New Nanohybrid Based on Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide and Silica Nanoparticles: Morphological, Structural and Thermal Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
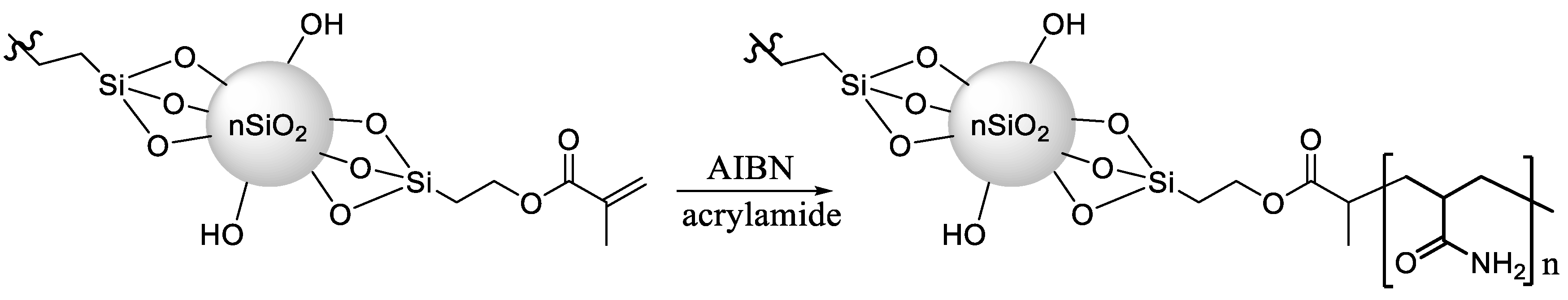
2.2. Nanohybrid Synthesis
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
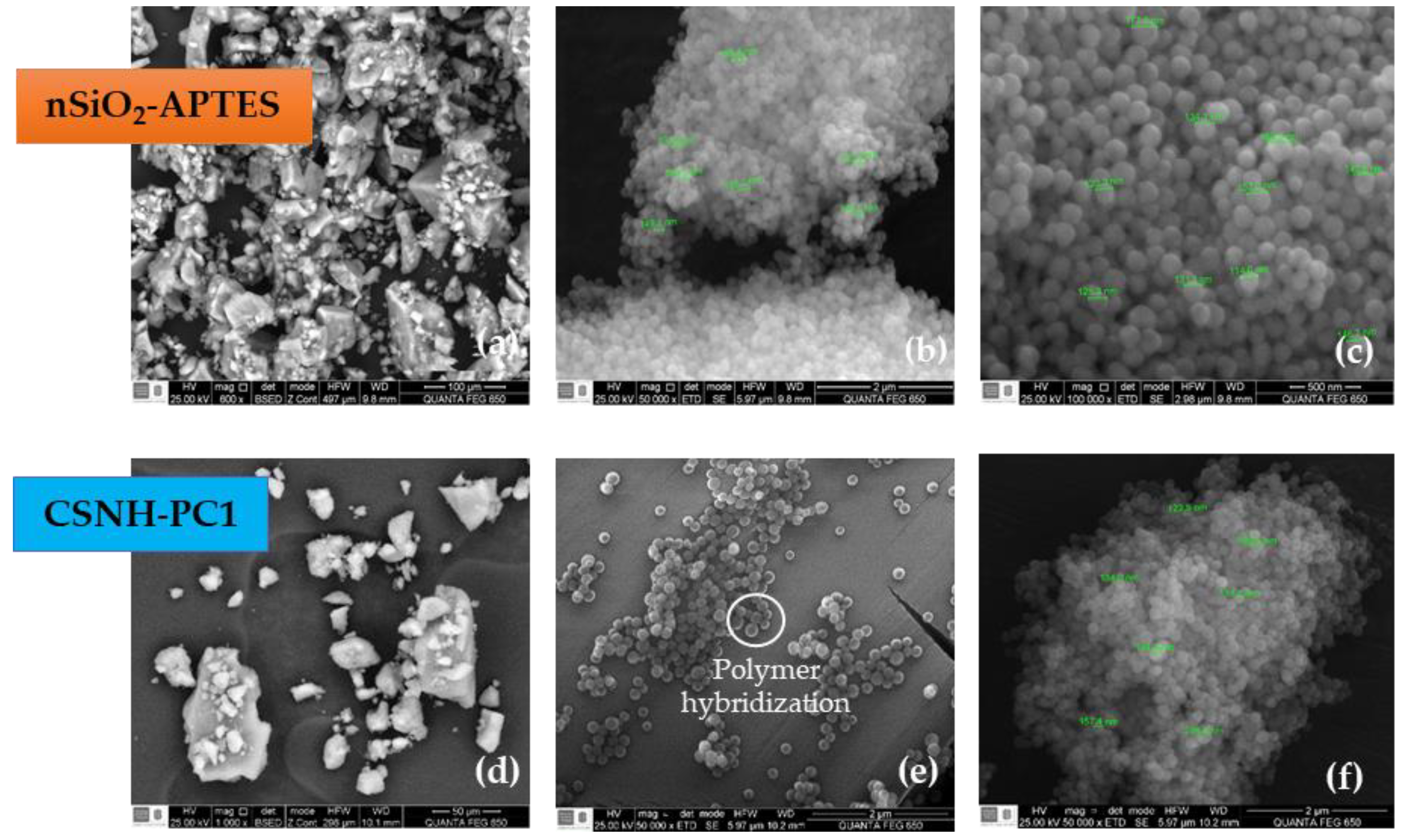
3.1. SEM Results
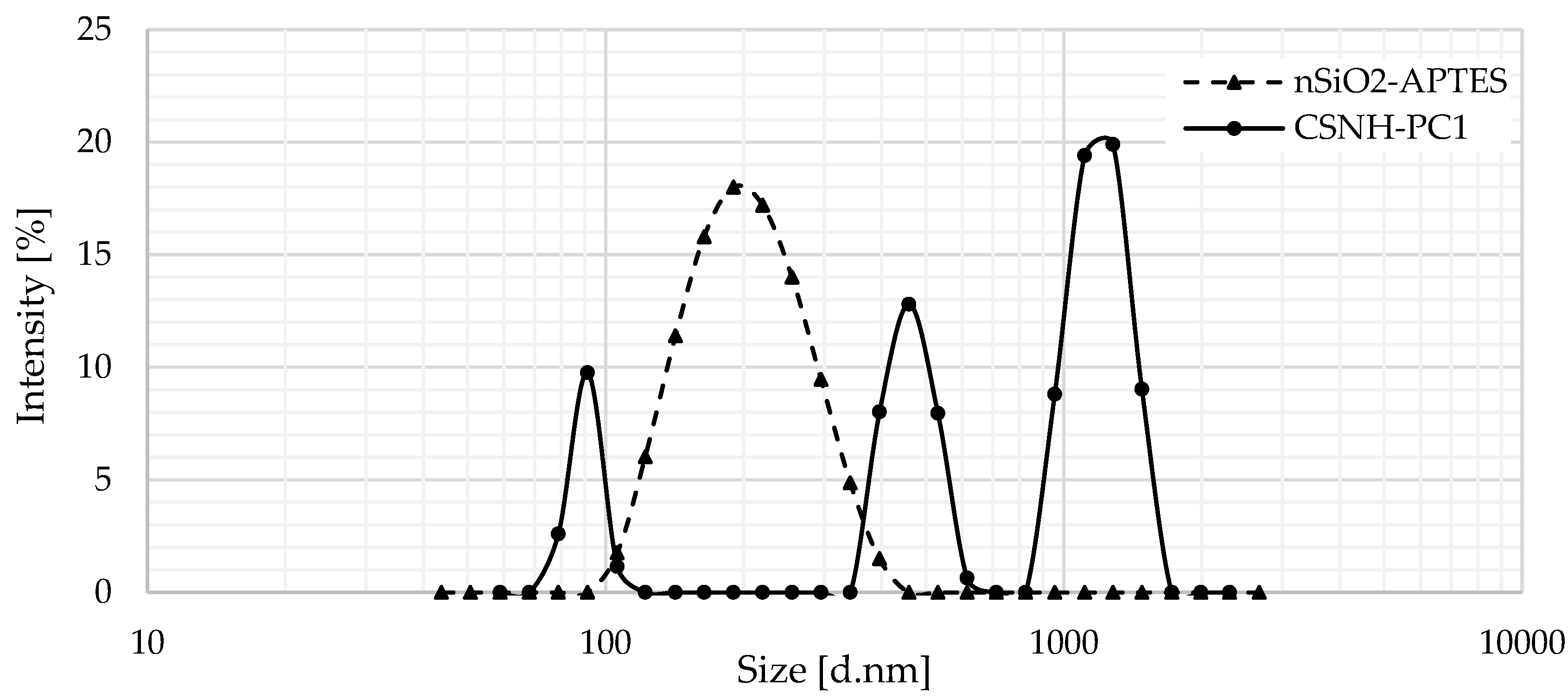
3.2. DLS Results
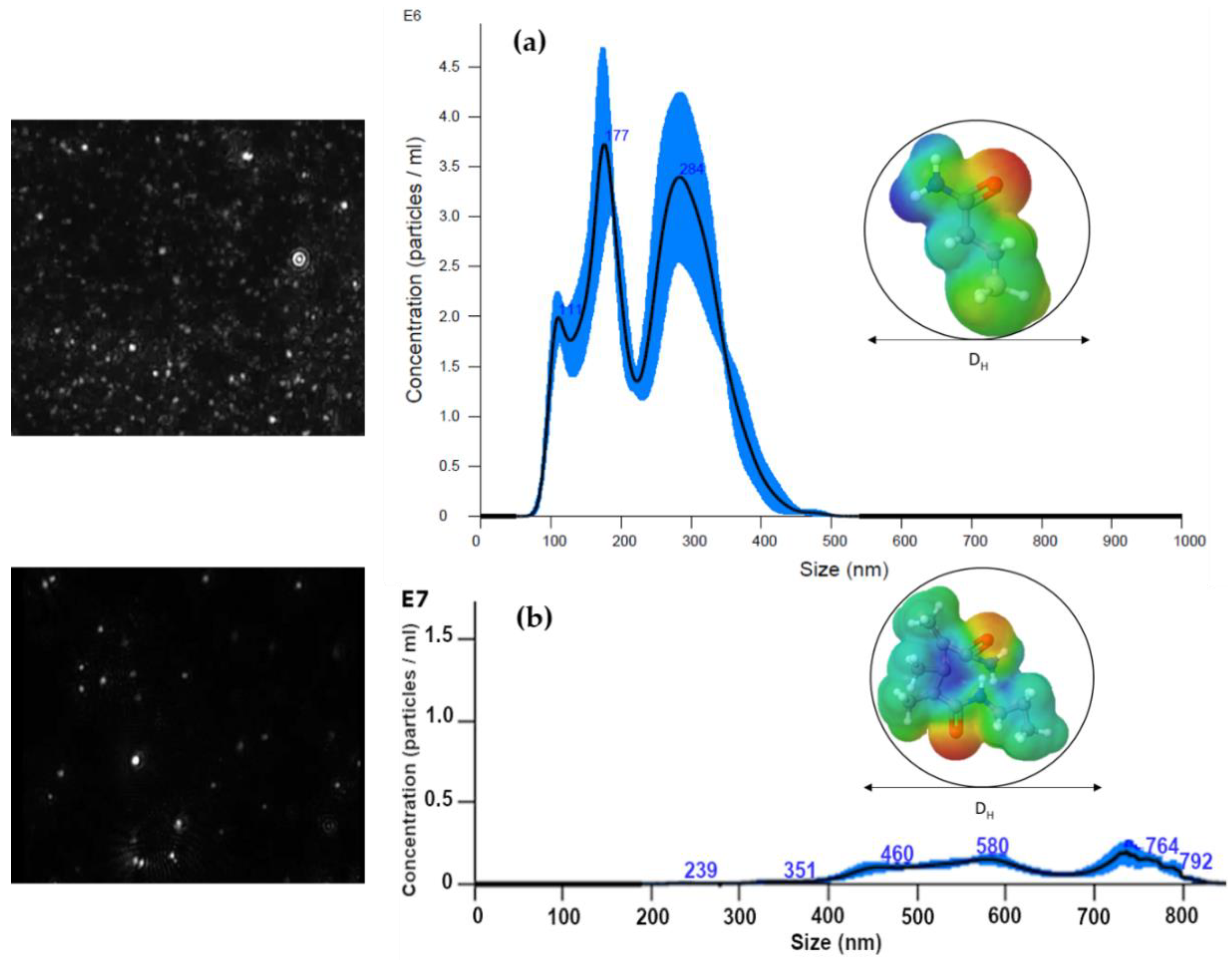
3.3. Hydrodynamic Radius by NTA
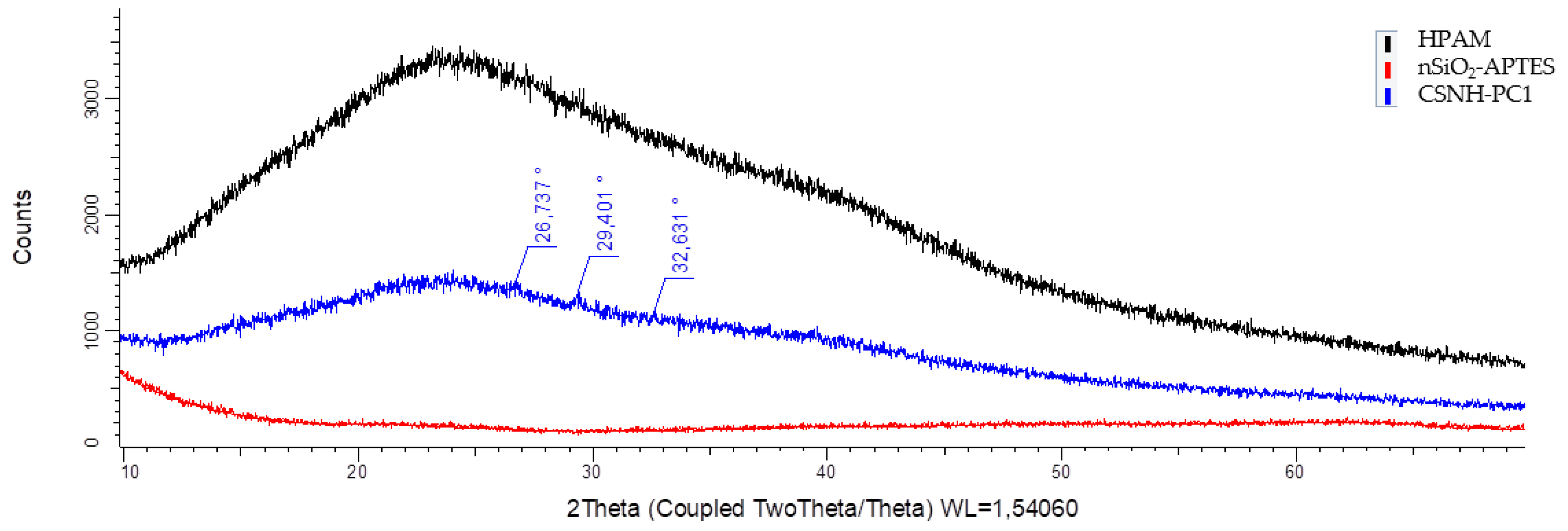
3.4. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Results
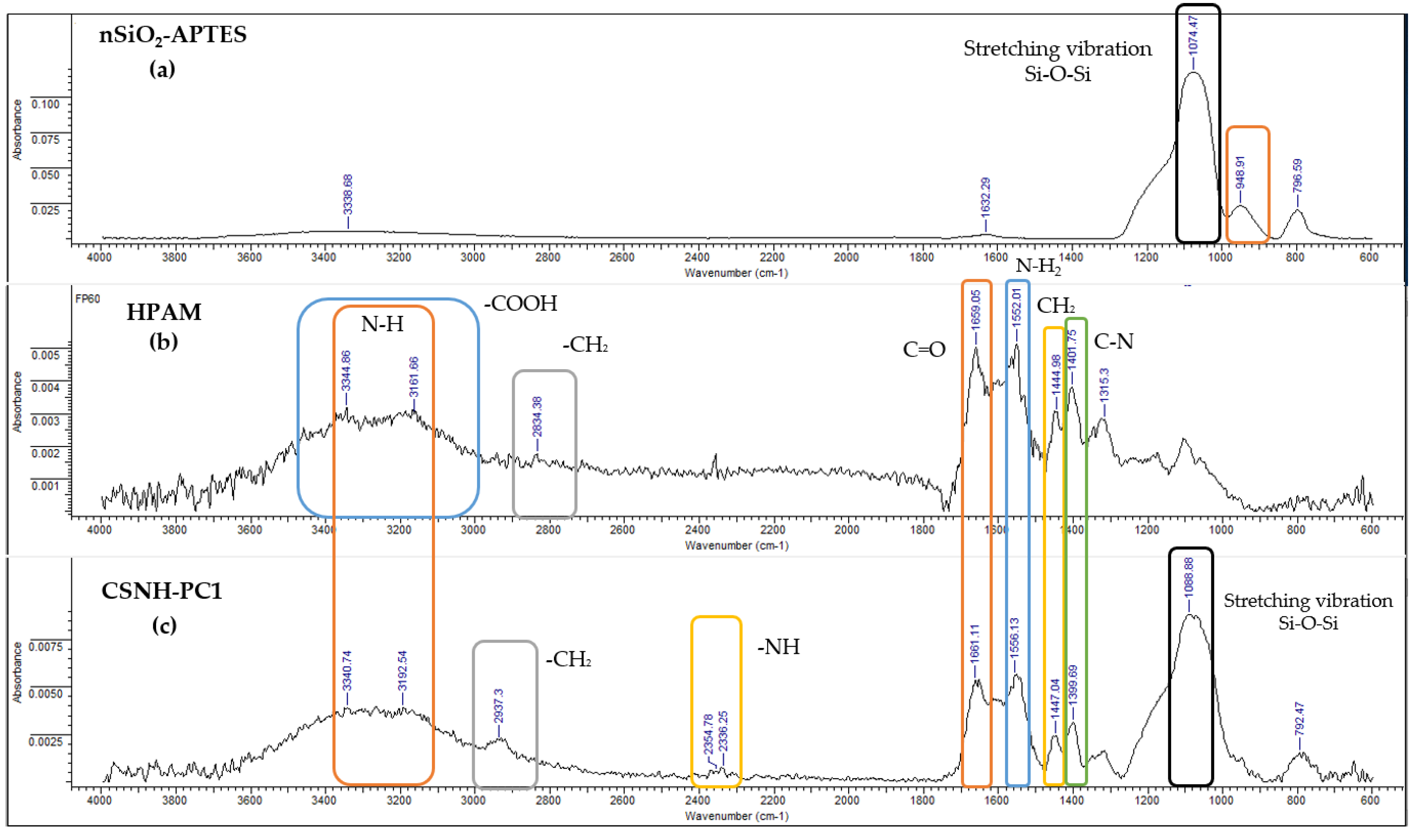
3.5. ATR-FTIR Results
- 3340 cm−1 (–NH stretching vibration and –OH stretching vibration) [46];
- 2937 cm−1 (–CH2 stretching vibration);
- 1661 cm−1 (C=O stretching vibration);
- 1399 cm−1 (C–N stretching vibration);
- 1088 cm−1 (Si–O–Si asymmetric stretching vibration) and;
- 792 cm−1 (Si–O–Si symmetric stretching vibration).
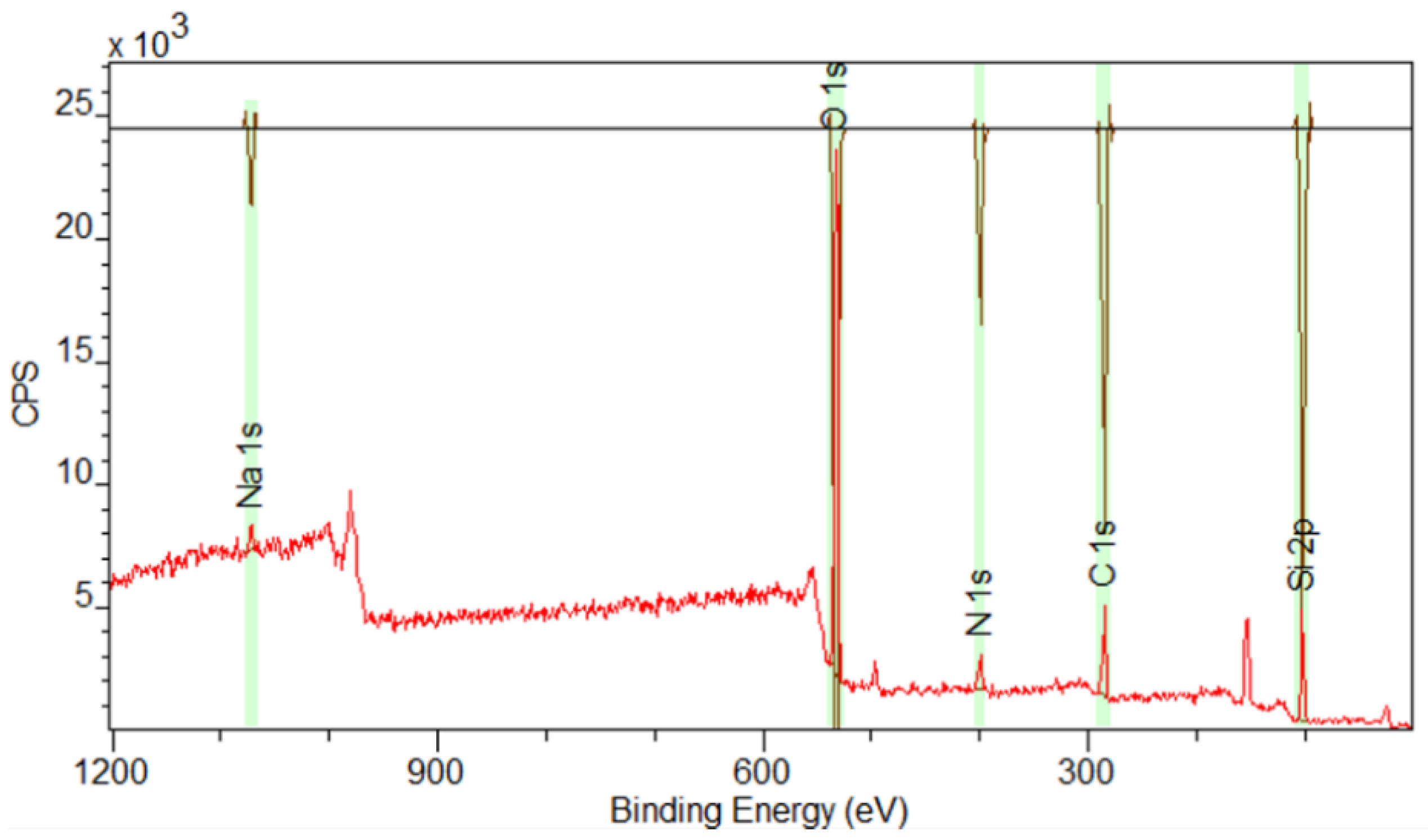
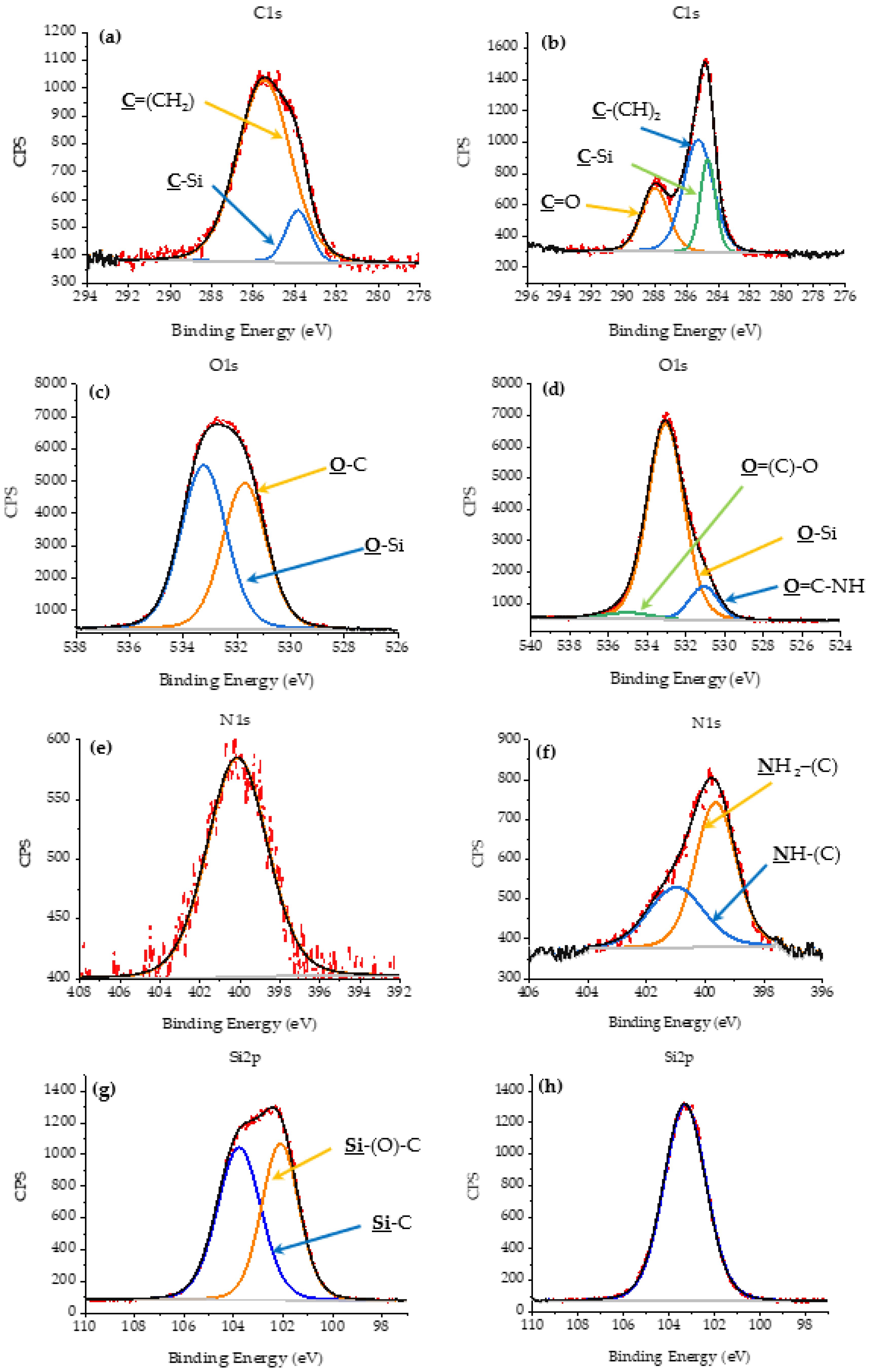
3.6. X-Ray Spectroscopy (XPS) Analysis
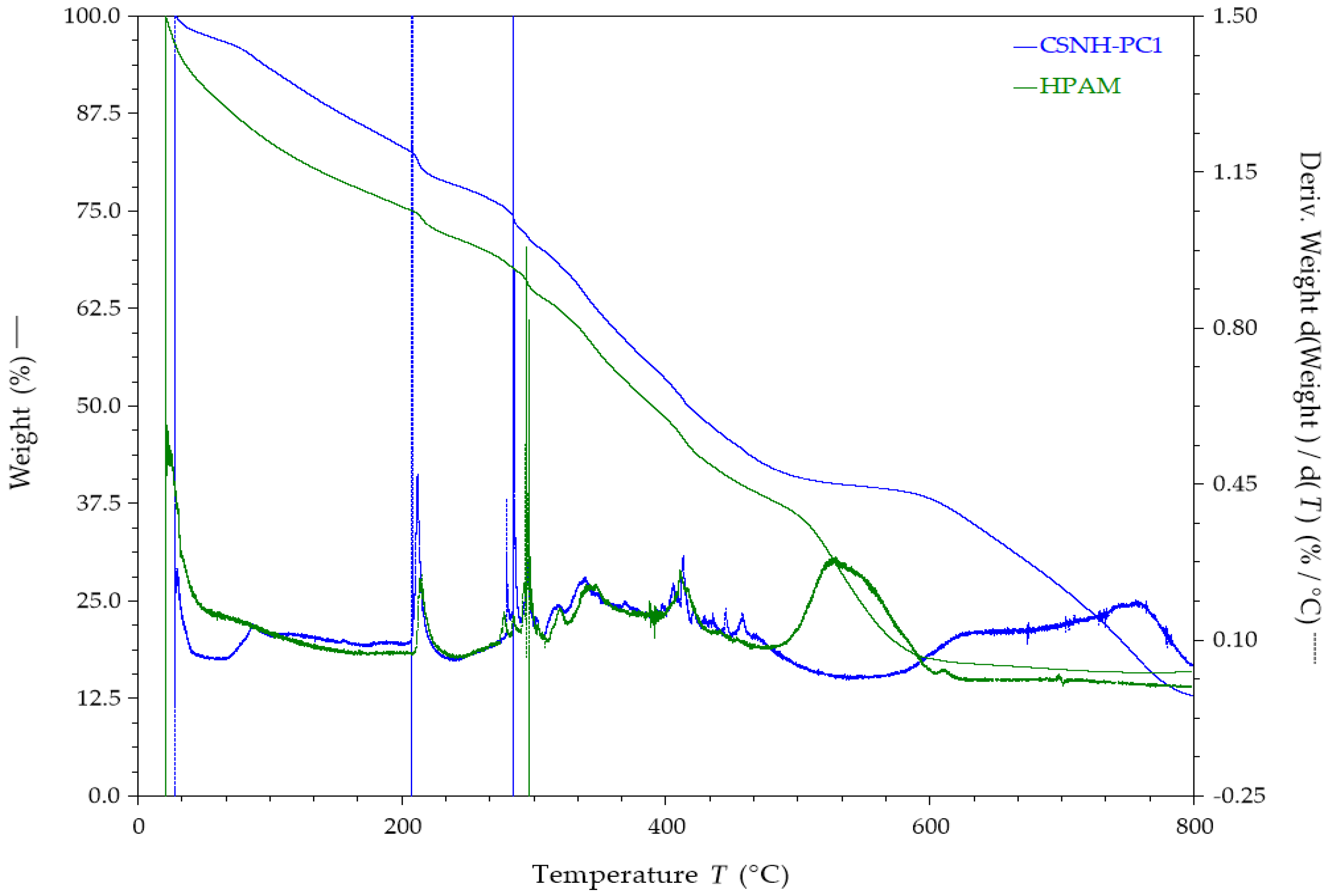
3.7. Thermal Properties—TGA Results
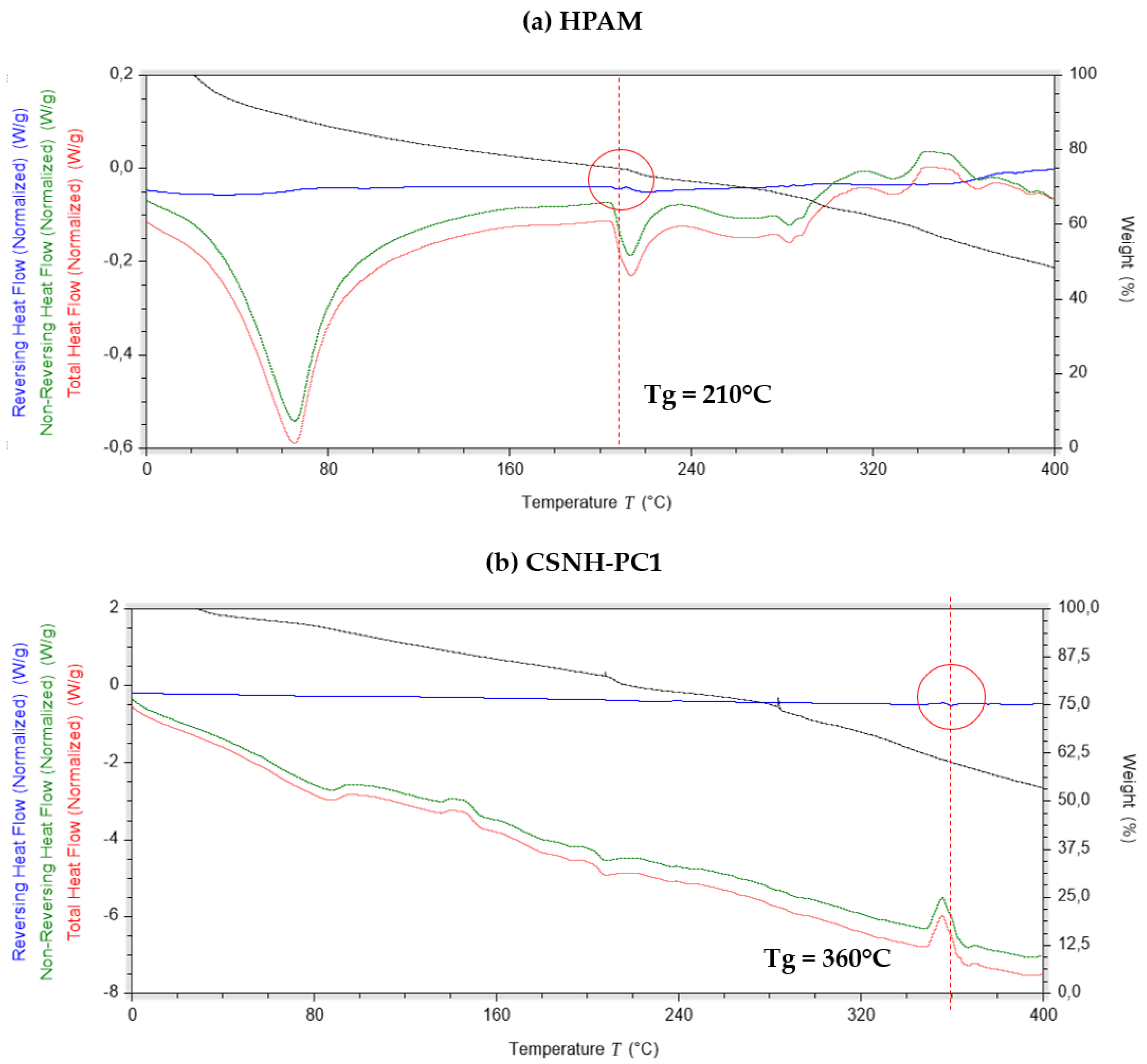
3.8. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Characterization Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yokoyama, T.; Masuda, H.; Suzuki, M.; Ehara, K.; Nogi, K.; Fuji, M.; Fukui, T.; Suzuki, H.; Tatami, J.; Hayashi, K.; et al. Basic properties and measuring methods of nanoparticles. In Nanoparticle Technology Handbook, 2nd ed.; Hosokawa, M., Nogi, K., Naito, M., Yokoyama, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 3–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.A.; Padavettan, V. Synthesis of silica nanoparticles by sol-gel: Size-dependent properties, surface modification, and applications in silica-polymer nanocomposites—A review. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, A.F.; Han, J.-H.; Kim, B.-C.; Rather, I.A. The intertwine of nanotechnology with the food industry. Saudi J. Boil. Sci. 2017, 25, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, R.; Brandhoff, P.; Weigel, S.; Marvin, H.; Bouwmeester, H.; Aschberger, K.; Rauscher, H.; Amenta, V.; Arena, M.; Moniz, F.B.; et al. Inventory of Nanotechnology applications in the agricultural, feed and food sector. EFSA Support. Publ. 2014, 11, 1–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghian, G.; Hendraningrat, L. A review on applications of nanotechnology in the enhanced oil recovery part B: Effects of nanoparticles on flooding. Int. Nano Lett. 2015, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druetta, P.; Picchioni, F. Polymer and nanoparticles flooding as a new method for Enhanced Oil Recovery. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 177, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joonaki, E.; Ghanaatian, S. The Application of Nanofluids for Enhanced Oil Recovery: Effects on Interfacial Tension and Coreflooding Process. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 2599–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakoya, M.F.; Shah, S.N. Emergence of nanotechnology in the oil and gas industry: Emphasis on the application of silica nanoparticles. Petroleum 2017, 3, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negin, C.; Ali, S.; Xie, Q. Application of nanotechnology for enhancing oil recovery—A review. Petroleum 2016, 2, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, J.-P.; Zuin, S.; Wick, P. Is nanotechnology revolutionizing the paint and lacquer industry? A critical opinion. Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 442, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiazhagan, A.; Joseph, R. Nanotechnology—A new prospective in organic coating—Review. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2011, 2, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittnar, Z.; Bartos, P.J.M.; Nemecek, J.; Smilauer, V.; Zeman, J. Nanotechnology in Construction 3; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le voyageur Temps. Nanotechnology in medicine. Indian Hear. J. 2016, 68, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, L.M.; Dewan, K.; Bronaugh, R.L. Nanotechnology in cosmetics. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 85, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Alvarez, P.J.; Li, Q. Applications of nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3931–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boul, P.J.; Ajayan, P.M. Nanotechnology research and development in upstream oil and gas. Energy Technol. 2019, 8, 1901216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaba, M.T.; Al Dushaishi, M.F.; Abbas, A.K. A comprehensive review of nanoparticles applications in the oil and gas industry. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2020, 10, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althues, H.; Henle, J.; Kaskel, S. Functional inorganic nanofillers for transparent polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1454–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Yoo, B.R. Advanced silica/polymer composites: Materials and applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.Z.; Zhang, M.Q.; Ruan, W.H. Surface modification of nanoscale fillers for improving properties of polymer nanocomposites: A review. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2006, 22, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corredor, L.M.; Husein, M.M.; Maini, B. A review of polymer nanohybrids for oil recovery. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 272, 102018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Hu, N.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of polymer—Mesoporous silica nanocomposites. Materials 2010, 3, 4066–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenberg, B.A.; Tenne, R. Polymer-assisted fabrication of nanoparticles and nanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 40–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriminna, R.; Fidalgo, A.; Pandarus, V.; Béland, F.; Ilharco, L.M.; Pagliaro, M. The Sol–Gel Route to advanced silica-based materials and recent applications. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 6592–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Wu, S.; Shen, J. Polymer/silica nanocomposites: Preparation, characterization, properties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3893–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Cui, P.; Tian, X.; Zheng, K. Pyrolysis studies of polyethylene terephthalate/silica nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, L.I.; Anton, C.C. Effect of the textural characteristics of the new silicas on the dynamic properties of styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) vulcanizates. Polym. Compos. 1988, 9, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Wang, Q. Preparation of conductive polyaniline/nanosilica particle composites through ultrasonic irradiation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, M.; Shen, Z. The effects of atomic oxygen on polyimide resin matrix composite containing nano-silicon dioxide. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interactions Mater. Atoms 2006, 243, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Guo, Z.-X. The influence of interphase on nylon-6/nano-SiO2 composite materials obtained fromin situ polymerization. Polym. Int. 2003, 52, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiue, G.-H.; Kuo, W.-J.; Huang, Y.-P.; Jeng, R.-J. Microstructural and morphological characteristics of PS–SiO2 nanocomposites. Polymer 2000, 41, 2813–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gu, B. Self-assembly of two- and three-dimensional particle arrays by manipulating the hydrophobicity of silica nanospheres. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 22175–22180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-J.; Kang, K.-S. Fabrication of a crack-free large area photonic crystal with colloidal silica spheres modified with vinyltriethoxysilane. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 4039–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bershtein, V.A.; Egorova, L.M.; Yakushev, P.N.; Pissis, P.; Sysel, P.; Brozova, L. Molecular dynamics in nanostructured polyimide-silica hybrid materials and their thermal stability. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2002, 40, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberola, N.D.; Benzarti, K.; Bas, C.; Bomal, Y. Interface effects in elastomers reinforced by modified precipitated silica. Polym. Compos. 2001, 22, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronov, A.; Kohut, A.; Synytska, A.; Peukert, W. Mechanochemical modification of silica with poly(1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) by grinding in a stirred media mill. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 3708–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Pallares, R.M.; Thanh, N.T.K. Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: Comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12871–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hayakawa, S.; Shirosaki, Y.; Fujii, E.; Kawabata, K.; Tsuru, K.; Osaka, A. Sol-gel synthesis and microstructure analysis of amino-modified hybrid silica nanoparticles from aminopropyltriethoxysilane and tetraethoxysilane. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Han, K.; Koo, J. A novel method to evaluate dispersion stability of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 70, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, V.; Hawe, A.; Jiskoot, W. Critical Evaluation of Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) by NanoSight for the Measurement of Nanoparticles and Protein Aggregates. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wei, C.; Liang, S.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. Nanoencapsulated phase change materials with polymer-SiO2 hybrid shell materials: Compositions, morphologies, and properties. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 164, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Martin, J.C.; Huang, R.; Huang, W.; Liu, A.; Han, A.; Sun, L. Synthesis of silicon complexes from rice husk derived silica nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 9036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.; Wang, M.; Cai, J.; Xu, J.; Xia, C. Facile preparation of highly-dispersed cobalt-silicon mixed oxide nanosphere and its catalytic application in cyclohexane selective oxidation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Velázquez, A.R.; Velasco, M.A.; García, S.A.P.; Licea-Jiménez, L. Functionalization Effect on Polymer Nanocomposite Coatings Based on TiO2–SiO2 Nanoparticles with Superhydrophilic Properties. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Qin, X.; Lai, N.; Peng, Q.; Li, X.; Li, C. Synthesis and Performance of an Acrylamide Copolymer Containing Nano-SiO2 as Enhanced Oil Recovery Chemical. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Casa Software Ltd. User Manual: XPS Spectra; Acolyte Science: Wilmslow/Cheshire, UK, 2001; pp. 1–163. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, W.S.M.; Smekal, W.; Powell, C.J. Simulation of Electron Spectra for Surface Analysis (SESSA); Version 2.1.1; NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz-Strzałka, M.; Deryło-Marczewska, A.; Kozakevych, R.B. Silica nanocomposites based on silver nanoparticles-functionalization and pH effect. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 8, 1649–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, P.; Fydrych, P.; Cagniant, D.; Nanse, G.; Bimer, J.; Jankowska, A. The characterization of nitrogen-enriched activated carbons by IR, XPS and LSER methods. Carbon 2002, 40, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, L.J.; Giraldo, M.A.; Llanos, S.; Maya, G.; Zabala, R.D.; Nassar, N.N.; Franco, C.A.; Alvarado, V.; Cortés, F.B. The effects of SiO2 nanoparticles on the thermal stability and rheological behavior of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide based polymeric solutions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 159, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, B.J.; Siegel, R.W.; Schadler, L.S. Glass-transition temperature behavior of alumina/PMMA nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 4371–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, R.; Deng, H.; Putz, K.W.; Brinson, L. Effect of particle agglomeration and interphase on the glass transition temperature of polymer nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, D.; Pyun, J.; Patterson, G.D.; Kowalewski, T.; Matyjaszewski, K. Synthesis and characterization of silica-graft-polystyrene hybrid nanoparticles: Effect of constraint on the glass-transition temperature of spherical polymer brushes. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2002, 40, 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongwa, P.; Nygaard, R.; Bai, B. Evaluation of a nanocomposite hydrogel for water shut-off in enhanced oil recovery applications: Design, synthesis, and characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 128, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.-M.; Zheng, S.-R.; Zheng, Y.-P. Matrix Materials in Polymer Matrix Composites and Technology, Composites Science and Engineering; Woodhead Publishing Series: Sawston, Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 101–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Quirós, H.A.; Casanova-Yepes, H.F. Effect of the functionalization of silica nanoparticles as a reinforcing agent on dental composite materials. Revista Facultad de Ingeniería Universidad de Antioquia 2015, 1, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Lv, G.; Zuo, Y.; Mu, Y. Thermal and crystallization studies of nano-hydroxyapatite reinforced polyamide 66 biocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
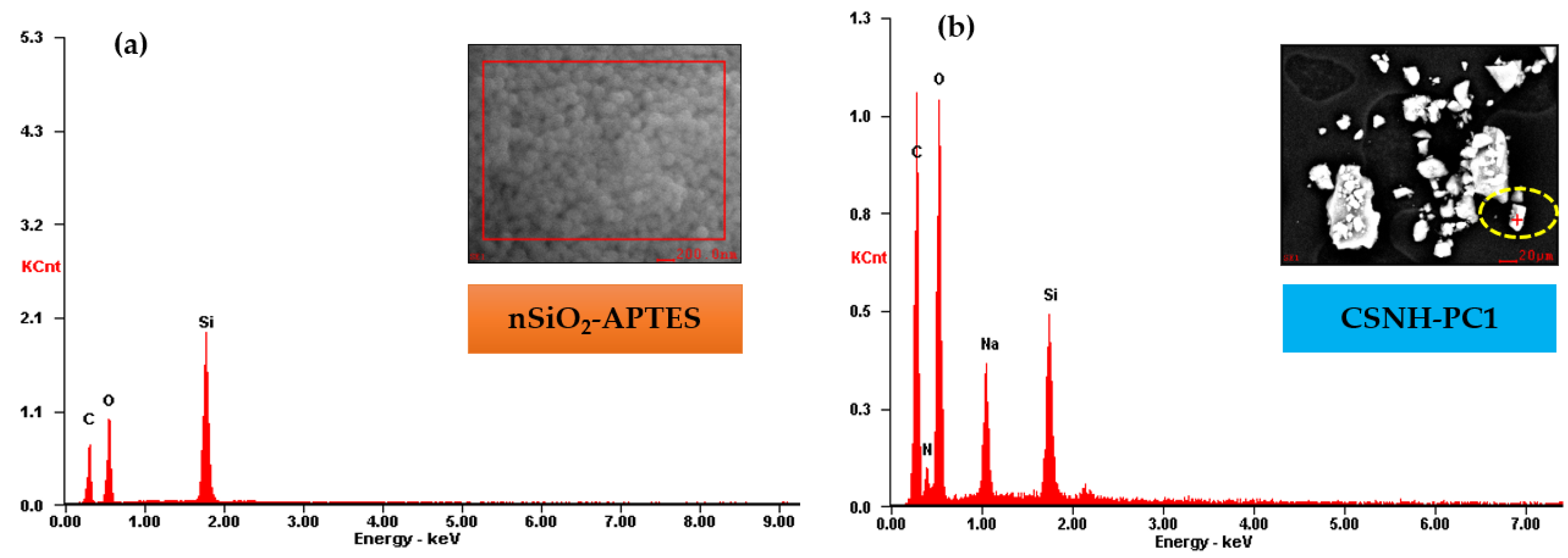
| Element | nSiO2-APTES | CSNH-PC1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt% | At% | Wt% | At% | |
| C | 36.29 | 47.16 | 37.79 | 45.92 |
| N | 0.50 | 0.50 | 8.95 | 9.32 |
| O | 41.51 | 40.50 | 41.60 | 37.95 |
| Si | 22.20 | 12.34 | 5.14 | 2.67 |
| Na | 6.52 | 4.14 | ||
| Energy Level | Functional Groups | CSNH-PC1 | nSiO2-APTES | NIST Database | Zienkiewicz et al. | Burg et al. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1s | C–(CH2) | 285.3 | 285.5 | 285.4 | 285.0 | |
| C–(Si) | 284.7 | 283.9 | 284.4 | |||
| C=(O) | 288.0 | 287.6 | 287.9 | |||
| O1s | O=(C)–O | 534.4 | 535.1 | 532.0 | ||
| O=(C)–NH | 531.1 | 531.7 | 530.7 | 531.2 | ||
| O–(Si) | 533.0 | 533.2 | 532.3 | 532.7 | 530.3 | |
| N1s | NH2–(C) | 399.7 | 400.1 | 399.2 | 399.9 | |
| NH–(C)–O | 401.0 | 400.0 | ||||
| Si2p | Si–(O)–C | 103.3 | 103.8 | 102.9 | 103.5 | |
| Si–(C) | 102.1 | 101.7 | 101.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-Cañas, M.C.; Quintero, H.I.; Corredor, L.M.; Manrique, E.; Romero Bohórquez, A.R. New Nanohybrid Based on Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide and Silica Nanoparticles: Morphological, Structural and Thermal Properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051152
Ruiz-Cañas MC, Quintero HI, Corredor LM, Manrique E, Romero Bohórquez AR. New Nanohybrid Based on Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide and Silica Nanoparticles: Morphological, Structural and Thermal Properties. Polymers. 2020; 12(5):1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051152
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-Cañas, María C., Henderson I. Quintero, Laura M. Corredor, Eduardo Manrique, and Arnold R. Romero Bohórquez. 2020. "New Nanohybrid Based on Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide and Silica Nanoparticles: Morphological, Structural and Thermal Properties" Polymers 12, no. 5: 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051152
APA StyleRuiz-Cañas, M. C., Quintero, H. I., Corredor, L. M., Manrique, E., & Romero Bohórquez, A. R. (2020). New Nanohybrid Based on Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide and Silica Nanoparticles: Morphological, Structural and Thermal Properties. Polymers, 12(5), 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051152








