Cellulose Aerogel Derived Hierarchical Porous Carbon for Enhancing Flavin-Based Interfacial Electron Transfer in Microbial Fuel Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
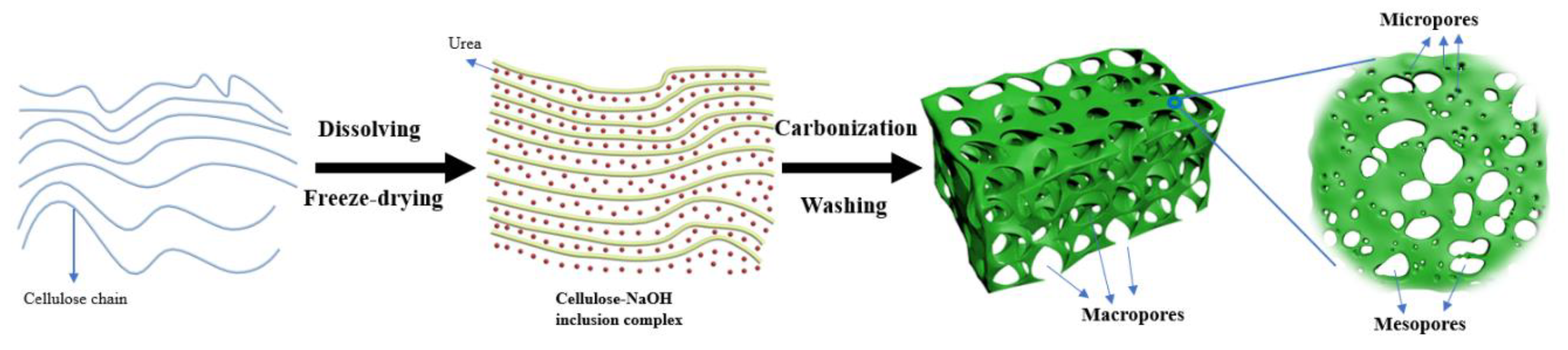
2.2. Porous Carbon Preparation
2.3. Calculation of Molecular Weight of Cellulose
2.4. Bacteria Culture
2.5. MFC Set-Up and Operation
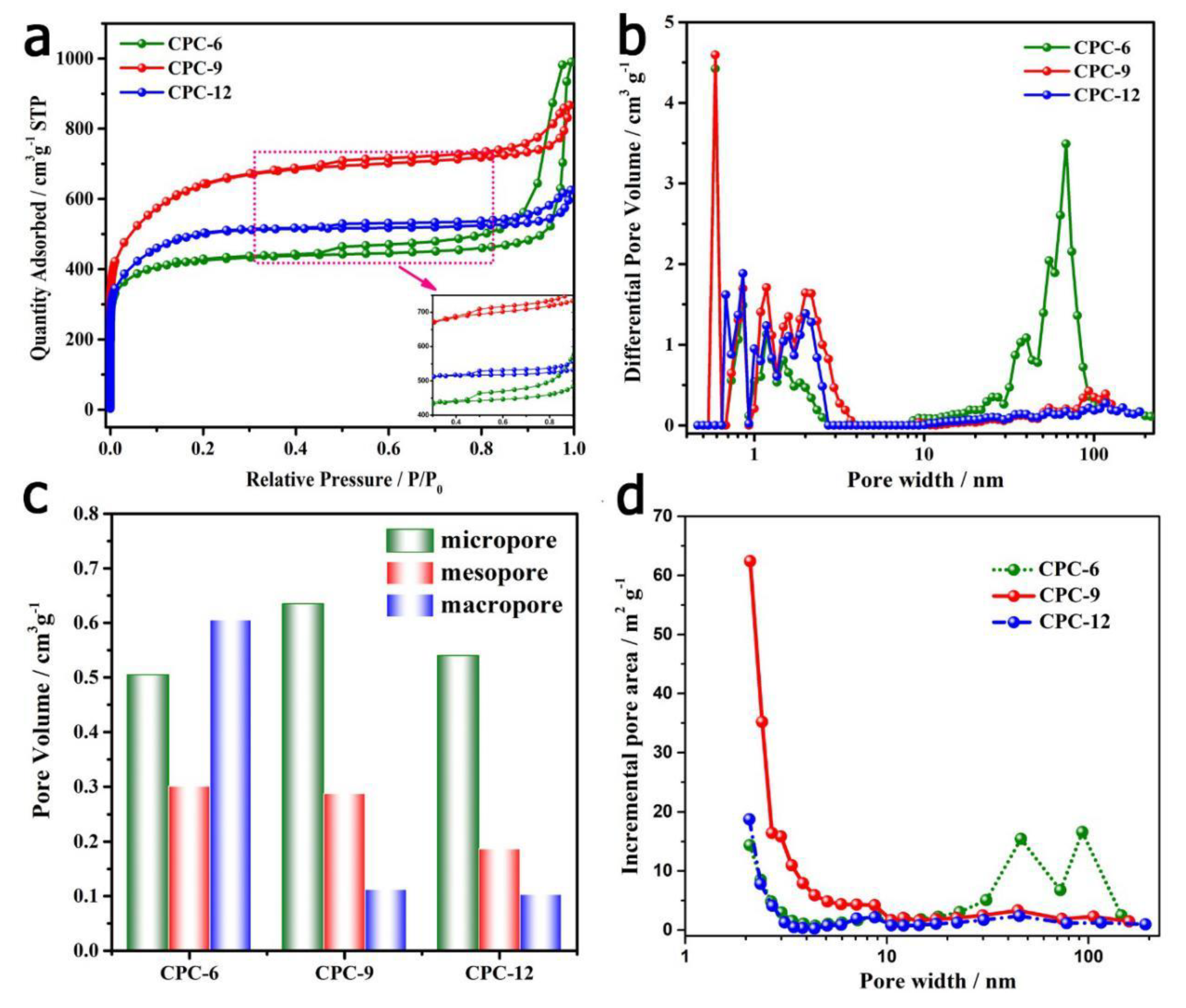
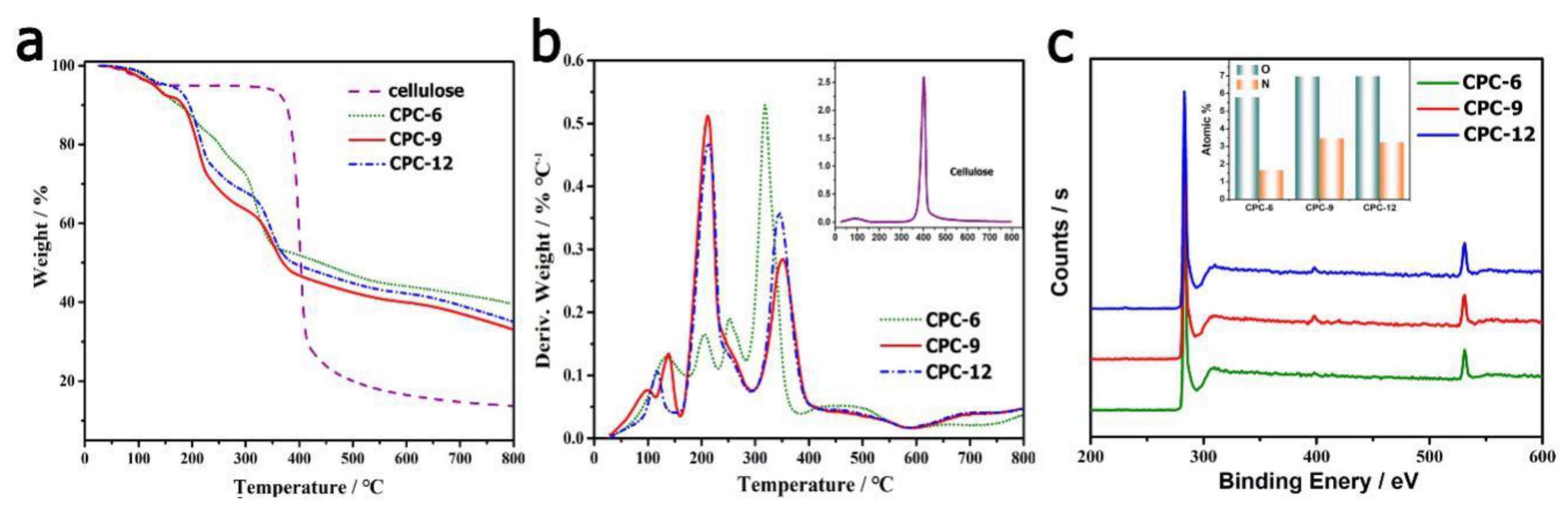
2.6. Physical Characterization
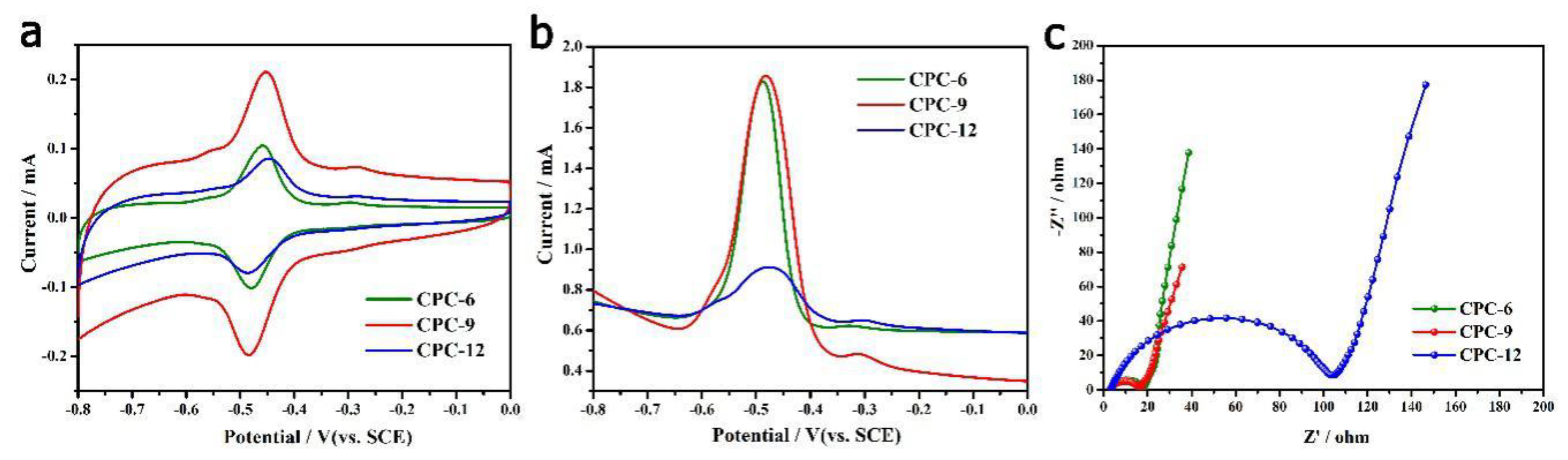
2.7. Electrochemical Characterization
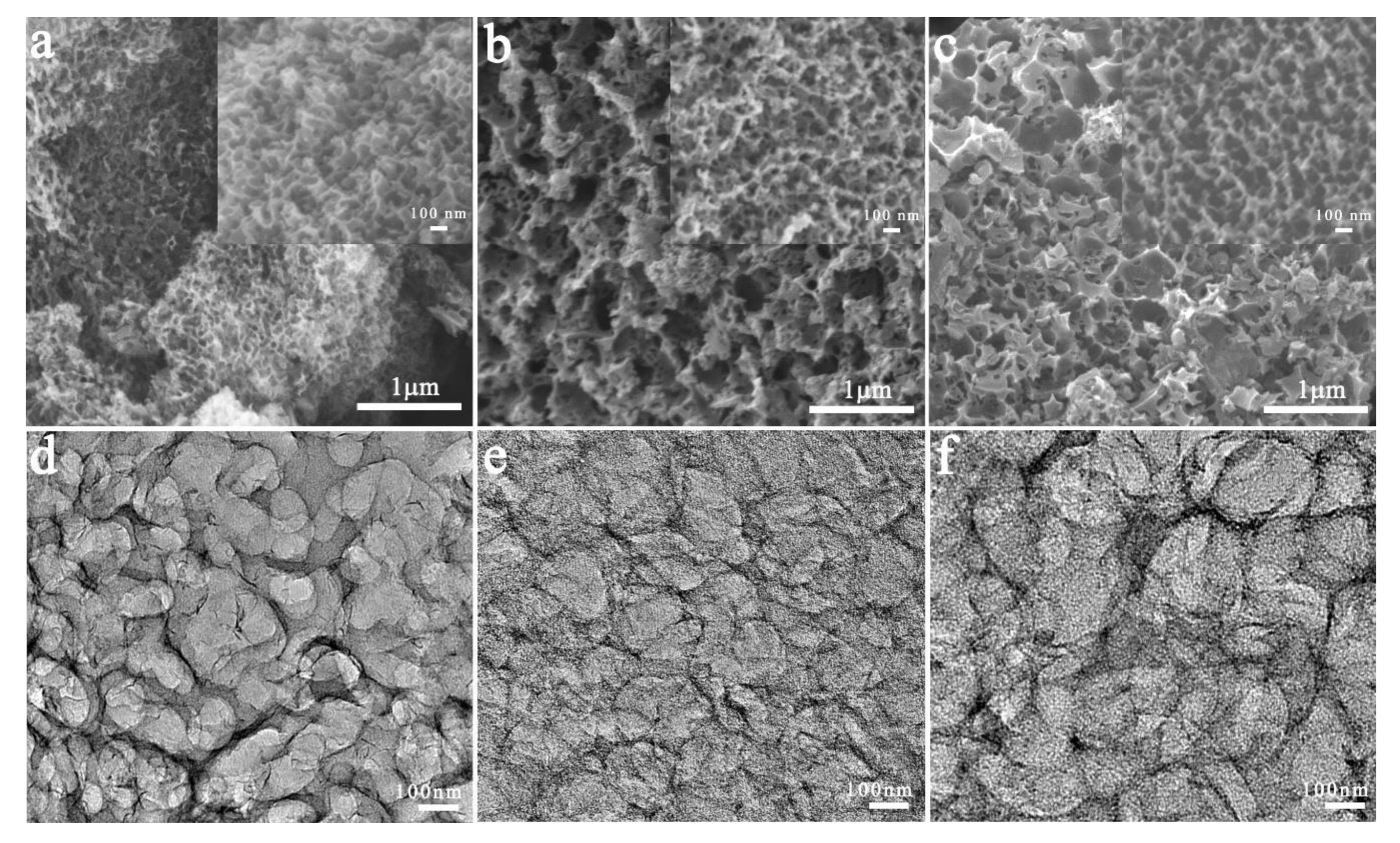
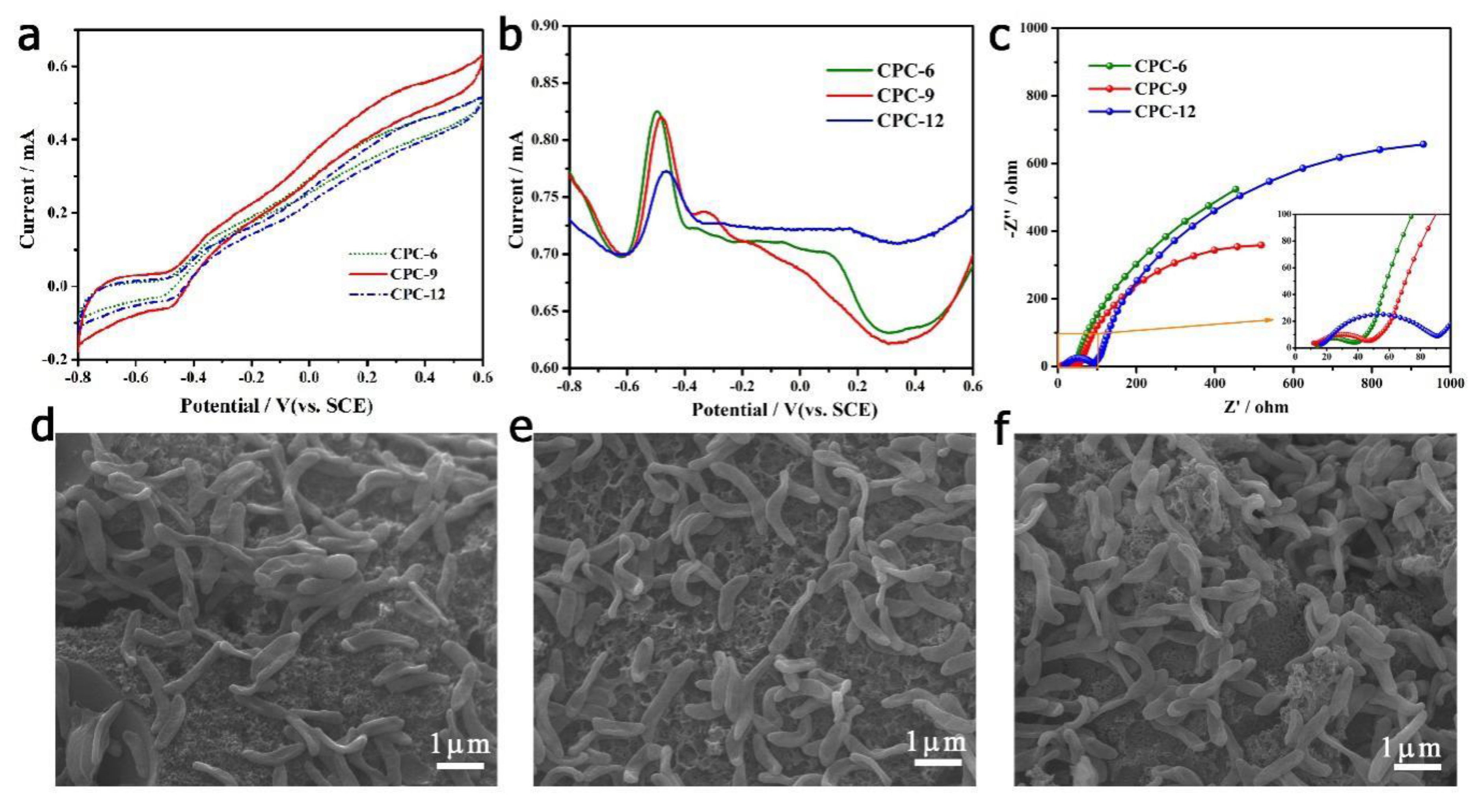
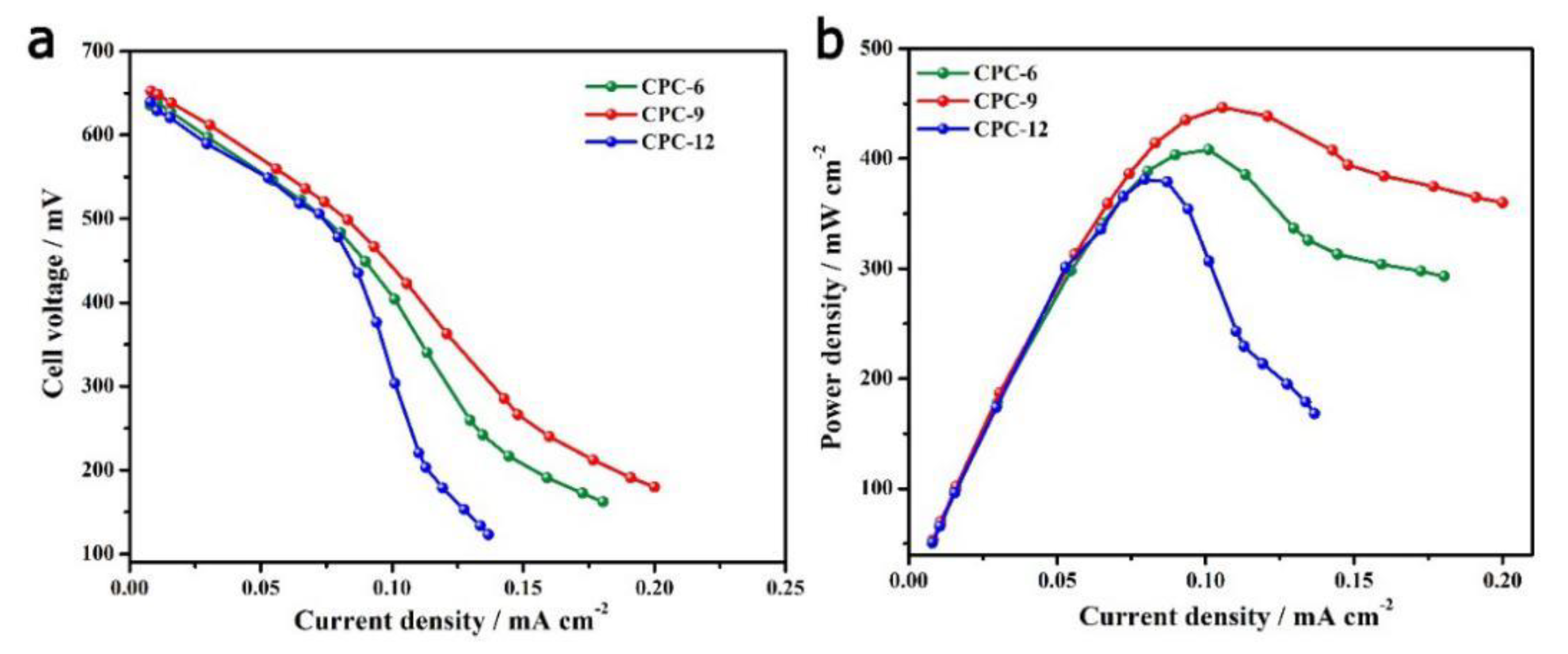
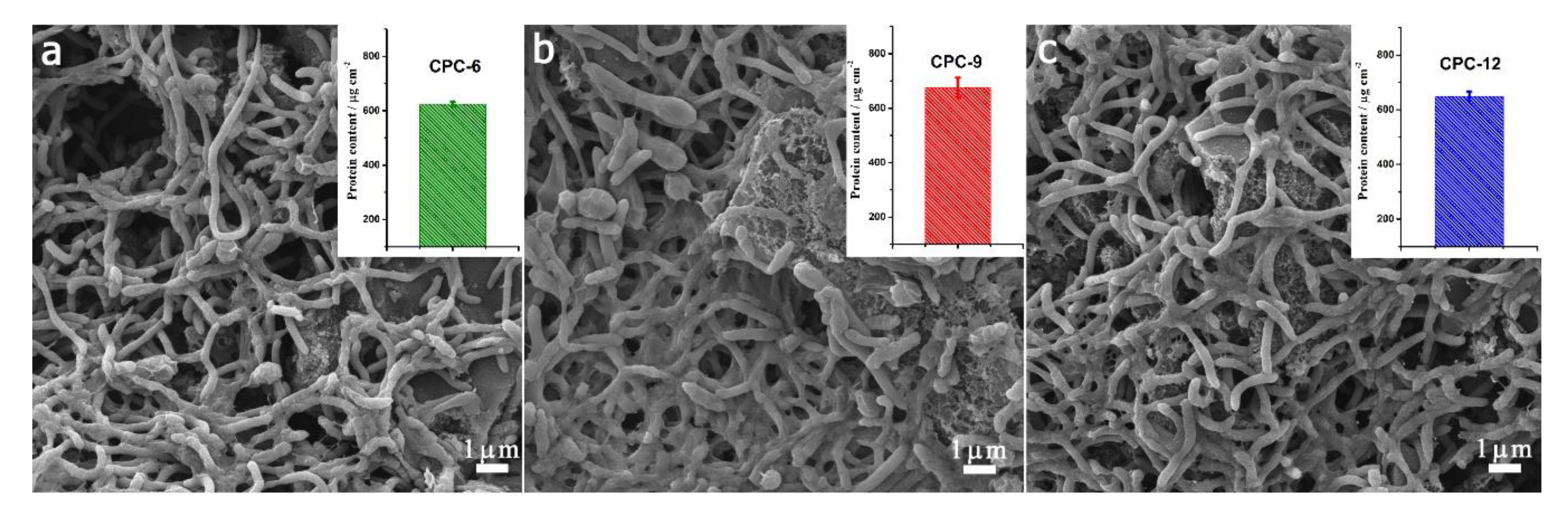
3. Results & Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Logan, B.E.; Hamelers, B.; Rozendal, R.; Schröder, U.; Keller, J.; Freguia, S.; Aelterman, P.; Verstraete, W.; Rabaey, K. Microbial Fuel Cells: Methodology and Technology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5181–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.J.; Lefebvre, O.; Tan, Z.; Ng, H.Y. Microbial fuel-cell-based toxicity sensor for fast monitoring of acidic toxicity. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flexer, V.; Chen, J.; Donose, B.C.; Sherrell, P.; Wallace, G.G.; Keller, J. The nanostructure of three-dimensional scaffolds enhances the current density of microbial bioelectrochemical systems. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Hu, J.; Lieber, A.M.; Jackan, C.S.; Biffinger, J.C.; Fitzgerald, L.A.; Ringeisen, B.R.; Lieber, C.M. Nanoparticle Facilitated Extracellular Electron Transfer in Microbial Fuel Cells. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 6737–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevin, K.P.; Lovley, D.R. Mechanisms for Fe(III) oxide reduction in sedimentary environments. Geomicrobiol. J. 2002, 19, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lies, D.P.; Hernandez, M.E.; Kappler, A.; Mielke, R.E.; Gralnick, J.A.; Newman, D.K. Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 Uses Overlapping Pathways for Iron Reduction at a Distance and by Direct Contact under Conditions Relevant for Biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2005, 71, 4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsili, E.; Baron, D.B.; Shikhare, I.D.; Coursolle, D.; Gralnick, J.A.; Bond, D.R. Shewanella Secretes flavins that mediate extracellular electron transfer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3968–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.I.; Marcus, A.K.; Lee, H.S.; Parameswaran, P.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Rittmann, B.E. A kinetic perspective on extracellular electron transfer by anode-respiring bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Qiao, Y.; Wu, X.-S.; Ma, C.-X.; Li, X.; Li, C.M. Synergistic effect of titanium dioxide nanocrystal/reduced graphene oxide hybrid on enhancement of microbial electrocatalysis. J. Power Sources 2015, 276, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Jangir, Y.; El-Naggar, M.Y. Disentangling the roles of free and cytochrome-bound flavins in extracellular electron transport from Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 198, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Qiao, Y.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Wu, X.-S.; Xie, J.-L.; Yu, S.-H.; Guo, J.; Li, C.M. Tailoring Unique Mesopores of Hierarchically Porous Structures for Fast Direct Electrochemistry in Microbial Fuel Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1501535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wu, X.-S.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, R.-J.; Luo, X. Tailoring of pore structure in mesoporous carbon for favourable flavin mediated interfacial electron transfer in microbial fuel cells. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 9597–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Hou, H.; Zhao, F. Cellulose-derived nitrogen and phosphorus dual-doped carbon as high performance oxygen reduction catalyst in microbial fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2015, 273, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Liang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Dong, H.; Zheng, M.; Hu, H.; Liu, Y. Bark-Based 3D Porous Carbon Nanosheet with Ultrahigh Surface Area for High Performance Supercapacitor Electrode Material. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13827–13835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Zhao, Z.; Tian, J.; Li, H.; Sang, Y.; Yu, G.; Cai, H.; Liu, H.; Wong, C.P.; Umar, A. Hierarchical porous carbon aerogel derived from bagasse for high performance supercapacitor electrode. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 12120–12129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tong, X.; Zhuo, H.; Zhong, L.; Peng, X.; Wang, S.; Sun, R. 3D hierarchical porous N-doped carbon aerogel from renewable cellulose: An attractive carbon for high-performance supercapacitor electrodes and CO2 adsorption. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 15788–15795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Sun, X.; Gaddam, R.R.; Kumar, N.A.; Zhao, X.S. Electrocapacitive properties of nitrogen-containing porous carbon derived from cellulose. J. Power Sources 2017, 360, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhu, S.; Peng, J.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, G.; Guo, X.; Zhao, N.; Ma, Y.; Ma, L. Synthesis of micro- and meso-porous carbon derived from cellulose as an electrode material for supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 241, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fei, B.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Tian, G.; Jiang, Z. Porous nanoplatelets wrapped carbon aerogels by pyrolysis of regenerated bamboo cellulose aerogels as supercapacitor electrodes. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 180, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, L. Unique Gelation Behavior of Cellulose in NaOH/Urea Aqueous Solution. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Zhao, P.; Hu, K.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, G. Dissolution of cellulose in aqueous NaOH/urea solution: Role of urea. Cellulose 2014, 21, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L. Dilute solution properties of cellulose in LiOH/urea aqueous system. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 3093–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Hu, T.; Fan, W. Cellulose generated-microporous carbon nanosheets with nitrogen doping. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 9126–9132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.; Evereet, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, H.; Hu, Y.; Tong, X.; Zhong, L.; Peng, X.; Sun, R. Sustainable hierarchical porous carbon aerogel from cellulose for high-performance supercapacitor and CO2 capture. Ind. Crop Prod. 2016, 87, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Qiao, Y.; Shi, Z.; Tang, W.; Li, C.M. Hierarchically Porous N-Doped Carbon Nanotubes/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite for Promoting Flavin-Based Interfacial Electron Transfer in Microbial Fuel Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 11671–11677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretto, L.M.; Pepe, N.; Ugo, P. Voltammetry of redox analytes at trace concentrations with nanoelectrode ensembles. Talanta 2004, 62, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Kim, B.; Chang, I.S. Tracking of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 biofilm formation of a microbial electrochemical system via differential pulse voltammetry. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 254, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Lv, Z.; Yang, X.; Wei, C. Anode modification with capacitive materials for a microbial fuel cell: An increase in transient power or stationary power. Phys. Chem. Chem.Phys. 2014, 16, 10464–10472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Precursor | Gelation/Regeneration | NaOH wt%: Urea wt% | Atmosphere | Subsequent Activation | Max. SBET (m2 g−1) @temperature (Cº) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cellulose (cotton linter) | Y | 12:7 | NH3 | N.A. | 615@800 | [16] |
| microcrystalline cellulose | Y | 7:12 | N2 | N.A. | 781@600 | [17] |
| microcrystalline cellulose | Y | 7.5:12 | N2 | N.A. | 646@700 | [18] |
| cellulose (cotton linter) | Y | 12:7 | CO2 | N.A. | 1364@800 | [25] |
| bamboo fibers | Y | 7:12 | Ar | KOH | 1085@900 | [19] |
| cellulose extracted from bagasse | Y | 7.5:11.5 | N2 | KOH | 2065@900 | [15] |
| cellulose | N | 8(KOH):12 | N2 | N.A. | 1854@800 | [23] |
| α-cellulose | N | 6:6 | Ar | N.A. | 1308@800 | this work |
| α-cellulose | N | 6:9 | Ar | N.A. | 2052@800 | this work |
| α-cellulose | N | 6:12 | Ar | N.A. | 1562@800 | this work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; He, X.; Wang, R.-J.; Lu, Z.-S.; Qiao, Y. Cellulose Aerogel Derived Hierarchical Porous Carbon for Enhancing Flavin-Based Interfacial Electron Transfer in Microbial Fuel Cells. Polymers 2020, 12, 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030664
Wang D, Wang Y, Yang J, He X, Wang R-J, Lu Z-S, Qiao Y. Cellulose Aerogel Derived Hierarchical Porous Carbon for Enhancing Flavin-Based Interfacial Electron Transfer in Microbial Fuel Cells. Polymers. 2020; 12(3):664. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030664
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Deng, Ying Wang, Jing Yang, Xiu He, Rui-Jie Wang, Zhi-Song Lu, and Yan Qiao. 2020. "Cellulose Aerogel Derived Hierarchical Porous Carbon for Enhancing Flavin-Based Interfacial Electron Transfer in Microbial Fuel Cells" Polymers 12, no. 3: 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030664
APA StyleWang, D., Wang, Y., Yang, J., He, X., Wang, R.-J., Lu, Z.-S., & Qiao, Y. (2020). Cellulose Aerogel Derived Hierarchical Porous Carbon for Enhancing Flavin-Based Interfacial Electron Transfer in Microbial Fuel Cells. Polymers, 12(3), 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030664







