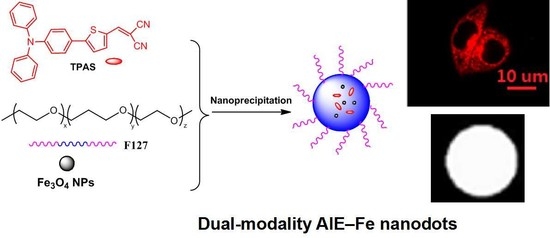
Fabrication and Application of Dual-Modality Polymer Nanoparticles Based on an Aggregation-Induced Emission-Active Fluorescent Molecule and Magnetic Fe3O4
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Instruments
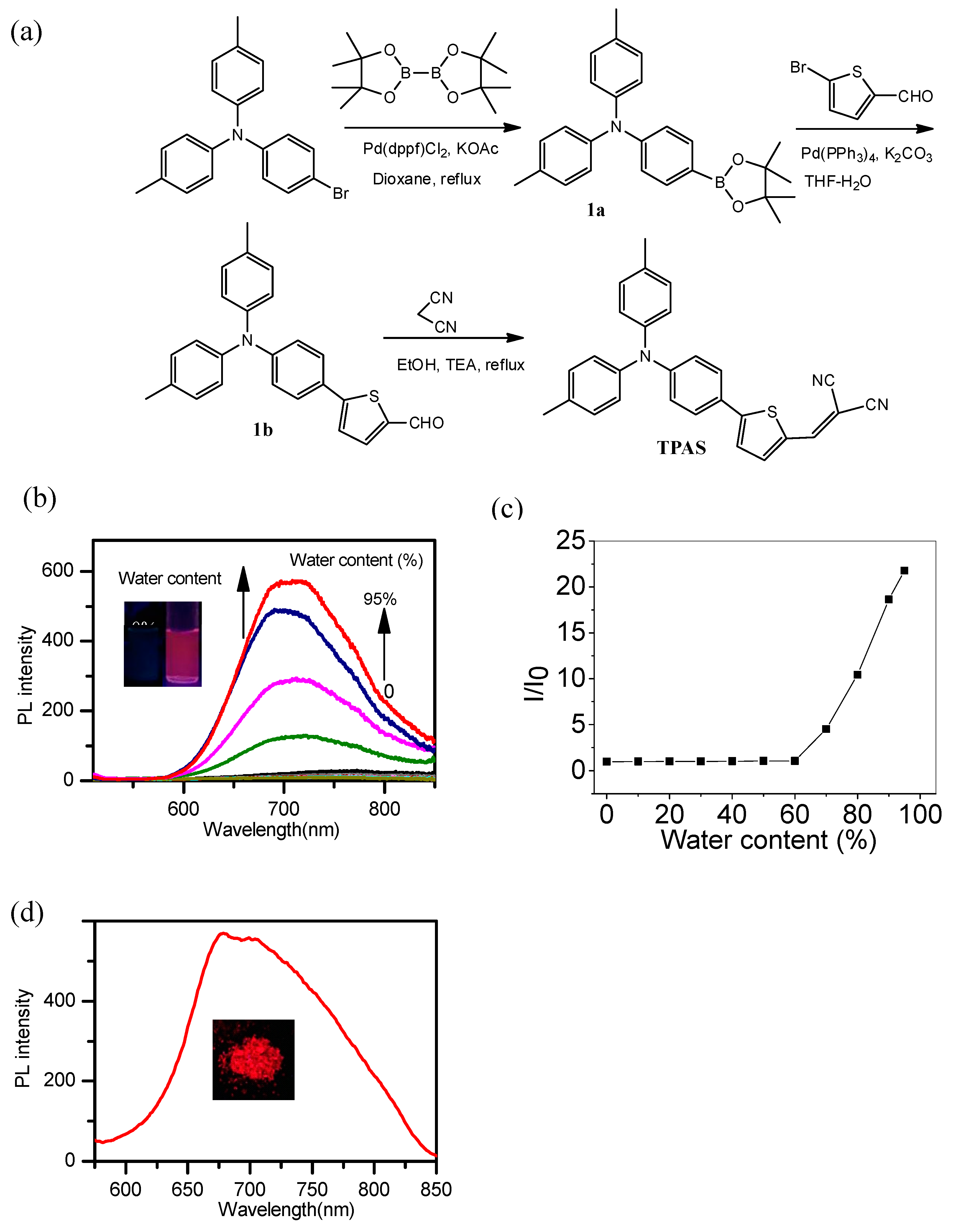
2.2. Synthesis of Target Dye (TPAS)
2.2.1. Synthesis of 1a
2.2.2. Synthesis of 1b
2.2.3. Synthesis of TPAS
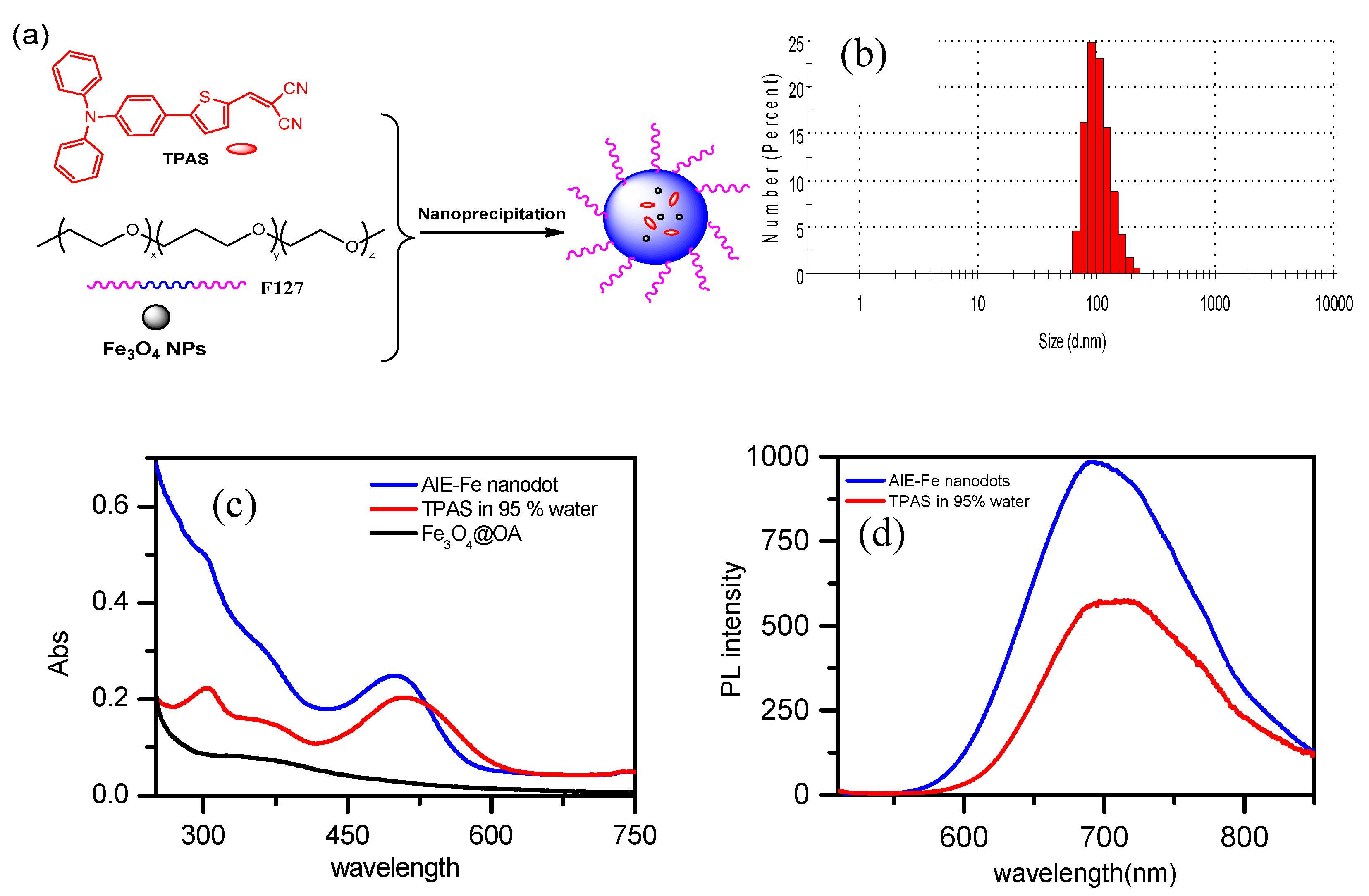
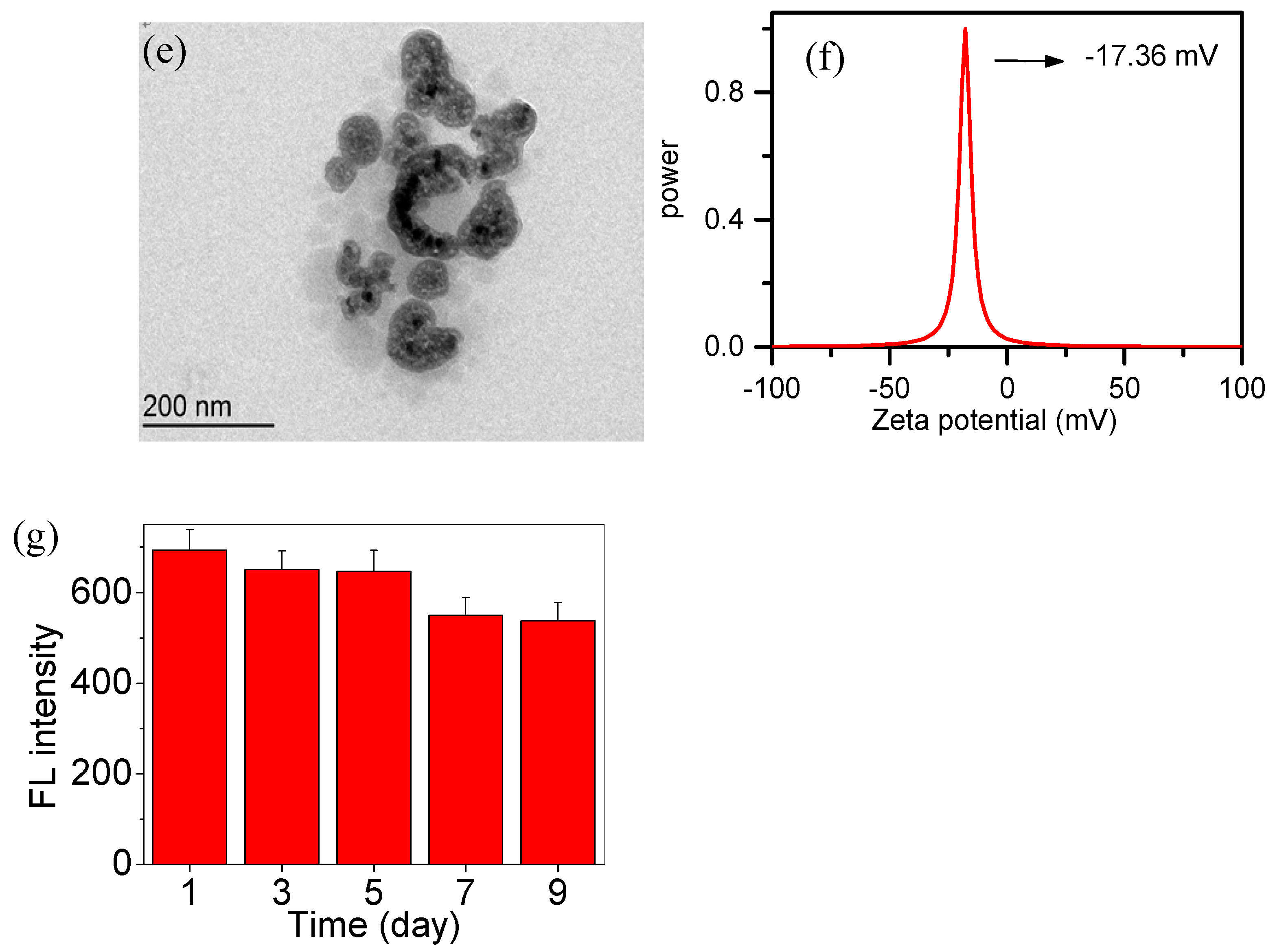
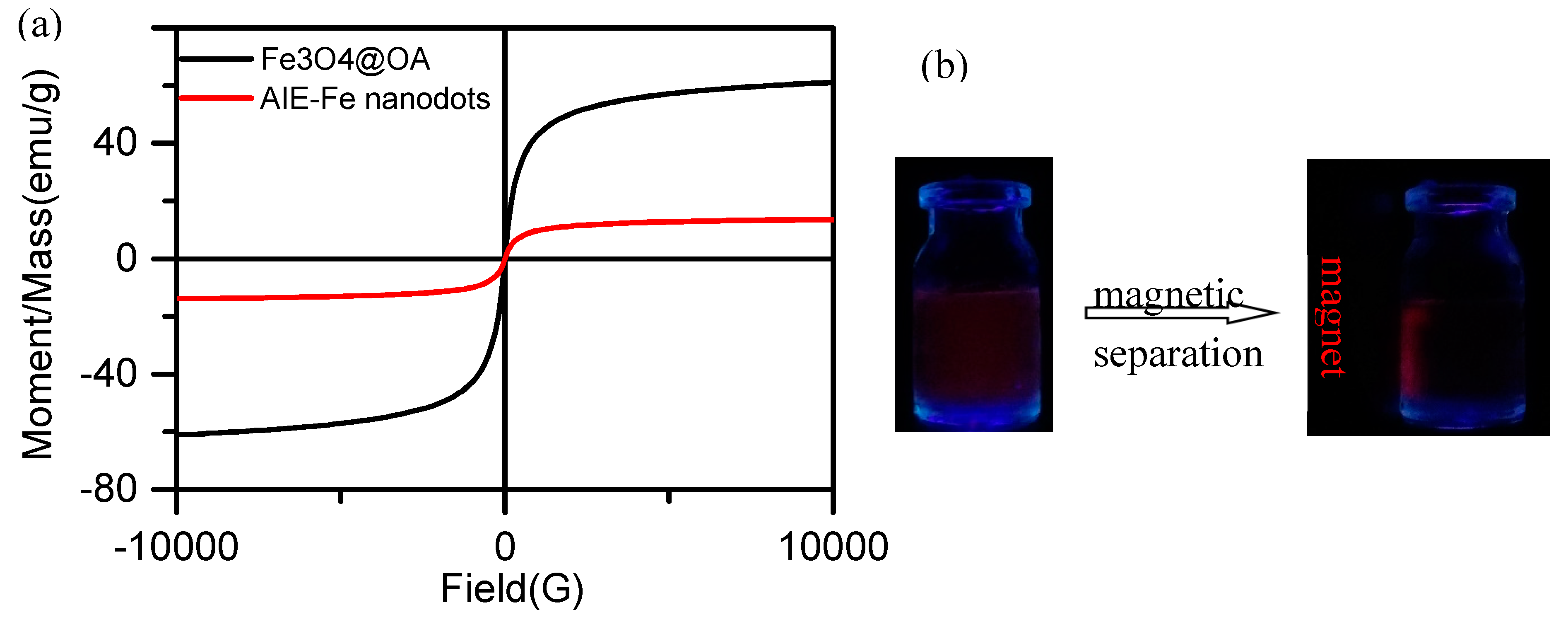
2.3. Fabrication of AIE–Fe Hybrid Nanodots
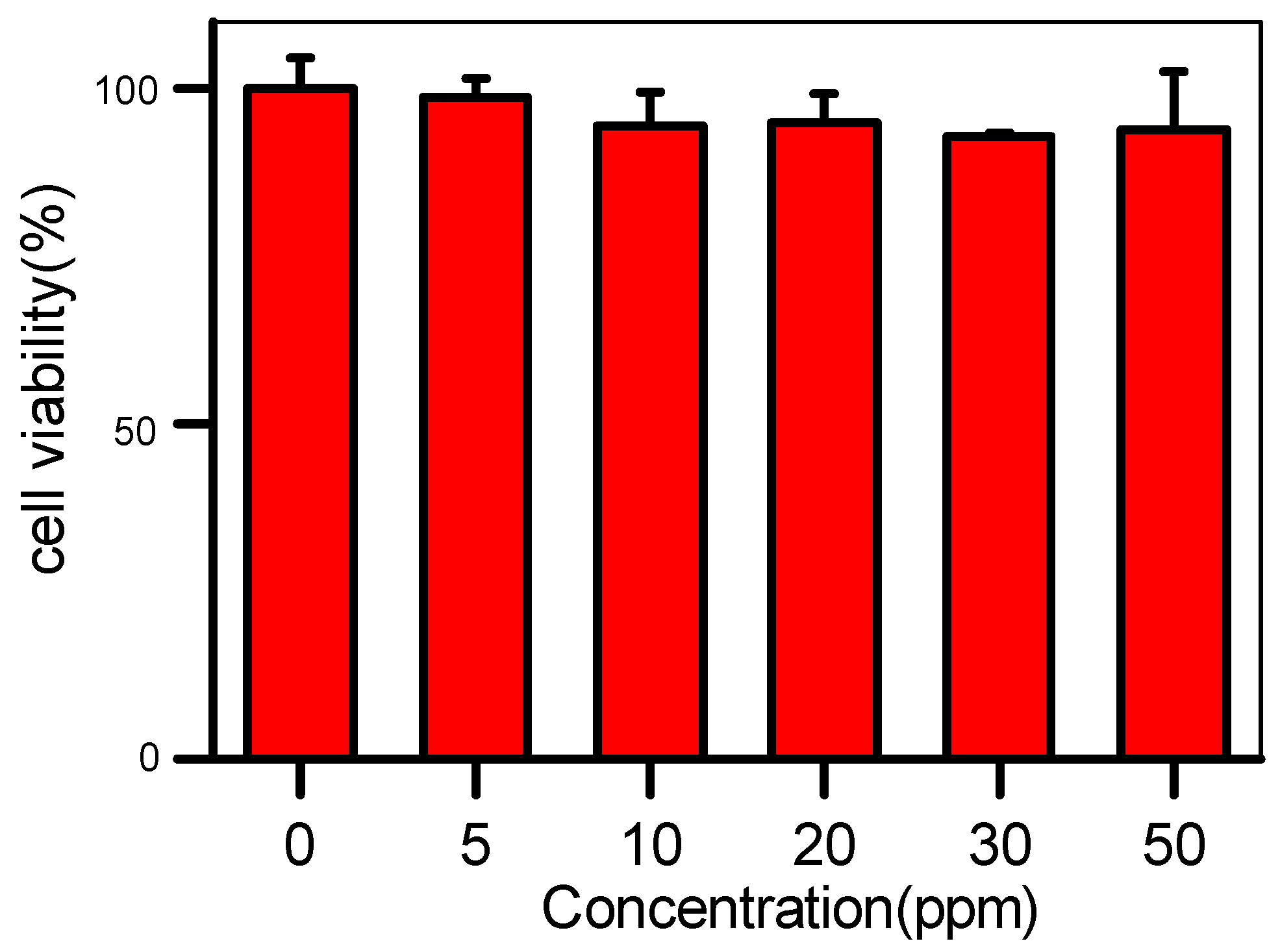
2.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
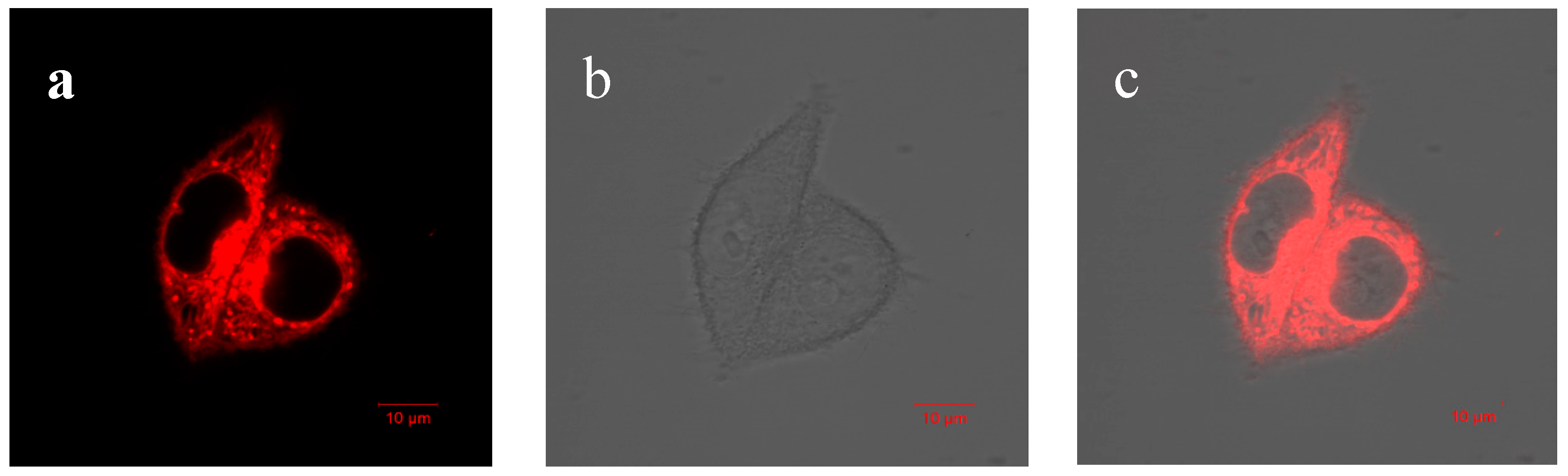
2.5. Fluorescence Imaging in HeLa Cells with AIE–Fe Nanodots
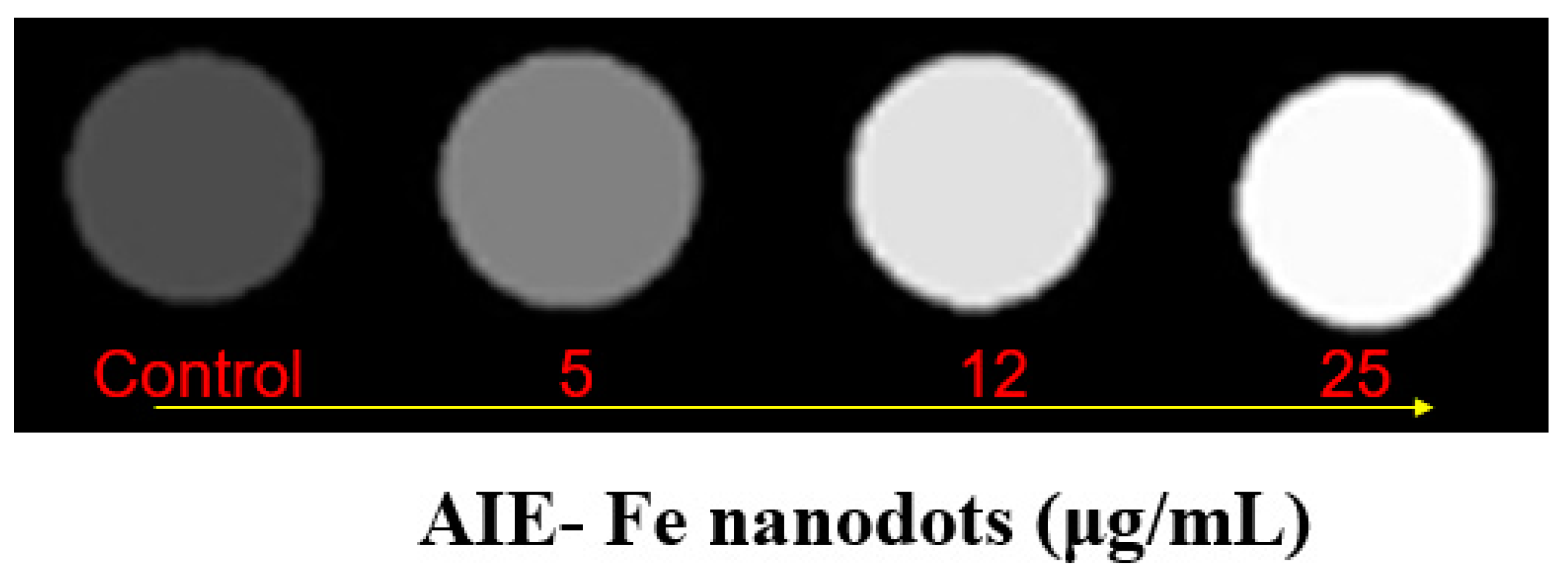
2.6. In Vitro MRI Studies
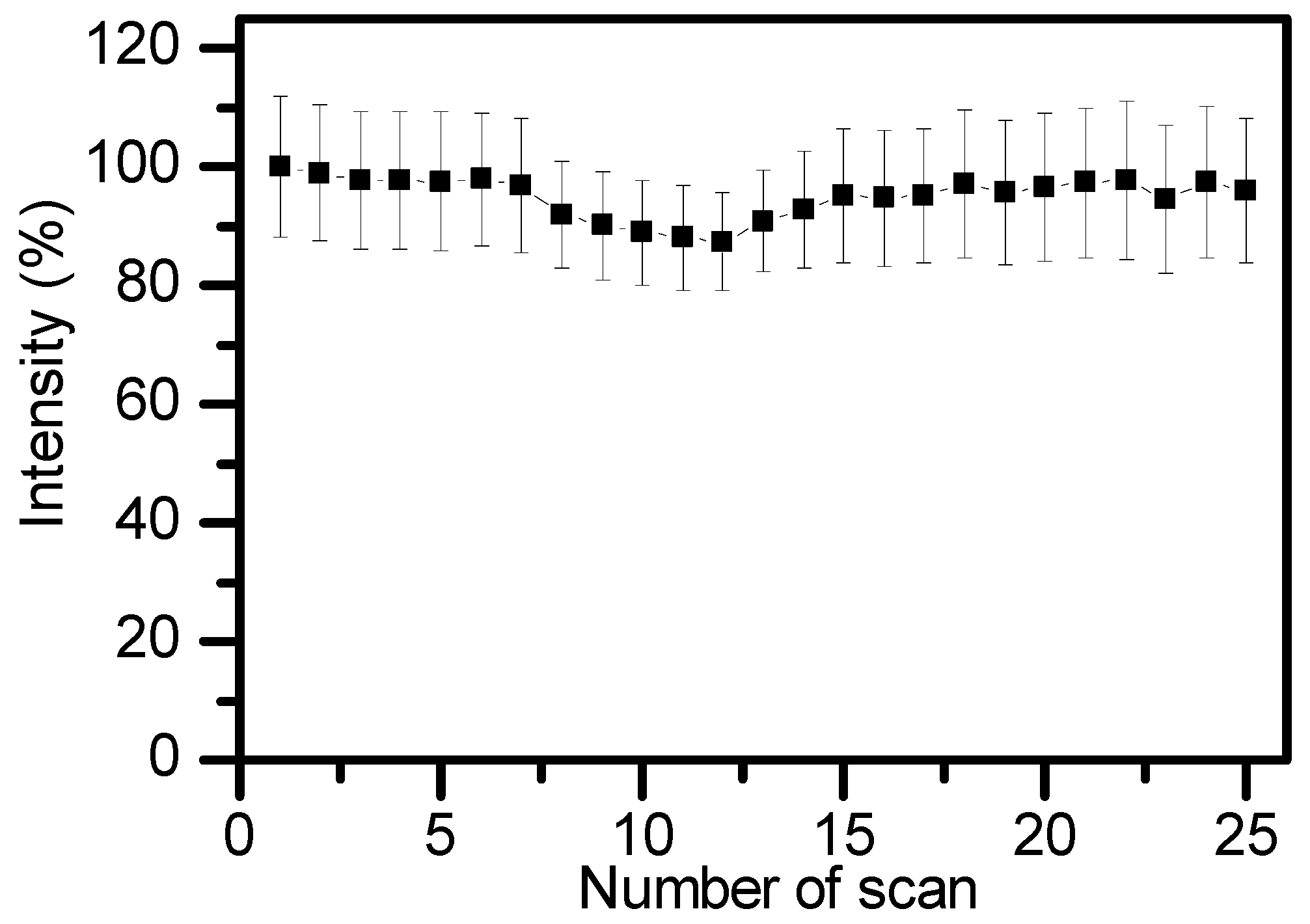
3. Results and Discussion
Fabrication of Fe3O4@TPAS Dots
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, G.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, L.; Chi, X. Tunable T1 and T2 contrast abilities of manganese-engineered iron oxide nanoparticles through size control. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10404–10412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhu, X.; Chen, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, F. Water-stable NaLuF4-based upconversion nanophosphors with long-term validity for multimodal lymphatic imaging. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6201–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhirde, A.; Xie, J.; Swierczewska, M.; Chen, X. Nanoparticles for cell labeling. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.S.; Park, J.C.; Nah, H.; Woo, S.; Oh, J.; Kim, K.M.; Cheon, G.J.; Chang, Y.; Yoo, J.; Cheon, J. A hybrid nanoparticle probe for dual-modality positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6259–6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Ding, D.; Huo, D.; Pu, K.Y.; Thao, N.N.P.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, B. Conjugated polymer based nanoparticles as dual-modal probes for targeted in vivo fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, K.; Hsu, A.R.; Xu, C.; Xie, J.; Sun, S.; Chen, X. PET/MRI dual-modality tumor imaging using arginine-glycine-aspartic (RGD)-conjugated radiolabeled iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, R.; Yang, P.; He, F.; Gai, S.; Li, C.; Dai, Y. A yolk-like multifunctional platform for multimodal imaging and synergistic therapy triggered by a single near-infrared light. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 1630–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Dai, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, C. Ultra-small BaGdF5-based upconversion nanoparticles as drug carriers and multimodal imaging probes. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Z.; Huang, S. Multifunctional NaYF4:Yb, Er@mSiO2@Fe3O4-PEG nanoparticles for UCL/MR bioimaging and magnetically targeted drug delivery. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 1839–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.E.; Koo, H.; Sun, I.C.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C. Multifunctional nanoparticles for multimodal imaging and theragnosis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2656–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.C.; Hou, Y.; Zeng, J.F.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, P.S.; Jing, L.H.; Shangguan, D.H.; Gao, M.Y. Dual-ratiometric target-triggered fluorescent probe for simultaneous quantitative visualization of tumor microenvironment protease activity and pH in vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erogbogbo, F.; Yong, K.T.; Hu, R.; Law, W.C.; Ding, H.; Chang, C.W. Biocompatible magneto fluorescent probes: Luminescent silicon quantum dots coupled with superparamagnetic iron (III) oxide. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5131–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, M.; Shi, M.; Feng, W.; Li, F. Core-shell Fe3O4@NaLuF4:Yb, Er/Tm nanostructure for MRI, CT and upconversion luminescence tri-modality imaging. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 4618–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Leung, N.L.C.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: Together we shine, united we soar! Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11718–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Qin, A.; Tang, Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: The whole is more brilliant than the parts. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5429–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Mao, D.; Li, K.; Wang, X.; Qin, W.; Liu, R.; Chiam, D.S.; Tomcazk, N.; Yang, Z.; Tang, B.Z.; et al. Precise and long-term tracking of adipose-derived stem cells and their regenerative capacity via superb bright and stable organic nanodots. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12620–12631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Goh, C.C.; Feng, G.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, R.; Tomczak, N.; Geng, J.; Tang, B.Z.; Ng, L.G.; et al. Ultrabright organic dots with aggregation-induced emission characteristics for real-time two-photon intravital vasculature imaging. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6083–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Qin, W.; Ding, D.; Tomczak, N.; Geng, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, B.; et al. Photostable fluorescent organic dots with aggregation-induced emission (AIE dots) for noninvasive long-term cell tracing. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Z.Y.; Sun, X.Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Shangguan, D.H.; Yang, W.; Gao, M.Y. Protease-activated ratiometric fluorescent probe for pH mapping of malignant tumors. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3199–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Su, H.F.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Shan, G.G.; Leung, A.C.S.; Lee, M.M.S.; Sung, H.H.Y.; Williams, I.D.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Facile synthesis of red/NIR AIE luminogens with simple structures, bright emissions, and high photostabilities, and their applications for specific Imaging of lipid droplets and image-guided photodynamic therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1704039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Gao, K.; Shao, Z. Cellulose nanofiber/single-walled carbon nanotube hybrid non-woven macrofiber mats as novel wearable supercapacitors with excellent stability, tailor ability and reliability. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 4083–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, S.; Tanushi, A.; Kusamoto, T.; Kochi, S.; Sato, T.; Nishihara, H.A. luminescent organic radical with two pyridyl groups: High photostability and dual stimuli-responsive properties, with theoretical analyses of photophysical processes. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 1996–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altinoğlu, E.I. Near-infrared emitting fluorophore-doped calcium phosphate nanoparticles for in vivo imaging of human breast cancer. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
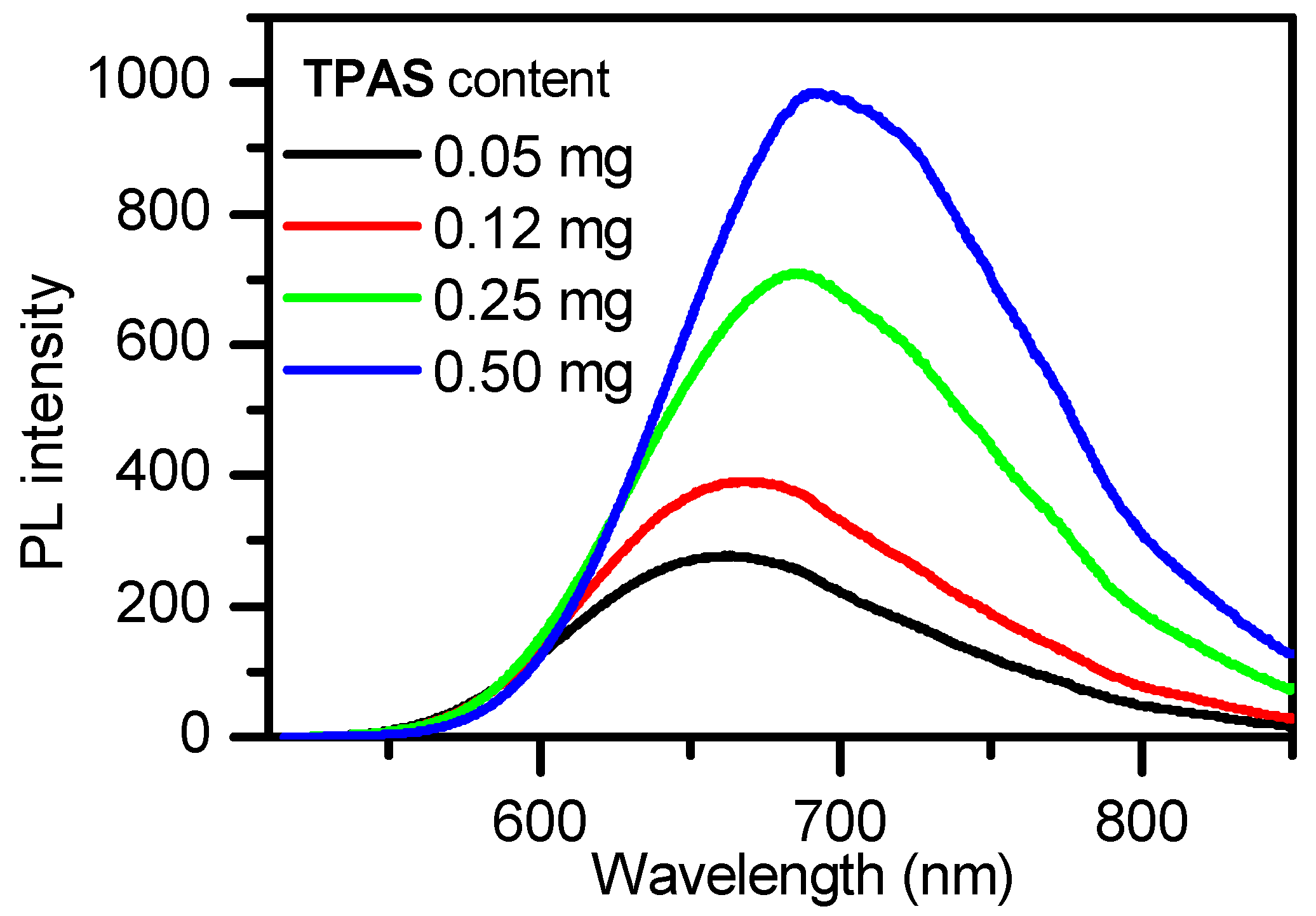
| No. | Fe3O4 (mg) | Φ (%) | DLS Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.50 | 10.5 | 106.7 |
| 2 | 0.25 | 10.9 | 93.5 |
| 3 | 0.12 | 12.9 | 99.7 |
| 4 | 0.05 | 13.8 | 102.8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Huang, M.; Tang, H.; Cao, D.; Zhao, Y. Fabrication and Application of Dual-Modality Polymer Nanoparticles Based on an Aggregation-Induced Emission-Active Fluorescent Molecule and Magnetic Fe3O4. Polymers 2019, 11, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020220
Wang L, Huang M, Tang H, Cao D, Zhao Y. Fabrication and Application of Dual-Modality Polymer Nanoparticles Based on an Aggregation-Induced Emission-Active Fluorescent Molecule and Magnetic Fe3O4. Polymers. 2019; 11(2):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020220
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lingyun, Meiying Huang, Hao Tang, Derong Cao, and Yu Zhao. 2019. "Fabrication and Application of Dual-Modality Polymer Nanoparticles Based on an Aggregation-Induced Emission-Active Fluorescent Molecule and Magnetic Fe3O4" Polymers 11, no. 2: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020220
APA StyleWang, L., Huang, M., Tang, H., Cao, D., & Zhao, Y. (2019). Fabrication and Application of Dual-Modality Polymer Nanoparticles Based on an Aggregation-Induced Emission-Active Fluorescent Molecule and Magnetic Fe3O4. Polymers, 11(2), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020220