Halloysite Nanotubes Coated by Chitosan for the Controlled Release of Khellin. Polymers. 2020; 12(8):1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081766
Chicago/Turabian StyleLisuzzo, Lorenzo, Giuseppe Cavallaro, Stefana Milioto, and Giuseppe Lazzara. 2020. "Halloysite Nanotubes Coated by Chitosan for the Controlled Release of Khellin" Polymers 12, no. 8: 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081766
APA StyleLisuzzo, L., Cavallaro, G., Milioto, S., & Lazzara, G. (2020). Halloysite Nanotubes Coated by Chitosan for the Controlled Release of Khellin. Polymers, 12(8), 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081766








