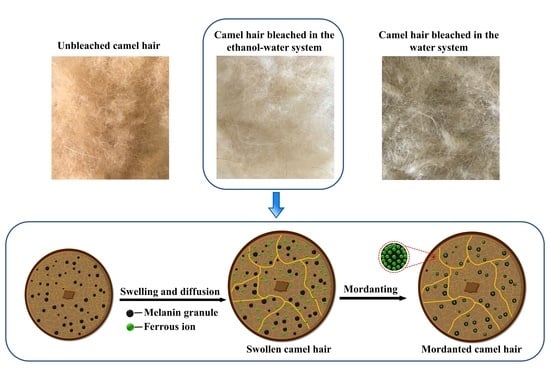
Protective Bleaching of Camel Hair in a Neutral Ethanol–Water System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
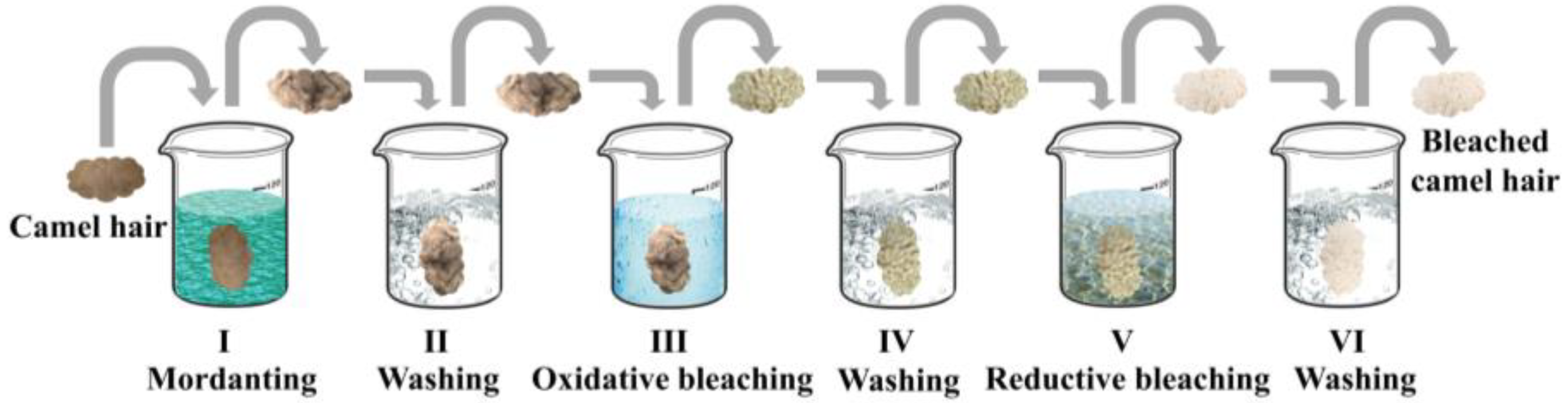
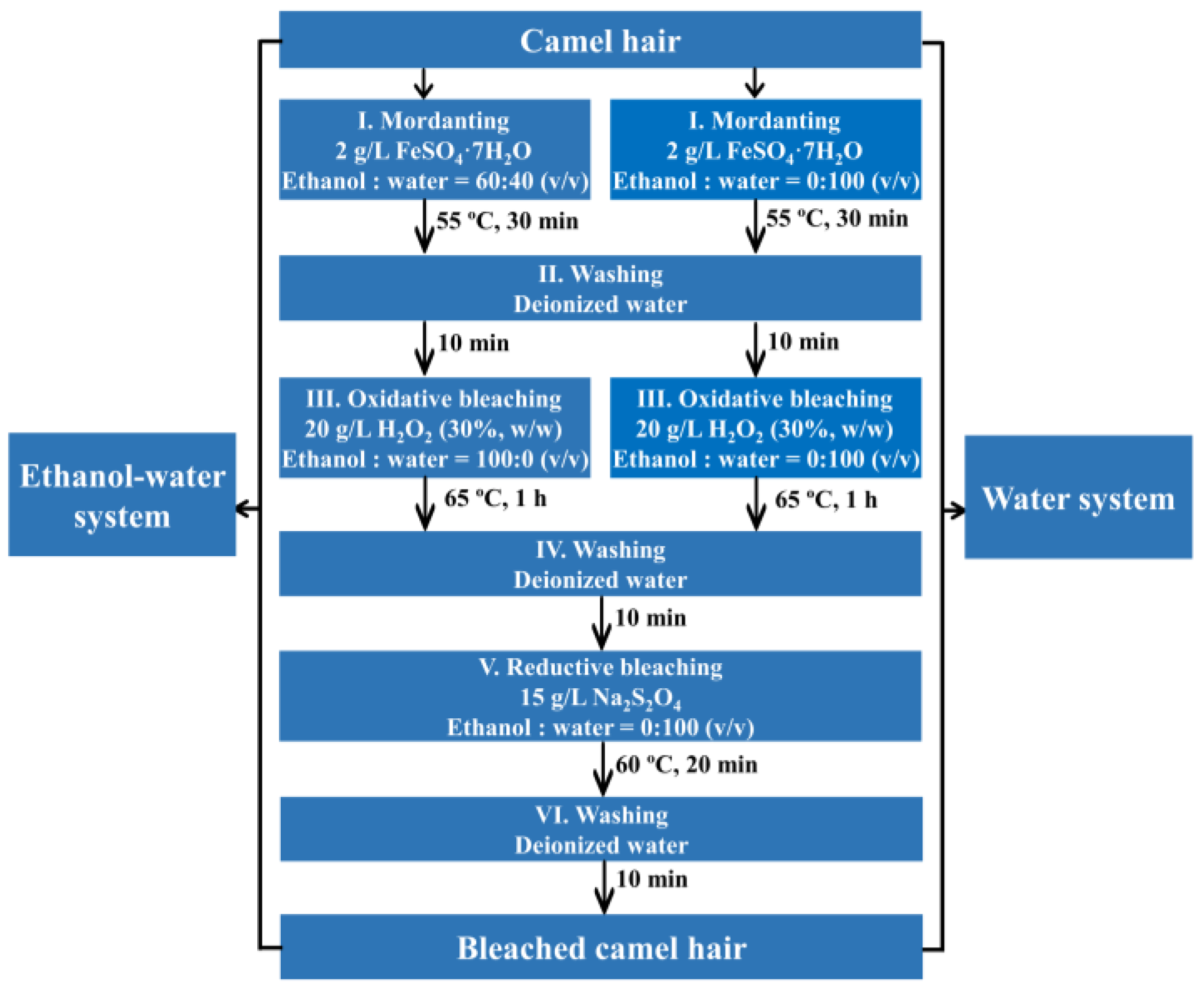
2.2. Bleaching
2.2.1. Mordanting
2.2.2. Oxidative Bleaching
2.2.3. Reductive Bleaching
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Weight Loss
2.3.2. Degree of Whiteness
2.3.3. Mechanical Properties
2.3.4. Swelling Ratio
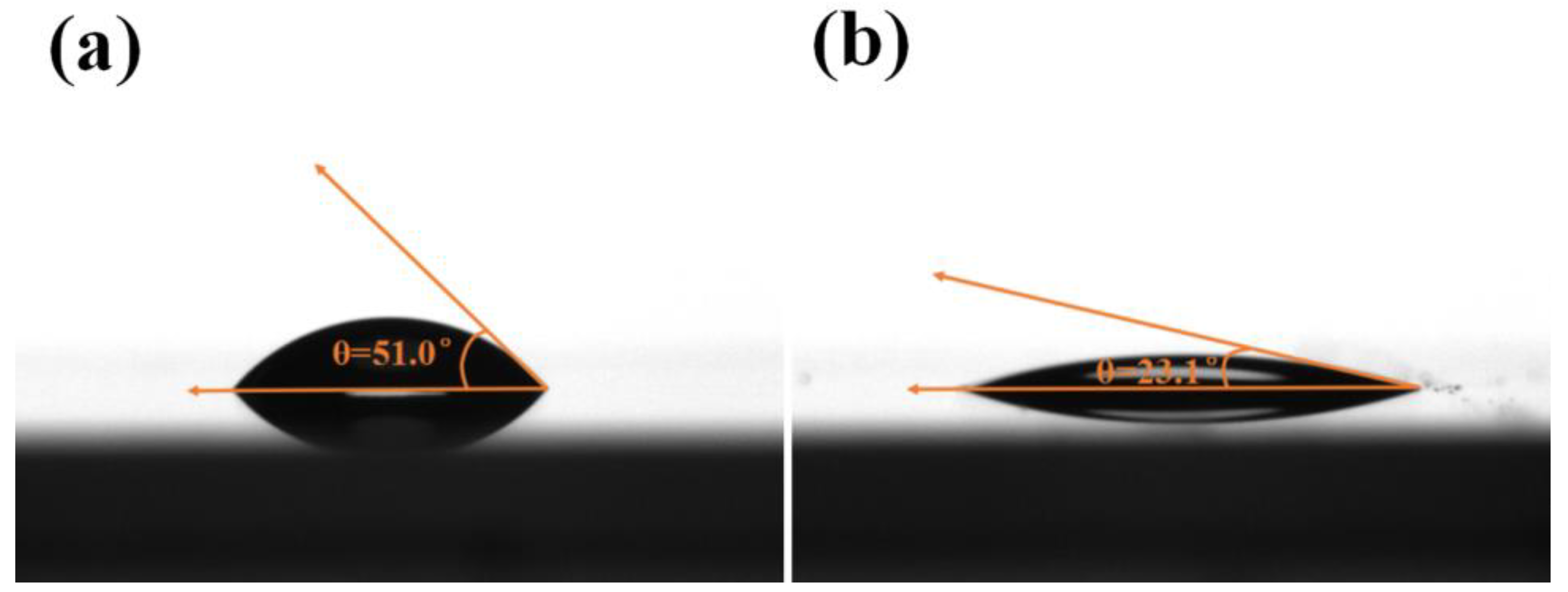
2.3.5. Contact Angles
2.3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.3.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.3.9. X-ray Diffraction
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Degree of Whiteness and Weight Loss
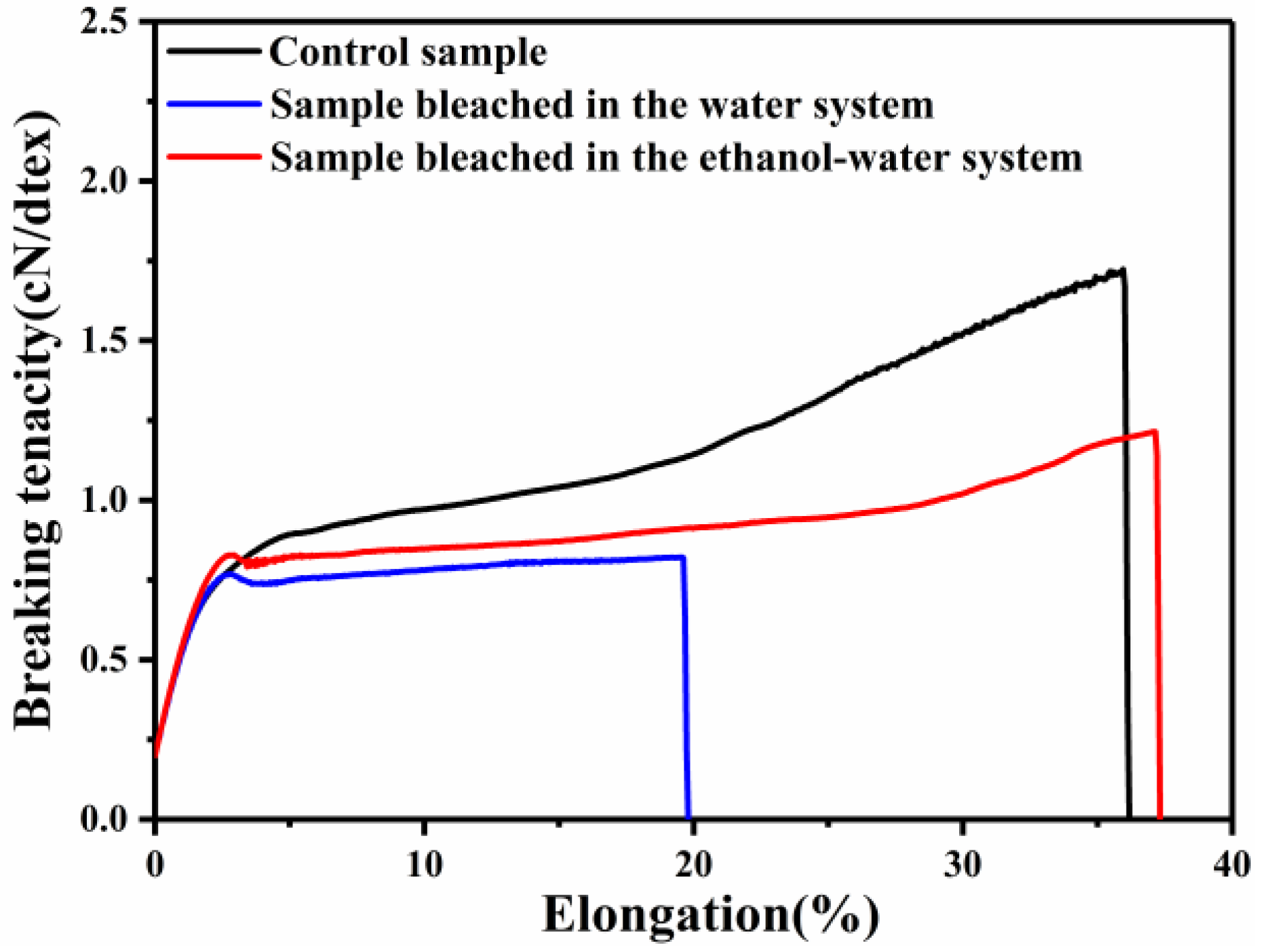
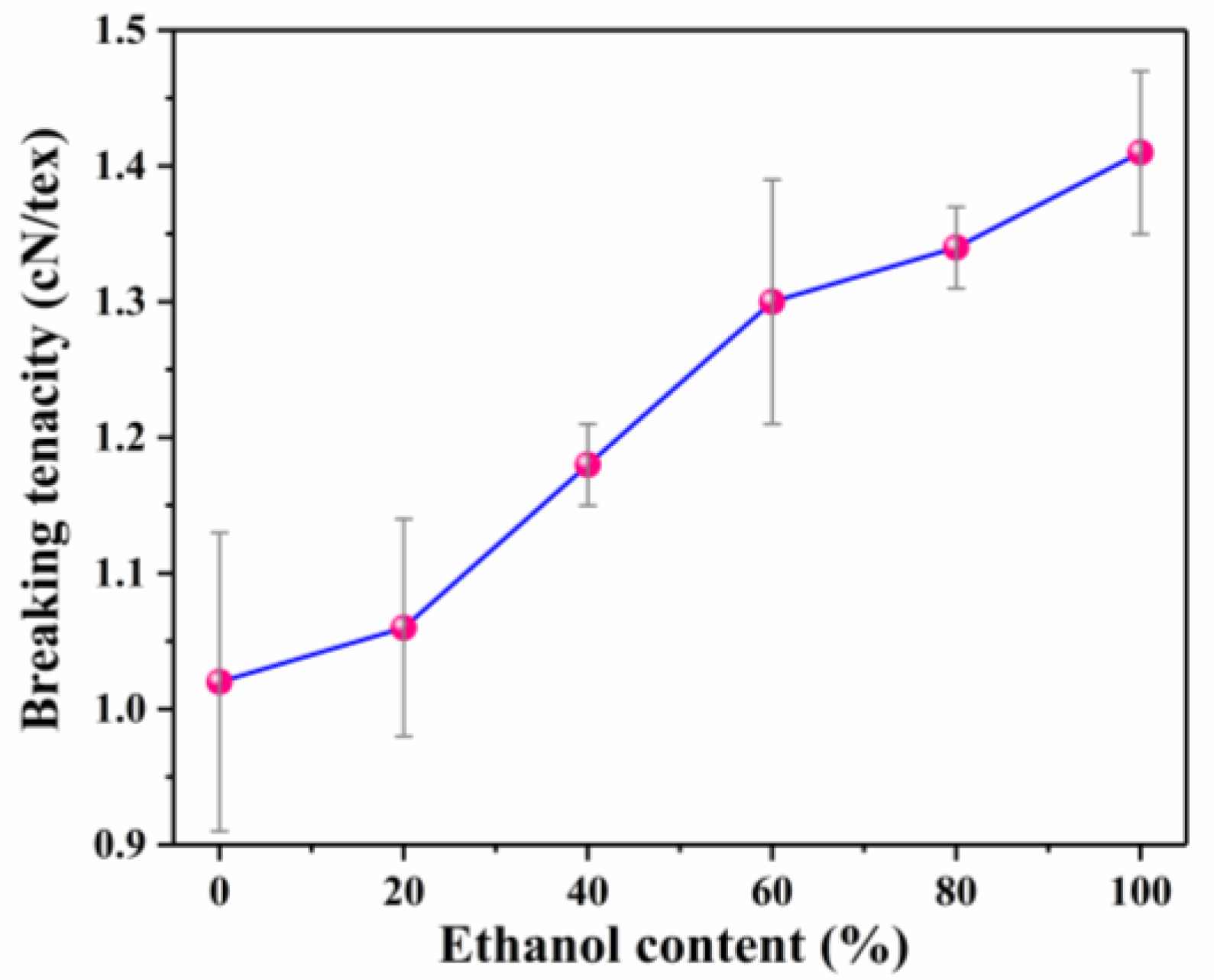
3.2. Mechanical Properties
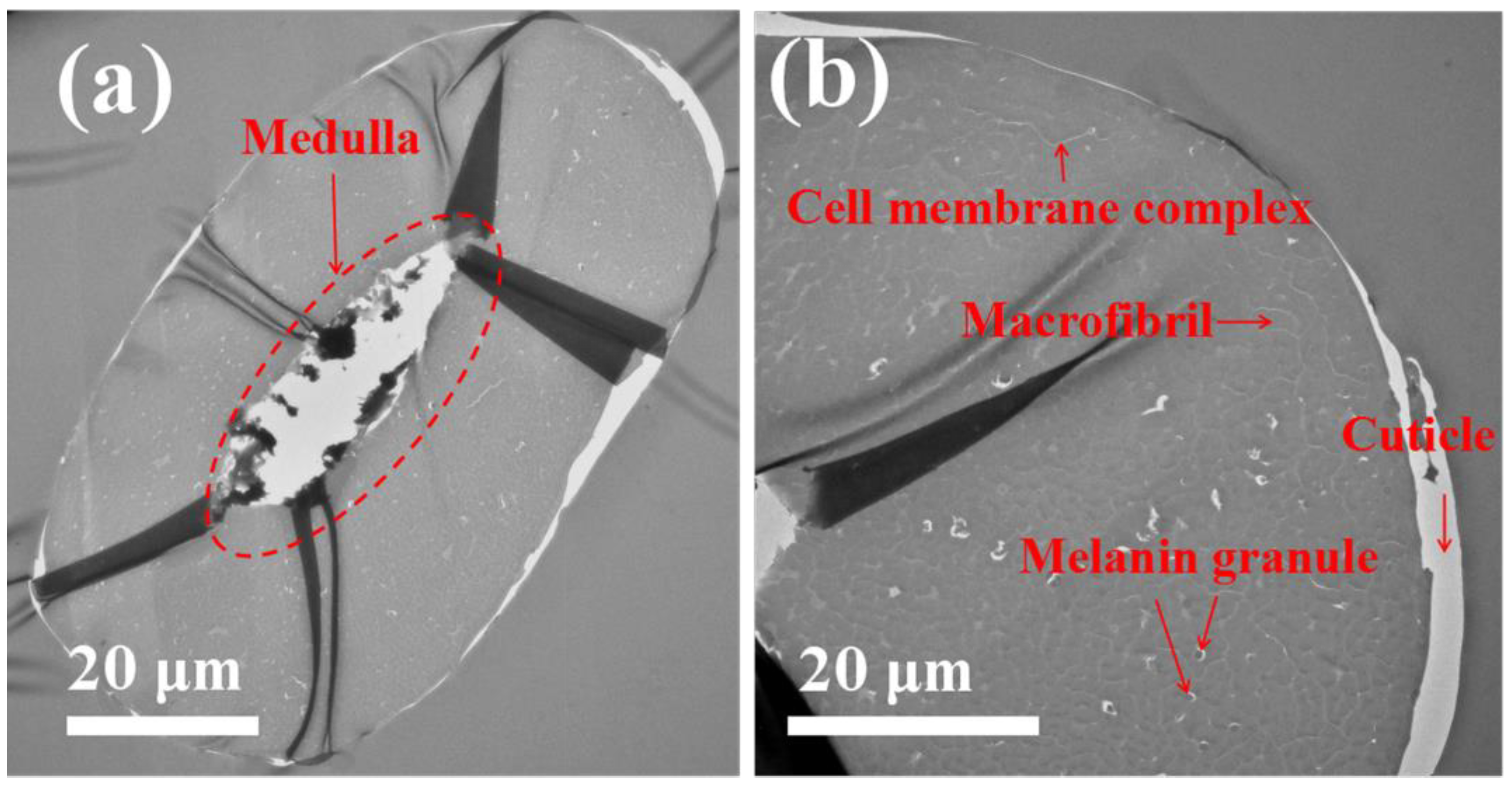
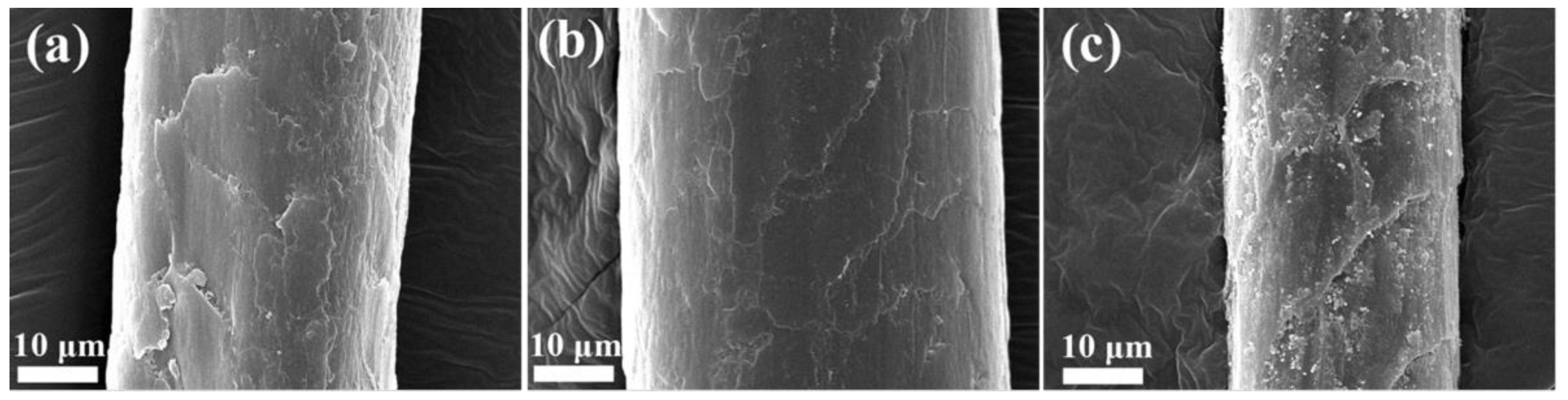
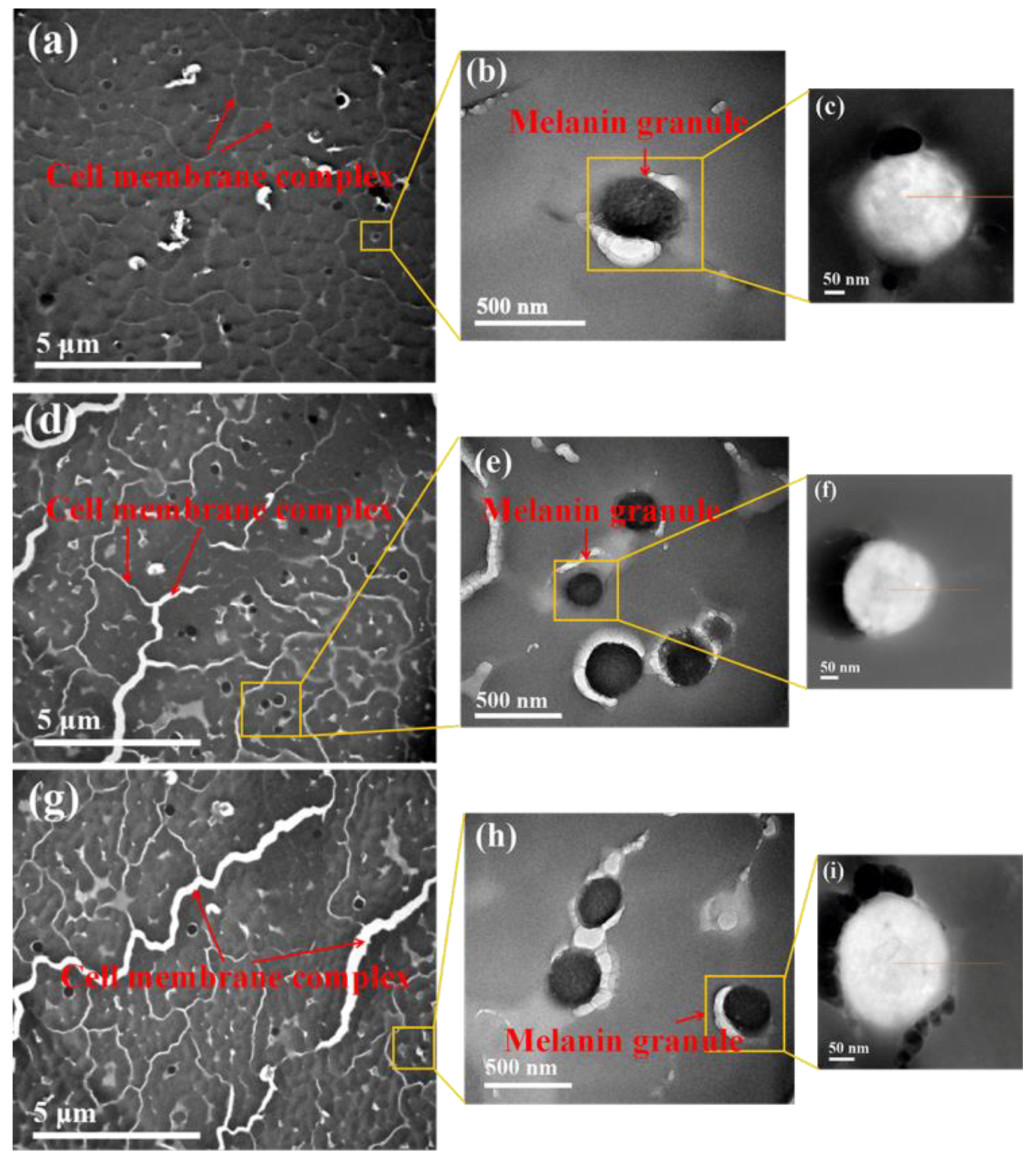
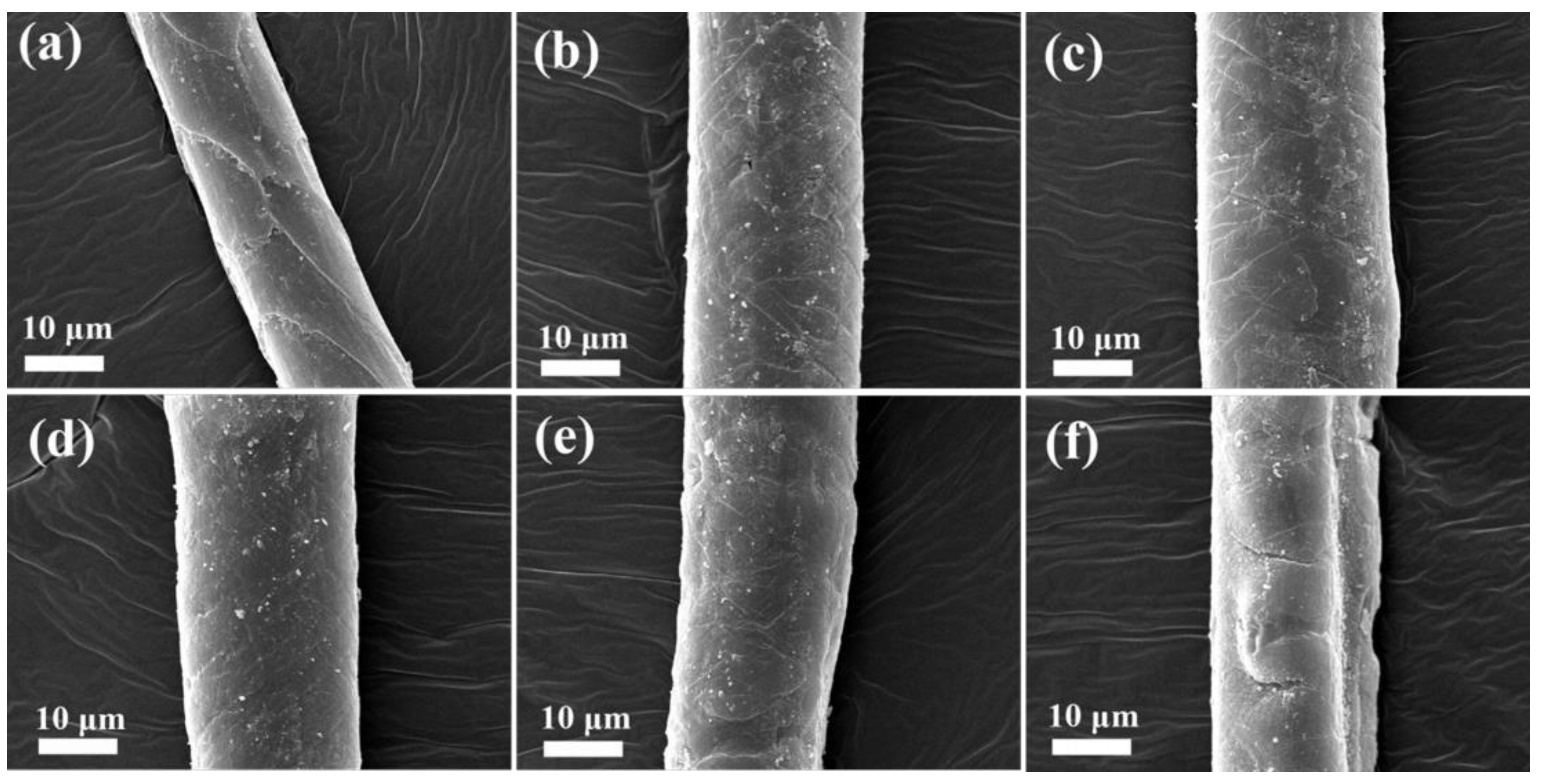
3.3. SEM
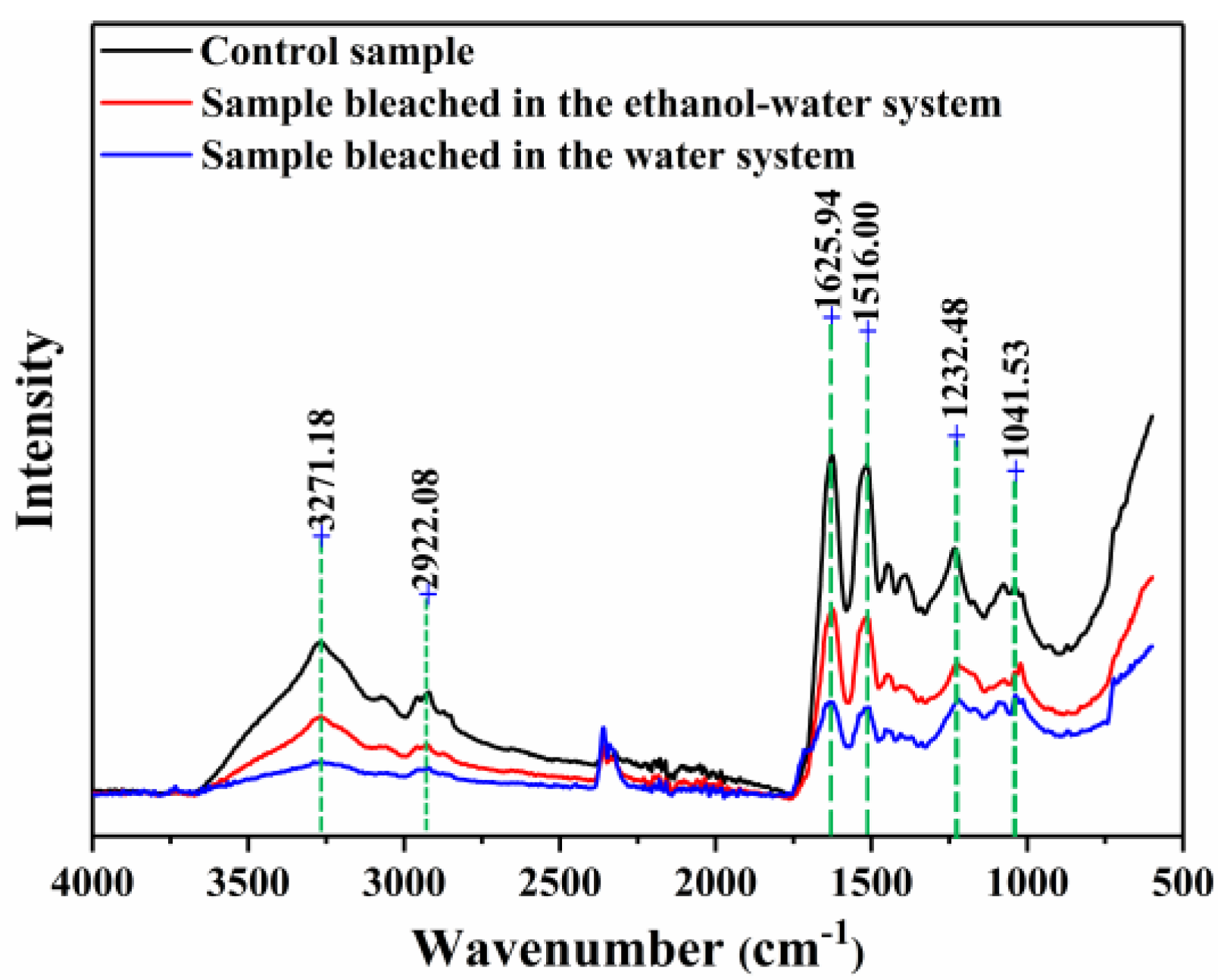
3.4. FTIR
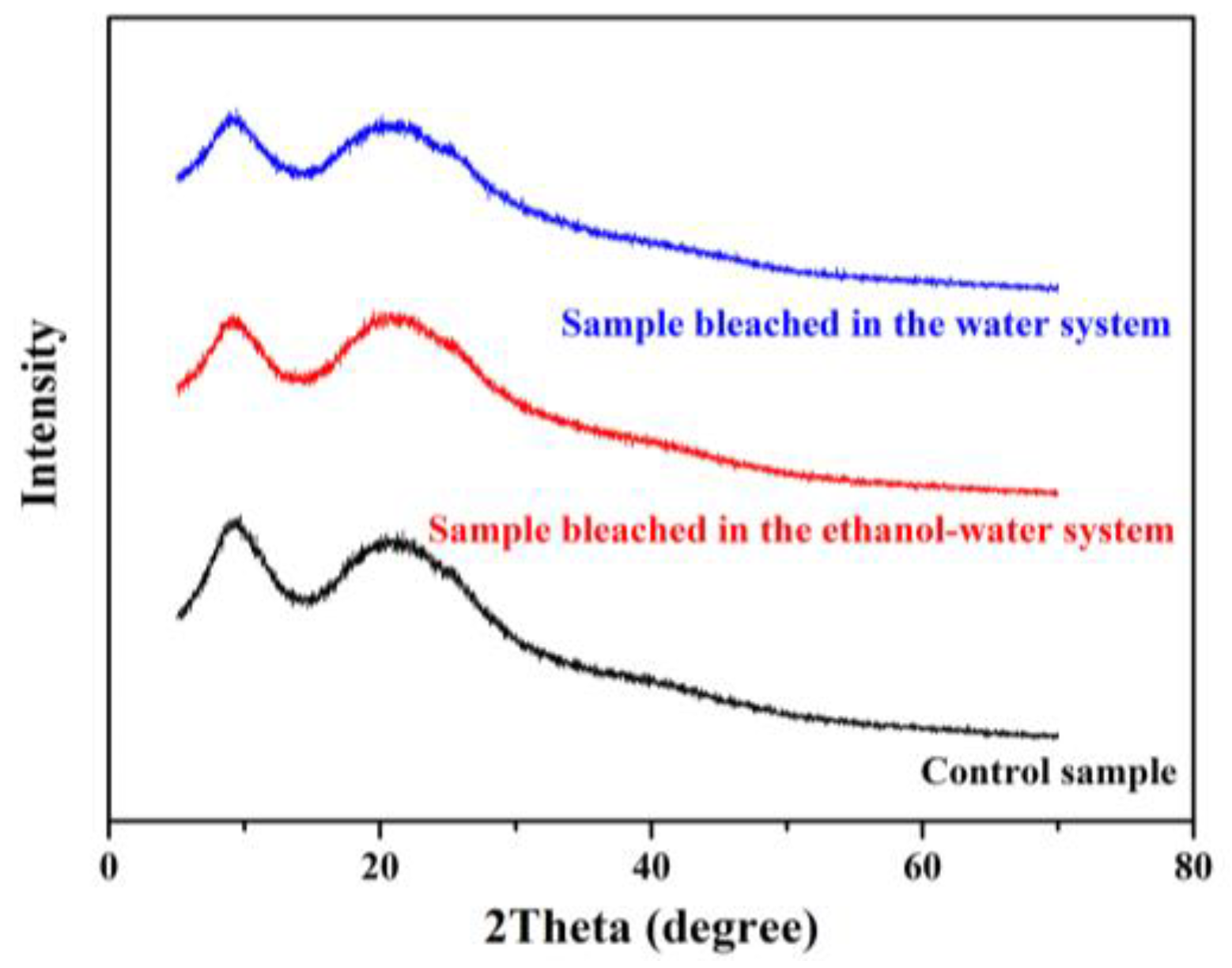
3.5. XRD
3.6. Effects of Ethanol on Mordanting
3.7. Effects of Ethanol on Oxidative Bleaching
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, A.; Pant, S. Studies on camel hair—Merino wool blended knitted fabrics. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2013, 38, 317–319. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Gong, J.; Zhang, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, J. Preparation of biocolorant and eco-dyeing derived from polyphenols based on laccase-catalyzed oxidative polymerization. Polymers 2018, 10, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-W.; Guan, J.-P.; Chen, G.; Yang, X.-H.; Tang, R.-C. Adsorption and flame retardant properties of bio-based phytic acid on wool fabric. Polymers 2016, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Yu, W.; Xu, W.; Cui, W.; Shen, X. Effects of corona discharge treatment on the surface properties of wool fabrics. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 207, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millington, K.R.; King, A.L.; Hatcher, S.; Drum, C. Whiter wool from fleece to fabric. Color. Technol. 2011, 127, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khishigsuren, A.; Nakajima, M.; Takahashi, M. Effects of ferrous mordanting on bleaching of camel hair. Text. Res. J. 2001, 71, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porubská, M.; Hanzlíková, Z.; Braniša, J.; Kleinová, A.; Hybler, P.; Fülöp, M.; Ondruška, J.; Jomová, K. The effect of electron beam on sheep wool. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 111, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.G.; Chen, D.Z.; Wang, X.G. Surface modification and bleaching of pigmented wool. Text. Res. J. 2001, 71, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, S.M.; Safi, S.; Moghadam, M.K.; Zamani, M. Bleaching of black pigmented karakul wool fibers using copper sulfate as catalyst. Fiber Polym. 2014, 15, 2297–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.L.; Hocker, H.; Schafer, K. Handle of bleached knitted fabric made from fine yak hair. Text. Res. J. 2000, 70, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifoglu, M.; Marmer, W.N.; Carr, C.M. Effect of urea on bleaching of wool with hydrogen-peroxide under alkaline and acidic conditions. Text. Res. J. 1989, 59, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; Takahashi, M.; Khishigsuren, A. Using sodium bisulfite as a rinsing auxillary in bleaching cashmere. Text. Res. J. 2002, 72, 51–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harizi, T.; Dhouib, S.; Msahli, S.; Sakli, F. Bleaching process investigation of tunisian dromedary hair. ISRN Text. 2013, 2013, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Mohammad, F.; Chen, G.Q.; Tang, R.C.; Xing, T.L. Enzymatic processing of natural fibres: White biotechnology for sustainable development. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 2256–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargunamani, D.; Selvakumar, N. A study on the effects of ozone treatment on the properties of raw and degummed mulberry silk fabrics. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 2644–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, C.; Fischer, U.; Hungerbühler, K. What is a green solvent? A comprehensive framework for the environmental assessment of solvents. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, A.E.; Plevin, R.J.; Turner, B.T.; Jones, A.D.; O’Hare, M.; Kammen, D.M. Ethanol can contribute to energy and environmental goals. Science 2006, 311, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldemberg, J. Ethanol for a sustainable energy future. Science 2007, 315, 808–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Cheng, J. Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.M.; Koranyi, T.I.; Boot, M.D.; Hensen, E.J.M. Ethanol as capping agent and formaldehyde scavenger for efficient depolymerization of lignin to aromatics. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4941–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, F.; Periolatto, M.; Rovero, G.; Giansetti, M. Alcohol-assisted dyeing processes: A chemical substitution study. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, D.; Xu, W.; Cao, G. Examination of the dyeing properties of pigment printing fabrics in a water-ethanol mixed solvent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, F.; Periolatto, M. Glycerol in comparison with ethanol in alcohol-assisted dyeing. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 33, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hurren, C.J.; Wang, X.G. Comparative analysis of two selective bleaching methods on alpaca fibers. Fiber Polym. 2003, 4, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahtiyari, M.I.; Duran, K. A study on the usability of ultrasound in scouring of raw wool. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 41, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, M.F.; Liotier, P.J.; Seveno, D.; Fuentes, C.; Van Vuure, A.; Drapier, S. Wetting and swelling property modifications of elementary flax fibres and their effects on the liquid composite molding process. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 97, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eva, A.P.; Csilla, C. Contact angle as function of surface roughness of different wood species. Surf. Interface 2017, 8, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Montazer, M.; Pajootan, E.; Lessan, F. Microbial trans-glutaminase enhances the physical and mechanical properties of depigmented wool. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxer, G.; Whewell, C.S. Adsorption of metal ions by naturally pigmented keratin fibres. J. Soc. Dyers Colour. 1953, 69, 83–84. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.L.; Hu, J.L.; Hui, D. Tensile-relaxation study of camel hair fiber at elastic stretching region: Analytical model and experiment. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2016, 91, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsobkallo, K.; Aksakal, B.; Darvish, D. Analysis of the contribution of the microfibrils and matrix to the deformation processes in wool fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, E168–E179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, B.M. A mechanical model for wool and other keratin fibers. Text. Res. J. 1969, 39, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crewther, W.G. The stress—Strain characteristics of animal fibers after reduction and alkylation. Text. Res. J. 1965, 35, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milczarek, P.; Zielinski, M.; Garcia, M.L. The mechanism and stability of thermal transitions in hair keratin. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1992, 270, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feughelman, M. A two-phase structure for keratin fibers. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feughelman, M.; Robinson, M.S. The relationship between some mechanical properties of single wool fibers and relative humidity1. Text. Res. J. 1967, 37, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feughelman, M. Natural protein fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 83, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.B.; Liu, Y.B.; Yang, S.T.; Liu, J.Z. Characterization of secondary structure transformation of stretched and slenderized wool fibers with ftir spectra. J. Eng. Fabr. Fibers 2008, 3, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Shen, X.L.; Xu, W.L. Effect of hydrogen peroxide treatment on the properties of wool fabric. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 10012–10016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.L.; Ke, G.Z.; Wu, J.H.; Wang, X.G. Modification of wool fiber using steam explosion. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 2168–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henchey, L.K.; Jochim, A.L.; Arora, P.S. Contemporary strategies for the stabilization of peptides in the alpha-helical conformation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, N.; Guo, Q.P. Blend films of natural wool and cellulose prepared from an ionic liquid. Cellulose 2010, 17, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzuhara, A. Analysis of internal structure changes in black human hair keratin fibers resulting from bleaching treatments using raman spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1047, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowley, S.R.; Fang, C.; Merrill-Skoloff, G.; Furie, B.C.; Furie, B. Protein disulfide isomerase secretion following vascular injury initiates a regulatory pathway for thrombus formation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dopieralski, P.; Ribas-Arino, J.; Anjukandi, P.; Krupicka, M.; Marx, D. Unexpected mechanochemical complexity in the mechanistic scenarios of disulfide bond reduction in alkaline solution. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukada, M.; Shiozaki, H.; Freddi, G.; Crighton, J.S. Graft copolymerization of benzyl methacrylate onto wool fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 64, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Z.; Zhai, Q.; Zhao, X.F.; Min, X.M.; Zhu, Q.H.; Li, J.H. Modified wool-iron biopolymer-based complex as an active heterogeneous decontamination photocatalyst. J. Energy Chem. 2016, 25, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeder, J.D.; Bishop, D.G.; Jones, L.N. Internal lipids of wool fibers. Text. Res. J. 1983, 53, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreplak, L.; Merigoux, C.; Briki, F.; Flot, D.; Doucet, J. Investigation of human hair cuticle structure by microdiffraction: Direct observation of cell membrane complex swelling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1547, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Yao, Y. Isolation, characterization of melanin derived from ophiocordyceps sinensis, an entomogenous fungus endemic to the tibetan plateau. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 113, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, G.; Li, L.; Tang, K.; Huang, K.; Feng, S.; Dong, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B. High-yield preparation of k-birnessite layered nanoflake. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 218, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Cheng, D. Component-dependent electrocatalytic activity of pdcu bimetallic nanoparticles for hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 246, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feughelman, M.; Snaith, J.W. The swelling of crystalline alpha-keratin by alcohols. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1964, 79, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Lee, T.R. Contact Angle and Wetting Properties; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Maestro, A.; Guzman, E.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G. Contact angle of micro- and nanoparticles at fluid interfaces. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 19, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrei, M.M.; Davoudi, M.; Chase, G.G.; Tafreshi, H.V. Effects of roughness on droplet apparent contact angles on a fiber. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 180, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.H.; Zhang, C.H.; Li, L.L.; Jiang, J. Iron terephthalate metal-organic framework: Revealing the effective activation of hydrogen peroxide for the degradation of organic dye under visible light irradiation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 148, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H.J.; Sedlak, D.L.; Lee, C. Ph-dependent reactivity of oxidants formed by iron and copper-catalyzed decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, A.L.; Doyle, F.M.; Sedlak, D.L. Kinetics and efficiency of H2O2 activation by iron-containing minerals and aquifer materials. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6454–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Jin, Z.H.; Li, T.L.; Zhang, H.; Gao, S. Preparation of spherical iron nanoclusters in ethanol-water solution for nitrate removal. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereck, A. Bleaching of pigmented speciality animal fibres and wool. Color. Technol. 1994, 24, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.A.; Darwish, A.A.; El-Shishtawy, R.M. Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on activated wool. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, A.N.; Xing, G.W.; Miller, C.J.; Waite, T.D. Fenton-like copper redox chemistry revisited: Hydrogen peroxide and superoxide mediation of copper-catalyzed oxidant production. J. Catal. 2013, 301, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.A.W.; Garrett, B.; Naqvi, K.R.; Fulop, A.; Godfrey, S.P.; Marsh, J.M.; Chechik, V. Mechanistic insights into the bleaching of melanin by alkaline hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunford, H.B. Oxidations of iron(ii)/(iii) by hydrogen peroxide: From aquo to enzyme. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 233, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhurst, H.A. Effect of organic substances on the γ-ray oxidation of ferrous sulfate. J. Chem. Phys. 1951, 19, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, C.; Sutherland, R.G.; Verrall, R.E. Cavitation-induced oxidation of aerated aqueous iron (2+) solutions in the presence of aliphatic alcohols. J. Phys. Chem. 1980, 84, 2920–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.Y.; Chen, Y.M.; James-Kracke, M.; Wixom, P.; Cheng, Y. Ethanol-induced cell death by lipid peroxidation in PC12 cells. Neurochem. Res. 1997, 22, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knecht, K.T.; Bradford, B.U.; Mason, R.P.; Thurman, R.G. In vivo formation of a free radical metabolite of ethanol. Mol. Pharmacol. 1990, 38, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
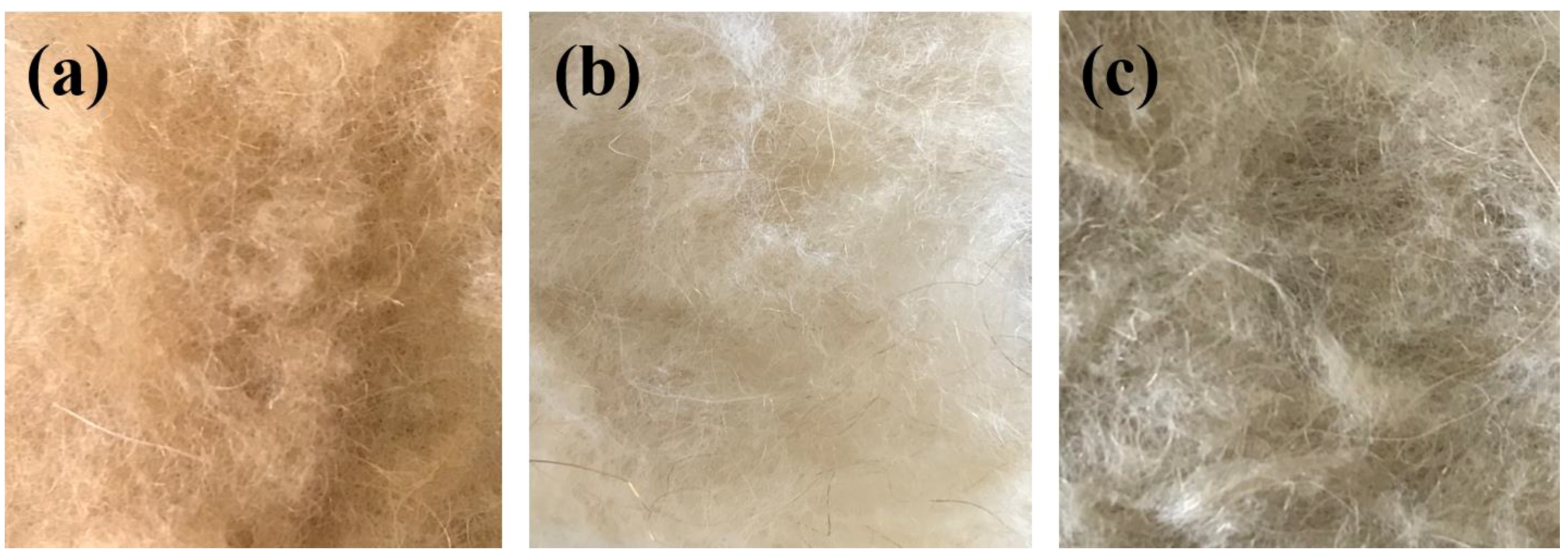



| Camel Hair | Degree of Whiteness | Whiteness Increase (%) | Weight Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control samples | 12.3 ± 0.2 | - | - |
| Samples bleached in the ethanol–water system | 32.4 ± 1.5 | 163.1 ± 0.3 | 10.1 ± 0.2 |
| Samples bleached in the water system | 19.0 ± 0.8 | 54.1 ± 0.2 | 9.1 ± 0.1 |
| Camel Hair | Breaking Tenacity (cN/dtex) | Minimum and Maximum of Breaking Tenacity (cN/dtex) | Breaking Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control sample | 1.65 ± 0.19 | 1.13/2.55 | 36.18 ± 4.03 |
| Sample bleached in the ethanol–water system | 1.24 ± 0.32 | 0.70/2.12 | 30.53 ± 11.12 |
| Sample bleached in the water system | 0.84 ± 0.22 | 0.48/1.24 | 16.74 ± 3.92 |
| System | Swelling Bath | Db (μm) | Da (μm) | Rs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 2 g/L FeSO4·7H2O Ethanol:water = 0:100 (v/v) | 21.29 ± 0.34 | 21.62 ± 0.55 | 1.02 ± 0.03 |
| Ethanol–water | 2 g/L FeSO4·7H2O Ethanol:water = 60:40 (v/v) | 23.15 ± 1.21 | 24.95 ± 1.34 | 1.14 ± 0.08 |
| Ethanol–water | 2 g/L FeSO4·7H2O Ethanol:water = 80:20 (v/v) | 23.70 ± 1.41 | 27.88 ± 1.38 | 1.20 ± 0.02 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, L.; Zhang, C.; Xu, W.; Zhu, K.; Wang, A.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W. Protective Bleaching of Camel Hair in a Neutral Ethanol–Water System. Polymers 2018, 10, 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070730
Xia L, Zhang C, Xu W, Zhu K, Wang A, Tian Y, Wang Y, Xu W. Protective Bleaching of Camel Hair in a Neutral Ethanol–Water System. Polymers. 2018; 10(7):730. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070730
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Liangjun, Chunhua Zhang, Wenfang Xu, Kundi Zhu, Aming Wang, Ye Tian, Yunli Wang, and Weilin Xu. 2018. "Protective Bleaching of Camel Hair in a Neutral Ethanol–Water System" Polymers 10, no. 7: 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070730
APA StyleXia, L., Zhang, C., Xu, W., Zhu, K., Wang, A., Tian, Y., Wang, Y., & Xu, W. (2018). Protective Bleaching of Camel Hair in a Neutral Ethanol–Water System. Polymers, 10(7), 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070730