Lightweight, Anisotropic, Compressible, and Thermally-Insulating Wood Aerogels with Aligned Cellulose Fibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
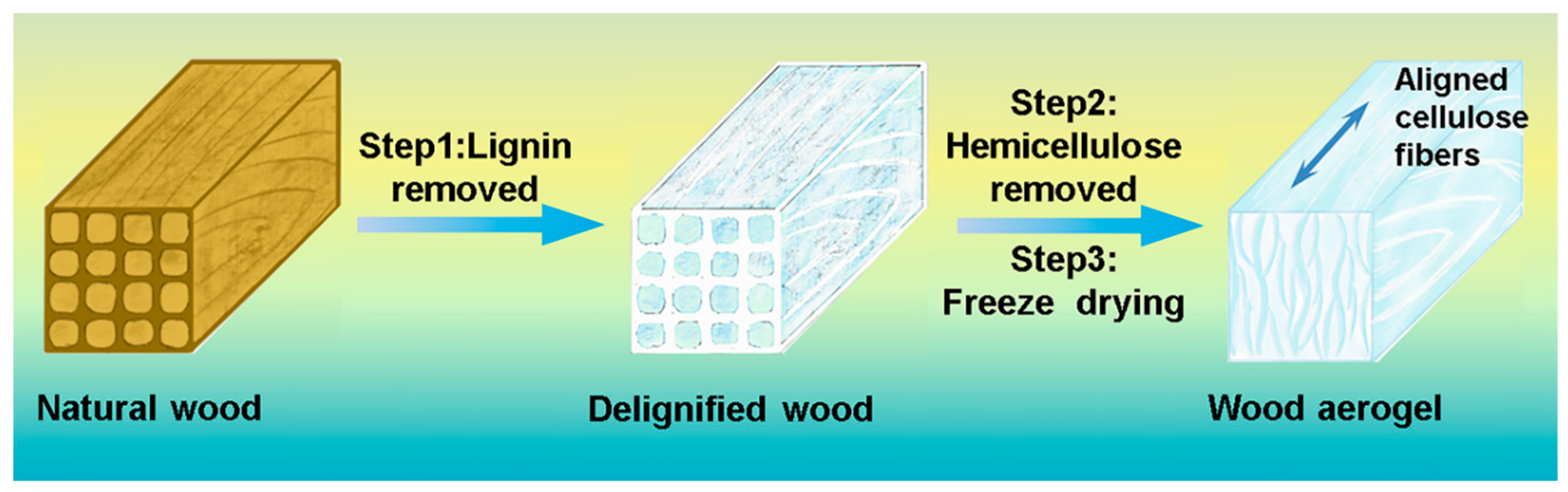
2.2. Preparation of Wood Aerogels
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
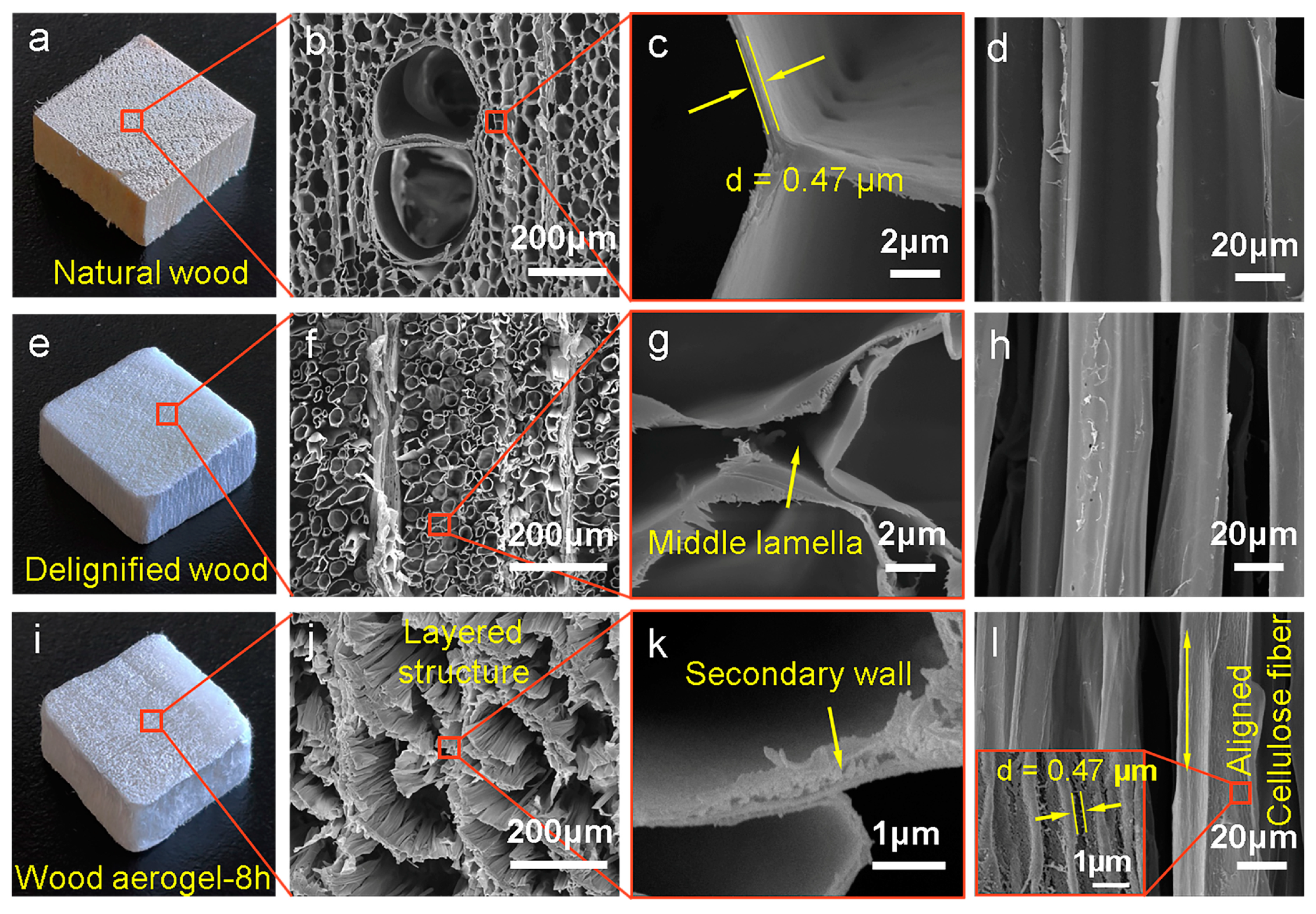
3.1. Morphology and Structure
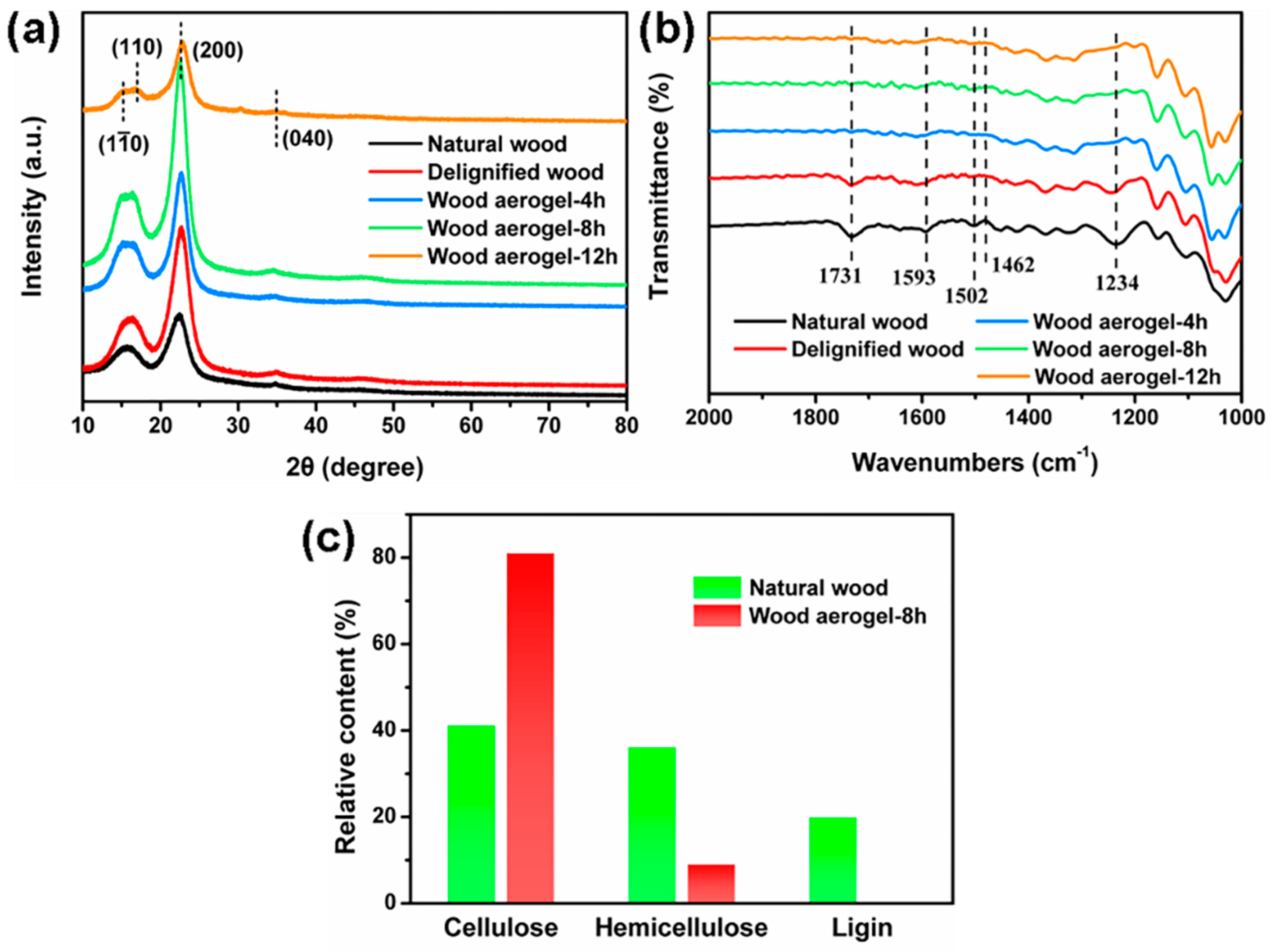
3.2. Chemical Characterization
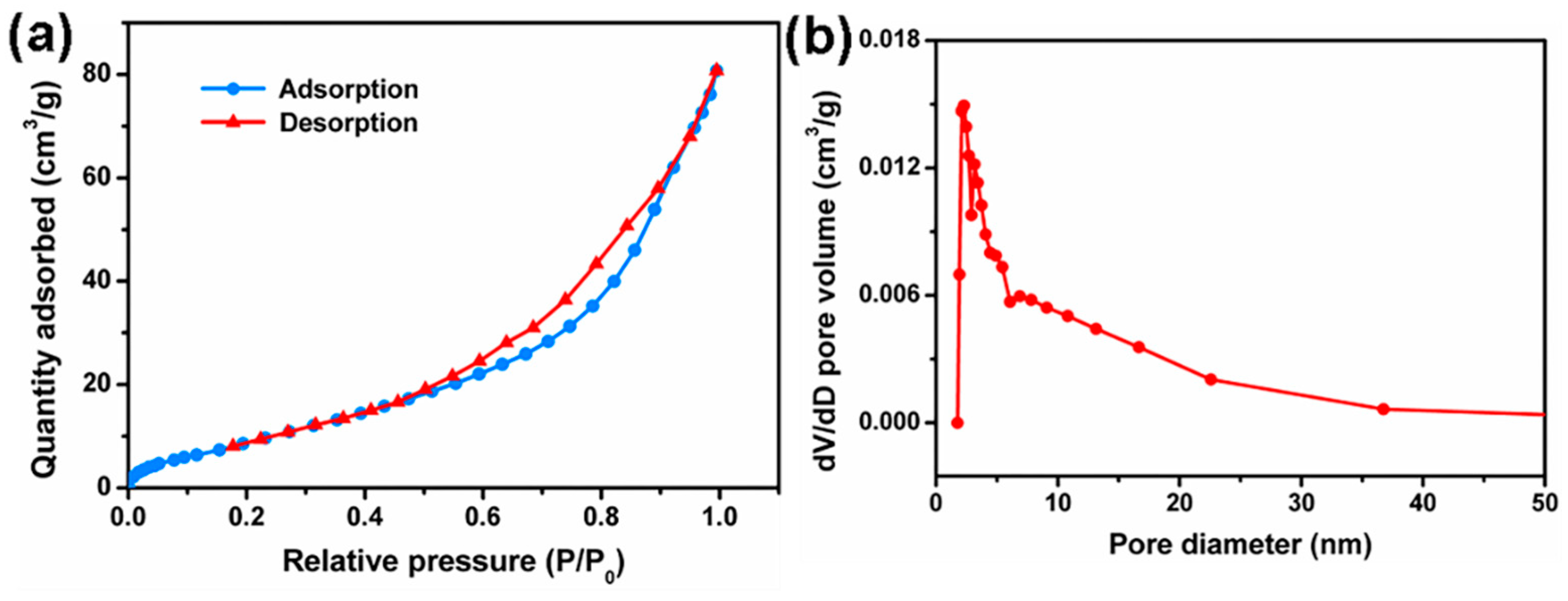
3.3. Specific Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution Analysis
3.4. Thermal Stability
3.5. Mechanical Compressibility
3.6. Thermal Insulation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cuce, E.; Cuce, P.M.; Wood, C.J.; Riffat, S.B. Toward aerogel based thermal superinsulation in buildings: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, P.M.; Betts, R.A.; Jones, C.D.; Spall, S.A.; Totterdell, I.J. Acceleration of global warming due to carbon-cycle feedbacks in a coupled climate model. Nature 2000, 408, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakatos, Á.; Kalmár, F. Investigation of thickness and density dependence of thermal conductivity of expanded polystyrene insulation materials. Mater. Struct. 2013, 46, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.M.; Giama, E. Environmental performance evaluation of thermal insulation materials and its impact on the building. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicklein, B.; Kocjan, A.; Salazar-Alvarez, G.; Carosio, F.; Camino, G.; Antonietti, M.; Bergström, L. Thermally insulating and fire-retardant lightweight anisotropic foams based on nanocellulose and graphene oxide. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Liu, S.; Feng, J.; Kimura, S.; Wada, M.; Kuga, S.; Zhang, L. Cellulose-silica nanocomposite aerogels by in situ formation of silica in cellulose gel. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2076–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, A.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, J. A special material or a new state of matter: A review and reconsideration of the aerogel. Materials 2013, 6, 941–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R. Silica aerogels having high flexibility and hydrophobicity prepared by sol-gel method. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 21262–21268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebel, M.; Rigacci, A.; Achard, P. Aerogel-based thermal superinsulation: An overview. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Hierarchical Cellular Structured Ceramic Nanofibrous Aerogels with Temperature-Invariant Superelasticity for Thermal Insulation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 29056–29064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, Z. Eggplant-derived SiC aerogels with high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption and thermal insulation properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, M.; Panahi-Sarmad, M.; Abrisham, M.; Amirkiai, A.; Asghari, N.; Golbaten-Mofrad, H.; Karimpour-Motlagh, N.; Goodarzi, V.; Bahramian, A.R.; Zahiri, B. Nanostructure of Aerogels and Their Applications in Thermal Energy Insulation. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 5319–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, R.J.; Martini, A.; Nairn, J.; Simonsen, J.; Youngblood, J. Cellulose nanomaterials review: Structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3941–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siró, I.; Plackett, D. Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: A review. Cellulose 2010, 17, 459–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Kramer, F.; Moritz, S.; Lindström, T.; Ankerfors, M.; Gray, D.; Dorris, A. Nanocelluloses: A new family of nature-based materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5438–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, Y.; Lucia, L.A.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose nanocrystals: Chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3479–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chen, C.; Yang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Kierzewski, I.; Liu, B.; He, S. Highly compressible, anisotropic aerogel with aligned cellulose nanofibers. ACS Nano 2017, 12, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Z.; Pastel, G.; Xu, S.; Jia, C.; Dai, J.; Chen, C.; Gong, A. Anisotropic, lightweight, strong, and super thermally insulating nanowood with naturally aligned nanocellulose. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, A.; Dai, J.; Hitz, E.; Luo, W.; Hu, L. Wood-Based Nanotechnologies toward Sustainability. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoine, N.; Bergström, L. Nanocellulose-based foams and aerogels: Processing, properties, and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16105–16117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yi, X.; Zeng, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Comparative study of aerogels obtained from differently prepared nanocellulose fibers. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoumis, G. Science and Technology of Wood: Structure, Properties, Utilization; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 115. [Google Scholar]
- Schoch, W.; Heller, I.; Schweingruber, F.H.; Kienast, F. Wood Anatomy of Central European Species; Swiss Federal Institure for Forest: Birmensdorf, Switzerland, 2004.
- Qiu, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Gao, L.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y. Transparent wood bearing a shielding effect to infrared heat and ultraviolet via incorporation of modified antimony-doped tin oxide nanoparticles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 172, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Jiang, F.; Hu, P.; Kuang, Y.; He, S.; Li, T.; Chen, C.; Murphy, A.; Yang, C.; Yao, Y. Anisotropic, Mesoporous Microfluidic Frameworks with Scalable, Aligned Cellulose Nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7362–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Li, T.; Chen, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Kong, W.; Liu, D.; Jiang, B.; He, S.; Kuang, Y. A Highly Conductive Cationic Wood Membrane. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 1902772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runkel, R.O. Uber die Herstellung von Zellstoff aus Holz der Gattung Eucalyptus and Versuche mit zwei unterschiedlichen Eucalyptusarten. Das Pap. 1949, 3, 476–490. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, L. Rapid dissolution of cellulose in LiOH/urea and NaOH/urea aqueous solutions. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Lu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, J. Hydrothermal synthesis of zirconium dioxide coating on the surface of wood with improved UV resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 321, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.; Martin, A., Jr.; Conrad, C. An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knill, C.J.; Kennedy, J.F. Degradation of cellulose under alkaline conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 51, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Xiao, S.; Gan, W.; Liu, Q.; Amer, H.; Rosenau, T.; Li, J.; Lu, Y. Mussel adhesive-inspired design of superhydrophobic nanofibrillated cellulose aerogels for oil/water separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9047–9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompsett, G.; Krogh, L.; Griffin, D.; Conner, W. Hysteresis and scanning behavior of mesoporous molecular sieves. Langmuir 2005, 21, 8214–8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Superelastic and superhydrophobic nanofiber-assembled cellular aerogels for effective separation of oil/water emulsions. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhonen, J.T.; Kettunen, M.; Ras, R.H.; Ikkala, O. Hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogels as floating, sustainable, reusable, and recyclable oil absorbents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1813–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Li, C.; Liang, H.W.; Chen, J.F.; Yu, S.H. Ultralight, flexible, and fire-resistant carbon nanofiber aerogels from bacterial cellulose. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2925–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diascorn, N.; Calas, S.; Sallee, H.; Achard, P.; Rigacci, A. Polyurethane aerogels synthesis for thermal insulation–textural, thermal and mechanical properties. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2015, 106, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L. Approach for predicting effective thermal conductivity of aerogel materials through a modified lattice Boltzmann method. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 132, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Tang, G. Effective thermal conductivity of the solid backbone of aerogel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 64, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Bi, C.; Zhao, Y.; Tao, W. Thermal transport in nano-porous insulation of aerogel: Factors, models and outlook. Energy 2015, 90, 701–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, L.K.; Perondi, D.; Zampieri, V.B.; Zattera, A.J.; Santana, R.M. Cellulose/biochar aerogels with excellent mechanical and thermal insulation properties. Cellulose 2019, 26, 9071–9083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Aliheidari, N.; Zhang, X.; Ameli, A. Strong ultralight foams based on nanocrystalline cellulose for high-performance insulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 218, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Fang, W.-Z.; Li, Y.-M.; Tao, W.-Q. Experimental study of the thermal conductivity of polyurethane foams. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 115, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Feng, J.; Zhang, C. Thermal conductivity of low density carbon aerogels. J. Porous Mater. 2012, 19, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetiner, I.; Shea, A.D. Wood waste as an alternative thermal insulation for buildings. Energy Build. 2018, 168, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Shan, Y.; Wu, L.; Mu, X.; Peng, H.; Jiang, Y. High-strength and morphology-controlled aerogel based on carboxymethyl cellulose and graphene oxide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, S.; Chen, W.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, K.; Jin, K.; Yu, H.; Buehler, M.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Biopolymer nanofibrils: Structure, modeling, preparation, and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 85, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


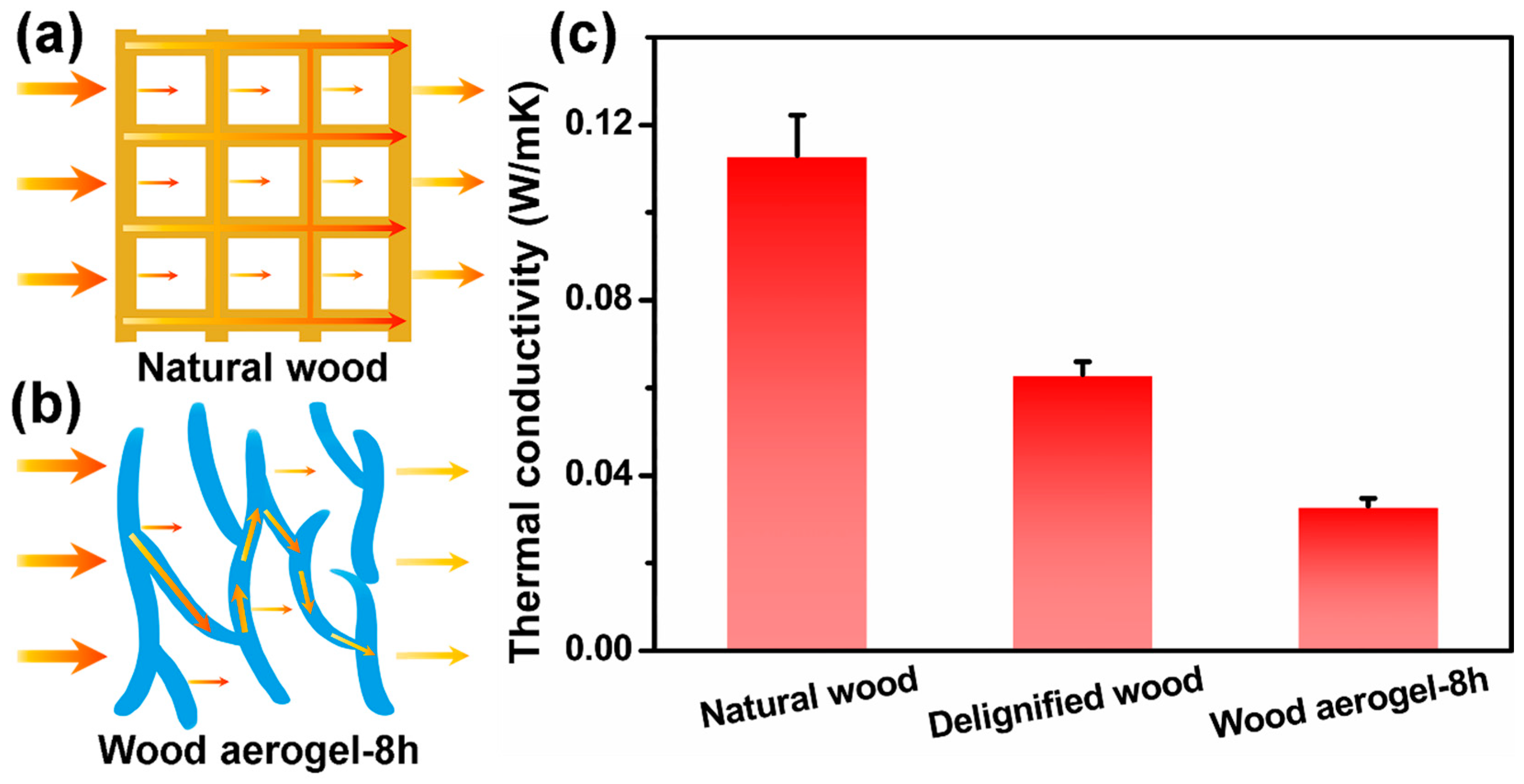
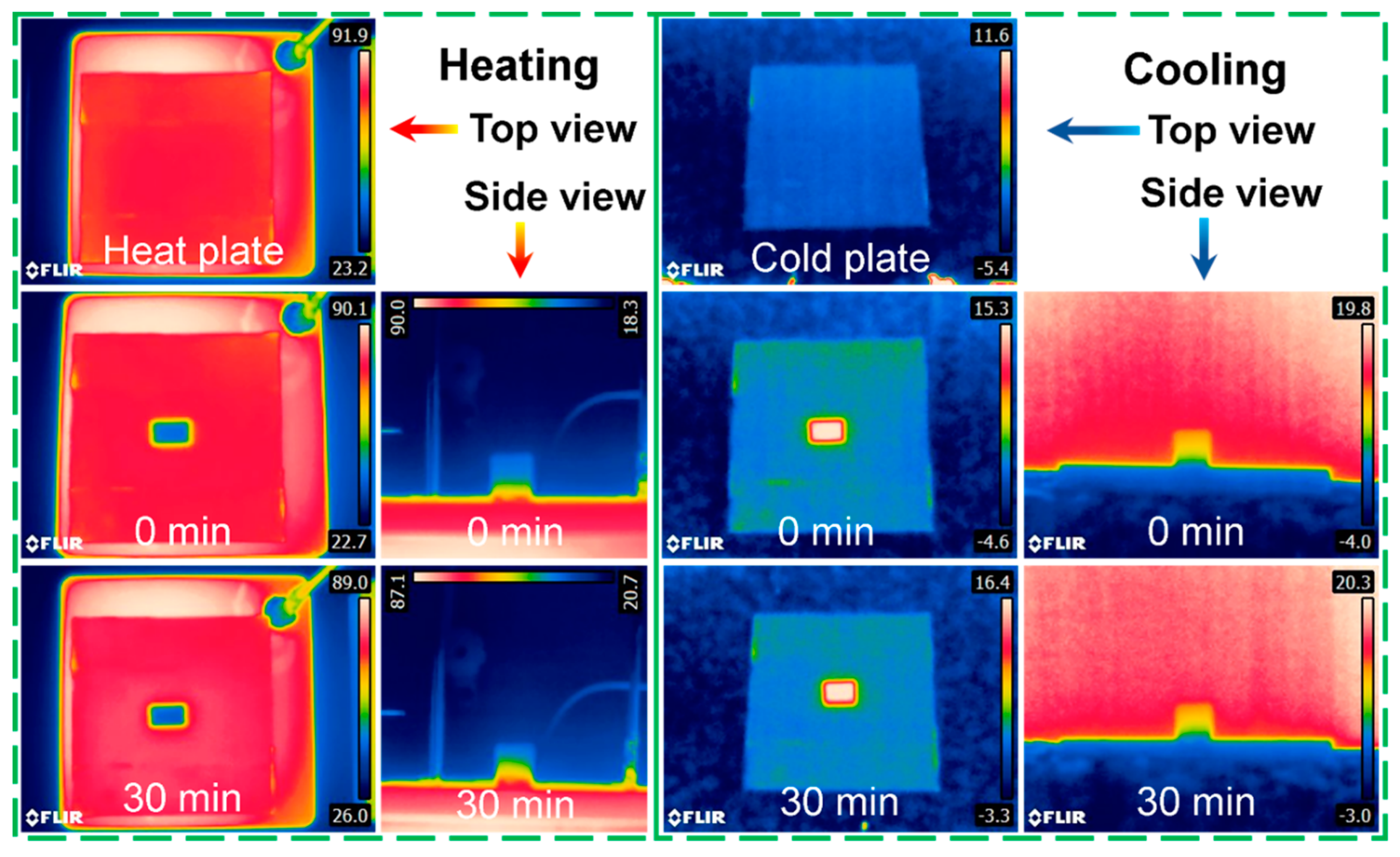
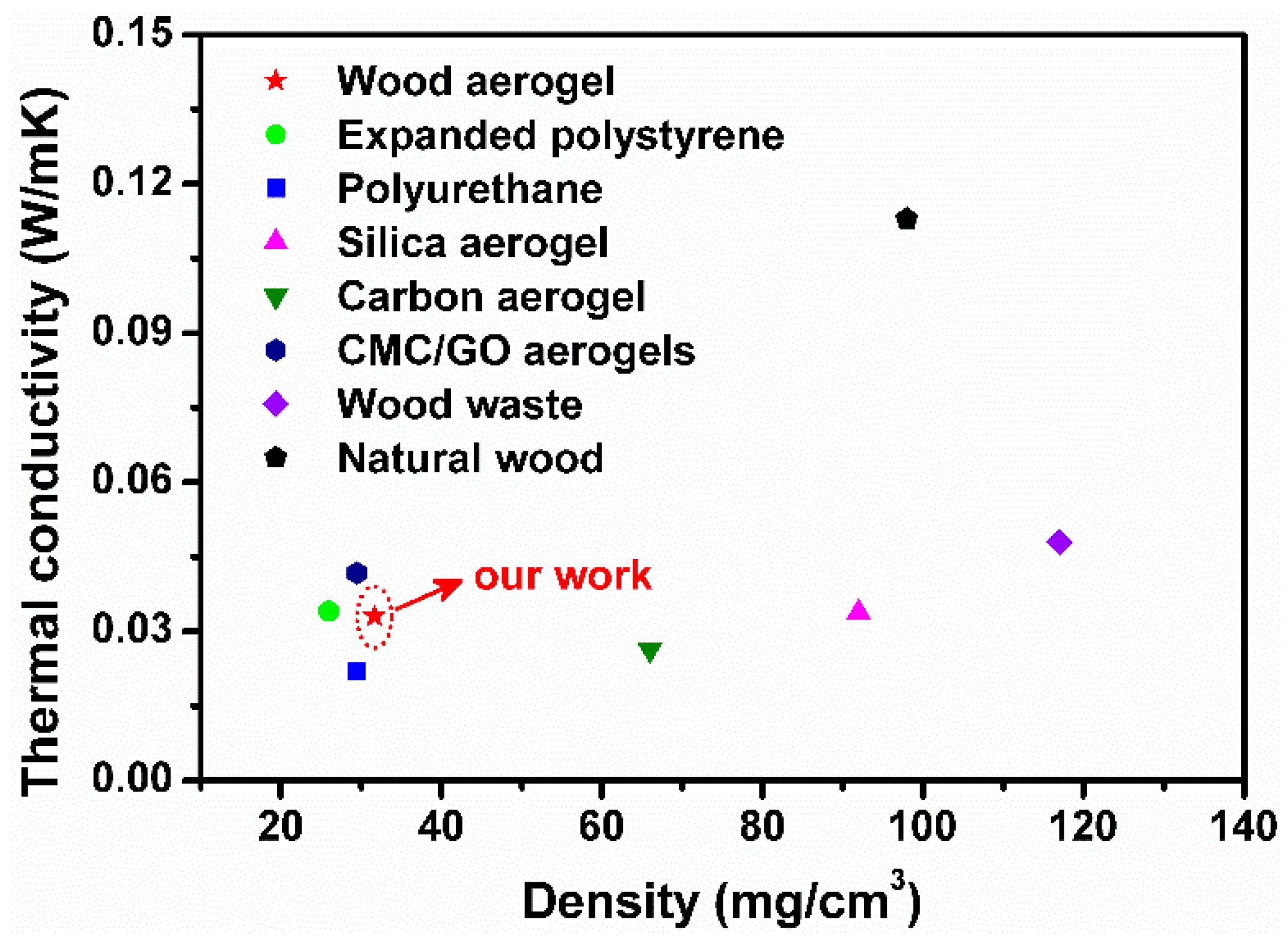
| Sample | BET Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Diameter (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural wood | 7.24 | 12.94 | 0.019 |
| Delignified wood | 17.29 | 3.81 | 0.036 |
| Wood aerogel-4 h | 18.06 | 6.69 | 0.086 |
| Wood aerogel-8 h | 32.18 | 7.63 | 0.146 |
| Wood aerogel-12 h | 21.99 | 7.55 | 0.100 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Bi, H.; Lin, X.; Cai, L.; Xu, M. Lightweight, Anisotropic, Compressible, and Thermally-Insulating Wood Aerogels with Aligned Cellulose Fibers. Polymers 2020, 12, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010165
Sun H, Bi H, Lin X, Cai L, Xu M. Lightweight, Anisotropic, Compressible, and Thermally-Insulating Wood Aerogels with Aligned Cellulose Fibers. Polymers. 2020; 12(1):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010165
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Hao, Hongjie Bi, Xin Lin, Liping Cai, and Min Xu. 2020. "Lightweight, Anisotropic, Compressible, and Thermally-Insulating Wood Aerogels with Aligned Cellulose Fibers" Polymers 12, no. 1: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010165
APA StyleSun, H., Bi, H., Lin, X., Cai, L., & Xu, M. (2020). Lightweight, Anisotropic, Compressible, and Thermally-Insulating Wood Aerogels with Aligned Cellulose Fibers. Polymers, 12(1), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010165







