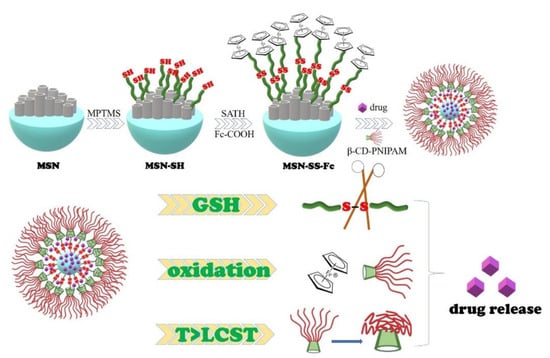
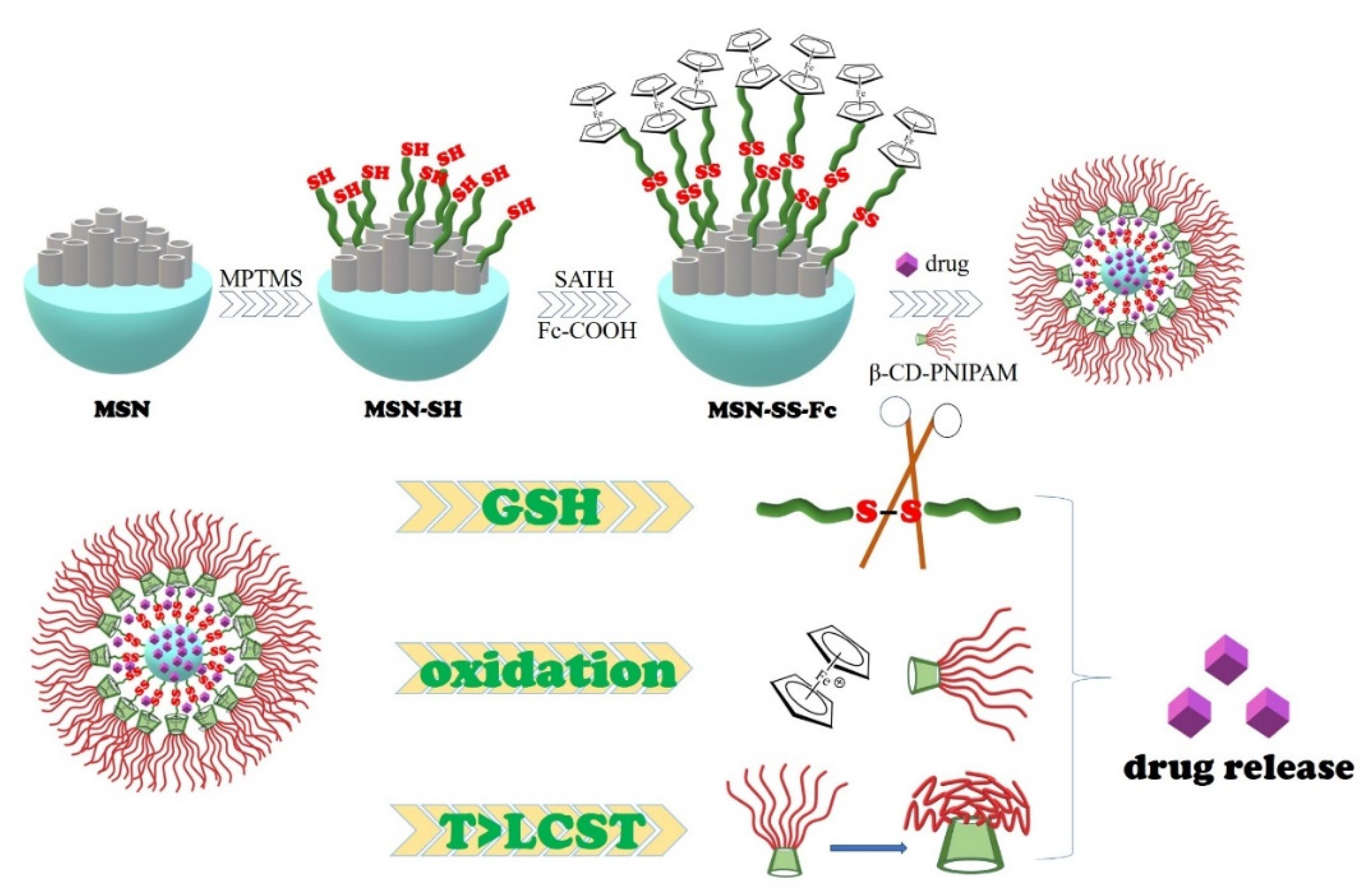
Multi-Responsive Nanocarriers Based on β-CD-PNIPAM Star Polymer Coated MSN-SS-Fc Composite Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Preparation of Ferrocene Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
2.3.1. Preparation of MSNs
2.3.2. Synthesis of MSN-SH
2.3.3. Synthesis of MSN-SS-NH2
2.3.4. Synthesis of MSN-SS-Fc
2.4. Preparation of MSN-SS-Fc@β-CD-PNIPAM Nanoparticles and Drug Loading
2.5. Drug Release from MSN-SS-Fc@β-CD-PNIPAM Nanoparticles
3. Results and Discussion
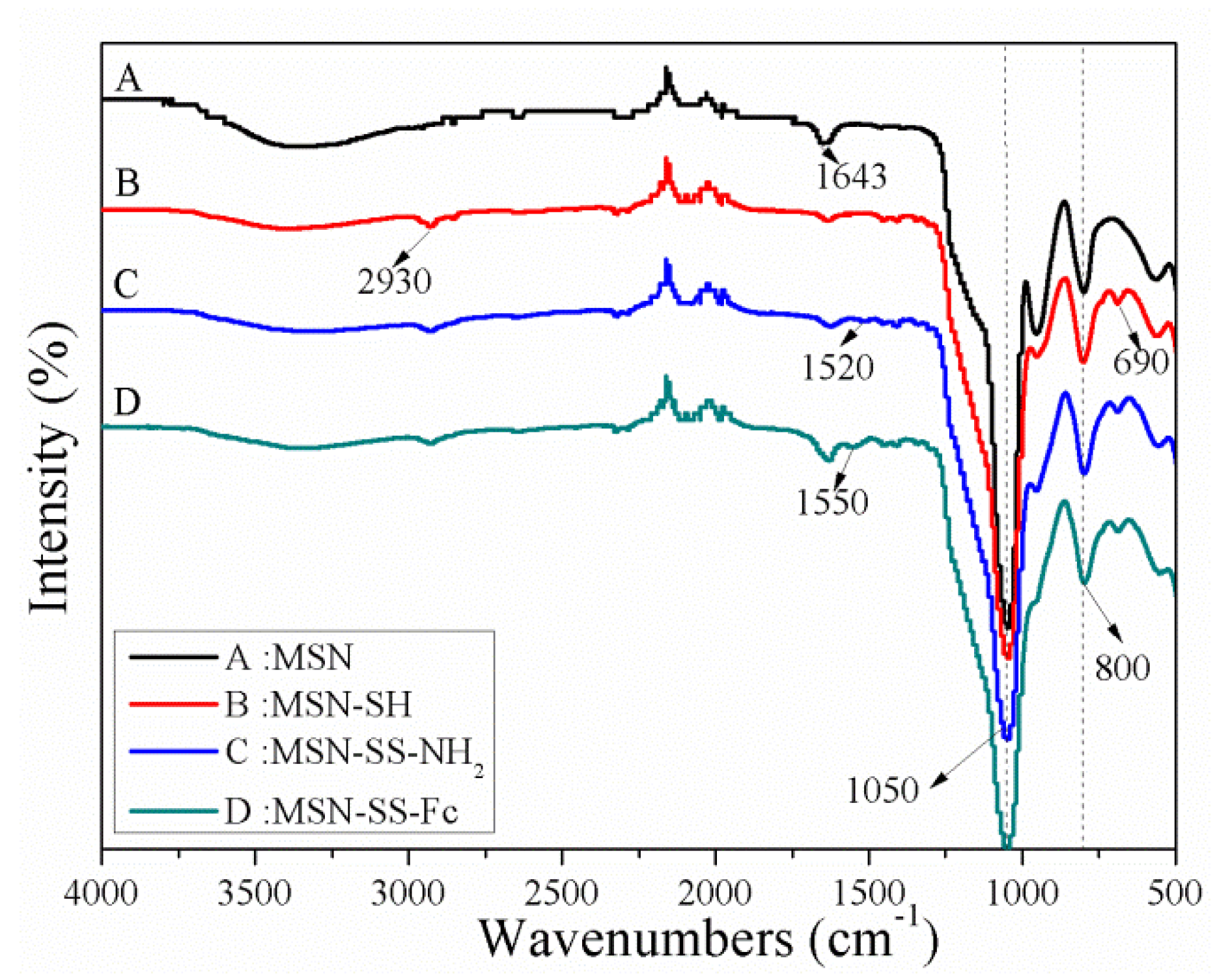
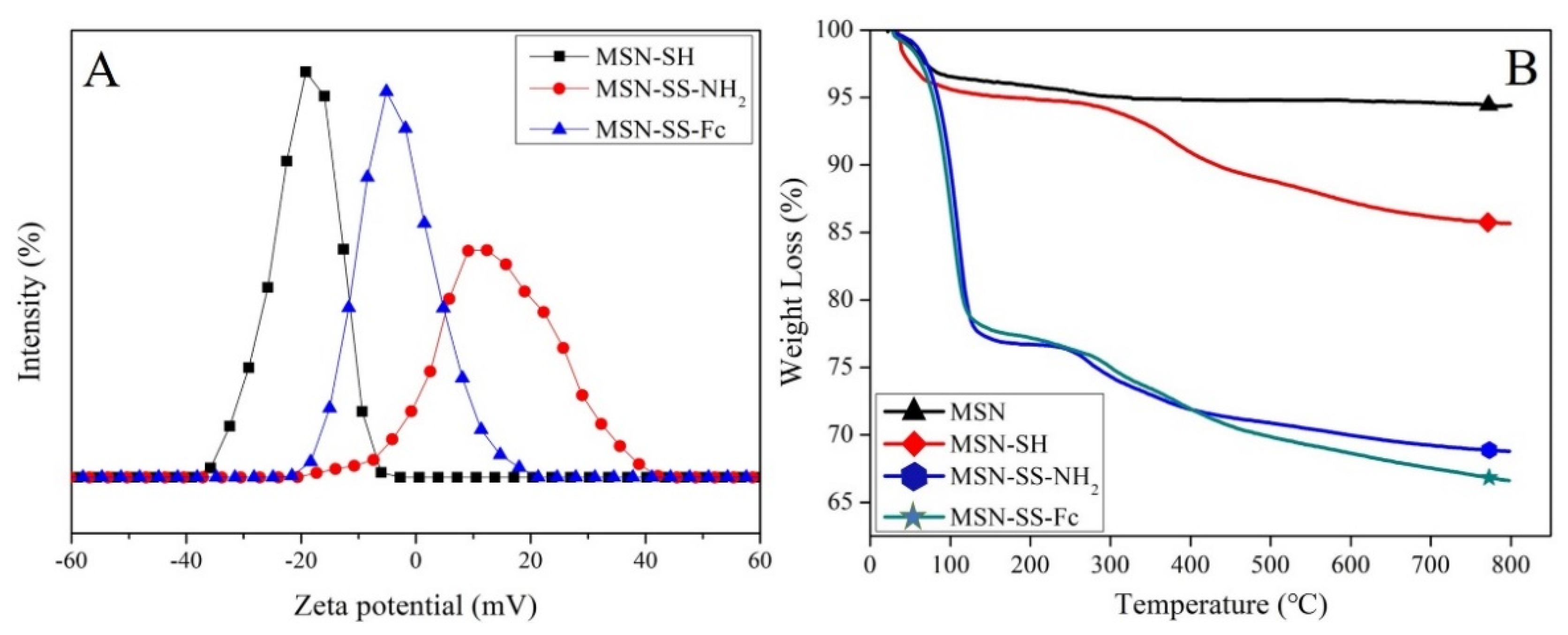
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocarriers
3.2. Encapsulation Drugs in Complex Nanoparticles
3.3. Multi-Responsive Drug Release from Complex Nanoparticles
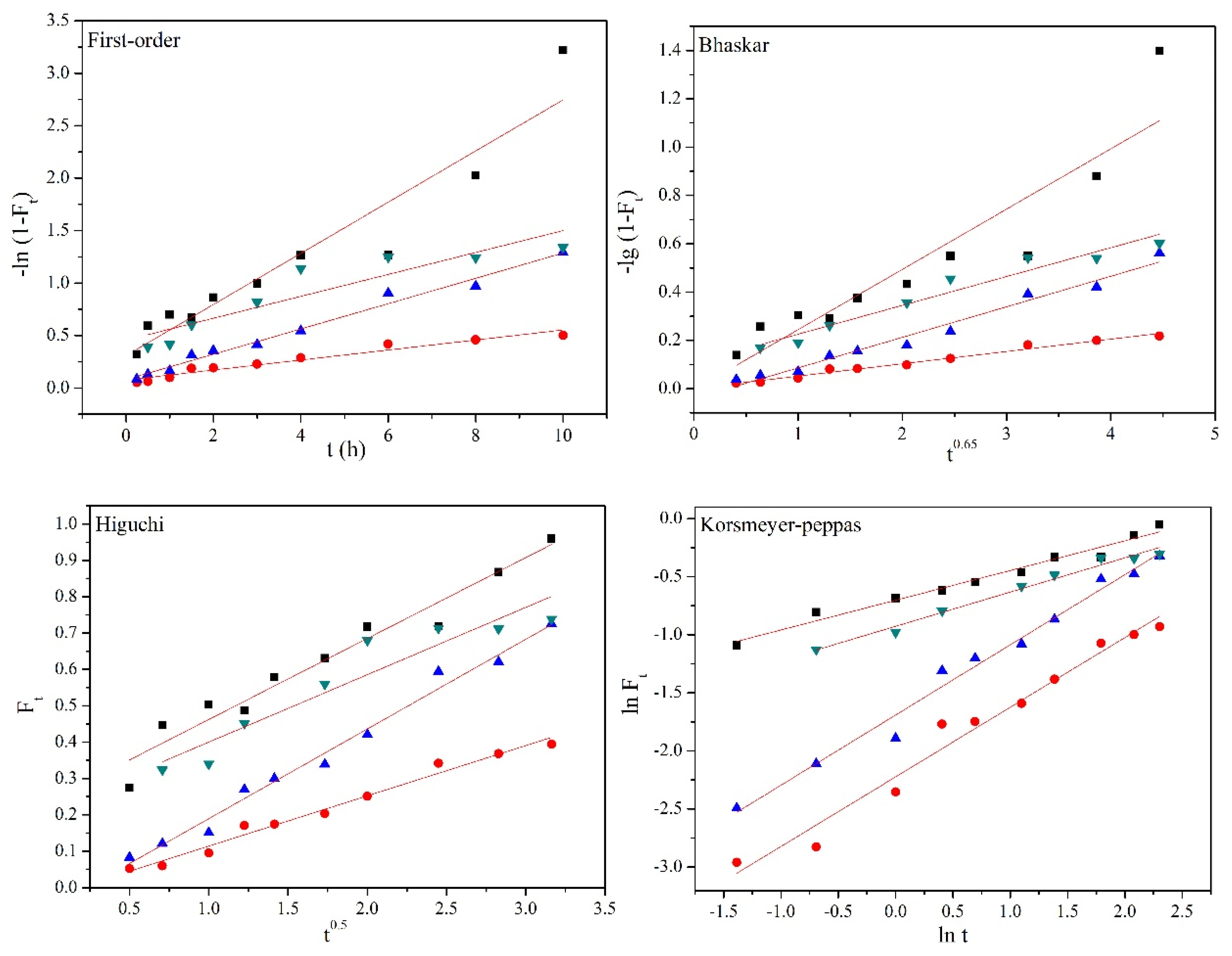
3.4. In Vitro Release Kinetics of Drugs
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.Y.; Song, S.B.; Han, K.S.; Wu, X.W.; Chen, L.Z.; Hu, Y.S.; Wang, J.S.; Liu, B. Characterization, in vitro evaluation and comparative study on the cellular internalization of mesoporous silica nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2019, 284, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Meng, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J. Formation of thermo-sensitive polyelectrolyte complex micelles from two biocompatible graft copolymers for drug delivery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 2163–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Li, G.; Yu, N.; Meng, Y.; Liu, X. Synthesis of thermo-sensitive polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles from CS-g-PNIPAM and SA-g-PNIPAM for controlled drug release. Macromol. Res. 2014, 22, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.N.; Zhao, X.H.; Zu, Y.G.; Wang, L.; Deng, Y.P.; Wu, M.F.; Wang, H.M. Enhanced solubility and bioavailabitity of apigenin via preparation of solid dispersions of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, N.; Qin, J.R.; Fan, Y.W.; Li, Z.K.; Song, B.T. Long time release of water soluble drug from hydrophilic nanofibrous material. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47922–47930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Quan, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Niu, B.; Wu, B.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, N.; Guo, F.; Guo, L.; Liu, X. Synthesis of temperature/pH dual-sensitive supramolecular micelles from beta-cyclodextrin-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) star polymer for drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B 2018, 172, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tao, Z.J.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, S.; Zhang, F.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.Y.; Wang, J.D. YSA-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles effectively target EphA2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Cancer Chemoth. Pharm. 2018, 81, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, S.S.; Jo, N.J.; Ha, C.S. Folic acid-polyethyleneimine functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a controlled release nanocarrier. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 6217–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.; Lin, X.W.; Ke, L.J.; Li, B.F.; Xu, L.; Lv, T.T.; Li, Z.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Gao, Y. Dual-responsive nanosystem for precise molecular subtyping and resistant reversal of EGFR targeted therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Cao, B.; Snyder, N.R.; Woeppel, K.M.; Eles, J.R.; Cui, X.T. ROS responsive resveratrol delivery from LDLR peptide conjugated PLA-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles across the blood-brain barrier. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.F.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, C.G.; Gao, W.; Fan, X.B.; Wu, G.Q. A facile strategy to fabricate a pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticle end-capped with amphiphilic peptides by self-assembly. Colloids Surf. B. 2019, 179, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Sun, W.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Y.B.; Wang, P. pH-responsive nanoreservoirs based on hyaluronic acid end-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.T.; Lin, X.L.; Wu, S.; Liang, Q.; Yang, L.; Gao, Y.J.; Ge, Z.Z. NOX4-driven ROS formation regulates proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer cells through the GLI1 pathway. Cell. Signal. 2018, 46, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Mo, X.; An, F.; Ji, X.; Lu, Y. 2’,4’-Dihydroxy-6’-methoxy-3’,5’-dimethylchalcone, a potent Nrf2/ARE pathway inhibitor, reverses drug resistance by decreasing glutathione synthesis and drug efflux in BEL-7402/5-FU cells. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 119, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kengen, J.; Deglasse, J.P.; Neveu, M.A.; Mignion, L.; Desmet, C.; Gourgue, F.; Jonas, J.C.; Gallez, B.; Jordan, B.F. Biomarkers of tumour redox status in response to modulations of glutathione and thioredoxin antioxidant pathways. Free Radical Res. 2018, 52, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Guo, L.; Ma, S.; Liu, J. Complex micelles formed from two diblock copolymers for applications in controlled drug release. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. 2009, 47, 1804–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Xie, Z.; Liu, M.; Sun, H.; Zhu, H.; Guo, H. Research on redox-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with PEG via a disulfide bond linker as drug carrier materials. Colloids Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Hu, J.; Han, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y. Transferrin gated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for redox-responsive and targeted drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B. 2017, 152, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, S.P.H.; Yazdimamaghani, M.; Ghandehari, H. Glutathione-sensitive hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2018, 282, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, G.Q.; Vargas, M.D.; Ronconi, C.M. Nanoreservoir operated by ferrocenyl linker oxidation with molecular oxygen. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 6034–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Pan, S.; Niu, D.; He, J.; Jia, X.; Hao, J.; Gu, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, P.; Li, Y. Facile synthesis of organosilica-capped mesoporous silica nanocarriers with selective redox-triggered drug release property for safe tumor chemotherapy. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 5, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebright, Y.W.; Chen, Y.; Kim, Y.; Ebright, R.H. S-2-(4-azidosalicylamido)ethylthio-2-thiopyridine: Radioiodinatable, cleavable, photoactivatible cross-linking agent. Bioconjugate Chem. 1996, 7, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Yu, J.S.; Yan, Y.A.; Yang, D.C.; Wang, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xu, G.H.; He, D.N.; Huang, G. Biodegradable polyester/modified mesoporous silica composites for effective bone repair with self-reinforced properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 1461–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Liu, T.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Tang, F. The absorption, distribution, excretion and toxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in mice following different exposure routes. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Almalik, A.; Khashab, N.M. Mesoporous silica and organosilica nanoparticles: Physical chemistry, biosafety, delivery strategies, and biomedical applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1700831–1700905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Guo, L.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, T. Self-assembled nanoparticles from thermo-sensitive polyion complex micelles for controlled drug release. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Qi, M.; Yu, N.N.; Liu, X. Hybrid vesicles co-assembled from anionic graft copolymer and metal ions for controlled drug release. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wyman, I. Supramolecular nanostructures based on cyclodextrin and poly(ethylene oxide): Syntheses, structural characterizations and applications for drug delivery. Polymers 2016, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, C. pH and redox-operated nanovalve for size-selective cargo delivery on hollow mesoporous silica spheres. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2016, 480, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Nie, W.; He, C.L.; Zhou, X.J.; Chen, L.; Qiu, K.X.; Wang, W.Z.; Yin, Z.Q. Effect of pH-responsive alginate/chitosan multilayers coating on delivery efficiency, cellular uptake and biodistribution of mesoporous silica nanoparticles based nanocarriers. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 8447–8460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perioli, L.; Posati, T.; Nocchetti, M.; Bellezza, F.; Costantino, U.; Cipiciani, A. Intercalation and release of antiinflammatory drug diclofenac into nanosized ZnAl hydrotalcite-like compound. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 53, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.A. pH-sensitive microemulsion-filled gellan gum hydrogel encapsulated apigenin: Characterization and in vitro release kinetics. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 178, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Huang, Q.; Zeng, H.; Du, J.; Xu, S.; Chen, C. Hydrotalcite-gated hollow mesoporous silica delivery system for controlled drug release. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2019, 274, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Yuan, P.; Annabi-Bergaya, F.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; He, H. Loading and in vitro release of ibuprofen in tubular halloysite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 96, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Samples | C% | H% | S% | N% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSNs | 1.69 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.19 |
| MSN-SH | 6.23 | 1.40 | 3.58 | 0.16 |
| MSN-SS-Fc | 7.77 | 1.86 | 3.72 | 1.37 |
| m0/ma (%) | DOX | NAP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLC (%) | EE (%) | DLC (%) | EE (%) | |
| 20 | 12.01 | 68.27 | 11.76 | 49.58 |
| 40 | 23.22 | 75.63 | 20.00 | 62.50 |
| 60 | 31.56 | 76.87 | 27.69 | 71.23 |
| 80 | 38.28 | 77.85 | 32.12 | 70.76 |
| 100 | 41.81 | 71.86 | 34.64 | 66.26 |
| Release Medium | Firs-order | Bhaskar | Higuchi | Korsmeyer–Peppas | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | R2 | R2 | R2 | n | |
| 10 mM GSH | 0.899 | 0.841 | 0.950 | 0.972 | 0.26 |
| 0.1% H2O2 | 0.946 | 0.981 | 0.980 | 0.971 | 0.60 |
| 0.5% H2O2 | 0.983 | 0.973 | 0.984 | 0.982 | 0.69 |
| 42 °C | 0.823 | 0.945 | 0.886 | 0.980 | 0.29 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, F.; Li, G.; Ma, S.; Zhou, H.; Chen, X. Multi-Responsive Nanocarriers Based on β-CD-PNIPAM Star Polymer Coated MSN-SS-Fc Composite Particles. Polymers 2019, 11, 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101716
Guo F, Li G, Ma S, Zhou H, Chen X. Multi-Responsive Nanocarriers Based on β-CD-PNIPAM Star Polymer Coated MSN-SS-Fc Composite Particles. Polymers. 2019; 11(10):1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101716
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Feng, Guiying Li, Songmei Ma, Hengquan Zhou, and Xinyi Chen. 2019. "Multi-Responsive Nanocarriers Based on β-CD-PNIPAM Star Polymer Coated MSN-SS-Fc Composite Particles" Polymers 11, no. 10: 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101716
APA StyleGuo, F., Li, G., Ma, S., Zhou, H., & Chen, X. (2019). Multi-Responsive Nanocarriers Based on β-CD-PNIPAM Star Polymer Coated MSN-SS-Fc Composite Particles. Polymers, 11(10), 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101716