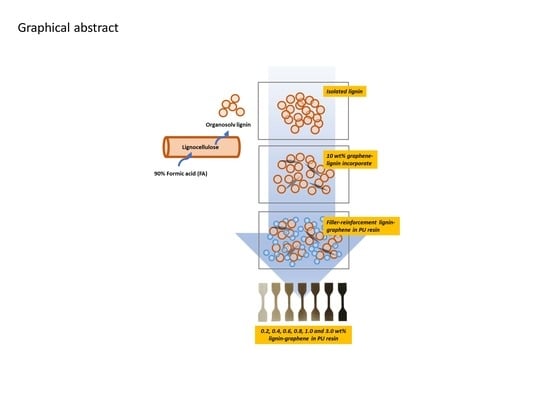
Evaluation of the Compatibility of Organosolv Lignin-Graphene Nanoplatelets with Photo-Curable Polyurethane in Stereolithography 3D Printing
Abstract
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, F.; Mohan, D.; Sajab, M.S.; Bakarudin, S.B.; Kaco, H. Evaluation of the Compatibility of Organosolv Lignin-Graphene Nanoplatelets with Photo-Curable Polyurethane in Stereolithography 3D Printing. Polymers 2019, 11, 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101544
Ibrahim F, Mohan D, Sajab MS, Bakarudin SB, Kaco H. Evaluation of the Compatibility of Organosolv Lignin-Graphene Nanoplatelets with Photo-Curable Polyurethane in Stereolithography 3D Printing. Polymers. 2019; 11(10):1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101544
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Fathirrahman, Denesh Mohan, Mohd Shaiful Sajab, Saiful Bahari Bakarudin, and Hatika Kaco. 2019. "Evaluation of the Compatibility of Organosolv Lignin-Graphene Nanoplatelets with Photo-Curable Polyurethane in Stereolithography 3D Printing" Polymers 11, no. 10: 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101544
APA StyleIbrahim, F., Mohan, D., Sajab, M. S., Bakarudin, S. B., & Kaco, H. (2019). Evaluation of the Compatibility of Organosolv Lignin-Graphene Nanoplatelets with Photo-Curable Polyurethane in Stereolithography 3D Printing. Polymers, 11(10), 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101544