Smart Microneedles with Porous Polymer Coatings for pH-Responsive Drug Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Coating Solution Preparation and Porous MN Fabrication
2.3. Characterization and Parametric Study
2.4. In Vitro pH-Responsive Drug Release of Porous Coated MNs
2.5. Insertion Capability and Diffusion Kinetics of Calcein Dye from Porous Coated MNs in Porcine Skin
2.6. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM)
3. Results and Discussion
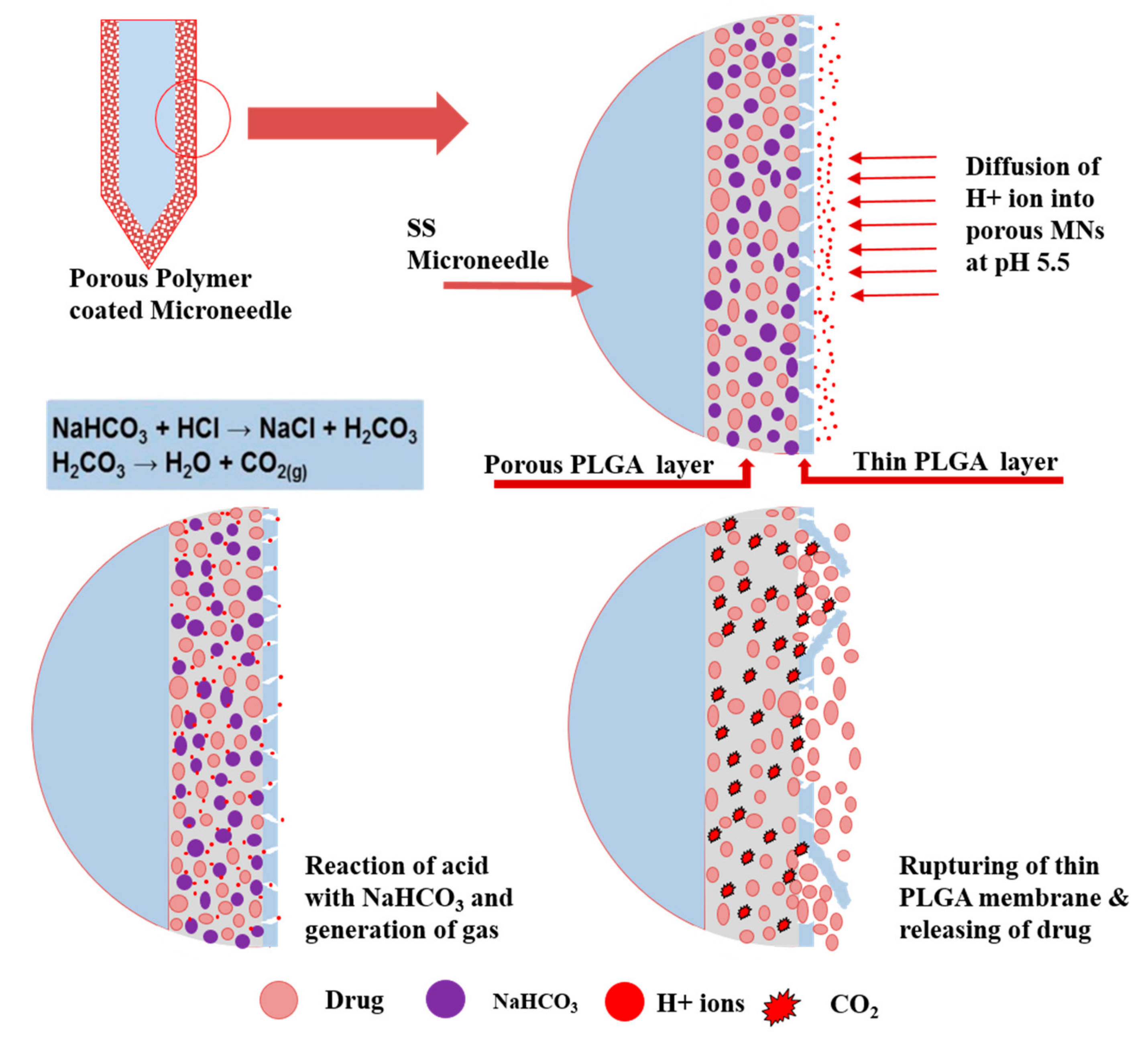
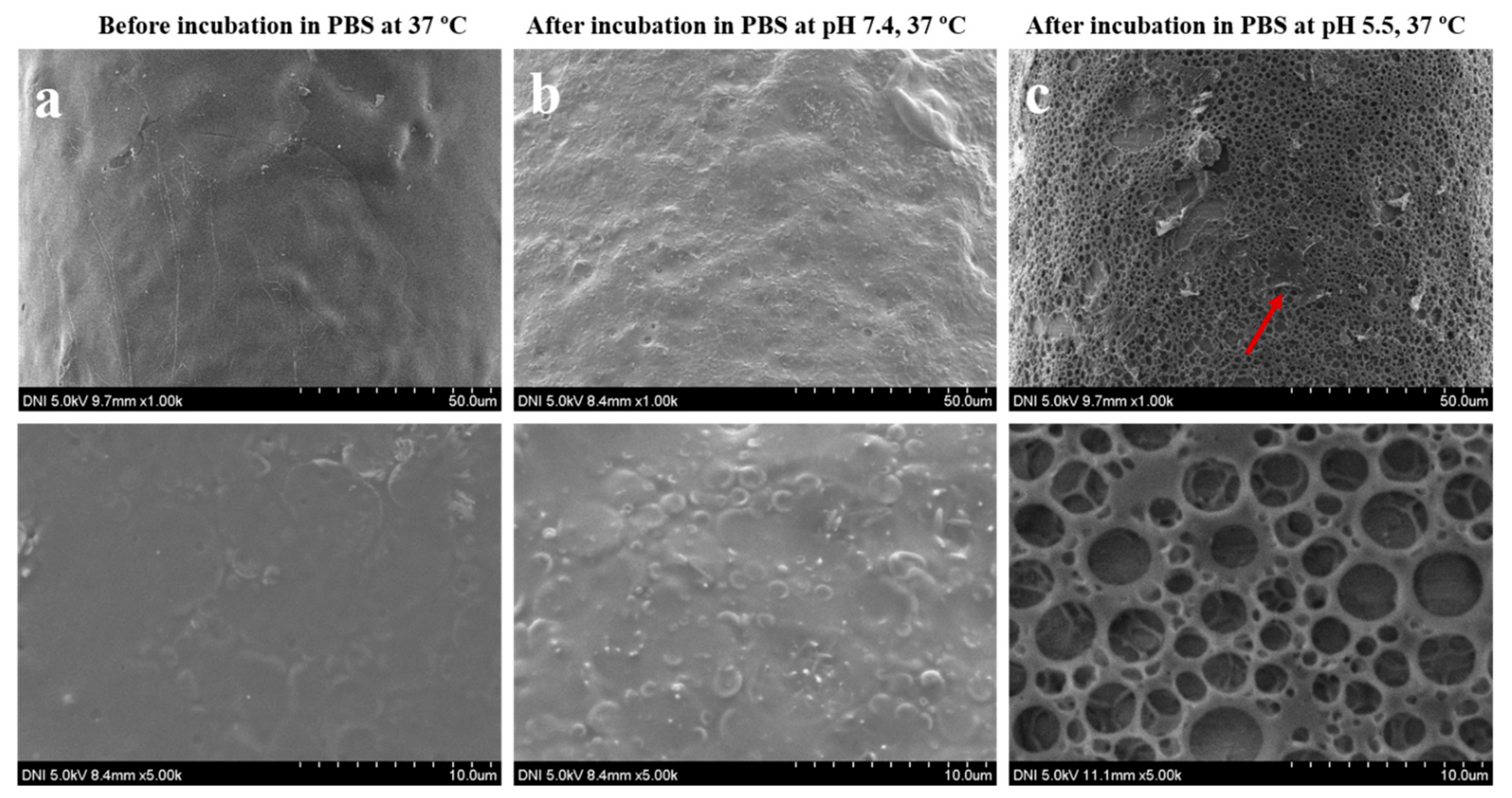
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of pH-Responsive Porous Coated MNs
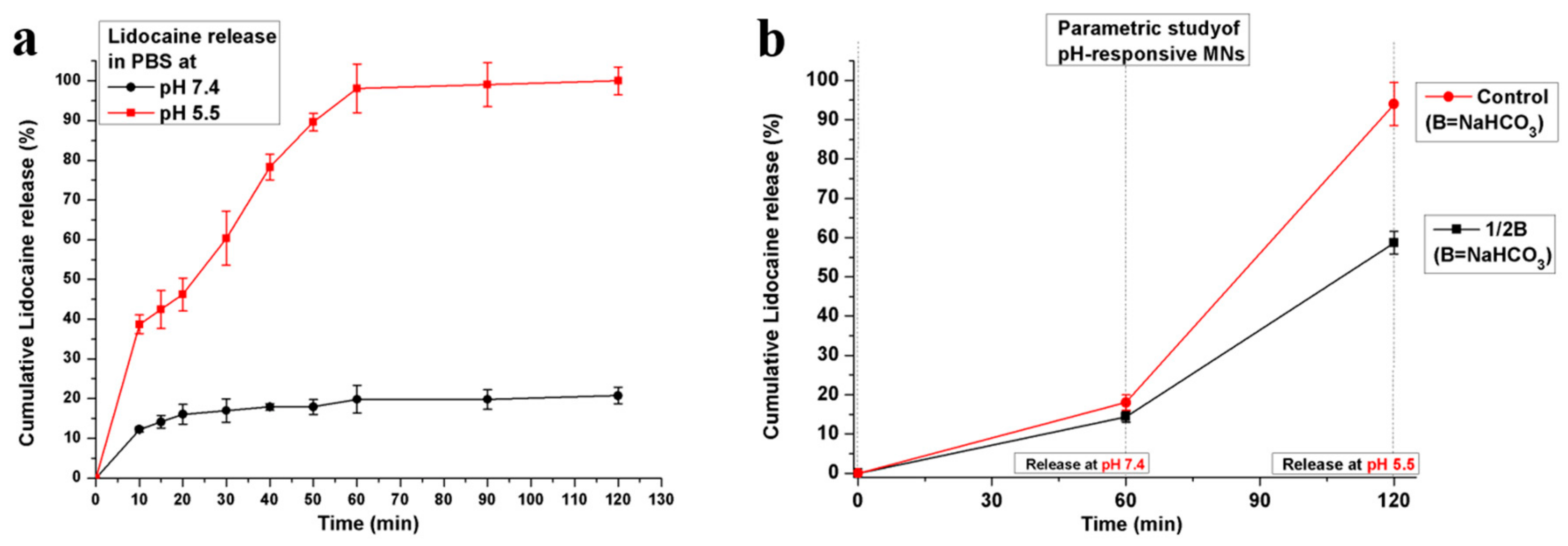
3.2. In Vitro Drug Release of Porous Coated MNs in Response to pH Changes
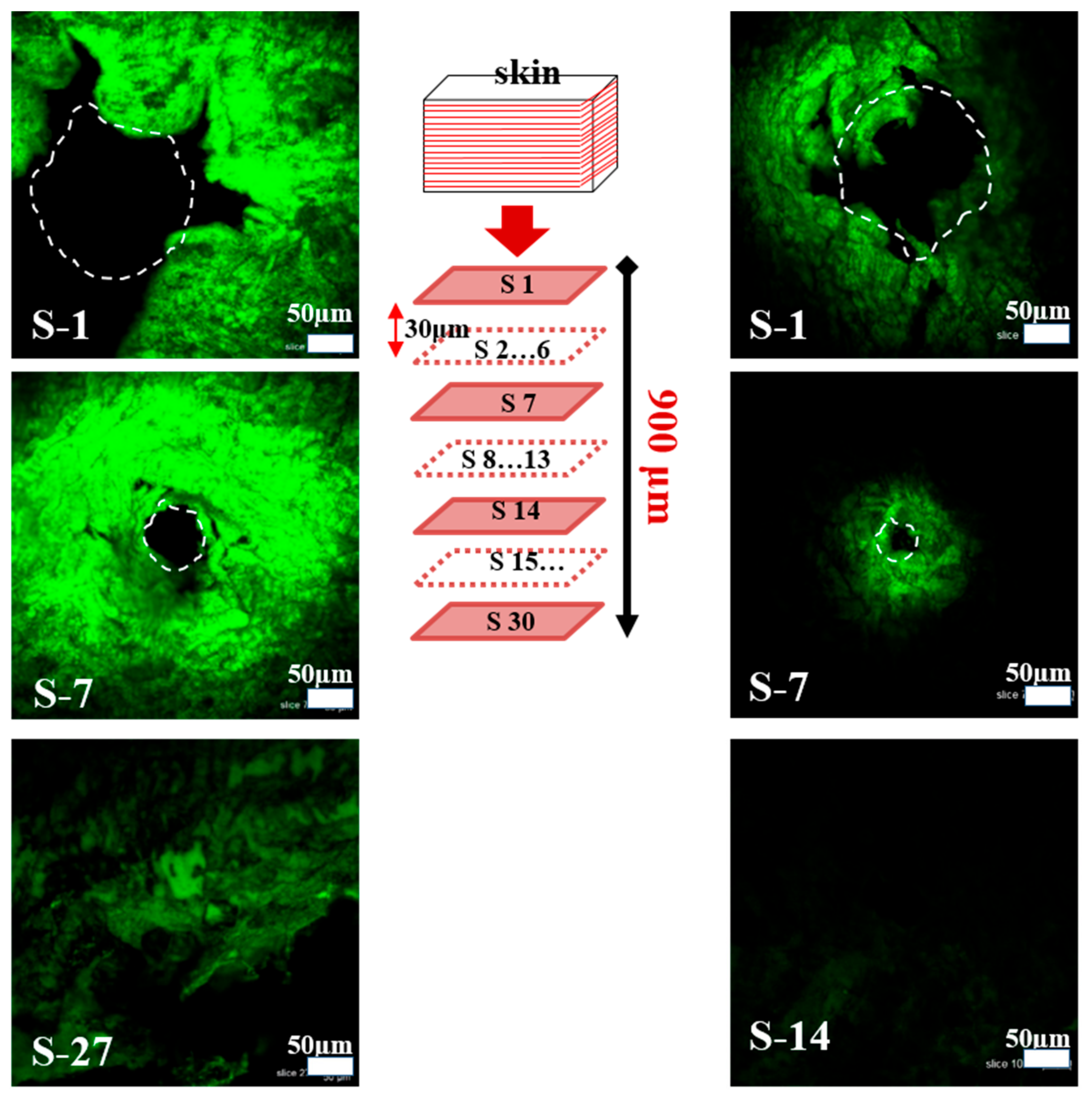
3.3. Insertion Capability and Diffusion Kinetics of Calcein Dye from MNs in Porcine Skin
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeMuth, P.C.; Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Ai-Ling, M.L.; Hammond, P.T.; Irvine, D.J. Composite dissolving microneedles for coordinated control of antigen and adjuvant delivery kinetics in transcutaneous vaccination. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Mitragotri, S.; Langer, R. Current status and future potential of transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudice, E.L.; Campbell, J.D. Needle-free vaccine delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Langer, R. Transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruss-Ustun, A.; Rapiti, E.; Hutin, Y. Sharps Injuries: Global Burden of Disease from Sharps Injuries to Health-Care Workers; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- DeMuth, P.C.; Su, X.; Samuel, R.E.; Hammond, P.T.; Irvine, D.J. Nano-layered microneedles for transcutaneous delivery of polymer nanoparticles and plasmid DNA. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4851–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.Y.; Choi, S.-O.; Prausnitz, M.R. Fabrication of dissolving polymer microneedles for controlled drug encapsulation and delivery: Bubble and pedestal microneedle designs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4228–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Ise, A.; Morita, H.; Hasegawa, R.; Ito, Y.; Sugioka, N.; Takada, K. Two-Layered dissolving microneedles for percutaneous delivery of peptide/protein drugs in rats. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roointan, A.; Farzanfar, J.; Mohammadi-Samani, S.; Behzad-Behbahani, A.; Farjadian, F. Smart pH responsive drug delivery system based on poly (HEMA-co-DMAEMA) nanohydrogel. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 552, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, J.; Qi, B.; Tao, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, C.; Peng, H.; Shi, J. Multifunctional Fibers to Shape Future Biomedical Devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Xiao, C.; Xiao, H.; Yang, H.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Electrospun polymer biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 90, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Matsukawa, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Yoshino, H. Drug release characteristics of multi-reservoir type microspheres with poly (dl-lactide-co-glycolide) and poly (dl-lactide). J. Control. Release 2005, 106, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broaders, K.E.; Grandhe, S.; Fréchet, J.M. A biocompatible oxidation-triggered carrier polymer with potential in therapeutics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 133, 756–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Chen, F. pH-Responsive Drug-Delivery Systems. Chem. Asian J. 2015, 10, 284–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, W.; Mo, R.; Di, J.; Subramanian, V.; Gu, X.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Bio-Inspired synthetic nanovesicles for glucose-responsive release of insulin. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3495–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun-Wada, G.-H.; Wada, Y.; Futai, M. Lysosome and lysosome-related organelles responsible for specialized functions in higher organisms, with special emphasis on vacuolar-type proton ATPase. Cell Struct. Funct. 2003, 28, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Xu, W.; Li, Z.; Song, W.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Immunomodulatory Nanosystems. Adv. Sci. 2019, 1900101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, R.M.; Hurley, J.; Salmaso, S.; Kale, A.; Tolcheva, E.; Levchenko, T.; Torchilin, V. “SMART” drug delivery systems: Double-Targeted pH-responsive pharmaceutical nanocarriers. Bioconjug. Chem. 2006, 17, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yu, J.; Qian, C.; Lu, Y.; Kahkoska, A.R.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. H2O2-responsive vesicles integrated with transcutaneous patches for glucose-mediated insulin delivery. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhu, J.; Liu, D.; Jiang, G. Microneedles Integrated with ZnO Quantum-Dot-Capped Mesoporous Bioactive Glasses for Glucose-Mediated Insulin Delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 2473–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.-J.; Lin, Y.-J.; Hu, Y.-C.; Chiang, W.-L.; Chen, K.-J.; Yang, W.-C.; Liu, H.-L.; Fu, C.-C.; Sung, H.-W. Multidrug release based on microneedle arrays filled with pH-responsive PLGA hollow microspheres. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5156–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Park, H.J.; Hwang, S.; Park, J. Preparation of alginate beads for floating drug delivery system: Effects of CO2 gas-forming agents. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 239, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Y.; DiSanto, R.; Sun, W.; Ranson, D.; Ligler, F.S.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Microneedle-Array patches loaded with hypoxia-sensitive vesicles provide fast glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8260–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocak, G.; Tuncer, C.; Bütün, V.J.P.C. pH-Responsive polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 144–176. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.M.; Yosipovitch, G.J.A.D.-V. Skin pH: From basic science to basic skin care. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2013, 93, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, J.R.; Grinstein, S.; Orlowski, J. Sensors and regulators of intracellular pH. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Kim, C.M.; Kim, G.M. Solvent effects on the porosity and size of porous PLGA microspheres using gelatin and PBS as porogens in a microfluidic flow-focusing device. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 7775–7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Jiang, G.; Yu, W.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, S.; Liu, Y. H2O2-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles integrated with microneedle patches for the glucose-monitored transdermal delivery of insulin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8200–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Kim, C.M.; Kim, G.M. Porous polymer coatings on metal microneedles for enhanced drug delivery. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zarnitsyn, V.G.; Ye, L.; Wen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Pan, L.; Skountzou, I.; Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Yang, C. Immunization by vaccine-coated microneedle arrays protects against lethal influenza virus challenge. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7968–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfield, A.; Meurens, F.; Ricklin, M.E. The immunology of the porcine skin and its value as a model for human skin. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 66, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, A.; Khan, H.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, G.M. Smart Microneedles with Porous Polymer Coatings for pH-Responsive Drug Delivery. Polymers 2019, 11, 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111834
Ullah A, Khan H, Choi HJ, Kim GM. Smart Microneedles with Porous Polymer Coatings for pH-Responsive Drug Delivery. Polymers. 2019; 11(11):1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111834
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Asad, Haroon Khan, Hye Jin Choi, and Gyu Man Kim. 2019. "Smart Microneedles with Porous Polymer Coatings for pH-Responsive Drug Delivery" Polymers 11, no. 11: 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111834
APA StyleUllah, A., Khan, H., Choi, H. J., & Kim, G. M. (2019). Smart Microneedles with Porous Polymer Coatings for pH-Responsive Drug Delivery. Polymers, 11(11), 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111834





