Effect of Mold Opening Process on Microporous Structure and Properties of Microcellular Polylactide–Polylactide Nanocomposites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Compounds
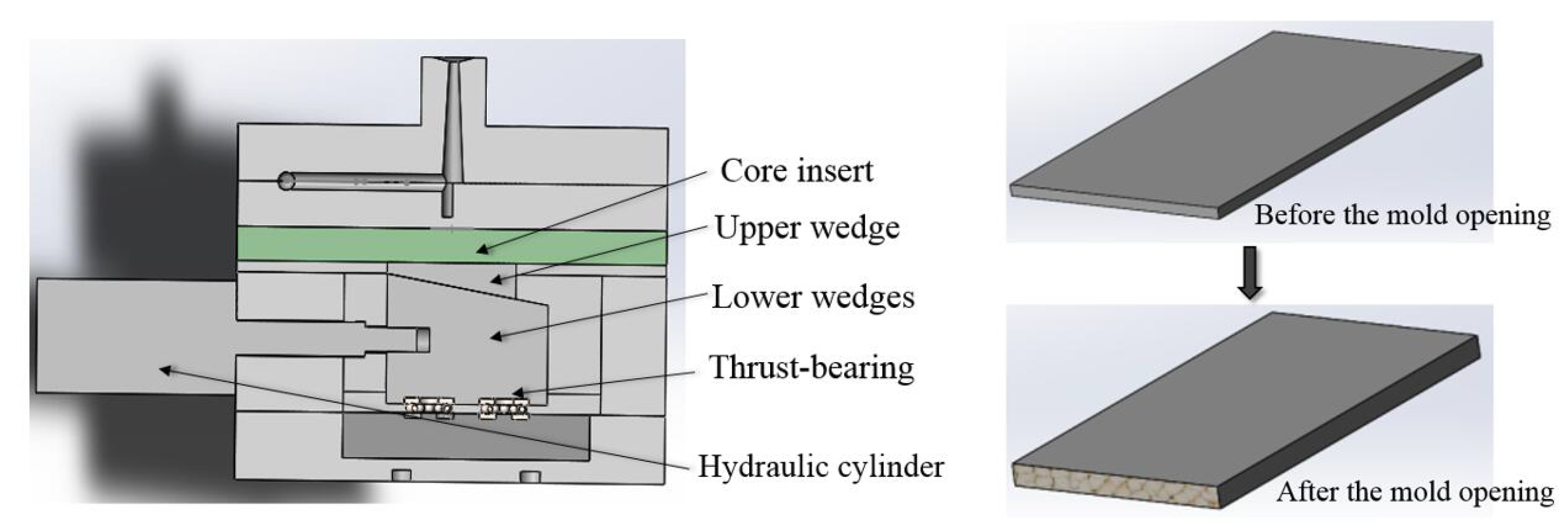
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Foam Characterization
2.5. Tensile Testing
2.6. Surface Quality Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cell Structure
3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.3. Surface Quality
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heino, A.; Naukkarinen, A.; Kulju, T. Characteristics of poly(l-)lactic acid suture applied to fascial closure in rats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 1996, 30, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyatma, N.E.; Copinet, A.; Lan, T. Mechanical and Barrier Properties of Biodegradable Films Made from Chitosan and Poly (Lactic Acid) Blends. J. Polym. Environ. 2004, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auras, R.; Harte, B.; Selke, S. An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 835–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schut, J.H. Foamed PLA shows promise in biodegradable meat trays. Polym.-Plast. Technol. 2007, 53, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J. Microcellular Injection Molding. Int. Polym. Process. 2011, 20, 202–214. [Google Scholar]
- Pantani, R.; Sorrentino, A.; Volpe, V. Foam injection molding of poly (lactic acid) with physical blowing agents. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 3098–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M. Processing technologies for poly (lactic acid). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 820–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameli, A.; Jahani, D.; Nofar, M. Processing and characterization of solid and foamed injection-molded polylactide with talc. J. Cell. Plast. 2013, 49, 351–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.S.; Park, C.B.; Kim, S.G. Reducing Material Costs with Microcellular/Fine-celled Foaming. J. Cell. Plast. 2007, 43, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahani, D.; Ameli, A.; Jung, P.U. Open-cell cavity-integrated injection-molded acoustic polypropylene foams. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, S.; Kramschuster, A.; Yang, L. Microcellular injection-molding of polylactide with chain-extender. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. 2009, 29, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameli, A.; Nofar, M.; Jahani, D. Development of high void fraction polylactide composite foams using injection molding: Crystallization and foaming behaviors. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofar, M.; Park, C.B. Poly (lactic acid) foaming. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1721–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, S.; Kramschuster, A.; Lee, J. Microcellular processing of polylactide–hyperbranched polyester–nanoclay composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 2732–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Chu, R.K.M.; Leung, S.N. A batch foaming visualization system with extensional stress-inducing ability. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Ohshima, M. Visual observation and numerical studies of polymer foaming behavior of polypropylene/carbon dioxide system in a core-back injection molding process. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Taki, K.; Ohshima, M. Visual observation and numerical studies of N2, vs. CO2, foaming behavior in core-back foam injection molding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2012, 52, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spörrer, A.N.J.; Altstädt, V. Controlling Morphology of Injection Molded Structural Foams by Mold Design and Processing Parameters. J. Cell. Plast. 2007, 43, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, P.; Fischer, M.; Kirschling, H. Versatility for mass production in MuCell injection moulding. Kunstst. Plast. Eur. 2005, 95, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Heim, H.P.; Tromm, M. General aspects of foam injection molding using local precision mold opening technology. Polymer 2015, 56, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Lee, J.W.S.; Naguib, H.E. Effect of Processing Parameters on the Mechanical Properties of Injection Molded Thermoplastic Polyolefin (TPO) Cellular Foams. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2008, 293, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, T.; Pillot, C.; Carrot, C.; Ruiz, J.A.R.; Vincent, M.; Billon, N. Polypropylene structural foams: Measurements of the core, skin and overall mechanical properties with evaluation of predictive models. J. Cell. Plast. 2017, 53, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaeli, W.; Florez, L.; Obeloer, D.; Brinkmann, M. Analysis of the impact properties of structural foams. J. Cell. Plast. 2009, 45, 321–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, V.; De Filitto, M.; Klofacova, V. Effect of mold opening on the properties of PLA samples obtained by foam injection molding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reglero Ruiz, J.A.; Vincent, M.; Agassant, J.; Claverie, A.; Huck, S. Morphological analysis of microcellular PP produced in a core-back injection process using chemical blowing agents and gas counter pressure. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 2465–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaayegan, V.; Wang, G.; Park, C.B. Study of the Bubble Nucleation and Growth Mechanisms in High-Pressure Foam Injection Molding through in-situ Visualization. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 76, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaayegan, V.; Wang, C.; Costa, F. Effect of the melt compressibility and the pressure drop rate on the cell-nucleation behavior in foam injection molding with mold opening. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 92, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameli, A.; Jahani, D.; Nofar, M. Development of high void fraction polylactide composite foams using injection molding: Mechanical and thermal insulation properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 90, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, W.; Xie, P. Effect of Microcellular Foams from Polylactic Acid of Different Melt Strength. Plastics 2016, 5, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.S.; Jing, W.; Yoon, J.D. Strategies to Achieve a Uniform Cell Structure with a High Void Fraction in Advanced Structural Foam Molding. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 9457–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, H.; Turng, L.S. Measurement of gas solubility and diffusivity in polylactide. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2006, 246, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.F.; Park, C.B.; Suh, N.P.; Suh, N.P. A microcellular processing study of poly (ethylene terephthalate) in the amorphous and semicrystalline states. Part I: Microcell nucleation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofar, M.; Tabatabaei, A.; Park, C.B. Effects of nano-/micro-sized additives on the crystallization behaviors of PLA andPLA/CO2, mixtures. Polymer 2013, 54, 2382–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofar, M.; Zhu, W.; Park, C.B. Crystallization Kinetics of Linear and Long-Chain-Branched Polylactide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 13789–13798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Thermal, Mechanical and Rheological Behavior of Poly (lactic acid)/Talc Composites. J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 20, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Injection Molding Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Barrel temperature (°C) | 185 |
| Mold temperature (°C) | 25 |
| Screw speed (rpm) | 400 |
| Melt pressure (MPa) | 18 |
| Injecting speed (mm/s) Plasticizing stroke (mm) | 100 60 |
| N2 injecting pressure (MPa) | 12 |
| N2 wt % content (%) | 0.6 |
| Degree of mold opening (mm) | 2 |
| Mold opening delay time (s) | 1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, P.; Wu, G.; Cao, Z.; Han, Z.; Zhang, Y.; An, Y.; Yang, W. Effect of Mold Opening Process on Microporous Structure and Properties of Microcellular Polylactide–Polylactide Nanocomposites. Polymers 2018, 10, 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050554
Xie P, Wu G, Cao Z, Han Z, Zhang Y, An Y, Yang W. Effect of Mold Opening Process on Microporous Structure and Properties of Microcellular Polylactide–Polylactide Nanocomposites. Polymers. 2018; 10(5):554. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050554
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Pengcheng, Gaojian Wu, Zhida Cao, Zhizhong Han, Youchen Zhang, Ying An, and Weimin Yang. 2018. "Effect of Mold Opening Process on Microporous Structure and Properties of Microcellular Polylactide–Polylactide Nanocomposites" Polymers 10, no. 5: 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050554
APA StyleXie, P., Wu, G., Cao, Z., Han, Z., Zhang, Y., An, Y., & Yang, W. (2018). Effect of Mold Opening Process on Microporous Structure and Properties of Microcellular Polylactide–Polylactide Nanocomposites. Polymers, 10(5), 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050554





