Improving Fire Retardancy of Beech Wood by Graphene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Preparation
2.2. Graphene Production Technique
2.3. Fire Test Apparatus
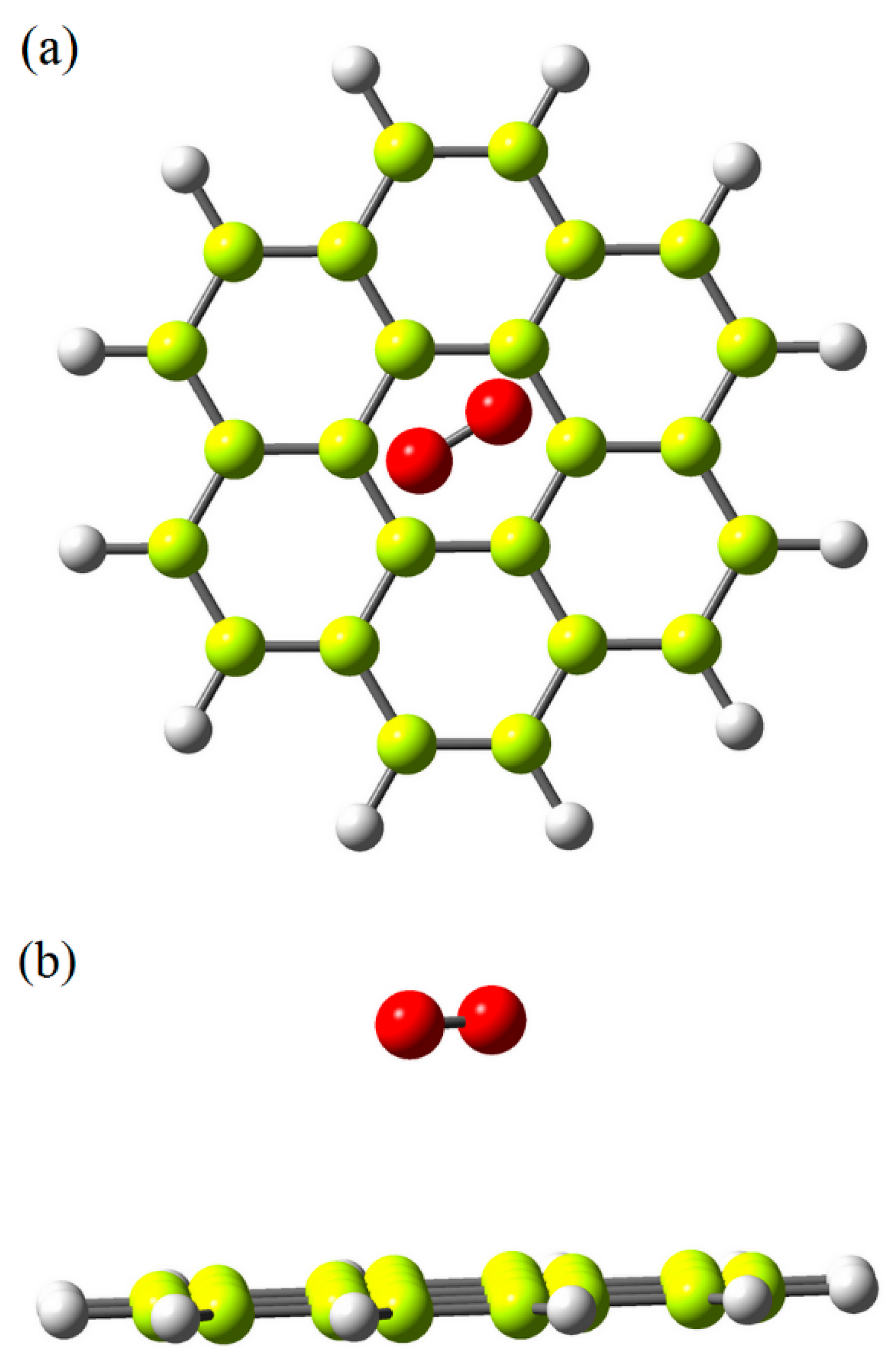
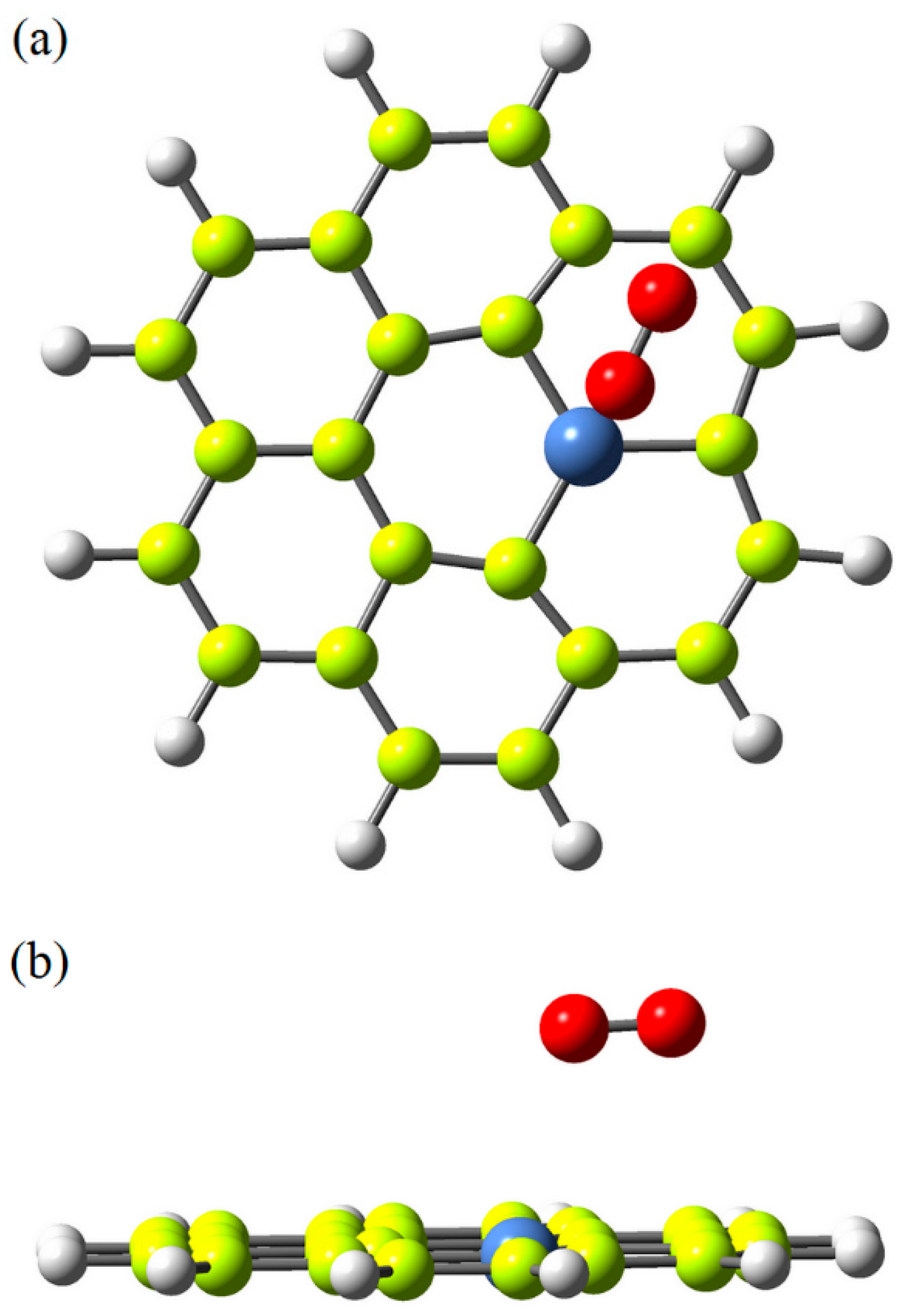
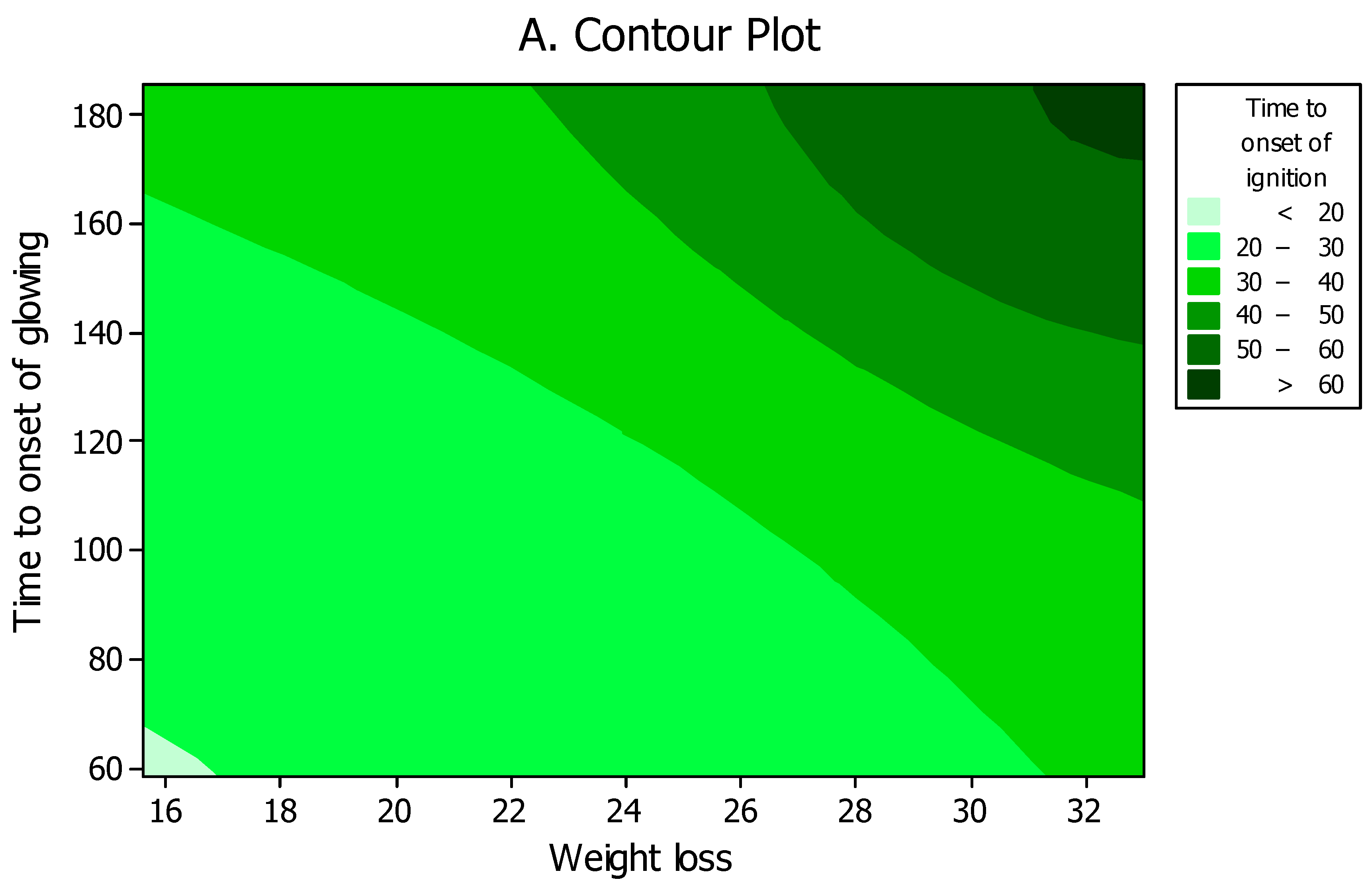
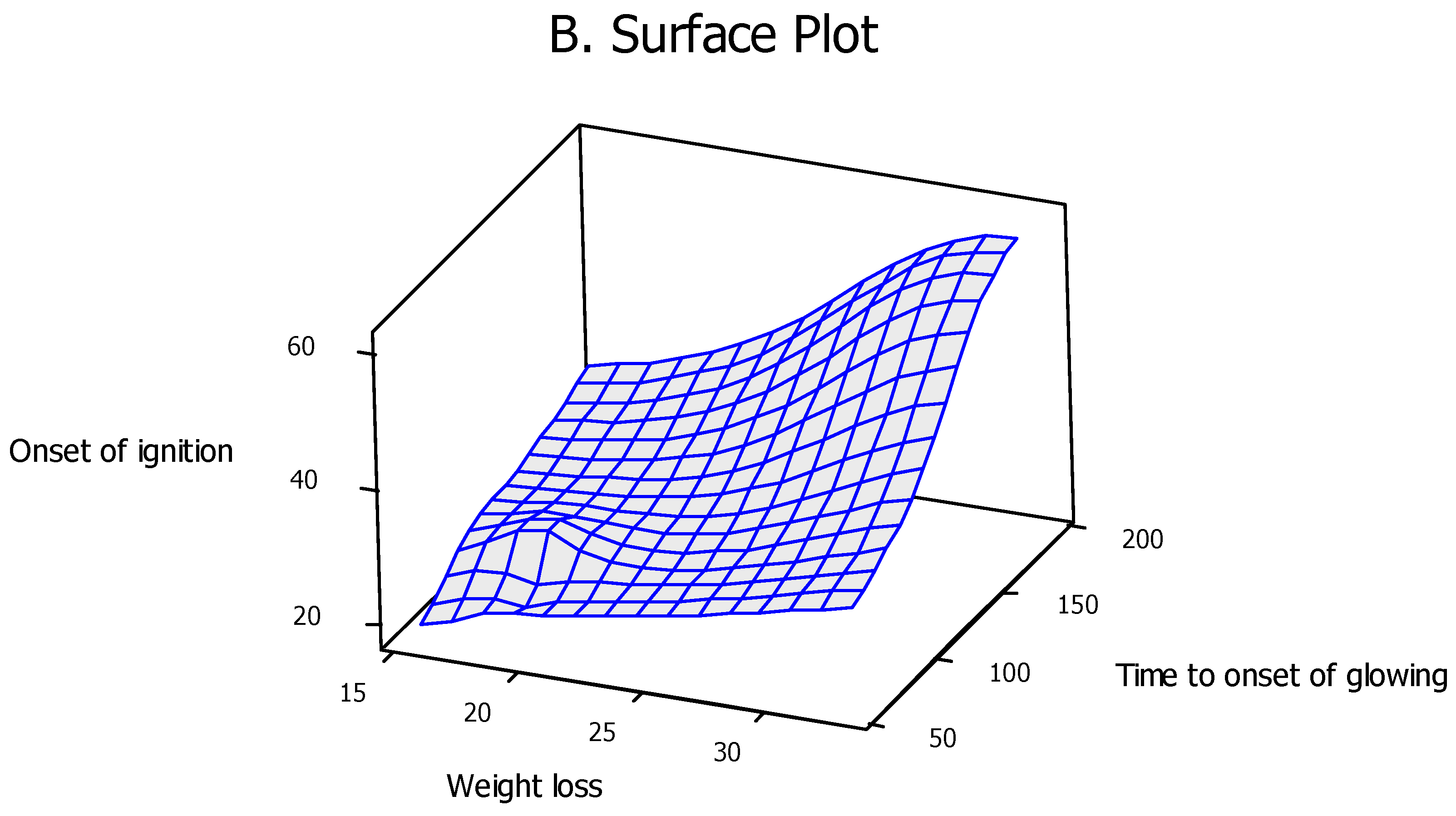
2.4. Computational Modeling and Simulation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
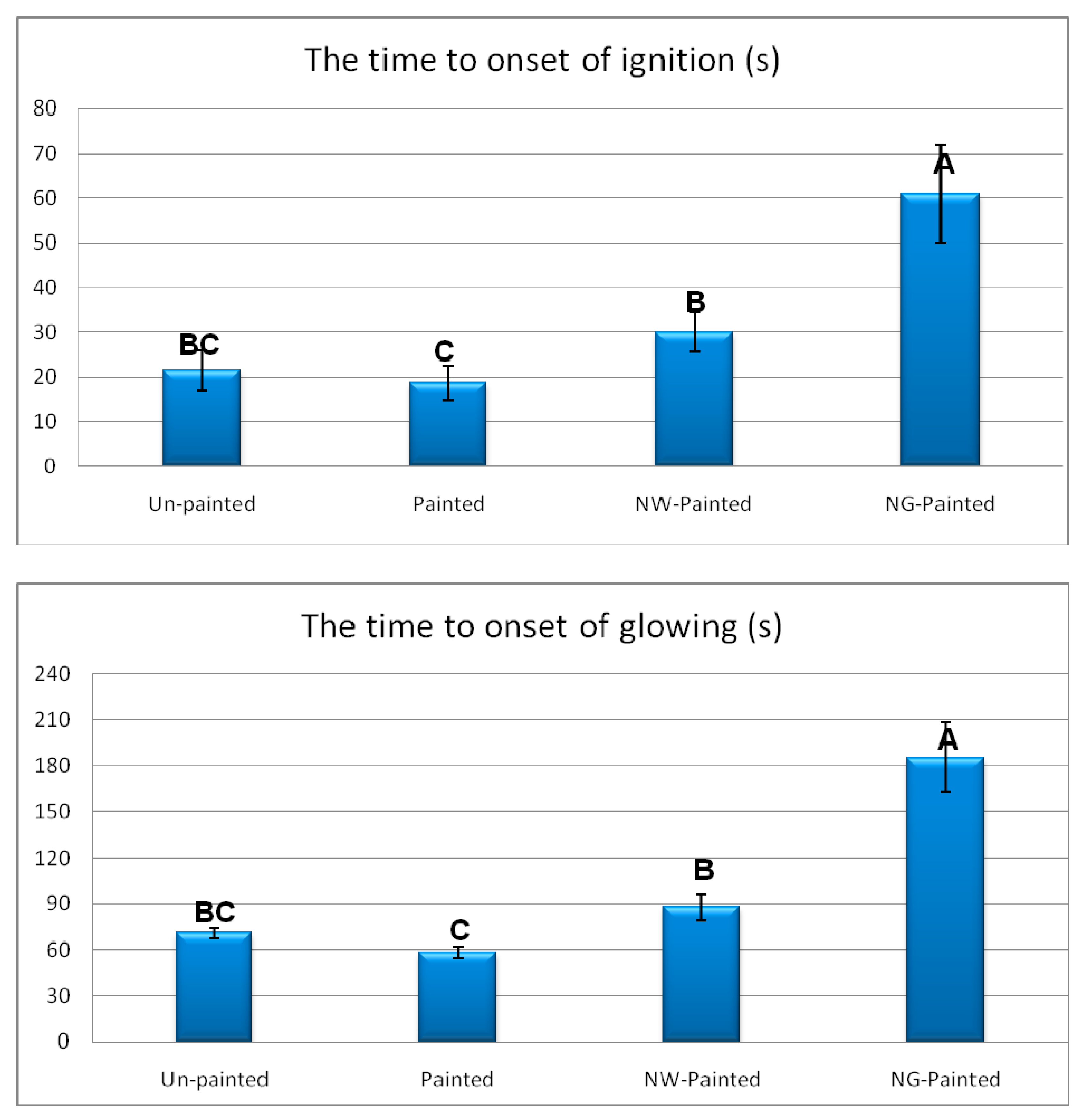
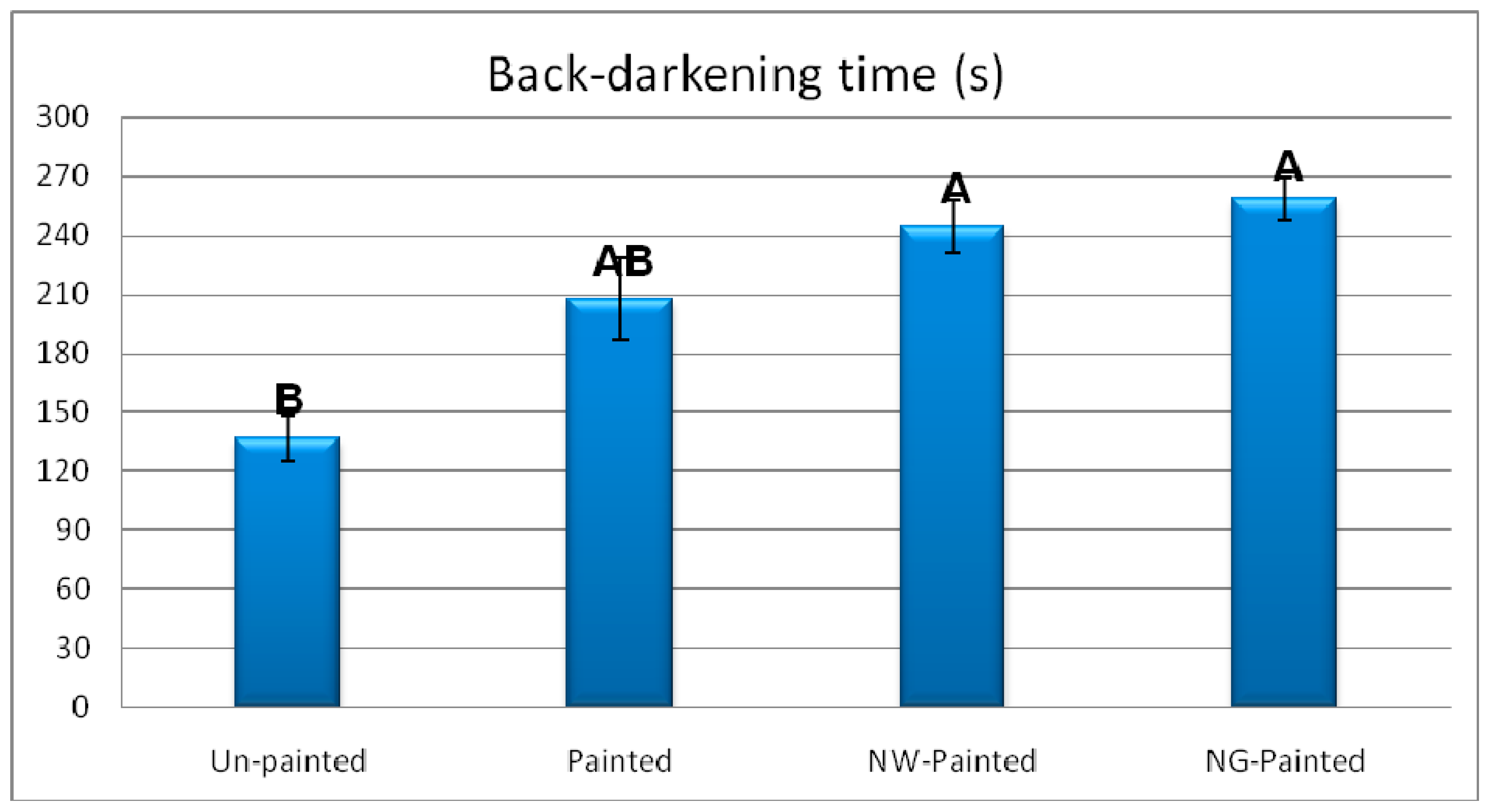
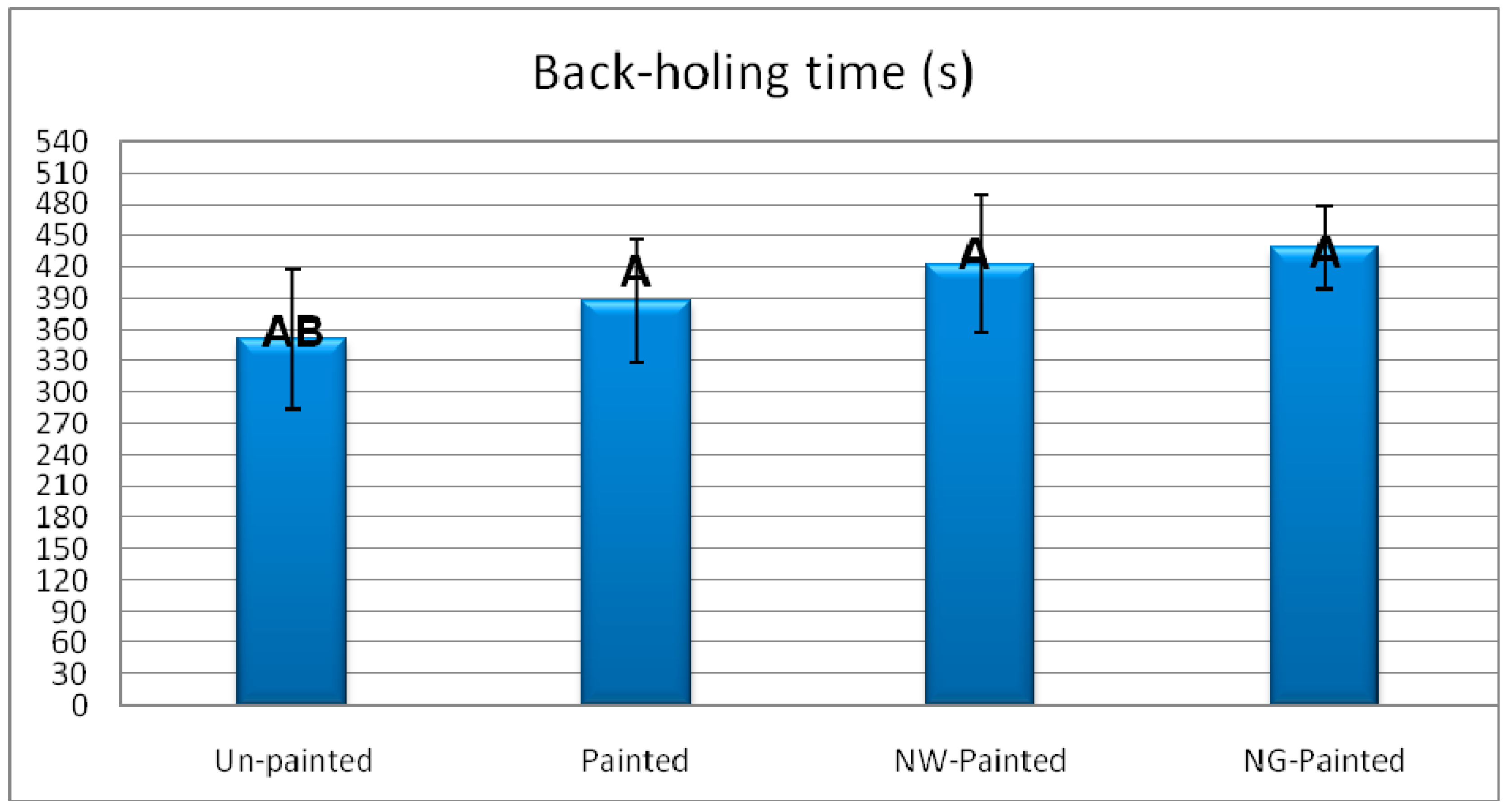
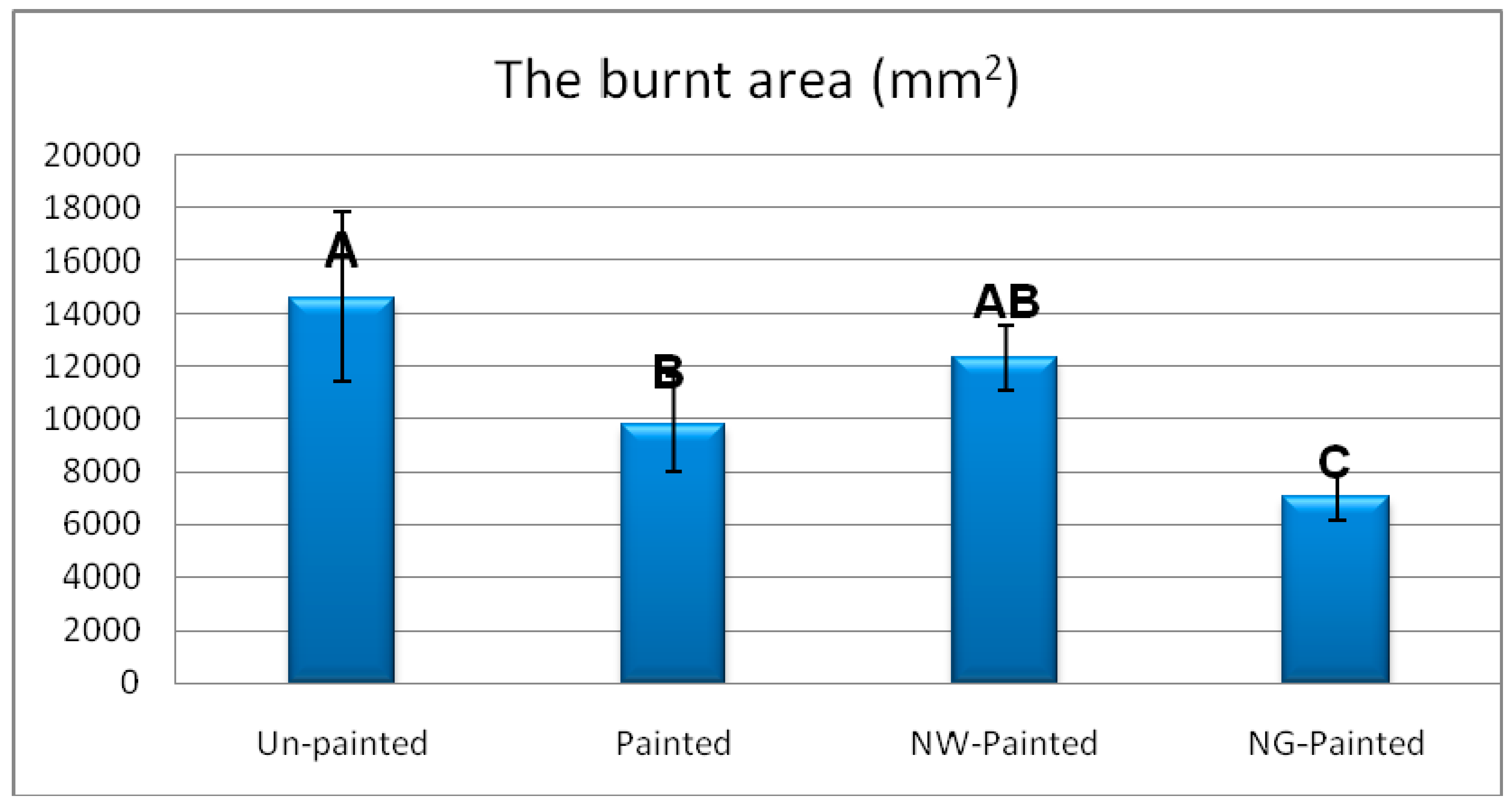
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Behling, M.; Piketty, M.G.; Morello, T.F.; Bouillet, J.P.; Mesquita Neto, F.; Laclau, J.P. Eucalyptus plantations and the steel industry in Amazonia—A contribution from the 3-PG model. Bois et Forets Des Tropiques 2011, 309, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherelli, S.G.; Sartori, M.M.P.; Prospero, A.G.; Ballarin, A.W. Heartwood and sapwood in eucalyptus trees: Non-conventional approach to wood quality. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias 2018, 90, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantanis, G.; Terzi, E.; Kartal, S.N.; Papadopoulos, A. Evaluation of mold, decay and termite resistance of pine wood treated with zinc- and copper- based nanocompounds. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 90, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.N.; Duquesnoy, P.; Cragg, S.M.; Pitman, A.J. The resistance of wood modified with linear chain carboxylic acid anhydrides to attack by the marine wood borer Limnoria quadripunctata Hothius. Int. Biodegrad. Biodeterior. 2008, 61, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.N.; Avtzis, D.; Avtzis, N. The biological effectiveness of wood modified with linear chain carboxylic acid anhydrides against the subterranean termites Reticulitermes flavipes. Holz als Roh und Werkstoff 2003, 66, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.N. Chemical modification of solid wood and wood raw materials for composites production with linear chain carboxylic acid anhydrides: A brief Review. BioResources 2010, 5, 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.F.; Karlsson, O.; Mantanis, G.I.; Sandberg, D. Fire performance and leach resistance of pine wood impregnated with guayl-urea phosphate/boric acid and a melamin-formaldehyde resin. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östman, B.A.L.; Tsantaridis, L.D. Heat release and classification of fire retardant wood products. Fire Mater. 1995, 19, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeVan, S.; Winandy, J.E. Effect of fire retardant treatments on wood strength: A review. Wood Fiber Sci. 1990, 22, 113–131. [Google Scholar]
- White, R.H.; Sweet, M.S. Flame retardancy of wood: Present status, recent problems, and future fields. In Proceedings of the 3rd Annual BCC Conference on Flame Retardance, Stamford, CT, USA, 19–21 May 1992; pp. 250–257. [Google Scholar]
- Winandy, J.E. Thermal degradation of the fire-retardant treated wood. For. Prod. J. 2001, 51, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Winandy, J.E.; Wang, Q.; White, R.H. Fire-retardant-treated strandboard: Properties and fire performance. Wood Fiber Sci. 2008, 40, 62–71. [Google Scholar]
- Mantanis, G. Aqueous Fire Retardant; WO 02/102926 A1; World Intellectual Property Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mantanis, G.; Martinka, J.; Lykidis, C.; Ševčík, L. Technological properties and fire performance of medium density fibreboard (MDF) treated with selected polyphosphate-based fire retardants. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.N.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Nanomaterials and chemical modification technologies for enhanced wood properties: A review. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayani, S.; Taghiyari, H.R.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Physical and mechanical properties of thermally-modified beech wood impregnated with silver nano-suspension and their relationship with the crystallinity of cellulose. Polymers 2019, 11, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghiyari, H.; Esmailpour, A.; Papadopoulos, A. Paint Pull-Off Strength and Permeability in Nanosilver-Impregnated and Heat-Treated Beech Wood. Coatings 2019, 9, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.N.; Taghiyari, H.R. Innovative wood surface treatments based on nanotechnology. Coatings 2019, 9, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantanis, G.; Papadopoulos, A.N. The sorption of water vapour of wood treated with a nanotechnology compound. Wood Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, N.; Sulochana, C.; Kumar, B.R. Flow and heat transfer in MHD dusty nanofluid past a stretching/shrinking surface with non-uniform heat source/sink. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 117–140. [Google Scholar]
- Suganya, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Saravanan, A. Construction of active bio-nanocomposite by inseminated metal nanoparticles onto activated carbon: Probing to antimicrobial activity. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, V.; Taghiyari, H.R.; Schmidt, O.; Maleki, S.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Mechanical and physical properties of Oriented Strand Lumber (OSL): The effect of fortification level of nanowollastonite on UF resin. Polymerss 2019, 11, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantanis, G.I.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Reducing the thickness swelling of wood based panels by applying a nanotechnology compound. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2010, 68, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajvidi, M.; Gardner, D.J.; Bousfield, D.W. Cellulose Nanomaterials as Binders: Laminate and Particulate Systems. J. Renew. Mater. 2016, 4, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayata, U.; Akcay, C.; Esteves, B. Determination of decay resistance against Pleurotus ostreatus and Coniophora puteana fungus of heat-treated Scots pine, oak and beech wood species. Maderas Ciencia y Tecnologia 2017, 19, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silveira, A.G.; Santini, E.J.; Kulczynski, S.M.; Trevisan, R.; Wastowski, A.D.; Gatto, D.A. Tannic extract potential as natural wood preservative of Acacia mearnsii. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias 2017, 89, 3031–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humar, M.; Lesar, B.; Thaler, N.; Krzisnik, D.; Kregar, N.; Drnovsek, S. Quality of copper impregnated wood in Slovenian hardware stores. Drvna Industrija 2018, 69, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.; Ghodskhah Daryaei, M.; Torkaman, J.; Oladi, R.; Tajick Ghanbary, M.A.; Bari, E.; Yilgor, N. Natural decomposition of hornbeam wood decayed by the white rot fungus Trametes versicolor. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 2017, 89, 2647–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Bari, E.; Schmidt, O.; Tajick Ghanbary, M.A.; Karimi, A.; Tahir, P.M.D. Effects of nanowollastonite on biological resistance of particleboard made from wood chips and chicken feather against Antrodia vaillantii. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 90, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Ghorbanali, M.; Tahir, P.M.D. Effects of improvement in thermal conductivity coefficient by nano-wollastonite on physical and mechanical properties in medium-density fiberboard (MDF). BioResources 2014, 9, 4138–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Majidinajafabadi, R.; Vahidzadeh, R. Wollastonite to hinder growth of Aspergillus niger fungus on cotton textile. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias 2018, 90, 2797–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Tajvidi, M.; Taghiyari, R.; Mantanis, G.I.; Esmailpour, A.; Hosseinpourpia, R. Nanotechnology for wood quality improvement and protection. Nanomater. Agric. For. Appl. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Karimi, A.; Tahir, P.M.D.; Choo, A.C.Y. Effects of nanotechnology on fluid flow in agricultural and wood-based composite materials. In Agricultural Biomass Based Potential Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 73–89. [Google Scholar]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of grapheme. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsnelson, M.; Iosifovich, M. Graphene: Carbon in Two Dimensions, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Haghighi Poshtiri, A.; Taghiyari, H.R.; Karimi, A.N. Fire-retarding properties of nano-wollastonite in solid wood. Philipp. Agric. Sci. 2014, 97, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Soltani, A.; Hosseinpourpia, R.; Adamopoulos, S.; Taghiyari, H.R.; Ghaffari, E. Effects of heat-treatment and nano-wollastonite impregnation on fire properties of solid wood. BioResources 2016, 11, 8953–8967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmailpour, A.; Taghiyari, H.R.; Nouri, P.; Jahangiri, A. Fire-retarding properties of nanowollastonite in particleboard. Fire Mater. 2018, 42, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuningsih, I.; Sekartining Rahayu, I.; Lumongga, D.; Darmawan, W. Wettability and adherence of acrylic paints on long and short rotation teaks. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghazadeh, M.; Golikand, A.N.; Ghaemi, M. Synthesis, characterization, and electrochemical properties of ultrafine β-Ni(OH)2 nanoparticles. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 8674–8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, K.; Wu, Z.S.; Li, R.; Liu, X.; Graf, R.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Exfoliation of Graphite into Graphene in Aqueous Solutions of Inorganic Salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6083–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheykhifard, Z.; Majid Mohseni, S.M.; Tork, B.; Hajiali, M.R.; Jamilpanah, L.; Rahmati, B.; Haddadi, F.; Hamdi, M.; Morteza Mohseni, S.; Mohammadbeigi, M.; et al. Magnetic graphene/Ni-nano-crystal hybrid for small field magnetoresistive effect synthesized via electrochemical exfoliation/deposition technique. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 4171–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghiyari, H.R. Fire-retarding properties of nano-silver in solid woods. Wood Sci. Technol. 2012, 45, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, T.; Kino, H.; Yu, J.; Han, M.J. User’s Manual of OpenMX, Version 3.8. 2018. Available online: http://www.openmx-square.org/openmx_man3.8/openmx.html (accessed on 1 January 2018).
- Majidi, R. A biosensor for hydrogen peroxide detection based on electronic properties of carbon nanotubes. Mol. Phys. 2012, 111, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidi, R. Electronic properties of graphyne nanotubes filled with small fullerenes: A density functional theory study. J. Comput. Electron. 2016, 15, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimme, S. Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1787–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannozzi, P.; Car, R.; Scoles, G. Oxygen adsorption on graphite and nanotubes. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorescu, D.C.; Jordan, K.D.; Avouris, P. Theoretical study of oxygen adsorption on graphite and the (8,0) single-walled carbon nanotube. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 11227–11232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, E.; Varshney, V.; Roy, A.K. Thermal properties of graphene: Fundamentals and applications. MRS Bull. 2012, 37, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Esmailpour, A.; Majidi, R.; Taghiyari, H.R.; Ganjkhani, M.; Mohseni Armaki, S.M.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Improving Fire Retardancy of Beech Wood by Graphene. Polymers 2020, 12, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020303
Esmailpour A, Majidi R, Taghiyari HR, Ganjkhani M, Mohseni Armaki SM, Papadopoulos AN. Improving Fire Retardancy of Beech Wood by Graphene. Polymers. 2020; 12(2):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020303
Chicago/Turabian StyleEsmailpour, Ayoub, Roya Majidi, Hamid R. Taghiyari, Mehdi Ganjkhani, Seyed Majid Mohseni Armaki, and Antonios N. Papadopoulos. 2020. "Improving Fire Retardancy of Beech Wood by Graphene" Polymers 12, no. 2: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020303
APA StyleEsmailpour, A., Majidi, R., Taghiyari, H. R., Ganjkhani, M., Mohseni Armaki, S. M., & Papadopoulos, A. N. (2020). Improving Fire Retardancy of Beech Wood by Graphene. Polymers, 12(2), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020303





