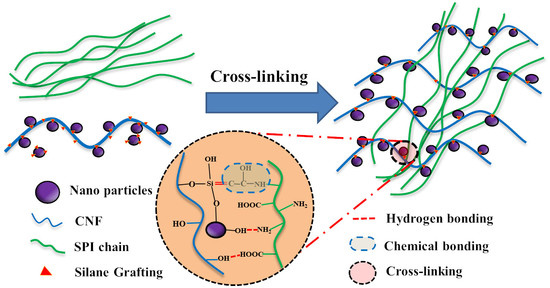
Preparation and Characterization of Soy Protein Isolate-Based Nanocomposite Films with Cellulose Nanofibers and Nano-Silica via Silane Grafting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
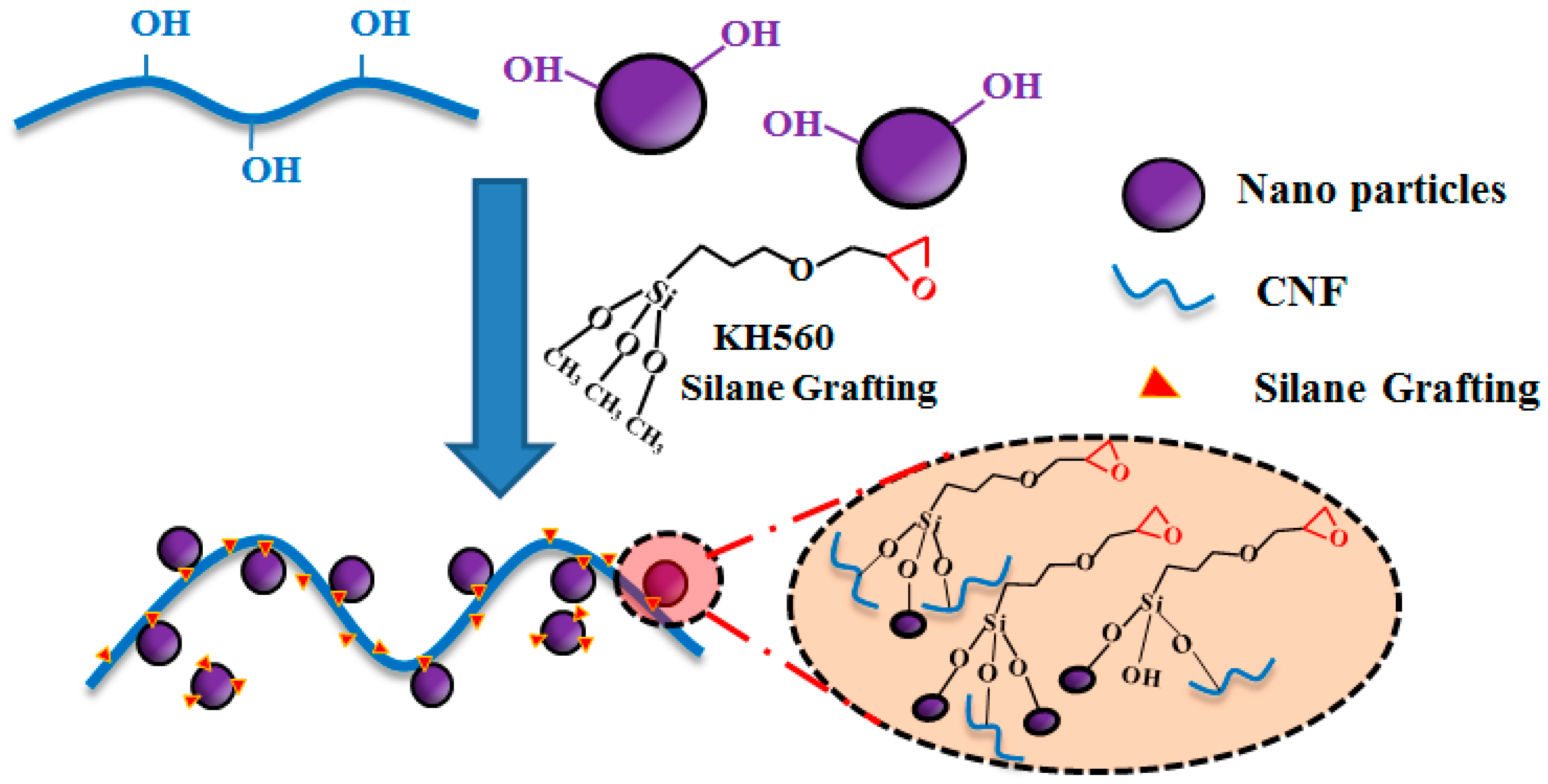
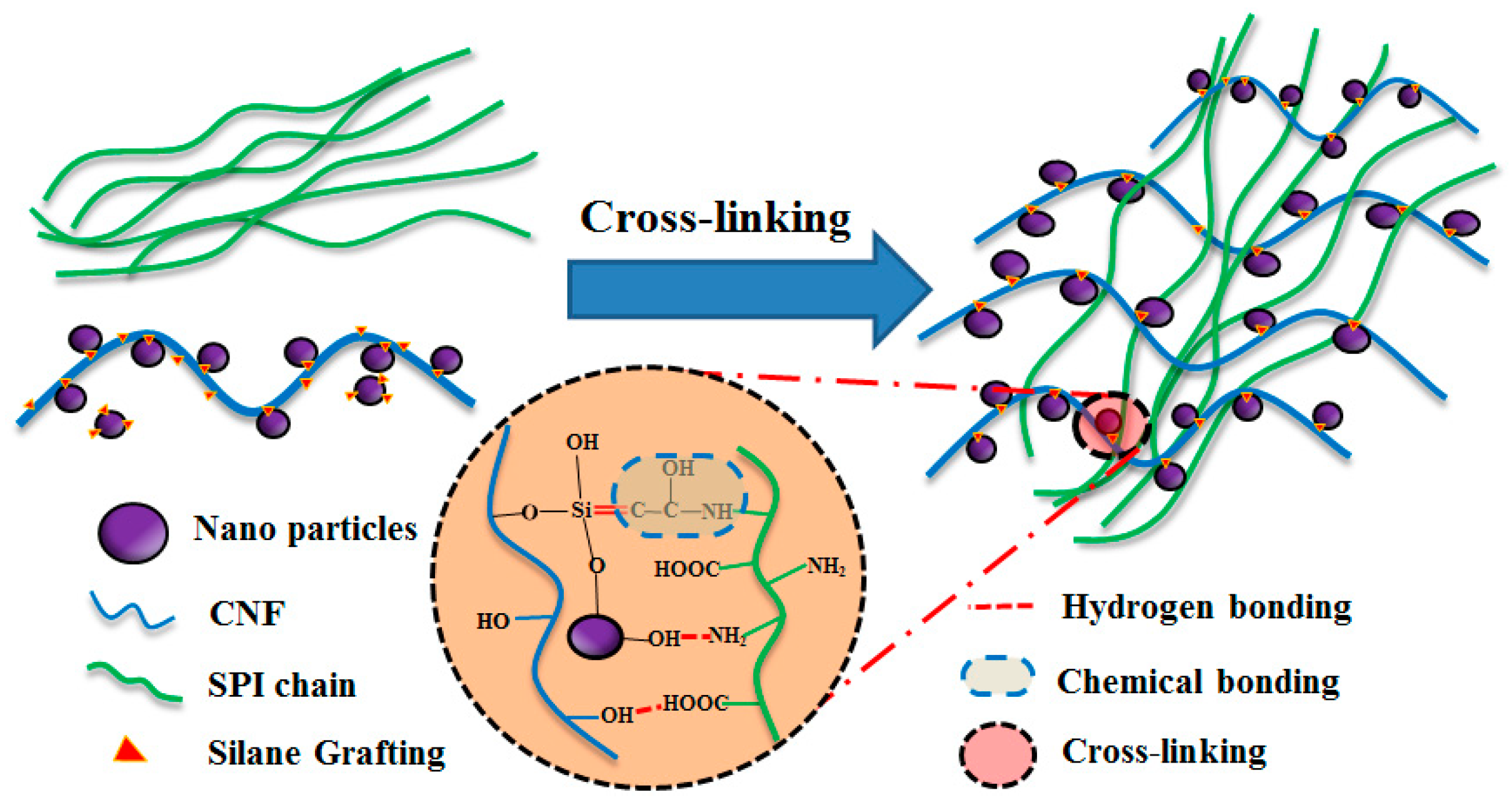
2.2. Surface Modification of the O@CNF/NS by Silane Grafting
2.3. Preparation of SPI/O@CNF/NS Films
2.4. Characterization of SPI/O@CNF/NS Composite Films
2.4.1. Mechanical Properties
2.4.2. Total Soluble Matter
2.4.3. Water Uptake
2.4.4. Water Vapor Permeability (WVP)
2.4.5. Surface Contact Angle
2.4.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis (FTIR)
2.4.7. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.4.8. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.4.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
3. Results
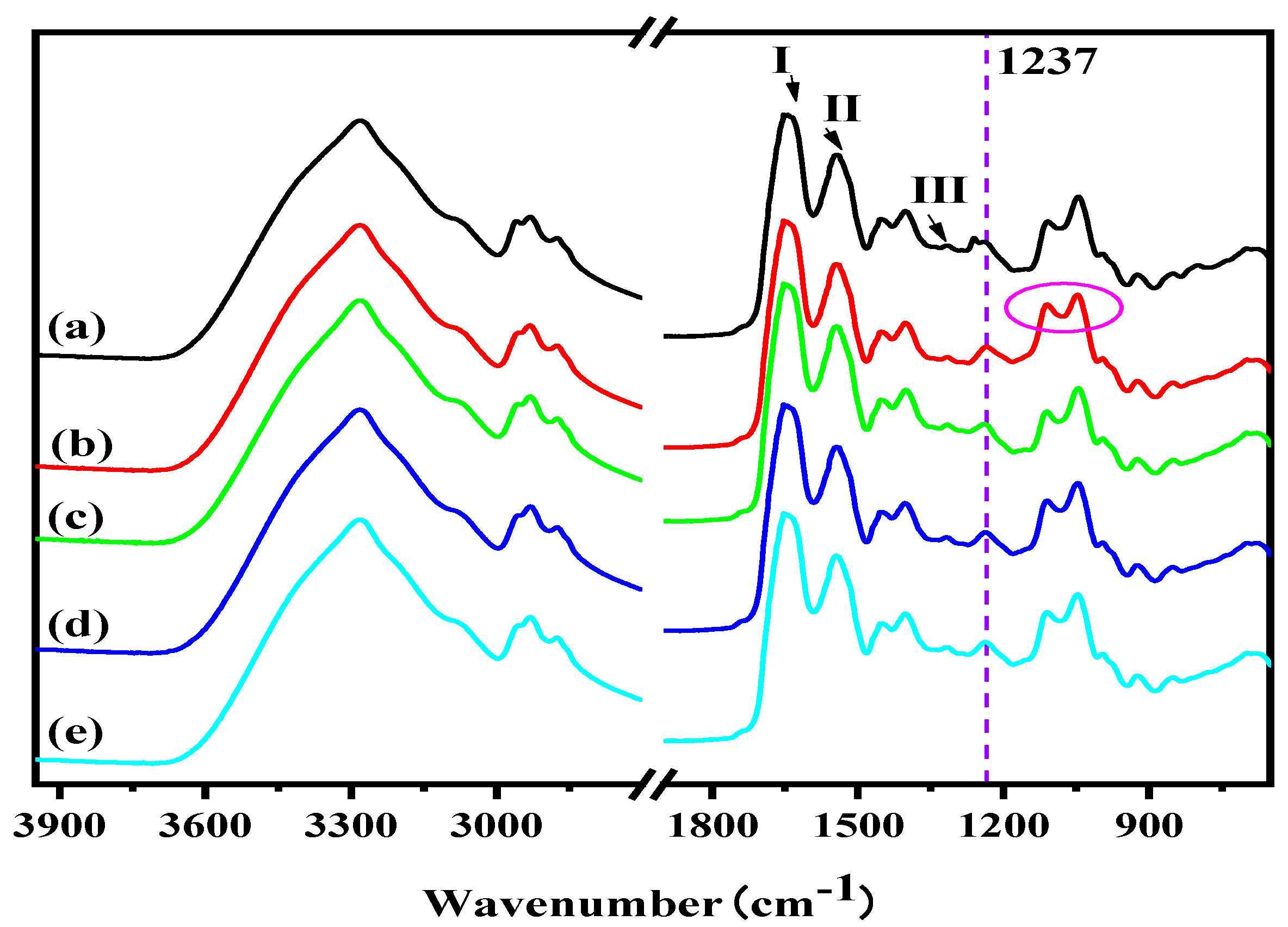
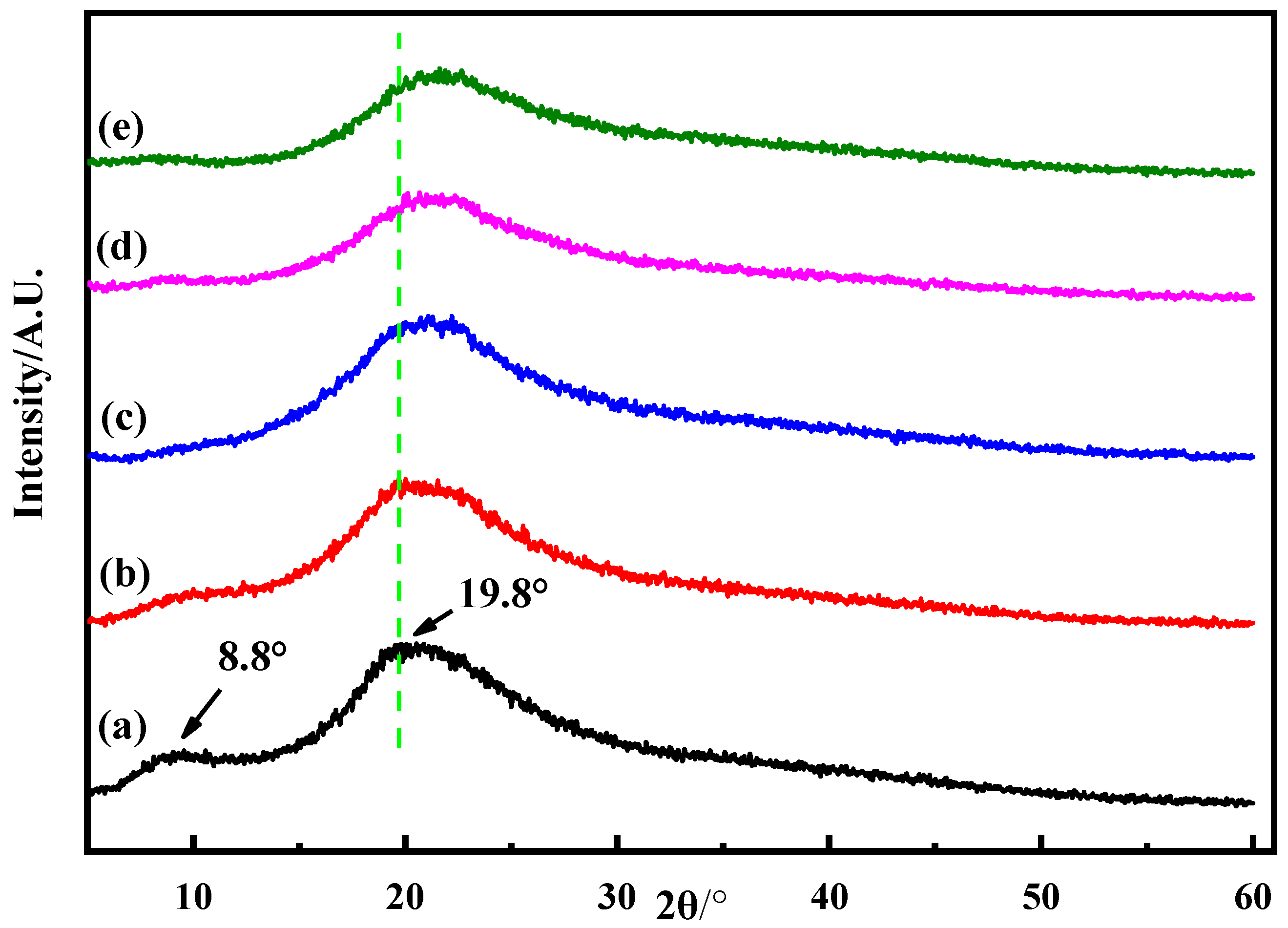
3.1. Structural Analysis
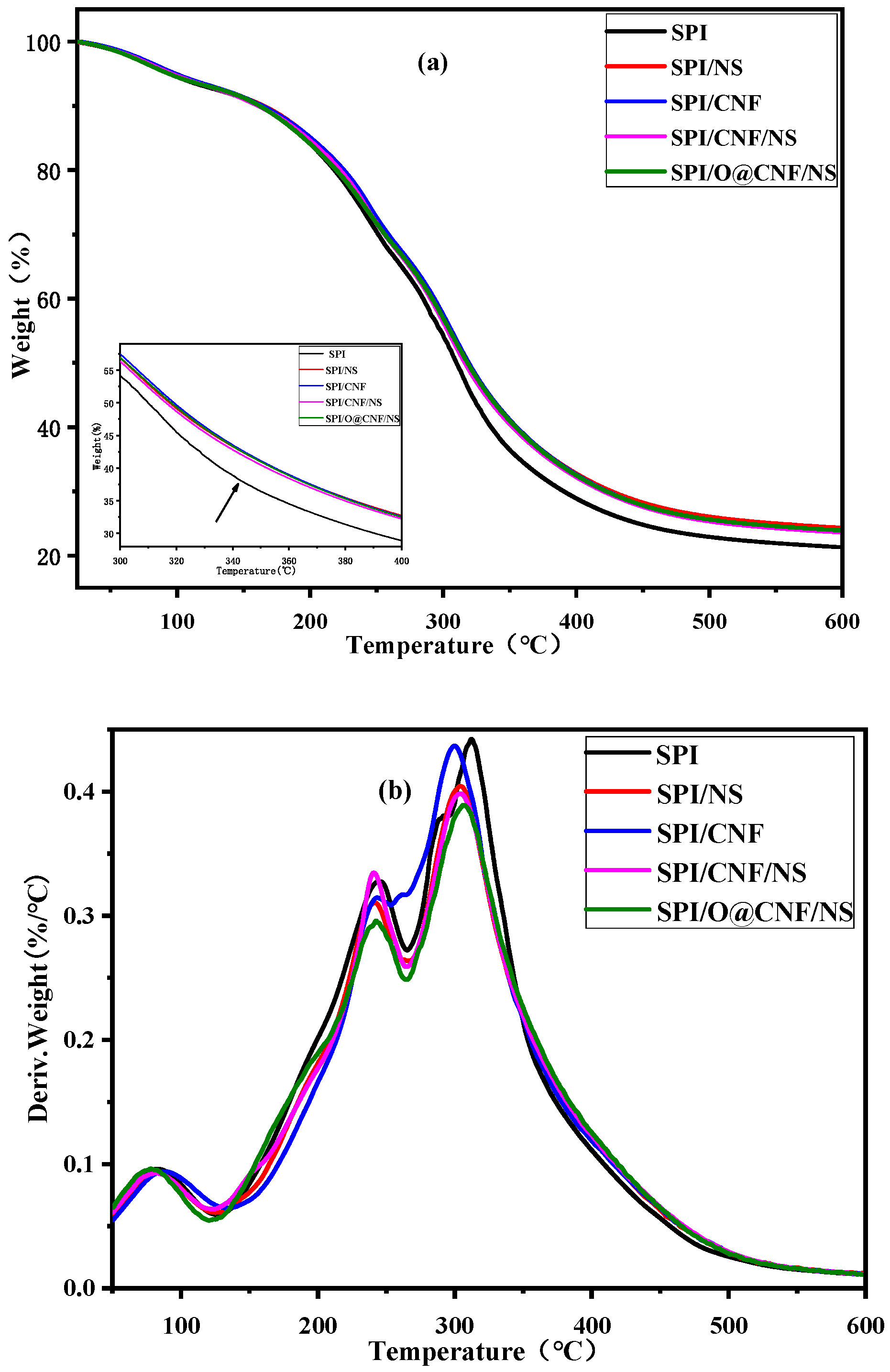
3.2. Thermal Stabilities Analysis
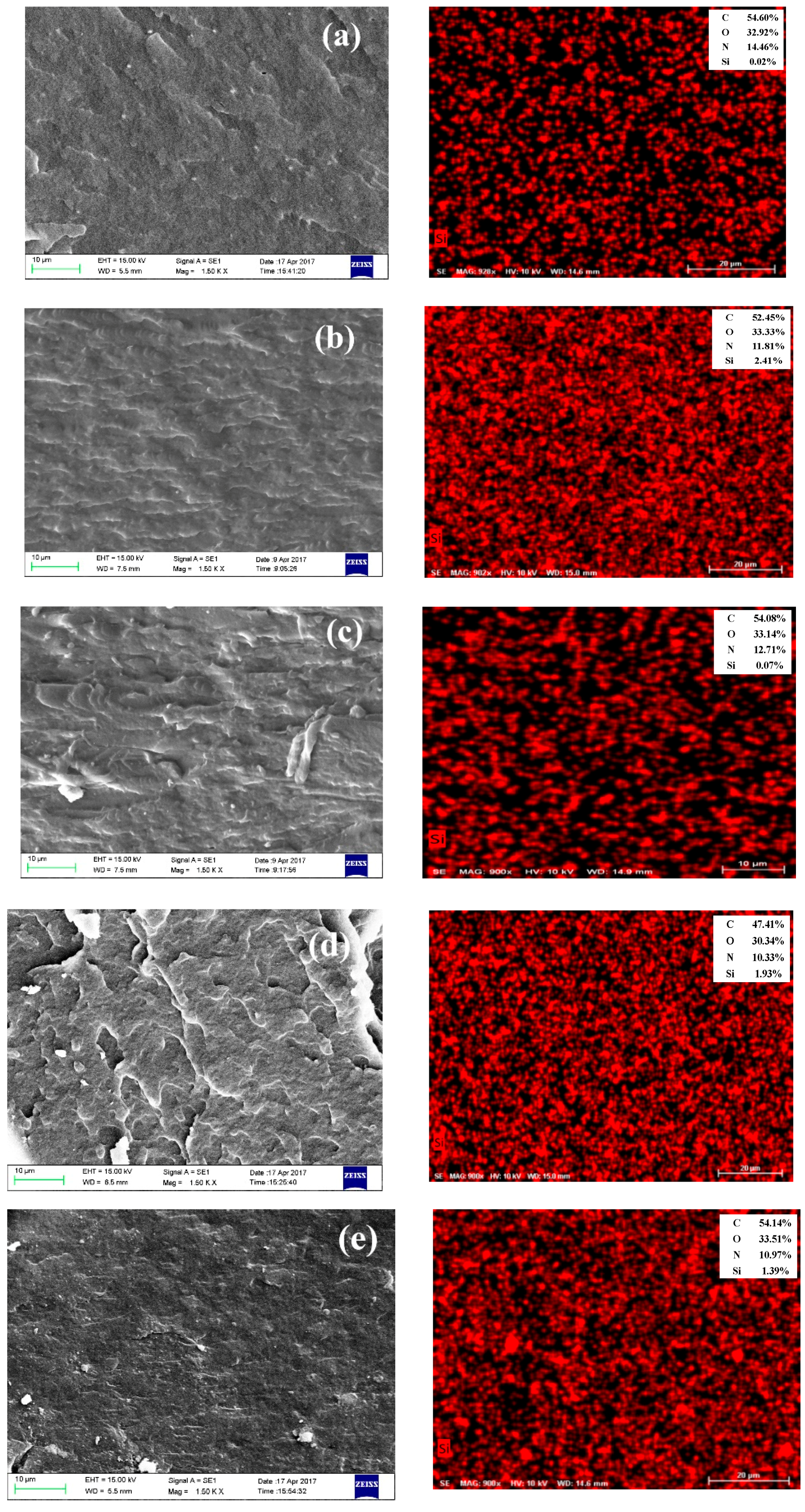
3.3. Morphology
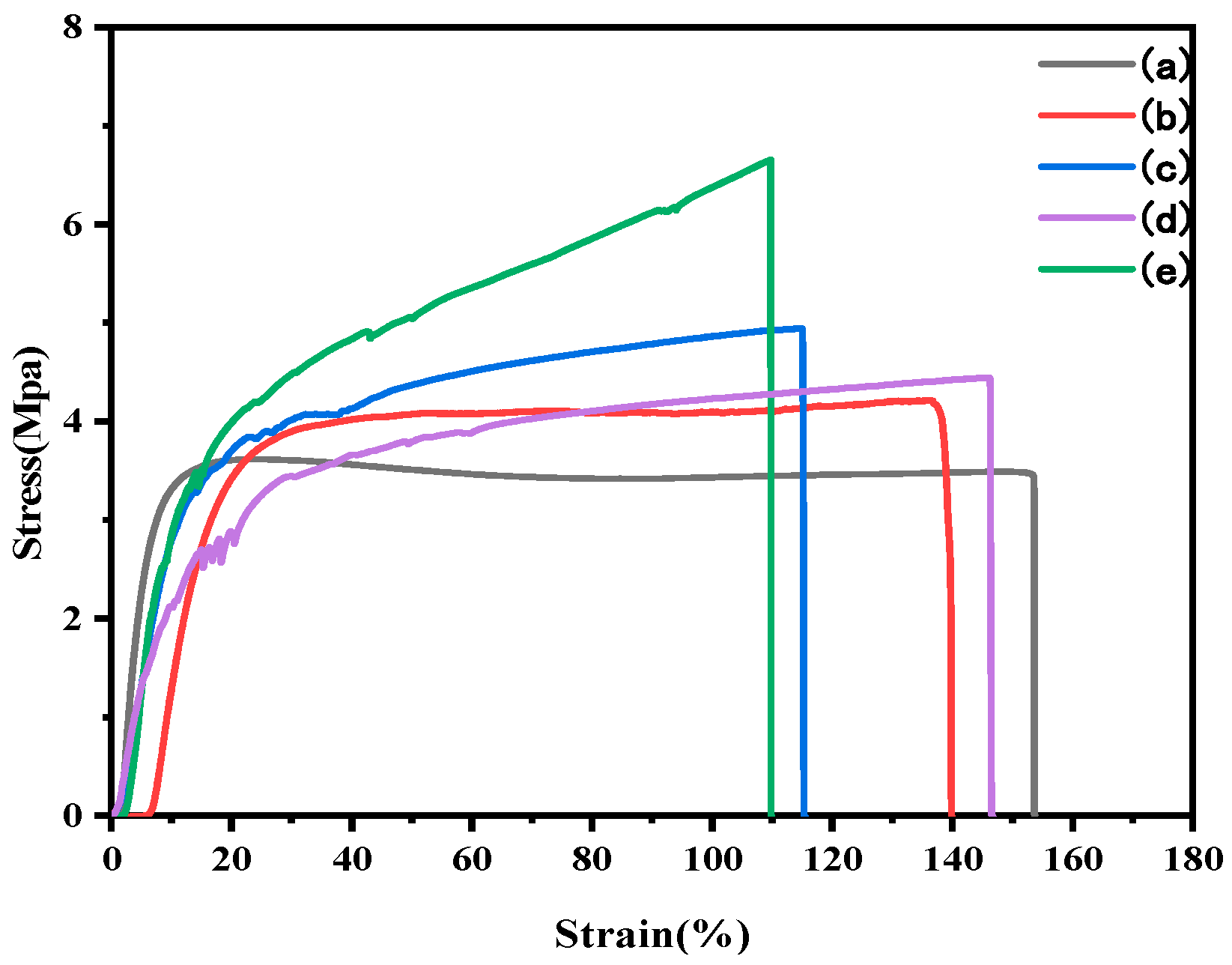
3.4. Mechanical Properties
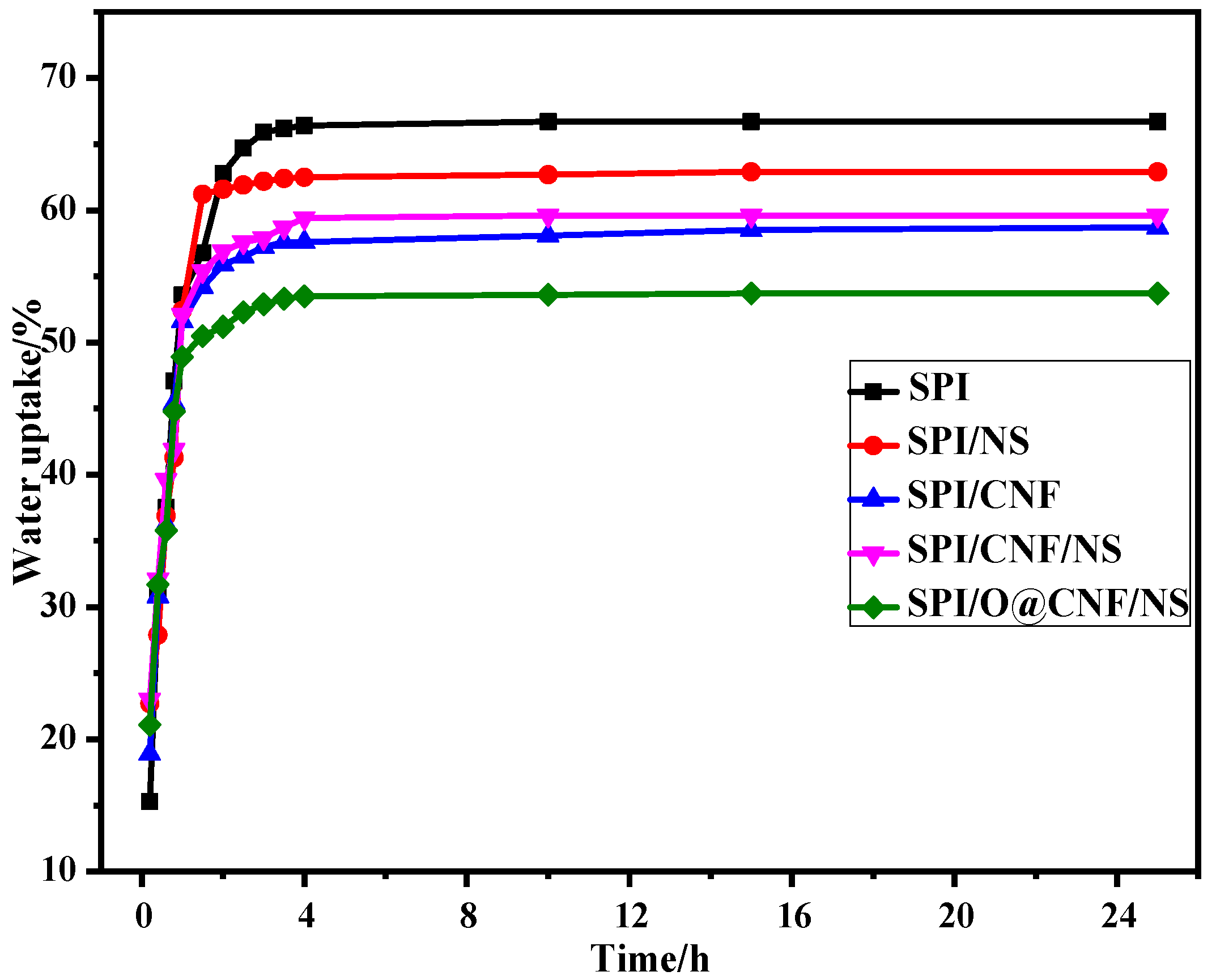
3.5. Water Resistance Properties of SPI-based Films
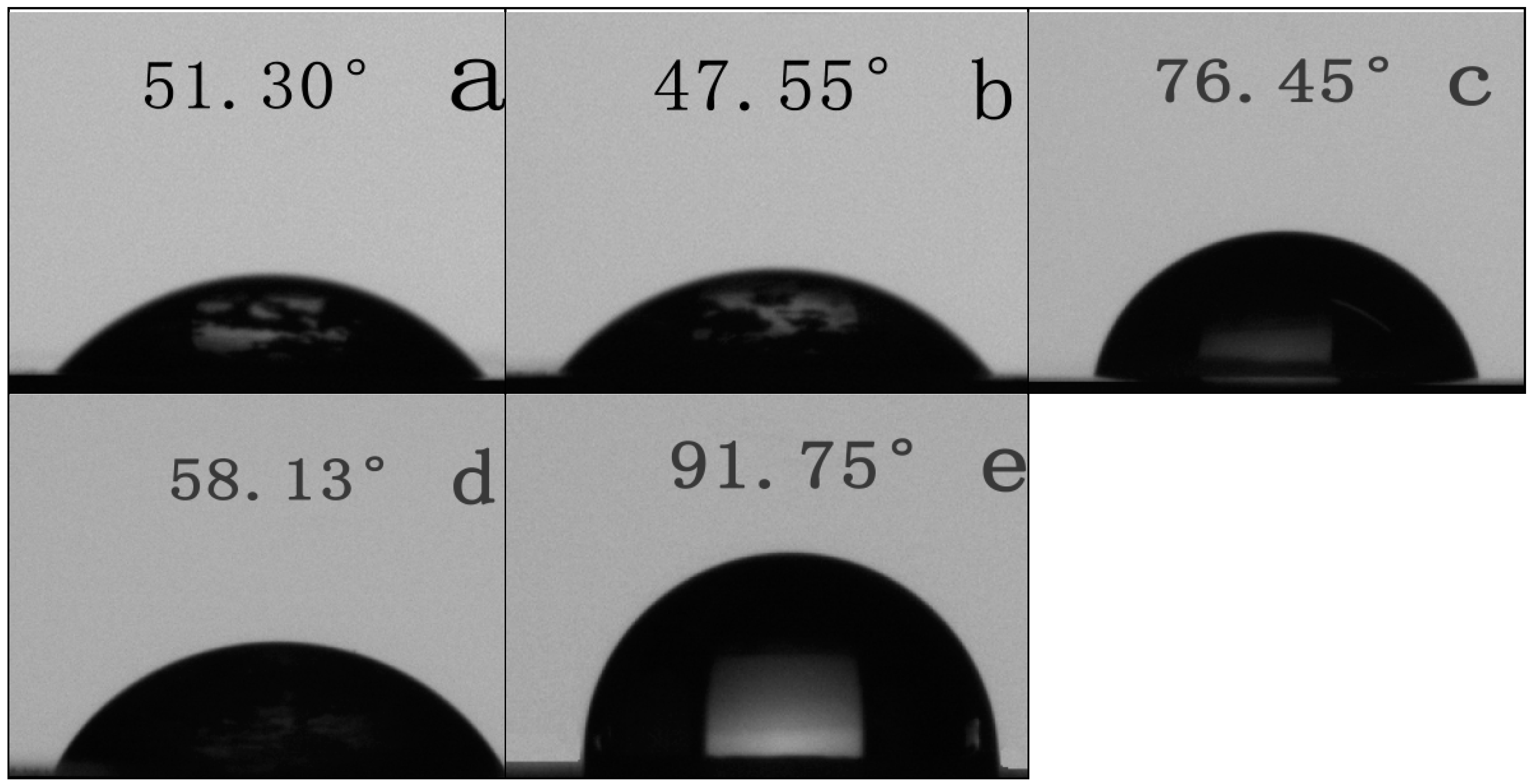
3.6. Surface Hydrophilic Property of SPI-based Films
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siracusa, V.; Rocculi, P.; Romani, S.; Dalla Rosa, M. Biodegradable polymers for food packaging: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.F.; Cui, S.W.; Wang, Q.; Mine, Y.; Poysa, V. Heat induced gelling properties of soy protein isolates prepared from different defatted soybean flours. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibhai, Z.; Mondor, M.; Moresoli, C.; Ippersiel, D.; Lamarche, F. Production of soy protein concentrates/isolates: Traditional and membrane technologies. Desalination 2006, 191, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojijo, V.; Ray, S.S. Processing strategies in bionanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1543–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.J.; Brewer, M.S. In situ examination of starch granule-soy protein and wheat protein interactions. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Bijalwan, V.; Basu, S.; Kesarwani, A.K.; Mazumder, K. Effect of beta-glucan-fatty acid esters on microstructure and physical properties of wheat straw arabinoxylan films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 161, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Du, G.; Wu, Z.; Xi, X.; Dong, Z. Cross-linked soy-based wood adhesives for plywood. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2014, 50, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminska, I.; Das, M.R.; Coffinier, Y.; Niedziolka-Jonsson, J.; Sobczak, J.; Woisel, P.; Lyskawa, J.; Opallo, M.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. Reduction and Functionalization of Graphene Oxide Sheets Using Biomimetic Dopamine Derivatives in One Step. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2012, 4, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.C.; Li, K.; Li, J.Z. A general bio-inspired, novel interface engineering strategy toward strong yet tough protein based composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 447, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kang, H.J.; Zhao, S.J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.F.; Li, J.Z. Polyphenol-induced cellulose nanofibrils anchored graphene oxide as nanohybrids for strong yet tough soy protein nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.F.; Yuan, X.Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Lu, X.Z.; Zhang, L.D.; Wang, S.B. Physicochemical properties of soy protein isolate/carboxymethyl cellulose blend films crosslinked by Maillard reactions: Color, transparency and heat-sealing ability. Mat. Sci. Eng. C Mater. 2012, 32, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Yu, X.Y.; Pilla, S. Mechanical and moisture sensitivity of fully bio-based dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose cross-linked soy protein isolate films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, A.; Igarzabal, C.I.A. Nanocrystal-reinforced soy protein films and their application as active packaging. Food Hydrocolloids 2015, 43, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverria, I.; Eisenberg, P.; Mauri, A.N. Nanocomposites films based on soy proteins and montmorillonite processed by casting. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 449, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kang, H.J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.F.; Li, J.Z. Improvement of interfacial interactions using natural polyphenol-inspired tannic acid-coated nanoclay enhancement of soy protein isolate biofilms. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 401, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sandeep, K.P.; Alavi, S.; Truong, V.D.; Gorga, R.E. Preparation and characterization of bio-nanocomposite films based on soy protein isolate and montmorillonite using melt extrusion. J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshy, R.R.; Mary, S.K.; Thomas, S.; Pothan, L.A. Environment friendly green composites based on soy protein isolate—A review. Food Hydrocolloids 2015, 50, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, J.W.; Chen, Y.; Xia, W.S.; Xiong, Y.L.L.; Wang, H.X. Enhanced physicochemical properties of chitosan/whey protein isolate composite film by sodium laurate-modified TiO2 nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 138, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.F.; Zhang, H.L.; Mi, H.Y.; Cai, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.Q.; Gong, S.Q. High-performance flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators consisting of porous cellulose nanofibril (CNF)/poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) aerogel films. Nano Energy 2016, 26, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, Y.; Nakaya, M.; Matsui, E.; Hotta, A. Structural and mechanical properties of cellulose composites made of isolated cellulose nanofibers and poly(vinyl alcohol). Compos. Part A 2015, 73, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhao, G.M.; Pan, M.Z.; Zhuang, L.L.; Li, D.G.; Zhang, R. Crystallization and mechanical properties of reinforced PHBV composites using melt compounding: Effect of CNCs and CNFs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 168, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, C.; Moreau, C.; Bertoncini, P.; Bizot, H.; Chauvet, O.; Cathala, B. Cellulose Nanocrystal-Assisted Dispersion of Luminescent Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Layer-by-Layer Assembled Hybrid Thin Films. Langmuir 2012, 28, 12463–12471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.S.; Jiang, F.; Hsieh, Y.L.; Nitin, N. Cellulose nanofibrils improve dispersibility and stability of silver nanoparticles and induce production of bacterial extracellular polysaccharides. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 6226–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, H.; Napadensky, E.; Orlicki, J.A.; Snyder, J.F.; Chantawansri, T.L.; Kapllani, A. Cellulose Nanofibrils and Diblock Copolymer Complex: Micelle Formation and Enhanced Dispersibility. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.J.; Dong, Y.M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.F.; Li, L.; Li, J.Z. Preparation of cross-linked soy protein isolate-based environmentally-friendly films enhanced by PTGE and PAM. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 67, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoni, C.G.; Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; Olsen, C.W.; Bilbao-Sainz, C.; McHugh, T.H. Mechanical and water barrier properties of isolated soy protein composite edible films as affected by carvacrol and cinnamaldehyde micro and nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocolloids 2016, 57, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.F.; Xia, C.L.; Dong, Y.M.; Yan, Y.T.; Li, J.Z.; Shi, S.Q.; Cai, L.P. Soy protein isolate-based films reinforced by surface modified cellulose nanocrystal. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 80, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokoszka, S.; Debeaufort, F.; Hambleton, A.; Lenart, A.; Voilley, A. Protein and glycerol contents affect physico-chemical properties of soy protein isolate-based edible films. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2010, 11, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.J.; Wang, Q.C.; Zhang, S.F. Reinforced soy protein isolate-based bionanocomposites with halloysite nanotubes via mussel-inspired dopamine and polylysine codeposition. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Song, X.S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.F.; Li, J.Z. High-Performance and Fully Renewable Soy Protein Isolate-Based Film from Microcrystalline Cellulose via Bio-Inspired Poly(dopamine) Surface Modification. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4354–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jin, S.; Chen, H.; He, J.; Li, J. A High-Performance Soy Protein Isolate-Based Nanocomposite Film Modified with Microcrystalline Cellulose and Cu and Zn Nanoclusters. Polymer 2017, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Bhat, A.H.; Yusra, A.F.I. Green composites from sustainable cellulose nanofibrils: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 963–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, G.; Bras, J.; Dufresne, A. Cellulosic Bionanocomposites: A Review of Preparation, Properties and Applications. Polymer 2010, 2, 728–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.; Strumia, M.C.; Igarzabal, C.I.A. Cross-linked soy protein as material for biodegradable films: Synthesis, characterization and biodegradation. J. Food Eng. 2011, 106, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Films | SPI (g) | Deionized Water (g) | Glycerol (g) | NS (g) | CNF (g) | O@CNF/NS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI | 6 | 114 | 1.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SPI/NS | 6 | 114 | 1.8 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 |
| SPI/CNF | 6 | 114 | 1.8 | 0 | 0.3 | 0 |
| SPI/CNF/NS | 6 | 114 | 1.8 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0 |
| SPI/O@CNF/NS | 6 | 114 | 1.8 | 0 | 0 | 0.15 |
| Films | Ti1 (°C) * | Tmax1 (°C) ** | Ti2 (°C) * | Tmax2 (°C) ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI | 125.70 | 244.80 | 265.13 | 312.31 |
| SPI/NS | 122.21 | 241.57 | 261.52 | 303.77 |
| SPI/CNF | 124.13 | 243.71 | 260.20 | 299.91 |
| SPI/CNF/NS | 121.35 | 240.87 | 262.34 | 303.98 |
| SPI/O@CNF/NS | 123.79 | 242.63 | 263.40 | 306.57 |
| Films | Thickness (mm) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Elastic Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI | 0.098 (0.010) | 3.49 (0.19) | 153.54 (13.56) | 145.45 (11.38) |
| SPI/NS | 0.109 (0.015) | 4.22 (0.20) | 139.48 (23.77) | 202.67 (8.70) |
| SPI/CNF | 0.105 (0.003) | 4.94 (0.26) | 117.45 (9.05) | 191.66 (6.05) |
| SPI/CNF/NS | 0.099 (0.009) | 4.44 (0.27) | 146.20 (13.26) | 186.20 (20.18) |
| SPI/O@CNF/NS | 0.142 (0.003) | 6.65 (0.14) | 109.62 (6.84) | 342.46 (23.45) |
| Films | Moisture Content (%) | Total Soluble Matter (%) | Water Uptake (%) | Diffusion Coefficient (10−10cm2/s) | Water Vapor Permeability (× 10−15g·cm−1·s−1·MPa−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI | 11.00 (0.43) | 51.43 (0.99) | 66.7 (0.23) | 2.00 | 5.60 (0.30) |
| SPI/NS | 10.93 (0.19) | 40.20 (0.81) | 62.9 (0.29) | 1.76 | 6.20 (0.41) |
| SPI/CNF | 12.43 (0.28) | 39.62 (0.89) | 58.7 (0.38) | 1.43 | 5.60 (0.23) |
| SPI/CNF/NS | 13.00 (0.37) | 39.80 (0.70) | 59.6 (0.34) | 1.69 | 5.20 (0.21) |
| SPI/O@CNF/NS | 13.02 (0.23) | 37.52 (0.47) | 53.7 (0.16) | 1.34 | 5.10 (0.18) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Z.; Mo, L.; Liao, M.; He, H.; Sun, J. Preparation and Characterization of Soy Protein Isolate-Based Nanocomposite Films with Cellulose Nanofibers and Nano-Silica via Silane Grafting. Polymers 2019, 11, 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111835
Qin Z, Mo L, Liao M, He H, Sun J. Preparation and Characterization of Soy Protein Isolate-Based Nanocomposite Films with Cellulose Nanofibers and Nano-Silica via Silane Grafting. Polymers. 2019; 11(11):1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111835
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Zhiyong, Liuting Mo, Murong Liao, Hua He, and Jianping Sun. 2019. "Preparation and Characterization of Soy Protein Isolate-Based Nanocomposite Films with Cellulose Nanofibers and Nano-Silica via Silane Grafting" Polymers 11, no. 11: 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111835
APA StyleQin, Z., Mo, L., Liao, M., He, H., & Sun, J. (2019). Preparation and Characterization of Soy Protein Isolate-Based Nanocomposite Films with Cellulose Nanofibers and Nano-Silica via Silane Grafting. Polymers, 11(11), 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111835