Biomimetic Growth of Hydroxyapatite on Electrospun CA/PVP Core–Shell Nanofiber Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrospinning
2.3. Mineralization in the SBF Solution
2.4. Measurement and Characterization
2.4.1. Solution Properties
2.4.2. SEM and EDS
2.4.3. TEM
2.4.4. FTIR
2.4.5. XRD
2.4.6. Thermal Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Properties of Spinning Solutions
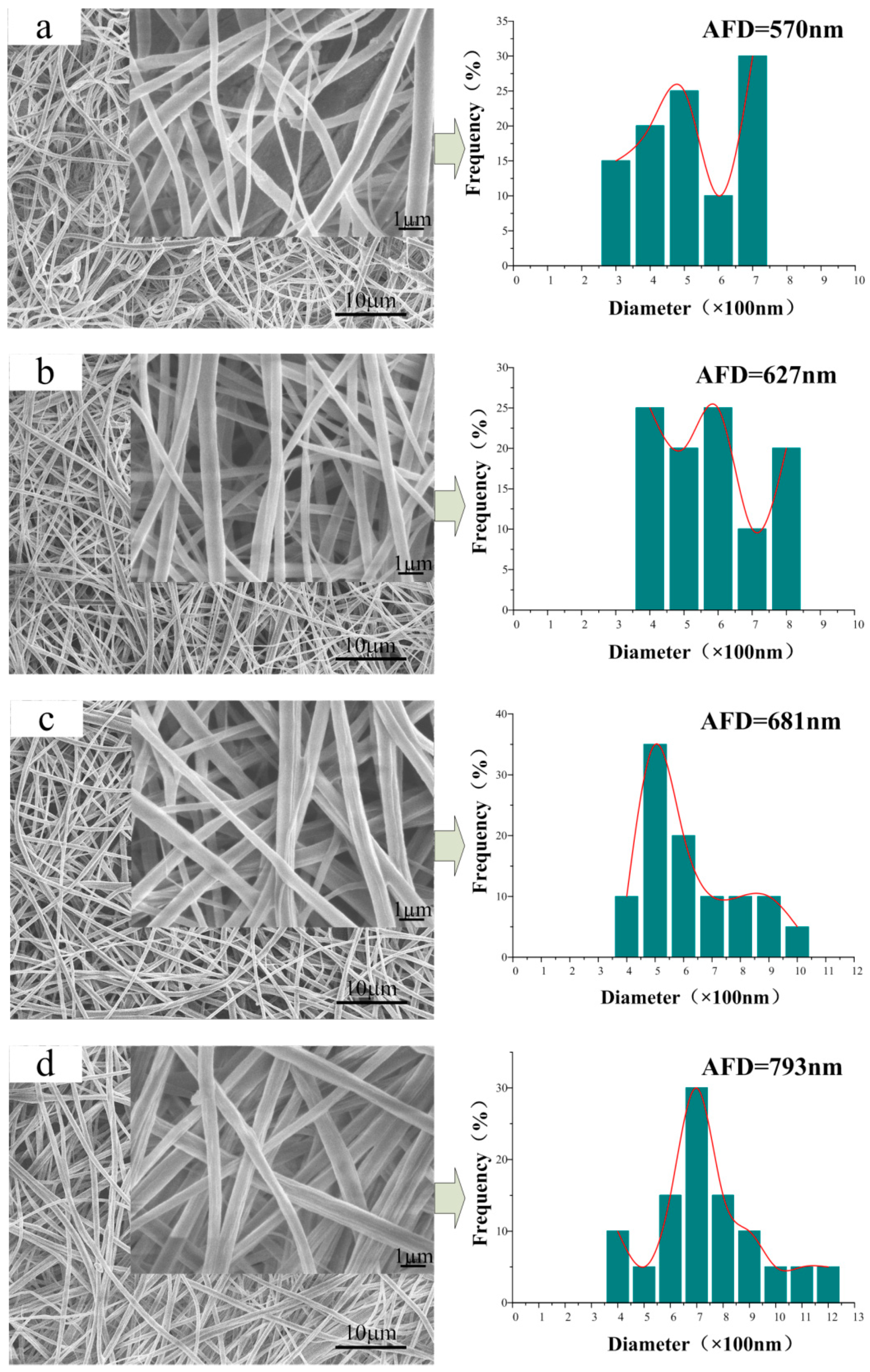
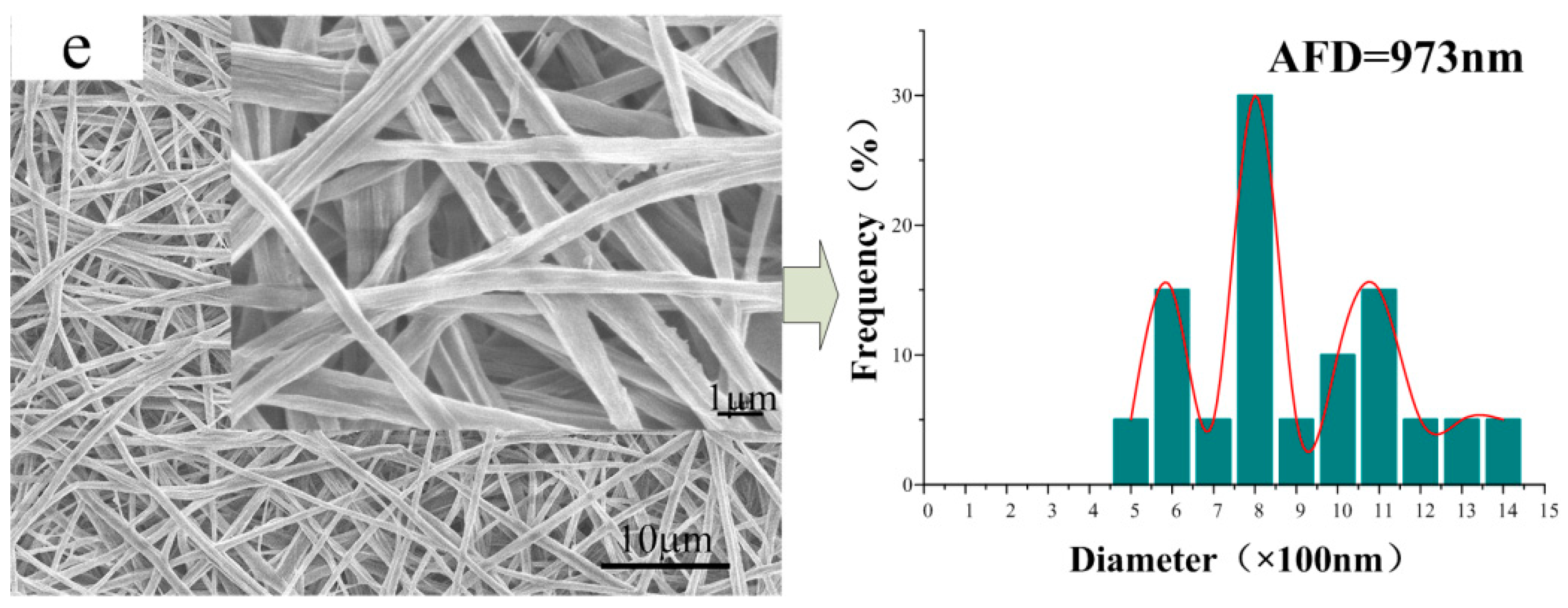
3.2. Morphology of the CA/PVP Nanofibers Membranes
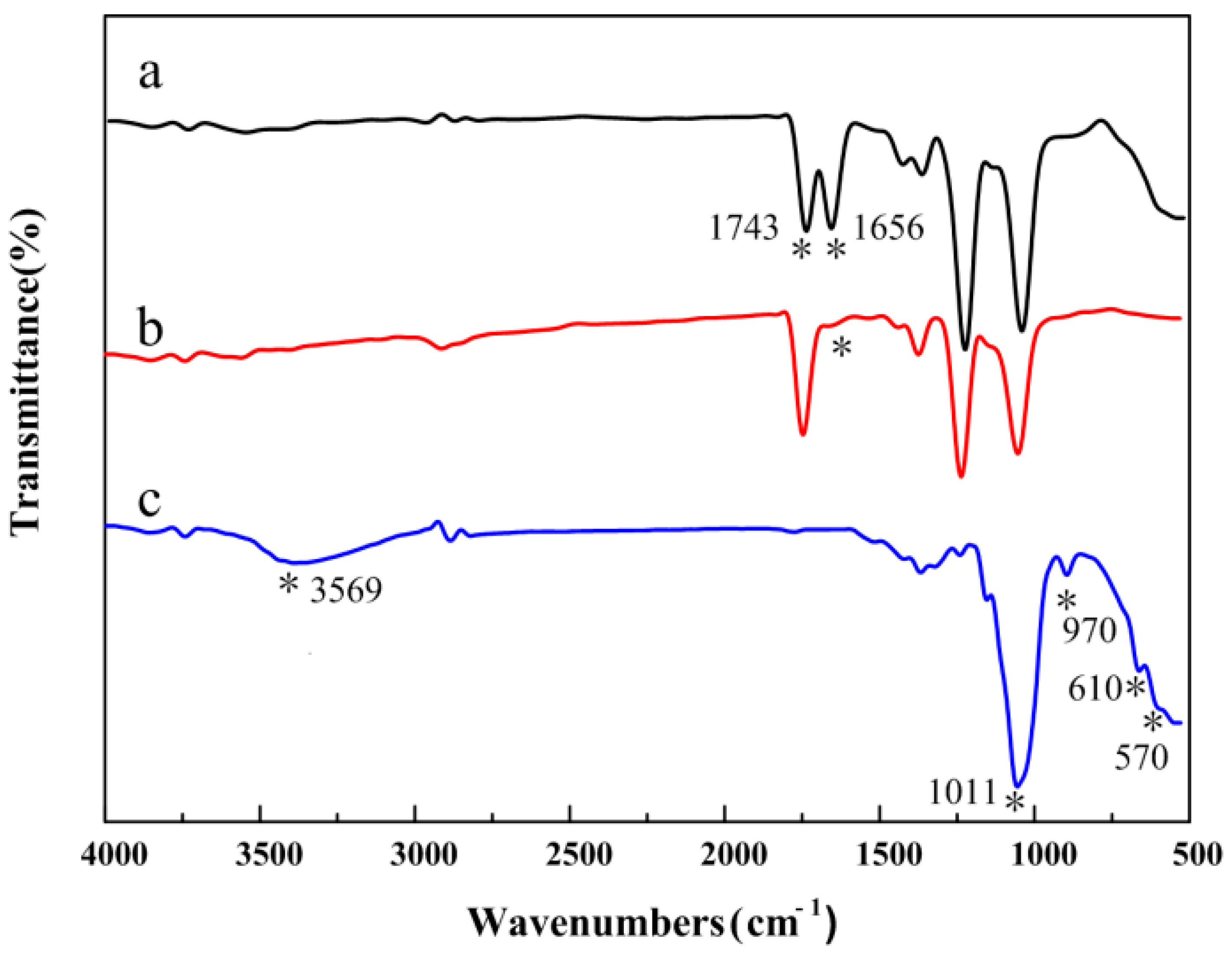
3.3. Composition of the CA/PVP Hybrid Nanofibers
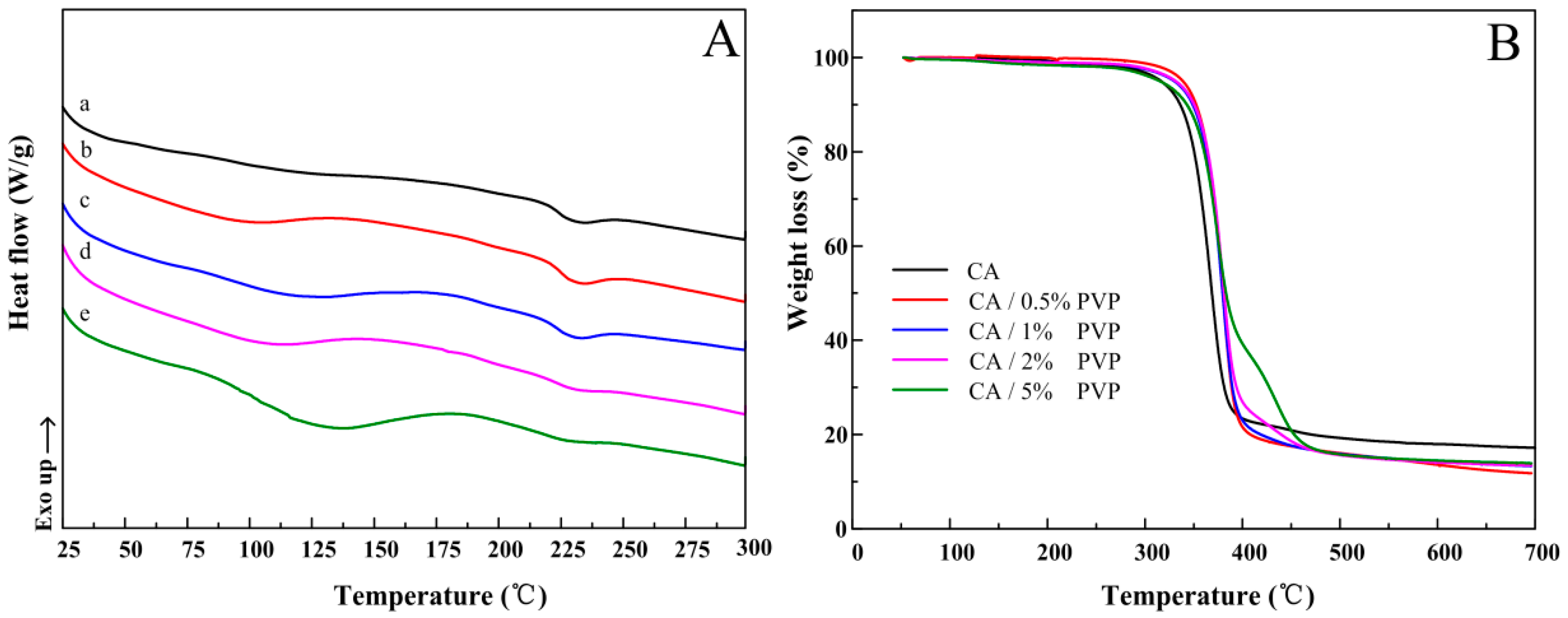
3.4. Thermal Properties
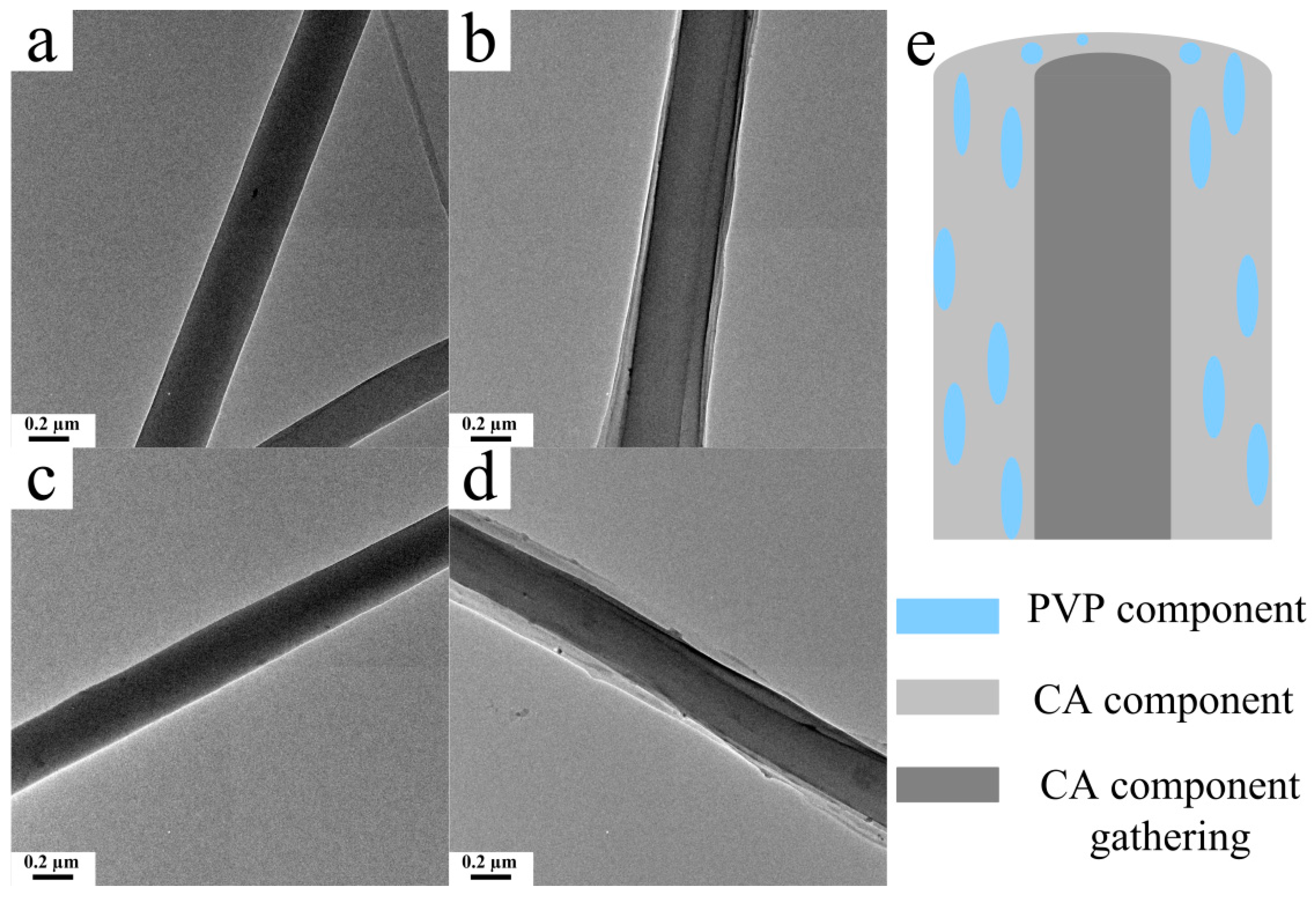
3.5. Microstructure of the CA/PVP Hybrid Nanofibers
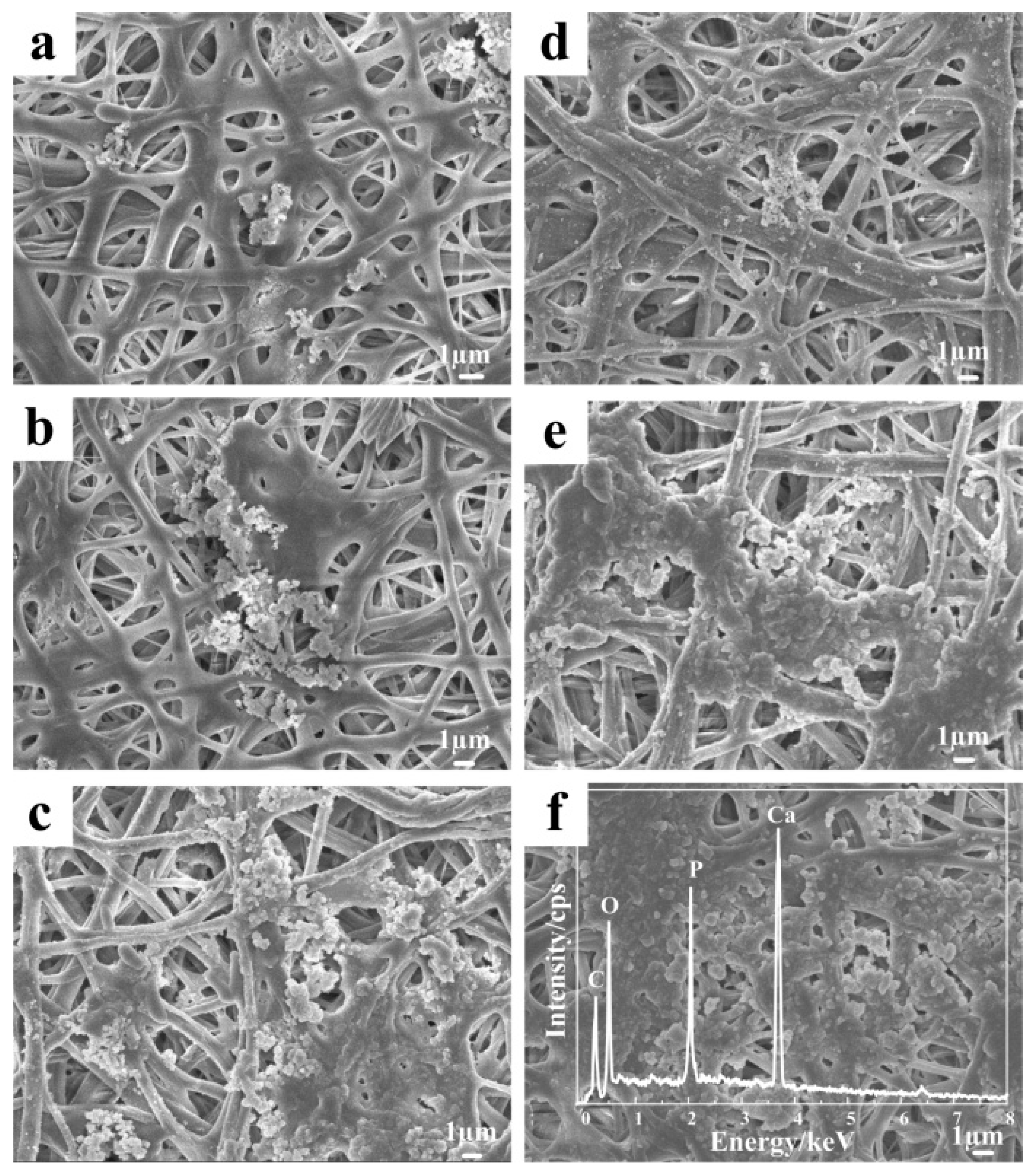
3.6. Mineralization of the Nanofibers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, M.; Wu, Y.S.; Kan, E.C.; Fan, J. Breathable and flexible piezoelectric ZnO@PVDF fibrous nanogenerator for wearable applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.Z.; Xue, H.L.; Li, L.L.; Dou, Y.L.; Wu, Z.N.; Zhang, P.P. Fabrication and morphology study of electrospun cellulose acetate/polyethylenimine nanofiber. Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 2889–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.A.; Yang, Y.; Buffington, A.N.; Romero, F.N.; Green, M.D. Preparation and characterization of crosslinked electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous membranes. Polymer 2018, 134, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, N.; Zainal, A. Cellulose acetate electrospun nanofibrous membrane: fabrication, characterization, drug loading and antibacterial properties. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2016, 39, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Ortega, M.; Nájera-Luna, A.; Rodríguez-Félix, D.; Encinas, J.C.; Rodriguez-Felix, F.; Romero, J.; Herrera-Franco, P.J. Preparation, characterization and release of amoxicillin from cellulose acetate and poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) coaxial electrospun fibrous membranes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1772–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Jeon, H.; Ryu, W. Direct modulus measurement of single composite nanofibers of silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 122, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupančič, Š.; Sinha-Ray, S.; Sinha-Ray, S.; Kristl, J.; Yarin, A.L. Long-term sustained ciprofloxacin release from pmma and hydrophilic polymer blended nanofibers. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 13, 295–305. [Google Scholar]
- Zupančič, Š.; Sinha-Ray, S.; Sinha-Ray, S.; Kristl, J.; Yarin, A.L. Controlled release of ciprofloxacin from core–shell nanofibers with monolithic or blended core. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Guo, Z.Z.; Xue, B.; Zhou, C.R. Fabrication of hydroxyapatite nanofiber via electrospinning as a carrier for protein. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, V.; Gloria, A.; Raucci, M.G.; De Santis, R.; Ambrosio, L. Bio-inspired composite and cell instructive platforms for bone regeneration. Int. Mater. Rev. 2012, 57, 256–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, F.A.; Kanjwal, M.A.; Macossay, J.; Barakat, N.A.M.; Kim, H.Y. A simple approach for synthesis, characterization and bioactivity of bovine bones to fabricate the polyurethane nanofiber containing hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Express Polym. Lett. 2012, 6, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Feng, Z.Q.; Wang, T.; Ren, Z.Z.; Ma, S.S.; Wu, J.H.; Sun, D.P. A novel fluffy hydroxylapatite fiber scaffold with deep interconnected pores designed for three-dimensional cell culture. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.H.; Cui, Z.X.; Wang, Q.T.; Liu, Q.; Liu, C.T. Biomimetic composite scaffolds based on mineralization of hydroxyapatite on electrospun poly (ɛ-caprolactone)/nanocellulose fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 143, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.X.; Huang, C.; Jin, X.Y.; Ke, Q.F. An electrospun poly (ε-caprolactone) nanocomposite fibrous mat with a high content of hydroxyapatite to promote cell infiltration. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 25228–25235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanir, T.E.; Hasirci, V.; Hasirci, N. Electrospinning of chitosan/poly(lactic acid–co–glycolic acid)/hydroxyapatite composite nanofibrous mats for tissue engineering applications. Polym. Bull. 2014, 71, 2999–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.M.; Asran, A.S.; Michler, G.H.; Simon, P.; Kim, J.S. Electrospun PVA/HAp nanocomposite nanofibers: biomimetics of mineralized hard tissues at a lower level of complexity. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2008, 3, 046003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, E.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.; Yang, S.Y.; Yang, D.; Yang, K.; Lee, J.; Shin, J.; Yang, H.S.; Ryu, W.; Cho, S.W. Electrospun Silk Fibroin Nanofibrous Scaffolds with Two-Stage Hydroxyapatite Functionalization for Enhancing the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2018, 10, 7614–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Li, S.; Wang, D.L.; Han, X.; Lai, X.L. Fabrication of Collagen/HAP Electrospun Scaffolds with Perfect HAP Nanorods Along Nanofiber Orientation. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2018, 10, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardelli, G.; Chiono, V.; Vozzi, G.; Pracella, M.; Ahluwalia, A.; Barbani, N.; Cristallini, C.; Glusti, P. Blends of poly-(ε-caprolactone) and polysaccharides in tissue engineering applications. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.N.; Wang, J.N.; Liu, X.Q.; Xiong, X.P.; Liu, H.Q. Biomimetic growth of hydroxyapatite on phosphorylated electrospun cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Electrospun porous cellulose acetate fibers from volatile solvent mixture. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 2291–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendouli, S.; Sobti, N.; Bensouissi, A.; Avci, A.; Eskizeybek, V.; Achour, S. Modification of cellulose acetate nanofibers with PVP/Ag addition. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2014, 28, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapountzi, E.; Braiek, M.; Chateaux, J.F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Lagarde, F. Recent advances in electrospun nanofiber interfaces for biosensing devices. Sensors 2017, 17, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Zhang, X.; Nishimoto, S.; Liu, Z.Y.; Tryk, D.A.; Murakami, T.; Fujishima, A. Large-scale fabrication of Ag nanoparticles in PVP nanofibres and net-like silver nanofibre films by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 075605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.B.; Li, Z.Y.; Hong, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Qiu, S.L.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. Influence of solvents on the formation of ultrathin uniform poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) nanofibers with electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. Part B 2004, 42, 3721–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsekova, P.B.; Spasova, M.G.; Manolova, N.E.; Markova, N.D.; Rashkov, I.B. Electrospun curcumin-loaded cellulose acetate/polyvinylpyrrolidone fibrous materials with complex architecture and antibacterial activity. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Li, P.; Hao, S.; Yang, H.; Lan, Z. A polyblend electrolyte (PVP/PEG+ KI+ I2) for dye-sensitized nanocrystalline TiO2 solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 5334–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Tong, Y.; Liu, S. Fabrication of well-aligned PPV/PVP nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 991–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Saleemi, S.; Khatri, Z.; Abro, M.I.; Kim, J.S. Co-electrospun poly (ɛ-caprolactone)/cellulose nanofibers-fabrication and characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Fang, X.; Zhang, X.F.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Li, B.; Ma, X.C. Cellulose acetate–poly (N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) blend membrane for pervaporation separation of methanol/MTBE mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 64, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; White, K.; Yu, D.G.; Zhao, X.Y. Sustained-release multiple-component cellulose acetate nanofibers fabricated using a modified coaxial electrospinning process. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Mao, H.; Yu, D.G.; Williams, G.R.; Jin, M. Highly stable coated polyvinylpyrrolidone nanofibers prepared using modified coaxial electrospinning. Fiber. Polym. 2014, 15, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Shanti, R.; Morris, E. Characterization of conducting cellulose acetate based polymer electrolytes doped with “green” ionic mixture. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.H.; Ki, S.J.; Jeon, J.H.; Che, H.L.; Park, I.K.; Kee, C.D.; Oh, I.K. Electroactive bio-composite actuators based on cellulose acetate nanofibers with specially chopped polyaniline nanoparticles through electrospinning. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 87, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.N.; Kang, M.; Sivaiah, K.; Ravi, M.; Ratnakaram, Y.C. Enhanced electrical properties of polyethylene oxide (PEO)+ polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP): Li+ blended polymer electrolyte films with addition of Ag nanofiller. Ionics 2016, 22, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Ortega, M.M.; Montaño-Figueroa, A.G.; Rodríguez-Félix, D.E.; Munive, G.T.; Herrera-Franco, P.J. Amoxicillin embedded in cellulose acetate-poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) fibers prepared by coaxial electrospinning: Preparation and characterization. Mater. Lett. 2012, 76, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazilevsky, A.V.; Yarin, A.L.; Megaridis, C.M. Co-electrospinning of core− shell fibers using a single-nozzle technique. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2311–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.F.; Rahman, A.; Zhou, Z.; Pelot, D.D.; Sinha-Ray, S.; Chen, B.; Payne, S.; Yarin, A.L. Electrospinning core-shell nanofibers for interfacial toughening and self-healing of carbon-fiber/epoxy composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.C.; Fang, D.W.; Wang, N.N.; Jiang, S.; Nie, J.; Yu, Q.; Ma, G.P. Preparation of PVDF/PVP core–shell nanofibers mats via homogeneous electrospinning. Polymer 2014, 55, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Y.; Fang, D.W.; Song, G.Q.; Nie, J.; Chen, B.L.; Ma, G.P. Fabrication of core–shell nanofibers by single capillary electrospinning combined with vapor induced phase separation. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 2917–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.L.; Li, D.W.; He, J.; Liu, Y.Y.; Ahmad, F.; Liu, Y.L.; Deng, X.D.; Ye, Y.J.; Yin, D.C. A novel layer-structured scaffold with large pore sizes suitable for 3D cell culture prepared by near-field electrospinning. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 86, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzaoui, K.; Lamhamdi, A.; Mejdoubi, E.M.; Berrahah, M.; Hammouti, B.; Elidrissi, A.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Al-Deyab, S.S. Synthesis and characterization of composite based on cellulose acetate and hydroxyapatite application to the absorption of harmful substances. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Cui, X.J.; Kao, Y.B.; Wang, H.Y.; Wen, J.H. Elecrtospinning PTMC/Gt/OA-HA composite fiber scaffolds and the biocompatibility with mandibular condylar chondrocytes. Colloids Surf. A 2016, 499, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
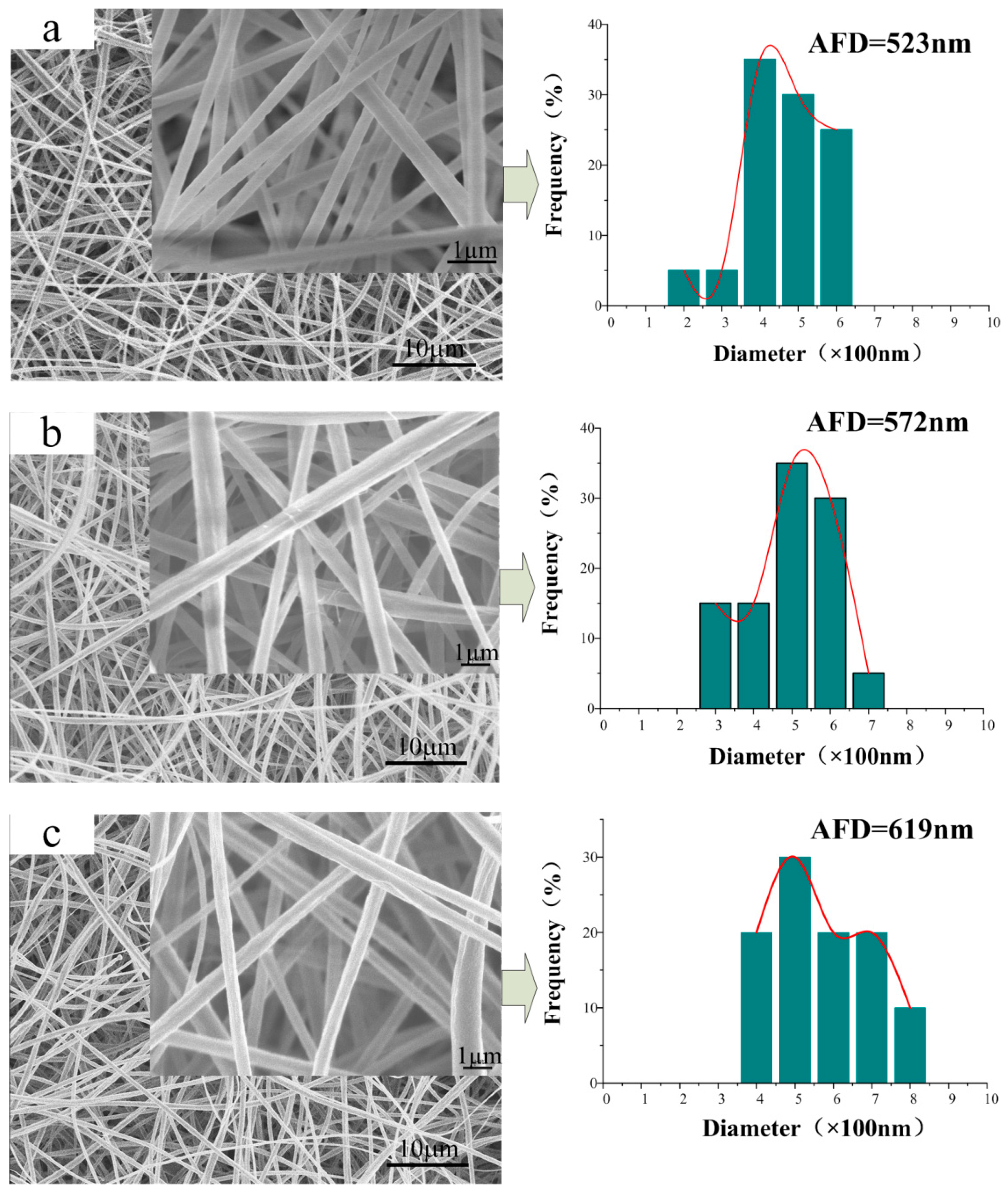
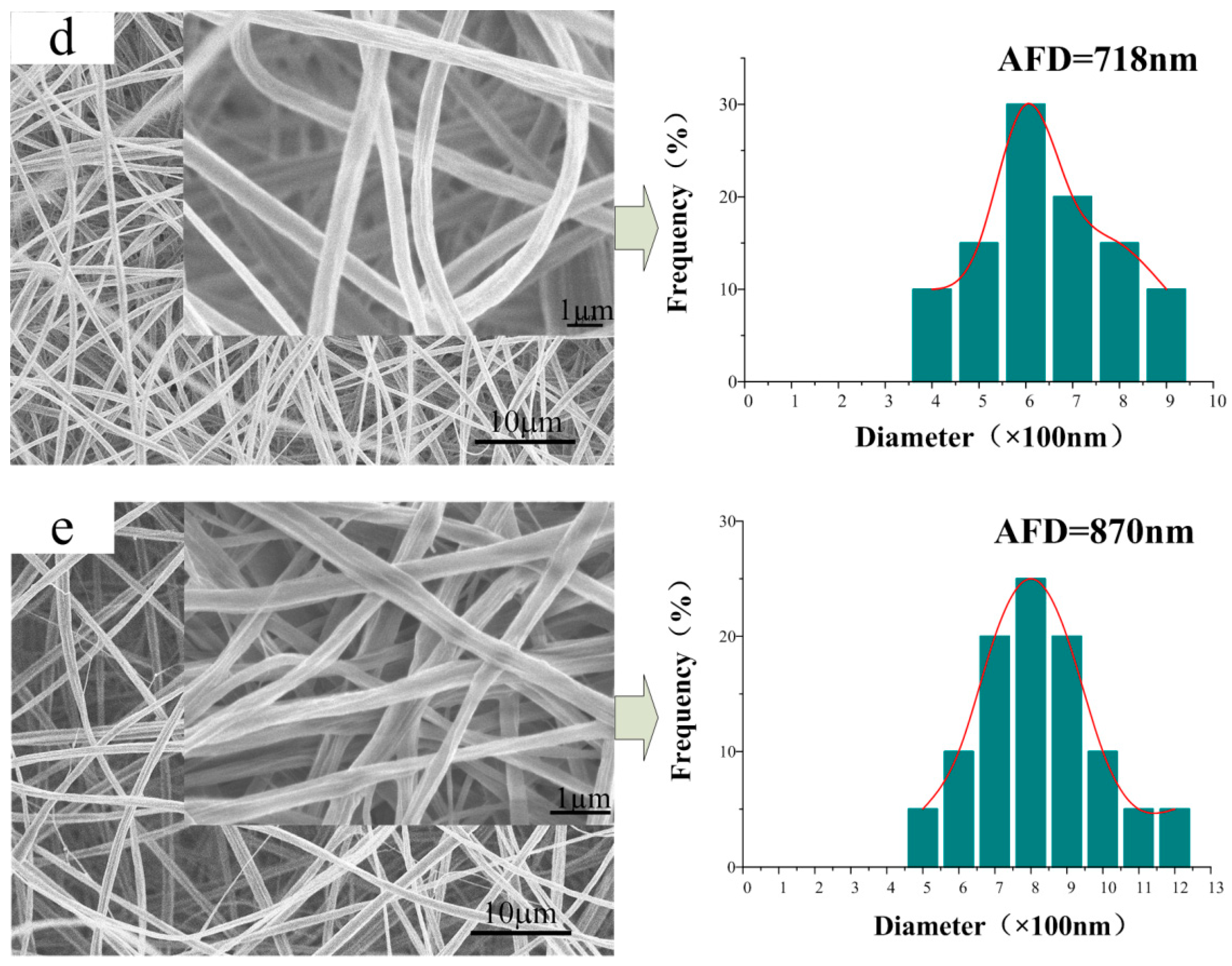
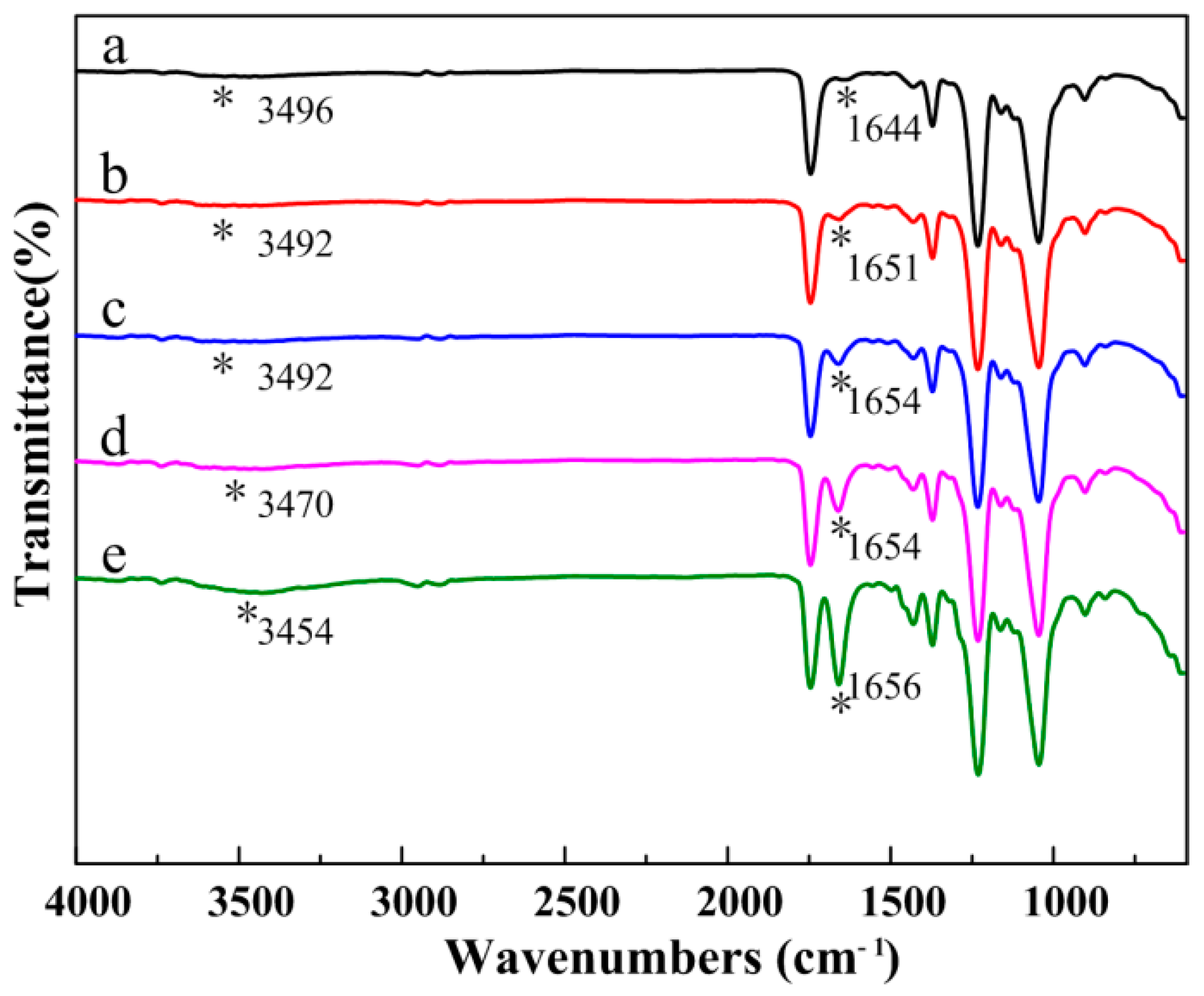
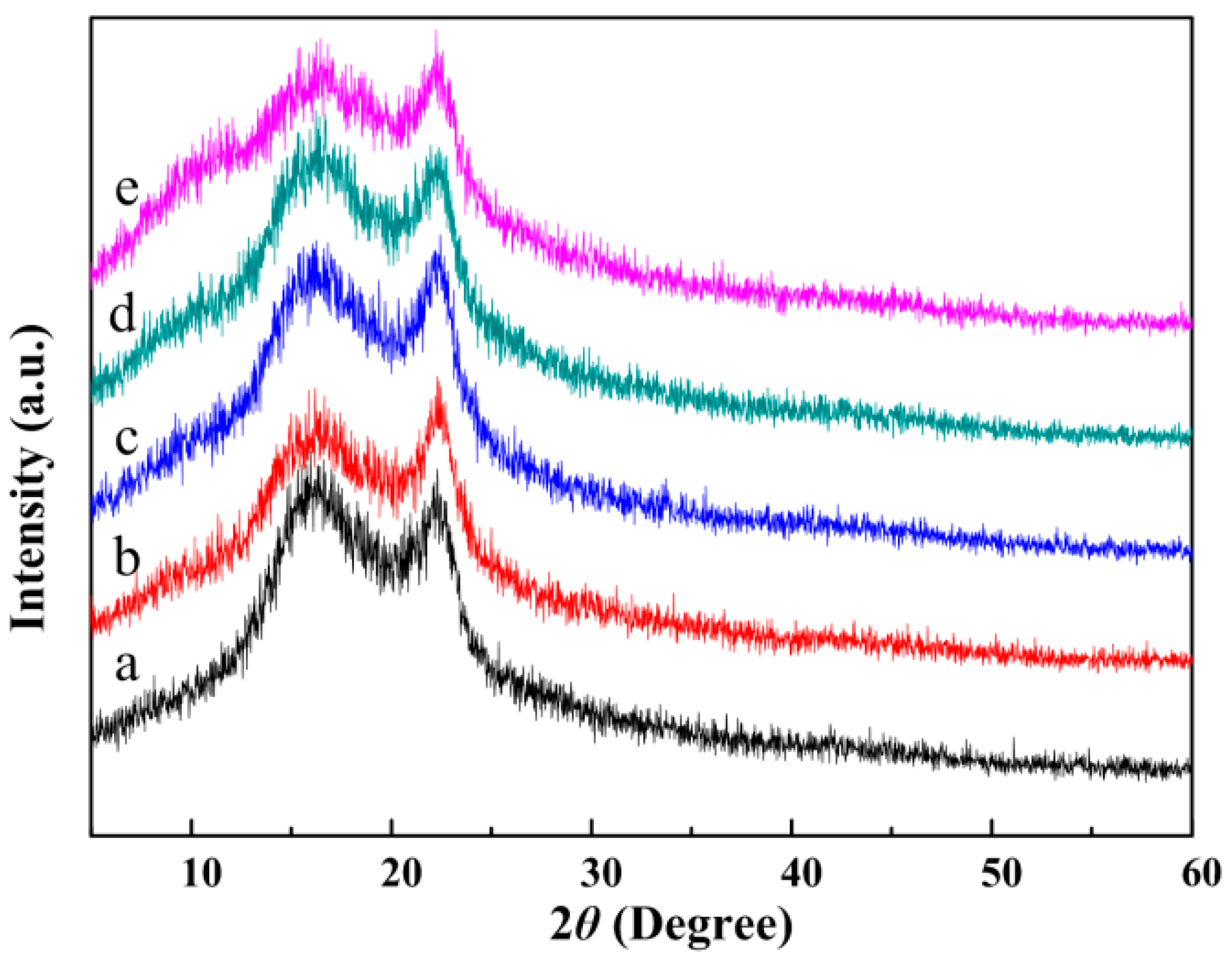
| Sample | CA Content (%) | PVP Content (%) | Acetone/H2O Mass (g) | Conductivity (mS/cm) | Shear Viscosity (mPa·s) | Surface Tension (mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 10 | 0 | 25.5/4.5 | 24.4 | 270 | 34.20 |
| CA/0.5% PVP | 10 | 0.5 | 25.5/4.5 | 23.6 | 311 | 34.10 |
| CA/1% PVP | 10 | 1 | 25.5/4.5 | 22.0 | 321 | 33.93 |
| CA/2% PVP | 10 | 2 | 25.5/4.5 | 16.3 | 335 | 33.76 |
| CA/5% PVP | 10 | 5 | 25.5/4.5 | 11.5 | 363 | 33.36 |
| Sample | Tm (°C) | Tg (°C) | Ti (°C) | Td1 (°C) | Td2 (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 231.89 | 188.28 | 267.43 | 365.21 | - |
| CA/0.5% PVP | 231.84 | 189.31 | 267.12 | 378.35 | 428.27 |
| CA/1% PVP | 231.79 | 193.37 | 269.68 | 378.45 | 434.22 |
| CA/2% PVP | 231.58 | 207.31 | 269.54 | 379.36 | 434.26 |
| CA/5% PVP | 229.62 | 207.75 | 270.85 | 375.38 | 434.20 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, H.; Dou, Y. Biomimetic Growth of Hydroxyapatite on Electrospun CA/PVP Core–Shell Nanofiber Membranes. Polymers 2018, 10, 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10091032
Hou J, Wang Y, Xue H, Dou Y. Biomimetic Growth of Hydroxyapatite on Electrospun CA/PVP Core–Shell Nanofiber Membranes. Polymers. 2018; 10(9):1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10091032
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Jiazi, Yihuan Wang, Hailong Xue, and Yanli Dou. 2018. "Biomimetic Growth of Hydroxyapatite on Electrospun CA/PVP Core–Shell Nanofiber Membranes" Polymers 10, no. 9: 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10091032
APA StyleHou, J., Wang, Y., Xue, H., & Dou, Y. (2018). Biomimetic Growth of Hydroxyapatite on Electrospun CA/PVP Core–Shell Nanofiber Membranes. Polymers, 10(9), 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10091032





