An Accurate Estimate of the Free Energy and Phase Diagram of All-DNA Bulk Fluids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
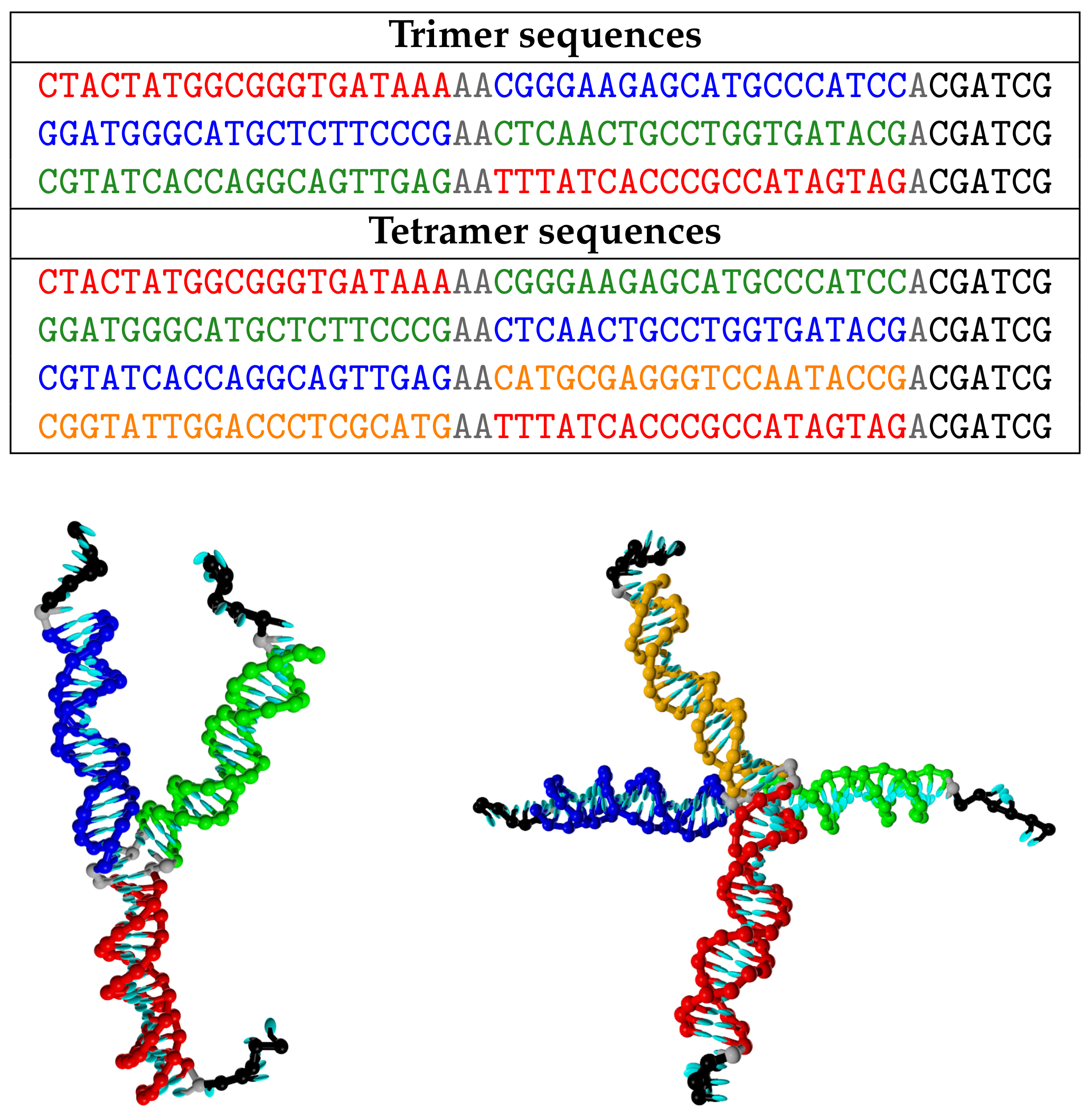
2.1. DNA Sequences
2.2. Numerical Methods
2.3. Theoretical Framework
3. Results
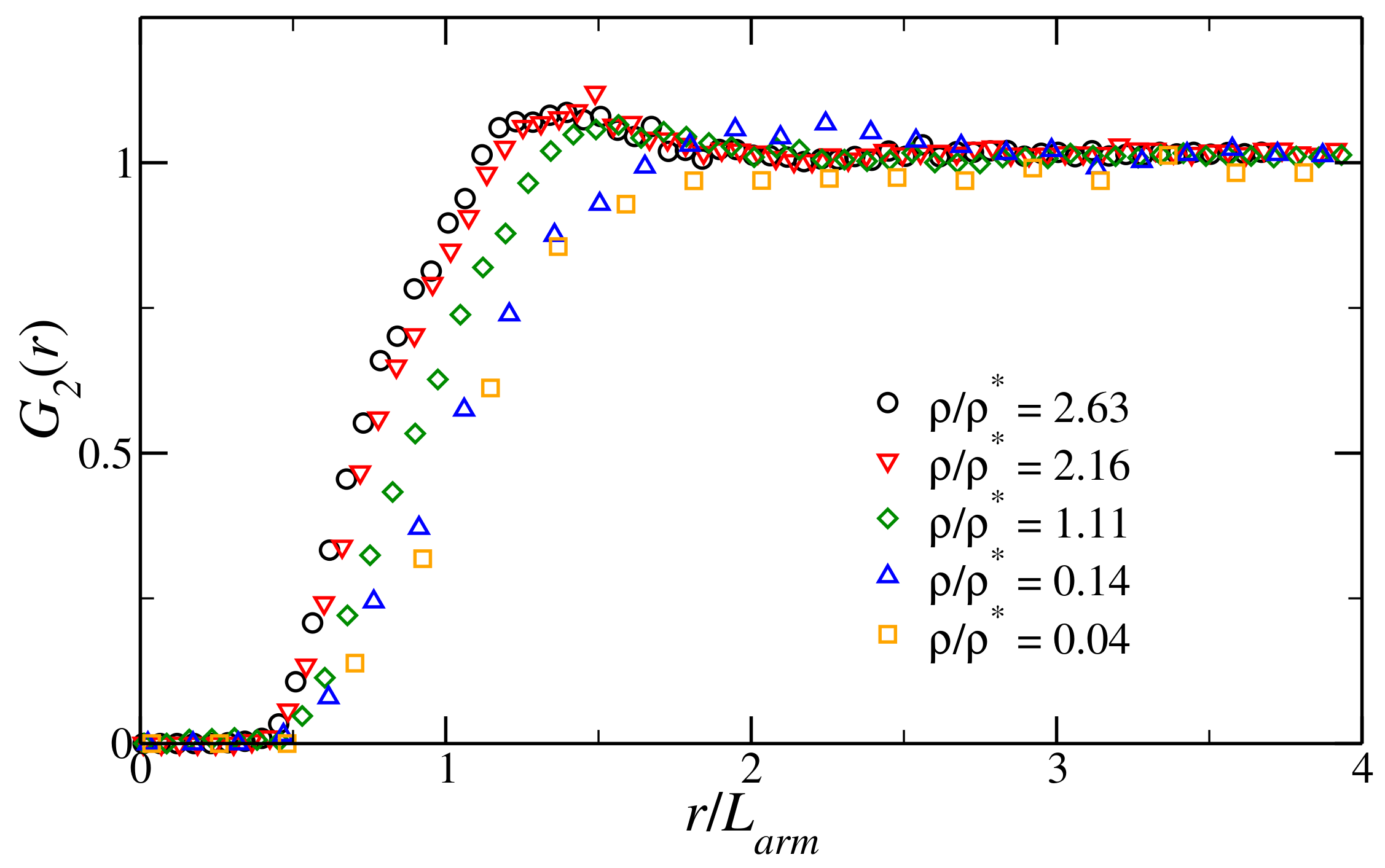
3.1. Structural Properties of the Fluid
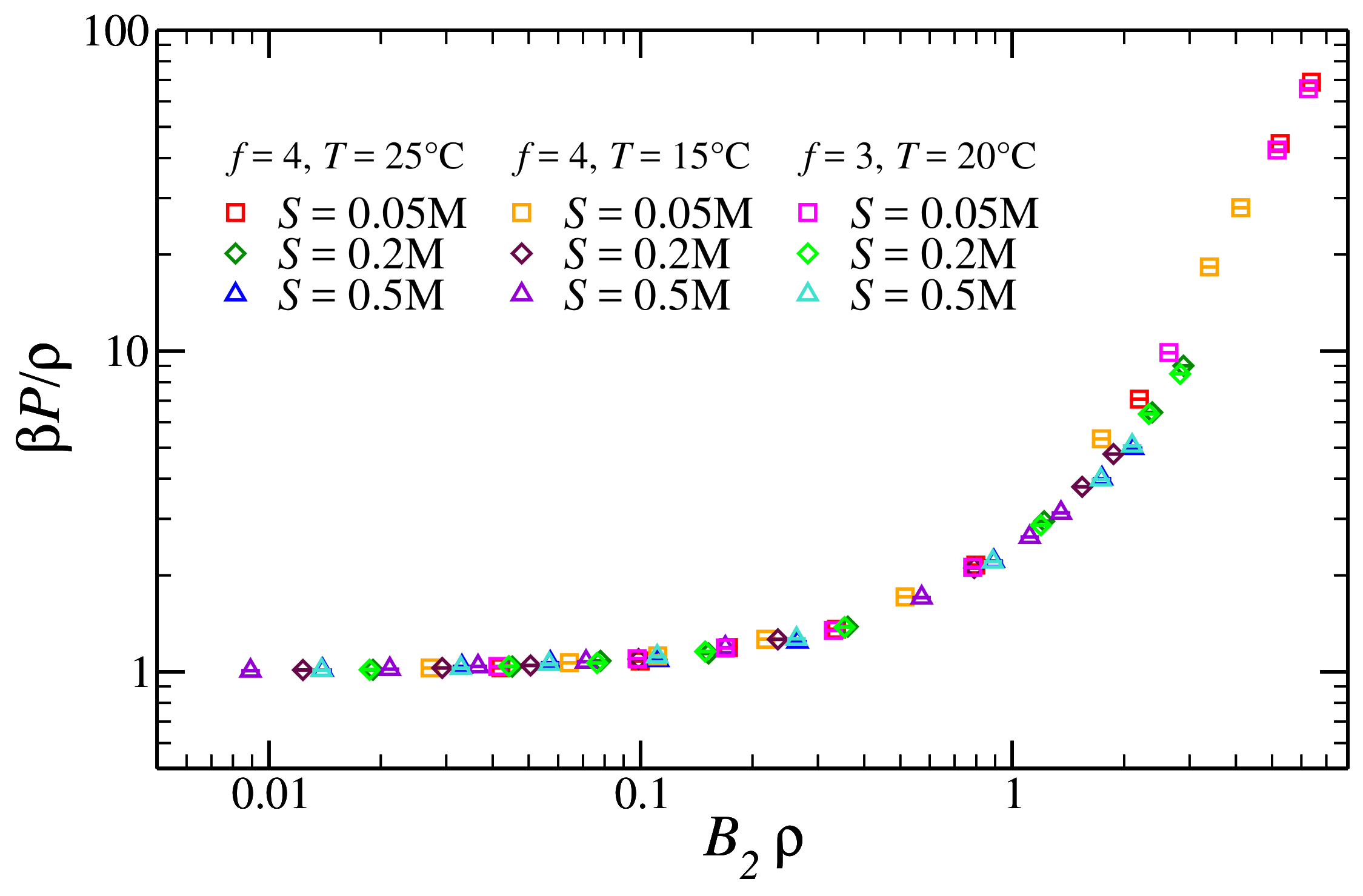
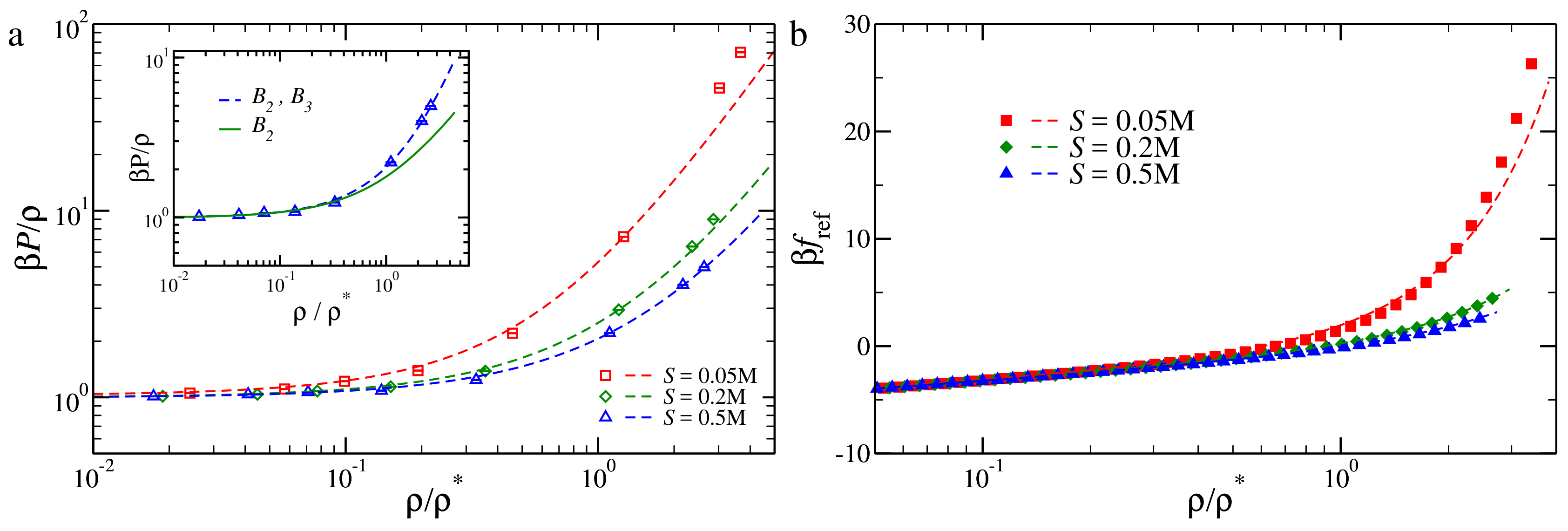
3.2. Pressure of the Reference Fluid
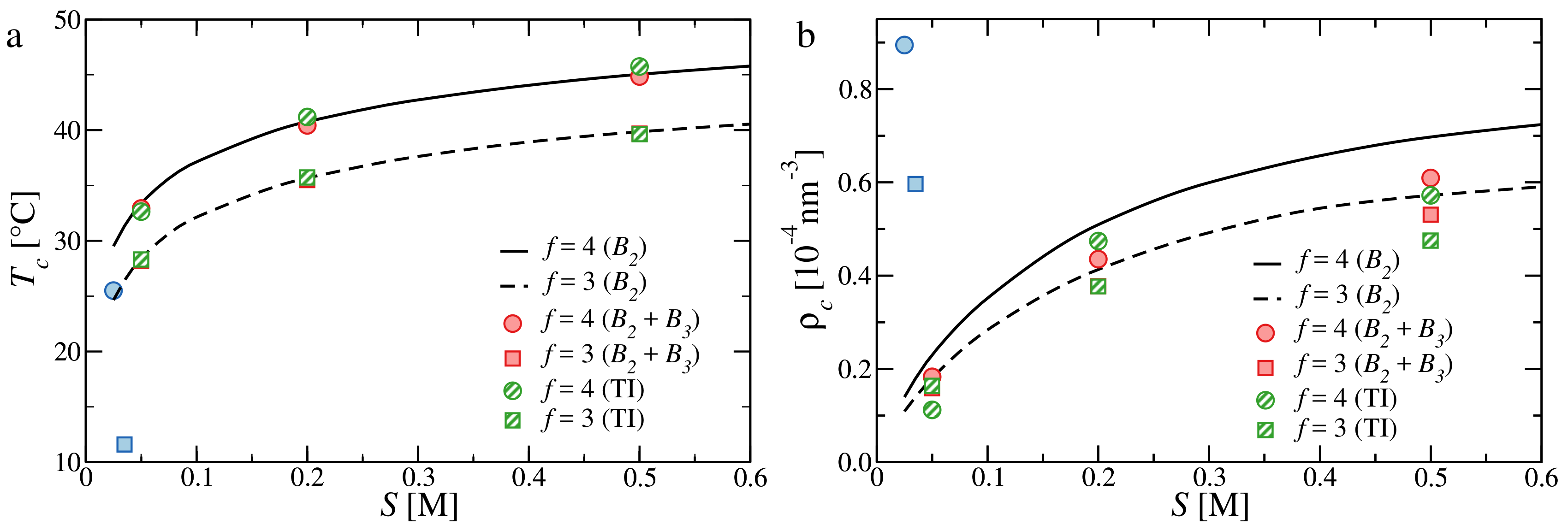
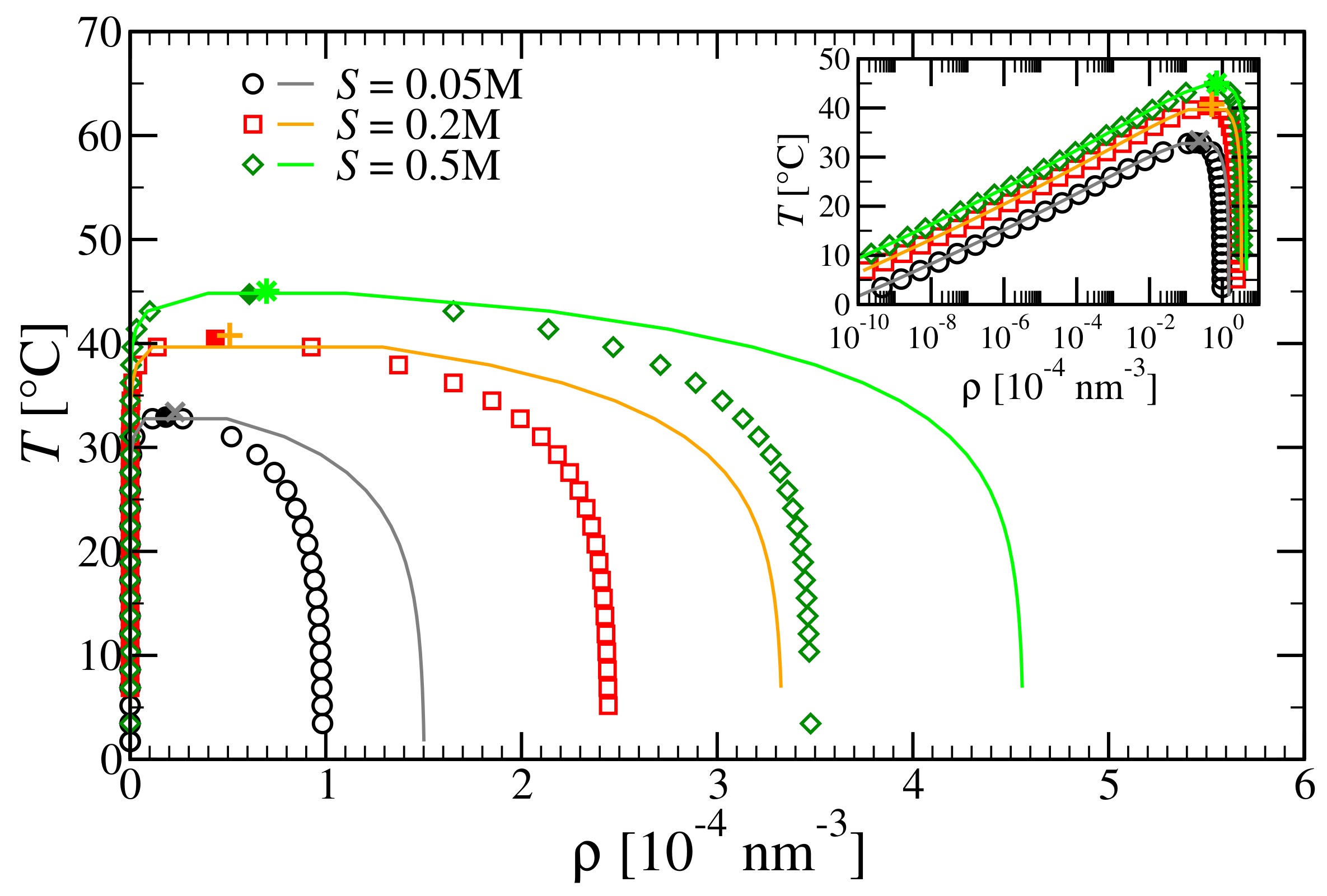
3.3. Critical Points and Coexistence
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Calculation of the Hybridization Free Energy
| Sequence | (kcal/mol) | (cal/K·mol) | (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CG/GC | −9.8 | −24.38 | −2.24 |
| GA/CT | −7.8 | −21.02 | −1.28 |
| AT/TA | −7.2 | −21.34 | −0.58 |
| TC/AG | −7.8 | −21.02 | −1.28 |
| CG/GC | −9.8 | −24.38 | −2.24 |
| kcal/mol cal/K·mol. |
| kcal/mol cal/K·mol. |
| kcal/mol cal/K·mol. |
| kcal/mol cal/K·mol. |
References
- Seeman, N.C. DNA in a material world. Nature 2003, 421, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeman, N.C. DNA Nanotechnology: Novel DNA Constructions. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1998, 27, 225–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Michele, L.; Eiser, E. Developments in Understanding and Controlling Self-Assembly of DNA-Functionalized Colloids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 3115–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.R.; Seeman, N.C.; Mirkin, C.A. Programmable Materials and the Nature of the DNA Bond. Science 2015, 347, 1260901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maye, M.M.; Kumara, M.T.; Nykypanchuk, D.; Sherman, W.B.; Gang, O. Switching binary states of nanoparticle superlattices and dimer clusters by DNA strands. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varrato, F.; Di Michele, L.; Belushkin, M.; Dorsaz, N.; Nathan, S.H.; Eiser, E.; Foffi, G. Arrested demixing opens route to bigels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19155–19160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winfree, E.; Liu, F.; Wenzler, L.A.; Seeman, N.C. Design and Self-Assembly of Two-Dimensional DNA Crystals. Nature 1998, 394, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biffi, S.; Cerbino, R.; Bomboi, F.; Paraboschi, E.M.; Asselta, R.; Sciortino, F.; Bellini, T. Phase Behavior and Critical Activated Dynamics of Limited-Valence DNA Nanostars. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15633–15637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank-Kamenetskii, M.D. Biophysics of the DNA molecule. Phys. Rep. 1997, 288, 13–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D. The road from biology to materials. Mater. Today 2003, 6, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, Y.H.; Ruiz, R.C.; Peng, S.; Lee, J.B.; Luo, D. Engineering DNA-based functional materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5730–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Derrien, T.L.; Cui, J.; Xu, C.; Luo, D. From cells to DNA materials. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, K.; Ricketts, S.; Robertson-Anderson, R.M. DNA as a model for probing polymer entanglements: Circular polymers and non-classical dynamics. Polymers 2016, 8, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xi, W. Nucleobase-Containing Polymers: Structure, Synthesis, and Applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vologodskii, A. Biophysics of DNA; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alberts, B. Molecular Biology of the Cell; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, G. DNA Phase Transition in Charge Neutralization and Comformation Induced by Trivalent-Hydrolysed Metal Ions. Polymers 2018, 10, 394. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Sae-Ueng, U.; Li, D.; Lander, G.C.; Zuo, X.; Jönsson, B.; Rau, D.; Shefer, I.; Evilevitch, A. Solid-to-fluid–like DNA transition in viruses facilitates infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14675–14680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosberg, A.; Rabin, Y.; Havlin, S.; Neer, A. Crumpled globule model of the three-dimensional structure of DNA. Europhys. Lett. 1993, 23, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenduzzo, D.; Orlandini, E.; Stasiak, A.; Tubiana, L.; Micheletti, C. DNA–DNA interactions in bacteriophage capsids are responsible for the observed DNA knotting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22269–22274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, A. Topological constraints and chromosome organization in eukaryotes: A physical point of view. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, J.T.; Kivel, A.N.; Atkinson, L.P.; Stevens, T.J.; Laue, E.D.; Virnau, P. Are There Knots in Chromosomes? Polymers 2017, 9, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tseng, Y.D.; Kwon, S.Y.; d’Espaux, L.; Bunch, J.S.; McEuen, P.L.; Luo, D. Controlled assembly of dendrimer-like DNA. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaBean, T.H.; Li, H. Constructing novel materials with DNA. Nano Today 2007, 2, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, E.; Xing, Y.; Chen, P.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, D.; Xu, L.; Fan, Q.; Liu, D. A pH-triggered, fast-responding DNA hydrogel. Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 7796–7799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Peng, S.; Yang, D.; Roh, Y.H.; Funabashi, H.; Park, N.; Rice, E.J.; Chen, L.; Long, R.; Wu, M.; et al. A mechanical metamaterial made from a DNA hydrogel. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomboi, F.; Romano, F.; Leo, M.; Fernandez-Castanon, J.; Cerbino, R.; Bellini, T.; Bordi, F.; Filetici, P.; Sciortino, F. Re-entrant DNA Gels. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SantaLucia, J., Jr.; Hicks, D. The Thermodynamics of DNA Structural Motifs. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2004, 33, 415–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertheim, M.S. Fluids with Highly Directional Attractive Forces. I. Statistical Thermodynamics. J. Stat. Phys. 1984, 35, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertheim, M.S. Fluids with Highly Directional Attractive Forces. II. Thermodynamic Perturbation Theory and Integral Equations. J. Stat. Phys. 1984, 35, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, E.; Handle, P.H.; Likos, C.N.; Sciortino, F.; Rovigatti, L. Condensation and demixing in solutions of DNA nanostars and their mixtures. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2094–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Michele, L.; Mognetti, B.M.; Yanagishima, T.; Varilly, P.; Ruff, Z.; Frenkel, D.; Eiser, E. Effect of Inert Tails on the Thermodynamics of DNA Hybridization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6538–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomboi, F.; Biffi, S.; Cerbino, R.; Bellini, T.; Bordi, F.; Sciortino, F. Equilibrium Gels of Trivalent DNA-Nanostars: Effect of the Ionic Strength on the Dynamics. Eur. Phys. J. E 2015, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Castanon, J.; Bomboi, F.; Rovigatti, L.; Zanatta, M.; Paciaroni, A.; Comez, L.; Porcar, L.; Jafta, C.J.; Fadda, G.C.; Bellini, T.; et al. Small-Angle Neutron Scattering and Molecular Dynamics Structural Study of Gelling DNA Nanostars. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 145, 084910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, E.; Capone, B.; Coluzza, I.; Rovigatti, L.; van Oostrum, P.D.J. Limiting the valence: advancements and new perspectives on patchy colloids, soft functionalized nanoparticles and biomolecules. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 19847–19868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: http://dna.physics.ox.ac.uk (accessed on 1 February 2017).
- Doye, J.P.; Ouldridge, T.E.; Louis, A.A.; Romano, F.; Šulc, P.; Matek, C.; Snodin, B.E.; Rovigatti, L.; Schreck, J.S.; Harrison, R.M.; et al. Coarse-Graining DNA for Simulations of DNA Nanotechnology. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 12, 6253–6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snodin, B.E.K.; Randisi, F.; Mosayebi, M.; Šulc, P.; Schreck, J.S.; Romano, F.; Ouldridge, T.E.; Tsukanov, R.; Nir, E.; Louis, A.A.; et al. Introducing Improved Structural Properties and Salt Dependence into a Coarse-Grained Model of DNA. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 142, 234901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, J.; Tartaglia, P.; Sciortino, F. Reversible gels of patchy particles: role of the valence. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131, 014504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovigatti, L.; Šulc, P.; Reguly, I.Z.; Romano, F. A Comparison between Parallelization Approaches in Molecular Dynamics Simulations on GPUs. J. Comput. Chem. 2015, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccotti, G.; Ryckaert, J. Molecular dynamics simulation of rigid molecules. Comput. Phys. Rep. 1986, 4, 346–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovigatti, L.; de las Heras, D.; Tavares, J.; da Gama, M.T.; Sciortino, F. Computing the Phase Diagram of Binary Mixtures: A Patchy Particle Case Study. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 164904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, E.; Largo, J.; Tartaglia, P.; Zaccarelli, E.; Sciortino, F. Phase Diagram of Patchy Colloids: Towards Empty Liquids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 168301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SantaLucia, J. A Unified View of Polymer, Dumbbell, and Oligonucleotide DNA Nearest-Neighbor Thermodynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhardt, A.; Frenkel, D. DNA Brick Self-Assembly with an Off-Lattice Potential. Soft Matter 2016, 15, 20395–20414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watzlawek, M.; Löwen, H.; Likos, C.N. The anomalous structure factor of dense star polymer solutions. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1998, 10, 8189–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bloomfield, V.A. Osmotic pressure of semidilute solutions of flexible, globular, and stiff-chain polyelectrolytes with added salt. Macromolecules 1990, 23, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likos, C.N. Effective interactions in Soft Condensed Matter Physics. Phys. Rep. 2001, 348, 267–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, E.; Capone, B. Design of Self-Assembling Materials, Chapter 1; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, E.; Tartaglia, P.; Zaccarelli, E.; Sciortino, F. Theoretical and Numerical Study of the Phase Diagram of Patchy Colloids: Ordered and Disordered Patch Arrangements. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 128, 144504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Locatelli, E.; Rovigatti, L. An Accurate Estimate of the Free Energy and Phase Diagram of All-DNA Bulk Fluids. Polymers 2018, 10, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040447
Locatelli E, Rovigatti L. An Accurate Estimate of the Free Energy and Phase Diagram of All-DNA Bulk Fluids. Polymers. 2018; 10(4):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040447
Chicago/Turabian StyleLocatelli, Emanuele, and Lorenzo Rovigatti. 2018. "An Accurate Estimate of the Free Energy and Phase Diagram of All-DNA Bulk Fluids" Polymers 10, no. 4: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040447
APA StyleLocatelli, E., & Rovigatti, L. (2018). An Accurate Estimate of the Free Energy and Phase Diagram of All-DNA Bulk Fluids. Polymers, 10(4), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040447