QCM-Based HCl Gas Sensors Using Spin-Coated Aminated Polystyrene Colloids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the Aminated PS (a-PS) Colloidal Beads
2.3. Preparation of a-PS-Coated Quartz Crystals
2.4. Characterization
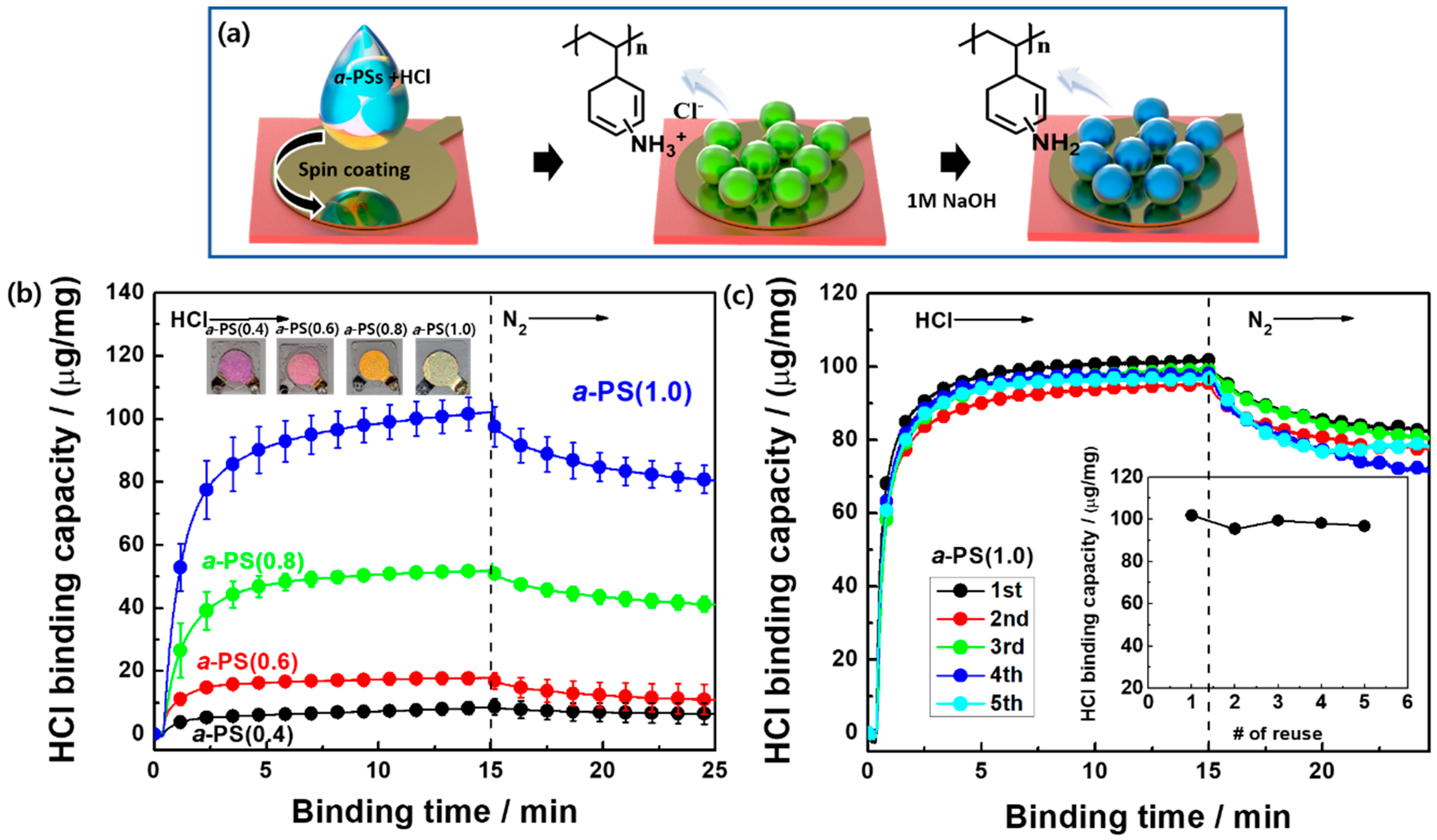
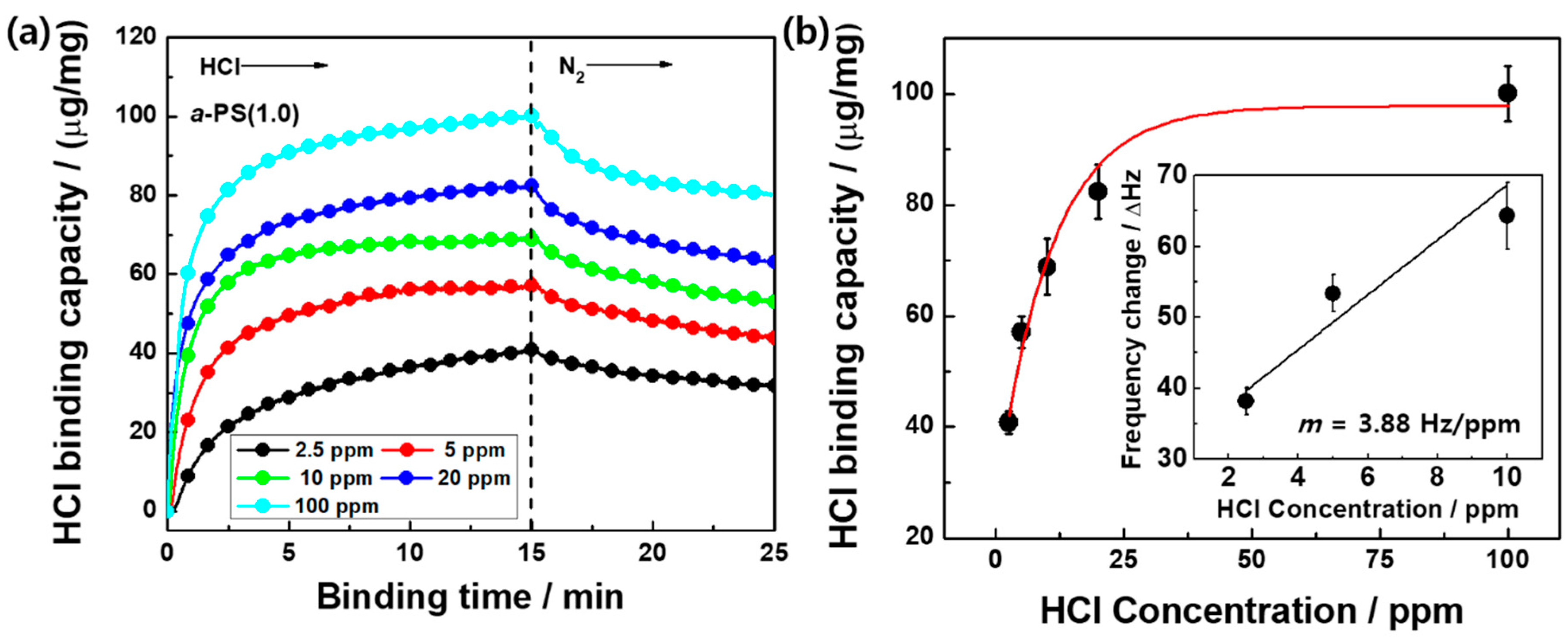
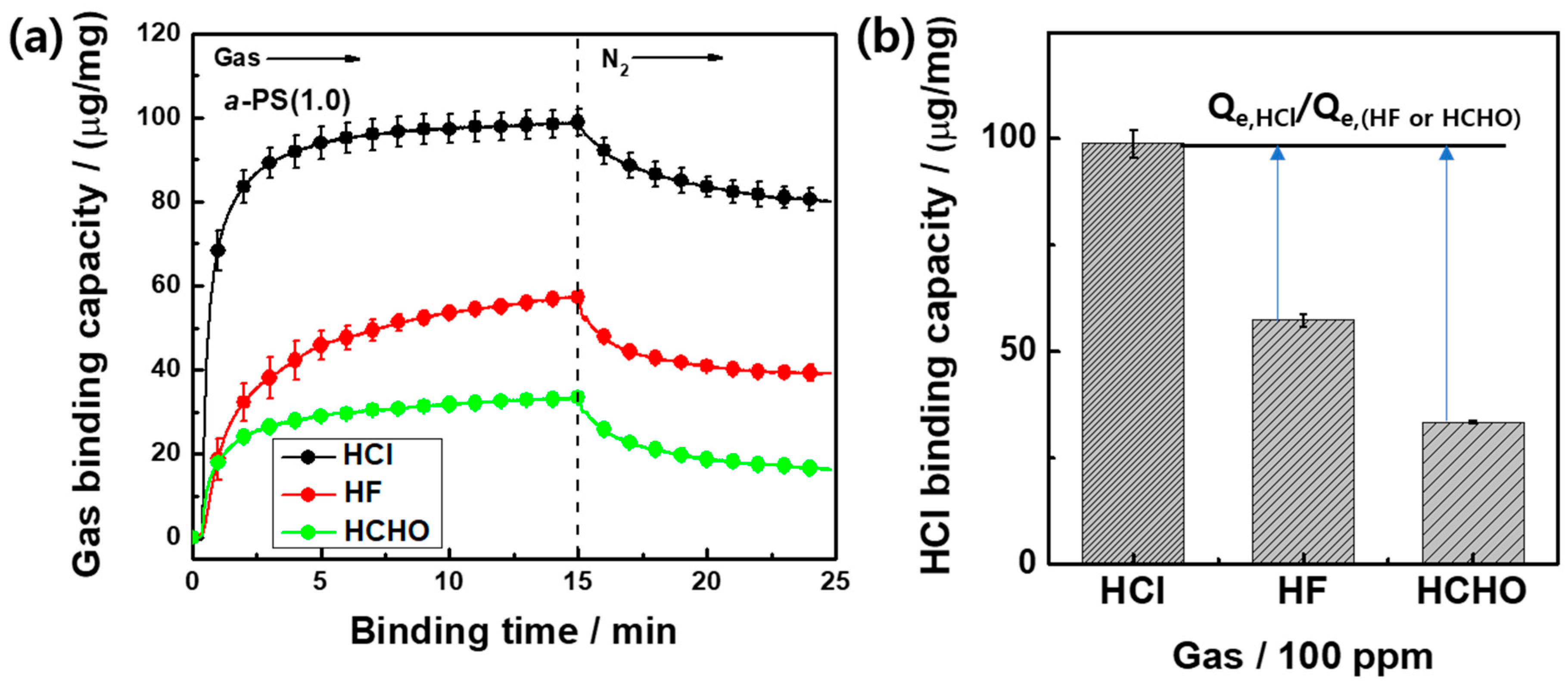
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orzel, R.A. Toxicological aspects of firesmoke: Polymer pyrolysis and combustion. Occup. Med. 1993, 8, 414–429. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, A. Semiconductor metal oxide gas sensors: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2018, 229, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Farha, F.; Li, Q.; Wan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ning, H. Review on smart gas sensing technology. Sensors 2019, 19, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Yan, X.; Xue, Q. NH3 and HCl sensing characteristics of polyaniline nanofibers deposited on commercial ceramic substrates using interfacial polymerization. Synth. Met. 2010, 160, 2452–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.-Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.-K. Colorimetric and fluorescent sensor constructing from the nanofibrous membrane of porphyrinated polyimide for the detection of hydrogen chloride gas. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 148, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Aono, T.; Ueda, G.; Tsutsumi, C.; Hayase, N.; Mabuchi, M.; Sadaoka, Y. Development of an eco-friendly optical sensor element based on tetraphenylporphyrin derivatives dispersed in biodegradable polymer: Effects of substituents of tetraphenylporphyrins on HCl detection and biodegradation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.-Z.; Shan, G.-G.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Su, Z.-M. Schiff-base as highly sensitive and reversible chemosensors for HCl gas. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supriyatno, H.; Yamashita, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Sadaoka, Y. Optochemical sensor for HCl gas based on tetraphenylporphyrin dispersed in styrene-acrylate copolymers: Effects of glass transition temperature of matrix on HCl detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 85, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itagaki, Y.; Deki, K.; Nakashima, S.-I.; Sadaoka, Y. Development of porphyrin dispersed sol–gel films as HCl sensitive optochemical gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 117, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, M.; Castillero, P.; Roales, J.; Pedrosa, J.M.; Brittle, S.; Richardson, T.; González-Elipe, A.R.; Barranco, A. A transparent TMPyP/TiO2 composite thin film as an HCl sensitive optochemical gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 150, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cui, H.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Cao, Y.; Liu, T.; Fang, Y. Alternative copolymerization of a conjugated segment and a flexible segment and fabrication of a fluorescent sensing film for HCl in the vapor phase. Chem. Asian J. 2013, 8, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuguchi, M.; Kadowaki, Y.; Noda, K.; Naganawa, R. HCl gas monitoring based on a QCM using morpholine-functional styrene-co-chloromethylstyrene copolymer coatings. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 120, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuguchi, M.; Kadowaki, Y. Poly(acrylamide) derivatives for QCM-based HCl gas sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 130, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuguchi, M.; Harada, N.; Omori, S. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanoparticles for QCM-based gas sensing of HCl. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuguchi, M.; Tada, A. Fabrication of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanoparticles using a simple spray-coating method and applications for a QCM-based HCl gas sensor coating. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 251, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuguchi, M.; Fujii, S. HCl gas sensor coating based on poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanoparticles prepared from water-methanol binary solvent. Sensors 2018, 18, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuguchi, M.; Takaoka, K.; Kai, H. HCl gas adsorption/desorption properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) brushes grafted onto quartz resonator for gas-sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, S.T.; Park, O.O.; Im, S.H. Size control of highly monodisperse polystyrene particles by modified dispersion polymerization. Macromol. Res. 2010, 18, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; He, J. Facile size-controllable syntheses of highly monodisperse polystyrene nano- and microspheres by polyvinylpyrrolidone-mediated emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippides, A.; Budd, P.M.; Price, C.; Cuncliffe, A. The nitration of polystyrene. Polymer 1993, 34, 3509–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauerbrey, G. Use of quartz vibration for weighing thin films on a microbalance. Z. Phys. 1959, 155, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donjuan-Medrano, A.L.; Montes-Rojas, A. Comparison of sensitivity constants of an electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance determined by potentiostatic deposition of Tl, Pb, Ag and Cu films. Curr. Top. Electrochem. 2012, 17, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.K.; Yola, M.L.; Atar, N. A novel molecular imprinted nanosensor based quartz crystal microbalance for determination of kaempferol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 194, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diñeiro, Y.; Menéndez, M.I.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tuñón-Blanco, P. Computational predictions and experimental affinity distributions for a homovanillic acid molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.X.; Shen, Z.; Vargas, T.; Sun, W.J.; Ruan, R.M.; Xie, Z.D.; Qiu, G.Z. Attachment of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans onto different solid substrates and fitting through langmuir and freundlich equations. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 2129–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.-J.; Park, J. QCM-Based HCl Gas Sensors Using Spin-Coated Aminated Polystyrene Colloids. Polymers 2020, 12, 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071591
Jin Y-J, Park J. QCM-Based HCl Gas Sensors Using Spin-Coated Aminated Polystyrene Colloids. Polymers. 2020; 12(7):1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071591
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Young-Jae, and Jinyoung Park. 2020. "QCM-Based HCl Gas Sensors Using Spin-Coated Aminated Polystyrene Colloids" Polymers 12, no. 7: 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071591
APA StyleJin, Y.-J., & Park, J. (2020). QCM-Based HCl Gas Sensors Using Spin-Coated Aminated Polystyrene Colloids. Polymers, 12(7), 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071591





