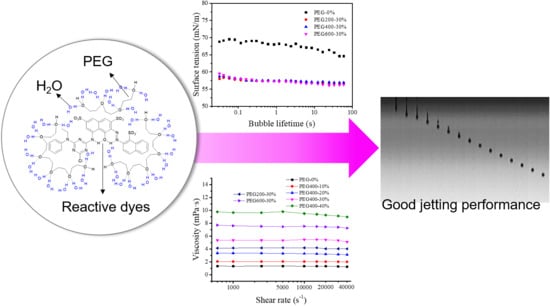
Jetting Performance of Polyethylene Glycol and Reactive Dye Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
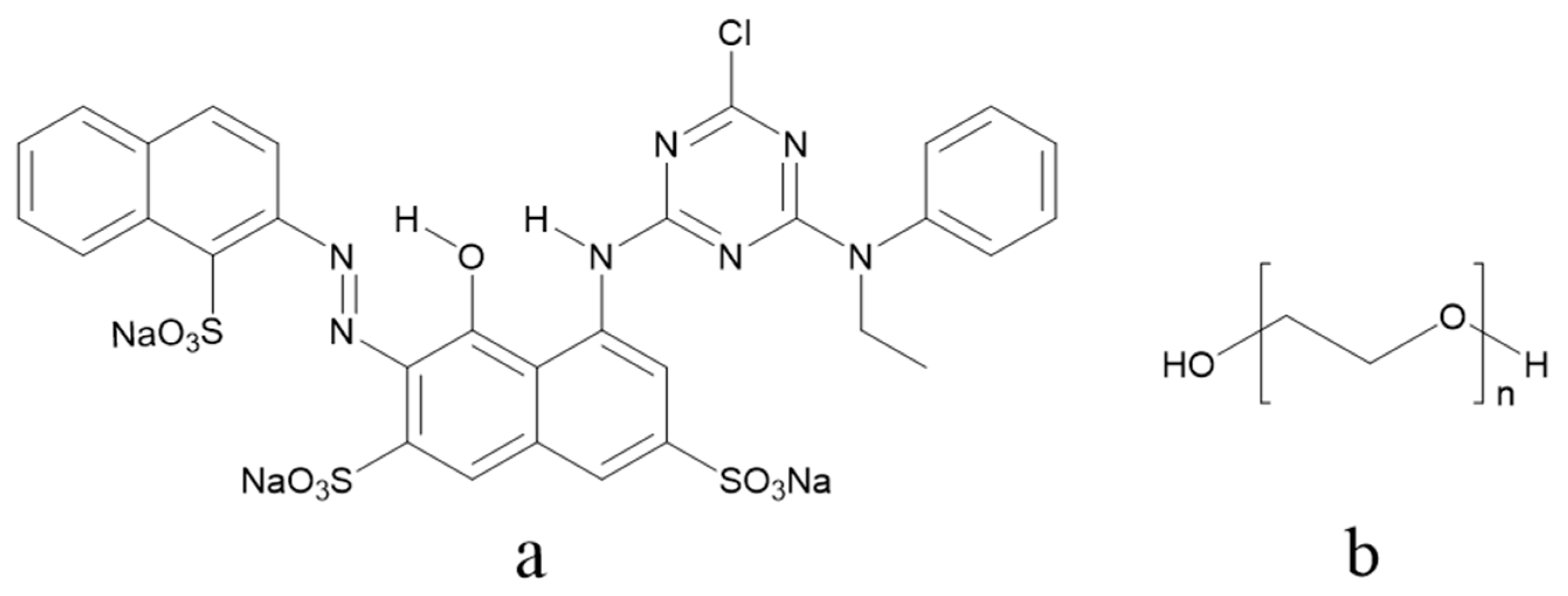
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PEG–Dye Mixed Solutions
2.3. Measurement of Visible Absorption Spectra
2.4. Test of Rheological Property and Surface Tensions
2.5. Density Measurement and Z Value Calculation
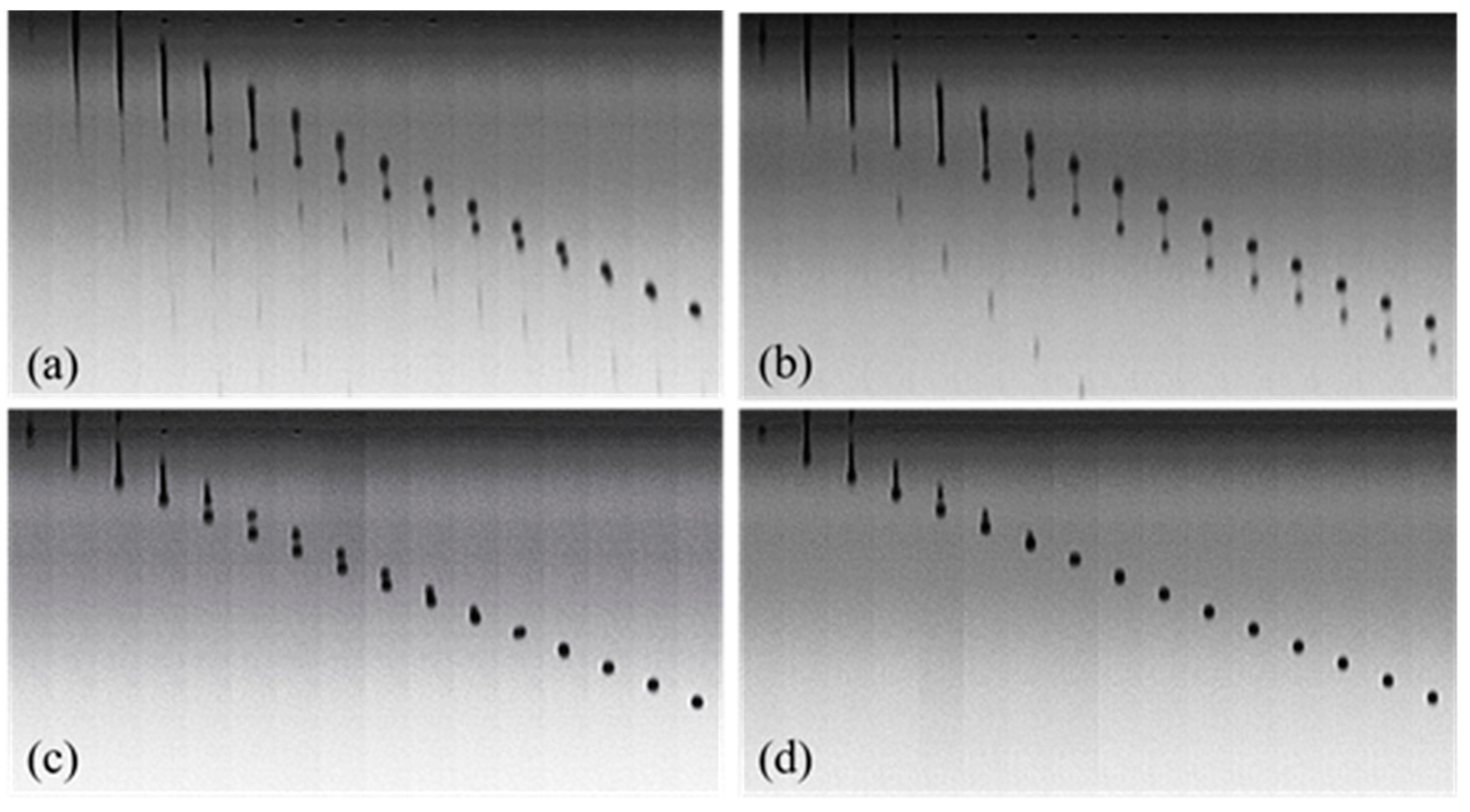
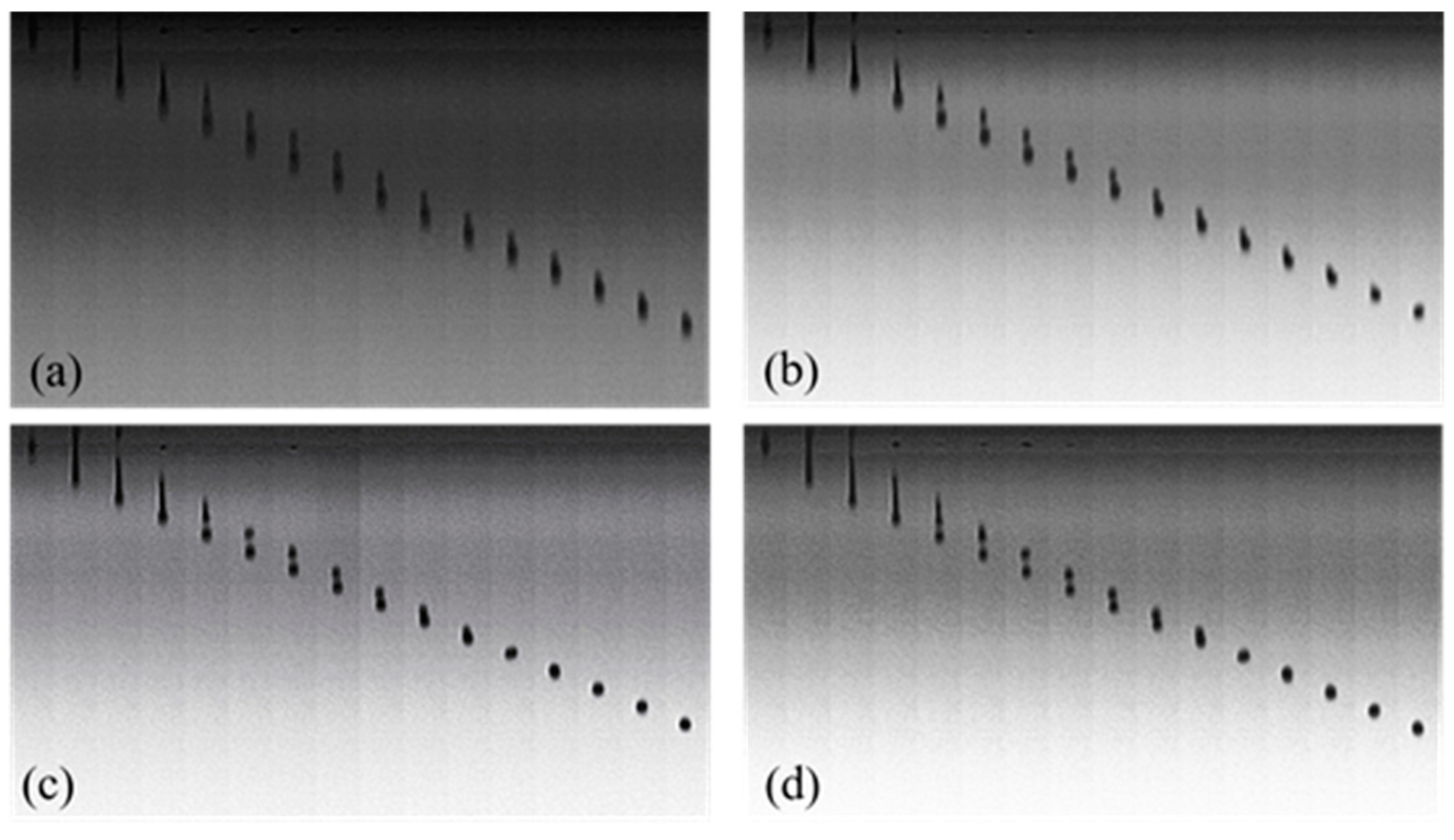
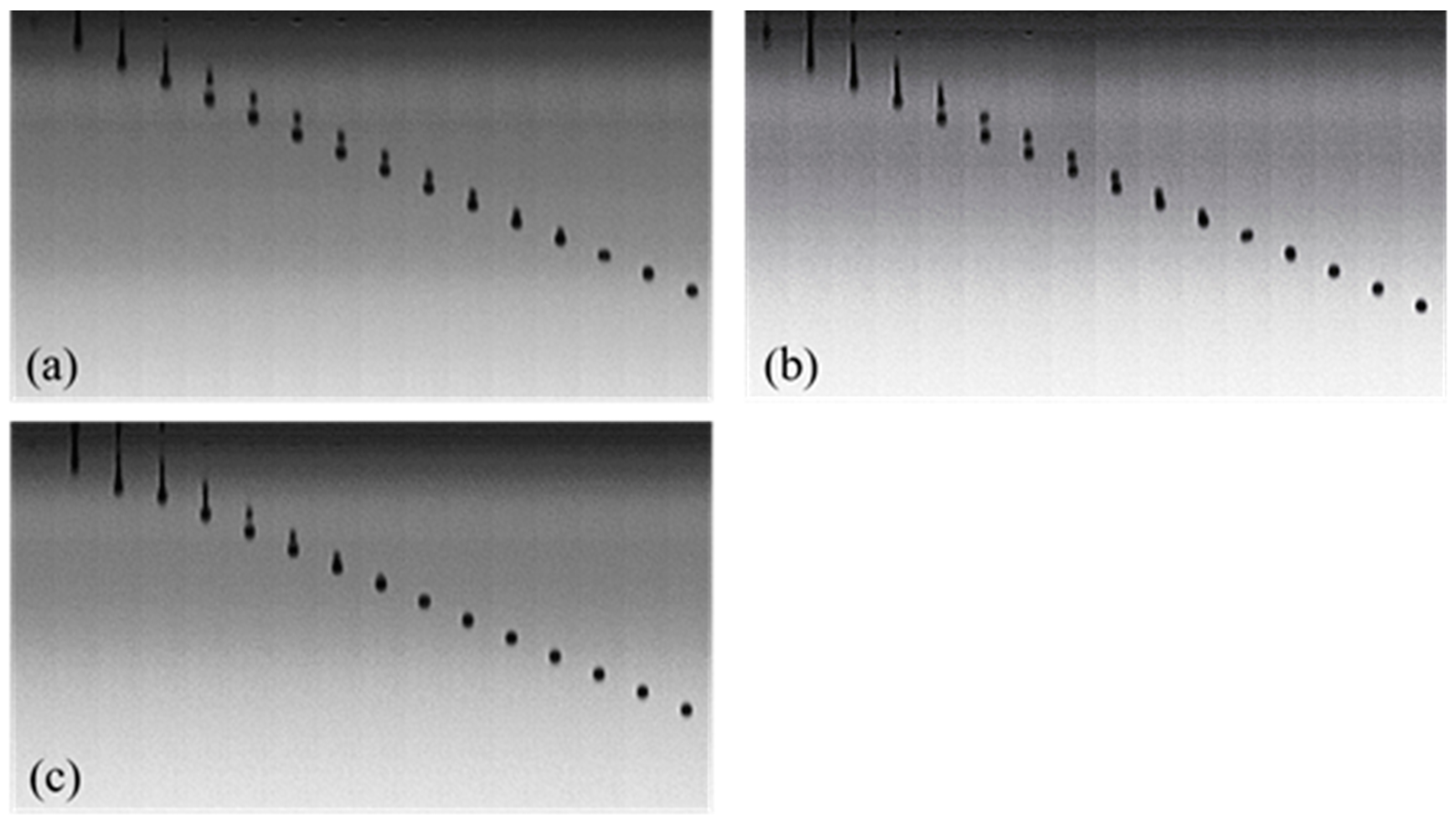
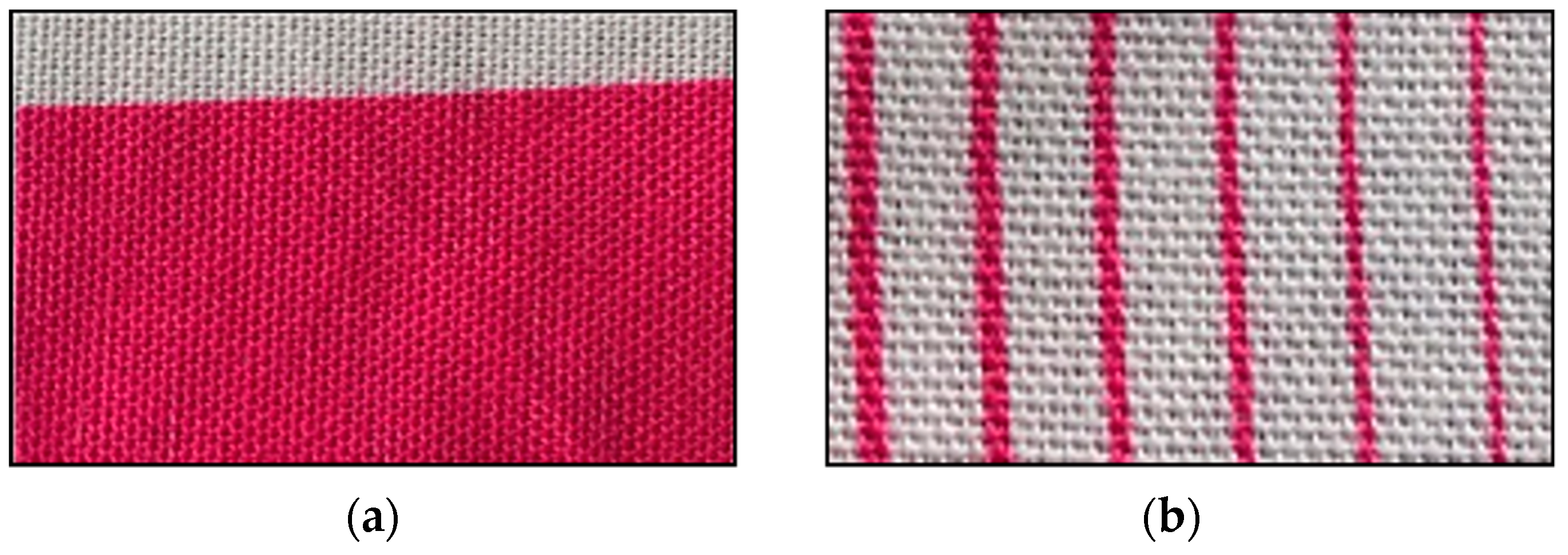
2.6. Observation of Droplet Formation and Inkjet Printing
3. Results and Discussion
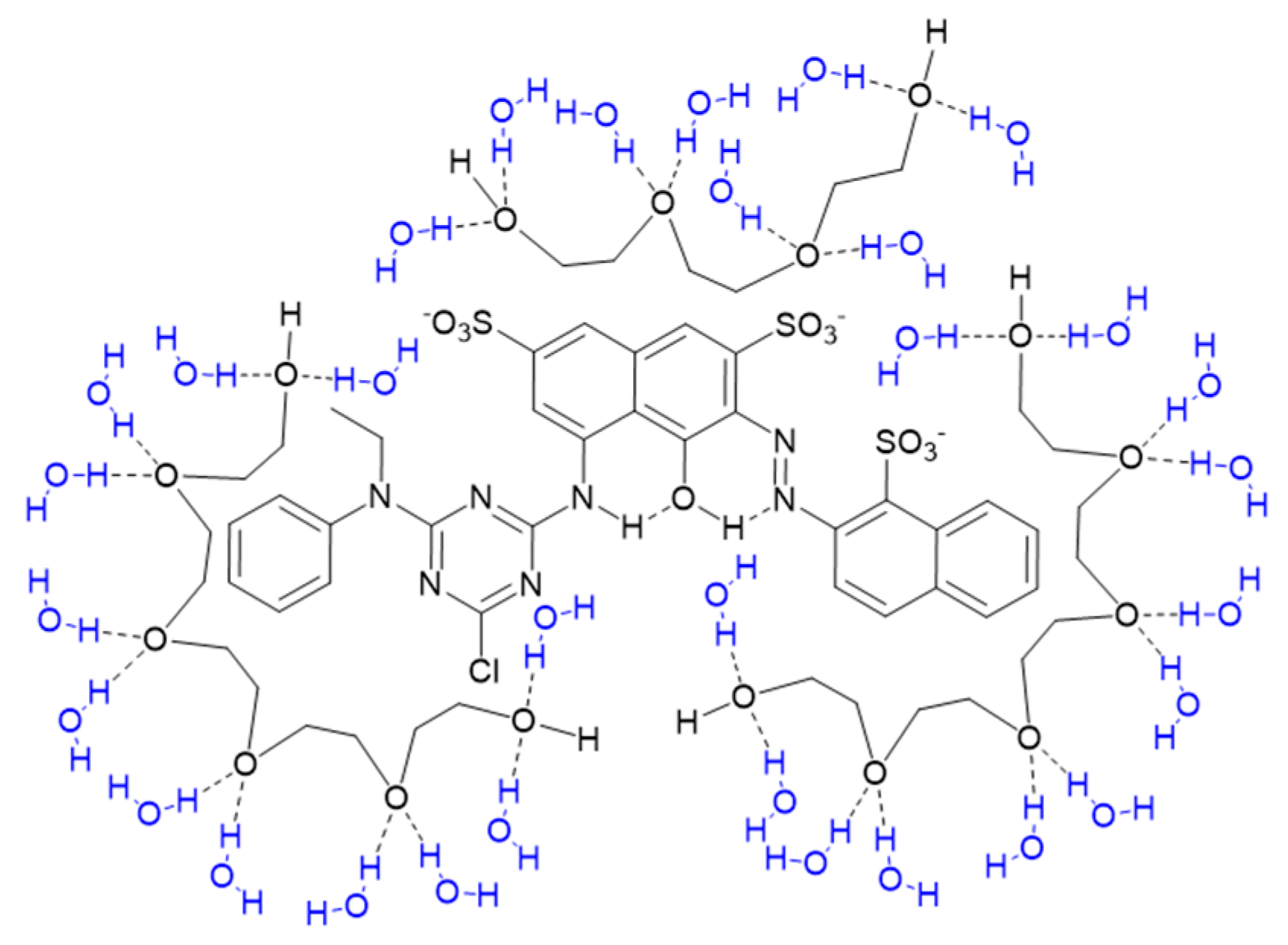
3.1. Visible Absorption Spectra of PEG and Reactive Dye Solutions
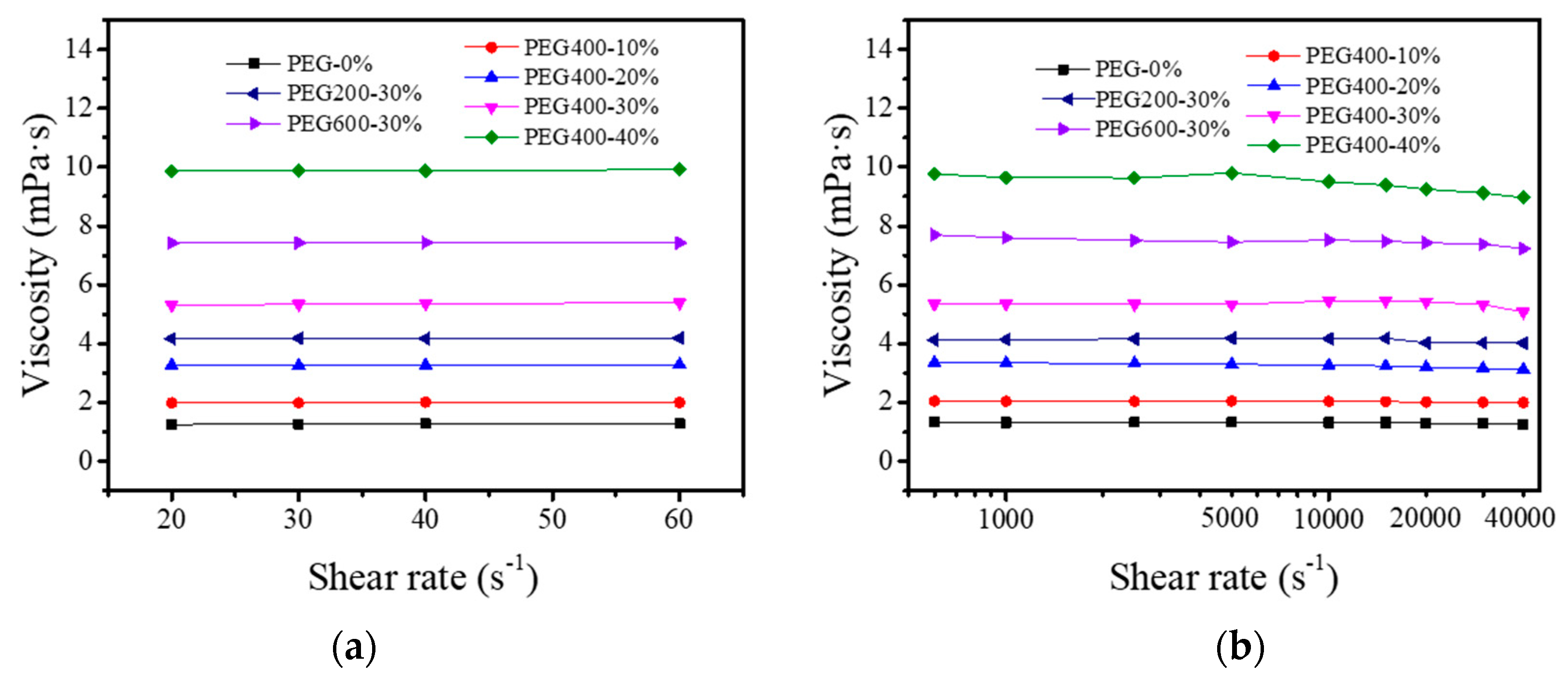
3.2. Rheology of the PEG–Dye Solutions
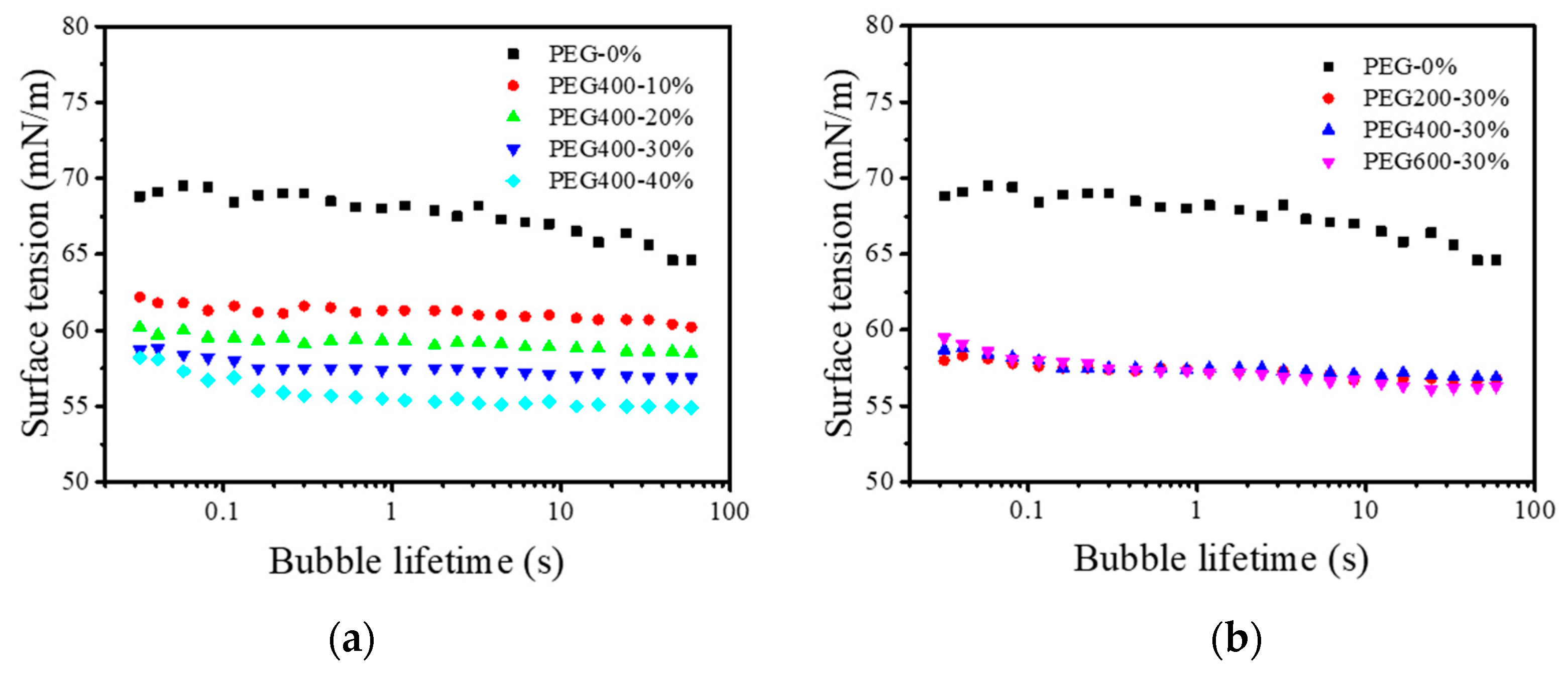
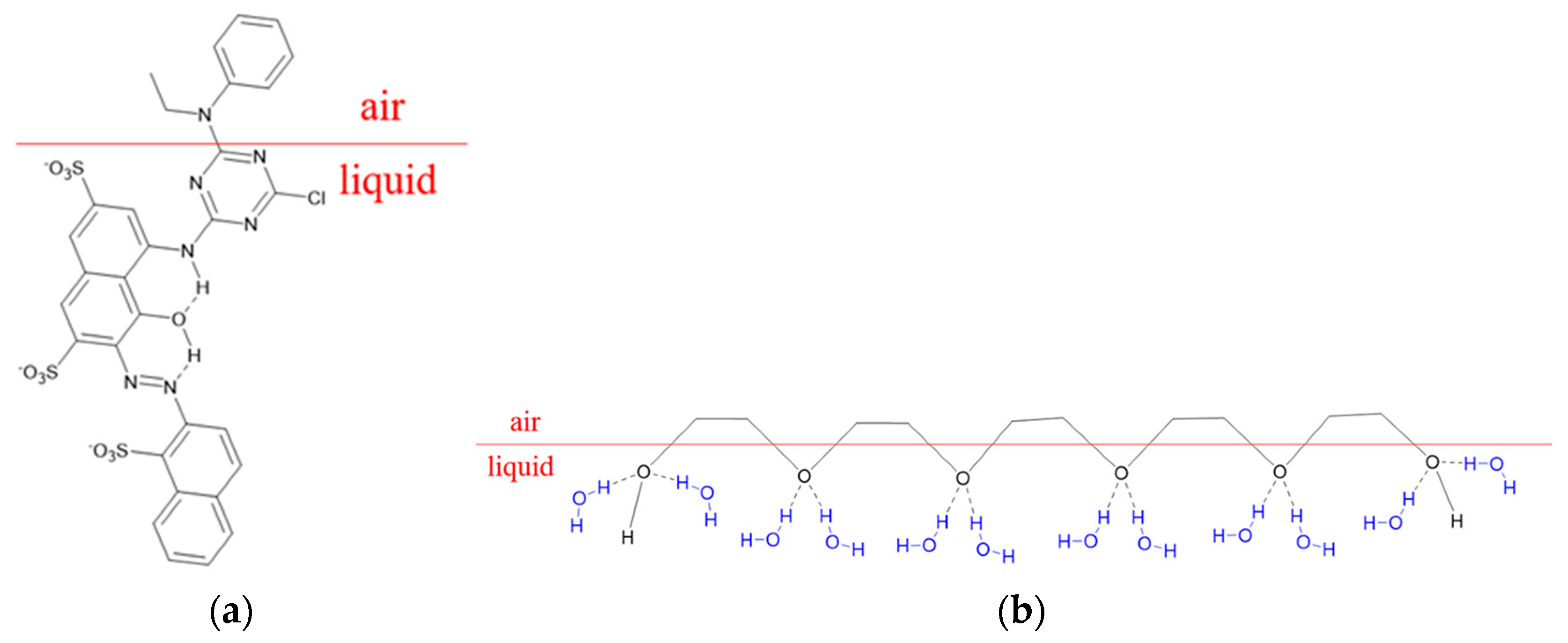
3.3. Surface Tensions of the PEG–Dye Solutions
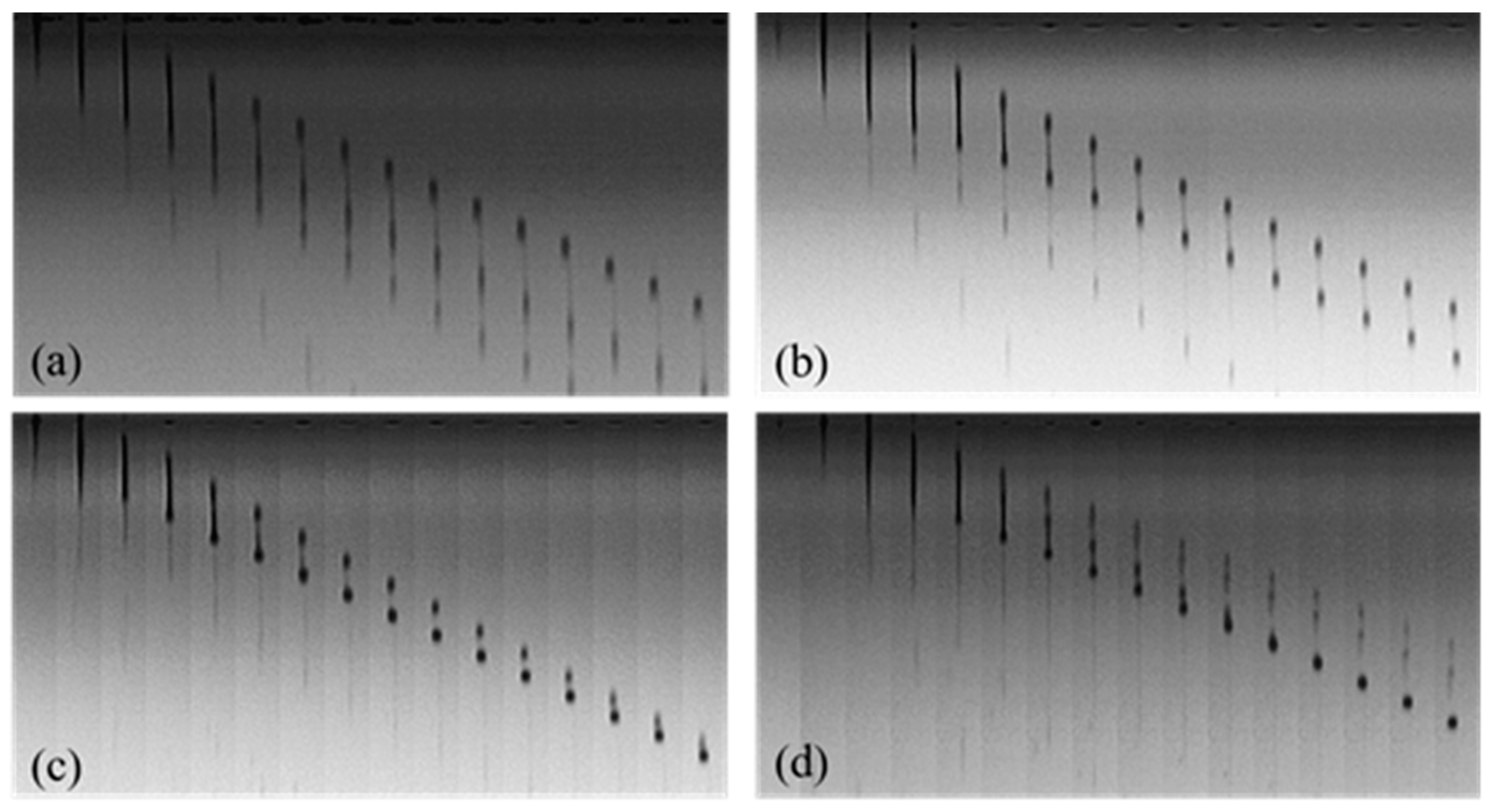
3.4. Droplet Formation and Inkjet Printing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, J.; Seipel, S.; Nierstrasz, V.A. Digital inkjet functionalization of water-repellent textile for smart textile application. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 13216–13229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fang, K.; Gao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. Effect of cotton fabric pretreatment on drop spreading and colour performance of reactive dye inks. Color. Technol. 2016, 132, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Naarani, V. Improvement of the lightfastness of reactive inkjet printed cotton. Dyes Pigment. 2007, 74, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Yan, K. A one-step inkjet printing technology with reactive dye ink and cationic compound ink for cotton fabrics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisal, S.; Tronci, A. Predictive modelling of colour strength and ink penetration (%) of inkjet-printed cotton. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Shamey, R.; Chapman, L.P.; Freeman, H.S. Pretreatment effects on pigment-based textile inkjet printing—Colour gamut and crockfastness properties. Color. Technol. 2019, 135, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gong, H.; Lu, S.; Ni, B.; Liu, M.; Gao, C.; Huang, Y.; Han, F. Synthesis and characterization of carboxymethyl potato starch and its application in reactive dye printing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Fang, K.; Liu, X.; Cai, Y.; An, F. Effect of cotton cationization using copolymer nanospheres on ink-jet printing of different fabrics. Polymers 2018, 10, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Fang, K.; Ren, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, R.; Chen, W.; Xie, R.; Shi, Z.; Hao, L. Inkjet printable and self-curable disperse dyes/p(st-ba-maa) nanosphere inks for both hydrophilic and hydrophobic fabrics. Polymers 2018, 10, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, Y. Reactive Dye Ink-Jet Printing on Wool Fabrics; University of Leeds: Leeds, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhang, L.; An, Y.; Ma, W.; Fu, S. Relationship between silk fabric pretreatment, droplet spreading, and ink-jet printing accuracy of reactive dye inks. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoath, S.D.; Jung, S.; Hsiao, W.-K.; Hutchings, I.M. How pedot:Pss solutions produce satellite-free inkjets. Org. Electron. 2012, 13, 3259–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Baek, J. Numerical study on the effects of non-dimensional parameters on drop-on-demand droplet formation dynamics and printability range in the up-scaled model. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 082103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijshoff, H. Drop dynamics in the inkjet printing process. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 36, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoath, S.D. Fundamentals of Inkjet Printing: The Science of Inkjet and Droplets; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, D.; Kim, D.; Moon, J. Influence of fluid physical properties on ink-jet printability. Langmuir 2009, 25, 2629–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christanti, Y.; Walker, L.M. Surface tension driven jet break up of strain-hardening polymer solutions. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 2001, 100, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddara, Y.M.; Howlader, M.M.R. Integration of heterogeneous materials for wearable sensors. Polymers 2018, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-Y.; Hirata, Y.; Hamada, K. Relationship between the dye/additive interaction and inkjet ink droplet formation. Dyes Pigments 2012, 95, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-Y.; Hirata, Y.; Hamada, K. Dye aggregation and interaction of dyes with a water-soluble polymer in ink-jet ink for textiles. Color. Technol. 2012, 128, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, D.J. Textile digital printing technologies. Text. Prog. 2005, 37, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.W.; Yuen, C.W.M. Digital ink-jet printing on textiles. Res. J. Text. Appar. 2012, 16, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, M.; Hiraga, Y.; Kasuya, K.; Aida, T.M.; Watanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Smith, R.L. Viscosity and density of poly(ethylene glycol) and its solution with carbon dioxide at 353.2k and 373.2k at pressures up to 15mpa. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2015, 97, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanot, C.; Trivedi, S.; Gupta, A.; Pandey, S.; Pandey, S. Dynamic viscosity versus probe-reported microviscosity of aqueous mixtures of poly(ethylene glycol). J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2012, 45, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallan, H.C.; Sadie, J.A.; Kitsomboonloha, R.; Volkman, S.K.; Subramanian, V. Systematic design of jettable nanoparticle-based inkjet inks: Rheology, acoustics, and jettability. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13470–13477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Park, Y. Inkjet etching of polymers and its applications in organic electronic devices. Polymers 2017, 9, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooperwhite, J.J.; Fagan, J.E.; Tirtaatmadja, V.; Lester, D.R.; Boger, D.V. Drop formation dynamics of constant low-viscosity, elastic fluids. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 2002, 106, 29–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, N.; Ainsley, C.; Derby, B. Ink-jet delivery of particle suspensions by piezoelectric droplet ejectors. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
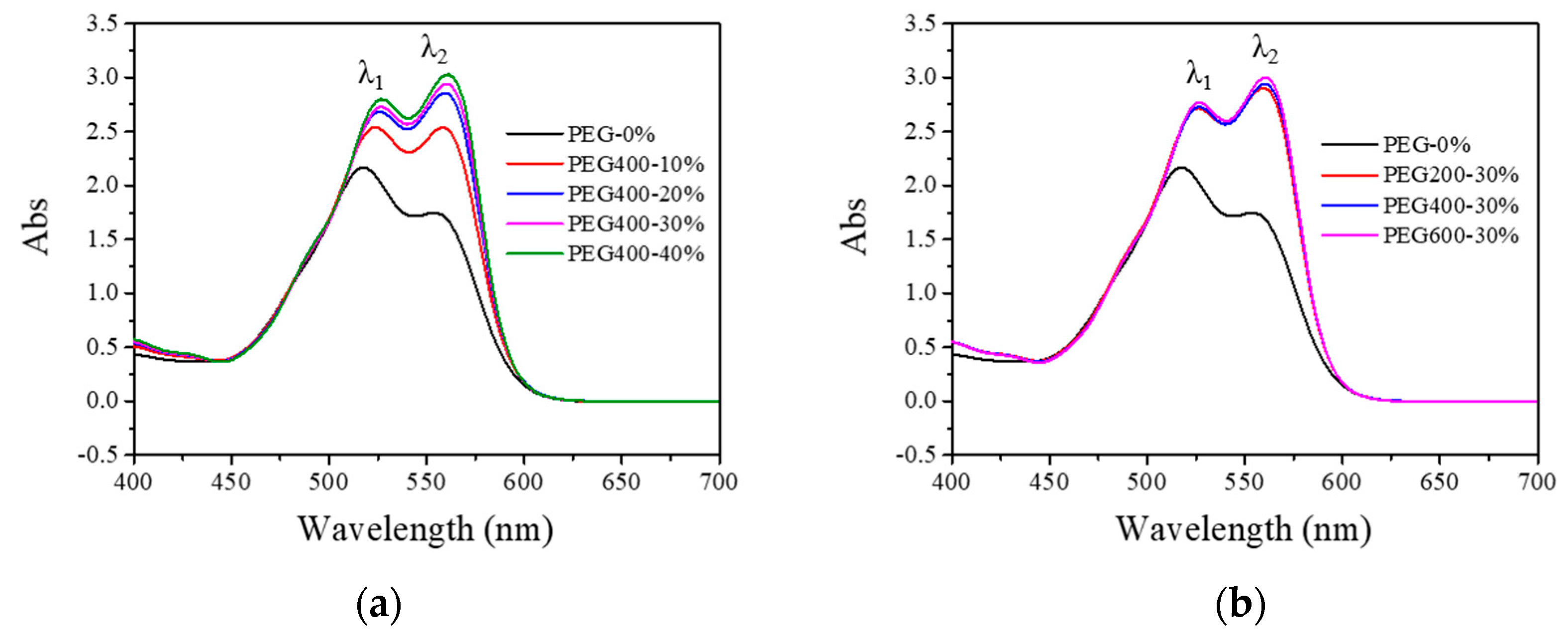
| Peak Positions | Wavelengths (nm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% PEG | 10% PEG400 | 20% PEG400 | 30% PEG400 | 40% PEG400 | 30% PEG200 | 30% PEG600 | |
| λ1 | 518 a | 524 | 526 | 527 | 527 | 526 | 527 |
| λ2 | 554 | 558 a | 560 a | 560 a | 561 a | 559 a | 561 a |
| PEG | 0% PEG | 10% PEG400 | 20% PEG400 | 30% PEG400 | 40% PEG400 | 30% PEG200 | 30% PEG600 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| γ a (mN/m) | 65.4 | 60.5 | 58.6 | 57.0 | 55.0 | 56.8 | 56.2 |
| ρ (kg/m3) | 1027 | 1044 | 1061 | 1080 | 1097 | 1078 | 1080 |
| η b (mPa·s) | 1.3 | 2.0 | 3.3 | 5.5 | 9.5 | 4.2 | 7.5 |
| Z | 28.2 | 17.8 | 10.7 | 6.4 | 3.7 | 8.3 | 4.6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Z.; Fang, K.; Song, Y.; Sun, F. Jetting Performance of Polyethylene Glycol and Reactive Dye Solutions. Polymers 2019, 11, 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040739
Tang Z, Fang K, Song Y, Sun F. Jetting Performance of Polyethylene Glycol and Reactive Dye Solutions. Polymers. 2019; 11(4):739. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040739
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Zhiyuan, Kuanjun Fang, Yawei Song, and Fuyun Sun. 2019. "Jetting Performance of Polyethylene Glycol and Reactive Dye Solutions" Polymers 11, no. 4: 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040739
APA StyleTang, Z., Fang, K., Song, Y., & Sun, F. (2019). Jetting Performance of Polyethylene Glycol and Reactive Dye Solutions. Polymers, 11(4), 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040739