Sulfonation and Characterization of Tert-Butyl Styrene/Styrene/Isoprene Copolymer and Polypropylene Blends for Blood Compatibility Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
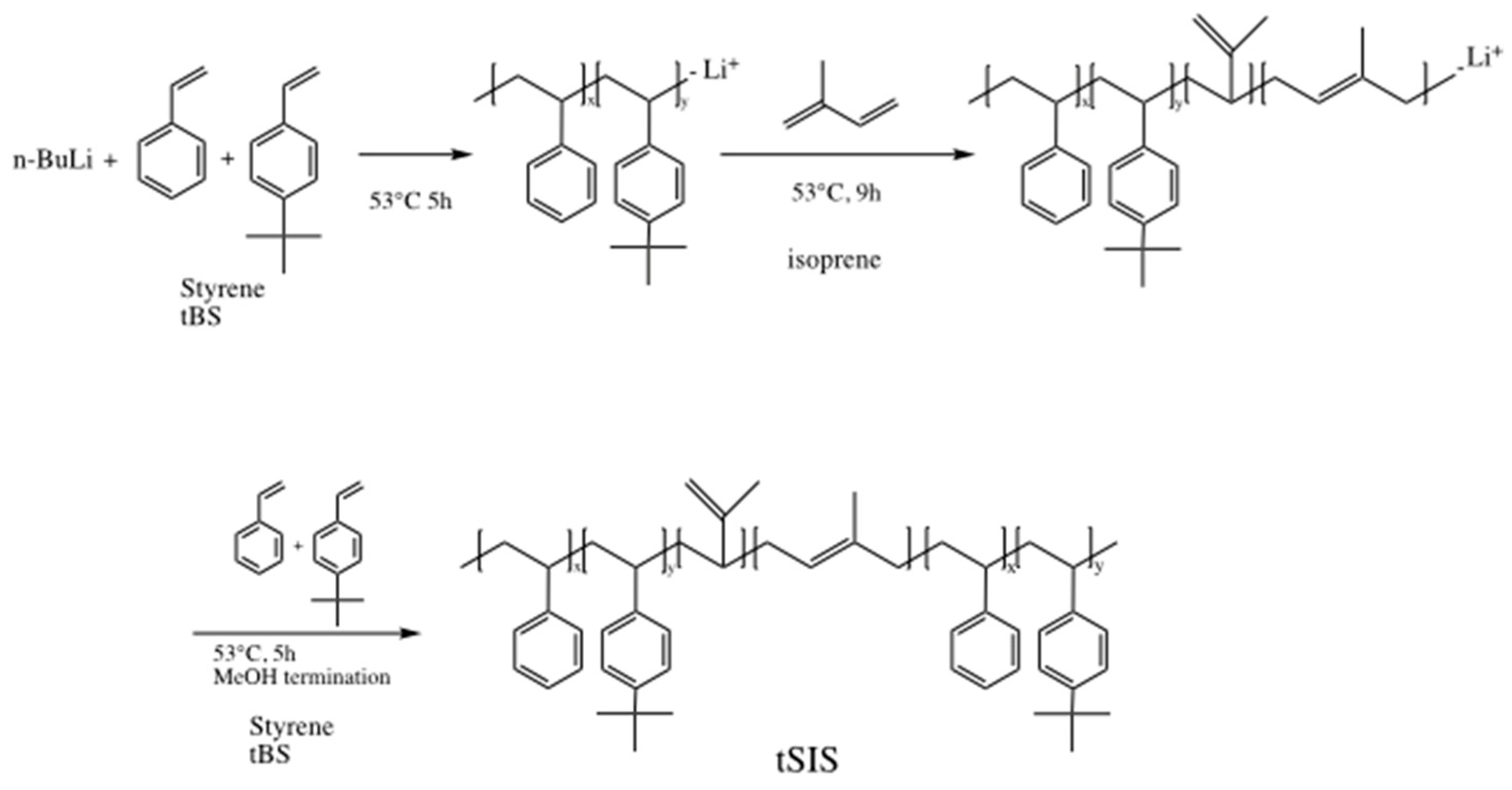
2.2. Synthesis of tBS-Styrene-Isoprene Block Copolymer (tSIS)
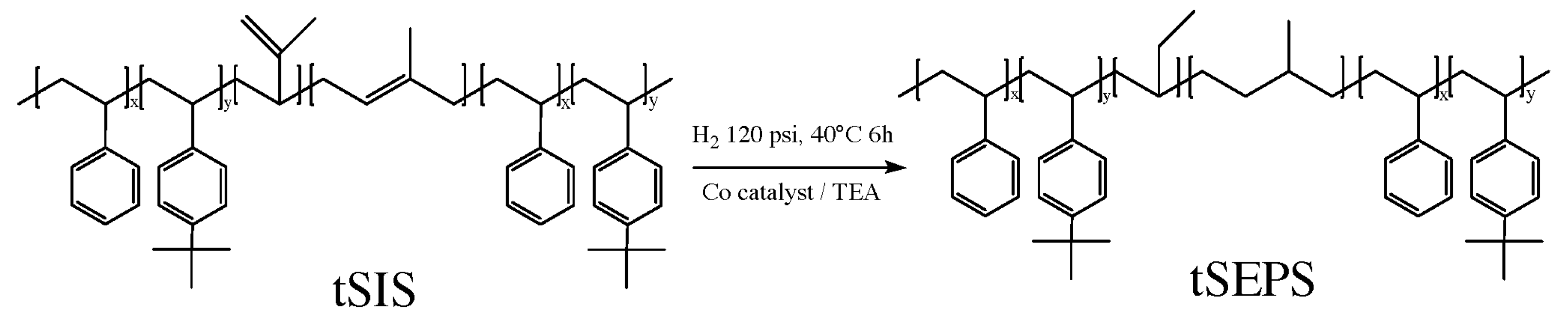
2.3. Hydrogenation of tSIS Copolymer
2.4. Preparation of Film Made by Blending Hydrogenated tSIS (tSEPS) with PP
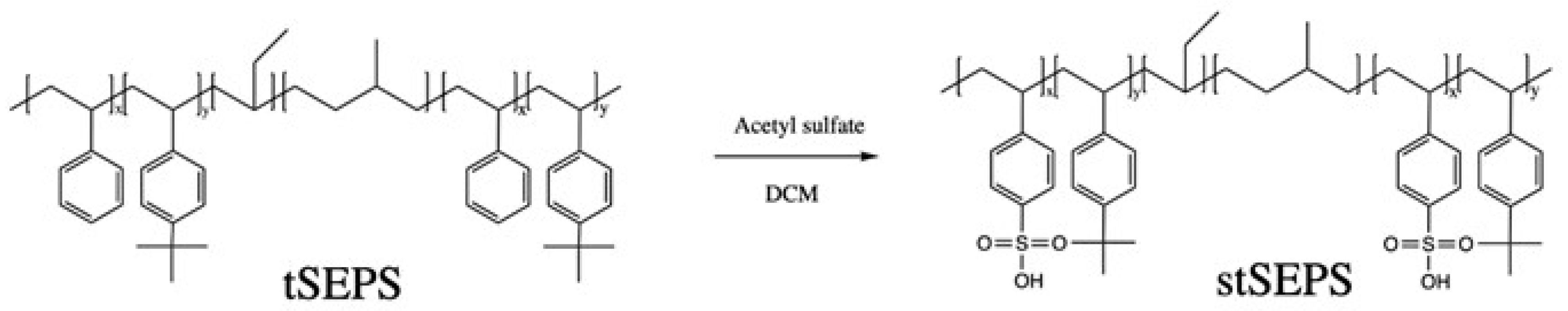
2.5. Sulfonation of tSEPS/PP Film
2.6. Water Uptake Analysis
2.7. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.8. Tensile Strength Analysis
2.9. Platelet Adhesion Assay
3. Results
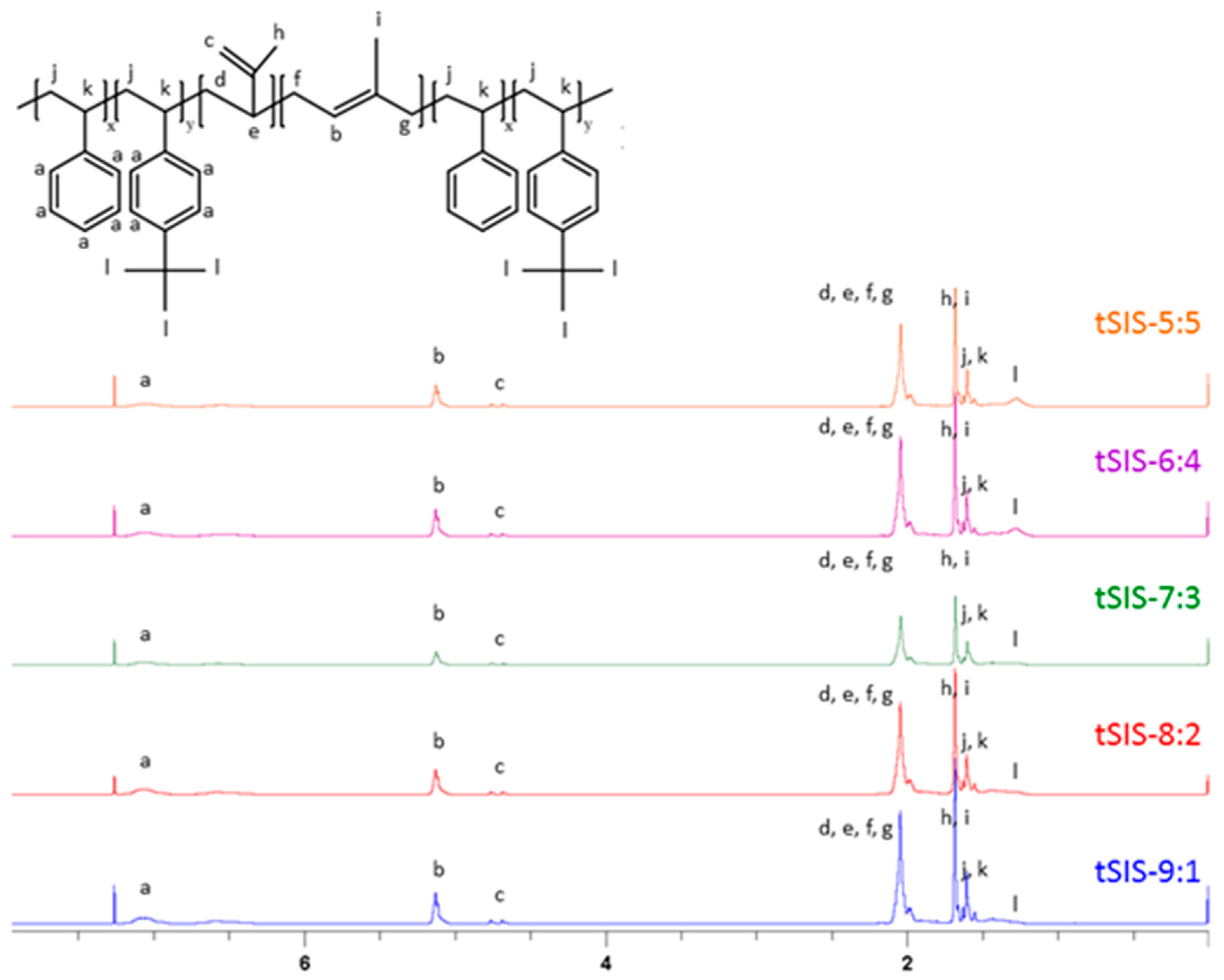
3.1. Characterization of tBS-Styrene-Isoprene Block Copolymer (tSIS) and Hydrogenated tSIS Copolymer (tSEPS)
3.2. Characterization of Sulfonation of tSEPS/PP Film (stSEPS/PP)
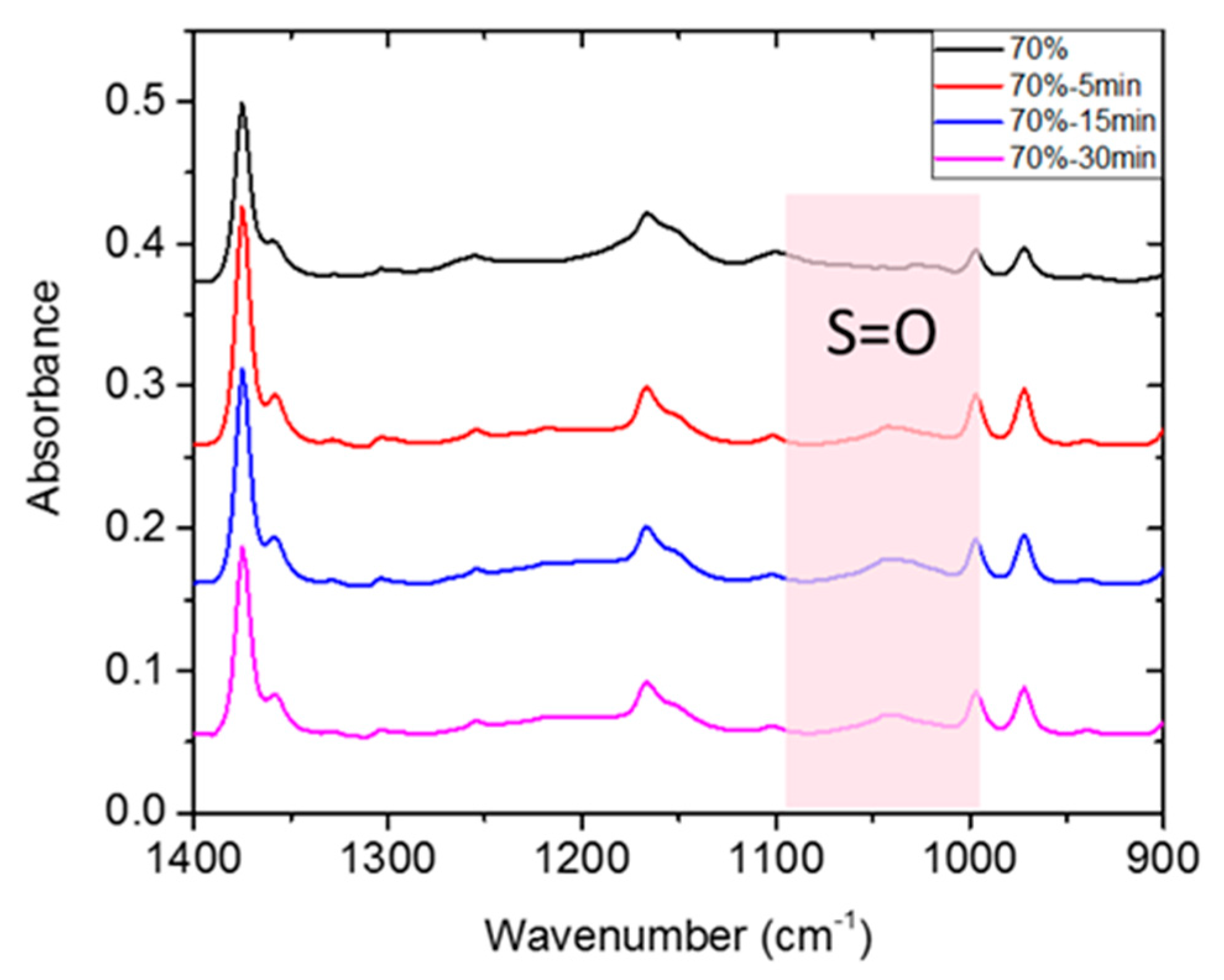
3.2.1. ATR-FTIR and ESCA Analysis
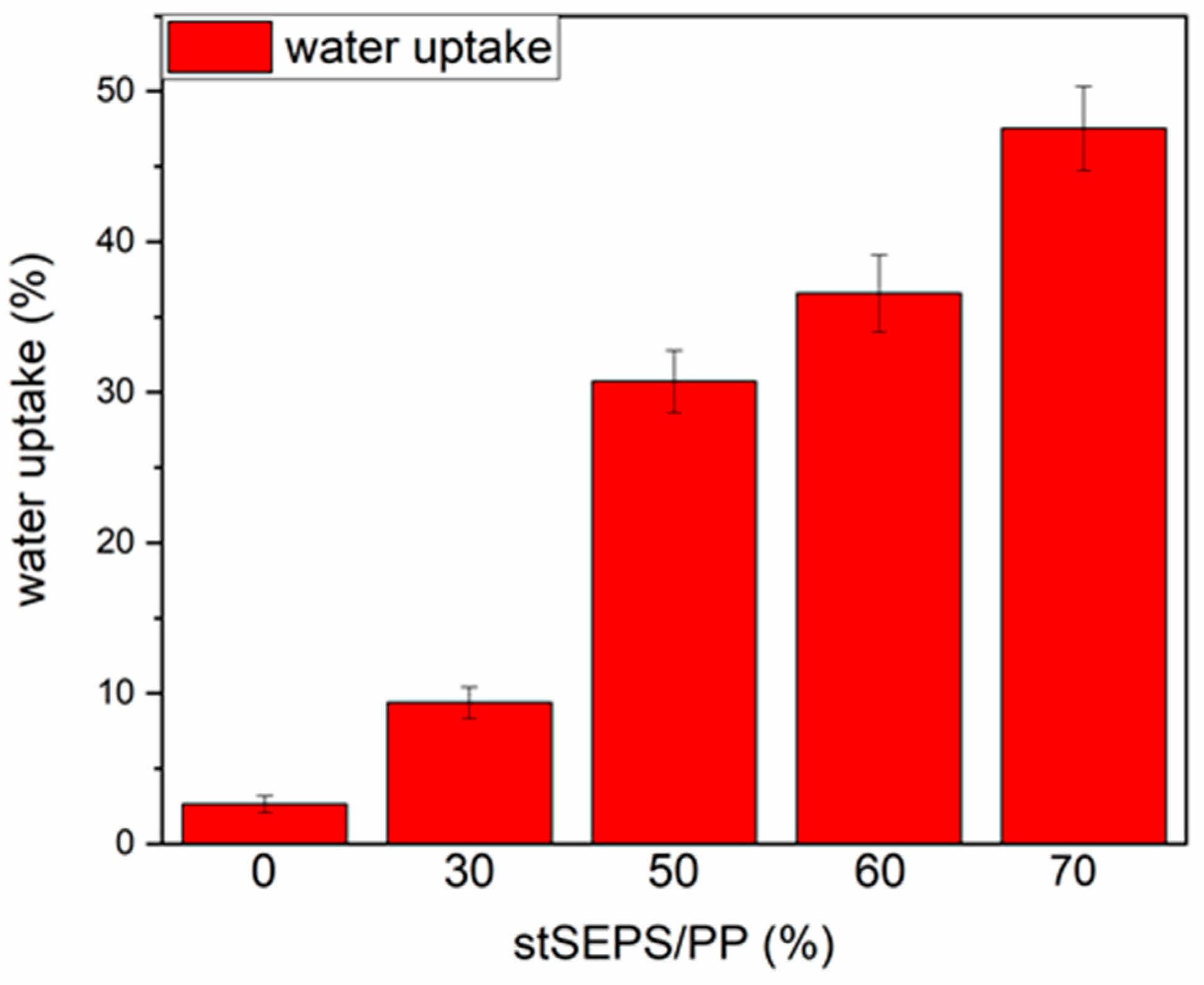
3.2.2. Surface Hydrophilicity of stSEPS/PP Film
3.2.3. Analysis of Thermal and Mechanical Properties
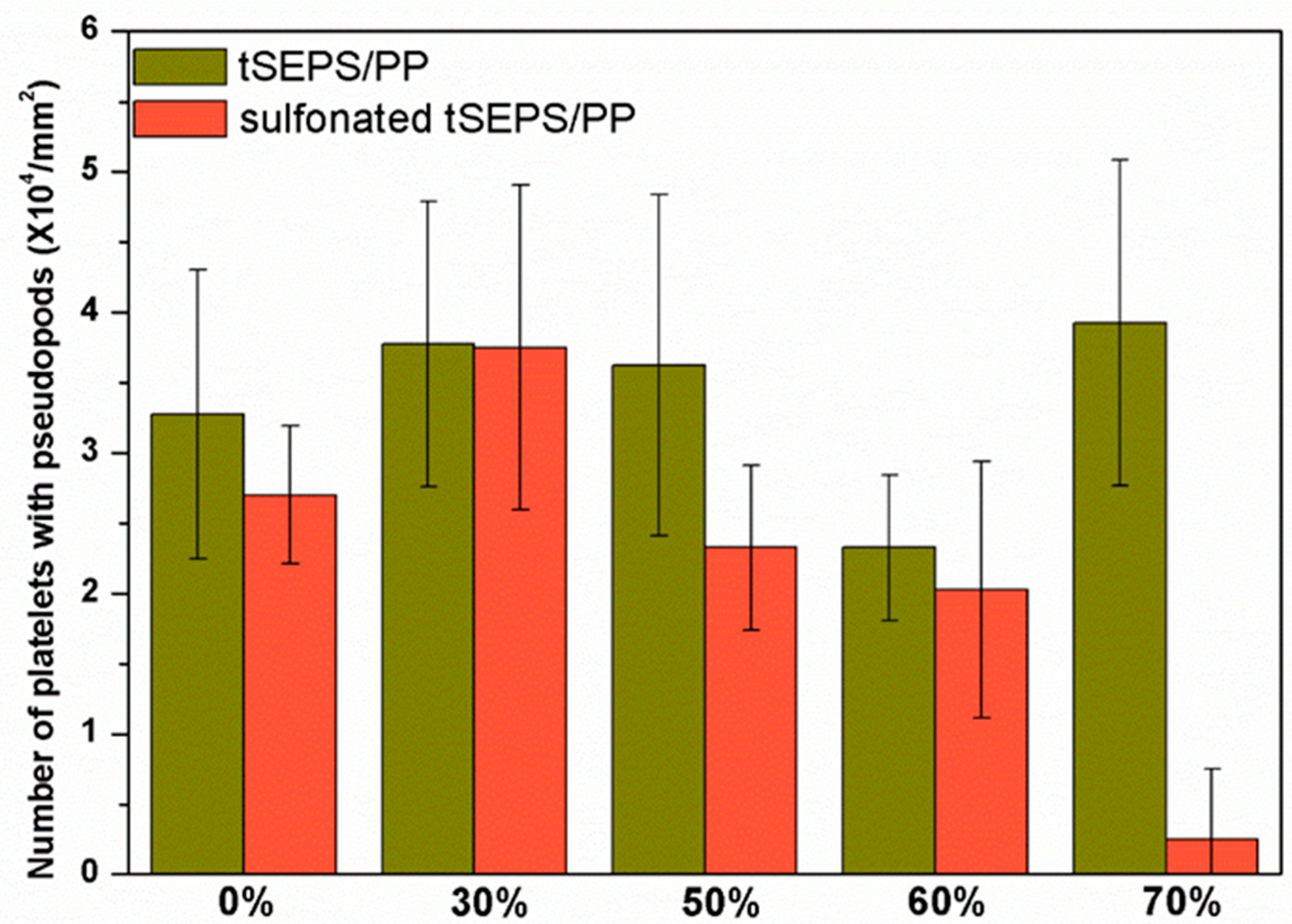
3.2.4. Platelet Adhesion Testing on Non-Sulfonated and Sulfonated tSEPS/PP Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van der Meer, P.F.; Reesink, H.W.; Panzer, S.; Wong, J.; Ismay, S.; Keller, A.; Pink, J.; Buchta, C.; Compernolle, V.; Wendel, S.; et al. Should DEHP be eliminated in blood bags? Vox Sang. 2014, 106, 176–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prowse, C.V.; de Korte, D.; Hess, J.R.; van der Meer, P.F.; Biomedical Excellence for Safer Transfusion (BEST) Collaborative. Commercially available blood storage containers. Vox Sang. 2014, 106, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giangrande, P.L.F. The history of blood transfusion. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 110, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmen, R. The selection of plastic materials for blood bags. Transfus. Med. Rev. 1993, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, R.J.; Rubin, R.J. Plasticizers from plastic devices extraction, metabolism, and accumulation by biological systems. Science 1970, 170, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scientific Committee on Emerging and Newly-Identified Health Risks. Opinion on the Safety of Medical Devices Containing DEHP Plasticized PVC or Other Plasticizers on Neonates and Other Groups Possibly at Risk (2015 Update); EU Publications: Luxembourg, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Moriguchi, N.; Zhu, J.; Yamana, Y. Characterization of polypropylene/hydrogenated styrene-isoprene-styrene block copolymer blends and fabrication of micro-pyramids via micro hot embossing of blend thin-films. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 92212–92221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hylton, D.M.; Shalaby, S.W.; Latour, R.A., Jr. Direct correlation between adsorption-induced changes in protein structure and platelet adhesion. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2005, 73A, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masashi Kaneko, H.S. Sulfonation of Poly(propylene) Films with Fuming Sulfuric Acid. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2004, 206, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, M.; Ueno, T.; Horino, H.; Chujyo, S.; Asai, H. Fine structures and physical properties of styrene-butadiene block copolymers. Polymer 1968, 9, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-H.; Lico, L.S.; Huang, T.-Y.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chang, C.-L.; Arco, S.D.; Hung, S.-C. Synthesis of the heparin-based anticoagulant drug Fondaparinux. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 9876–9879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paule Carreno, M.J.; Michel, K.; Denis, L. Regulation by sulphonate groups of complement activation induced by hydroxymethyl groups on polystyrene surfaces. Biomaterials 1993, 14, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.K.; Lee, N.Y.; Park, K.D.; Kim, Y.H.; Cho, H.I.; Min, B.G. Heparin-like anticoagulant activity of sulphonated poly(ethylene oxide) and sulphonated poly(ethylene oxide)-grafted polyurethane. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkema, A.Z.; Cooper, S.L. Effect of carboxylate and/or sulphonate ion incorporation on the physical and blood-contacting properties of a polyetherurethane. Biomaterials 1991, 12, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkema, A.Z.; Visser, S.A.; Cooper, S.L. Physical and blood-contacting properties of polyurethanes based on a sulfonic acid-containing diol chain extender. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 1371–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.K.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Min, B.G.; Cho, H.I. Negative cilia concept for thromboresistance: Synergistic effect of PEO and sulfonate groups grafted onto polyurethanes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velichkova, R.; Toncheva, V.; Antonov, C.; Alexandrov, V.; Pavlova, S.; Dubrovina, L.; Gladkova, E. Styrene-Isoprene block copolymers. II. Hydrogenation and solution properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1991, 42, 3083–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckingham, B.S.; Register, R.A. Synthesis and phase behavior of block-random copolymers of styrene and hydrogenated isoprene. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4313–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y. Synthesis and characterisation of HSIBR used as viscosity index improver for lubricants. Lubr. Sci. 2012, 24, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Hydrogenated styrene-isoprene-butadiene rubber: Optimisation of hydrogenation conditions and performance evaluation as viscosity index improver. Lubr. Sci. 2015, 27, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, B.D.; Beyer, F.L.; Long, T.E. Synthesis and SAXS characterization of sulfonated SEPS triblock copolymers. Polym. Prepr. 2006, 47, 456–457. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, R.A.; Sen, A.; Willis, C.L.; Pottick, L.A. Sulfonation of alkenes by chlorosulfuric acid, acetyl sulfate, and trifluoroacetyl sulfate. Polymer 1991, 32, 1867–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Tanaka, Y. 1H-NMR study of polyisoprenes. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Ed. 1979, 17, 3551–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zeng, X.; Wu, W. Epoxidation of styrene-isoprene-styrene block copolymer and its use for hot-melt pressure sensitive adhesives. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2008, 47, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orujalipoor, I.; Polat, K.; Huang, Y.-C.; İde, S.; Şen, M.; Jeng, U.S.; Ağçeli, G.K.; Cihangir, N. Partially sulfonated styrene-(ethylene-butylene)-styrene copolymers: Nanostructures, bio and electro-active properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 225, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, K.; Sen, M. Preparation and characterization of a thermoplastic proton-exchange system based on SEBS and polypropylene blends. Express Polym. Lett. 2017, 11, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, H.; Ito, S. Conformational change restricted selectivity in the surface sulfonation of polypropylene with sulfuric Acid. Langmuir 1997, 13, 3982–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singare, P.U.; Lokhande, R.S.; Madyal, R.S. Thermal degradation studies of polystyrene sulfonic and polyacrylic carboxylic cationites. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2010, 80, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Funabashi, K.; Yusa, H.; Kikuchi, M. Influence of functional sulfonic acid group on pyrolysis characteristics for cation exchange resin. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 1987, 24, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Styrenic Block (g) | Isoprenic Block (g) | Styrenic Block (g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Styrene | tBS | Isoprene | Styrene | tBS | |
| tSIS5:5 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 1 |
| tSIS6:4 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 10 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| tSIS7:3 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 10 | 1.4 | 0.6 |
| tSIS8:2 | 1.6 | 0.4 | 10 | 1.6 | 0.4 |
| tSIS9:1 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 10 | 1.8 | 0.2 |
| tSEPS (g) | PP (g) | Mineral Oil (g) | Total Weight (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tSEPS/PP-0% | 0.0 | 3.0 | 0.3 | 3.3 |
| tSEPS/PP-30% | 0.9 | 2.1 | 0.3 | 3.3 |
| tSEPS/PP-50% | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 3.3 |
| tSEPS/PP-60% | 1.8 | 1.2 | 0.3 | 3.3 |
| tSEPS/PP-70% | 2.1 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 3.3 |
| tSEPS/PP-100% | 3.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 3.3 |
| tSIS-5:5 | tSIS-6:4 | tSIS-7:3 | tSIS-8:2 | tSIS-9:1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Styrene: tBS (wt ratio) | 5:5 | 6:4 | 7:3 | 8:2 | 9:1 |
| Styrenic ratio (the*) | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Styrenic ratio (exp*) | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 |
| Styrene: tBS (the*) | 1.54 | 2.31 | 3.59 | 6.15 | 13.85 |
| Styrene: tBS (exp*) | 0.56 | 0.83 | 1.63 | 2.00 | 2.51 |
| C1s (%) | O1s (%) | S2p (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| stSEPS/PP-0% | 96.38 | 3.27 | 0.36 |
| stSEPS/PP-30% | 97.06 | 2.65 | 0.29 |
| stSEPS/PP-50% | 95.28 | 4.02 | 0.70 |
| stSEPS/PP-60% | 91.90 | 7.30 | 0.80 |
| stSEPS/PP-70% | 91.08 | 8.69 | 0.23 |
| SO3 2p1/2 | SO3 2p3/2 | SO2 2p1/2 | SO2 2p3/2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 171.2 eV | 170.0 eV | 170.3 eV | 169.1 eV | |
| stSEPS/PP-0% | 22.18 | 44.36 | 11.15 | 22.30 |
| stSEPS/PP-30% | 23.53 | 47.05 | 9.81 | 19.62 |
| stSEPS/PP-50% | 29.58 | 59.15 | 3.76 | 7.51 |
| stSEPS/PP-60% | 29.81 | 59.62 | 3.52 | 7.04 |
| stSEPS/PP-70% | 26.51 | 53.02 | 6.82 | 13.64 |
| Styrene: tBS | Tdmax (°C) | tSEPS # (%) | Tdmax (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tSIS | tSEPS | tSEPS/PP | stSEPS/PP | ||
| 5:5 | 393.18 | 452.44 | 0% | 438.22 | 432.73 |
| 6:4 | 391.15 | 448.52 | 30% | 452.45 | 453.44 |
| 7:3 | 381.86 | 441.73 | 50% | 435.26 | 444.19 |
| 8:2 | 391.59 | 440.63 | 60% | 435.23 | 446.27 |
| 9:1 | 384.96 | 449.63 | 70% | 447.13 | 457.02 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | Strain at Break (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| tSEPS-7:3 | 0.46 ± 0.06 | 134.65 ± 5.97 |
| tSEPS #/PP-0% | 16.87 ± 1.21 | 4.99 ± 0.68 |
| tSEPS/PP-30% | 8.13 ± 0.36 | 9.32 ± 0.95 |
| tSEPS/PP-50% | 5.11 ± 0.29 | 18.89 ± 5.63 |
| tSEPS/PP-60% | 2.78 ± 0.12 | 27.96 ± 0.93 |
| tSEPS/PP-70% | 1.08 ± 0.00 | 43.83 ± 4.17 |
| stSEPS/PP-0% | 22.45 ± 0.55 | 3.83 ± 0.24 |
| stSEPS/PP-30% | 13.19 ± 1.09 | 6.94 ± 0.87 |
| stSEPS/PP-50% | 7.21 ± 0.38 | 12.31 ± 0.44 |
| stSEPS/PP-60% | 2.06 ± 0.41 | 6.38 ± 0.87 |
| stSEPS/PP-70% | 1.15 ± 0.56 | 6.97 ± 0.86 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, B.-H.; Chuang, Y.-H.; Cheng, C.-H.; Lin, J.-C. Sulfonation and Characterization of Tert-Butyl Styrene/Styrene/Isoprene Copolymer and Polypropylene Blends for Blood Compatibility Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061351
Tsai B-H, Chuang Y-H, Cheng C-H, Lin J-C. Sulfonation and Characterization of Tert-Butyl Styrene/Styrene/Isoprene Copolymer and Polypropylene Blends for Blood Compatibility Applications. Polymers. 2020; 12(6):1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061351
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Bin-Hong, Yung-Han Chuang, Chi-Hui Cheng, and Jui-Che Lin. 2020. "Sulfonation and Characterization of Tert-Butyl Styrene/Styrene/Isoprene Copolymer and Polypropylene Blends for Blood Compatibility Applications" Polymers 12, no. 6: 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061351
APA StyleTsai, B.-H., Chuang, Y.-H., Cheng, C.-H., & Lin, J.-C. (2020). Sulfonation and Characterization of Tert-Butyl Styrene/Styrene/Isoprene Copolymer and Polypropylene Blends for Blood Compatibility Applications. Polymers, 12(6), 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061351






