Integration of Polylactide into Polyethylenimine Facilitates the Safe and Effective Intracellular siRNA Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
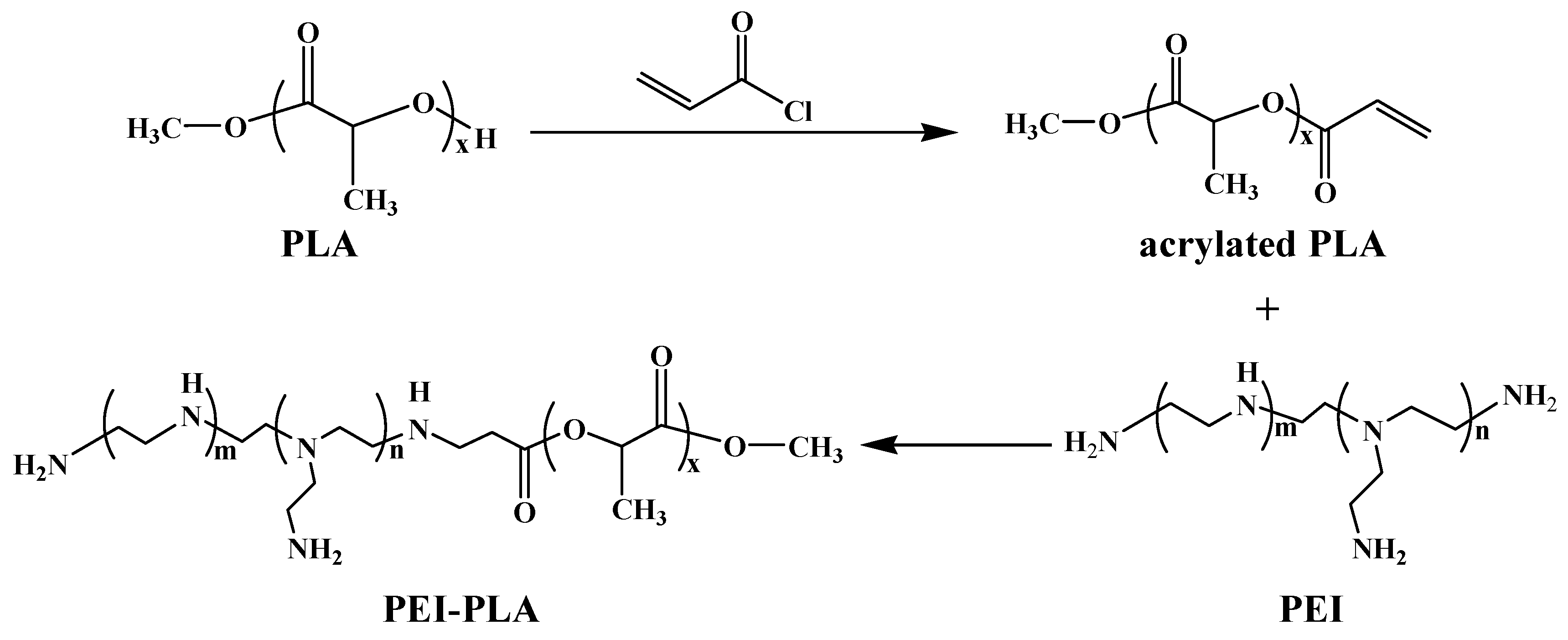
2.2. Synthesis of Acrylated PLA
2.3. Synthesis of PEI-PLA Copolymer
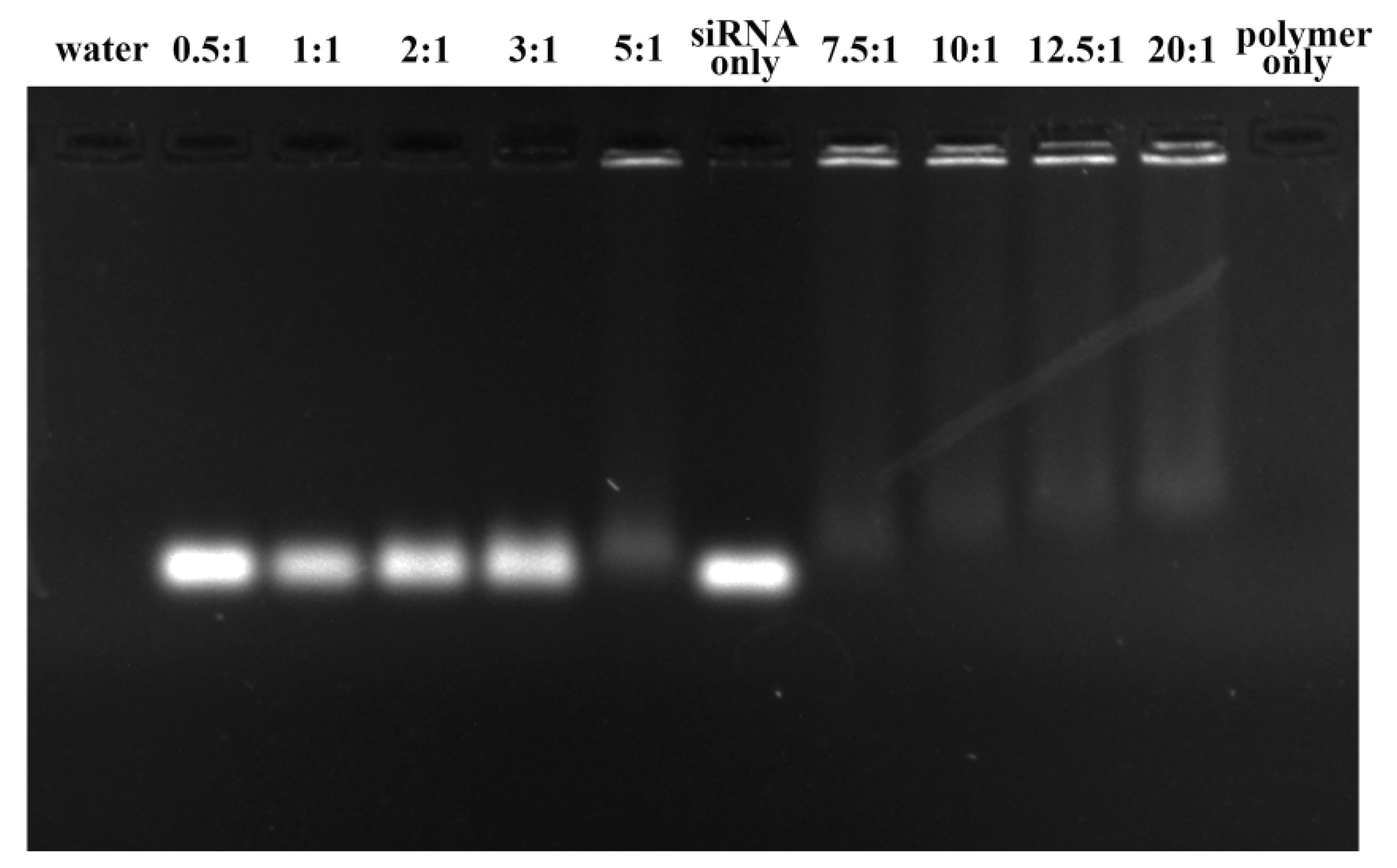
2.4. Determination of siRNA Complexation by Gel Retardation Assay
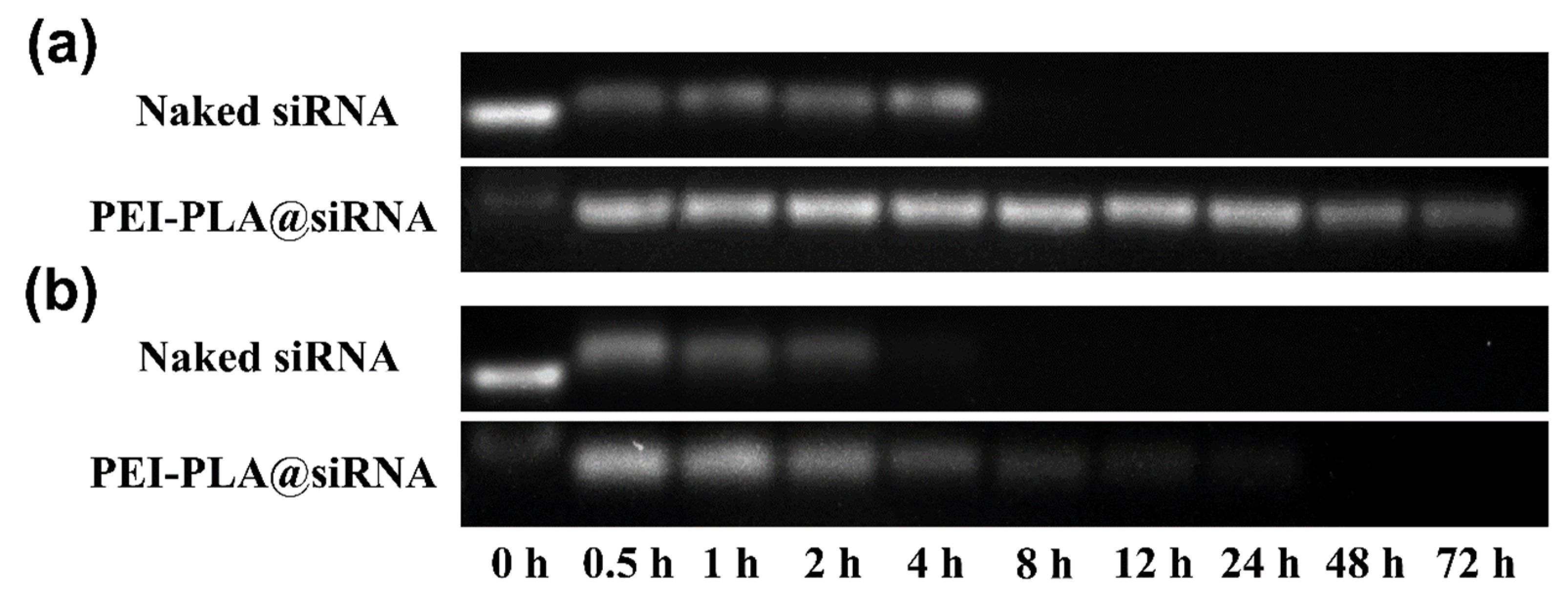
2.5. Determination of the Serum Stability of siRNA Polyplex
2.6. Cytotoxicity of PEI-PLA Copolymer
2.7. Cellular Internalization of siRNA Polyplex
2.8. Gene Silencing Efficiency In Vitro
2.8.1. Real-Time PCR Assays for mRNA Level of PKM2 Gene
2.8.2. Western Blot Analysis of PKM2 Expression
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of PEI-PLA Copolymer
3.2. Gel Retardation Assay of the PEI-PLA@siRNA Polyplex
3.3. Serum Stability of PEI-PLA@siRNA Polyplex
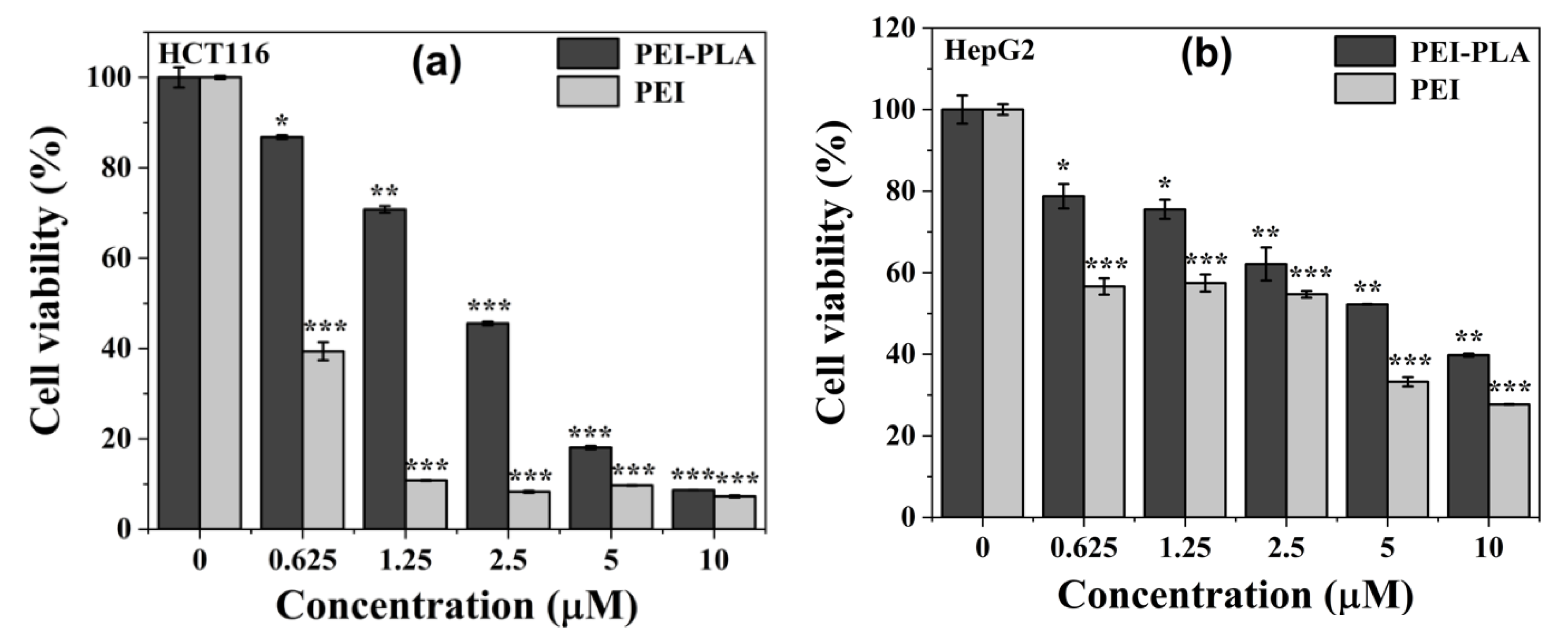
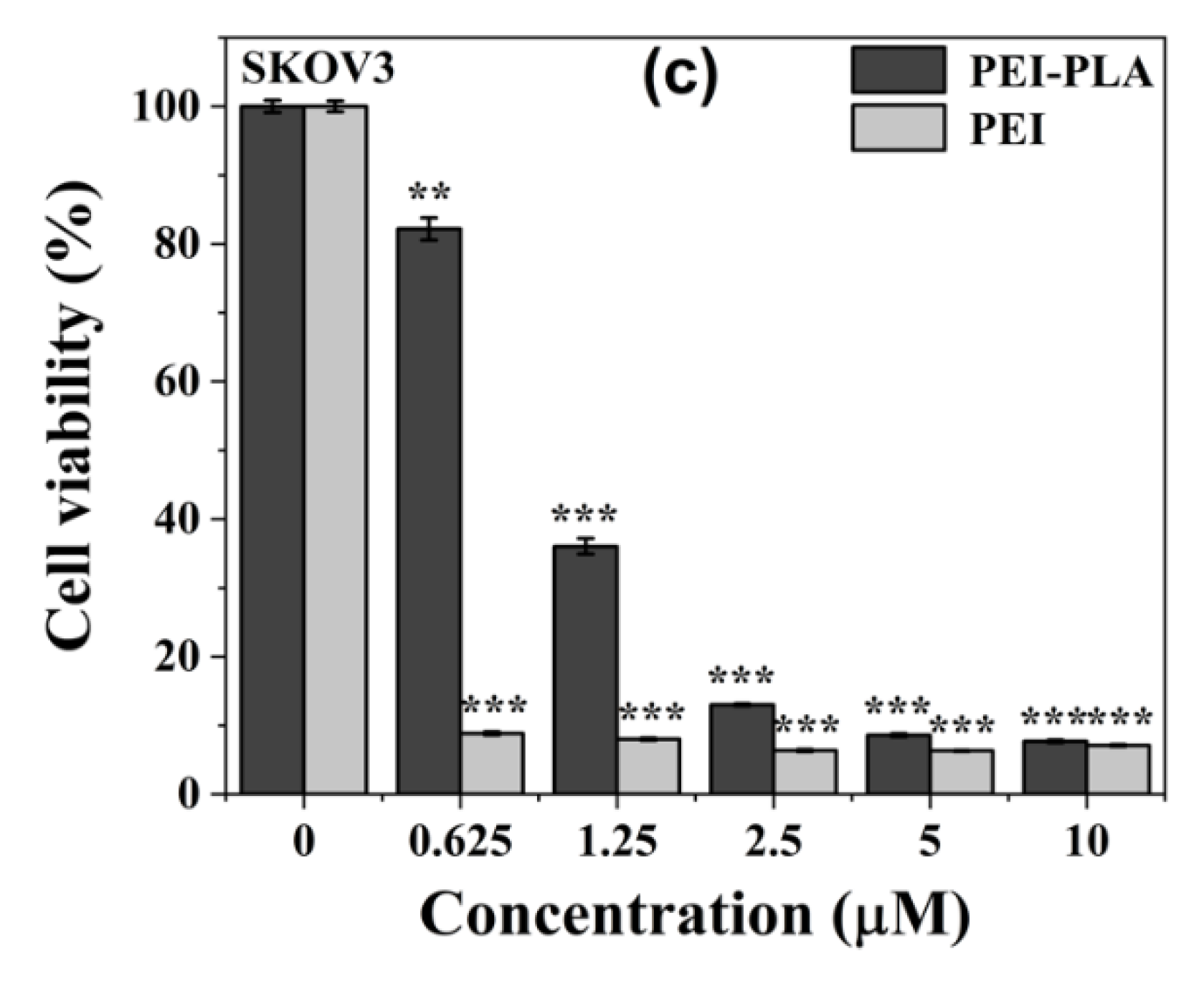
3.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of PEI-PLA Copolymer
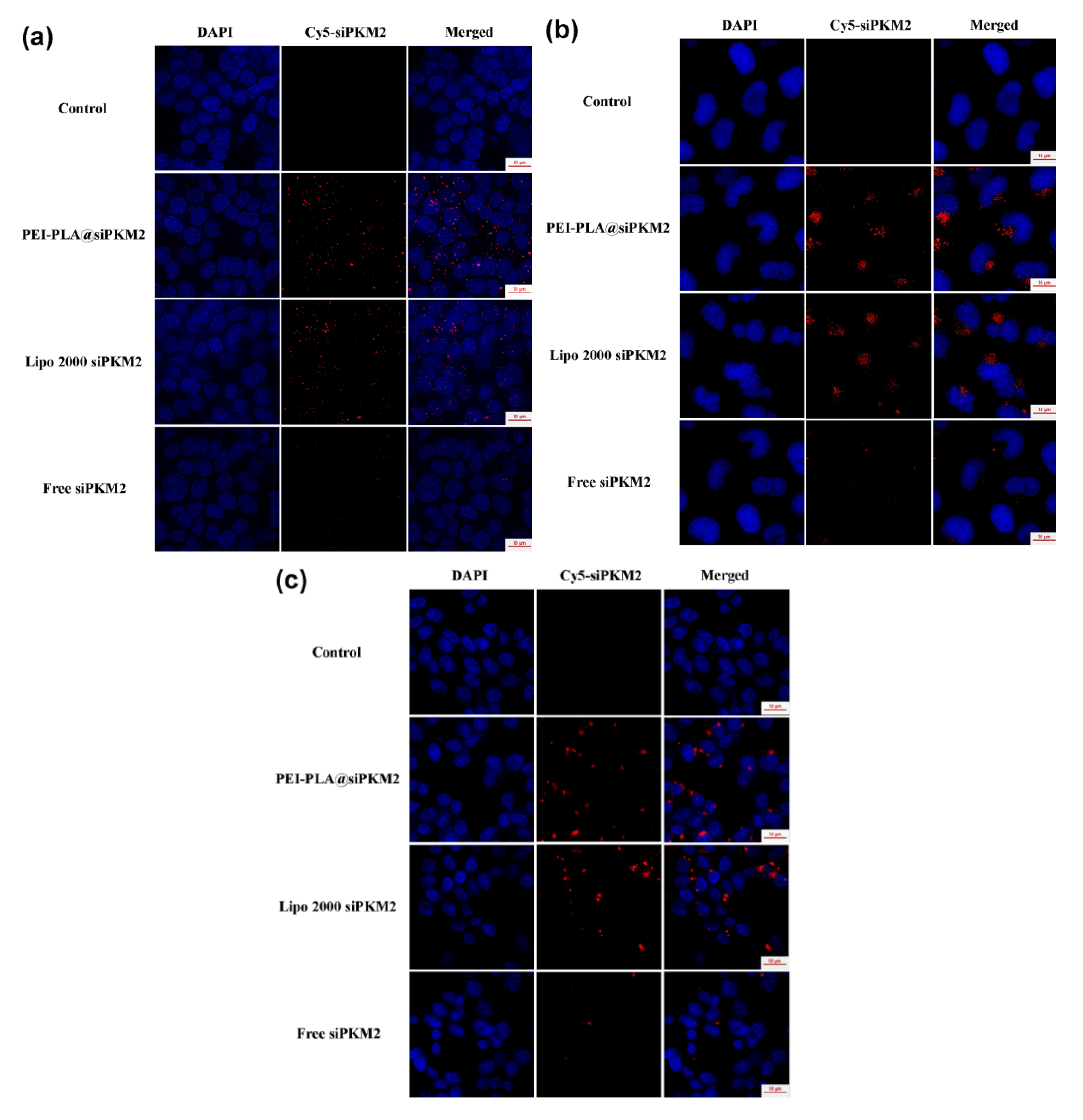
3.5. Intracellular Trafficking of PEI-PLA@siRNA Polyplex
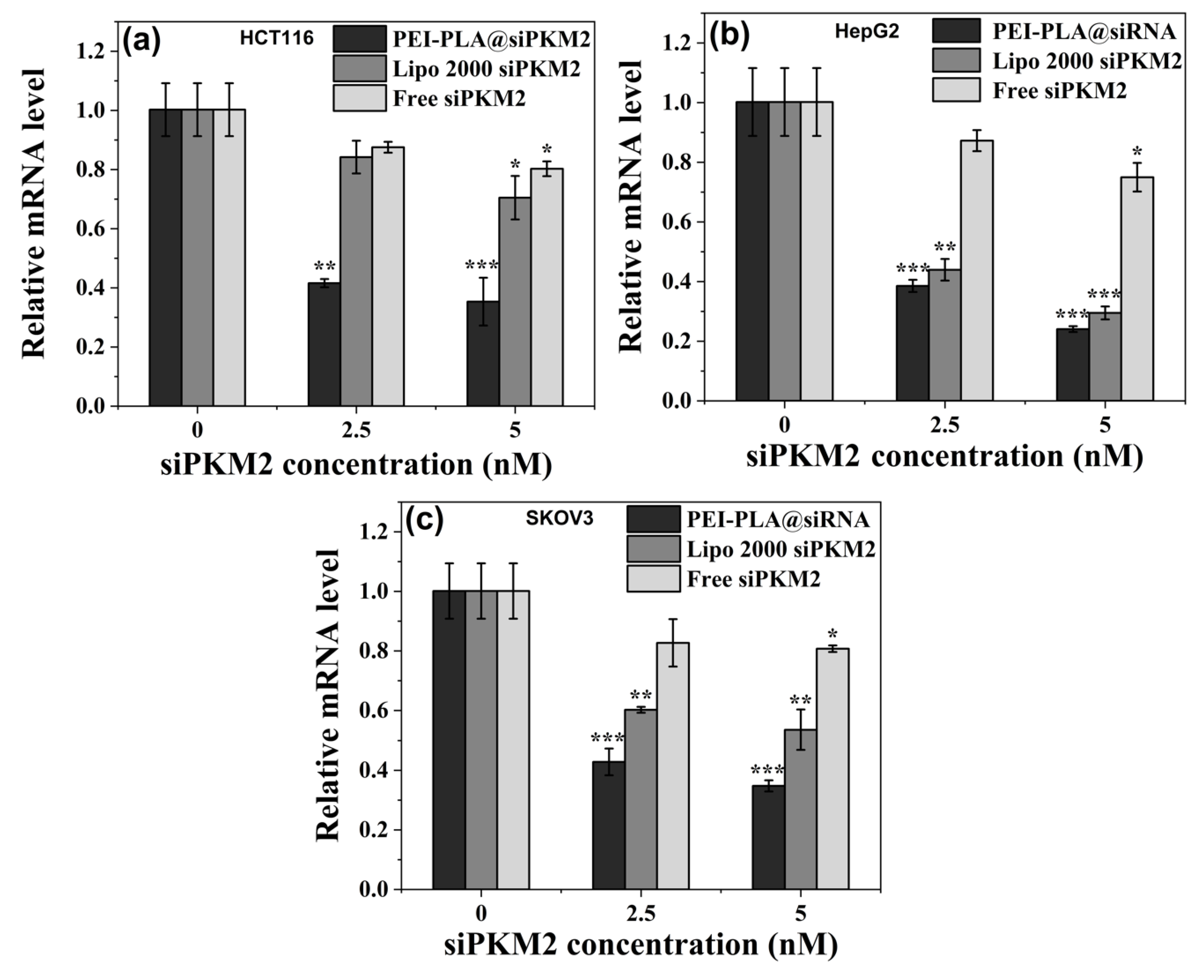
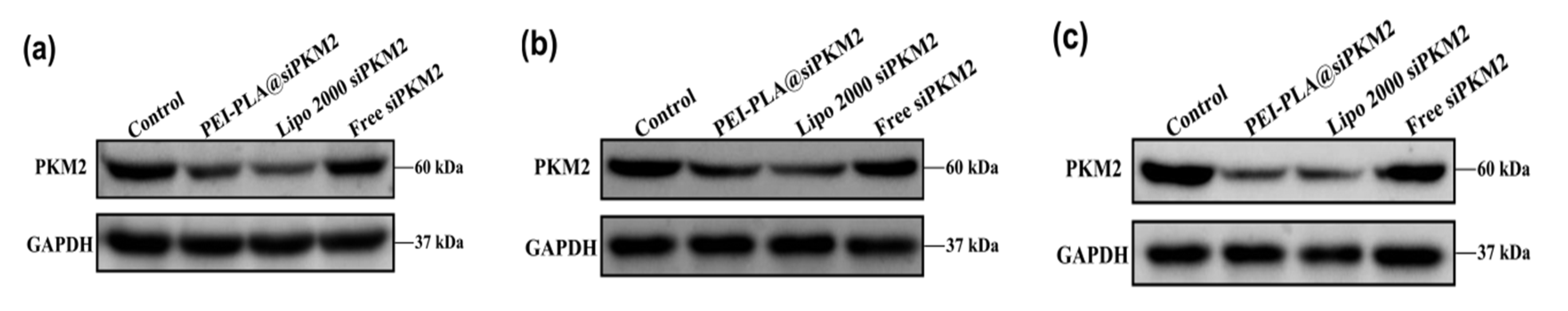
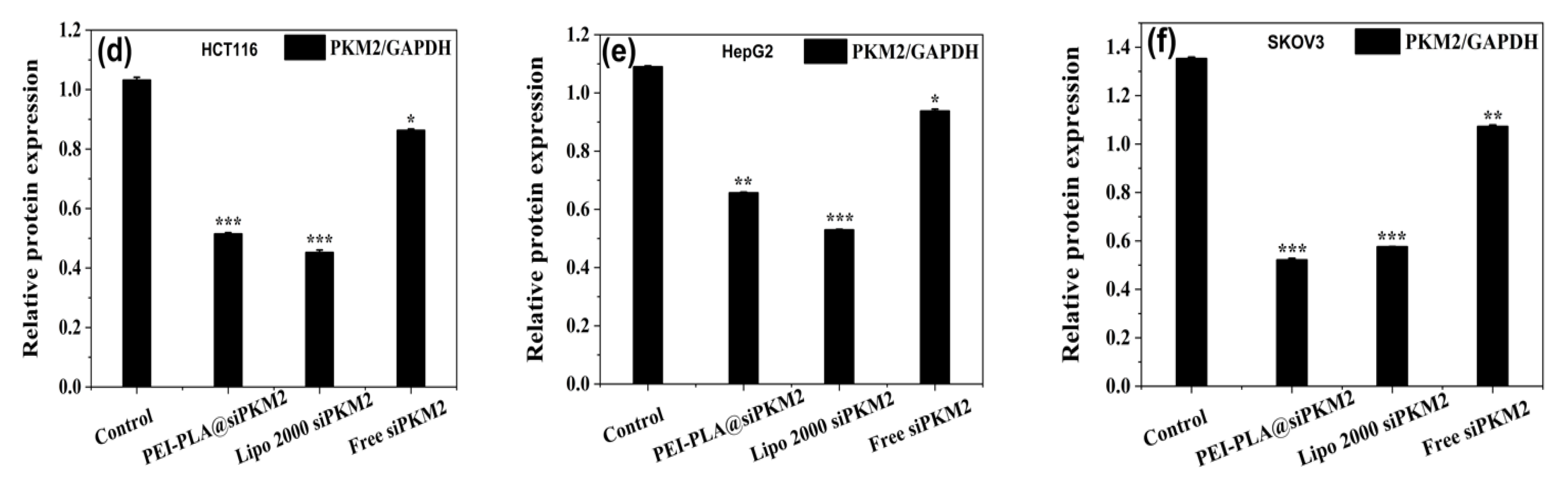
3.6. Suppressive Effect of PEI-PLA@siRNA Polyplex on PKM2 Gene Expression
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tekade, R.K.; Tekade, M.; Kesharwani, P.; D’Emanuele, A. RNAi-combined nano-chemotherapeutics to tackle resistant tumors. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 1761–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, G.; Guo, Y.; Lv, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X. A double-targeted magnetic nanocarrier with potential application in hydrophobic drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 91, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, D.; Burmester, J.K. Gene Therapy for Cancer Treatment: Past, Present and Future. Clin. Med. Res. 2006, 4, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, R.S.; Qin, B.; Cheng, K. Peptides Used in the Delivery of Small Noncoding RNA. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3395–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.D.; Vorhies, J.S.; Senzer, N.; Nemunaitis, J. siRNA vs. shRNA: Similarities and differences. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, D.; Patra, B.C.; Kar, A.; Chini, D.S.; Ghosh, S.; Patra, S.; Bhattacharya, M. Promising approaches of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) mediated cancer gene therapy. Gene 2019, 719, 144071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shigdar, S.; Shamaileh, H.A.; Gantier, M.P.; Yin, W.; Xiang, D.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S.-F.; Hou, Y.; Wang, P.; et al. Challenges and opportunities for siRNA-based cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 2017, 387, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, D.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, L.-P. Polyester based nanovehicles for siRNA delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wei, Y.; Gong, C. Polymeric Nanocarriers for Non-Viral Gene Delivery. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 739–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Uthaman, S.; Nurunnabi, M.; Mallick, S.; Oh, K.S.; Kang, S.-W.; Cho, S.; Kang, H.; Lee, Y.-K.; Huh, K.M. Synthesis and characterization of bioreducible cationic biarm polymer for efficient gene delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Zhang, X.Q.; Xu, X. Biomaterials in siRNA Delivery: A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 2715–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Mangala, L.S.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Kong, X.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K. RNA interference-based therapy and its delivery systems. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, S.W.S.; Stenzel, M.; Yang, J.L. Nanoparticle-siRNA: A potential cancer therapy? Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 98, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Feng, S.S. Nanocarriers for delivery of siRNA and co-delivery of siRNA and other therapeutic agents. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 2199–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanasty, R.; Dorkin, J.R.; Vegas, A.; Anderson, D. Delivery materials for siRNA therapeutics. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, R.; Alwani, S.; Badea, I. Polymeric Nanoparticles in Gene Therapy: New Avenues of Design and Optimization for Delivery Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Huo, S.; Hardie, J.; Liang, X.-J.; Rotello, V.M. Progress and perspective of inorganic nanoparticles based siRNA delivery system. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzano, G.; Costa, D.F.; Torchilin, V.P. siRNA Delivery by Stimuli-Sensitive Nanocarriers. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 4566–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, N. Cationic Polymer Optimization for Efficient Gene Delivery. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Park, T.-E.; Singh, B.; Maharjan, S.; Firdous, J.; Cho, M.-H.; Kang, S.-K.; Yun, C.-H.; Choi, Y.-J.; Cho, C.-S. Major degradable polycations as carriers for DNA and siRNA. J. Control. Release 2014, 193, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Zheng, M.; Tao, W.; Chung, R.; Jin, D.; Ghaffari, D.; Farokhzad, O.C. Challenges in DNA Delivery and Recent Advances in Multifunctional Polymeric DNA Delivery Systems. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2231–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Ni, D.; Yan, Y.; Pan, X.; Chen, X.; Guan, J.; Xiong, X.; Liu, L. Safe and efficient gene delivery based on rice bran polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.P.; Sawant, K.K. Polyethylenimine: A versatile, multifunctional non-viral vector for nucleic acid delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 904–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, F.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Sun, J.; Marshall, B.; Lee, R.J.; Teng, L.; Yang, Z.; Xie, J. Polyethylenimine-based Formulations for Delivery of Oligonucleotides. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 2264–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlman, J.E.; Barnes, C.; Khan, O.; Thiriot, A.; Jhunjunwala, S.; Shaw, T.E.; Xing, Y.; Sager, H.B.; Sahay, G.; Speciner, L.; et al. In vivo endothelial siRNA delivery using polymeric nanoparticles with low molecular weight. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Hua, M.; Liu, C.; Chen, T. Dextran–g–PEI nanoparticles as a carrier for co-delivery of adriamycin and plasmid into osteosarcoma cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanya, G.R.; Caroline, D.S.; Rekha, M.R.; Sreenivasan, K. Histidine and arginine conjugated starch-PEI and its corresponding gold nanoparticles for gene delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Jin, G.; Kang, L.; Chen, L.; Gao, Z.; Huang, W. Smart polymeric nanoparticles with pH-responsive and PEG-detachable properties for co-delivering paclitaxel and survivin siRNA to enhance antitumor outcomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2405–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Li, Q.; Zhao, C.; Lu, J.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Deng, X.; Ge, G.; Wu, Y. Auto-fluorescent polymer nanotheranostics for self-monitoring of cancer therapy via triple-collaborative strategy. Biomaterials 2019, 194, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.B.; Liu, H.Y.; Lv, Y.-Y.; Liu, X.F.; Guo, Y.; Sun, C.K.; Xu, L. Enhanced In Vitro Antitumor Efficacy and Strong Anti-Cell-Migration Activity of a Hydroxycamptothecin-Encapsulated Magnetic Nanovehicle. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 14037–14046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Semenza, G.L. Emerging roles of PKM2 in cell metabolism and cancer progression. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Lu, Z. Regulation and function of pyruvate kinase M2 in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 339, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, N.; Ojo, D.; Yan, J.; Tang, D. PKM2 contributes to cancer metabolism. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yang, P.; Li, Z. The multifaceted regulation and functions of PKM2 in tumor progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2014, 1846, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Kim, H.C.; Su, H.; Wang, F.; Wolfram, J.; Kirui, D.; Mai, J.; Mu, C.; Ji, L.-N.; Mao, Z.-W.; et al. Cyclodextrin and Polyethylenimine Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Delivery of siRNA Cancer Therapeutics. Theranostics 2014, 4, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, T.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Z.; Liu, H.; Lin, J.; Liu, C.; Mao, Z.W.; Nie, S. Chitosan layered gold nanorods as synergistic therapeutics for photothermal ablation and gene silencing in triple-negative breast cancer. Acta Biomater. 2015, 25, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.; Ye, H.; Li, Y.; Liang, Q.; Li, X.; Yin, L. Multivalency-assisted membrane-penetrating siRNA delivery sensitizes photothermal ablation via inhibition of tumor glycolysis metabolism. Biomaterials 2019, 223, 119463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Nguyen, J.; Steele, T.; Merkel, O.; Kissel, T. A new synthesis method and degradation of hyper-branched polyethylenimine grafted polycaprolactone block mono-methoxyl poly (ethylene glycol) copolymers (hy-PEI-g-PCL-b-mPEG) as potential DNA delivery vectors. Polymer 2009, 50, 3895–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Anderson, G.J.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Reversal of pancreatic desmoplasia by re-educating stellate cells with a tumour microenvironment-activated nanosystem. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, M.S.; Fang, B.A.; Zhang, P.; Hu, Z.; Gu, S.; Weng, K.C.; Gray, J.W.; Chen, F.F. Nanoparticle-Mediated Systemic Delivery of siRNA for Treatment of Cancers and Viral Infections. Theranostics 2014, 4, 872–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, M.; Schubert, S.; Ochrimenko, S.; Fischer, D.; Schubert, U.S. Branched and linear poly(ethylene imine)-based conjugates: Synthetic modification, characterization, and application. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4755–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Mi, Y.; Feng, S.S. siRNA-based nanomedicine. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
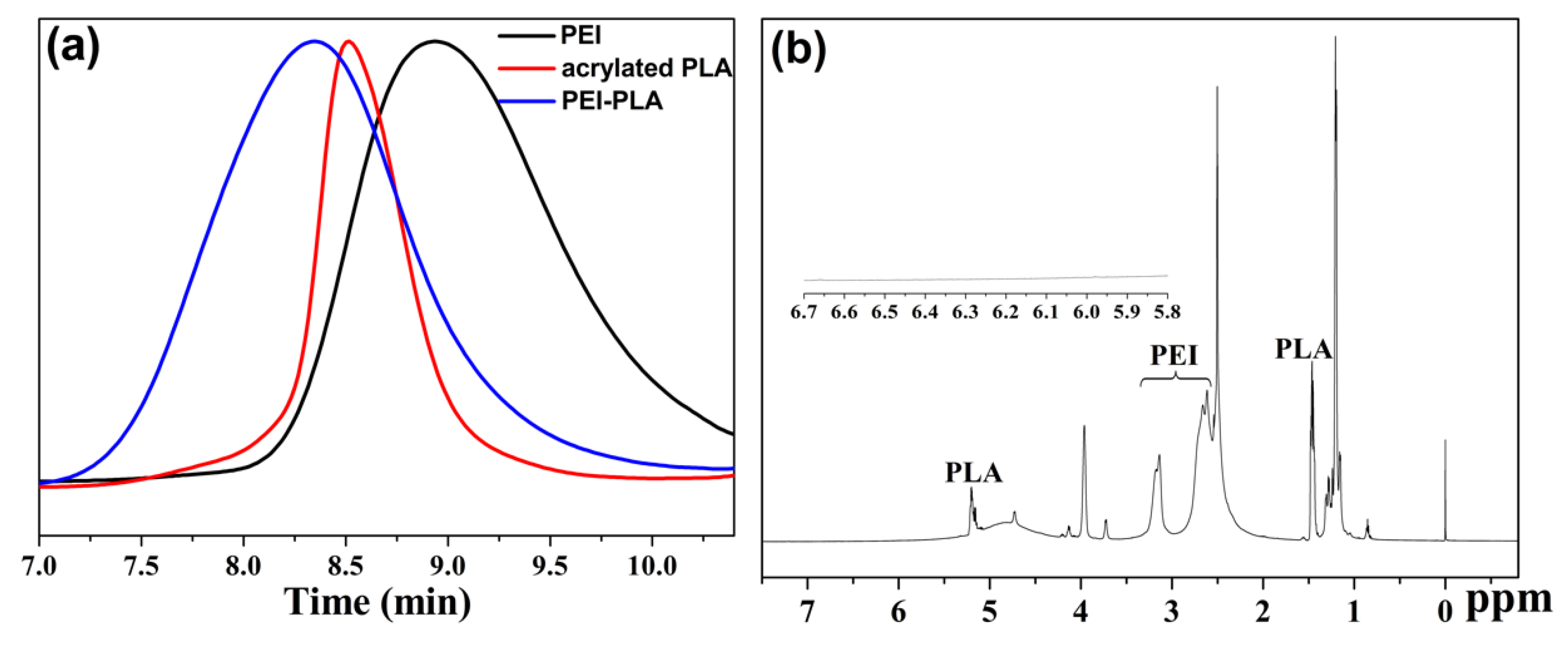
| Sample | Molecular Weight (Da) | PDI | Retention Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEI | 5453 | 2.073 | 8.99 |
| Acrylated PLA | 14,253 | 1.300 | 8.55 |
| PEI-PLA | 21,644 | 2.369 | 8.34 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, G.-B.; Meng, X.; Yang, P.; Li, B.; Stauber, R.H.; Li, Z. Integration of Polylactide into Polyethylenimine Facilitates the Safe and Effective Intracellular siRNA Delivery. Polymers 2020, 12, 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020445
Ding G-B, Meng X, Yang P, Li B, Stauber RH, Li Z. Integration of Polylactide into Polyethylenimine Facilitates the Safe and Effective Intracellular siRNA Delivery. Polymers. 2020; 12(2):445. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020445
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Guo-Bin, Xue Meng, Peng Yang, Binchun Li, Roland H Stauber, and Zhuoyu Li. 2020. "Integration of Polylactide into Polyethylenimine Facilitates the Safe and Effective Intracellular siRNA Delivery" Polymers 12, no. 2: 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020445
APA StyleDing, G.-B., Meng, X., Yang, P., Li, B., Stauber, R. H., & Li, Z. (2020). Integration of Polylactide into Polyethylenimine Facilitates the Safe and Effective Intracellular siRNA Delivery. Polymers, 12(2), 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020445







