Efficient Oil/Water Separation Membrane Derived from Super-Flexible and Superhydrophilic Core–Shell Organic/Inorganic Nanofibrous Architectures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. PVDF-HFP/Cu(CH3COO)2 Nanofibrous Membrane Prepared by Electrospinning Process
2.3. PVDF-HFP/CuO Nanofibrous Membrane Prepared by Heating Process
2.4. PVDF-HFP/CuO-Nanosheet Nanofibrous Membrane Prepared by Hydrothermal Process
2.5. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
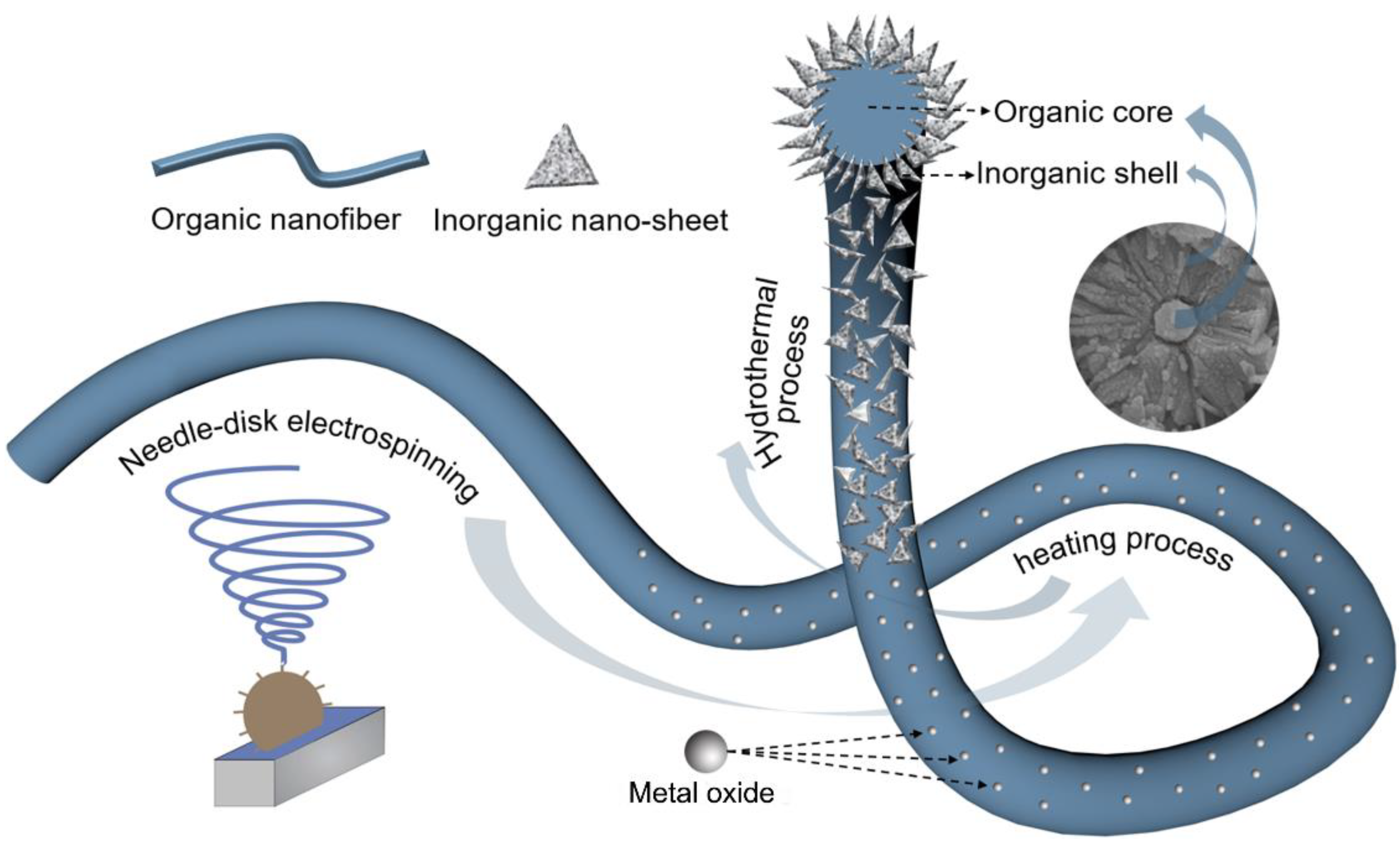
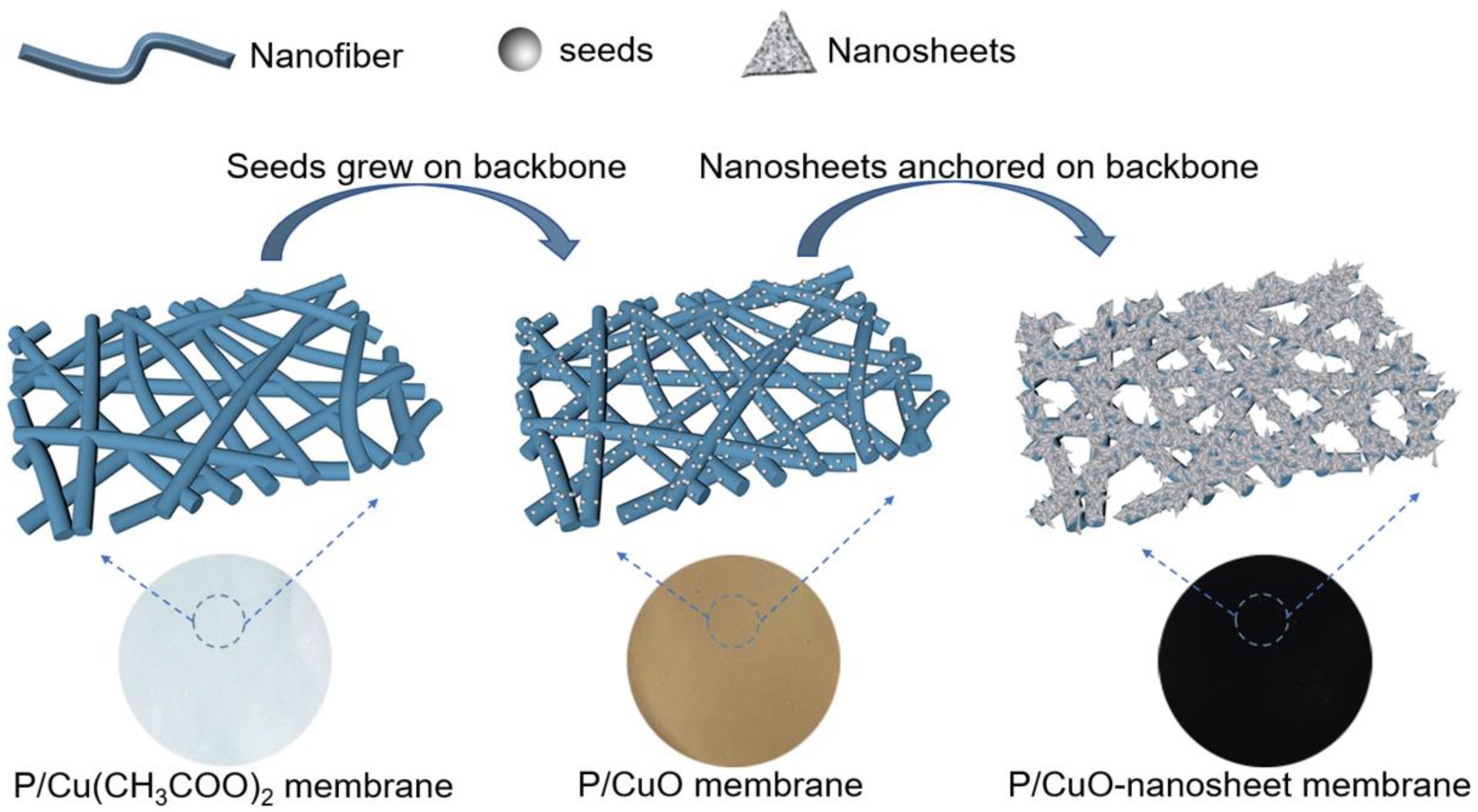
3.1. Evolution of P/CuO-Nanosheet Membrane Formation Process
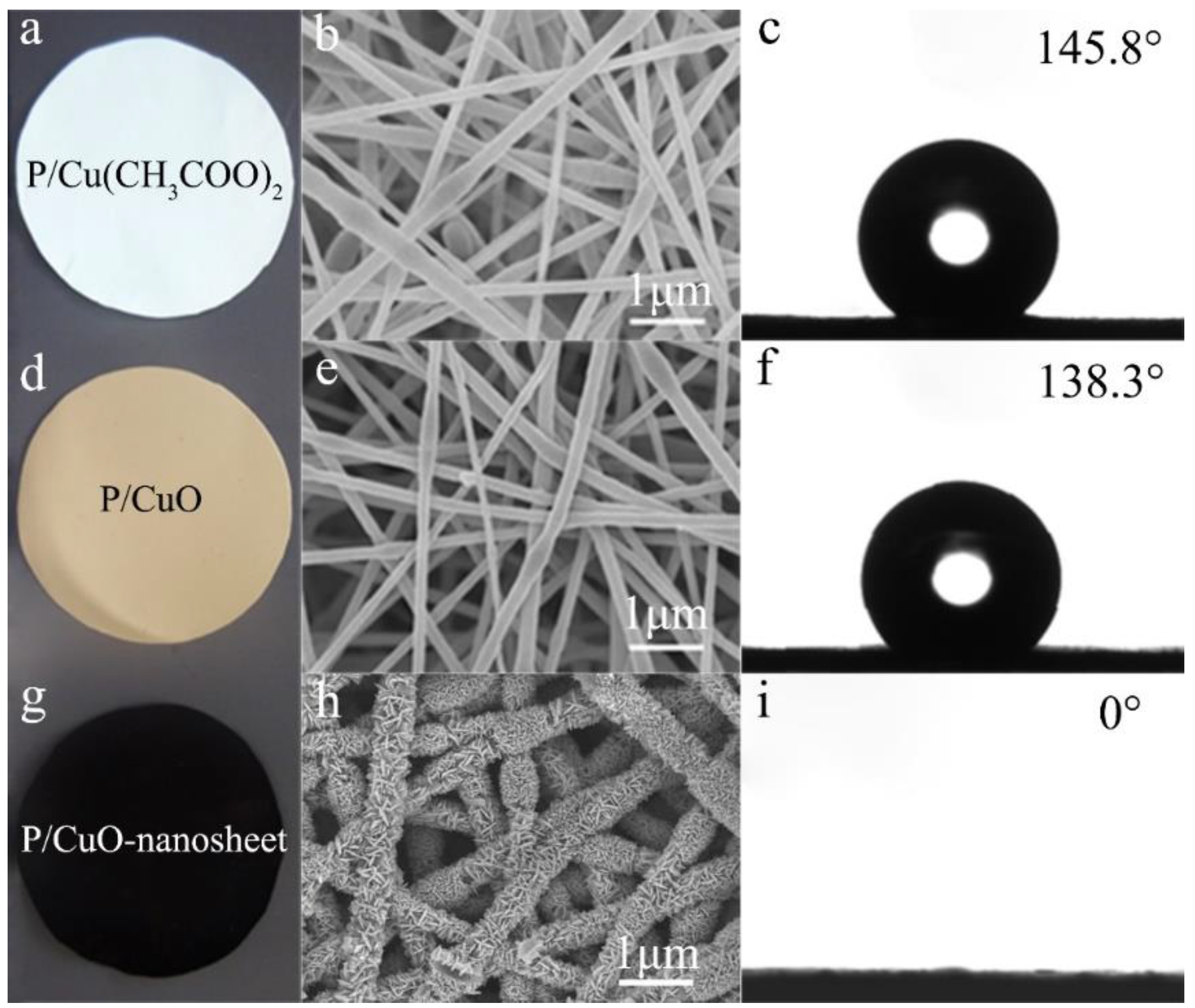
3.2. The Morphology and Structure of the Resulting Membranes
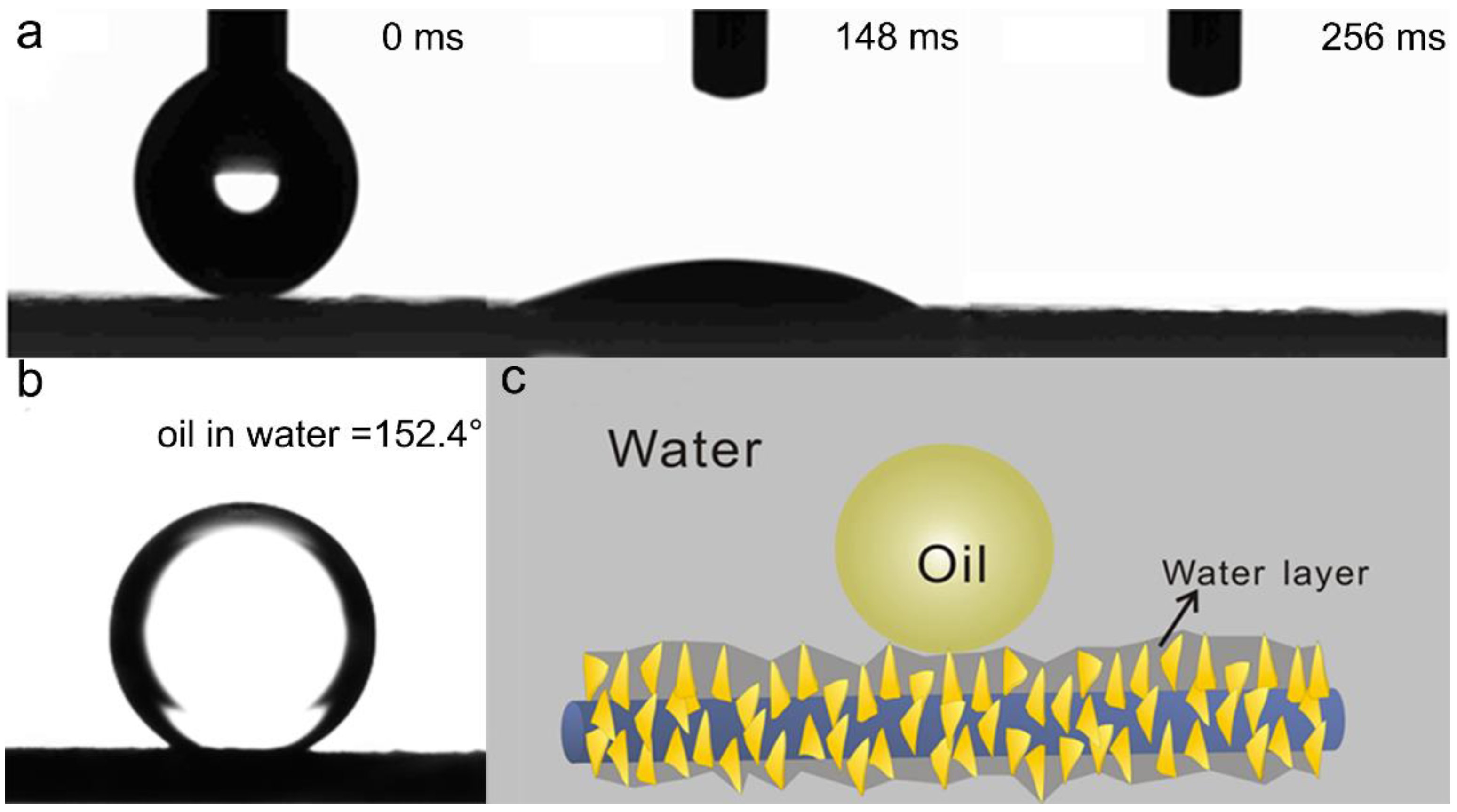
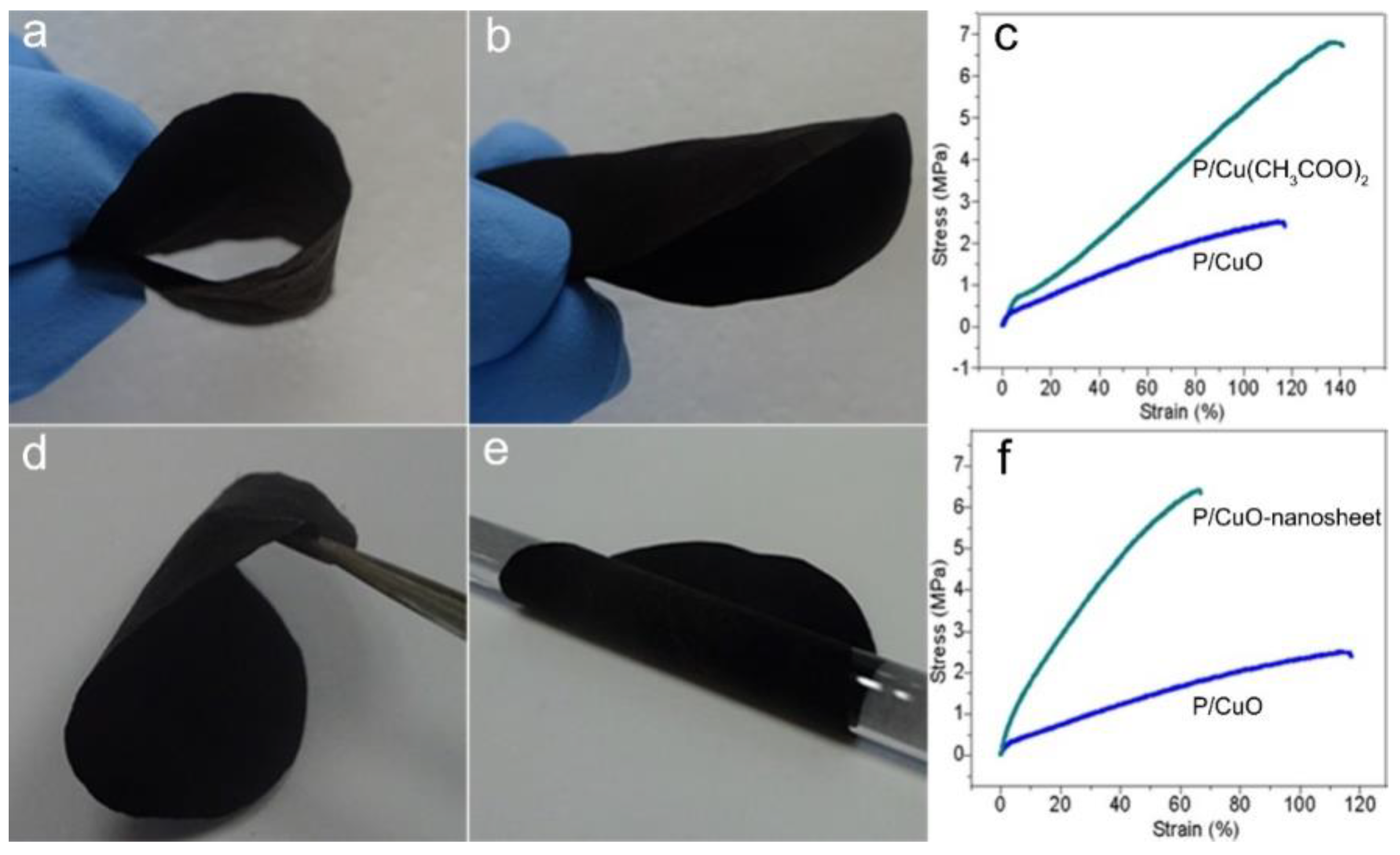
3.3. The Wettability and Mechanical Properties of the P/CuO Nano-Sheet Membrane
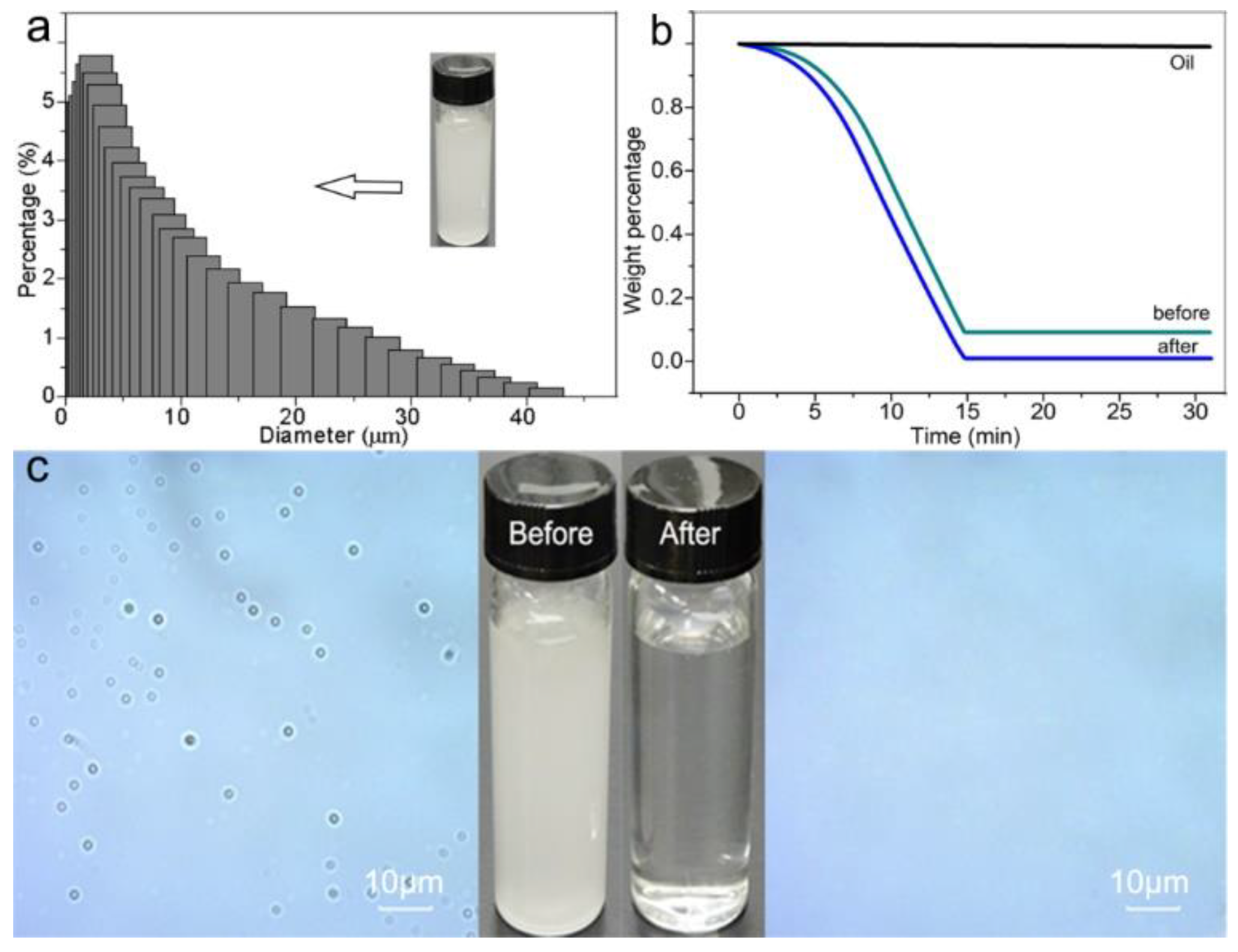
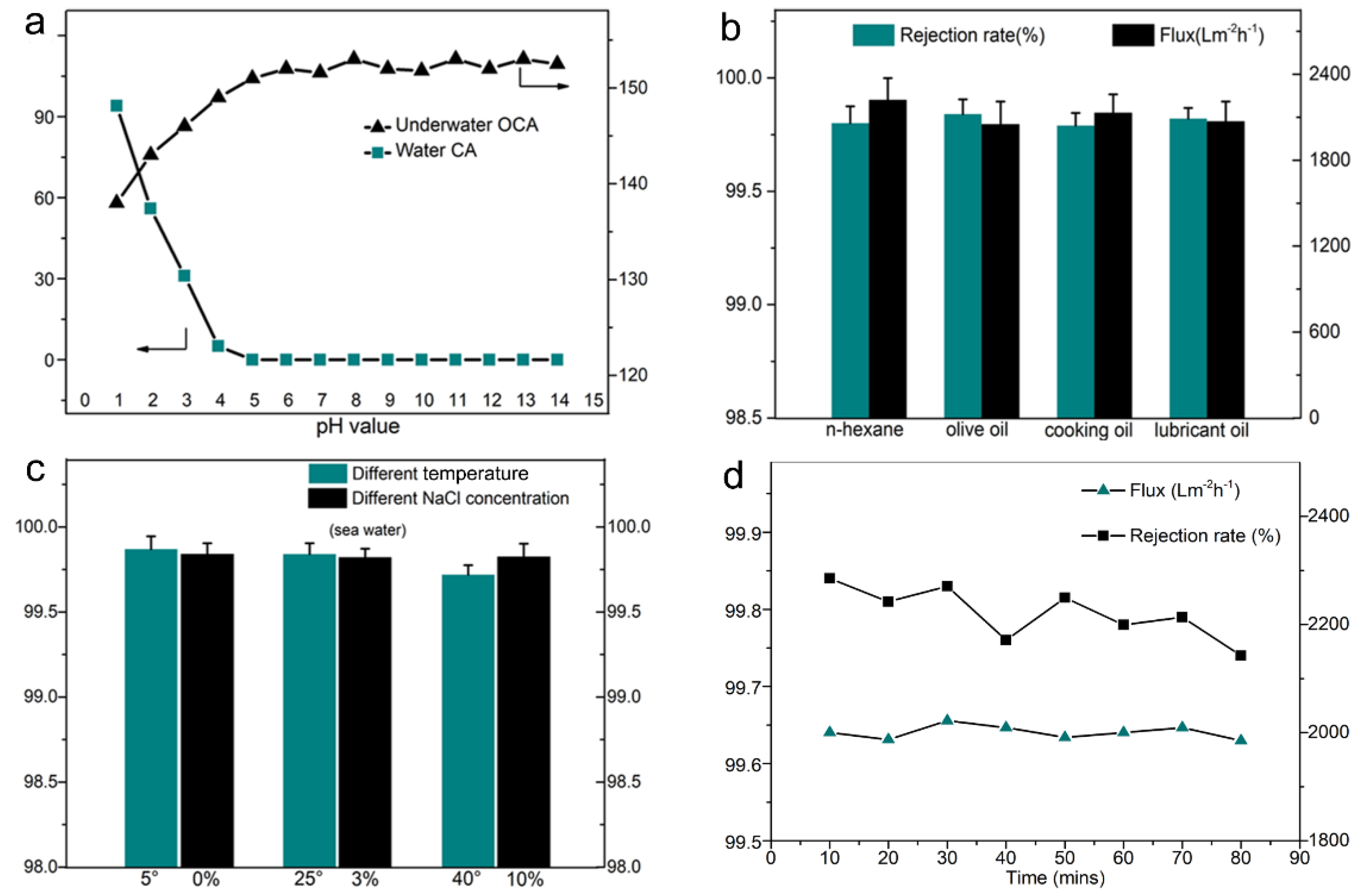
3.4. The Membrane Performance for Oil/Water Separation
3.5. The Proposed Formation Mechanism of P/CuO Nano-Sheet Membrane
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Judd, S.J. Membrane technology costs and me. Water Res. 2017, 122, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.E.; Elimelech, M. Membrane-based processes for sustainable power generation using water. Nature 2012, 488, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Mariñas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thavasi, V.; Singh, G.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun nanofibers in energy and environmental applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.A.; Lagally, M.G.; Nuzzo, R.G. Synthesis, assembly and applications of semiconductor nanomembranes. Nature 2011, 477, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gin, D.L.; Noble, R.D. Designing the next generation of chemical separation membranes. Science 2011, 332, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Duan, G.; Mei, C.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Electrospun nanofiber reinforced composites: A review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2685–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, W.; Xing, J.; Xu, L.; He, J. Humidity-induced porous poly (lactic acid) membrane with enhanced flux for oil-water separation. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, D.D. Hierarchically multifunctional TiO2 nano-thorn membrane for water purification. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6542–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Sun, D.D. Hierarchical 3D dendritic TiO2 nanospheres building with ultralong 1D nanoribbon/wires for high performance concurrent photocatalytic membrane water purification. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4126–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Kang, M.; Huang, C.; Fu, G. Fabrication of highly durable and robust superhydrophobic-superoleophilic nanofibrous membranes based on a fluorine-free system for efficient oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 570, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzenis, Y. Spinning continuous fibers for nanotechnology. Science 2004, 304, 1917–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, J. Learning from nature’s best. Nature 2015, 519, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Superelastic and superhydrophobic nanofiber-assembled cellular aerogels for effective separation of oil/water emulsions. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. A super-hydrophobic and super-oleophilic coating mesh film for the separation of oil and water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2012–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kang, R.; Tang, X.; She, H.; Yang, Y.; Zha, F. Superhydrophobic meshes that can repel hot water and strong corrosive liquids used for efficient gravity-driven oil/water separation. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7638–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Cheng, H.; Fane, A.G.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H. Recent development of advanced materials with special wettability for selective oil/water separation. Small 2016, 12, 2186–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Miyazaki, K.; Hori, T. Fabrication of polydopamine-coated superhydrophobic fabrics for oil/water separation and self-cleaning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 370, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xu, L.; Xue, Z.; Feng, L.; Peng, J.; Wen, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X. Dual-scaled porous nitrocellulose membranes with underwater superoleophobicity for highly efficient oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padaki, M.; Murali, R.S.; Abdullah, M.S.; Misdan, N.; Moslehyani, A.; Kassim, M.A.; Hilal, N.; Ismail, A.F. Membrane technology enhancement in oil-water separation. A review. Desalination 2015, 357, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. Low-Density Open Cellular Sponges as Functional Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15520–15538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Zhou, G.; Jiang, S.; Fan, P.; Hou, H. Flexible and refractory tantalum carbide-carbon electrospun nanofibers with high modulus and electric conductivity. Mater. Lett. 2017, 200, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Xue, L.; Liu, F.; Jiang, L. An intelligent superwetting PVDF membrane showing switchable transport performance for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2943–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.S.; Kang, S.H.; Tang, S.K.Y.; Smythe, E.J.; Hatton, B.D.; Grinthal, A.; Aizenberg, J. Bioinspired self-repairing slippery surfaces with pressure-stable omniphobicity. Nature 2011, 477, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Seeger, S. Oil/water separation with selective superantiwetting/superwetting surface materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2328–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Cheng, J.; Hou, K.; Zhao, A.; Pi, P.; Wen, X.; Xu, S. Superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic titania nanowires surface for oil repellency and oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 301, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. A novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic hydrogel-coated mesh for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Xue, Z.; Gao, J.; Meng, J.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Clam’s shell inspired high-energy inorganic coatings with underwater low adhesive superoleophobicity. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3401–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Meng, J.; Hao, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. A scalable method toward superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic PVDF membranes for effective oil/water emulsion separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 14896–14904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Cha, D.; Wang, P. A self-cleaning underwater superoleophobic mesh for oil-water separation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, W.B.; Shi, Z.; Wang, D.; Jin, J.; Jiang, L. Nanowire-haired inorganic membranes with superhydrophilicity and underwater ultralow adhesive superoleophobicity for high-efficiency oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4192–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, D.; Liu, Z.; Bai, H.; Sun, D.D.; Song, X. A new nano-engineered hierarchical membrane for concurrent removal of surfactant and oil from oil-in-water nanoemulsion. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Cao, R.; Wei, A.; Zhao, J.; He, J. Superflexible/superhydrophilic PVDF-HFP/CuO-nanosheet nanofibrous membrane for efficient microfiltration. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Greiner, A. Air-Blowing-Assisted Coaxial Electrospinning toward High Productivity of Core/Sheath and Hollow Fibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 1800669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, R.; He, J. Active generation of multiple jets for producing nanofibres with high quality and high throughput. Mater. Des. 2016, 94, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ang, K.K.J.; He, J. Needle-disk electrospinning inspired by natural point discharge. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Bai, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, D.D. Optimization and an insightful property-activity study of electrospun TiO2/CuO composite nanofibers for efficient photocatalytic H2 generation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 140, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, C.; Xu, B.; Wang, T.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. Influence of temperature on nitrogen fate during hydrothermal carbonization of food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Li, Y.; Long, P.; Gao, Y.; Qin, C.; Cao, C.; Feng, Y.; Feng, W. Hydrothermal preparation of fluorinated graphene hydrogel for high-performance supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2016, 312, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Long, H.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Lu, P. Controlled growth and characteristics of single-phase Cu2O and CuO films by pulsed laser deposition. Vacuum 2009, 83, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Wallace, G.G. Tin nanoparticles decorated copper oxide nanowires for selective electrochemical reduction of aqueous CO2 to CO. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 10710–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, D.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Lu, L.; Wang, X. Highly dispersed CuO nanoparticles prepared by a novel quick-precipitation method. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 3324–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghana, S.; Kabra, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Padmavathy, N. Understanding the pathway of antibacterial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 12293–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Tiwari, B.; Zhang, D.; Yap, Y.K. Water purification: Oil-water separation by nanotechnology and environmental concerns. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, W.Y.; Bobra, M.; Bobra, A.M.; Maijanen, A.; Suntio, L.; Mackay, D. The water solubility of crude oils and petroleum products. Oil Chem. Pollut. 1990, 7, 57–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liang, W.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Biomimetic super-lyophobic and super-lyophilic materials applied for oil/water separation: A new strategy beyond nature. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 336–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, H.; Shao, X.; Li, D.; Yu, H.; Han, M. Three-Dimensionally Oriented Aggregation of a Few Hundred Nanoparticles into Monocrystalline Architectures. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Qin, D.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Q.; Li, Z.; Bai, H.; Sun, D.D. Efficient Oil/Water Separation Membrane Derived from Super-Flexible and Superhydrophilic Core–Shell Organic/Inorganic Nanofibrous Architectures. Polymers 2019, 11, 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11060974
Liu Z, Qin D, Zhao J, Feng Q, Li Z, Bai H, Sun DD. Efficient Oil/Water Separation Membrane Derived from Super-Flexible and Superhydrophilic Core–Shell Organic/Inorganic Nanofibrous Architectures. Polymers. 2019; 11(6):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11060974
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhi, Detao Qin, Jianghui Zhao, Quan Feng, Zhengtao Li, Hongwei Bai, and Darren Delai Sun. 2019. "Efficient Oil/Water Separation Membrane Derived from Super-Flexible and Superhydrophilic Core–Shell Organic/Inorganic Nanofibrous Architectures" Polymers 11, no. 6: 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11060974
APA StyleLiu, Z., Qin, D., Zhao, J., Feng, Q., Li, Z., Bai, H., & Sun, D. D. (2019). Efficient Oil/Water Separation Membrane Derived from Super-Flexible and Superhydrophilic Core–Shell Organic/Inorganic Nanofibrous Architectures. Polymers, 11(6), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11060974





